Experimental and simulation of diffusion model and characteristics of explosive cloud at different wind fields
-
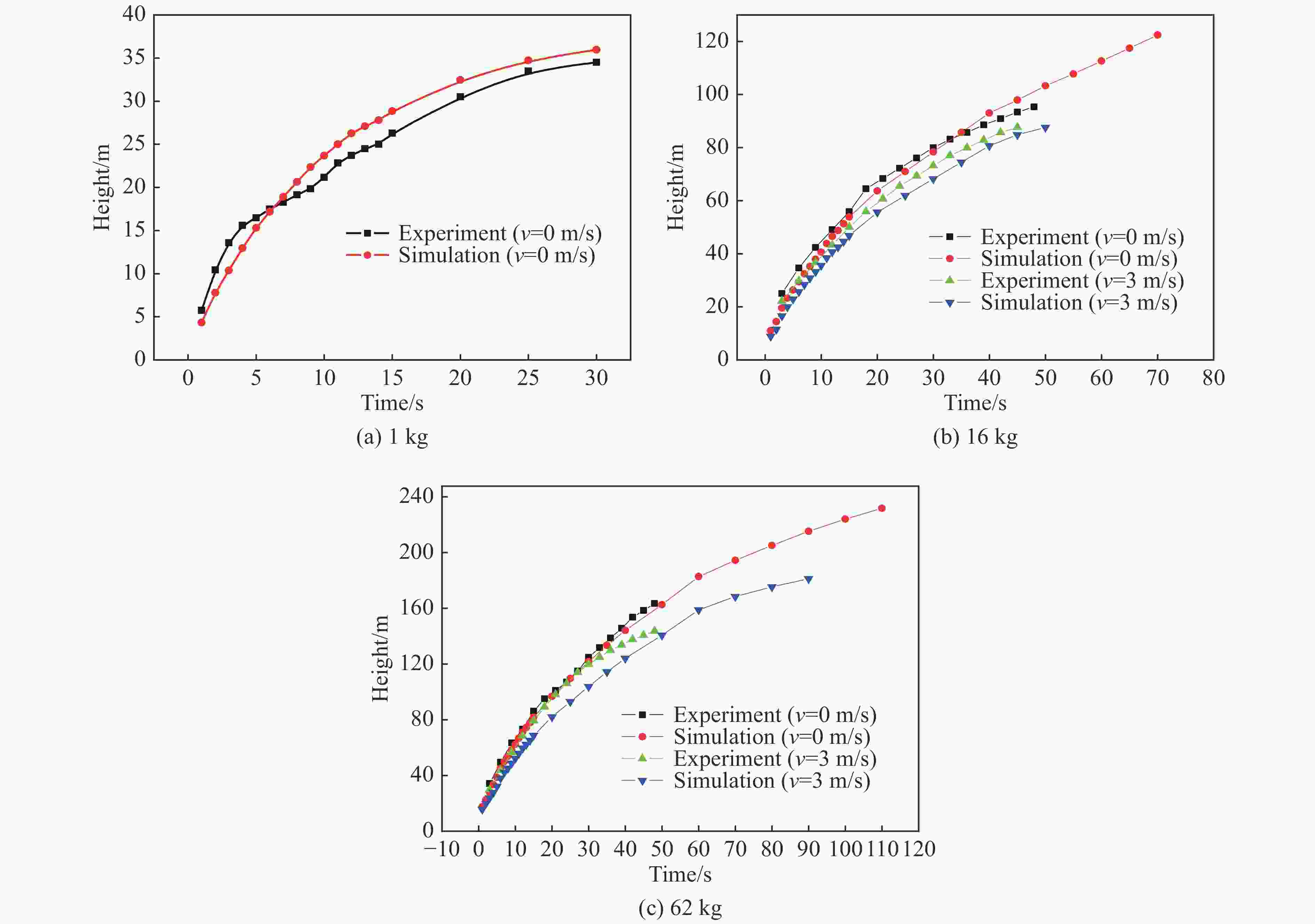
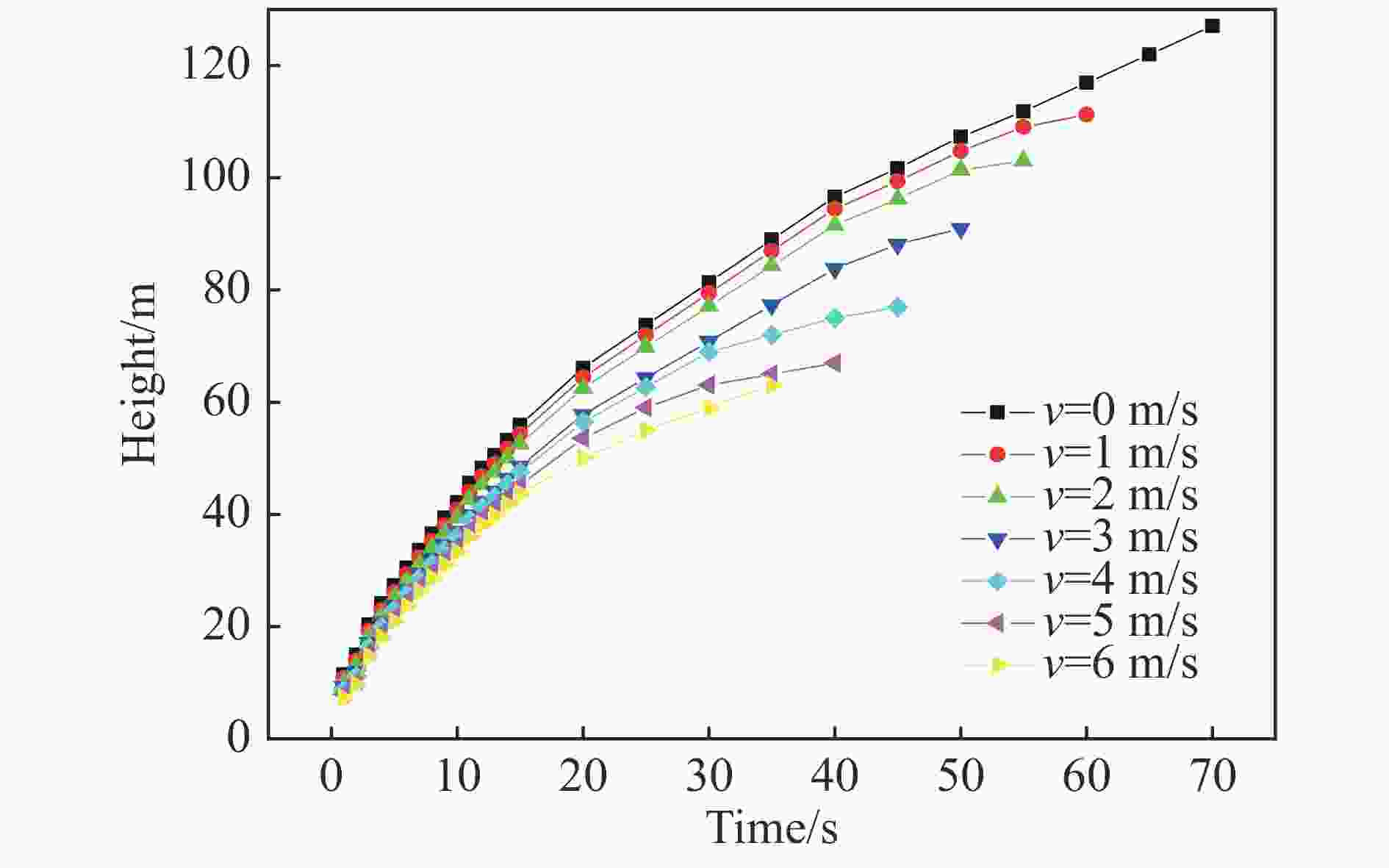
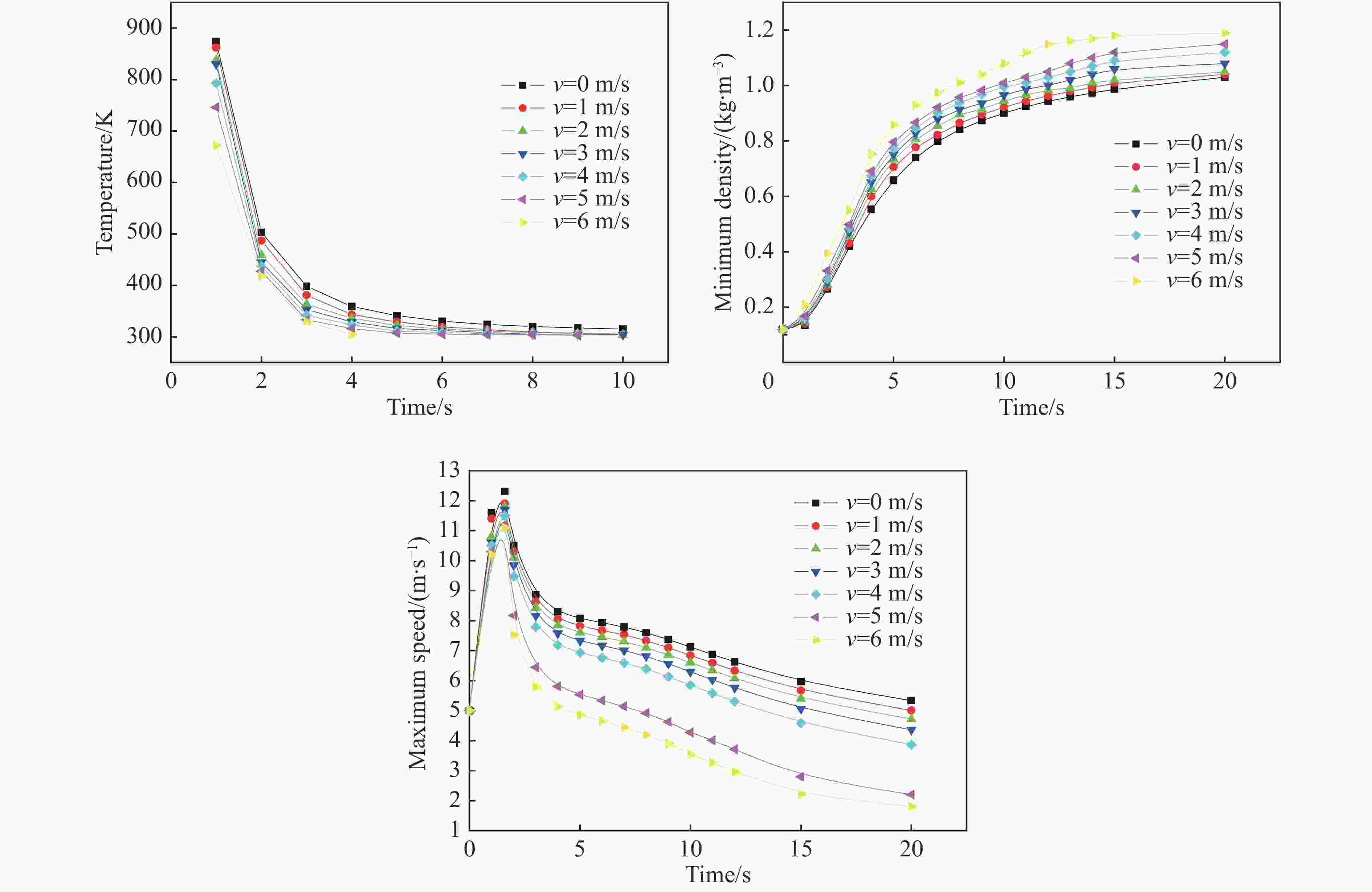
摘要: 为获取不同风场下TNT爆炸烟云扩散时空分布规律与高度变化模型,本文理论描述了爆炸烟云扩散过程与机理,开展了不同水平风速下烟云扩散的计算流体力学(computational fluid dynamics, CFD)仿真和外场时空分布实验,建立了不同水平风速下烟云高度随时间变化模型及烟云最终高度计算模型,分析了烟云扩散过程中形态、温度、密度、速度变化规律。研究结果显示:CFD方法仿真烟云分布结果与实验结果基本一致,大气稳定且无风条件下烟云高度随时间呈指数0.5的幂函数关系,最终高度与爆炸当量可拟合为指数0.47的幂函数模型;水平风会加快烟云与空气混合的速度,导致幂函数模型中指数参数随风速变大而呈线性减小规律,风速越大烟云上升速度衰减越快、上升时间越短、最终高度越低。Abstract: In order to obtain the spatial and temporal distribution law and height variation model of TNT explosion cloud diffusion under different wind Fields, this paper theoretically describes the diffusion process and mechanism of the explosion cloud, and carries out the computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation and the field-time distribution experiment of the cloud diffusion under different horizontal wind speeds, and analyzes the diffusion process of the cloud. Morphology, temperature, density and speed change law were established, and the variation model of cloud height with time at different u-wind speeds and the final height calculation model of cloud were established. The results show that the CFD method simulation cloud diffusion results are consistent with the experimental results. The cloud height has a power function with an exponent of 0.5 under windless conditions. The final height and explosive equivalent can be fitted to a power function model with an index of 0.47. The horizontal wind will speed up the mixing of the cloud and the air, causing the exponential parameter of the power function model to decrease linearly with the wind speed becoming larger. The higher the wind speed, the faster the decay rate of the cloud, the shorter the rise time, and the lower the final height.
-
表 1 实验分组表
Table 1. Experiment group table
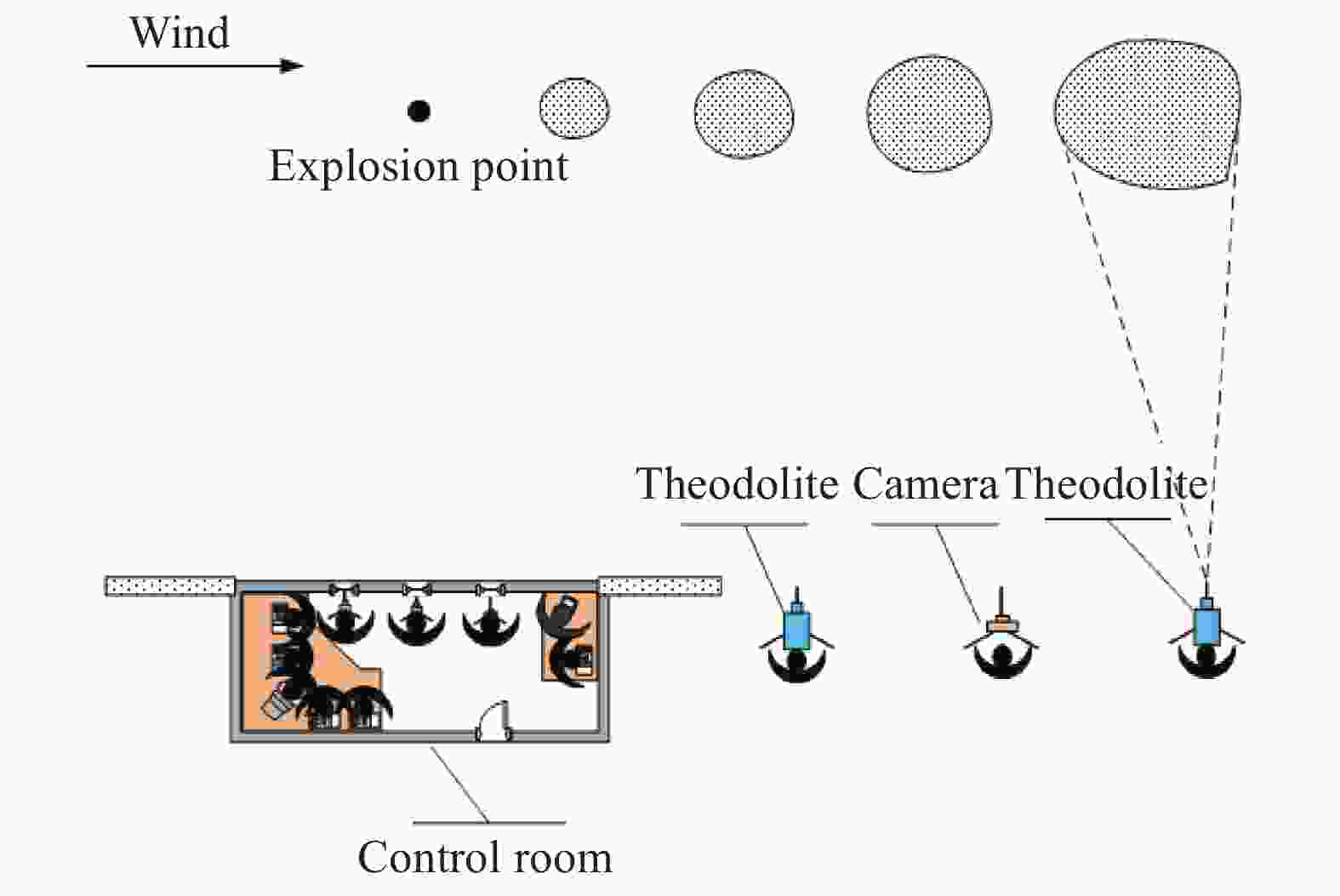
分组 M/kg v/(m∙s−1) 分组 M/kg v/(m∙s−1) 1 1 <0.5 (无风) 4 16 3±0.5(典型风) 2 16 <0.5 (无风) 5 62 3±0.5(典型风) 3 62 <0.5 (无风) 注:M为TNT当量,v为风速。 -
[1] 周宣赤. 基于爆炸现场痕迹反演爆源参数方法及应用[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2014: 3−14. [2] CHURCH H W. Cloud rise from high explosive detonations: TID-4500 [R]. USA: Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), 1969. [3] THIELEN H, SCHRODL E. Blast experiments for the derivation of initial cloud dimensions after a “Dirty Bomb” event: Koln- 50667 [R]. Germany, 2004. [4] SHARON A, HALEVY I, SATTINGER D, et al. Cloud rise model for radiological dispersal devices events [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2012, 54: 603–610. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.02.050. [5] MAKHVILADZE G M, ROBERTS J P, YAKUSH S E. Modelling of atmospheric pollution by explosions [J]. Environmental Software, 1995, 10(2): 117–127. DOI: 10.1016/0266-9838(94)00005-R. [6] KANSA E J. A time dependant buoyant puff model for explosion sources: UCRL-ID-128733 [R]. USA: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 1997. [7] KANARSKA Y, LOMOV I, GLENN L, et al. Numerical simulation of cloud rise phenomena associated with nuclear bursts [J]. Annals of Nuclear Energy, 2009, 36(10): 1475–1483. DOI: 10.1016/j.anucene.2009.08.009. [8] 郑毅. 瞬时热源(爆炸烟云)浮力涡环研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2008: 12−40. [9] 李晓丽, 郑毅, 刘伟, 等. 爆炸烟云运动的试验与数值模拟研究初探 [J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2011, 31(2): 131–135. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2011.02.002.LI X L, ZHENG Y, LIU W, et al. Numerical modeling and experimental research on the movement of the explosion clouds [J]. Nuclear Electronics and Detection Technology, 2011, 31(2): 131–135. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-0934.2011.02.002. [10] ZHANG X, MOUSSA N A, GROSZMANN D E, et al. A simple analytical buoyant puff rise model [C] // Proceedings of JANNAF Safety and Environmental Protection Subcommittee Meeting. Tampa, Florida, 1995. [11] BROWN R C, KOLB C E, CONANT J A, et al. Source characterization model (SCM) [R]. Washington: United States Department of Energy, 2004. [12] 段中山, 过惠平, 冯孝杰, 等. 爆炸烟云扩散的时空分布模型及特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(5): 054202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0380.DUAN Z S, GUO H P, FENG X J, et al. Temporal and spatial distribution models of explosive cloud diffusion and their characteristics [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(5): 054202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0380. [13] LEBEL L, BOURGOUIN P, CHOUHAN S, et al. The sensitivity of atmospheric dispersion calculations in near-field applications: modeling of the FullScale RDD experiments with operational models in Canada, part I [J]. Health Physics, 2016, 110(5): 499–517. DOI: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000365. [14] KWAK H Y, KANG K M, KO I, et al. Fire-ball expansion and subsequent shock wave propagation from explosives detonation [J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2012, 59: 9–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2012.04.022. [15] ABDUL-KARIM N, BLACKMAN C S, GILL P P, et al. The spatial distribution patterns of condensed phase post-blast explosive residues formed during detonation [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 316: 204–213. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.081. [16] FEDINA E, FUREBY C. Investigating ground effects on mixing and afterburning during a TNT explosion [J]. Shock Waves, 2013, 23(3): 251–261. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-012-0420-9. [17] 曹毅. 基于Fluent的大气雾霾流场研究[D]. 山东: 青岛科技大学, 2018: 31−43. [18] MISHRA K B, WEHRSTEDT K D, KREBS H. Boiling liquid expanding vapour explosion (BLEVE) of peroxy-fuels: experiments and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation [J]. Energy Procedia, 2015, 66: 149–152. DOI: 10.1016/j.egypro.2015.02.082. -






 下载:
下载: