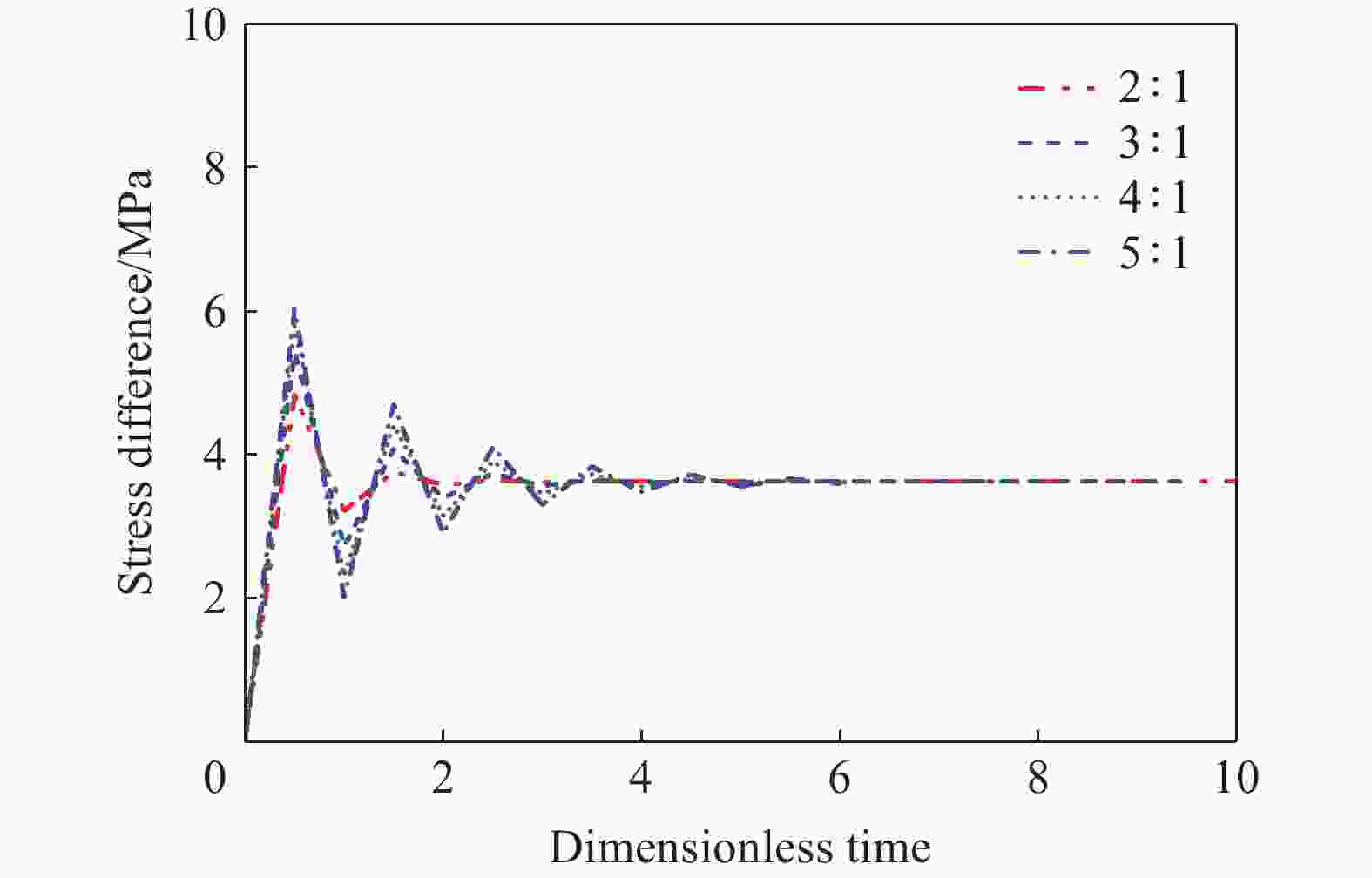
| [1] |
LIU F, LI Q M. Strain-rate effect of polymers and correction methodology in a SHPB test [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 161: 104109. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104109.
|
| [2] |
LIU P, HU D A, WU Q K, et al. Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of interfacial effect in SHPB tests for concrete-like materials [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 163: 414–427. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.118.
|
| [3] |
KARIEM M A, BEYNON J H, RUAN D. Misalignment effect in the split Hopkinson pressure bar technique [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 47: 60–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2012.03.006.
|
| [4] |
NIE H L, MA W F, HE X L, et al. Misalignment tolerance in one-side and symmetric loading Hopkinson pressure bar experiments [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2022, 35(2): 273–281. DOI: 10.1007/s10338-021-00267-3.
|
| [5] |
GUO Y B, GAO G F, JING L, et al. Dynamic properties of mortar in high-strength concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 165: 104216. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104216.
|
| [6] |
PANOWICZ R, JANISZEWSKI J, KOCHANOWSKI K. Effects of sample geometry imperfections on the results of split Hopkinson pressure bar experiments [J]. Experimental Techniques, 2019, 43(4): 397–403. DOI: 10.1007/s40799-018-0293-7.
|
| [7] |
BRIZARD D, JACQUELIN E. Uncertainty quantification and global sensitivity analysis of longitudinal wave propagation in circular bars: application to SHPB device [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2018, 134: 264–271. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.11.005.
|
| [8] |
YANG H S, LI Y L, ZHOU F H. Propagation of stress pulses in a Rayleigh-Love elastic rod [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 153: 103854. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103854.
|
| [9] |
BRAGOV A M, LOMUNOV A K, LAMZIN D A, et al. Dispersion correction in split-Hopkinson pressure bar: theoretical and experimental analysis [J]. Continuum Mechanics and Thermodynamics, 2022, 34(4): 895–907. DOI: 10.1007/s00161-019-00776-0.
|
| [10] |
RIGBY S E, BARR A D, CLAYTON M. A review of Pochhammer-Chree dispersion in the Hopkinson bar [J]. Engineering and Computational Mechanics, 2018, 171(1): 3–13. DOI: 10.1680/jencm.16.00027.
|
| [11] |
REN L, YU X M, HE Y, et al. Numerical investigation of lateral inertia effect in dynamic impact testing of UHPC using a split-Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 246: 118483. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118483.
|
| [12] |
ROTARIU A N, TRANĂ E, MATACHE L. Young’s modulus calculus using split Hopkinson bar tests on long and thin material samples [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(9): 3058. DOI: 10.3390/ma15093058.
|
| [13] |
AGHAYAN S, BIELER S, WEINBERG K. Determination of the high-strain rate elastic modulus of printing resins using two different split Hopkinson pressure bars [J]. Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials, 2022, 26(4): 761–773. DOI: 10.1007/s11043-021-09511-2.
|
| [14] |
ZHANG Q M, HUANG X M, GUO R, et al. Study on dynamic impact response and optimal constitutive model of Al-Mg-Si aluminum alloy [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(21): 7618. DOI: 10.3390/ma15217618.
|
| [15] |
CHEN J P, TAO W J, HUAN S, et al. Data processing of wave propagation in viscoelastic split Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. AIP Advances, 2022, 12(4): 045210. DOI: 10.1063/5.0083888.
|
| [16] |
ZHOU Z P, GAO D D, LIN G J, et al. Static and dynamic mechanical properties of epoxy nanocomposites reinforced by hybridization with carbon nanofibers and block ionomers [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2022, 271: 108638. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2022.108638.
|
| [17] |
PRAKASH G, SINGH N K, GUPTA N K. Flow behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V alloy in a wide range of strain rates and temperatures under tensile, compressive and flexural loads [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 176: 104549. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104549.
|






 下载:
下载: