An equivalent calculation method for confined-blast load based on saturated response time
-
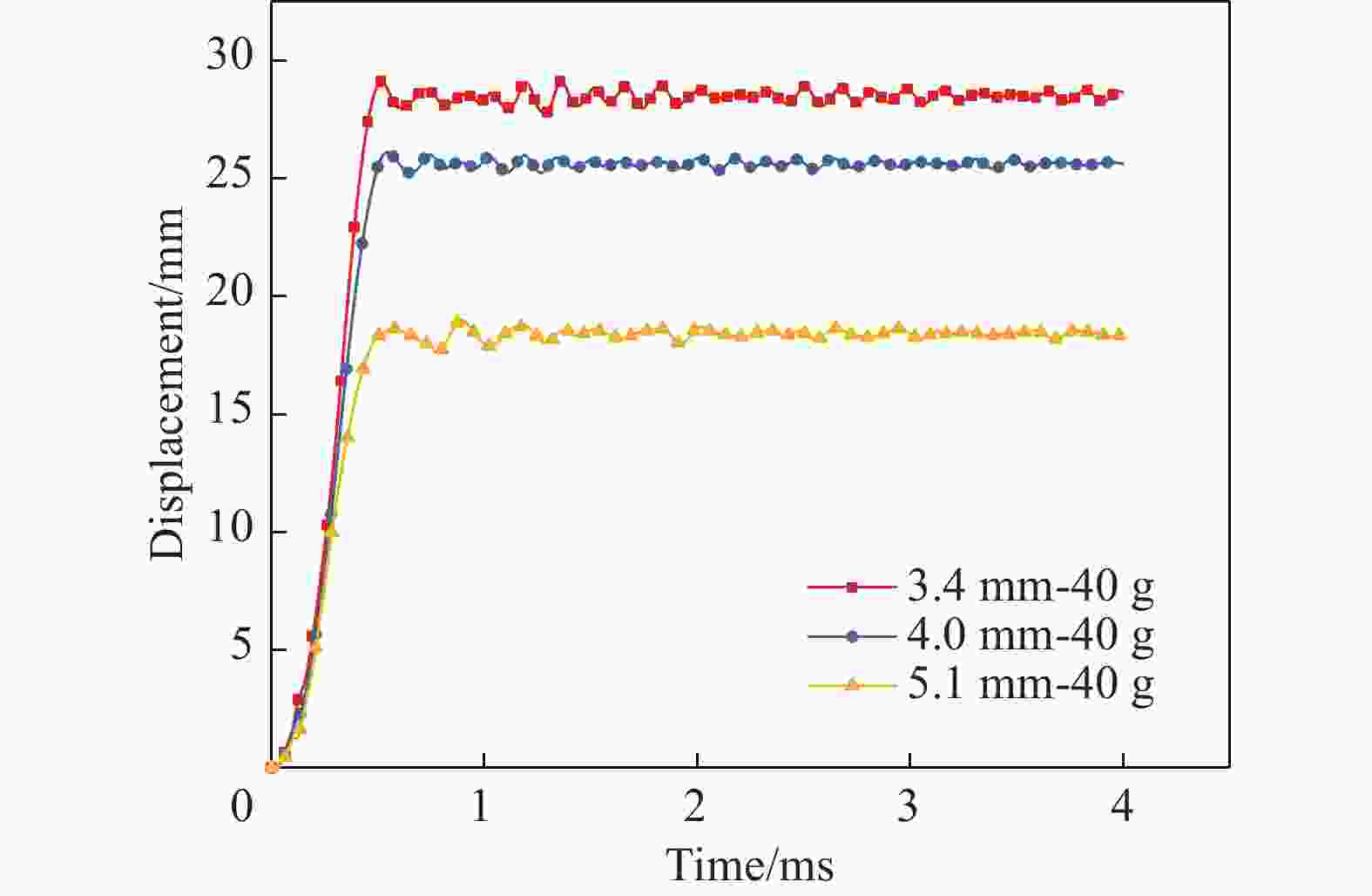
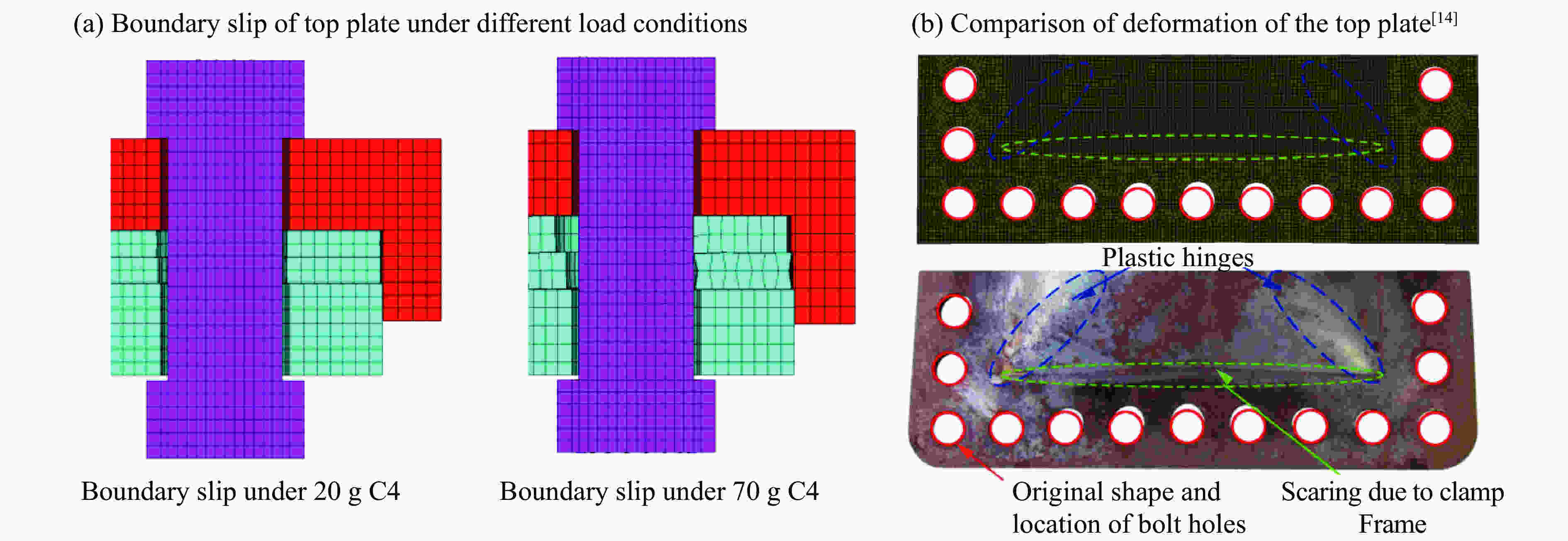
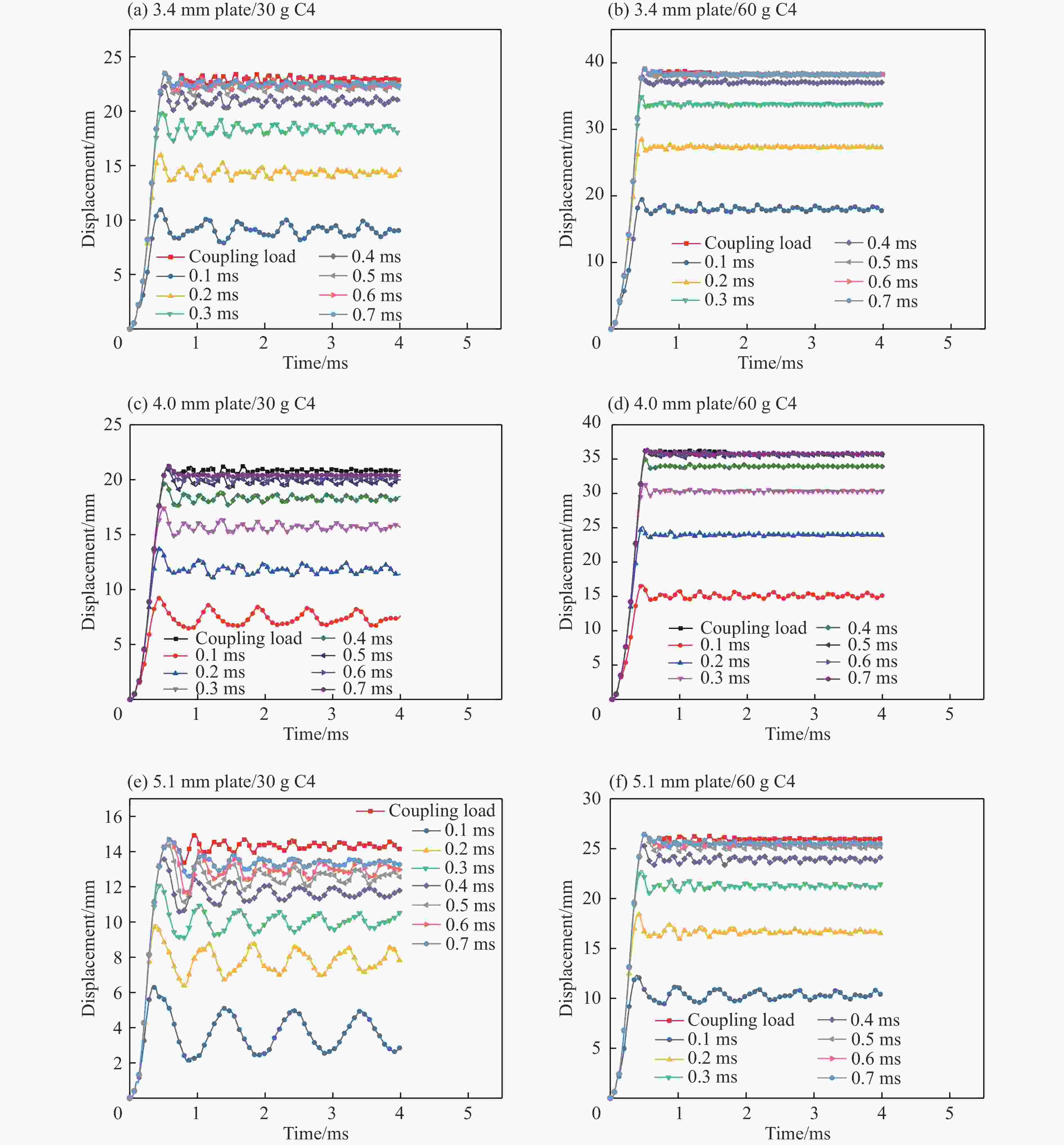
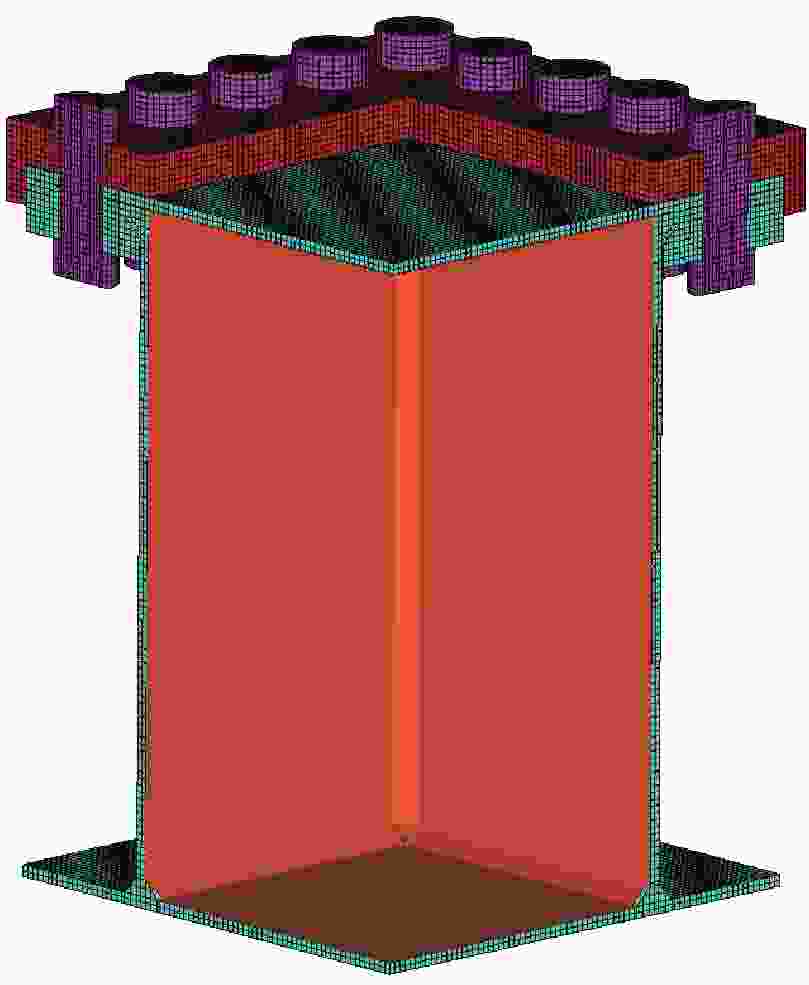
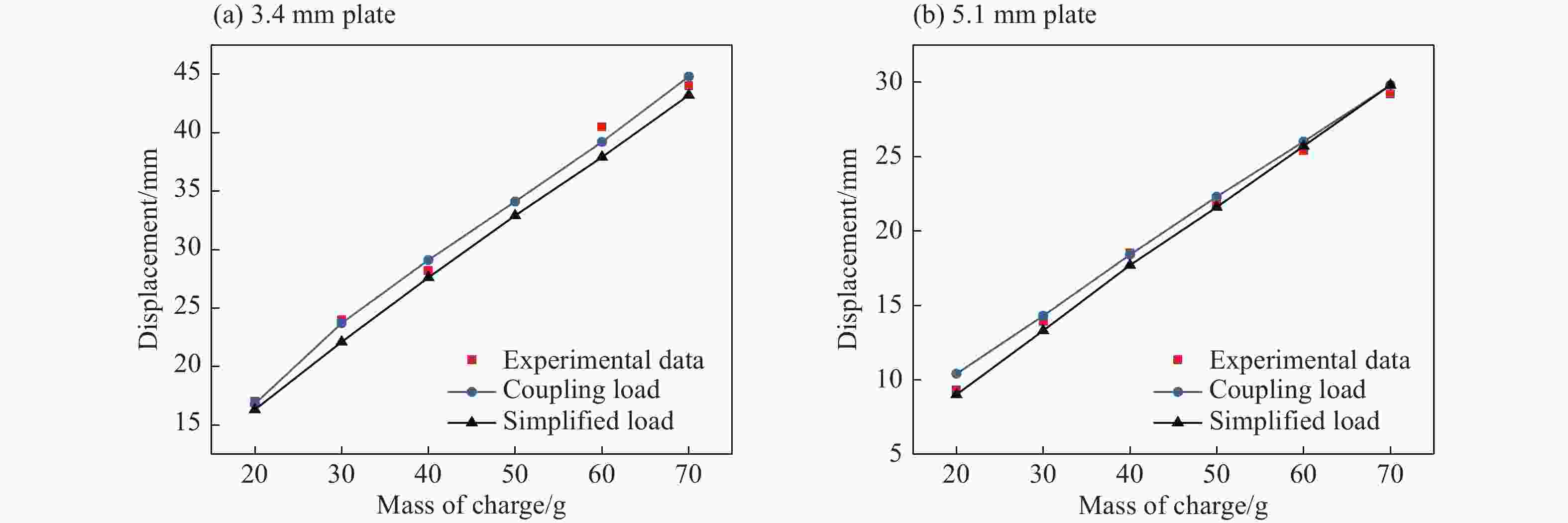
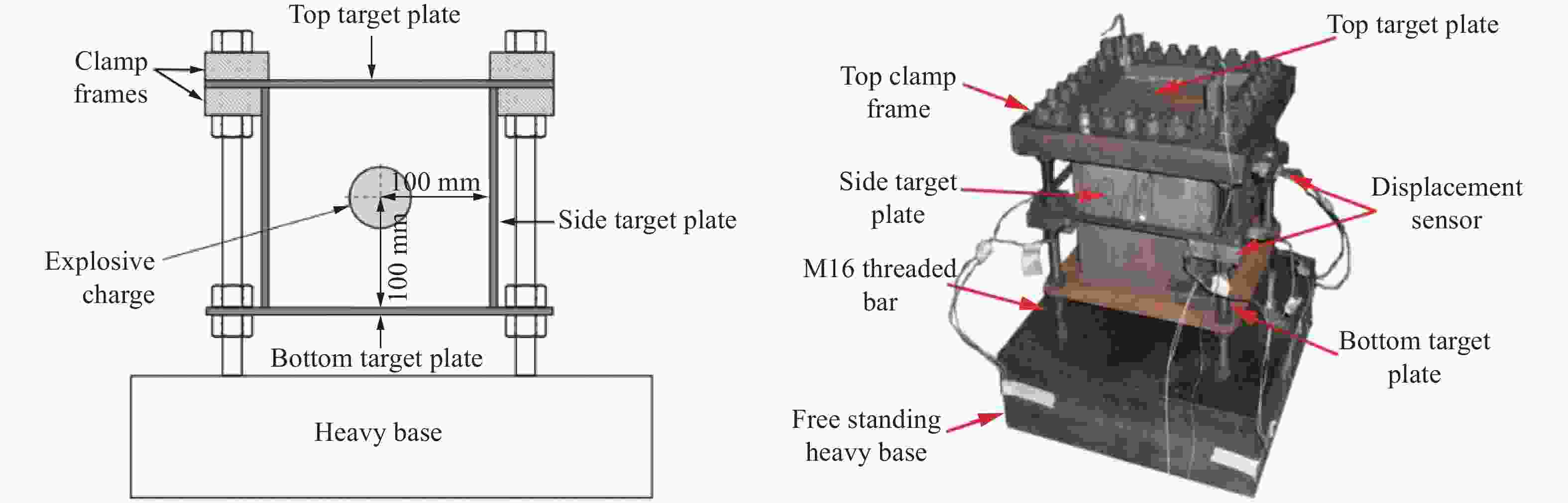
摘要: 针对舱内爆炸载荷形式复杂、作用时间长、缺乏有效的简化描述方法的问题,首先采用显式动力学计算程序开展了内爆载荷作用下钢板动态响应的数值计算,在与试验结果对比验证的基础上分析了金属板的内爆载荷饱和冲量。通过对216种不同爆炸载荷加载时长与金属板响应关系的分析,提出了内爆炸载荷作用下结构最大变形所对应的饱和时间计算经验公式,并给出了饱和时间的无量纲系数建议值。考虑到内爆载荷初始冲击波的影响,结合爆炸载荷饱和作用时间的规律,提出了封闭空间爆炸载荷的矩形载荷等效方法,对比了18组简化载荷与耦合载荷分别作用下钢板的动力响应,验证了等效方法的有效性。Abstract: Due to the complex form and long duration of the load from a confined explosion, it is usually difficult to propose an uniform simplified formula to describe the confined blast load effectively, which can be applied in the predicting the dynamic response of structures. In present paper, the explicit dynamic code Autodyn was employed to predict the response of steel plates under confined blast load numerically. The effectiveness of the numerical method was validated by comparing the numerical and experimental results, and then the characteristic of saturated impulse of steel plate was analyzed. The numerical simulations of 216 plates, which experience different load durations, were conducted. Based on analyzing the relationship between the duration of confined blast load and the subsequent dynamic response of these steel plates, a simplified formula was deduced to determine the saturated time that corresponding to the maximum deformation of plate, and a guide value of the parameter of the dimensionless saturated time was presented. Considering the influence of initial shock wave of confined explosion, combined with the law of saturation action time of explosion load, a rectangular load equivalent method for the confined blast load is proposed. The dynamic response of metal plate under 18 groups of simplified and fully-coupling load is compared, and the effectiveness of the equivalent method is verified.
-
Key words:
- confined-blast load /
- steel plate /
- saturated impulse /
- equivalent method
-
表 1 Johnson-Cook模型材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of Johnson-Cook model
板厚/mm 材料 A/MPa B/MPa n C m 3.4 低碳钢 233.47 480.37 0.356 5 0.036 9 0.665 5 4.0 低碳钢 221.67 361.35 0.474 6 0.048 1 0.665 5 5.1 300WAsteel 263.58 519.64 0.384 3 0.025 9 0.665 5 表 2 夹持结构材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters of holding device
部件 状态方程 刚体约束 强度模型 体积模量/GPa 剪切模量/GPa 上压板 Rigid No − 159 81.8 下压板 Rigid Yes − 159 81.8 螺栓 Linear − Elastic 159 81.8 表 3 C4炸药JWL状态方程参数
Table 3. JWL EOS parameters of explosive C4
ρ/(g·cm−3) A/GPa B/GPa R1 R2 w E/(GJ·m−3) 1.601 609.8 12.95 4.500 1.400 0.250 9.000 表 4 无量纲饱和冲量参数
Table 4. Parameters of dimensionless saturation impulse
板厚/mm 饱和时间/ms 板长/m 材料密度/(g·cm−3) 屈服强度/MPa λ 3.4 0.6 0.2 7.83 233.47 16.4 4.0 0.6 0.2 7.83 221.67 16.0 5.1 0.6 0.2 7.83 263.58 17.4 表 5 等效矩形载荷换算
Table 5. Equivalent rectangular load
板厚/mm 药量/g 饱和冲量/(Pa·s) 等效压力/kPa 等效时间/μs 3.4 20 2 312.63 4 133.46 559.49 30 3 198.58 5 808.93 550.63 40 4 035.65 7 363.20 548.08 50 4 856.17 8 910.56 544.99 60 5 617.45 10 378.59 541.25 70 6 369.51 11 877.10 536.28 4.0 20 2 358.52 4 190.00 562.89 30 3 273.74 5 916.10 553.36 40 4 136.70 7 534.59 549.03 50 4 975.16 9 137.39 544.48 60 5 762.89 10 656.95 540.76 70 6 560.27 12 250.34 535.52 5.1 20 2 434.13 4 266.77 570.49 30 3 401.43 6 059.57 561.33 40 4 315.98 7 753.58 556.64 50 5 204.07 9 435.92 551.52 60 6 053.82 11 069.43 546.90 70 6 916.35 12 757.55 542.14 -
[1] EDRI I, SAVIR Z, FELDGUN V R, et al. On blast pressure analysis due to a partially confined explosion: I: experimental studies [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2011, 2: 1–20. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.2.1.1. [2] HU Y, WU C, Lukaszewicz M, et al. Characteristics of confined blast loading in unvented structures [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2011, 2(1): 21–44. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.2.1.21. [3] 杨科之, 杨秀敏, 王年桥. 内爆荷载作用下结构等效静载计算方法 [J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 3(4): 31–33.YANG Kezhi, YANG Xiumin, WANG Nianqiao. Equivalent static load calculation method of structure subjected to internal explosion [J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2002, 3(4): 31–33. [4] GERETTO C, YUEN S C K, NURICK G N. An experimental study of the effects of degrees of confinement on the response of square mild steel plates subjected to blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 79: 32–44. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.08.002. [5] KUHL A L, REICHENBACH H. Combustion effects in confined explosions [J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2009, 32(2): 2291–2298. DOI: 10.1016/j.proci.2008.05.001. [6] KUHL A L, BELL J B, BECKNER V E, et al. Spherical combustion clouds in explosions [J]. Shock Waves, 2013, 23(3): 233–249. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-012-0410-y. [7] ZHAO Y P, YU T X, FANG J. Large dynamic plastic deflection of a simply supported beam subjected to rectangular pressure pulse [J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 1994, 64(3): 223–232. [8] ZHAO Y P, YU T X, FANG J. Saturation impulses for dynamically loaded structures with finite-deflections [J]. Structural Engineering & Mechanics, 1995, 3(6): 583–592. [9] ZHU L, YU T X. Saturated impulse for pulse-loaded elastic-plastic square plates [J]. International Journal of Solids & Structures, 1997, 34(14): 1709–1718. [10] NURICK G N, MARTIN J B. Deformation of thin plates subjected to impulsive loading: a review Part II: experimental studies [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1989, 8(2): 171–186. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(89)90015-8. [11] NURICK G N, MARTIN J B. Deformation of thin plates subjected to impulsive loading: a review: Part I: theoretical considerations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1989, 8(2): 159–170. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(89)90014-6. [12] Dragos J, WU C Q, Oehlers D J. Simplification of fully confined blasts for structural response analysis [J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 56(11): 312–326. [13] PICKERD V, BORNSTEIN H, MCCARTHY P, et al. Analysis of the structural response and failure of containers subjected to internal blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 95: 40–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.04.010. [14] GERETTO C. The effects of different degrees of confinement on the deformation of square plates subjected to blast loading [D]. Western Cape: University of Cape Town, 2012: 101−203. [15] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1985, 21(1): 31–48. DOI: 10.1016/0013-7944(85)90052-9. [16] ZHENG C, KONG X S, WU W G, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on the dynamic response of steel plates subjected to confined blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 113: 144–160. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.11.013. [17] URTIEW P A, HAYES B. Parametric study of the dynamic JWL-EOS for detonation products [J]. Combustion, Explosion, and Shock Waves, 1991, 27(4): 505–514. [18] XU W Z, KONG X S, ZHENG C, et al. Numerical method for predicting the blast wave in partially confined chamber [J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018, 2018(5): 1–17. -






 下载:
下载: