Experimental study on local damage effect of ultra-high performance concrete slabs under contact explosion
-
摘要: 为了研究超高性能混凝土(ultra-high performance concrete, UHPC)的抗接触爆炸性能,开展了C120、C150和C180等3种强度等级共24块UHPC临空板的接触爆炸实验,定量分析了不同药量时典型配筋与不配筋靶板的局部破坏特征,得到了UHPC的爆炸临界震塌系数、压缩系数和成坑系数。结果表明:相同药量下,UHPC板的正面破坏程度随材料强度的提升而减轻;强度越高,爆炸成坑系数和压缩系数越小,抗爆性能越好;配筋率较低时,钢筋对UHPC板正面爆坑尺寸及背面震塌破坏程度影响较小,但对板的整体变形起到了一定的减轻作用,能够减小板底的剩余挠度和裂缝宽度;C150靶板的爆炸临界震塌系数最小,不大于0.251 m/kg1/3,C120和C180靶板的爆炸临界震塌系数相近,不大于0.285 m/kg1/3。在设计、使用纤维含量较高的大尺寸UHPC构件时,应特别关注由纤维分布方向性引起的材料各向异性和结构力学性能的变化。Abstract: In order to study the contact explosion resistance of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC), 24 contact explosion experiments were conducted. The target slabs were cast in UHPC with or without reinforcement, and the compressive strength grades of the UHPCs were C120, C150 and C180. The slabs were laid on supporting ring beams and the back faces of the slabs were free. The TNT was placed on the center of the front face. The size of the target slab was 1.5 m×1.5 m×0.3 m, and the main reinforcements were
$\varnothing $ 12 HRB400 with 200 mm×200 mm grid distance. Based on the experiments, the local failure characteristics of typical reinforced and unreinforced target slabs under the shock of different explosive weights were quantitatively analyzed, and the critical collapse coefficient, compression coefficient and explosion crater coefficient of the UHPC slabs were obtained. The results show that, at the same explosive weight, the damage degree of the UHPC slabs decreases with the compressive strength. The higher the compressive strength, the smaller the compression coefficient and the explosion crater coefficient. When the reinforcement ratio is low, it has little effect on the front crater size and the back collapse damage degree of the UHPC slab, but has a certain role in reducing the residual deflection and crack width at the bottom of the slab. For the UHPCs in this paper, the critical collapse coefficient of the C150 slap is the smallest, no more than 0.251 m/kg1/3; and the C120 slap and C180 slap are similar, no more than 0.285 m/kg1/3. The critical collapse coefficients of the C180 UHPC is not the smallest because there are more steel fibers in the horizontal direction than in the vertical direction. When designing or using large size UHPC structures with high fiber content, special attention should be paid to the material anisotropy and the changes in structural mechanical properties due to the directivity of the fiber distribution. -
表 1 UHPC板的参数
Table 1. Parameters of the UHPC slabs
材料 抗压强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 数量 C120 125.2 7.12 5 PC120 125.2 7.12 5 C150 157.7 8.18 5 PC150 157.7 8.18 5 C180 182.8 9.34 4 表 2 试件的破坏状况
Table 2. Damage states of the slabs
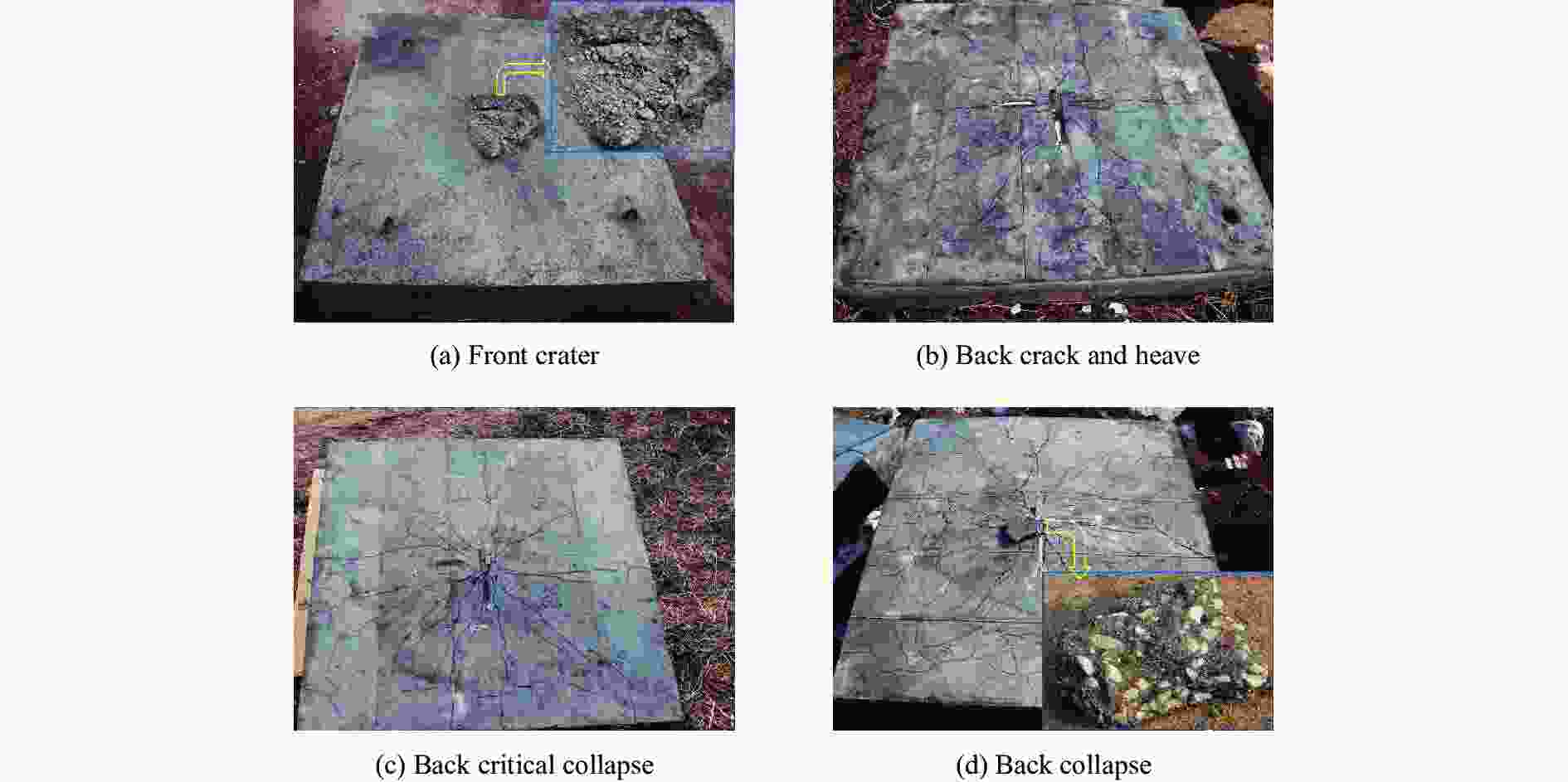
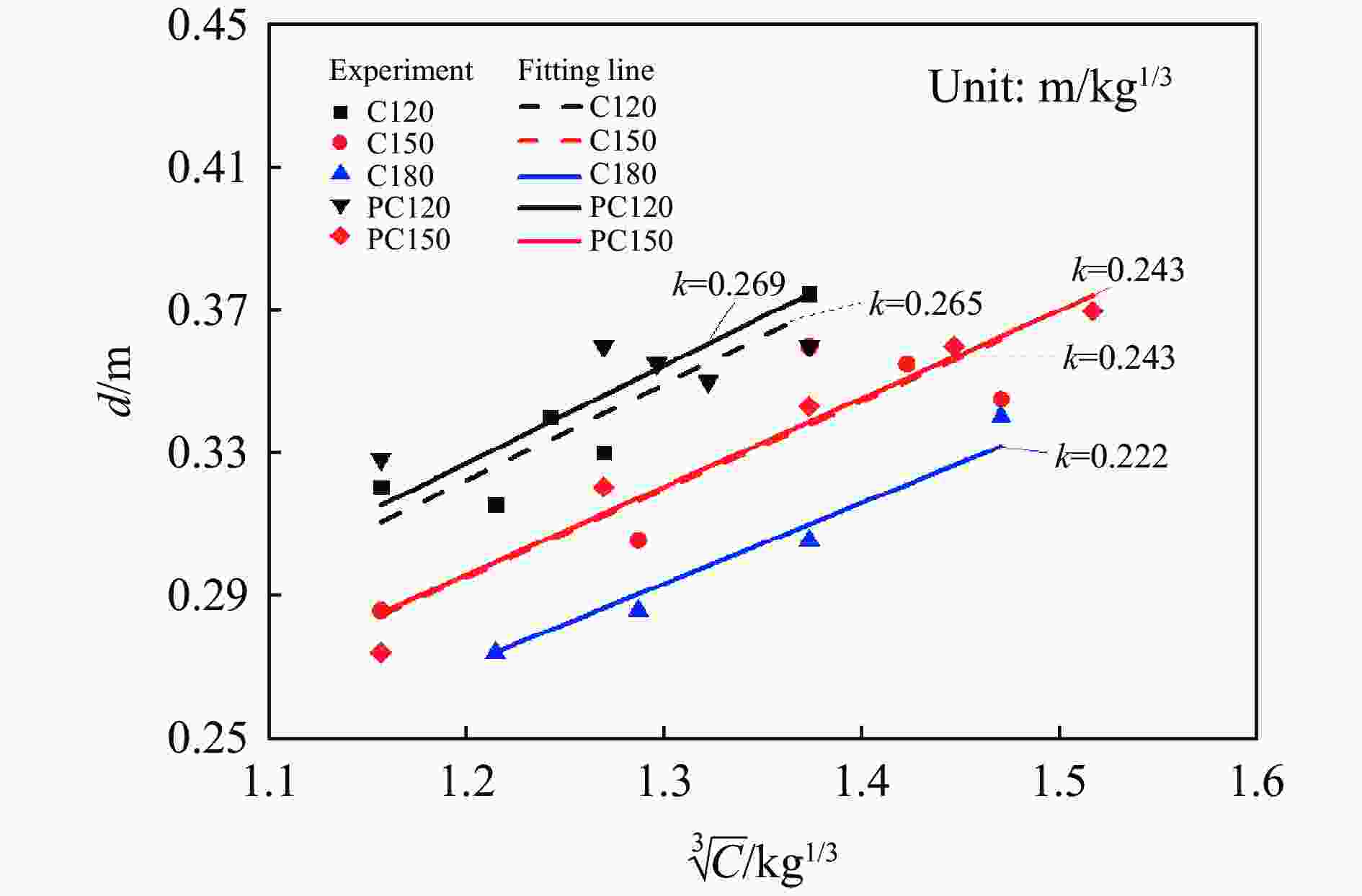
试件 药量/kg 正面 背面 直径/m 深度/m 剩余挠度/mm 震塌坑尺寸/mm 裂缝分布 C120-1 1.6 0.320 0.088 16 — 12条,最宽3.5 mm C120-2 1.8 0.315 0.092 28 — 14条,最宽9.9 mm C120-3 1.9 0.340 0.094 — 90×140深15 14条 C120-4 2.0 0.330 0.095 — 350×250深60 17条 C120-5 2.4 0.375 0.099 — 620×780深105 18条 PC120-1 1.6 0.328 0.092 10 — 11条,最宽1.9 mm PC120-2 2.0 0.360 0.098 28 — 13条,最宽2.4 mm PC120-3 2.1 0.355 0.100 — 40×50深30 15条 PC120-4 2.2 0.350 0.099 — 70×105深35 16条 PC120-5 2.4 0.360 0.102 — 100×200深60 16条 C150-1 1.6 0.285 0.076 8 — 6条,最宽2.0 mm C150-2 2.0 0.305 0.080 30 — 11条,最宽3.6 mm C150-3 2.4 0.360 0.084 49 — 13条,最宽7.5 mm C150-4 2.6 0.355 0.088 — 380×630深70 13条 C150-5 2.8 0.345 0.092 — 690×900深130 15条 PC150-1 1.6 0.273 0.079 9 — 8条,最宽2.0 mm PC150-2 2.0 0.320 0.080 15 — 11条,最宽2.2 mm PC150-3 2.4 0.343 0.083 22 — 14条,最宽3.8 mm PC150-4 2.7 0.360 0.088 — 230×470深55 14条 PC150-5 3.0 0.370 0.092 — 370×460深65 14条 C180-1 1.8 0.273 0.070 22 — 10条,最宽3.54 mm C180-2 2.0 0.285 0.075 — 150×145深50 12条 C180-3 2.4 0.305 0.078 — 650×735深95 13条 C180-4 2.8 0.340 0.086 — 705×895深110 15条 表 3 靶板正面的爆坑参数
Table 3. The front face anti-explosion parameters of the slabs
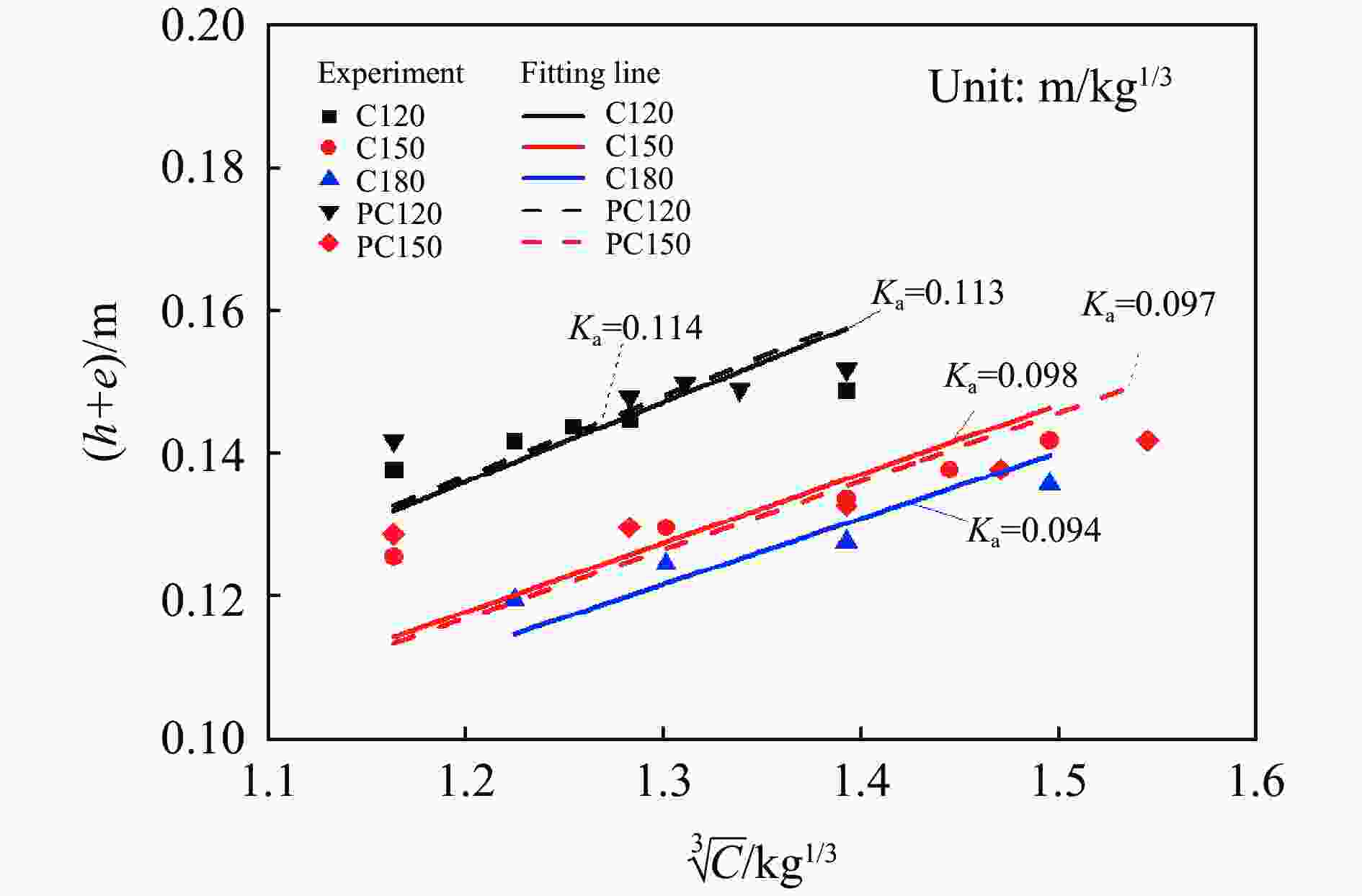
表 4 UHPC靶板的临界震塌系数
Table 4. Critical collapse factors of the UHPC slabs
材料 Kz0/(m·kg−1/3) C120 0.278~0.285 PC120 0.267~0.272 C150 0.243~0.251 PC150 0.238~0.251 C180 0.272~0.285 -
[1] DE LARRARD F, SEDRAN T. Optimization of ultra-high-performance concrete by the use of a packing model [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 1994, 24(6): 997–1009. DOI: 10.1016/0008-8846(94)90022-1. [2] SOBUZ H R, VISINTIN P, MOHAMED ALI M S, et al. Manufacturing ultra-high performance concrete utilising conventional materials and production methods [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 111: 251–261. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.02.102. [3] YANG S L, MILLARD S G, SOUTSOS M N, et al. Influence of aggregate and curing regime on the mechanical properties of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete (UHPFRC) [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2009, 23(6): 2291–2298. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.11.012. [4] CAMILETTI J, SOLIMAN A M, NEHDI M L. Effects of nano- and micro-limestone addition on early-age properties of ultra-high-performance concrete [J]. Materials and Structures, 2013, 46(6): 881–898. DOI: 10.1617/s11527-012-9940-0. [5] WANG D H, SHI C J, WU Z M, et al. A review on ultra high performance concrete: part Ⅱ. hydration, microstructure and properties [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 96: 368–377. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.095. [6] SHI C J, WANG D H, WU L M, et al. The hydration and microstructure of ultra high-strength concrete with cement-silica fume-slag binder [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2015, 61: 44–52. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2015.04.013. [7] WILLE K, NAAMAN A E, EL-TAWIL S, et al. Ultra-high performance concrete and fiber reinforced concrete: achieving strength and ductility without heat curing [J]. Materials and Structures, 2012, 45(3): 309–324. DOI: 10.1617/s11527-011-9767-0. [8] YAZICI H, YARDIMCI M Y, AYDIN S, et al. Mechanical properties of reactive powder concrete containing mineral admixtures under different curing regimes [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2009, 23(3): 1223–1231. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2008.08.003. [9] ABBAS S, SOLIMAN A M, NEHDI M L. Exploring mechanical and durability properties of ultra-high performance concrete incorporating various steel fiber lengths and dosages [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 75: 429–441. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.11.017. [10] KHOSRAVANI M R, WAGNER P, FRÖHLICH D, et al. Dynamic fracture investigations of ultra-high performance concrete by spalling tests [J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 201: 109844. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109844. [11] GUO Y B, GAO G F, JING L, et al. Quasi-static and dynamic splitting of high-strength concretes-tensile stress-strain response and effects of strain rate [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 125: 188–211. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.11.012. [12] 戎志丹, 孙伟. 粗集料对超高性能水泥基材料动态力学性能的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2009, 29(4): 361–366. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)04-0361-06.RONG Z D, SUN W. Influences of coarse aggregate on dynamic mechanical behaviors of ultrahigh-performance cementitious composites [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2009, 29(4): 361–366. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)04-0361-06. [13] 张想柏, 杨秀敏, 陈肇元, 等. 接触爆炸钢筋混凝土板的震塌效应 [J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 46(6): 765–768. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2006.06.004.ZHANG X B, YANG X M, CHEN Z Y, et al. Explosion spalling of reinforced concrete slabs with contact detonations [J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2006, 46(6): 765–768. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2006.06.004. [14] 王明洋, 张胜民, 国胜兵. 接触爆炸作用下钢板钢纤维混凝土遮弹层设计方法(Ⅰ) [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2002, 22(1): 40–45.WANG M Y, ZHANG S M, GUO S B. Design method of steel and steel-fiber concrete shelter plate under contact detonation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2002, 22(1): 40–45. [15] 胡金生, 杨秀敏, 周早生, 等. 接触爆炸对底部有土垫层纤维混凝土板破坏效应试验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2005, 25(2): 157–162. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2005)02-0157-06.HU J S, YANG X M, ZHOU Z S, et al. Experimental investigation on contact explosion damage effect to fiber reinforced concrete slab with soil bedding [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2005, 25(2): 157–162. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2005)02-0157-06. [16] 岳松林, 王明洋, 张宁, 等. 混凝土板在接触爆炸作用下的震塌和贯穿临界厚度计算方法 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2016, 36(4): 472–482. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0472-11.YUE S L, WANG M Y, ZHANG N, et al. A method for calculating critical spalling and perforating thicknesses of concrete slabs subjected to contact explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2016, 36(4): 472–482. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0472-11. [17] LI J, WU C Q, HAO H, et al. Experimental investigation of ultra-high performance concrete slabs under contact explosions [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 93: 62–75. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.02.007. [18] 葛涛, 潘越峰, 谭可可, 等. 活性粉末混凝土抗冲击性能研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(S1): 3553–3557. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.z1.148.GE T, PAN Y F, TAN K K, et al. Study on resistance of reactive powder concrete to impact [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(S1): 3553–3557. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.z1.148. [19] 戎志丹, 孙伟, 张云升, 等. 超高性能钢纤维混凝土抗二次接触爆炸性能研究 [J]. 华北水利水电大学学报, 2012, 33(6): 1–4. DOI: 10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2012.06.001.RONG Z D, SUN W, ZHANG Y S, et al. Study on the characteristics of ultra-high performance steel fiber reinforced concrete under the second explosion [J]. Journal of North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power, 2012, 33(6): 1–4. DOI: 10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2012.06.001. [20] WU H, HU F, FANG Q, et al. A comparative study for the impact performance of shaped charge JET on UHPC targets [J]. Defence Technology, 2019, 15(4): 506–518. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2019.04.005. [21] 王年桥. 防护结构计算原理与设计 [M]. 2版. 南京: 解放军理工大学工程兵工程学院, 2002. [22] 张云升, 张文华, 刘建忠. 超高性能水泥基复合材料 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. [23] 郑全平, 牛小玲, 汪剑辉, 等. 不同钢纤维掺量C30 RC板爆炸震塌试验研究 [J]. 防护工程, 2013, 35(1): 16–20.ZHENG Q P, NIU X L, WANG J H, et al. Experimental investigation into explosion spalling of C30 RC plates with different steel fiber content [J]. Protective Engineering, 2013, 35(1): 16–20. [24] 郑全平, 钱七虎, 周早生, 等. 钢筋混凝土震塌厚度计算公式对比研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2003, 20(3): 47–53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2003.03.009.ZHENG Q P, QIAN Q H, ZHOU Z S, et al. Comparative analysis of scabbing thickness estimation of reinforced concrete structures [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2003, 20(3): 47–53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2003.03.009. -








 下载:
下载: