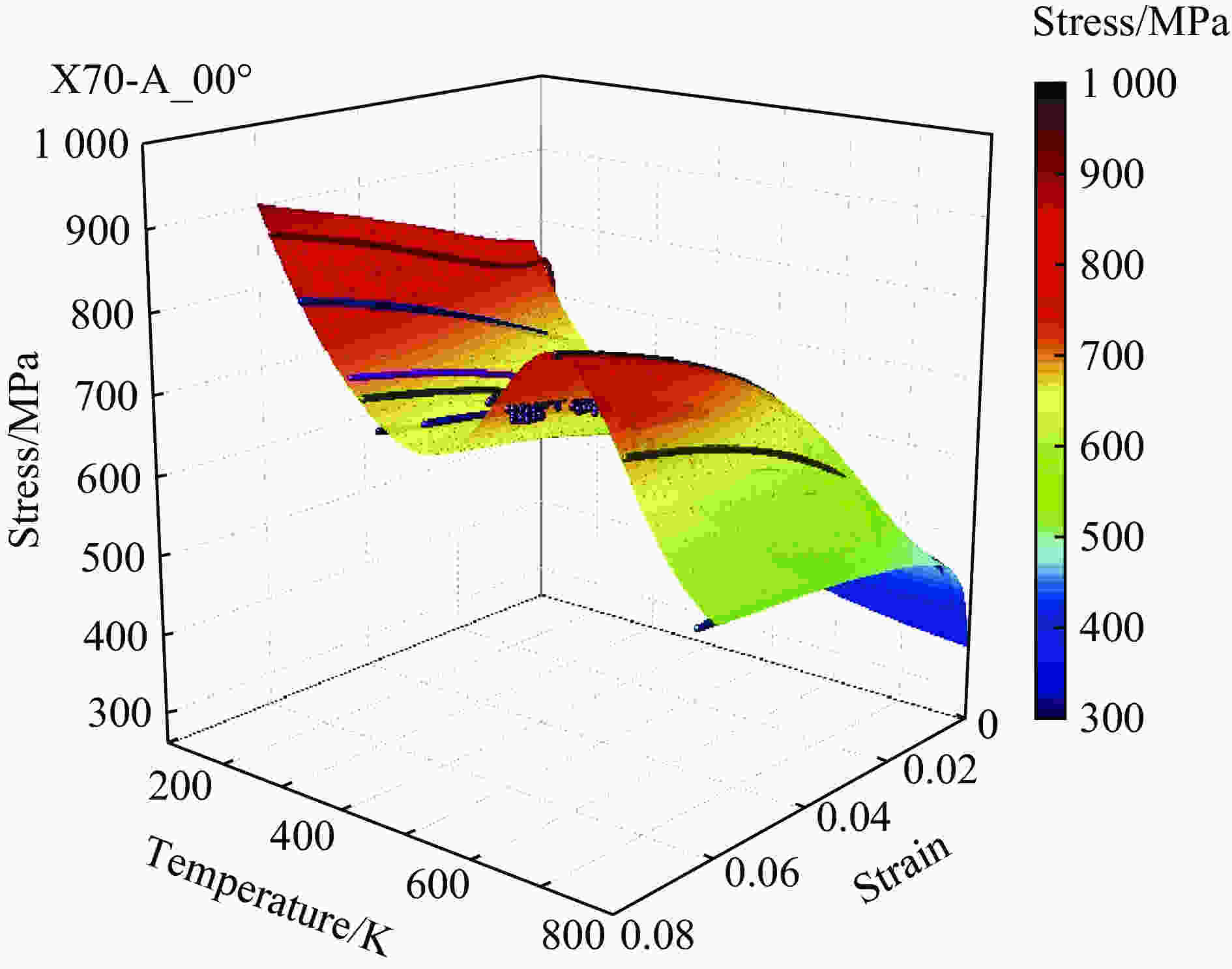
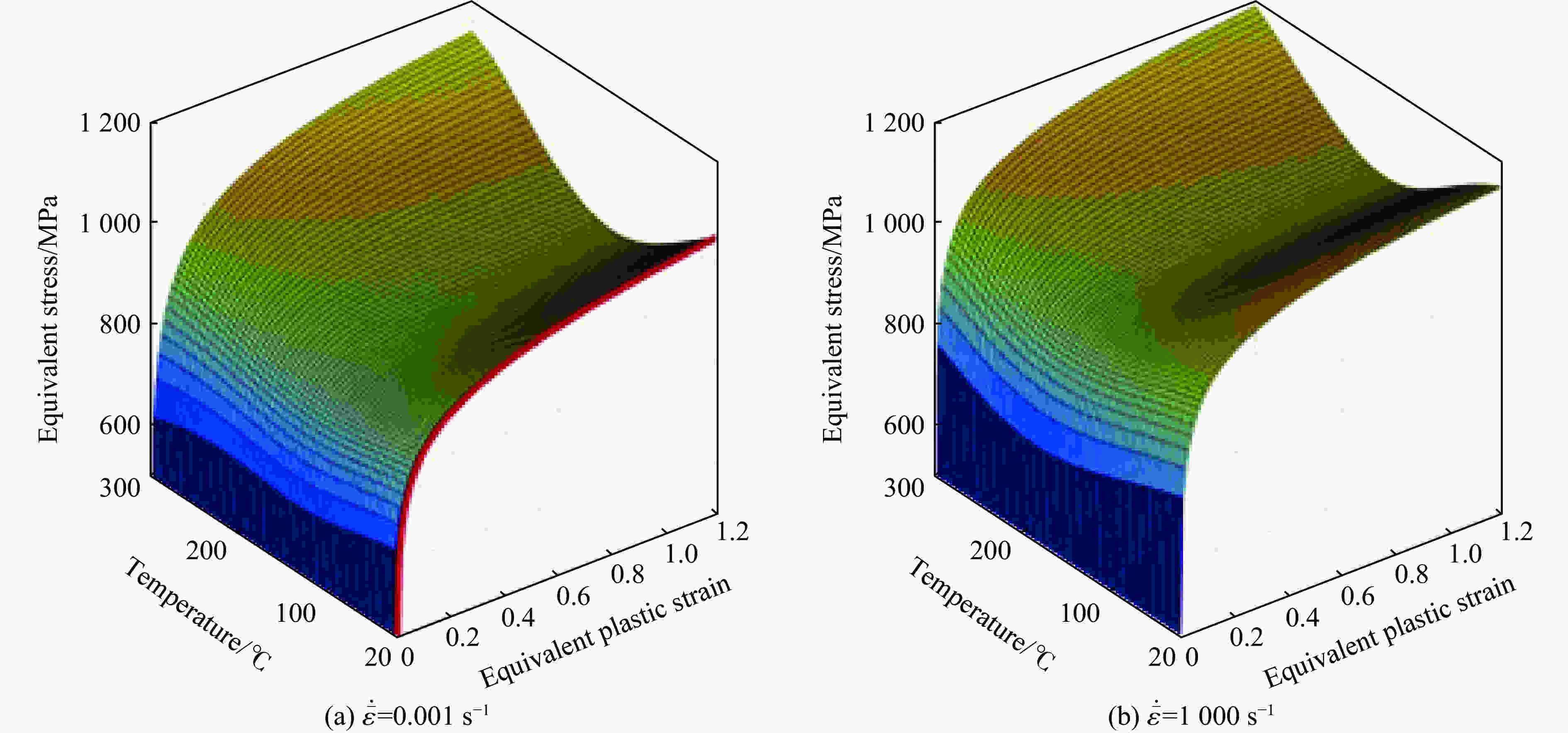
| [1] |
NEMAT-NASSER S, GUO W G. Thermomechanical response of DH-36 structural steel over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2003, 35(11): 1023–1047. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-6636(02)00323-X.
|
| [2] |
NEMAT-NASSER S, GUO W G. Thermomechanical response of HSLA-65 steel plates: experiments and modeling [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2005, 37(2): 379–405. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2003.08.017.
|
| [3] |
GUO W G, GAO X S. On the constitutive modeling of a structural steel over a range of strain rates and temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 561: 468–476. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.10.065.
|
| [4] |
CORNET C, WACKERMANN K, STÖCKER C, et al. Effects of temperature and hold time on dynamic strain aging in a nickel based superalloy [J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2014, 31(3): 226–232. DOI: 10.1179/1878641314Y.0000000018.
|
| [5] |
GANESAN V, LAHA K, NANDAGOPAL M, et al. Effect of nitrogen content on dynamic strain ageing behaviour of type 316LN austenitic stainless steel during tensile deformation [J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2014, 31(2): 162–170. DOI: 10.1179/1878641314Y.0000000009.
|
| [6] |
WANG J J, GUO W G, GAO X S, et al. The third-type of strain aging and the constitutive modeling of a Q235B steel over a wide range of temperatures and strain rates [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2015, 65: 85–107. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2014.08.017.
|
| [7] |
PORTEVIN A, LE-CHATELIER H. Heat treatment of aluminium-copper alloys [J]. Transaction of the American Society of Steel Treating, 1924, 5: 457–478.
|
| [8] |
MOTT N F, NABARRO F R N. Report of a conference on the strength of solids [M]. London: Physical Society, 1948.
|
| [9] |
COTTRELL A H, BILBY B A. Dislocation theory of yielding and strain ageing of iron [J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society: Section A, 1949, 62(1): 49–62. DOI: 10.1088/0370-1298/62/1/308.
|
| [10] |
SONG Y, GARCIA-GONZALEZ D, RUSINEK A. Constitutive models for dynamic strain aging in metals: strain rate and temperature dependences on the flow stress [J]. Materials, 2020, 13(7): 1794. DOI: 10.3390/ma13071794.
|
| [11] |
SONG Y, VOYIADJIS G Z. Constitutive modeling of dynamic strain aging for HCP metals [J]. European Journal of Mechanics-A: Solids, 2020, 83: 104034. DOI: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2020.104034.
|
| [12] |
ZHANG B, WANG J, WANG Y, et al. Dynamic strain-rate effect on uniaxial tension deformation of Ti5Al2.5Sn α-titanium alloy at various temperatures [J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2019, 36(6): 479–488. DOI: 10.1080/09603409.2019.1638659.
|
| [13] |
RAN J Q, ZHANG G Q, CHEN G P, et al. A multi-strain-rate damage model on fracture prediction in single-point diamond turning process [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 110(9): 2753–2765. DOI: 10.1007/s00170-020-06023-0.
|
| [14] |
CHEN G, LU L P, REN C Z, et al. Temperature dependent negative to positive strain rate sensitivity and compression behavior for 2024-T351 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 765: 569–585. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.196.
|
| [15] |
JING L, SU X Y, ZHAO L M. The dynamic compressive behavior and constitutive modeling of D1 railway wheel steel over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures [J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 1452–1461. DOI: 10.1016/j.rinp.2017.04.015.
|
| [16] |
WEAVER M L, NOEBE R D, KAUFMAN M J. Observations of dynamic strain aging in polycrystalline NiAl [J]. Intermetallics, 1996, 4(8): 593–600. DOI: 10.1016/0966-9795(96)00045-3.
|
| [17] |
SAMUEL K G, RAY S K, SASIKALA G. Dynamic strain ageing in prior cold worked 15Cr-15Ni titanium modified stainless steel (Alloy D9) [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2006, 355(1): 30–37. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2006.03.016.
|
| [18] |
LI X Y, ROTH C C, MOHR D. Machine-learning based temperature-and rate-dependent plasticity model: application to analysis of fracture experiments on DP steel [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2019, 118: 320–344. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2019.02.012.
|
| [19] |
KREYCA J, KOZESCHNIK E. State parameter-based constitutive modelling of stress strain curves in Al-Mg solid solutions [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2018, 103: 67–80. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2018.01.001.
|
| [20] |
TSAI C W, LEE C, LIN P T, et al. Portevin-Le Chatelier mechanism in face-centered-cubic metallic alloys from low to high entropy [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2019, 122: 212–224. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2019.07.003.
|
| [21] |
WEAVER M L, NOEBE R D, KAUFMAN M J. The influence of C and Si on the flow behavior of NiAl single crystals [J]. Scripta Materialia, 1996, 34(6): 941–948. DOI: 10.1016/1359-6462(95)00590-0.
|
| [22] |
CUNIBERTI A. Serrated yielding in long-range ordered 18R Cu-Zn-Al single crystals [J]. Intermetallics, 2006, 14(7): 776–779. DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2005.11.011.
|
| [23] |
VARADHAN S, BEAUDOIN A J, FRESSENGEAS C. Lattice incompatibility and strain-aging in single crystals [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2009, 57(10): 1733–1748. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2009.06.007.
|
| [24] |
GILAT A, WU X R. Plastic deformation of 1020 steel over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 1997, 13(6): 611–632. DOI: 10.1016/S0749-6419(97)00028-4.
|
| [25] |
ROBINSON J M, SHAW M P. Microstructural and mechanical influences on dynamic strain aging phenomena [J]. International Materials Reviews, 1994, 39(3): 113–122. DOI: 10.1179/imr.1994.39.3.113.
|
| [26] |
GIRONÈS A, LLANES L, ANGLADA M, et al. Dynamic strain ageing effects on superduplex stainless steels at intermediate temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 367(1): 322–328. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2003.10.293.
|
| [27] |
孟卫华, 郭伟国, 苏静, 等. DH-36钢的塑性流动统一本构关系研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2011, 43(5): 958–962. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-2011-5-lxxb2010-676.MENG W H, GUO W G, SU J, et al. Study of plastic flow unified constitutive relation for steel DH-36 [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2011, 43(5): 958–962. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-2011-5-lxxb2010-676.
|
| [28] |
孟卫华, 郭伟国, 王建军, 等. DH36钢拉伸塑性流动特性及本构关系 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2013, 33(4): 438–443. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2013)04-0438-06.MENG W H, GUO W G, WANG J J, et al. Tensile plasticity flow characteristics of DH36 steel and its constitutive relation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2013, 33(4): 438–443. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2013)04-0438-06.
|
| [29] |
张琼. 低碳钢拉伸形变时影响蓝脆的因素 [J]. 材料科学进展, 1988, 2(6): 87–91.ZHANG Q. Effect of factor of blue brittle of low-carbon steel for tensile deformation [J]. Materials Science Progress, 1988, 2(6): 87–91.
|
| [30] |
LI C C, LESLIE W C. Effects of dynamic strain aging on the subsequent mechanical properties of carbon steels [J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1978, 9(12): 1765–1775. DOI: 10.1007/BF02663406.
|
| [31] |
HONG S G, Lee S B. The tensile and low-cycle fatigue behavior of cold worked 316L stainless steel: influence of dynamic strain aging [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2004, 26(8): 899–910. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2003.12.002.
|
| [32] |
RODRIGUEZ P. Serrated plastic flow [J]. Bulletin of Materials Science, 1984, 6(4): 653–663. DOI: 10.1007/BF02743993.
|
| [33] |
FU S H, CHENG T, ZHANG Q C, et al. Two mechanisms for the normal and inverse behaviors of the critical strain for the Portevin-Le Chatelier effect [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(19): 6650–6656. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.08.035.
|
| [34] |
钱匡武, 彭开萍, 陈文哲. 金属动态应变时效现象中的“锯齿屈服” [J]. 福建工程学院学报, 2003, 1(1): 4–8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4348.2003.01.002.QIAN K W, PENG K P, CHEN W Z. Features of serrated yielding of dynamic strain aging phenomenon in metals and alloys [J]. Journal of Fujian University of Technology, 2003, 1(1): 4–8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4348.2003.01.002.
|
| [35] |
YILMAZ A. The Portevin–Le Chatelier effect: a review of experimental findings [J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2011, 12(6): 063001. DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/12/6/063001.
|
| [36] |
SAKTHIVEL T, LAHA K, NANDAGOPAL M, et al. Effect of temperature and strain rate on serrated flow behaviour of Hastelloy X [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 534: 580–587. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.12.011.
|
| [37] |
ROY A K, PAL J, MUKHOPADHYAY C. Dynamic strain ageing of an austenitic superalloy—Temperature and strain rate effects [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 474(1): 363–370. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2007.05.056.
|
| [38] |
KARABULUT H, GÜNDÜZ S. Effect of vanadium content on dynamic strain ageing in microalloyed medium carbon steel [J]. Materials & Design, 2004, 25(6): 521–527. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2004.01.005.
|
| [39] |
GÜNDÜZ S, ACARER M. The effect of heat treatment on high temperature mechanical properties of microalloyed medium carbon steel [J]. Materials & Design, 2006, 27(10): 1076–1085. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2005.01.020.
|
| [40] |
XIAO J Y, WANG J J, GUO W G, et al. The influence of heat treatment and strain rate on the third type strain ageing phenomenon [J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2019, 36(2): 104–110. DOI: 10.1080/09603409.2018.1467108.
|
| [41] |
YUAN K B, GUO W G, LI D W, et al. Influence of heat treatments on plastic flow of laser deposited Inconel 718: testing and microstructural based constitutive modeling [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2021, 136: 102865. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2020.102865.
|
| [42] |
YUAN K B, GUO W G, LI P H, et al. Thermomechanical behavior of laser metal deposited inconel 718 superalloy over a wide range of temperature and strain rate: testing and constitutive modeling [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2019, 135: 13–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2019.04.024.
|
| [43] |
MCCORMIGK P G. A model for the Portevin-Le Chatelier effect in substitutional alloys [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1972, 20(3): 351–354. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(72)90028-4.
|
| [44] |
VAN DEN BEUKEL A, KOCKS U F. The strain dependence of static and dynamic strain-aging [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1982, 30(5): 1027–1034. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(82)90211-5.
|
| [45] |
COTTRELL A H. LXXXVI. A note on the Portevin-Le Chatelier effect [J]. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science, 1953, 44(355): 829–832. DOI: 10.1080/14786440808520347.
|
| [46] |
CUDDY L J, LESLIE W C. Some aspects of serrated yielding in substitutional solid solutions of iron [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1972, 20(10): 1157–1167. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(72)90164-2.
|
| [47] |
SCHWARZ R B, FUNK L L. Kinetics of the Portevin-Le Chatelier effect in Al 6061 alloy [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1985, 33(2): 295–307. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(85)90148-8.
|
| [48] |
PICU R C, ZHANG D. Atomistic study of pipe diffusion in Al-Mg alloys [J]. Acta Materialia, 2004, 52(1): 161–171. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2003.09.002.
|
| [49] |
PENG K P, QIAN K W, CHEN W Z. Effect of dynamic strain aging on high temperature properties of austenitic stainless steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 379(1): 372–377. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.03.004.
|
| [50] |
CORBY C, CÁCERES C H, LUKÁČ P. Serrated flow in magnesium alloy AZ91 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 387: 22–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.01.077.
|
| [51] |
FRIEDEL J. Dislocations: international series of monographs on solid state physics [M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1964: 491.
|
| [52] |
LEE M H, KIM J H, CHOI B K, et al. Mechanical properties and dynamic strain aging behavior of Zr-1.5Nb-0.4Sn-0.2Fe alloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 428(1/2): 99–105. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.03.076.
|
| [53] |
钱匡武, 李效琦, 萧林钢, 等. 金属和合金中的动态应变时效现象 [J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 29(6): 8–23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2243.2001.06.003.QIAN K W, LI X Q, XIAO L G, et al. Dynamic strain aging phenomenon in metals and alloys [J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science), 2001, 29(6): 8–23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2243.2001.06.003.
|
| [54] |
张质良, 余大伟, 阮雪榆. “蓝脆”温度挤压特性的研究 [J]. 模具技术, 1983(2): 1–13.
|
| [55] |
王敏杰, 胡荣生, 刘培德. 金属切削中的蓝脆效应与热塑剪切失稳 [J]. 科学通报, 1990, 35(8): 634–636. DOI: 10.1360/csb1990-35-8-634.
|
| [56] |
KIM I S, KANG S S. Dynamic strain aging in SA508-class 3 pressure vessel steel [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 1995, 62(2): 123–129. DOI: 10.1016/0308-0161(95)93969-C.
|
| [57] |
CAILLARD D. Dynamic strain ageing in iron alloys: the shielding effect of carbon [J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 112: 273–284. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.04.018.
|
| [58] |
KOYAMA M, SHIMOMURA Y, CHIBA A, et al. Room-temperature blue brittleness of Fe-Mn-C austenitic steels [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2017, 141: 20–23. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.07.017.
|
| [59] |
VERMA P, RAO G S, CHELLAPANDI P, et al. Dynamic strain ageing, deformation, and fracture behavior of modified 9Cr-1Mo steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 621: 39–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.10.011.
|
| [60] |
SCHWINK C, NORTMANN A. The present experimental knowledge of dynamic strain ageing in binary f.c.c. solid solutions [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1997, 234(97): 1–7. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00139-1.
|
| [61] |
WOLFENDEN A, KINRA V K. M3D III: mechanics and mechanisms of materials damping [M]. West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International, 1997.
|
| [62] |
MARTIN R, TKALCEC I, MARI D, et al. Tempering effects on three martensitic carbon steels studied by mechanical spectroscopy [J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2008, 88(22): 2907–2920. DOI: 10.1080/14786430802406249.
|
| [63] |
TKALCEC I, MARI D. Internal friction in martensitic, ferritic and bainitic carbon steel; cold work effects [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2004, 370(1): 213–217. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2003.04.004.
|
| [64] |
TKALCEC I, MARI D, BENOIT W. Correlation between internal friction background and the concentration of carbon in solid solution in a martensitic steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 442(1): 471–475. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.03.115.
|
| [65] |
NIEMEYER T C, GRANDINI C R, FLORÊNCIO O. Stress-induced ordering due heavy interstitial atoms in Nb–0.3 wt.% Ti alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2005, 396(1): 285–289. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2005.01.045.
|
| [66] |
STRAHL A, GOLOVINA S B, GOLOVIN I S, et al. On dislocation-related internal friction in Fe-22-31 at.% Al [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2004, 378(1): 268–273. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2003.10.066.
|
| [67] |
郭伟国, 左红星, 孟卫华, 等. 第三种应变时效与机械波谱关联性探讨 [J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2012, 20(1): 128–134, 127. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20120126.GUO W G, ZUO H X, MENG W H, et al. Discussion of the relevancy of the third-type strain aging and mechanical spectroscopy [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2012, 20(1): 128–134, 127. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20120126.
|
| [68] |
彭开萍, 陈文哲, 钱匡武. 3004铝合金“反常”锯齿屈服现象的研究 [J]. 物理学报, 2006, 55(7): 3569–3575. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2006.07.061.PENG K P, CHEN W Z, QIAN K W. Study of an anomalous serrated yielding phenomenon in 3004 aluminum alloy [J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2006, 55(7): 3569–3575. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2006.07.061.
|
| [69] |
LEE S J, KIM J, KANE S N, et al. On the origin of dynamic strain aging in twinning-induced plasticity steels [J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(17): 6809–6819. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2011.07.040.
|
| [70] |
KARLSEN W, IVANCHENKO M, EHRNSTÉN U, et al. Microstructural manifestation of dynamic strain aging in AISI 316 stainless steel [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2009, 395(1): 156–161. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2009.10.047.
|
| [71] |
IVANCHENKO M, NEVDACHA V, YAGODZINSKYY Y, et al. Internal friction studies of carbon and its redistribution kinetics in Inconel 600 and 690 alloys under dynamic strain aging conditions [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006, 442(1): 458–461. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.207.
|
| [72] |
JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and date for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates, and high temperatures [C] // Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics. The Hague, Netherlands, 1983: 541−547.
|
| [73] |
LIANG R Q, KHAN A S. A critical review of experimental results and constitutive models for BCC and FCC metals over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 1999, 15(9): 963–980. DOI: 10.1016/S0749-6419(99)00021-2.
|
| [74] |
RULE W K, JONES S E. A revised form for the Johnson-Cook strength model [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1998, 21(8): 609–624. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)00081-X.
|
| [75] |
ZERILLI F J, ARMSTRONG R W. Dislocation-mechanics-based constitutive relations for material dynamics calculations [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1987, 61(5): 1816–1825. DOI: 10.1063/1.338024.
|
| [76] |
FOLLANSBEE P S, KOCKS U F. A constitutive description of the deformation of copper based on the use of the mechanical threshold stress as an internal state variable [J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1988, 36(1): 81–93. DOI: 10.1016/0001-6160(88)90030-2.
|
| [77] |
BODNER S R, PARTOM Y. Constitutive equations for elastic-viscoplastic strain-hardening materials [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1975, 42(2): 385–389. DOI: 10.1115/1.3423586.
|
| [78] |
NEMAT-NASSER S, GUO W G, CHENG J Y. Mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms of a commercially pure titanium [J]. Acta Materialia, 1999, 47(13): 3705–3720. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-6454(99)00203-7.
|
| [79] |
NEMAT-NASSER S, GUO W G. High strain-rate response of commercially pure vanadium [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2000, 32(4): 243–260. DOI: 10.1016/S0167-6636(99)00056-3.
|
| [80] |
RUSINEK A, KLEPACZKO J R. Shear testing of a sheet steel at wide range of strain rates and a constitutive relation with strain-rate and temperature dependence of the flow stress [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2001, 17(1): 87–115. DOI: 10.1016/S0749-6419(00)00020-6.
|
| [81] |
GAO C Y, ZHANG L C. Constitutive modelling of plasticity of fcc metals under extremely high strain rates [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2012, 32: 121–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2011.12.001.
|
| [82] |
KHAN A S, LIU H W. Variable strain rate sensitivity in an aluminum alloy: response and constitutive modeling [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2012, 35: 1–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2012.02.001.
|
| [83] |
CHENG J Y, NEMAT-NASSER S. A model for experimentally-observed high-strain-rate dynamic strain aging in titanium [J]. Acta Materialia, 2000, 48(12): 3131–3144. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-6454(00)00124-5.
|
| [84] |
HONG S I. Influence of dynamic strain aging on the apparent activation volume for deformation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1985, 76: 77–81. DOI: 10.1016/0025-5416(85)90082-5.
|
| [85] |
LEE K W, KIM S K, KIM K T, et al. Ductility and strain rate sensitivity of Zircaloy-4 nuclear fuel claddings [J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2001, 295(1): 21–26. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3115(01)00509-8.
|
| [86] |
LEE K O, LEE S B. Modeling of materials behavior at various temperatures of hot isostatically pressed superalloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012, 541: 81–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.02.005.
|
| [87] |
SU J, GUO W, MENG W, et al. Plastic behavior and constitutive relations of DH-36 steel over a wide spectrum of strain rates and temperatures under tension [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2013, 65: 76–87. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2013.06.002.
|
| [88] |
SHEN F H, MÜNSTERMANN S, LIAN J H. An evolving plasticity model considering anisotropy, thermal softening and dynamic strain aging [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2020, 132: 102747. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2020.102747.
|
| [89] |
郭扬波, 唐志平, 程经毅. 一种基于位错机制的动态应变时效模型 [J]. 固体力学学报, 2002, 23(3): 249–256. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-7805.2002.03.001.GUO Y B, TANG Z P, CHENG J Y. A dislocation-mechanics-based constitutive model for dynamic strain aging [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2002, 23(3): 249–256. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-7805.2002.03.001.
|
| [90] |
VOYIADJIS G Z, SONG Y, RUSINEK A. Constitutive model for metals with dynamic strain aging [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2019, 129: 352–360. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2018.12.012.
|
| [91] |
VOYIADJIS G Z, SONG Y. A physically based constitutive model for dynamic strain aging in inconel 718 alloy at a wide range of temperatures and strain rates [J]. Acta Mechanica, 2020, 231(1): 19–34. DOI: 10.1007/s00707-019-02508-6.
|







 下载:
下载: