Review on theoretical research of penetration effects into rock-like material
-
摘要: 近年来,随着超高速武器的发展,侵彻效应的研究重点逐渐由高速向超高速发展。随着弹体打击速度提高,侵彻机制发生变化,并触发强烈的成坑和地冲击效应。本文综述了大速度范围内岩石类介质侵彻效应的理论研究进展,讨论了长杆弹侵彻速度的分区,介绍了岩石类介质的侵彻、成坑、地冲击效应的理论模型,并对目前研究中尚有待解决的问题和下一步的研究方向进行了展望。Abstract: In recent years, as the developing of hyper-velocity weapons, the research emphasis of penetration effects is shifting from high-velocity penetration to hyper-velocity penetration. With the increasing of impact velocity of projectiles, the penetration mechanism changes, where effects as cratering and ground shock are induced. In this paper, progress in theoretical research of penetration into rock-like materials in a wide velocity range is reviewed, where velocity range is divided into zones, and theoretical models of penetration, cratering and ground shock are introduced. The existing problems concerned and research orientation in the future are also forecasted.
-
Key words:
- penetration /
- rock /
- concrete /
- theoretical research /
- cratering /
- ground shock
-
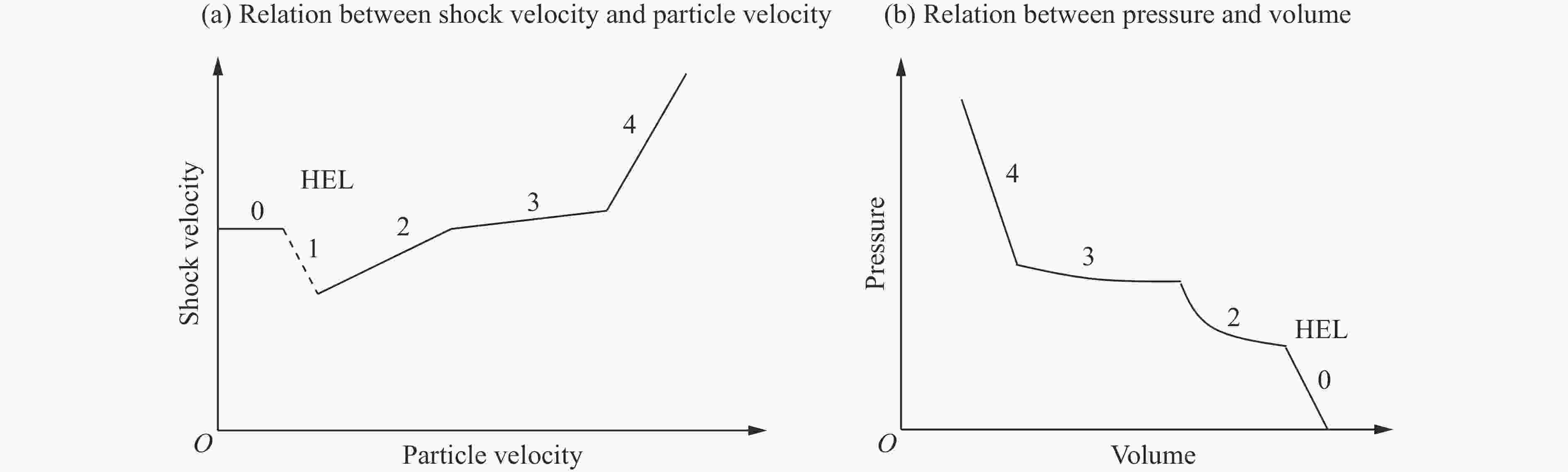
表 1 冲击压缩作用下典型硬岩分区行为特征[51]
Table 1. Dynamic behaviors of hard rock in different ranges under shock compression[51]
冲击压缩
状态
波形时间特征
应变状态特征
应力状态特征${c_0} = \sqrt {\displaystyle\frac{1}{{{\rho _0}}}\displaystyle\frac{{{\rm d}\sigma }}{{{\rm d}\varepsilon }}} $
小扰动传播速度$p\simfont\text{~} {{r}^{ - n}}$
应力波衰减特征冲击波速度
特征(图2(a))高应力
流体状态Δ=0~0.05
冲击波特征εθ=0
一维应变$\alpha = {\displaystyle\frac{{{\sigma _r}}}{{\sigma}_\theta} } \approx 1$ ${c_0} = \sqrt {\frac{K}{{{\rho _0}}}} $ n=−2.2~3.0 D>>cp 内摩擦拟
流体状态Δ=0.05~0.1
短波特征${\varepsilon _r} \gg {\varepsilon _\theta } \ne 0$
受限应变$\begin{array}{l}\alpha = {\displaystyle\frac{\sigma _r}{{\sigma }_\theta} } = {\alpha ^*}\\{\alpha _0} \simfont\text{<} {\alpha ^*} \simfont\text{<} 1\end{array}$ ${c_0} = \sqrt {\displaystyle\frac{{3K}}{{{\rho _0}\left( {1 + 2{\alpha ^*}} \right)}}} $
介于流体与固体之间n=1.4~1.8 D≈cp 低应力
固体状态Δ>0.1
弹塑性波特征${\varepsilon _r} + 2{\varepsilon _\theta } = 0$
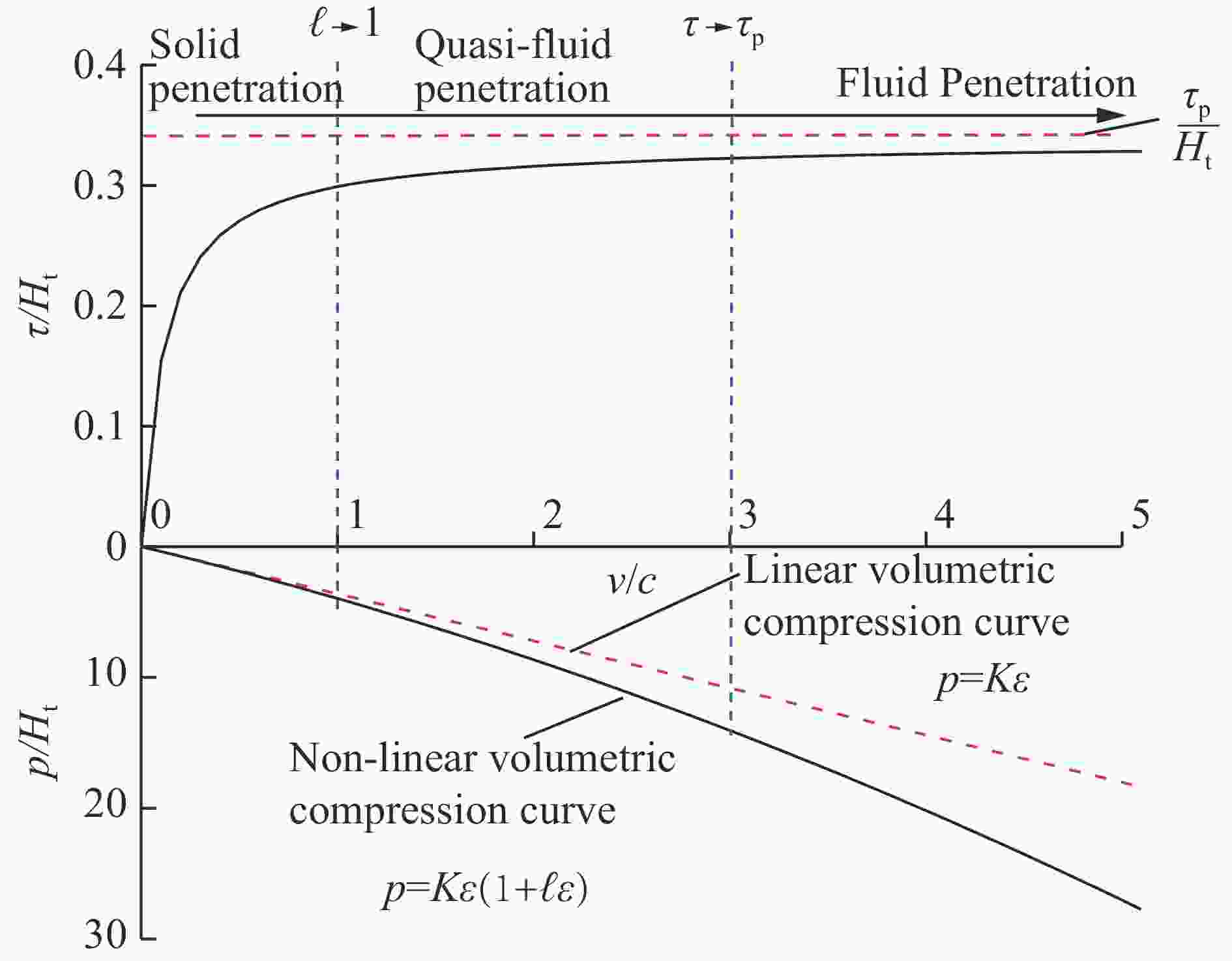
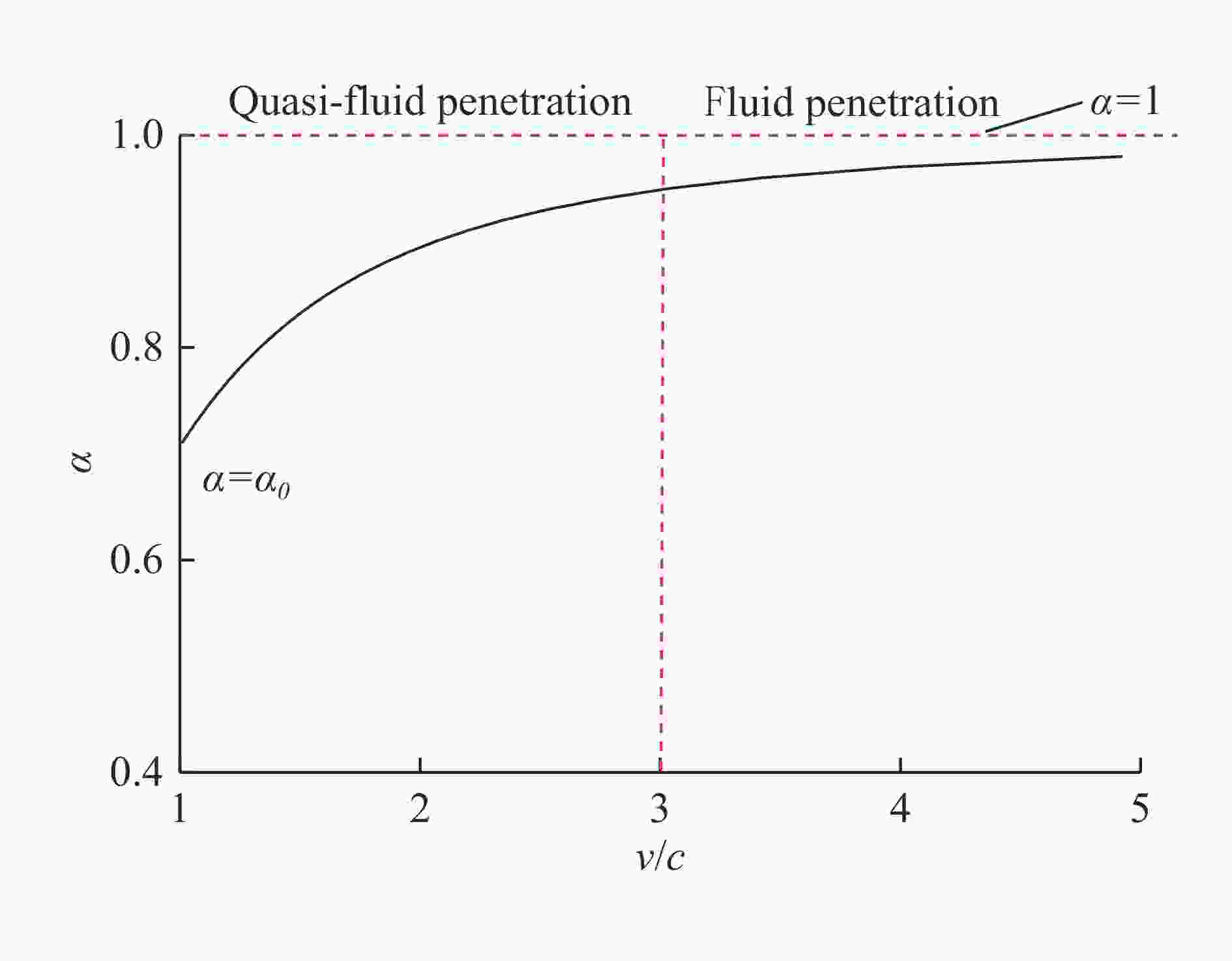
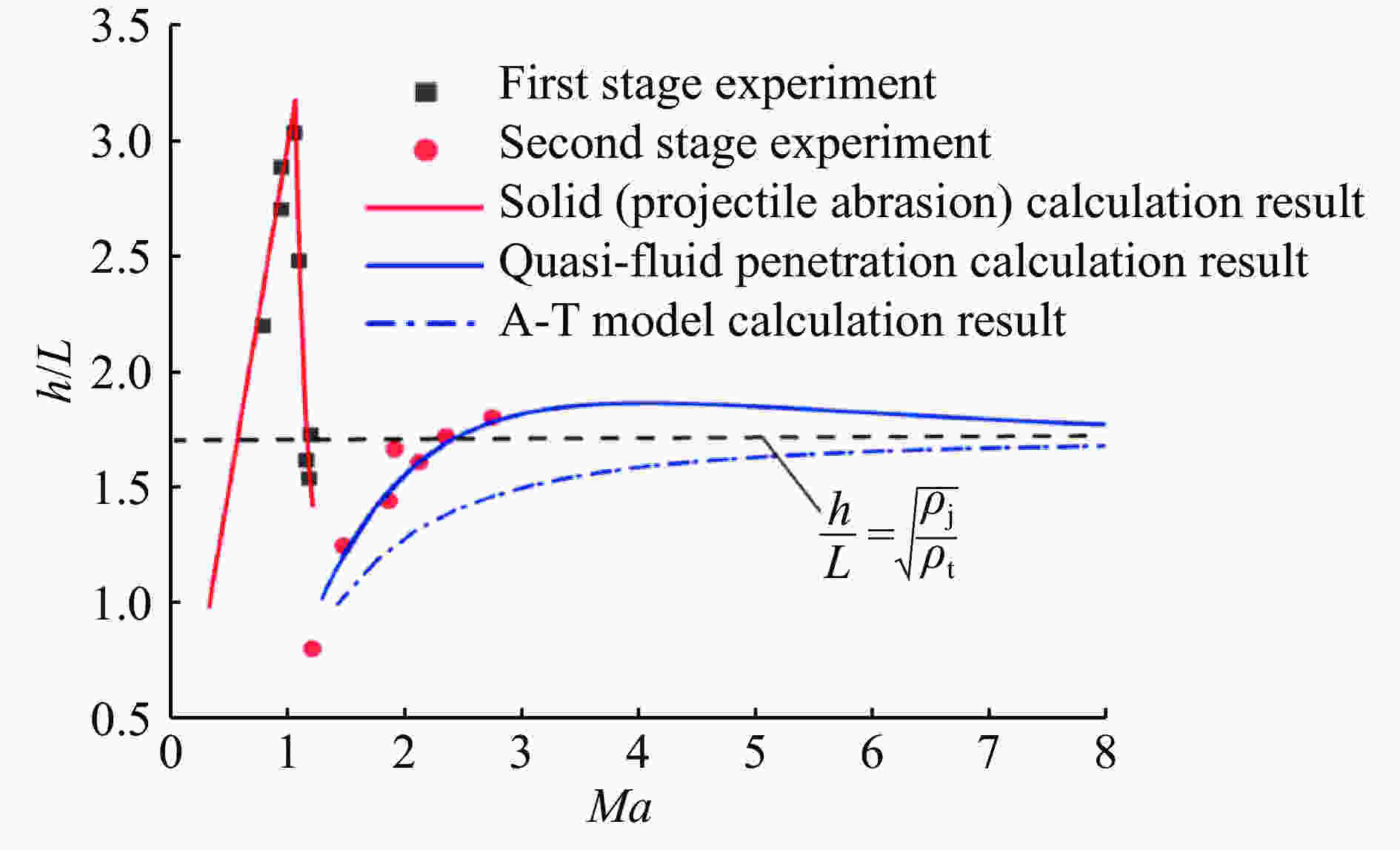
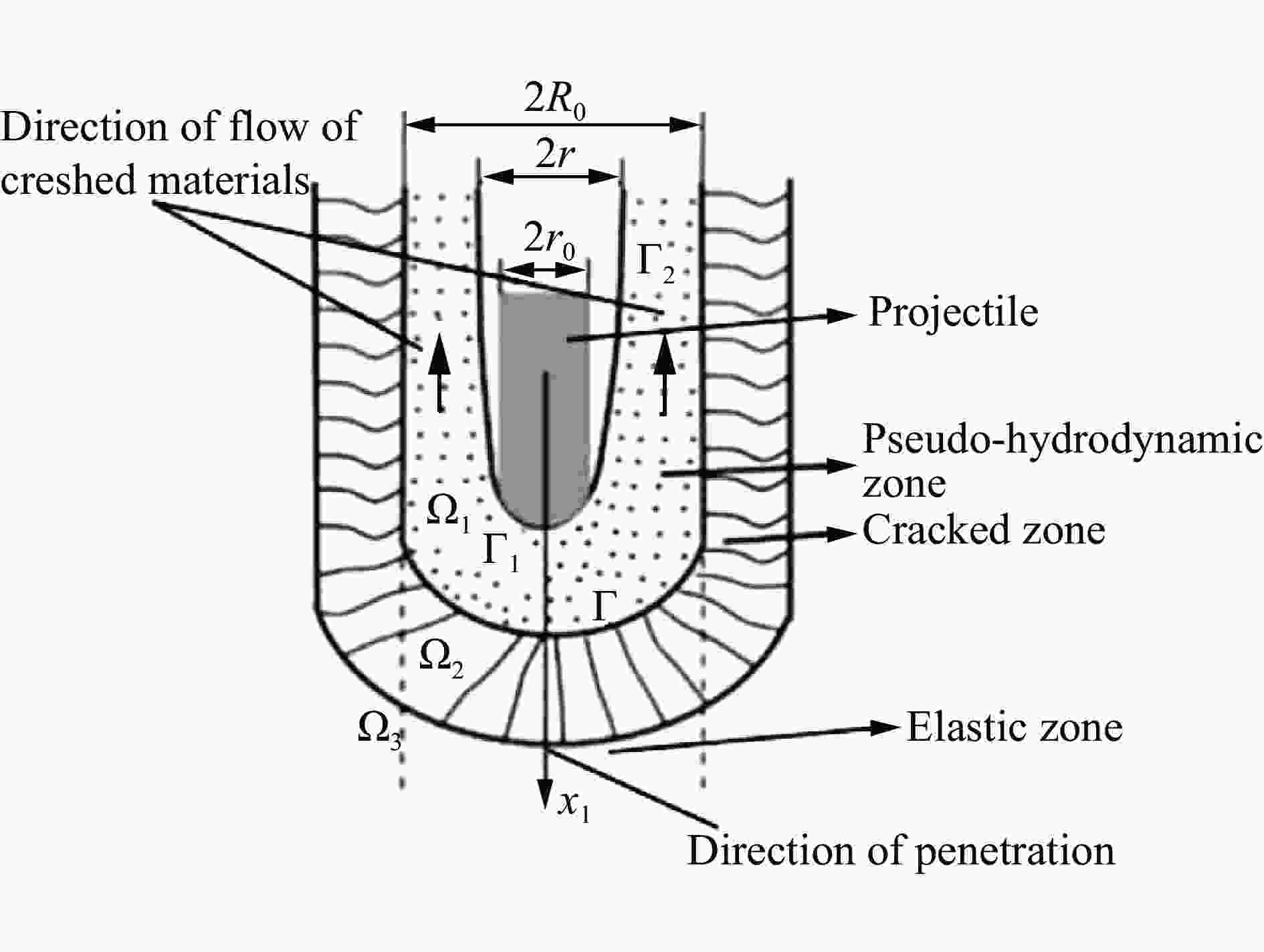
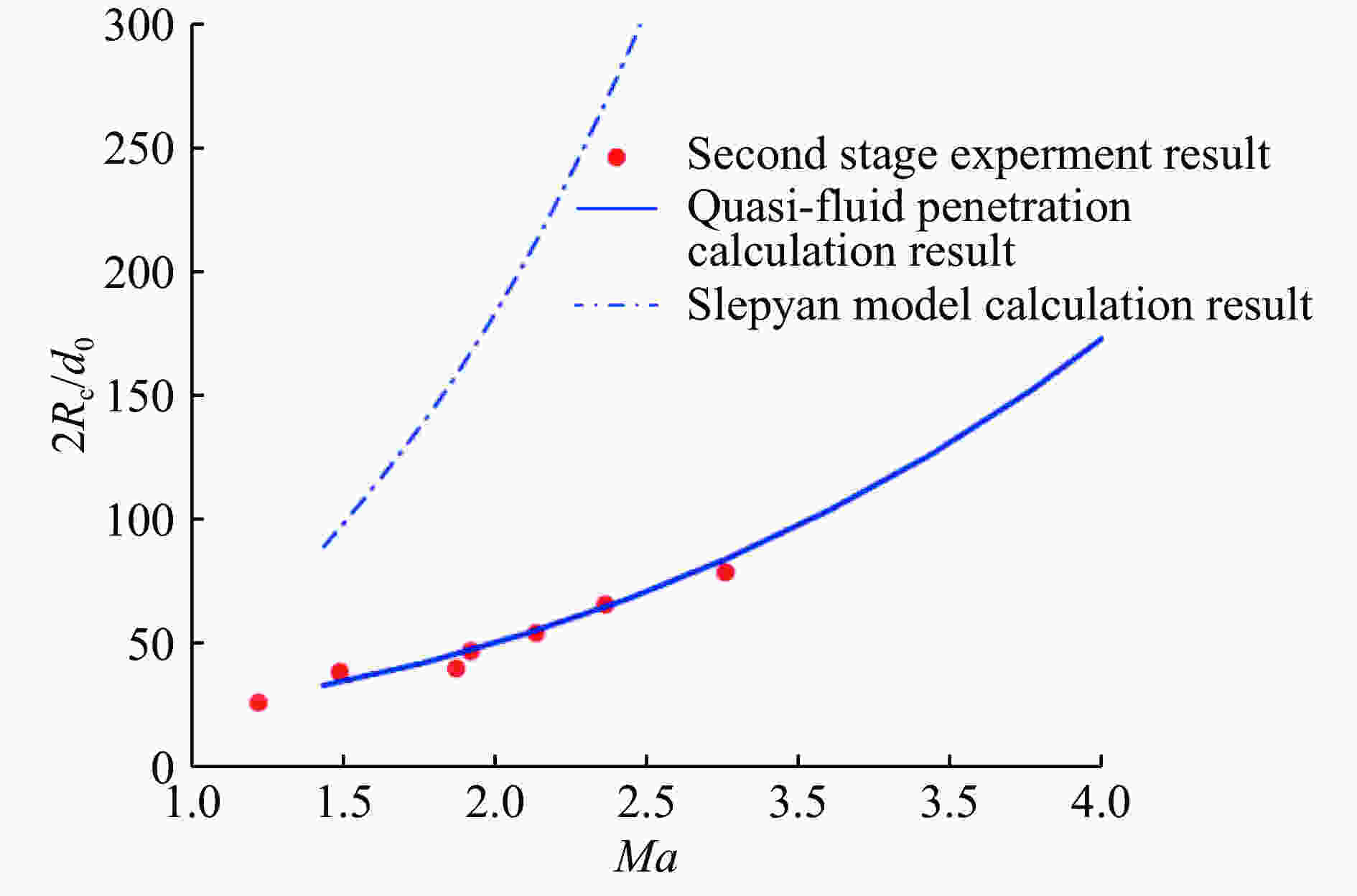
相容应变$\alpha = {\displaystyle\frac{{{\sigma _r}}}{{\sigma }_\theta }} = {\alpha _0}$ ${c_0} = \sqrt {\frac{{\left( {K + \displaystyle\frac{4}{3}\mu } \right)}}{{{\rho _0}}}} $ n=1.1~1.2 注:$\alpha = \displaystyle\frac{{1 - {\rm{sin}}\phi }}{{1 + {\rm{sin}}\phi }}$,ϕ为介质内摩擦角;${\alpha _0} = \displaystyle\frac{\upsilon }{{1 - \upsilon }}$,$\upsilon $为介质泊松比;ρ0为介质密度,K为体积模量,μ为剪切模量。 模型 [Yp] [Rt] 备注 A-T[42-44] Yp Rt ${Y_{\rm p}}{\rm{ = HEL = }}{\sigma _{\rm{yp}}}\left( {1 + \upsilon } \right)/\left( {1 - 2\upsilon } \right)$ ${R_{\rm t}}={\sigma _{\rm{yt} } }\left[ {\left( {2/3} \right) + \ln \left( {0.57{E_{\rm t} }/{\sigma _{\rm{yt} } } } \right)} \right]$ S-W-Z-S[78] $\displaystyle\frac{{{Y_{\rm p}}}}{4}$ $\displaystyle\frac{A}{{4{A_{\rm p}}}}{R_{\rm t}} + \displaystyle\frac{{3A - 4{A_{\rm p}}}}{{8{A_{\rm p}}}}{\rho _{\rm t}}{u^2}$ ${A_{\rm p}}$为长杆弹截面积 $A$为坑底面积,$A \simfont\text{≥} 2{A_{\rm p}}$ R-M-M[79] ${Y_{\rm p}}$ $\displaystyle\frac{{{A_{\rm t}}}}{{{A_{\rm p}}}}{R_{\rm t}} + \displaystyle\frac{{{A_{\rm t}} - {A_{\rm p}}}}{{2{A_{\rm p}}}}{\rho _{\rm t}}{u^2}$ ${A_{\rm p}}$为长杆弹截面积 ${A_{\rm p}}$为蘑菇头等效面积 ${R_{\rm t}}=\left( {{\sigma _{\rm{yt}}}/\sqrt 3 } \right)\left[ {1 + \ln \left( {\sqrt 3 {E_{\rm t}}/\left( {5 - 4v} \right){\sigma _{\rm{yt}}}} \right)} \right]$ A-W[80] ${\sigma _{\rm{yp}}}$ $\displaystyle\frac{7}{3}\ln \left( \alpha \right){\sigma _{\rm{yt}}}$ $\alpha $为靶体中塑性流动区的无量纲长度,由柱形空腔膨胀模型得到(${K_{\rm t}}$${G_{\rm t}}$为靶体的体积模量和剪切模量):
$\left( {1{\rm{ + }}\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm t}}{u^2}}}{{{\sigma _{\rm{yt}}}}}} \right)\sqrt {{K_{\rm t}} - {\rho _{\rm t}}{\alpha ^2}{u^2}} = \left( {1{\rm{ + }}\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm t}}{\alpha ^2}{u^2}}}{{2{G_{\rm t}}}}} \right)\sqrt {{K_{\rm t}} - {\rho _{\rm t}}{u^2}} $Z-H[81] $\displaystyle\frac{{{Y_{\rm p}}}}{4}$ $\displaystyle\frac{{{D^2}}}{{4D_{\rm p}^2}}{R_{\rm t}} + \displaystyle\frac{{\beta {D^2} - 4D_{\rm p}^2}}{{8D_{\rm p}^2}}{\rho _{\rm t}}{u^2}$ $\beta $为动阻力系数 L-W[73] ${Y_{\rm p}}$ $ S - {\rho _{\rm t}}u{U_{{\rm F}0}}\exp \left[ { - {{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{u - {U_{{\rm F}0}}}}{{n{U_{{\rm F}0}}}}} \right)}^2}} \right] + 2{\rho _{\rm t}}U_{{\rm F}0}^2\exp \left[ { - 2{{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{u - {U_{{\rm F}0}}}}{{n{U_{{\rm F}0}}}}} \right)}^2}} \right] $ $S$为静阻力,${U_{ {\rm F}0} } = \sqrt {{\rm HEL}/{\rho _{\rm t} } } $为临界侵彻速度,
$n$为可调系数表 3 地质类材料成坑效应的相似关系
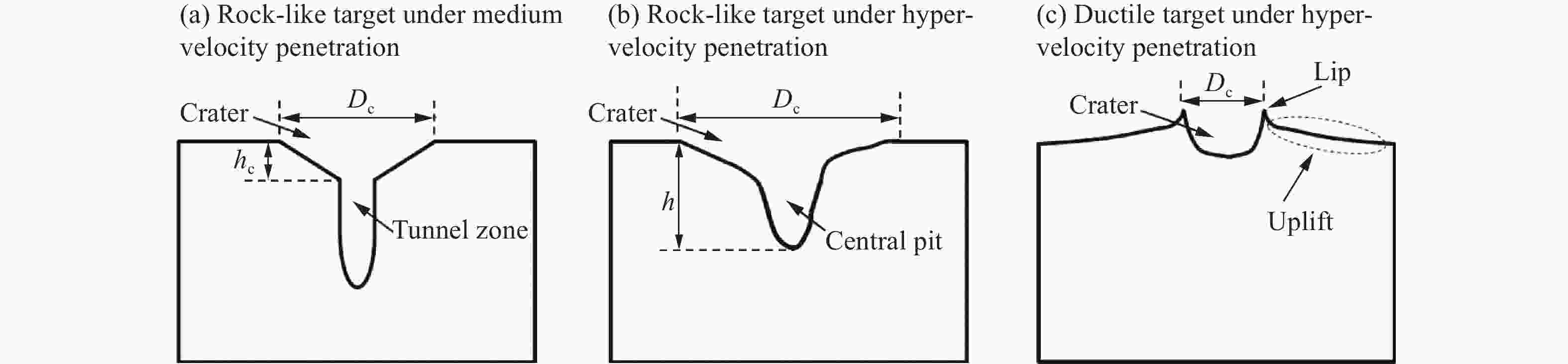
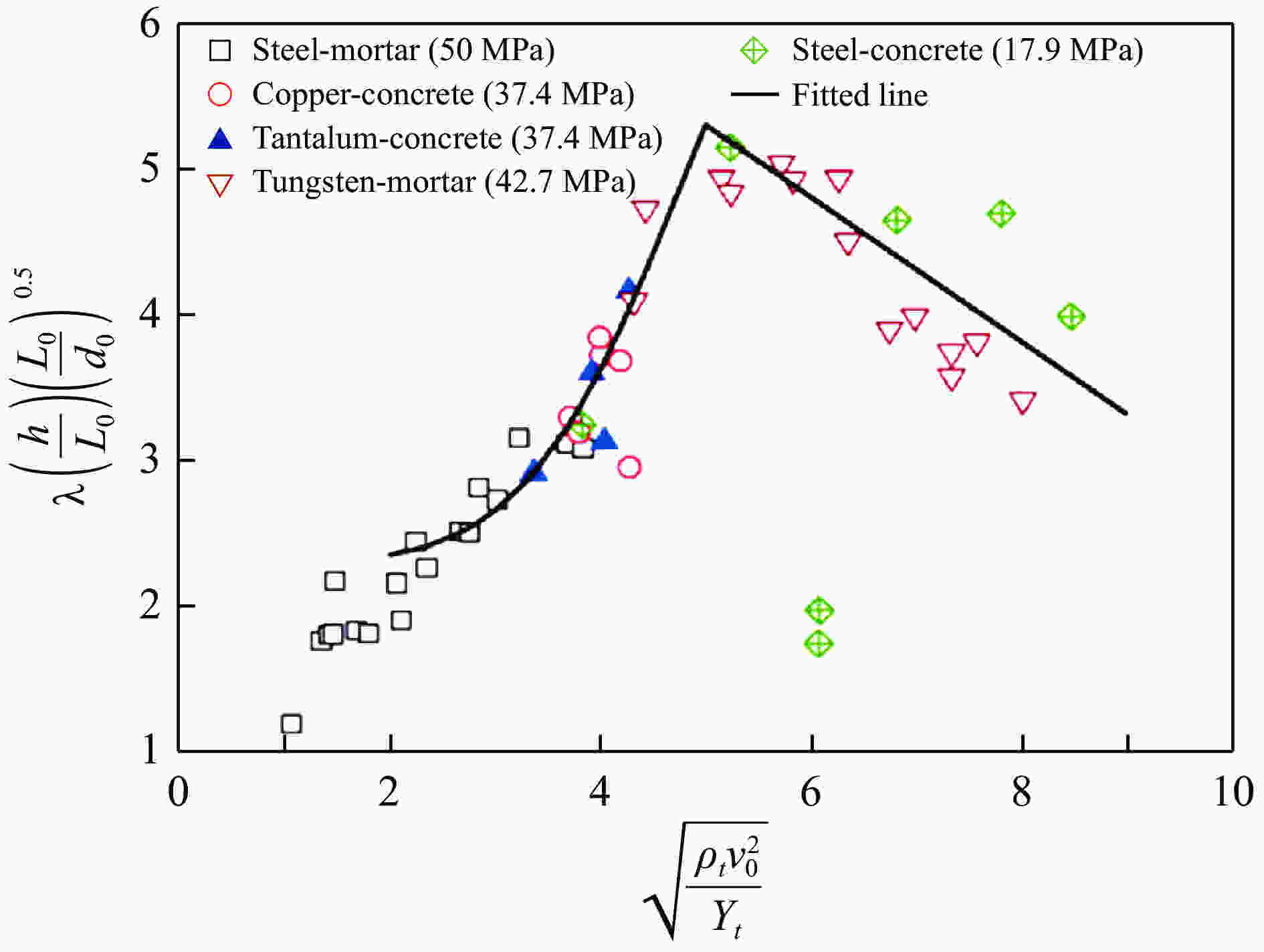
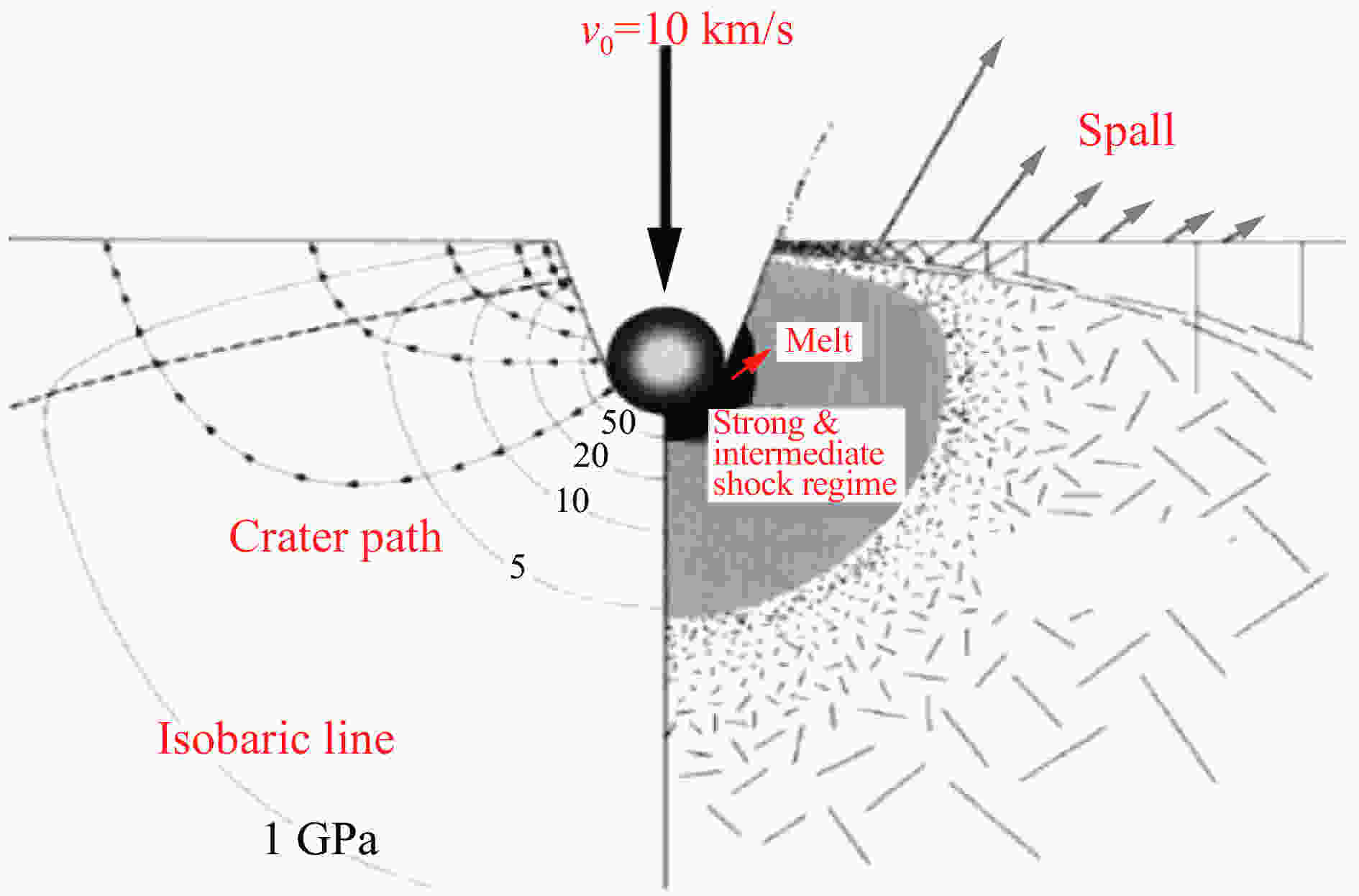
Table 3. Similarity laws of cratering effects in geological material
成坑参数 强度控制区域 重力控制区域 Vc $\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{t} } }{V_{\rm c} } } }{ { {m_{\rm{p} } } }} = {f_{ {V_{\rm{c} } }s} }\left( \varepsilon \right){\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{p} } }v_0^2} }{ { {Y_{\rm t}} } } } \right)^{\frac{ {3{\xi _1} } }{2} } }{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{t} } } }}{ { {\rho _{\rm{p} } } } } } \right)^{1 - 3{\xi _2} + \frac{3}{2}{\xi _1} } }$ $\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm{t}}}{V_{\rm c}}}}{{{m_{\rm{p}}}}} = {f_{{V_{\rm{c}}}g}}\left( \varepsilon \right){\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{v_0^2}}{{g{a_0}}}} \right)^{\frac{{3{\xi _1}}}{{2 + {\xi _1}}}}}{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm{t}}}}}{{{\rho _{\rm{p}}}}}} \right)^{\frac{{2 + {\xi _1} - 6{\xi _2}}}{{2 + {\xi _1}}}}}$ Dc ${D_{\rm{c} } }{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{t} } } }}{ { {m_{\rm{p} } } } } } \right)^{1/3} } = {f_{ {D_{\rm{c} } }s} }\left( \varepsilon \right){\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{p} } }v_0^2} }{ { {Y_{\rm t}} } } } \right)^{\frac{ { {\xi _1} } }{2} } }{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{t} } } }}{ { {\rho _{\rm{p} } } } } } \right)^{\frac{1}{3} - {\xi _2} + \frac{1}{2}{\xi _1} } }$ ${D_{\rm c}}{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm{t}}}}}{{{m_{\rm{p}}}}}} \right)^{1/3}} = {f_{{D_{\rm{c}}}g}}\left( \varepsilon \right){\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{v_0^2}}{{g{a_0}}}} \right)^{\frac{{{\xi _1}}}{{2 + {\xi _1}}}}}{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm{t}}}}}{{{\rho _{\rm{p}}}}}} \right)^{\frac{{2 + {\xi _1} - 6{\xi _2}}}{{3\left( {2 + {\xi _1}} \right)}}}}$ h $h{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{t} } } }}{ { {m_{\rm{p} } } } } } \right)^{1/3} } = {f_{ {h_{\rm{c} } }s} }\left( \varepsilon \right){\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{p} } }v_0^2} }{ { {Y_{\rm t}} } } } \right)^{\frac{ { {\xi _1} } }{2} } }{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{ { {\rho _{\rm{t} } } }}{ { {\rho _{\rm{p} } } } } } \right)^{\frac{1}{3} - {\xi _2} + \frac{1}{2}{\xi _1} } }$ $h{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm{t}}}}}{{{m_{\rm{p}}}}}} \right)^{1/3}} = {f_{{h_{\rm{c}}}g}}\left( \varepsilon \right){\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{v_0^2}}{{g{a_0}}}} \right)^{\frac{{{\xi _1}}}{{2 + {\xi _1}}}}}{\left( {\displaystyle\frac{{{\rho _{\rm{t}}}}}{{{\rho _{\rm{p}}}}}} \right)^{\frac{{2 + {\xi _1} - 6{\xi _2}}}{{3\left( {2 + {\xi _1}} \right)}}}}$ 表 4 地质类材料地冲击衰减指数n
Table 4. Power exponent n for attenuation of ground shock in geological material
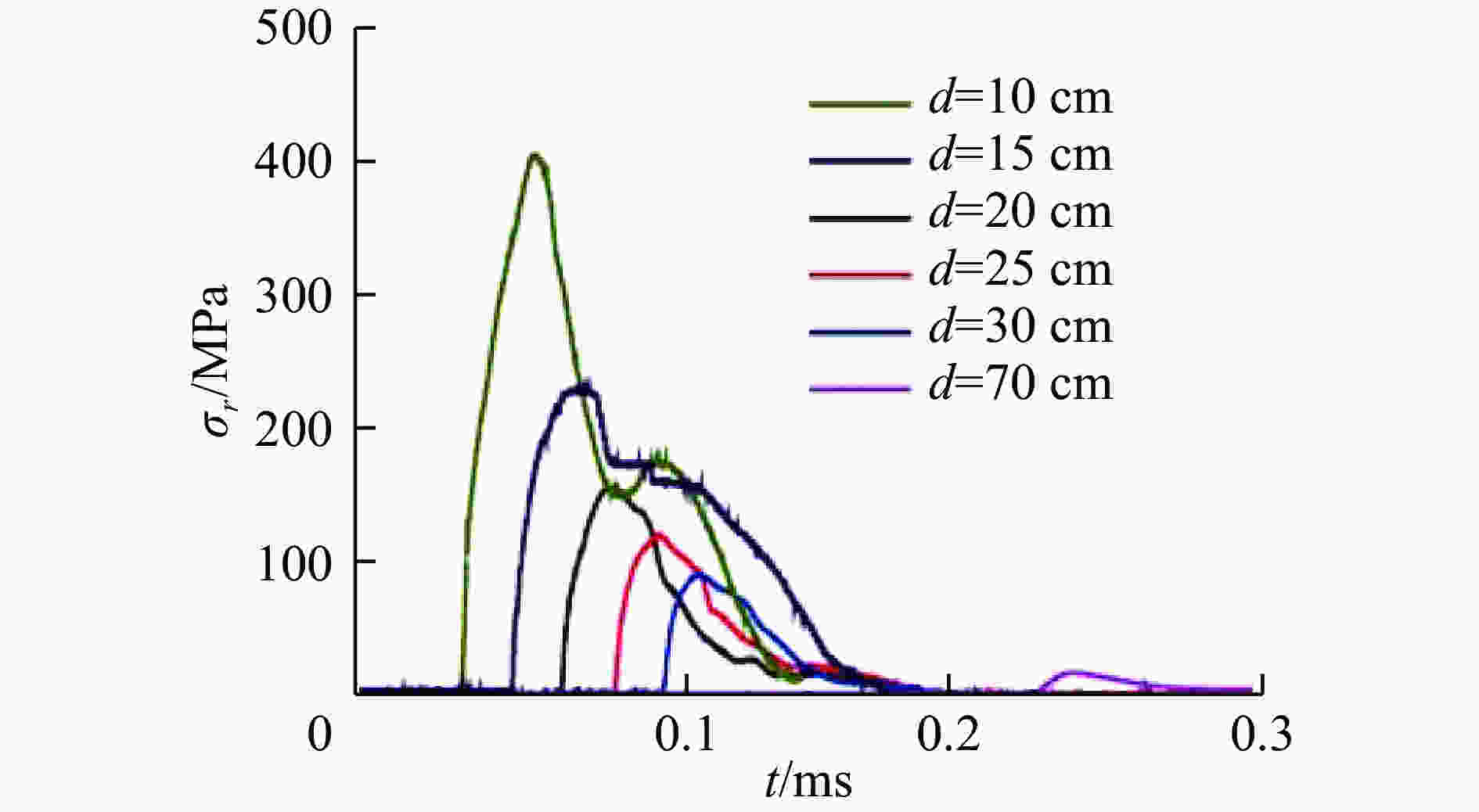
介质类型 作用类型 研究方法 爆炸当量(TNT)或撞击速度 n 花岗岩 化学爆炸 试验拟合 0.12 kg 2.12 核爆炸 试验拟合 4.8 kt/12.2 kt/56 kt 1.6 砂岩 化学爆炸 试验拟合 0.1 kg 2 石灰岩 化学爆炸 试验拟合 0.18~0.2 kg 2 撞击 数值计算 4~6 km/s 2 玄武岩 撞击 试验拟合 0.6~2.7 km/s 1.7±0.2 辉长-钙长岩 撞击 数值计算 4~45 km/s 0.2~2.95 冰 撞击 试验拟合 3.9~4.6 km/s 0.9~1.8 盐岩 核爆炸 试验拟合 1.1 kt/3.1 kt/25 kt 1.6 混凝土 化学爆炸 试验拟合 0.12 kg 1.53 细粘土 化学爆炸 试验拟合 0.2 kg 2.6 黏土 化学爆炸 试验拟合 0.4 kg 2.34 -
[1] 任辉启, 穆朝民, 刘瑞朝, 等. 精确制导武器侵彻效应与工程防护[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. [2] 杨秀敏, 邓国强. 常规钻地武器破坏效应的研究现状和发展 [J]. 后勤工程学院学报, 2016, 32(5): 1–9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7843.2016.05.001.YANG Xiumin, DENG Guoqiang. The research status and development of damage effect of conventional earth penetration weapon [J]. Journal of Logistical Engineering University, 2016, 32(5): 1–9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7843.2016.05.001. [3] 吴飚, 杨建超, 刘瑞朝. 有限厚块石砌体钢筋混凝土结构板抗贯穿性能的实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2013, 33(1): 73–78. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2013)01-0073-06.WU Biao, YANG Jianchao, LIU Ruichao. Experimental study on perforation resistance of composite targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2013, 33(1): 73–78. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2013)01-0073-06. [4] 王涛, 余文力, 王少龙. 美军钻地武器的现状及发展趋势 [J]. 飞航导弹, 2004, 8: 4–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-1319.2004.08.003 [5] 刘峥, 程怡豪, 邱艳宇, 等. 成层式防护结构抗超高速侵彻的数值分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(6): 1317–1324. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0181.LIU Zheng, CHENG Yihao, QIU Yanyu, et al. Numerical analysis on hypervelocity penetration into layered protective structure [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(6): 1317–1324. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0181. [6] 邓国强, 杨秀敏. 抗超高速武器最小安全防护层厚度计算 [J]. 防护工程, 2016, 38(1): 39–42.DENG Guoqiang, YANG Xiumin. Estimation method of safety protective layer depth resisting hypervelocity weapon impact [J]. Protective Engineering, 2016, 38(1): 39–42. [7] 闫焕敏, 张志刚, 葛涛, 等. 防护工程中遮弹层的研究进展 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2016, 39(1): 127–132. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20160105.001.YAN Huanmin, ZHANG Zhigang, GE Tao, et al. Research progress of bursting layer in protection engineering [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2016, 39(1): 127–132. DOI: 10.14024/j.cnki.1004-244x.20160105.001. [8] YOUNG C W. Penetration equations: SAND 97-2426 [R]. Sandia National Laboratories, 1997. [9] BERNARD R S. Creighton D. Projectile penetration in soil and rock analysis for non-normal impact: SL-79-15 AD-A081044 [R]. US Army Waterways Experimental Station, Vicksbury, 1979. [10] 火炸药及其制品工厂建筑结构设计规范: GB 51182-2016 [S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2017. [11] HEUZE F E. An overview of projectile penetration into geological materials, with emphasis on rocks [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1990, 27(1): 1–14. [12] PENG Y, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Geometrical scaling effect for penetration depth of hard projectile into concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 120: 46–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.05.010. [13] 邓国强, 杨秀敏. 超高速武器打击效应数值仿真 [J]. 科技导报, 2015, 33(16): 65–71. DOI: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.16.010.DENG Guoqiang, YANG Xiumin. Numerical simulation of damage effect of hypervelocity weapon on ground target [J]. Science and Technology Review, 2015, 33(16): 65–71. DOI: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.16.010. [14] 沈峰, 章青, 顾鑫. 弹丸侵彻混凝土靶板破坏过程的近场动力学模拟 [J]. 重庆大学学报, 2019, 42(1): 64–69. DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2019.01.006.SHEN Feng, ZHANG Qing, GU Xin. Peridynamics modeling for projectile penetrating into concrete [J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2019, 42(1): 64–69. DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2019.01.006. [15] ANTOUN T, GLENN L, WALTON O, et al. Simulation of hypervelocity penetration in limestone [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 33(1): 45–52. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.09.009. [16] 沈雁鸣, 陈坚强. 超高速碰撞相似律的数值模拟验证 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2011, 31(4): 343–348. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2011)04-0343-06.SHEN Yanming, CHEN Jianqiang. Numerically simulating verification of the comparability rule on hypervelocity impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2011, 31(4): 343–348. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2011)04-0343-06. [17] 施存程.超高速弹体对地质类材料撞击机理研究[D].南京: 解放军理工大学, 2015. [18] 李卧东, 王明洋, 施存程, 等. 地质类材料超高速撞击相似关系与实验研究综述 [J]. 防护工程, 2015, 37(2): 55–62.LI Wodong, WANG Mingyang, SHI Cuncheng, et al. Review of similarity laws and scaling experiments research of hypervelocity impact on geological material targets [J]. Protective Engineering, 2015, 37(2): 55–62. [19] 李干, 宋春明, 邱艳宇, 等. 超高速弹对花岗岩侵彻深度逆减现象的理论与实验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(1): 60–66. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.0584.LI Gan, SONG Chunming, QIU Yanyu, et al. Theoretical and experimental studies on the phenomenon of penetration depth reverse reduction in the penetration of granite by hyper-velocity projectiles [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(1): 60–66. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.0584. [20] FREW D J, FORRESTAL M J, HANCHAK S J. Penetration experiments with limestone targets and ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2000, 67(4): 841–845. doi: 10.1115/1.1331283 [21] 钱秉文, 周刚, 李进, 等. 钨合金弹体超高速撞击混凝土靶成坑特性研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(10): 1012–1017. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.10.004.QIAN Bingwen, ZHOU Gang, LI Jin, et al. Study of the crater produced by hypervelocity tungsten alloy projectile into concrete target [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(10): 1012–1017. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.10.004. [22] KONG X Z, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Projectile penetration into mortar targets with a broad range of striking velocities: test and analyses [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 106: 18–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.02.022. [23] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, et al. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(5): 465–476. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00048-F [24] 何翔, 徐翔云, 孙桂娟, 等. 弹体高速侵彻混凝土的效应实验 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0001-06.HE Xiang, XU Xiangyun, SUN Guijuan, et al. Experimental investigation on projectiles’ high-velocity penetration into concrete target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010, 30(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0001-06. [25] 赵晓宁. 高速弹体对混凝土侵彻效应研究 [D].南京: 南京理工大学, 2011. [26] MU Z C, ZHANG W. An investigation on mass loss of ogival projectiles penetrating concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38: 770–778. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.04.002. [27] 何丽灵, 陈小伟, 范瑛. 先进钻地弹高速侵彻实验中质量磨蚀侵蚀金相分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(5): 515–522. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)05-0515-08.HE Liling, CHEN Xiaowei, FAN Ying. Metallographic observation of reduced-scale advanced EPW after high-speed penetration [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(5): 515–522. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)05-0515-08. [28] ZHAO J, CHEN X W, JIN F N, et al. Depth of penetration of high-speed penetrator with including the effect of mass abrasion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37: 971–979. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.03.008. [29] GOLD V M, VRADIS G C, PEARSON J C. Concrete penetration by eroding projectiles: experiments and analysis [J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1996, 122(2): 145–152. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1996)122:2(145) [30] 徐晨阳.弹体高速侵彻典型岩石靶体作用过程研究 [D].南京: 南京理工大学, 2018. [31] 王明洋, 邱艳宇, 李杰, 等. 超高速长杆弹对岩石侵彻、地冲击效应理论与实验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(3): 564–572. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1348.WANG Mingyang, QIU Yanyu, LI Jie, et al. Theoretical and experimental study on rock penetration and ground impact effects of hypervelocity long rod projectile [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(3): 564–572. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1348. [32] 王明洋, 李杰, 李海波, 等. 岩石的动态压缩行为与超高速动能弹毁伤效应计算 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(6): 1200–1217. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0173.WANG Mingyang, LI Jie, LI Haibo, et al. Dynamic compression behavior of rock and simulation of damage effects of hypervelocity kinetic energy bomb [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(6): 1200–1217. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0173. [33] 王明洋, 岳松林, 李海波, 等. 超高速弹撞击岩石的地冲击效应等效计算 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(12): 2656–2663. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0473.WANG Mingyang, YUE Songlin, LI Haibo, et al. An equivalent calculation method of ground shock effects of hypervelocity projectile striking on rock [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(12): 2656–2663. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0473. [34] CHENG Y H, WANG M Y, SHI C C, et al. Constraining damage size and crater depth: a physical model of transient crater formation in rocky targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 81(6): 50–60. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.03.009. [35] 邓国强, 王丽梅, 胡圣伟. 动能钻地武器技术参数推测与破坏效应分析 [J]. 防护工程设计与研究, 2013, 11(1): 7–11. [36] 张德志, 张向荣, 林俊德, 等. 高强钢弹对花岗岩正侵彻的实验研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(9): 1612–1618. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.024ZHANG D Z, ZHANG X R, LIN J D, et al. Penetration experiments for normal impact into granite targets with high-strength steel prokectile [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(9): 1612–1618. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.024 [37] FORRESTAL M J, LEE L M, JENRETTE B D. Laboratory-scale penetration experiments into geological targets to impact velocities of 2.1 km/s [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1986, 53(2): 317–320. doi: 10.1115/1.3171758 [38] NELSON R W. Low-yield earth-penetrating nuclear weapons [J]. Science and Global Security, 2002, 10: 1–20. DOI: 10.1080/08929880290008386. [39] CHEN X W, LI Q M. Transition from nondeformable projectile penetration to semi-hydrodynamic penetration [J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2004: 123–127. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2004)130:1(123). [40] ANDERSON C E. Analytical models for penetration mechanics: a review [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 108: 3–26. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.03.018. [41] FORRESTAL M J, PIEKUTOWSKI A J. Penetration experiments with 6061-T6511 aluminum targets and spherical-nose steel projectiles at striking velocities between 0.5 and 3.0 km/s [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(1): 57–67. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00033-0 [42] ALEKSEEVSKII V P. Penetration of a rod into a target at high velocity [J]. Combustion, Explosion, and Shock Waves, 1966, 2(2): 63–66. [43] TATE A. A theory for the deceleration of long rods after impact [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1967, 15(6): 387–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(67)90010-5 [44] TATE A. Long rod penetration models-Part II. Extensions to the hydrodynamic theory of penetration [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1986, 28(9): 599–612. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7403(86)90075-5. [45] Wen H M, Lan B. Analytical models for the penetration of semi-infinite targets by rigid, deformable and erosive long rods [J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2010, 26(4): 573–583. DOI: 10.1007/s10409-010-0349-0. [46] 卢正操, 张元迪, 文鹤鸣, 等. 长杆弹侵彻半无限混凝土靶的理论研究 [J]. 现代应用物理, 2018, 9(4): 040102.LU Zhengcao, ZHANG Yuandi, WEN Heming, et al. Theoretical study on the penetration of long rods into semi-infinite concrete target [J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2018, 9(4): 040102. [47] SHEMYAKIN E I. Behavior of rocks under dynamic loads [J]. Soviet Mining, 1965, 2(1): 12–20. [48] SHEMYAKIN E I. Physical and mechanical fundamentals of unconventional technologies of solid mineral development [J]. Physical Mesomechanics, 2007, 10(1/2): 87–93. [49] 舍米亚金Е И. 弹塑性理论的动力学问题[M]. 戚承志, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. [50] AHRENS T J, JOHNSON M L. Rock physics and phase relations [M]. Washington D C: Gemological Insti-tute of America; 1995: 35−44. [51] 钱七虎, 王明洋. 岩土中的冲击爆炸效应[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2010. [52] LI Q M, REID S R, WEN H M, et al. Local impact effects of hard missile on concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 32: 224–284. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.04.005. [53] 楼建锋.侵彻半无限厚靶的理论模型与数值模拟研究[D]. 四川绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院, 2012. [54] 王政. 弹靶侵彻动态响应的理论与数值分析[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2005. [55] FORRESTAL M J, TZOU D Y. A spherical cavity-expansion penetration model for concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 1997, 34(31/32): 4127–4146. [56] FORRESTAL M J, LUK V K. Dynamic spherical cavity-expansion in a compressible elastic-plastic solid [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1988, 55(2): 275–279. doi: 10.1115/1.3173672 [57] 李志康, 黄风雷. 考虑混凝土孔隙压实效应的球形空腔膨胀理论 [J]. 岩土力学, 2010, 31(5): 1481–1485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.05.022LI Zhikang, HUANG Fenglei. A spherical cavity expansion theory of concrete considering voids compacted effects [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2010, 31(5): 1481–1485. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.05.022 [58] 黄民荣, 顾晓辉, 高永宏. 基于Griffith强度理论的空腔膨胀模型与应用研究 [J]. 力学与实践, 2009, 31(5): 30–34.HUANG Minrong, GU Xiaohui, GAO Yonghong. Cavity expansion model based on the Griffith strength theory and its application [J]. Mechanics inEngineering, 2009, 31(5): 30–34. [59] HE T, WEN H M, GUO X J. A spherical cavity expansion model for penetration of ogival-nosed projectiles into concrete targets with shear-dilatancy [J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2011, 27(6): 1001–1012. doi: 10.1007/s10409-011-0505-1 [60] FENG J, LI W, WANG X M, et al. Dynamic spherical cavity expansion analysis of rate-dependent concrete material with scale effect [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 84: 24–37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.05.005 [61] LUK V K, FORRESTAL M J, AMOS D E. Dynamic spherical cavity expansion of Strain-Hardening materials [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1991, 58(1): 1. doi: 10.1115/1.2897150 [62] 吴昊, 方秦, 龚自明, 等. 应用改进的双剪强度理论分析岩石靶体的弹体侵彻深度 [J]. 工程力学, 2009, 26(8): 216–222.WU Hao, FANG Qin, GONG Ziming, et al. Analysis on penetration depth of projectiles into rock targets based on the improved twin shear strength theory [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2009, 26(8): 216–222. [63] 曹扬悦也, 蒋志刚, 谭清华, 等. 基于Hoek-Brown准则的混凝土-岩石类靶侵彻模型 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(5): 48–53.CAO Yangyueye, JIANG Zhigang, TAN Qinghua, et al. Penetration model for concrete-rock targets based on Hoek-Brown criterion [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(5): 48–53. [64] OMIDVAR M, ISKANDER M, BLESS M. Response of granular media to rapid penetration [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 66: 60–82. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.12.004. [65] FORRESTAL M J, ALTMAN B S, CARGILE J D, et al. An empirical equation for penetration depth of ogive-nose projectiles into concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1994, 15(4): 395–405. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)80024-4 [66] 王明洋, 谭可可, 吴华杰, 等. 钻地弹侵彻岩石深度计算新原理与方法 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(9): 1863–1869. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.09.018WANG Mingyang, TAN Keke, WU Huajie, et al. New method of calculation of projectile penetration into rock [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(9): 1863–1869. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.09.018 [67] 何丽灵, 陈小伟, 夏源明. 侵彻混凝土弹体磨蚀的若干研究进展 [J]. 兵工学报, 2010, 31(7): 950–966.HE Liling, CHEN Xiaowei, XIA Yuanming. A review on the mass loss of projectile [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2010, 31(7): 950–966. [68] GUO L, HE Y, ZHANG X F, et al. Study mass loss at microscopic scale for a projectile penetration into concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 72: 17–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.05.001 [69] HE L L, CHEN X W, HE X. Parametric study on mass loss of penetrators [J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2010, 26: 585–597. doi: 10.1007/s10409-010-0341-8 [70] 何丽灵. 高速侵彻混凝土弹体的动力学行为研究-计及质量损失和头形钝化[D].合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2012. [71] 郑浩. 卵形弹体侵彻混凝土靶侵蚀效应研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2013. [72] 杨阳. 混凝土侵彻与贯穿若干问题研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2012. [73] LAN B, WEN H M. Alekseevskii-Tate revisited: an extension to the modified hydrodynamic theory of long rod penetration [J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2010, 53: 1364–1373. doi: 10.1007/s11431-010-0011-x [74] HERRMANN W, WILBECK J S. Review of hypervelocity penetration theories [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1987, 5: 307–322. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(87)90048-0 [75] BIRKHOFF G, MACDOUGALL D P, PUGH E M, et al. Explosives with lined cavities [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1948, 19(6): 563–582. doi: 10.1063/1.1698173 [76] ORPHAL D L. Explosions and impacts [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 33: 496–545. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.09.090. [77] ALLEN WA, ROGERS J W. Penetration of a rod into a semi-infinite target [J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 1961, 272: 275–84. doi: 10.1016/0016-0032(61)90559-2 [78] 孙庚辰, 吴锦云, 赵国志, 等. 长杆弹垂直侵彻半无限厚靶板的简化模型 [J]. 兵工学报, 1981(4): 1–8.SUN Gengchen, WU Jinyun, ZHAO Guozhi, et al. A simple model of the penetration of the long-rod penetrator against the plate with semi-infinite thickness at normal angle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 1981(4): 1–8. [79] ROSENBERG Z, MARMOR E, MAYSELESS M. On the hydrodynamic theory of long-rod penetration [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1990, 10(1): 483–486. [80] WALKER J D, ANDERSON C E. A time-dependent model for long-rod penetration [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 16(1): 19–48. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)00032-R [81] ZHANG L S, HUANG F L. Model for long-rod penetration into semi-infinite targets [J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2004, 13: 285–289. [82] ROSENBERG Z, DEKEL E. Further examination of long rod penetration: the role of penetrator strength at hypervelocity impacts [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24: 85–102. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00032-9 [83] ANDERSON Jr C E, WALKER J D. An examination of long-rod penetration [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1991, 11: 481–501. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(91)90015-8 [84] 焦文俊, 陈小伟. 长杆高速侵彻问题研究进展 [J]. 力学进展, 2019, 49: 201900. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-17-021.JIAO Wenjun, CHEN Xiaowei. Review on long-rod penetration at hypervelocity [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2019, 49: 201900. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-17-021. [85] ANDERSON Jr C E, LITTLEFIELD D L, Walker J D. Long-rod penetration, target resistance, and hyperve-locity impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1993, 14: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/0734-743X(93)90004-Q [86] LI J, WANG M Y, CHENG Y H. Analytical model of hypervelocity penetration into rock [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 384–394. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.08.008. [87] 李杰, 王明洋, 李海波, 等. 超高速动能武器侵彻岩石的毁伤评估与工程防护 [J]. 现代应用物理, 2018, 9(4): 040105.LI Jie, WANG Mingyang, LI Haibo, et al. The damage evaluation and protection of hypervelocity kinetic energy weapon penetrating rocks [J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2018, 9(4): 040105. [88] BURCHELL M J, WHITEHORN L. Oblique incidence hypervelocity impacts on rock [J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 2003, 341(1): 192–198. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-8711.2003.06385.x [89] TAKAGI Y, MIZUTANI H, SHIN-ICHI K. Impact fragmentation experiments of basalts and pyrophyllites [J]. Icarus, 1984, 59(3): 462–477. doi: 10.1016/0019-1035(84)90114-3 [90] DONALD E G. Displaced mass, depth, diameter, and effects of oblique trajectories for impact craters formed in dense crystalline rocks [J]. The Moon, 1973, 6(1-2): 32–44. doi: 10.1007/BF02630651 [91] DONALD E G. Impact cratering [C] // Lunar & Planetary Science Conference, 1th, 1974: 137−175. [92] KINSLOW R. High-velocity impact phenomena [M]. New York and London: Academic Press, 1970. [93] 张庆明, 黄风雷. 超高速碰撞动力学引论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000. [94] HOLSAPPLE K A, HOUSEN K R. A crater and its ejecta: an interpretation of deep impact [J]. Icarus, 2007, 191(2): 586–597. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2006.08.035 [95] HOLSAPPLE K A. The equivalent depth of burst for impact cratering [C] // Lunar & Planetary Science Conference, 11th, 1980: 2379−2401. [96] HOLSAPPLE K A, SCHMIDT R M. On the scaling of crater dimensions 2. Impact processes [J]. Journal of Geophysics Research, 1982, 87(B3): 1849–1870. doi: 10.1029/JB087iB03p01849 [97] HOLSAPPLE K A, SCHMIDT R M. Point source solutions and coupling parameters in cratering mechanics [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1987, 92(B7): 6350–6376. doi: 10.1029/JB092iB07p06350 [98] HOLSAPPLE K A. The scaling of impact processes in planetary sciences [J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1993, 21(1): 333–373. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.21.050193.002001 [99] HOUSEN K R, HOLSAPPLE K A. Impact cratering on porous asteroids [J]. Icarus, 2003, 163(1): 102–119. doi: 10.1016/S0019-1035(03)00024-1 [100] HOLSAPPLE K A, SCHMIDT R M. On the scaling of crater dimensions 1. Explosive processes [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 1980, 85(B12): 7247–7256. [101] SCHMIDT R M, HOUSEN K R. Some recent advances in the scaling of impact and explosion cratering [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1987, 5(1): 543–560. [102] HOLSAPPLE K A. Users Manual: Crater Sizes from Explosions or Impacts[DB/OL] Keith. aa. Washington. edu/craterdata/scaling/usermanual.html [103] WINKLER R, LUTHER R, POELCHAU M, et al. Subsurface deformation of experimental hypervelocity impacts in quartzite and marble targets [J]. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 2018, 53(8): 1733–1755. DOI: 10.1111/maps.13080. [104] POELCHAU M H, KENKMANN T, THOMA K, et al. The MEMIN research unit: Scaling impact cratering experiments in porous sandstones [J]. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 2013, 48(1): 8–22. [105] KENKMANN T, WÜNNEMANN K, DEUTSCH A, et al. Impact cratering in sandstone: the MEMIN pilot study on the effect of pore water [J]. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 2011, 46(6): 890–902. [106] DUFRESNE A, POELCHAU M H, KENKMANN T, et al. Crater morphology in sandstone targets: the MEMIN impact parameter study [J]. Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 2013, 48(1): 50–70. [107] POELCHAU M H, KENKMANN T, TOBIAS H, et al. Impact cratering experiments into quartzite, sandstone and tuff: the effects of projectile size and target properties on spallation [J]. Icarus, 2014, 242(2): 211–224. [108] POLANSKEY C A, THOMAS J A. Impact spallation experiments: Fracture patterns and spall velocities [J]. Icarus, 1990, 87(1): 140–155. doi: 10.1016/0019-1035(90)90025-5 [109] MURR L E, QUINONES S A, AYALA A, et al. The low-velocity-to-hypervelocity penetration transition for impact craters in metal targets [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1998, 256(1): 166–182. [110] 刘海鹏, 高世桥, 金磊, 等. 弹侵彻混凝土靶面成坑的分阶段分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(S2): 52–56.LIU Haipeng, GAO Shiqiao, JIN Lei, et al. Phase analysis on crater-forming of projectile penetrating into concrete target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(S2): 52–56. [111] LI Q M, CHEN X W. Dimensionless formulae for penetration depth of concrete target impacted by a non-deformable projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(1): 93–116. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00037-4 [112] 李大红, 熊大和. 石英砂岩冲击变质与裂隙分布 [J]. 地质地球化学, 1995(4): 87–91. [113] FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, GREEN M L, et al. Penetration of concrete targets with ogive-nose steel rods [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1998, 21(6): 489–497. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(98)00008-6 [114] 程怡豪, 李干, 岳松林, 等. 混凝土超高速侵彻效应实验与相似规律 [C] // 第十七届全国非线性振动暨第十四届全国非线性动力学和运动稳定性学术会议. 南京, 2019: 151−158. [115] AIZENBERG-STEPANENKO M V. Model of high-velocity penetration of an indenter into a medium [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 2007, 43(3): 254–272. [116] SLEPYAN L I. Calculation of the size of the crater formed by a high-speed impact [J]. Journal of Mining Science, 1978, 14(5): 465–471. [117] GUREVICH M I. The theory of jets in an ideal fluid [M]. London: Pergamon Press Ltd, 1966: 113−116. [118] MAXWELL D E. Simple Z model for cratering, ejection, and the overturned flap [M]. New York: Pergamon Press, 1977. [119] 邓国强, 杨秀敏. 超高速武器流体侵彻与装药浅埋爆炸效应的等效方法 [J]. 防护工程, 2015, 37(6): 27–32.DENG Guoqiang, YANG Xiumin. Effect equivalent method between fluid penetration of hypervecloity weapon and shallow detonation of explosive [J]. Protective Engineering, 2015, 37(6): 27–32. [120] OBERBECK V R. Laboratory simulation of impact cratering with high explosives [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76: 5732–5749. doi: 10.1029/JB076i023p05732 [121] BALDWIN R B. The Measure of the Moon [M]. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1963. [122] HOLSAPPLE K A. The equivalent depth of burst for cratering [J]. Lunar and Planetary Science, 1980, 6: 2379–2401. [123] MELOSH H J. Planetary surface processed [M]. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2011. [124] 哈努卡耶夫. 矿岩爆破物理过程[M]. 刘殿中, 译. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1980. [125] 程怡豪. 超高速弹体撞击混凝土和岩石毁伤机理研究[D]. 南京: 解放军理工大学, 2016. [126] Fundamentals of protective design for conventional weapons: TM5-855-1 [R]. US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, Mississippi: 1986. -






 下载:
下载: