Experimental study on dynamic response and failure mode transformation of reinforced concrete beams under impact
-
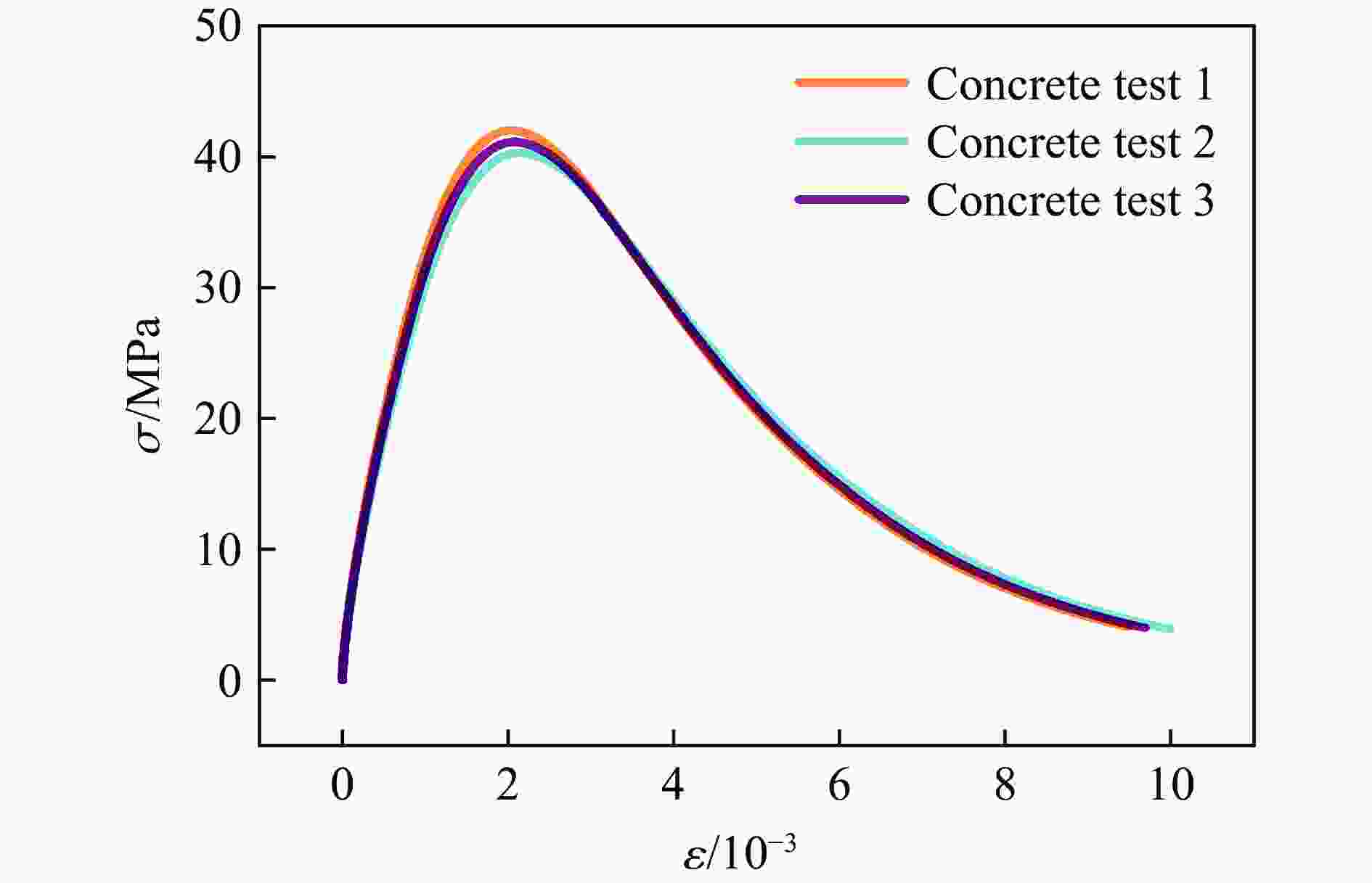
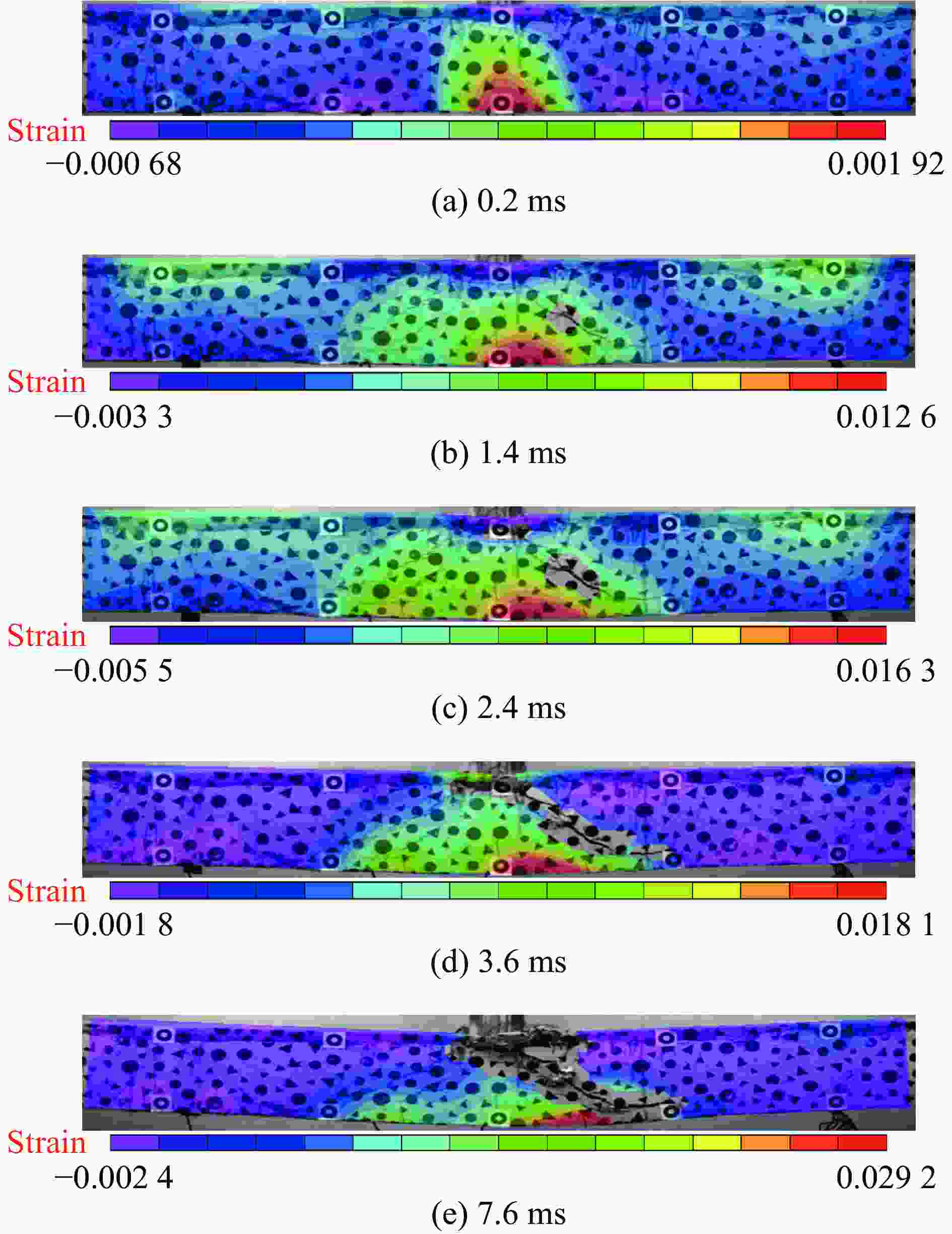
摘要: 随着结构配置和冲击能量等主要影响因素的变化,钢筋混凝土梁的冲击动力响应和破坏模式会发生转化。开展不同配置的钢筋混凝土梁的落锤冲击试验,综合测量获得冲击力、支座反力、钢筋与混凝土应变、冲击局部与结构整体变形等参数,重点分析不同混凝土强度、不同纵筋/箍筋配置以及不同冲击速度对钢筋混凝土梁的动力响应以及破坏模式的影响规律。试验表明:低速撞击下钢筋混凝土梁的位移峰值、残余位移随冲击速度的提高而增大,均与冲击动能与极限静承载力之比存在近似线性关系;混凝土强度越高、纵筋配筋率越高,相同冲击条件下梁所受的撞击力峰值越大,但整体位移响应越小;配箍率的变化对结构的局部响应和整体响应的影响均较小;结构受到撞击时剪切效应在前,弯曲效应在后,斜裂缝先于垂直裂缝出现;依据结构的破坏极限状态,判断梁在冲击作用下存在的弯曲破坏、弯剪破坏、剪切破坏和冲切破坏等4种破坏模式,结果表明:相同结构配置条件下,随冲击速度的不断提高,钢筋混凝土梁由弯曲破坏向弯剪破坏、剪切破坏和冲切破坏转化;冲击速度相同时,提高混凝土强度、配箍率或降低纵向钢筋配筋率,梁的破坏模式逐步由冲切、剪切破坏向弯曲破坏模式转化。结构的冲击破坏模式及其转化规律能够为结构的抗撞设计与防护提供参考。Abstract: By changing the main influencing factors such as structural configuration and impact energy, the impact dynamic response and failure mode of reinforced concrete beams would change. Drop hammer impact tests of reinforced concrete beams with different configurations were conducted, and the parameters of impact force, support reaction, reinforcement and concrete strain, impact local deformation and overall structural deformation of the structure were obtained by comprehensive measurements. The influence law of different concrete strength, different longitudinal reinforcement/stirrup configuration, and different impact velocity on the dynamic response and failure mode of reinforced concrete beams was thoroughly analyzed. The result of the experiment proves that the peak displacement and residual displacement of reinforced concrete beams under low-velocity impact increase with the improvement of impact velocity. Moreover, the peak displacement and residual displacement are approximately linearly related to the ratio of impact kinetic energy to static ultimate load. The higher the concrete strength and the greater the longitudinal reinforcement ratio are, the larger the peak impact force on the beam is under the equal impact conditions, whereas the smaller the overall displacement response is. Changing the stirrup ratio has little effect on the local response and the overall response of the structure. When the structure is impacted, the shear effect occurs first, the bending effect occurs last, and the oblique crack appears before the vertical crack. Four failure modes of a beam under impact are assessed in accordance with the failure limit state of the structure: bending failure, bending-shear failure, shear failure, and punching failure. According to the test results, with the improvement of the impact velocity, the reinforced concrete beam changes from bending failure to bending shear failure, shear failure and punching failure under the same structural arrangement. By increasing the concrete strength and stirrup ratio or decreasing the longitudinal reinforcement ratio, the failure mode of the beam gradually changes from punching failure to bending failure under the same impact velocity. The impact failure mode and its transformation law can provide important reference for anti-collision design and protection of structures.
-
Key words:
- reinforced concrete beams /
- drop hammer experiments /
- dynamic response /
- failure mode /
- punching failure
-
表 1 冲击试验工况
Table 1. Impact test conditions
结构配置 试验工况 落高/m v/(m·s−1) EI/J 混凝土:C20
底部纵筋:2$\varnothing $10
箍筋:$\varnothing $6@200B1-S (静载) B1-3.13 0.5 3.13 489.85 B1-5.42 1.5 5.42 1468.82 B1-7.00 2.5 7.00 2450.00 B1-9.39 4.5 9.39 4408.61 混凝土:C40
底部纵筋:2$ \varnothing$10
箍筋:$\varnothing $6@200B2-S (静载) B2-3.13 0.5 3.13 489.85 B2-4.25 1.5 5.42 1468.82 B2-7.00 2.5 7.00 2450.00 B2-9.39 4.5 9.39 4408.61 混凝土:C40
底部纵筋:2$\varnothing $14
箍筋:$\varnothing $6@200B3-S (静载) B3-3.13 0.5 3.13 489.85 B3-5.42 1.5 5.42 1468.82 B3-9.39 4.5 9.39 4408.61 B3-12.12 7.5 12.12 7344.72 混凝土:C40
底部纵筋:2$\varnothing $10
箍筋:$\varnothing $6@100B4-S (静载) B4-3.13 0.5 3.13 489.85 B4-5.42 1.5 5.42 1468.82 B4-7.00 2.5 7.00 2450.00 B4-9.39 4.5 9.39 4408.61 表 2 梁试件的静态承载力参数
Table 2. Static bearing capacity parameters of beam specimens
试件 xy/mm Fy/kN xu/mm Fu/kN B1-S 8.14 29.81 35.86 36.96 B2-S 6.97 29.76 31.75 38.48 B3-S 8.82 49.57 39.86 55.08 B4-S 6.25 31.96 31.64 39.03 表 3 落锤冲击试验结果
Table 3. Drop hammer impact test results
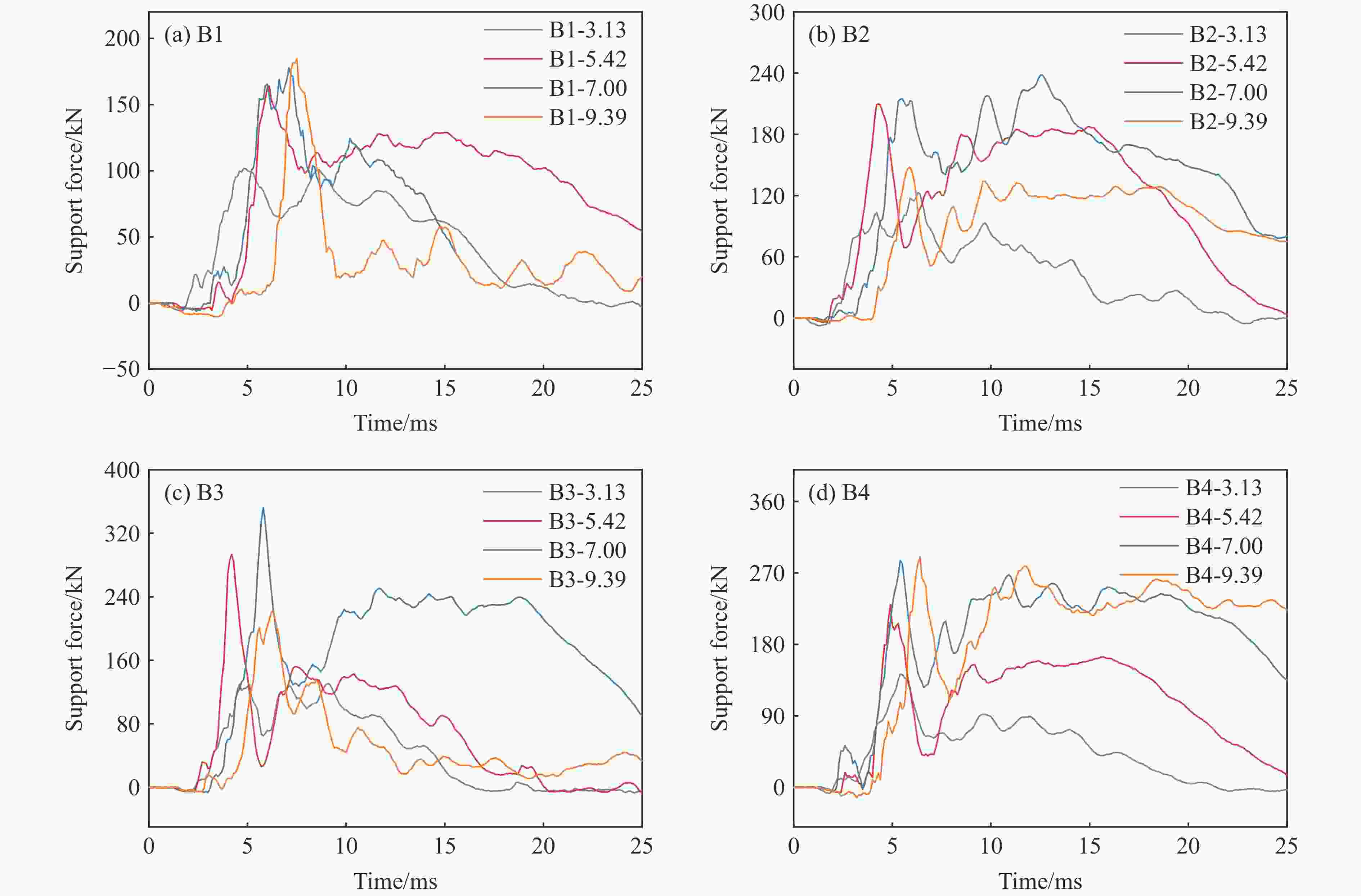
试件 混凝土强度 冲击速度v/(m·s−1) 冲击动能
EI/kJ冲击力峰值
pImax/kN支座反力峰值
pRmax/kN位移峰值
Dmax/mm残余位移Dr/mm B1-3.13 C20 3.13 0.49 168.10 101.48 13.60 3.71 B1-5.42 C20 5.42 1.47 268.64 163.90 37.10 19.96 B1-7.00 C20 7.00 2.45 415.29 177.75 70.97 58.21 B1-9.39 C20 9.39 4.41 627.57 184.76 垮塌 — B2-3.13 C40 3.13 0.49 291.69 122.85 12.21 3.83 B2-5.42 C40 5.42 1.47 616.70 231.68 27.33 15.77 B2-7.00 C40 7.00 2.45 726.94 238.19 50.07 34.55 B2-9.39 C40 9.39 4.41 868.77 147.89 81.90 64.45 B3-3.13 C40 3.13 0.49 257.75 124.76 10.40 0.38 B3-5.42 C40 5.42 1.47 570.26 293.24 21.69 9.56 B3-9.39 C40 9.39 4.41 1049.27 352.62 63.83 42.63 B3-12.12 C40 12.12 7.34 1285.89 219.83 垮塌 — B4-3.13 C40 3.13 0.49 268.00 142.44 12.62 4.19 B4-5.42 C40 5.42 1.47 627.47 230.03 29.16 18.68 B4-7.00 C40 7.00 2.45 744.12 285.57 47.78 31.38 B4-9.39 C40 9.39 4.41 903.26 290.69 82.43 64.33 表 4 梁的冲击破坏模式及转化规律
Table 4. Impact failure modes and transformation laws of beams
试件编号 加载速度v/(m·s−1) 破坏模式 破坏模式的转化 B1-S 静载 弯曲破坏 弯曲破坏→弯剪破坏→剪切破坏→冲切破坏 B1-3.13 3.13 弯曲破坏 B1-5.42 5.42 弯剪破坏 B1-7.00 7.00 剪切破坏 B1-9.39 9.39 冲切破坏 B2-S 静载 弯曲破坏 弯曲破坏→弯剪破坏→剪切破坏 B2-3.13 3.13 弯曲破坏 B2-5.42 5.42 弯曲破坏 B2-7.00 7.00 弯剪破坏 B2-9.39 9.39 剪切破坏 B3-S 静载 剪弯破坏 弯曲破坏→弯剪破坏→剪切破坏→冲切破坏 B3-3.13 3.13 弯曲破坏 B3-5.42 5.42 弯剪破坏 B3-9.39 9.39 弯剪破坏 B3-12.12 12.12 冲切破坏 B4-S 静载 弯曲破坏 弯曲破坏→弯剪破坏 B4-3.13 3.13 弯曲破坏 B4-5.42 5.42 弯曲破坏 B4-7.00 7.00 弯曲破坏 B4-9.39 9.39 弯剪破坏 -
[1] 王明洋, 杨晓宁, 卢浩, 等. 事故性冲击钢筋混凝土结构的计算原理与设计方法 [J]. 防护工程, 2020, 42(4): 1–14. DOI: CNKI:SUN:FHGC.0.2020-04-001.WANG M Y, YANG X N, LU H, et al. Computation and design of accidental impact on reinforced concrete structure [J]. Protective Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 1–14. DOI: CNKI:SUN:FHGC.0.2020-04-001. [2] HUGHES G, BEEBY A W. Investigation of the effect of impact loading on concrete beams [J]. Structural Engineer, 1982, 60(15): 45–52. [3] KISHI N, MIKAMI H, MATSUOKA K G. Impact behavior of shear-failure-type RC beams without shear rebar [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27(9): 955–968. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(01)00149-X. [4] 曾翔, 许斌. 无腹筋钢筋混凝土梁抗冲击行为试验研究 [J]. 土木工程学报, 2012, 45(9): 63–73. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2012.09.022.ZENG X, XU B. Experimental study on the impact-resistant behavior of RC beams without shear-resistant rebar [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2012, 45(9): 63–73. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2012.09.022. [5] 许斌, 曾翔. 冲击荷载作用下钢筋混凝土梁性能试验研究 [J]. 土木工程学报, 2014, 47(2): 41–51, 61. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2014.02.010.XU B, ZENG X. Experimental study on the behaviors of reinforced concrete beams under impact loadings [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2014, 47(2): 41–51, 61. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2014.02.010. [6] 霍静思, 胡开赢. RC梁冲击破坏机理试验研究与残余变形预测方法探讨 [J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(1): 112–117. DOI: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2017.01.014.HUO J S, HU K Y. Failure mechanism of RC beams under impact loading and discussion on prediction methods of residual deflection [J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2017, 44(1): 112–117. DOI: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2017.01.014. [7] COTSOVOS D M , STATHOPOULOS N D, ZERIS C A. Behavior of RC beams subjected to high rates of concentrated loading [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2008, 134(12): 1839–1851. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2008)134:12(1839). [8] COTSOVOS D M. A simplified approach for assessing the load-carrying capacity of reinforced concrete beams under concentrated load applied at high rates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(8): 907–917. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.01.005. [9] 刘飞, 罗旗帜, 蒋志刚. 低速冲击下RC梁的动态响应和破坏机理研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2015(5): 155–161. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.11.1089.LIU F, LUO Q Z, JIANG Z G. Dynamic responses and failure mechanism of RC beams to low velocity impact [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015(5): 155–161. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2013.11.1089. [10] 赵武超, 钱江. 冲击荷载下钢筋混凝土梁局部响应特征研究 [J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(3): 25–32. DOI: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2019.03.004.ZHAO W C, QIAN J. Study on local response characteristics of RC beams under impact loading [J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2019, 46(3): 25–32. DOI: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2019.03.004. [11] 赵武超, 钱江, 张文娜. 冲击荷载下钢筋混凝土梁的性能及损伤评估 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(1): 111122. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0288.ZHAO W C, QIAN J, ZHANG W N. Performance and damage evaluation of RC beams under impact loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(1): 015102. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0288. [12] 王银辉, 陆晓宏. 钢筋混凝土梁在冲击作用初期的惯性力分布 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(6): 2457–2463. DOI: CNKI:SUN:KXJS.0.2020-06-050.WANG Y H, LU X H. Inertial force distribution of reinforced concrete beams at the initial stage of impact [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(6): 2457–2463. DOI: CNKI:SUN:KXJS.0.2020-06-050. [13] PHAM T M, HAO H. Effect of the plastic hinge and boundary conditions on the impact behavior of reinforced concrete beams [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 102(4): 74–85. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.12.005. [14] LI H, CHEN W, HAO H. Influence of drop weight geometry and interlayer on impact behavior of RC beams [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 131: 222–237. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.04.028. [15] 王明洋, 王德荣, 宋春明. 钢筋混凝土梁在低速冲击下的计算方法 [J]. 兵工学报, 2006, 27(3): 399–405. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2006.03.004.WANG M Y, WANG D R, SONG C M. A calculation method of reinforced concrete beam under low velocity impact [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2006, 27(3): 399–405. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2006.03.004. [16] OHNUMA H, ITO C, NOMACHI S G. Dynamic response and local rupture of reinforced concrete beam and slab under impact loading[R]. IASMiRT, Brussels, Belgium. 1985. [17] FU Y, YU X, DONG X, et al. Investigating the failure behaviors of RC beams without stirrups under impact loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 137(3): 103432.1. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103432. [18] SUKONTASUKKUL P, MINDESS S. The shear fracture of concrete under impact loading using end confined beams [J]. Materials & Structures, 2003, 36(6): 372–378. DOI: 10.1007/bf02481062. [19] KISHI N, NAKANO O, MATSUOKA K G, et al. Experimental study on ultimate strength of flexural-failure-type RC beams under impact loading [R]. IASMiRT, Washington DC, USA, 2001. [20] FUJIKAKE K, LI B, SOEUN S. Impact response of reinforced concrete beam and its analytical evaluation [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2009, 135(8): 938–950. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0000039. [21] ZHAO D B, YI W J, KUNNATH S K. Shear mechanisms in reinforced concrete beams under impact loading [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2017, 143(9): 04017089. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001818. [22] 赵德博, 易伟建. 钢筋混凝土梁抗冲击性能和设计方法研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(11): 139–145. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.11.025.ZHAO D B, YI W J. Anti-impact behavior and design method for RC beams [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(11): 139–145. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.11.025. [23] 梅福林, 董新龙, 俞鑫炉. 不同落锤速度冲击下混凝土和RC梁破坏研究 [J]. 宁波大学学报(理工版), 2017, 30(5): 83–88.MEI F L, DONG X L, YU X L. On failure behavior of concrete and RC beam to different velocity impact [J]. Journal of Ningbo University (Natural Science & Engineering Edition), 2017, 30(5): 83–88. [24] KISHI N, MIKAMI H. Empirical formulas for designing reinforced concrete beams under impact loading [J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2012, 109(4): 509–519. [25] TACHIBANA S, MASUYA H, NAKAMURA S. Performance based design of reinforced concrete beams under impact [J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2010, 10(6):1069–1078. DOI: 10.5194/nhess-10-1069-2010. [26] CHUNG L, SHAH S P. Effect of loading rate on anchorage bond and beam-column joints [J]. ACI Structural Journal, 1989, 86(2): 132–142. DOI: 10.1016/0022-1694(89)90174-1. [27] FU H C, ERKI M A, SECKIN M. Review of effects of loading rate on reinforced concrete [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 1991, 117(12): 3660–3679. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1991)117:12(3660). [28] SOROUSHIAN P , CHOI K. Steel mechanical properties at different strain rates [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2015, 113(4): 663–672. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1987)113:4(663). [29] HONG S, KANG T H K. Dynamic strength properties of concrete and reinforcing steel subject to extreme loads [J]. ACI Structural Journal, 2016, 113(5): 983. DOI: 10.14359/51688754. -







 下载:
下载: