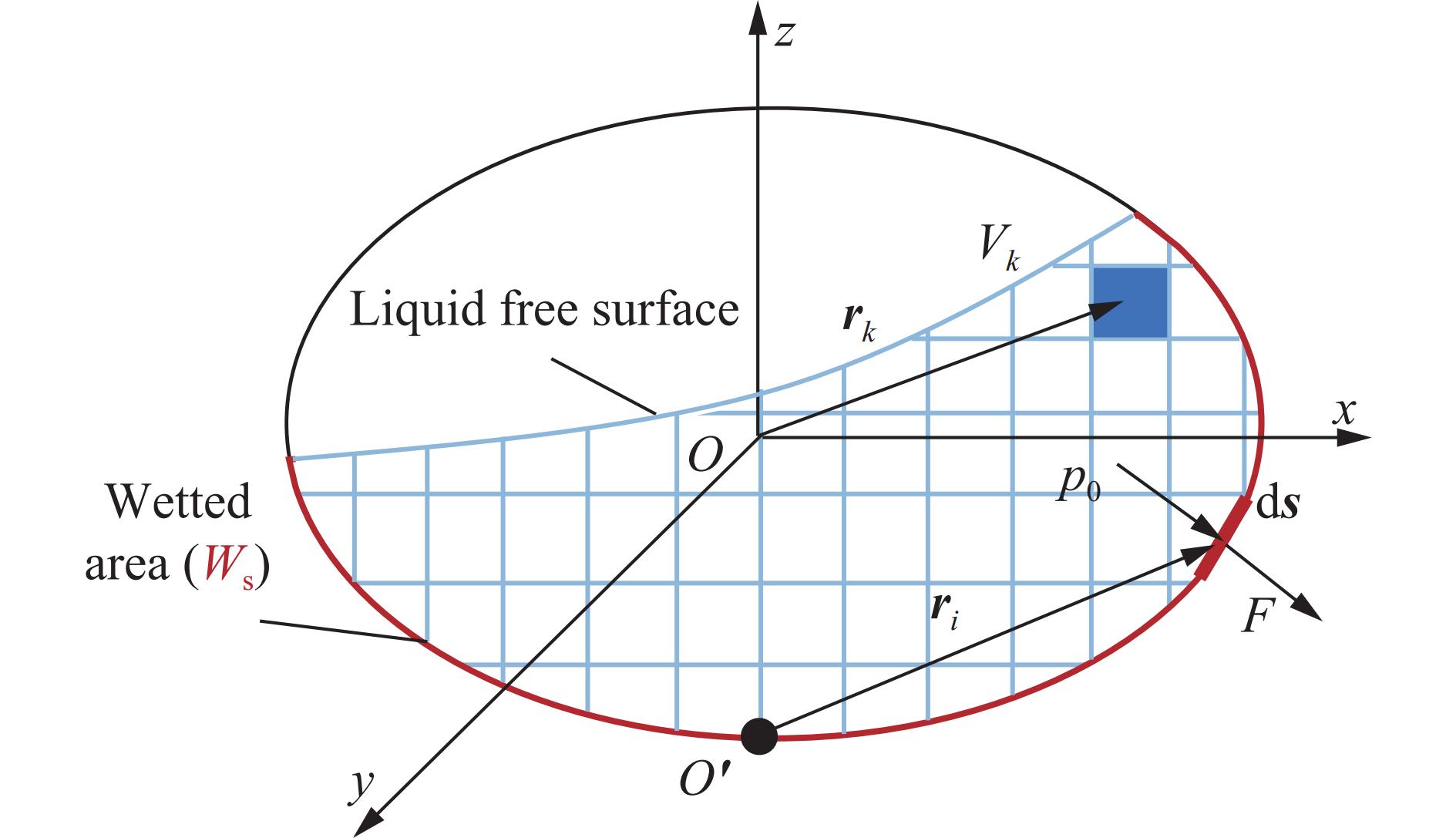
Response analysis of liquid sloshing in a tank with rigid baffles
-
摘要: 部分充液罐体内的液体在外部激励的作用下容易出现晃动现象,由液体晃动产生的附加力和力矩会对载液罐车产生不利影响。为了避免液罐车制动时其罐内液体产生较大幅度的晃动,提出了几种类型的防波板,并研究了防波板及其几何参数对液罐车内液体晃动的影响。首先,建立了基于有限体积法的液体晃动的数值模型。其次,对液体晃动现象进行了一系列的实验,通过将实验获得的液面波形与同等条件下数值模拟获得的结果进行对比,验证数值模型的有效性。最后,将验证后的数值模型用于分析防波板的几何参数对液体晃动响应的影响。研究结果表明,开孔防波板不仅可以有效降低罐内晃动响应参数的峰值,还可以明显缩短罐内晃动液体达到稳定的时间;防波板的开孔位置和孔的数量在车辆制动过程中对罐体内液体晃动引起的纵向力的峰值影响差别不大,但是对液体晃动引起的俯仰力矩的峰值的影响比较明显;晃动响应参数峰值的下降率会随着充液高度的增加呈先下降后上升的趋势,液体晃动引起的俯仰力矩的峰值取得最大值时,防波板对罐体内的液体晃动的抑制效果最差。Abstract: The liquid in partially filled tanks is prone to slosh under external excitation, and the additional forces and moments generated by liquid sloshing can have adverse effects on tank trucks. In order to avoid significant sloshing of the liquid in the tank when the tank truck brakes, several types of baffles were proposed, and the influence of baffles and their geometric parameters on the liquid sloshing inside the tank truck was studied. Firstly, a numerical model of liquid sloshing based on the finite volume method was established. Secondly, a series of liquid sloshing experiments were conducted. The effectiveness of the numerical model was verified by comparing the free surface waveforms obtained from the experiments at different times with those obtained from numerical simulations under the same conditions. Finally, the validated numerical model was used to analyze the influence of the geometric parameters of the baffle on the liquid sloshing response parameters under different liquid-filling conditions. The research results indicate that the perforated baffle can not only effectively suppress the peak of the sloshing response parameters in the tank but also significantly shorten the time for liquid sloshing to reach stability. The position and number of baffle orifices have little effect on the peak longitudinal force caused by liquid sloshing during vehicle braking, while the peak pitch moment is more significantly affected by the geometric parameters of the baffle. By studying liquid sloshing in the tank at different filling heights, it is found that the decrease rate of the peak value of the sloshing response parameter will first decrease and then increase with the increase of the filling height. When the peak value of pitch moment reaches its maximum value, the baffle has the worst suppression effect on liquid sloshing in a partially filled tank.
-
Key words:
- liquid sloshing /
- tank truck /
- baffle /
- longitudinal force /
- pitch moment
-
表 1 T1和T2b晃动响应参数峰值相对于T0罐的下降率
Table 1. Decrease rate of the peak sloshing response parameters of T1 and T2b relative to T0 tank
充液比/% T1相对于T0的下降率/% T2b相对于T0的下降率/% 纵向力 俯仰力矩 载荷转移 纵向力 俯仰力矩 载荷转移 40 27.8 23.6 26.6 29.6 31.9 34.4 60 29.3 21.9 19.4 29.7 29.6 28.8 80 30.0 38.0 45.4 32.4 53.4 68.2 表 2 T1和T2b罐晃动响应参数峰值
Table 2. Peak values of sloshing response parameters of T1 and T2b tanks
充液高度/m T1罐晃动响应参数峰值 T2b罐晃动响应参数峰值 纵向力/kN 俯仰力矩/(kN·m) 载荷转移/m 纵向力/kN 俯仰力矩/(kN·m) 载荷转移/m 0.715 23.7 105.8 1.56 23.4 88.1 1.26 0.815 28.6 130.6 1.58 27.7 112.5 1.35 0.915 32.9 147.0 1.50 33.0 133.8 1.35 1.015 38.5 153.6 1.34 37.6 138.2 1.19 1.115 42.7 155.7 1.18 42.2 142.3 1.06 1.215 46.7 149.1 0.97 45.9 130.1 0.82 1.315 50.4 135.8 0.75 48.3 113.6 0.60 -
[1] JIANG Z, SHI Z, JIANG H, et al. Investigation of the load and flow characteristics of variable mass forced sloshing [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(3): 033325. DOI: 10.1063/5.0142148. [2] KIM S P, CHUNG S M, SHIN W J, et al. Experimental study on sloshing reduction effects of baffles linked to a spring system [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 170: 136–147. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.10.001. [3] MARTINEZ-CARRASCAL J, GONZALEZ L M. On the experimental scaling and power dissipation of violent sloshing flows [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2022, 115: 103763. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2022.103763. [4] 刘汉武, 张华, 胡震宇, 等. 基于SPH方法航天器含贮箱液体晃动分离动力学研究 [J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2021, 51(8): 938–947. DOI: 10.1360/SST-2021-0123.LIU H W, ZHANG H, HU Z Y, et al. Simulation analysis of liquid sloshing separation in spacecraft with tank based on SPH method [J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2021, 51(8): 938–947. DOI: 10.1360/SST-2021-0123. [5] 林晓冬, 张锐, 刘芳, 等. 基于变分模态分解的复杂航天器姿态扰动分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(13): 303–309. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.13.036.LIN X D, ZHANG R, LIU F, et al. Attitude disturbance analysis for complex spacecraft based on variational mode decomposition [J]. Journal of Virbation and Shock, 2023, 42(13): 303–309. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.13.036. [6] LI X S, REN Y Y, ZHENG X L, et al. Model-free adaptive control for tank truck rollover stabilization [J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 1–16. DOI: 10.1155/2021/8417071. [7] 杨秀建, 吴相稷, 邢云祥, 等. 非满载液罐半挂汽车列车侧向耦合动力学模型 [J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(11): 244–254. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.11.026.YANG X J, WU X J, XING Y X, et al. Lateral dynamics modeling for partly filled tractor sem-trailer tank vehicle [J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(11): 244–254. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2018.11.026. [8] 包文红, 张应龙, 班涛, 等. 液罐车内液体晃动对防波板的冲击仿真 [J]. 油气储运, 2022, 41(9): 1087–1094. DOI: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2022.09.012.BAO W H, ZHANG Y L, BAN T, et al. Simulation on impact of liquid sloshing on baffles in liquid tankers [J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2022, 41(9): 1087–1094. DOI: 10.6047/j.issn.1000-8241.2022.09.012. [9] IRANITALAB A, KHATTAK A, BAHOUTH G. Statistical modeling of cargo tank truck crashes: rollover and release of hazardous materials [J]. Journal of Safety Research, 2020, 74: 71–79. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsr.2020.04.010. [10] CAVALAGLI N, BISCARINI C, FACCI A L, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of energy dissipation in a sloshing absorber [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2017, 68: 466–481. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2016.11.020. [11] POGULURI S K, CHO I H. Liquid sloshing in a rectangular tank with vertical slotted porous screen: based on analytical, numerical, and experimental approach [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 189: 106373. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106373. [12] FAN X S, HU Z H, ZHENG X. Research on influence of tank sloshing on ship motion response under different wavelengths [J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(17): 8647. DOI: 10.3390/app12178647. [13] YE W B, LIU J, LIN G, et al. High performance analysis of lateral sloshing response in vertical cylinders with dual circular or arc-shaped porous structures [J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2018, 81: 47–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.apor.2018.09.017. [14] SHAO J R, LI S M, LI Z R, et al. A comparative study of different baffles on mitigating liquid sloshing in a rectangular tank due to a horizontal excitation [J]. Engineering Computations, 2015, 32(4): 1172–1190. DOI: 10.1108/ec-12-2014-0251. [15] BAI W, LIU X, KOH C G. Numerical study of violent LNG sloshing induced by realistic ship motions using level set method [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2015, 97: 100–113. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.01.010. [16] WEN X, ZHAO W W, WAN D C. Multi-phase moving particle semi-implicit method for violent sloshing flows [J]. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 2022, 95: 1–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.euromechflu.2022.04.002. [17] ZHANG A M, LI S M, CUI P, et al. A unified theory for bubble dynamics [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(3): 033323. DOI: 10.1063/5.0145415. [18] LI S M, ZHANG A M, CUI P, et al. Vertically neutral collapse of a pulsating bubble at the corner of a free surface and a rigid wall [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2023, 962: A28. DOI: 10.1017/jfm.2023.292. [19] MA C L, XIONG C W, MA G W. Numerical study on suppressing violent transient sloshing with single and double vertical baffles [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 223: 108557. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.108557. [20] RAKHEJA S, SANKAR S, RANGANATHAN R. Roll plane analysis of articulated tank vehicles during steady turning [J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 1988, 17(1/2): 81–104. DOI: 10.1080/00423118808968896. [21] FANG Q, SUN J, QIU H X, et al. Experimental investigation of liquid sloshing in cylindrical tank with ring baffles under seismic excitation [J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2022, 48(4): 4785–4794. DOI: 10.1007/s13369-022-07182-w. [22] WANG Q Y, LIN G M, JIANG L, et al. Numerical and experimental study of anti-slosh performance of combined baffles in partially filled tank vehicles [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2022, 196: 104555. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2021.104555. [23] XUE M A, ZHENG J, LIN P, et al. Violent transient sloshing-wave interaction with a baffle in a three-dimensional numerical tank [J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2017, 16(4): 661–673. DOI: 10.1007/s11802-017-3383-8. [24] 曾宪君, 黄志涛, 邵家儒, 等. 基于SPH方法的罐式贮箱动力响应及稳定性研究 [J]. 机床与液压, 2021, 49(14): 24–30, 59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2021.14.005.ZENG X J, HUANG Z T, SHAO J R, et al. Dynamic response and stability analysis of storage tank based on SPH method [J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2021, 49(14): 24–30, 59. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2021.14.005. [25] JIN X, LIU M, ZHANG F, et al. Mitigation of liquid sloshing by multiple layers of dual horizontal baffles with equal/unequal baffle widths [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 263: 112184. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112184. [26] ZHANG E H, ZHU W Y, WANG L H. Influencing analysis of different baffle factors on oil liquid sloshing in automobile fuel tank [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2020, 234(13): 3180–3193. DOI: 10.1177/0954407020919584. [27] TSAO W H, HUANG L H, HWANG W S. An equivalent mechanical model with nonlinear damping for sloshing rectangular tank with porous media [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 242: 110145. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.110145. [28] REN Y, KHAYYER A, LIN P, et al. Numerical modeling of sloshing flow interaction with an elastic baffle using SPHinXsys [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 267: 113110. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113110. [29] WANG Q Y, JIANG L, CHAI M, et al. Numerical and experimental analysis of the effect of elastic membrane on liquid sloshing in partially filled tank vehicles [J]. Mechanics Based Design of Structures and Machines, 2021, 51(3): 1741–1757. DOI: 10.1080/15397734.2021.1875844. [30] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 液化气体汽车罐车: GB/T 19905—2017 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. [31] ROMERO J A, HILDEBRAND R, MARTINEZ M, et al. Natural sloshing frequencies of liquid cargo in road tankers [J]. International Journal of Heavy Vehicle Systems, 2005, 12(2): 121–138. DOI: 10.1504/IJHVS.2005.006379. [32] XUE M A, ZHENG J, LIN P. Numerical simulation of sloshing phenomena in cubic tank with multiple baffles [J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2012, 2012: 1–21. DOI: 10.1155/2012/245702. [33] 王琼瑶, 蒋开洪, RAKHEJA S, 等. 部分充液罐车内液体晃动的瞬态响应分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(17): 1–8. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2018.17.001.WANG Q Y, JIANG K H, RAKHEJA S, et al. Transient response analysis of liquid slosh in a liquid-partially filled tank truck [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(17): 1–8. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2018.17.001. -







 下载:
下载: