Mechanical properties of reactive powder concrete-filled steel tube after exposure to high temperature under impact loading
-
摘要: 采用霍普金森压杆装置对高温后钢管活性粉末混凝土(reactive powder concrete-filled steel tube,RPC-FST)进行冲击压缩实验,分析了应变率效应及温度效应对试件动态力学性能的影响。结果表明:高温(200、300 ℃)后RPC-FST仍具有较好的抗冲击能力、延性和完整性;冲击荷载作用下,RPC-FST的应变率效应明显弱于RPC的应变率效应;随着过火温度的提高,RPC-FST的峰值应力逐渐增大,变形能力增强,抗冲击能力提高。动力提高系数随过火温度的提高而增大,说明高温后RPC-FST的应变率效应更显著。Abstract: Experiments on reactive powder concrete-filled steel tube (RPC-FST) specimens after exposure to high temperature were performed by using a split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) apparatus, and the influences of strain rate effects and temperature effects on the dynamic behaviors of RPC-FST were investigated. Test results show that the RPC-FST specimens after exposure to high temperature have excellent impact-resistance, ductility and integrity. The strain rate effects of the RPC-FST specimens are weaker than those of the RPC specimens under impact loading. The peak stress of the RPC-FST specimens increases as the temperature increases, and the deformation capability and impact-resistance increase. The dynamic increase factor (DIF) increases as the temperature increases. It means that the strain rate effects of RPC-FST become more obvious after exposure to high temperature.
-
金属材料因其优异的力学性能而被广泛应用于航空航天、交通运输、能源、国防等重要工业领域,因此研究金属材料在不同加载条件的力学行为具有重要意义。然而,要在数值模拟中准确预测材料的塑性变形和失效过程,就要对材料的塑性模型及屈服准则提出更高的要求。在塑性本构模型的研究中,研究者多采用与应变率和温度有关的塑性流动模型,其中包括经验型[1-2]以及基于物理意义的模型[3-5]。近年来,人们发现应力状态对金属材料的塑性变形也存在较大影响,因此要在工程计算中获得精确的结构响应,必须建立考虑应力状态效应的塑性本构模型。
有关应力状态对材料塑性的影响目前已有较多研究。Spitzig等[6-7]在拉伸和压缩两种不同的应力状态下得到了两种调质钢在不同静水压力下的应力-应变曲线,发现材料的屈服应力和流动应力均对静水压力敏感,表明了材料的力学特性与静水压力的相关性。Hu等[8]认为材料在拉伸和压缩下的强度差不仅仅是静水压力引起的,应力状态也是导致强度差的主要因素,从而提出了考虑应力状态影响的各向同性材料屈服准则并用金属和聚合物材料进行实验验证。Cazacu等[9]发现用应力偏量的主值表示屈服函数可以很好地描述各向异性和拉压屈服不对称性材料的塑性行为。Driemeier等[10]采用光滑和预制缺口的拉伸试样和剪切试样,研究了应力强度、应力三轴度和罗德参数对铝合金材料塑性和失效行为的影响。Brünig等[11]采用实验和数值模拟相结合的方法,提出了一种基于应力三轴度和罗德参数的塑性模型和损伤准则,并讨论了应力三轴度对韧性金属损伤起始和演化的影响。Bai等[12]提出了一种与静水压力和罗德角相关的非对称金属塑性模型的一般形式,并详细讨论了修正方法,而后通过铝2024-T351的实验结果对新模型的准确性进行了验证。Gao等[13-14]注意到应力状态对铝5083合金的塑性响应和韧性断裂行为有明显的影响,提出了与静水压力和应力偏量的第三不变量相关的塑性失效模型,并发现应力三轴度主要影响材料的韧性断裂应变,而罗德角对塑性的影响较大。
目前,考虑材料应力状态效应的塑性特性及本构模型的研究大多是在准静态条件下进行的,而在动态加载条件下的相关研究较少。这是因为在高应变率下,材料受到应变率效应和应力状态效应的耦合作用[15-16],难以单独区分。此外,在进行不同加载条件的力学性能测试时,研究者们采用的试样类型和尺寸各异[17-20],导致实验结果较为分散,这也给综合考虑应变率和应力状态效应的本构模型的建立带来了困难。针对以上问题,许泽建等[21-22]提出了一种新型双剪切试样,可以在准静态和动态加载下获得材料在接近纯剪切条件下的流动应力曲线,从而实现了应力状态效应的解耦。采用该试样对多种金属材料在广泛应变率下的塑性流动、失效行为以及材料的剪切本构特性[23-26]进行了研究,发现材料的流动应力水平和加工硬化效应明显受到应力状态的影响;同时发现剪切本构模型对剪切测试中应力波和流动应力曲线的预测更加精确[27-28],因此在工程应用中确定本构模型时必须考虑材料所处的真实应力状态。
基于以上研究,本文中结合实验测试提出一个综合考虑应变率、温度和应力状态效应的塑性本构模型,并对其有效性进行验证,从而实现在复杂应力状态下准确预测金属材料和结构的塑性流变及动态响应行为。
1. 应力状态表征
在主应力空间中,与3个主应力坐标轴夹角相同且过原点的直线称为等倾线,与等倾线垂直且过原点的面称为π平面,如图1所示。在等倾线上,任意一点对应一个静水压力,其应力偏量为零,各个方向受到相同的压应力或拉应力。在π平面上只有应力偏量,其静水压力为零,主要与物体的塑性变形相关。
金属材料所处的应力状态一般用应力三轴度和罗德角来描述。应力三轴度
η 的表达式为:η = σmσe (1) σm=13(σ1+σ2+σ3) (2) σe=1√2√(σ1−σ2)2+(σ2−σ3)2+(σ3−σ1)2 (3) 式中:
σm 为静水压力,σe 为Mises等效应力,σ1 、σ2 、σ3 为3个主应力值且满足σ1⩾σ2⩾σ3 。可见,应力三轴度是一个与静水压力有关的无量纲量。应力偏张量
Sij 与材料的塑性变形相关,表达式为:Sij=σij−σmδij ,其中δij 为Kronecker 符号。应力偏张量的第二不变量J2 和第三不变量J3 分别定义为:J2=12SijSij=−(S1S2+S2S3+S3S1)=16[(σ1−σ2)2+(σ2−σ3)2+(σ3−σ1)2] (4) J3=det(Sij)=13SijSjkSkl=S1S2S3 (5) 式中:
S1 、S2 和S3 为3个主应力偏量,其中S1 为最大主应力偏量。在主应力空间中,应力状态矢量在π平面的投影与最大主应力偏量
S1 的夹角定义为罗德角θ ,其可以表示为应力偏张量的第三不变量的函数[29]:r=3√272J3 (6) ξ=(rσe)3=cos(3θ) (7) ˉθ=1−6π θ=1−2π arccosξ (8) 本文中采用均一化的罗德角参数
ˉθ ,取值范围为[−1, 1]。不同应力状态下,应力三轴度和罗德角参数的值不同,对单轴拉伸,有η=13,ˉθ=1 ;对单轴压缩,有η=−13,ˉθ=−1 ;在纯剪切条件下,则有η=ˉθ=0 。2. 实验方法及结果
实验材料为商用Ti-6Al-4V钛合金,其原始微观组织形貌如图2所示。分别采用单轴拉伸、单轴压缩和剪切3种不同的加载条件进行实验,获取材料在广泛应变率和温度下的力学特性。单轴拉伸、单轴压缩和剪切实验分别采用光滑圆棒试样、圆柱试样和新设计的双剪切试样[22],几何形状和尺寸如图3所示。其中,准静态实验采用MTS万能试验机,动态加载采用霍普金森压杆和拉杆,详细实验装置参见文献[25]。
图4为准静态和动态加载时材料在不同应力状态下的等效应力-等效应变曲线对比图。在剪切实验中,假设试样处于纯剪切应力状态,根据von-Mises假定,采用下式将剪应力
τ 转化为等效应力:σeq=√3τ (9) 对于大变形,采用下式将剪应变
γ 转化为等效应变[30]:εeq=ln√1+γ+γ2/2 (10) 由图4可知,在不同的加载条件下,材料的加工硬化效应有所差别。准静态加载时,Ti-6Al-4V在拉伸、压缩和剪切状态下,随着塑性应变的增加,材料的流动应力水平明显增高,其加工硬化效应均较为明显。然而在动态加载下,只在压缩状态下材料表现出明显的加工硬化效应,可见材料的加工硬化效应与应力状态相关。此外,无论准静态还是动态加载等效应力幅值均存在明显差别,且在纯剪切状态下流动应力水平最低,压缩状态下流动应力水平最高。Ti-6Al-4V材料在拉伸和压缩情况下的不对称性与多种因素相关,比如加工方式、晶粒尺寸和材料取向等。在本研究中,所有试样均沿棒材轴向方向取材,保证材料在拉伸、压缩和剪切条件下等效应力幅值差别是由应力状态引起的。因此,为了更好地表征材料的本构行为,应在塑性模型中考虑应力状态效应的影响。
3. 基于应力状态的塑性本构模型
为了更准确地表征金属材料的塑性行为,提出一种与材料应力状态相关的塑性本构模型,即在基本塑性模型的基础上将应力三轴度和罗德角参数的影响考虑在内。该模型中,材料的流动应力可表示为:
¯σ=σ(ε,˙ε,T)f(η)g(ˉθ) (11) 式中:
σ(ε,˙ε,T) 为任意一个包含应变、应变率和温度效应的塑性本构模型;f 和g 分别为应力三轴度和罗德角参数的函数,用于反映应力状态的影响。根据获得的实验数据,f 和g 分别采用如下形式:f(η)=1−cη(η−η0) (12) g(ˉθ)=1+c1|ˉθ−c2| (13) 式中:
cη 和η0 为与应力三轴度相关的材料参数,c1 和c2 为与罗德角参数相关的材料参数。由式(11)~(13)可知,可以通过选取适当的模型参数使得
¯σ 在η=ˉθ=0 时接近于¯σ=σ(ε,˙ε,T) ,因此可以根据剪切实验结果确定本构模型¯σ=σ(ε,˙ε,T) 。工程中常用Johnson-Cook(J-C)模型描述材料的应变率和温度效应,因此在本工作中选用J-C模型描述σ(ε,˙ε,T) 。J-C模型的表达式为:σ=(A+Bεn)(1+Cln˙ε∗)(1−T∗m) (14) T∗=(T−Tr)/(Tm−Tr) (15) 式中:
A 、B 、n、C 、m为材料常数,˙ε∗=˙ε/˙ε0 为无量纲塑性应变率,˙ε0 为参考应变率,Tr 为参考温度,Tm 为熔点温度。在本工作中参考应变率为1 s−1,熔点温度为1941 K,参考温度为93 K。采用剪切实验数据确定J-C模型的材料参数后,结合拉伸和压缩加载条件下的实验结果,可确定模型的应力状态参数
cη 、η0 、c1 和c2 。在确定模型参数时,使用回归分析和约束优化方法使模型的预测结果和实验数据的误差最小。在优化过程中,考虑了材料的绝热温升。本文中所确定的塑性本构模型参数见表1。表 1 新模型材料常数Table 1. Material constants of the new modelA/MPa B/MPa n C m cη η0 c1 c2 971.59 362.39 0.1298 0.0160 0.5839 0.0501 0 0.1692 0.4264 在主应力空间中,该模型的屈服面以及在π平面上的屈服轨迹如图5~6所示,其中图6同时给出了Mises和Tresca准则的屈服轨迹以方便比较。从屈服轨迹可以看出,在该模型中,当应力状态发生变化时,屈服面也随之改变。
由表1可知,在简单剪切状态下,新提出的塑性本构模型与J-C模型基本一致。将实验得到的剪应力和剪应变曲线转化为等效应力和等效应变曲线,并与模型计算结果进行比较,如图7所示。由图可知,在准静态加载条件下,该模型与实验数据吻合较好。在动态加载下,当应变率为1500 s−1、温度为873 K时,模型计算结果稍高于实验曲线,但误差仍较小。当应变率进一步提高至6500 s−1时,由于应力波的传播和惯性效应,实验曲线在初始阶段出现较大的震荡,但其流动应力与计算曲线较为接近。由以上分析可知,该模型可以准确反映剪切条件下材料的塑性流动特性。
为了比较J-C模型和新模型的预测效果,采用下式计算模型与实验的误差
Er :Er=1NN∑i|σ(i)exp−σ(i)modelσ(i)exp|×100% (16) 式中:
σexp 为实验测得的流动应力,σmodel 为本构模型测得的流动应力。图8为不同应变率和温度下获得的压缩实验曲线,图中还同时给出了分别由剪切实验拟合的J-C本构模型和本文提出的模型所计算得到的应力-应变曲线。由剪切实验拟合的J-C模型得到的曲线在准静态和动态加载情况下均明显低于实验曲线,模型与实验曲线的平均误差分别为25.2%和21.1%,这是由于J-C模型未能考虑应力状态效应对材料造成的影响,因此不能准确反映材料在不同加载条件下的塑性行为;在各应变率下,由新模型得到的应力-应变曲线均接近于实验结果。在动态加载情况下,实验曲线存在较大波动,但由新模型给出的两条曲线均与实验数据的整体应力水平吻合较好。新模型与实验结果的平均误差分别为3.7%、3.9%(见表2)。因此,应力状态对材料力学性能的影响不容忽视;相比J-C模型而言,新模型可以更准确地预测材料在不同应力状态下的等效应力-等效应变曲线。
表 2 不同应力状态下新模型和J-C模型(根据剪切试验结果建立)与拉压试验结果的平均误差Table 2. Average error of the new and J-C models under different stress states compared with the experimental results应力状态 准静态加载误差/% 动态加载误差/% J-C model New model J-C model New model 单轴压缩 25.2 3.7 21.1 3.9 单轴拉伸 10.5 1.5 9.7 4.8 图9为在单轴拉伸加载下,实验结果和两种模型计算所得应力-应变曲线的对比。在准静态加载下,由剪切实验得到的J-C模型的流动应力水平比实验值明显偏低,该现象与单轴压缩结果类似。在动态载荷下,J-C模型曲线整体明显低于实验曲线;然而,随着应变量的增加,其流动应力逐渐趋于实验值。新模型无论在准静态还是动态加载下,均能较好地反映材料的加工硬化情况和流动应力水平。两种模型与实验数据的平均误差见表2。因此,在拉伸和压缩载荷作用下,使用新模型能够更加准确地预测材料的应力-应变曲线,说明该模型可以准确描述材料的应力状态效应对其塑性流动特性的影响。
4. 模型的验证
为了检验所提出的模型对于复杂应力状态下材料流动特性的预测精度,设计了图10所示的压剪复合试样并开展动态测试。同时,通过编写用户自定义子程序将新模型嵌入ABAQUS有限元软件,并对压剪实验进行数值模拟。建模时,对入射杆、试样和透射杆进行三维实体建模,试样放置在入射杆与透射杆之间,且其端面接触设置为“硬接触”,不考虑各接触面的摩擦效应。入射杆与透射杆均采用C3D8R六面体缩减积分单元;由于要考虑试样在加载过程中的绝热温升,试样采用C3D10MT温度位移耦合单元。为了更好地模拟剪切区的应力应变场,在试样剪切区进行局部加密。模型装配图如图10(b)所示,模拟中各部分的材料和物理参数见表3。
表 3 有限元分析中各部件的物理参数Table 3. Physical parameters of each component in the finite element analysis部位 材料 ρ/
(g·mm−3)E/
GPaμ λ/
(W·m−1·°C)c/
(J·kg−1·°C)入射杆/透射杆 18Ni钢 8.0 190 0.3 − − 试样 Ti-6Al-4V 4.43 114 0.33 6.7 586 在数值模拟中分别采用J-C模型和新模型时,所得到的透射应变脉冲及力-位移曲线与实验结果的对比如图11所示。从压剪试样的模拟与实验对比分析可知,两种模型均能捕捉到应变波信号的变化趋势,但J-C模型明显低估了实验数据(见图11(a))。由图11(b)可知,J-C模型和新提出的模型在载荷-位移曲线的上升沿均与实验数据基本重合。随着位移的不断增加,由J-C模型所预测的载荷-位移曲线与实验曲线出现明显偏差,而新模型则始终与实验数据吻合较好。这说明新模型能够准确预测材料在复杂应力状态下的塑性变形行为。此外,为了分别研究应力三轴度和罗德角参数对屈服应力的影响程度,图12给出了新模型只考虑应力三轴度(
c1=0 )或罗德角参数(cη=0 )时的透射应变曲线和载荷-位移曲线。可以看到,当新模型只考虑罗德角参数的影响时,所得结果与新模型接近,基本可以正确反映材料的流动特性;当只考虑应力三轴度的影响时,其载荷-位移曲线和透射应变信号与实验结果均相差较大。因此可以看出,对于本文所设计的压剪试样,材料的塑性流动特性主要受到罗德角参数的影响,受应力三轴度的影响不明显。图13给出了新模型和J-C模型在36 、96 、146 μs 时所得到的试样剪切区内部的等效应力分布情况(图10(a)中红色框所示的A区域)。可以看出,在加载过程中,试样剪切区除边缘部分外,应力场始终均匀分布,且在相同时刻新模型的等效应力水平均高于J-C模型,该结果与两种模型预测的透射应变波信号和力-位移曲线情况相一致。这是由于在压剪状态下,材料的流动应力高于纯剪切情况下的流动应力,新模型考虑了复杂应力状态效应对材料塑性特性的影响,而J-C模型未能考虑该应力状态效应。因此,新模型可以更加精确地预测材料在高应变率、复杂应力状态下的力学响应。5. 结 论
(1)通过对Ti-6Al-4V钛合金材料开展单轴拉伸、单轴压缩和剪切加载下的力学性能测试发现材料的塑性流动应力水平存在明显差异。压缩实验中其流动应力水平最高,剪切流动应力最低,表明应力状态会影响材料的塑性行为。
(2)提出了一种考虑应力状态效应的塑性本构模型。该模型考虑了应力三轴度和罗德角参数对流动应力的影响,因此可以对材料在不同温度、应变率及应力状态下的力学行为进行描述。
(3)基于Ti-6Al-4V钛合金实验结果确定了新模型的材料参数,该模型对不同应力状态下的应力-应变曲线的预测结果与实验结果误差小于5%。
(4)采用新型压剪试样获得了材料在压剪复合状态下的实验曲线。采用ABAQUS中VUMAT用户子程序对压剪实验进行数值模拟,发现新模型的计算结果与实验数据的吻合程度优于J-C模型,表明该模型能够准确描述材料在复杂应力状态下的塑性行为。
-
表 1 RPC-FST冲击实验结果
Table 1. Experimental results of RPC-FST specimens under impact loading
编号 θmax/℃ p0/MPa v0/(m·s-1) σp/MPa σp/MPa ˉ˙ε/s-1 λdi s0b 20 0.8 12.1 218~227 223 95 1.31 s0c 20 1.0 14.3 242~250 247 122 1.45 s1b 200 0.8 12.3 235~240 237 100 1.56 s1c 200 1.0 14.0 249~255 252 122 1.66 s2b 300 0.8 12.2 245~250 247 100 1.64 s2c 300 1.0 14.1 265~272 268 121 1.77 表 2 RPC冲击实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results of RPC specimens under impact loading
编号 θmax/℃ p0/MPa v0/(m·s-1) σp/MPa σp/MPa ˉ˙ε/s-1 λdi s0b 20 0.8 12.0 192~200 195 107 1.63 s0c 20 1.0 14.1 211~220 215 116 1.79 s1b 200 0.8 12.1 204~207 206 100 2.17 s1c 200 1.0 14.2 219~224 221 125 2.33 s2b 300 0.8 12.0 205~214 209 90 2.22 s2c 300 1.0 14.2 231~241 237 120 2.52 表 3 动力提高系数的理论值与实验值的对比
Table 3. Comparisons of experimental and analytical dynamic increase factors
编号 θmax/℃ p0/MPa 平均应变率/s-1 动力提高系数 实验值 理论值 相对误差/% s0b 20 0.8 95 1.31 1.30 -0.9 s0c 20 1.0 122 1.45 1.36 -6.1 s1b 200 0.8 100 1.56 1.74 11.4 s1c 200 1.0 120 1.66 1.80 8.3 s2b 300 0.8 100 1.64 1.75 6.9 s2c 300 1.0 121 1.77 1.81 1.9 -
[1] Tian Zhimin, Wu Ping'an, Jia Jianwei. Dynamic response of RPC-filled steel tubular columns with high load carrying capacity under axial impact loading[J]. Transactions of Tianjin University, 2008, 14(6):441-449. doi: 10.1007/s12209-008-0076-9 [2] Bambach M R. Design of hollow and concrete filled steel and stainless steel tubular columns for transverse impact loads[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2011, 49(10):1251-1260. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2011.05.009 [3] Remennikov A M, Kong S Y, Uy B. Response of foam- and concrete-filled square steel tubes under low-velocity impact loading[J]. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2011, 25(5):373-381. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CF.1943-5509.0000175 [4] Yousuf M, Uy B, Tao Z, et al. Transverse impact resistance of hollow and concrete filled stainless steel columns[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2013, 82:177-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2013.01.005 [5] Han Linhai, Hou Chuanchuan, Zhao Xiaoling, et al. Behaviour of high-strength concrete filled steel tubes under transverse impact loading[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2014, 92(1):25-39. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=7f0b3eea375dbc763649c5047f08e777 [6] Wang Rui, Han Linhai, Hou Chuanchuan. Behavior of concrete filled steel tubular (CFST) members under lateral impact: Experiment and FEA model[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2013, 80(1):188-201. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0143974X12002106 [7] 何远明, 霍静思, 陈柏生.高温下钢管混凝土SHPB动态力学性能试验研究[J].工程力学, 2013, 30(1):52-58. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20132013051500003654He Yuanming, Huo Jingsi, Chen Baisheng. Impact tests on dynamic behavior of concrete-filled steel tube at elevated temperatures[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(1):52-58. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20132013051500003654 [8] 霍静思, 任晓虎, 肖岩.标准火灾作用下钢管混凝土短柱落锤动态冲击试验研究[J].土木工程学报, 2012, 45(4):9-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201200684144Huo Jingsi, Ren Xiaohu, Xiao Yan. Impact behavior of concrete-filled steel tubular stub columns under ISO-834 standard fire[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2012, 45(4):9-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201200684144 [9] 霍静思, 何远明, 肖莉平, 等.高温后钢管混凝土抗多次冲击力学性能试验研究[J].湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 39(9):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2974.2012.09.002Huo Jingsi, He Yuanmin, Xiao Liping, et al. Experimental study on the dynamic behavior of concrete-filled steel tube after exposure to high temperatures under multiple impact loadings[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2012, 39(9):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2974.2012.09.002 [10] 钟善桐.钢管混凝土结构[M].3版.北京:清华大学出版社, 2003:231-268. [11] Bischoff P H, Perry S H. Compressive behaviour of concrete at high strain rates[J]. Materials & Structures, 1991, 24(6):425-450. doi: 10.1007/BF02472016 [12] Davies E D H, Hunter S C. The dynamic compression testing of solids by the method of split Hopkinson pressure bar[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1963, 11(3):155-179. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(63)90050-4 [13] 混凝土结构设计规范: GB50010-2002[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2002: 13-15. [14] 金属材料室温拉伸试验方法: GB/T228-2002[S].北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2002: 10-12. [15] 王礼立.应力波基础[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2010:5-35. [16] 李志武, 许金余, 白二雷, 等.高温后混凝土SHPB试验研究[J].振动与冲击, 2012, 31(8):143-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.08.028Li Zhiwu, Xu Jinyu, Bai Erlei, et al. SHPB test for post-high-temperature concrete[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(8):143-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2012.08.028 [17] Song T Y. Concrete filled steel tube stub columns under combined temperature and loading[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2010, 66(3):369-384. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2009.10.010 [18] 林震宇, 吴炎海, 沈祖炎.圆钢管活性粉末混凝土轴压力学性能研究[J].建筑结构学报, 2005, 26(4):52-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2005.04.008Lin Zhenyu, Wu Yanhai, Shen Zuyan. Research on behavior of RPC filled circular steel tube column subjected to axial compression[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2005, 26(4):52-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6869.2005.04.008 [19] 李海艳.活性粉末混凝土高温爆裂及高温后力学性能研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012: 60, 96-97. [20] Comité Euro-International du Béton. Concrete structure under impact and impulsive loading: CEB Bulletin No.187[R]. Lausanne Switzerland, 1988. [21] 任晓虎, 霍静思, 陈柏生.高温后钢管混凝土短柱落锤动态冲击试验研究[J].振动与冲击, 2011, 30(11):67-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.11.015Ren Xiaohu, Huo Jingsi, Chen Baisheng. Dynamic behaviors of concrete-filled steel stub columns after exposure to high temperature[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(11):67-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.11.015 [22] Xiao Yan, Shan Jianhua, Zheng Qiu, et al. Experimental studies on concrete filled steel tubes under high strain rate loading[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2009, 21(10):569-577. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2009)21:10(569) [23] Jones N. Structural impact[M]. Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press, 1988:100-150. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)
-








 下载:
下载:




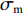
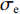









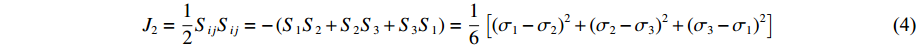


















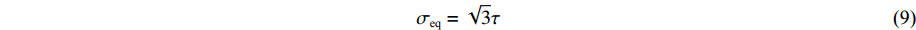















































 下载:
下载:
























