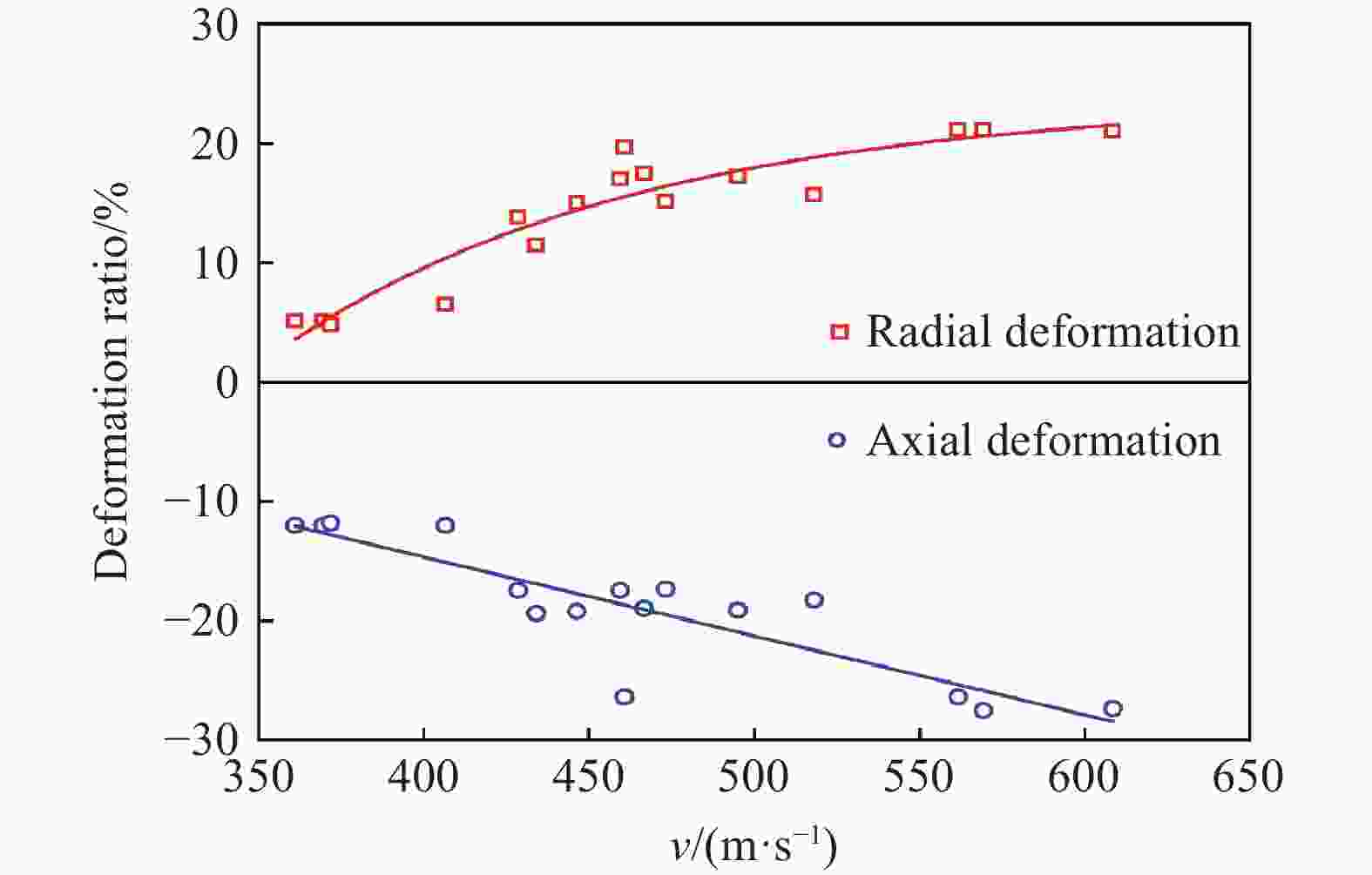
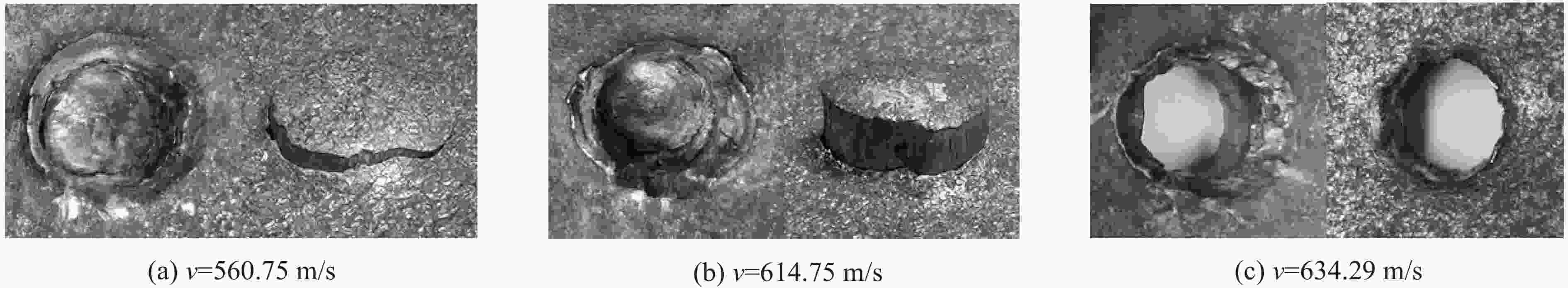
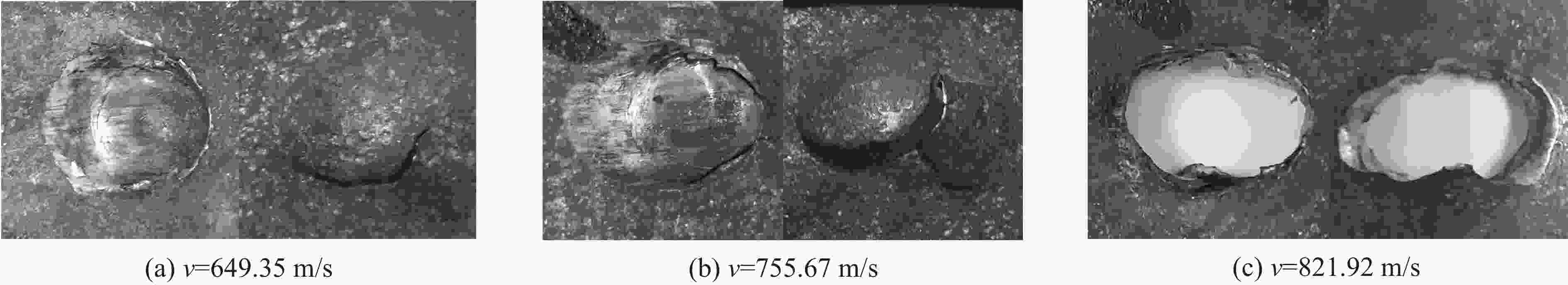
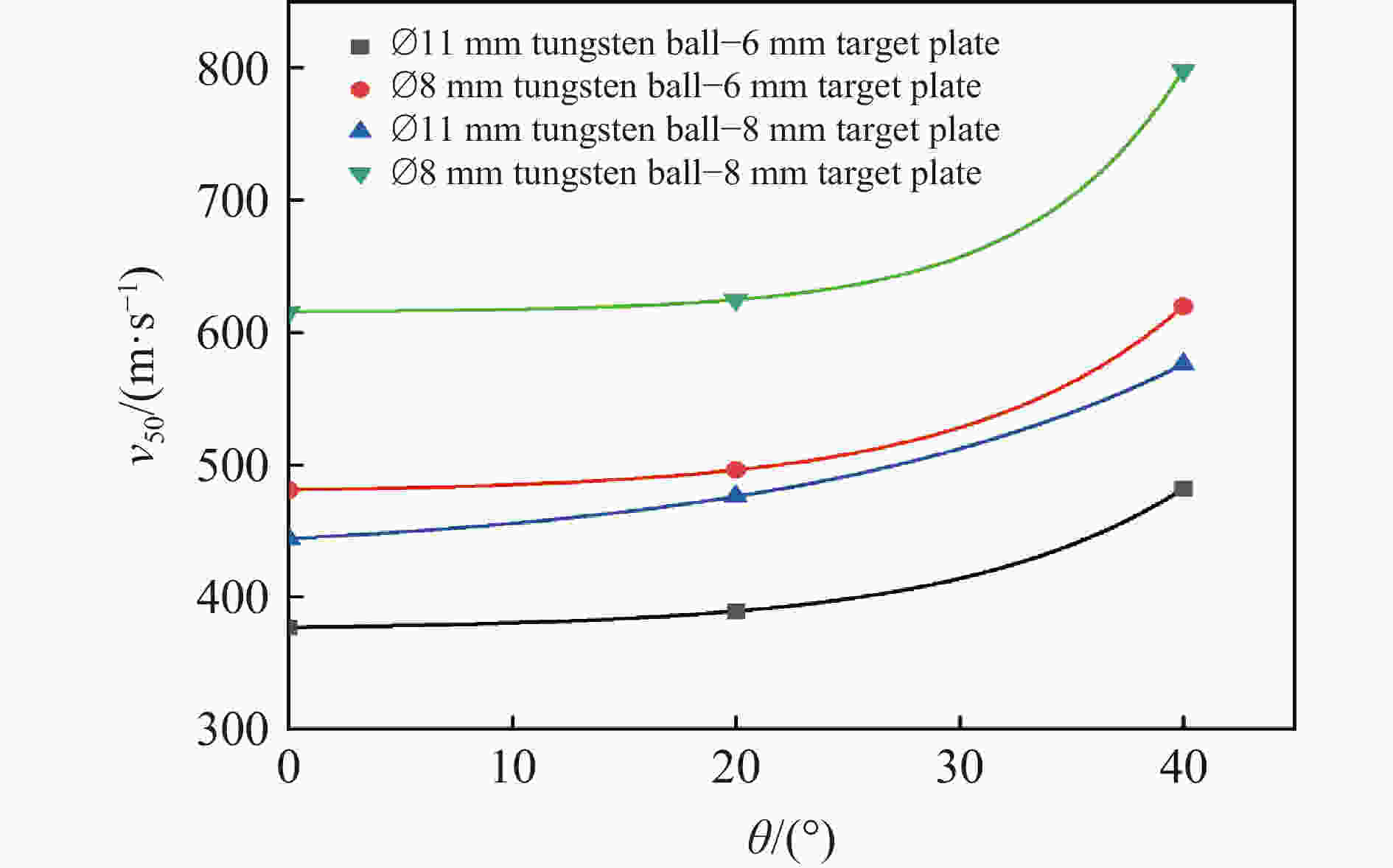
Oblique penetration effect of a tungsten ball on high hardness steel
-
摘要: 为研究高硬度钢板抗不同着角钨球的侵彻性能及破坏模式,通过弹道枪进行了
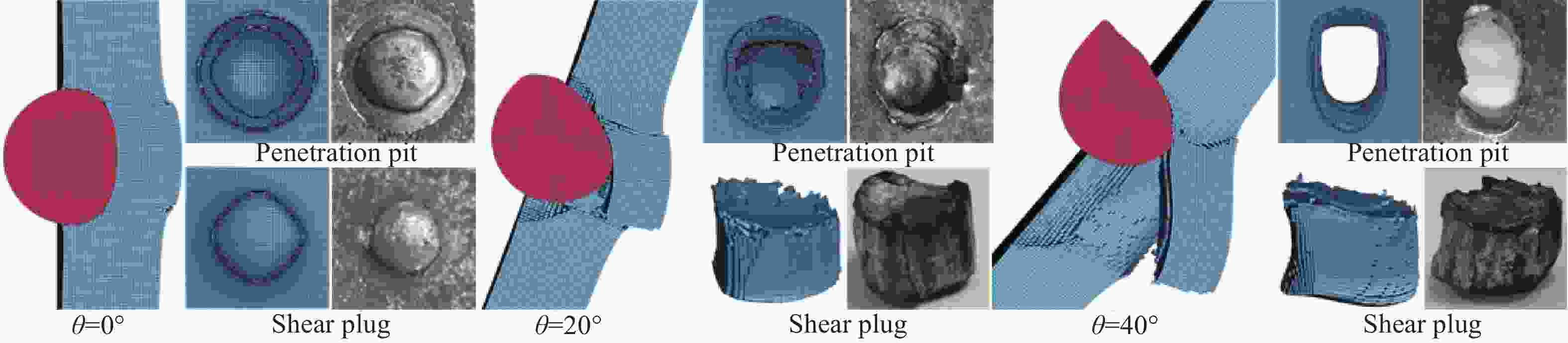
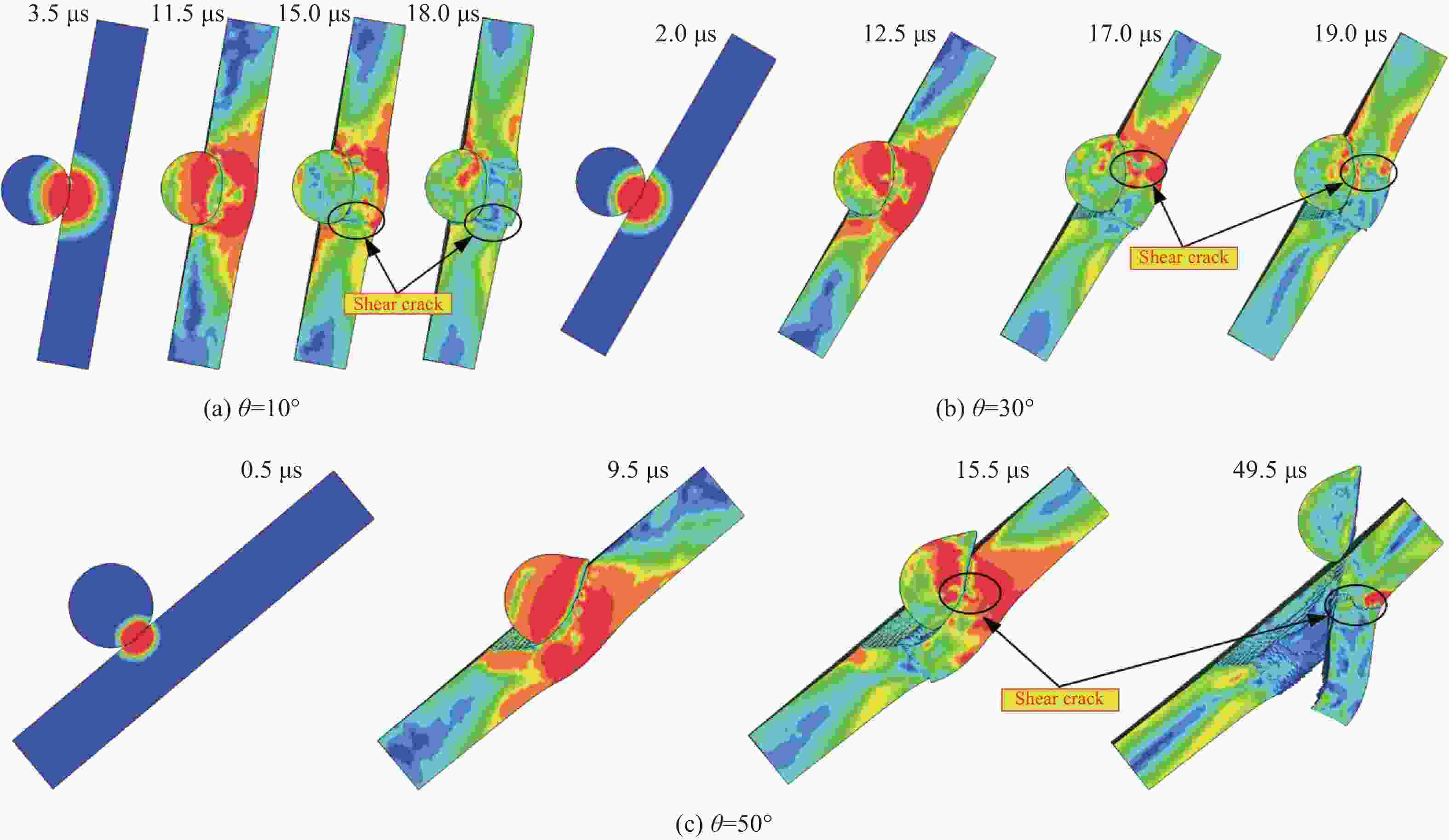
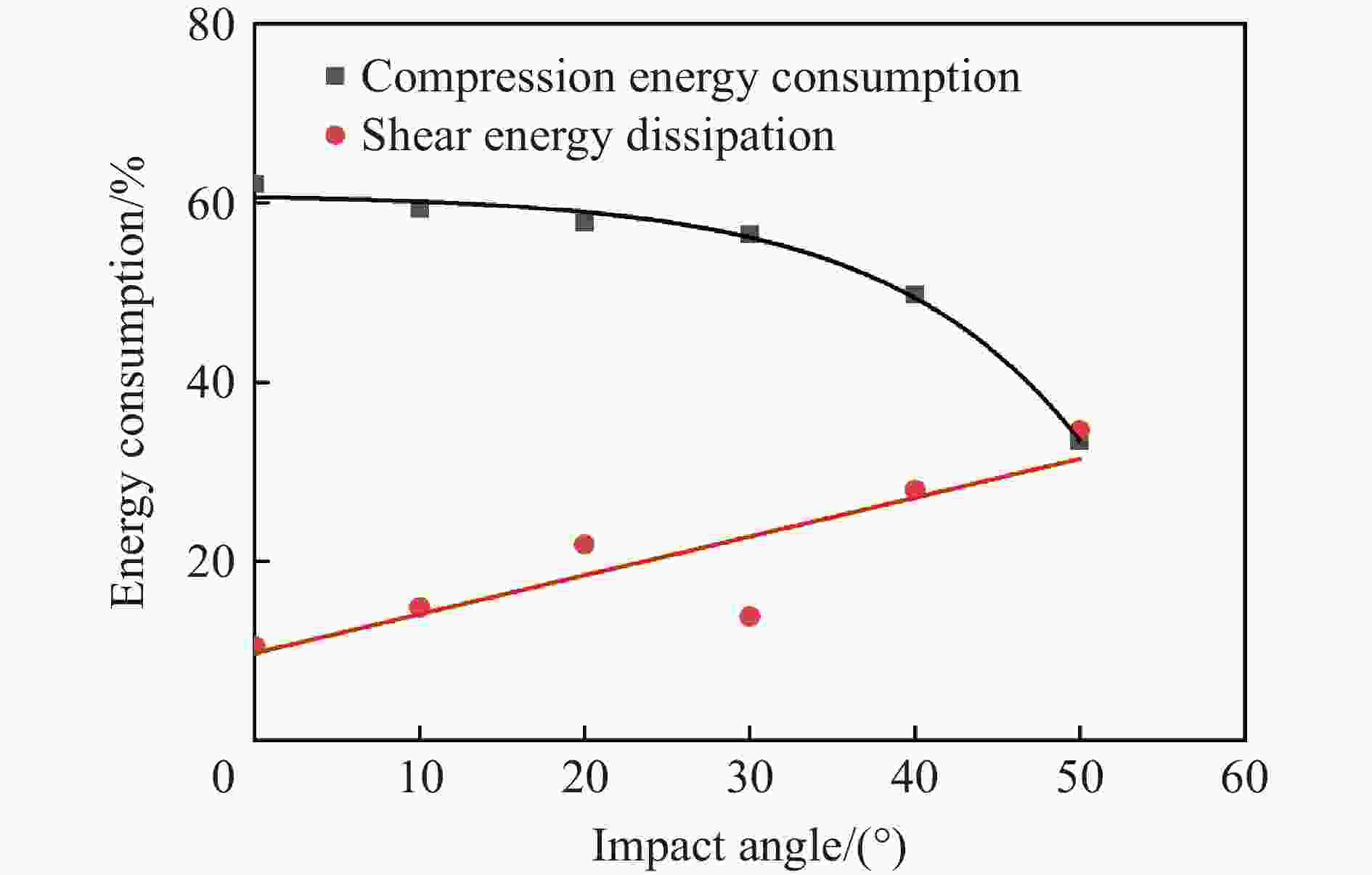
$ \varnothing $ 8 mm、$ \varnothing $ 11 mm钨合金球形破片以0°、20°、40°着角撞击厚度为6 mm、8 mm的高硬度钢板试验,得到了极限贯穿速度v50;分析了钨球轴向径向变形及靶板失效模式与撞击速度的关系,发现高硬度钢板失效模式主要为压缩开坑破坏和沿厚度方向剪切破坏。采用有限元方法对试验进行了模拟,验证了数值模型及参数的合理性,并运用数值模拟方法研究了撞击着角对靶板吸能模式影响,结合试验数据,修正已有极限贯穿速度计算公式。结果表明:随侵彻着角增大,极限贯穿速度提高,且着角越大,极限贯穿速度增长越快;随着角增大,靶板吸能模式逐渐由压缩开坑向剪切冲塞过渡,且着角大于50°时,剪切冲塞耗能将超过压缩开坑耗能;修正后极限贯穿速度计算公式适用范围更广、精度更高,具有较好工程应用价值。Abstract: In order to study the penetration performance and failure modes of high-hardness steel plates against tungsten balls with different angles, a ballistic gun was used to carry out$ \varnothing $ 8 mm,$ \varnothing $ 11 mm tungsten alloy spherical fragments at 0°, 20°, 40° angles to impact the thickness of 6 mm, 8 mm. In the hardness steel plate test, the limit penetration velocity (v50) of the fragments impacting the steel plate was obtained; the relationships between the axial and radial deformation of the tungsten ball after the impact and the failure mode of the target plate and the impact velocity were analyzed. It is found that the failure mode of the high hardness steel plate is mainly the compression opening. For the pit failure and shear failure along the thickness direction, the shear fracture increases as the angle increases. The experiment was simulated by the method of finite element simulation. The simulation results were compared with the test results. The damage morphology of the target plate and the limit penetration velocity were in good agreement. The validity of the numerical simulation model and parameters was verified, and the numerical simulation method was used. The influence of the impact angle on the energy absorption mode of the target plate was studied, and the existing calculation formula of the limit penetration velocity was revised based on the experimental data. The results show that as the penetration angle increases, the limit penetration velocity increases, and the larger the penetration angle, the faster the limit penetration velocity increases; the revised limit penetration velocity calculation formula has a wider application range and higher accuracy, and has better engineering applications. As the angle increases, the energy absorption mode of the target plate gradually changes from compression opening to shearing plugging, and when the angle exceeds 50°, the energy consumption of shearing plugging will exceed the energy consumption of compression opening. -
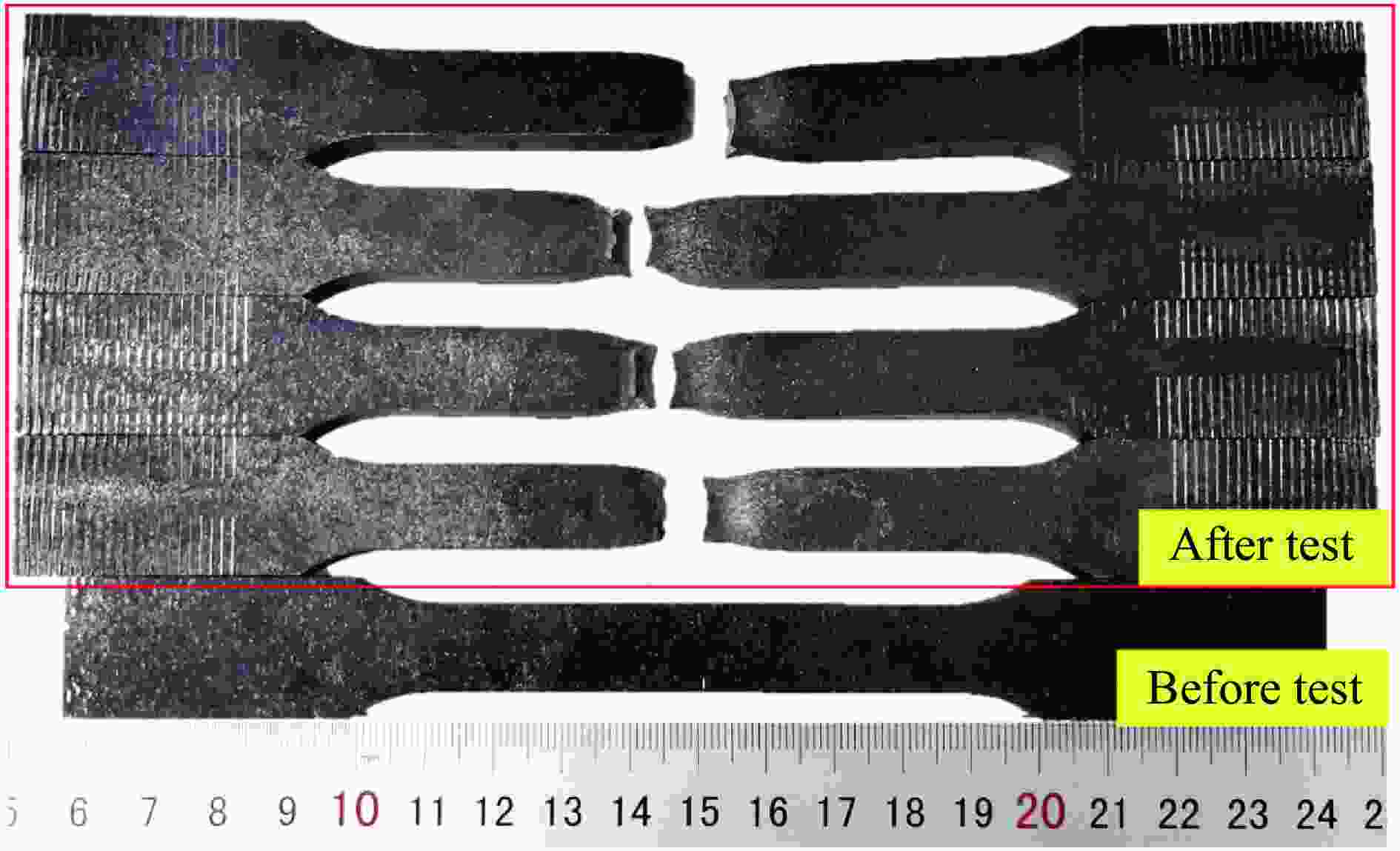
表 1 试验用93W4Ni3Fe合金破片材料基本力学性能
Table 1. Basic mechanical properties of missile target materials for test
材料 ρ/(g·cm−3) E/GPa σy/MPa σs/MPa δ/% HRC 93W4Ni3Fe 17.7 365 731 955 19~22 29 表 2 试验用22SiMn2TiB靶板材料基本力学性能
Table 2. Basic mechanical properties of 22SiMn2TiB target material for test
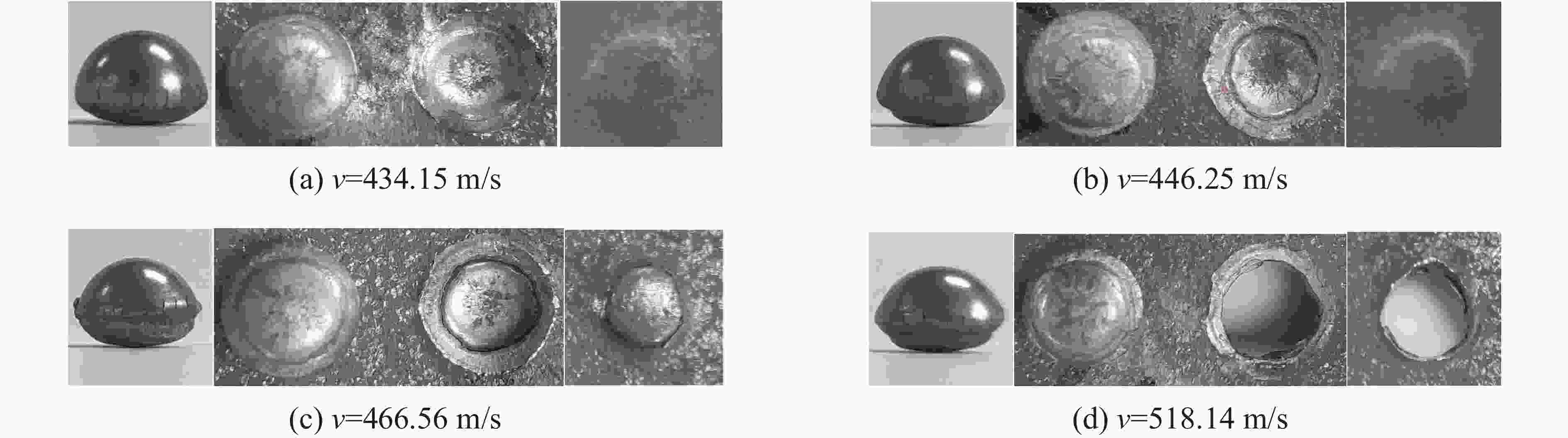
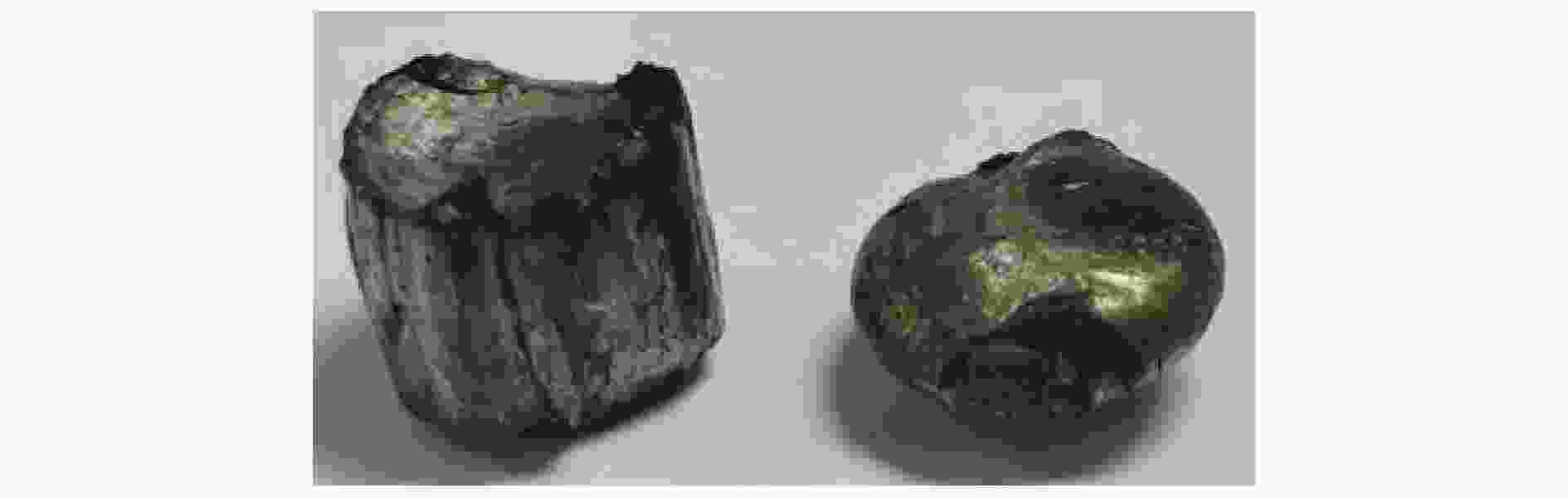
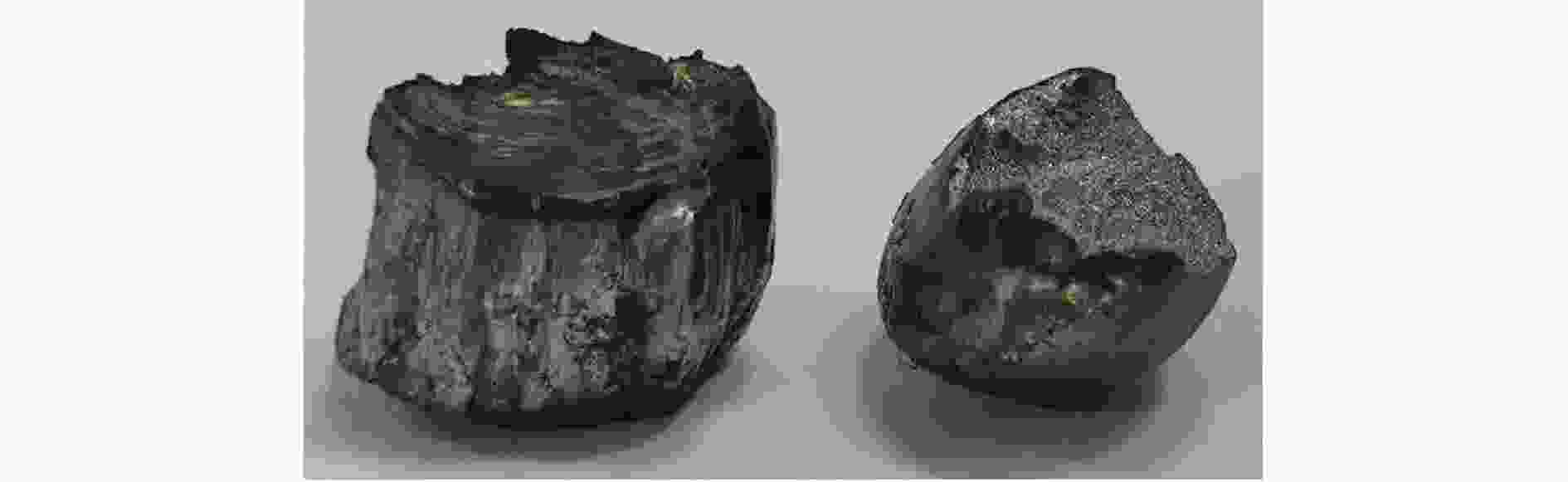
材料 h/mm 试验编号 ρ/( g·cm−3) E/GPa σy/MPa σs/MPa δ/% HRC 22SiMn2TiB 6 Test 1 7.781 197.203 1083.0 1516.5 12.60 46.8 Test 2 197.342 1068.5 1516.9 12.64 46.4 Test 3 196.983 1081.6 1514.3 12.16 46.5 Test 4 186.685 1080.4 1508.8 12.92 46.4 8 Test 1 7.785 186.746 1110.2 1569.9 14.40 46.2 Test 2 188.351 1080.5 1563.1 14.52 46.2 Test 3 192.603 1113.7 1574.1 15.92 46.0 Test 4 190.662 1072.4 1563.3 14.84 46.8 平均 7.783 192.070 1086.3 1540.9 13.75 46.4 表 3 钨球撞击22SiMn2TiB钢板的极限贯穿速度
Table 3. Expermental results of tungsten balls impacting 22SiMn2TiB steel plates
h/mm d/mm θ/(°) v/(m·s−1) 是否穿透 v50/( m·s−1) h/mm d/mm θ/(°) v/(m·s-1) 是否穿透 v50/( m·s-1) 6.23 8.00 0 434.15 否 480.80 8.27 0 460.83 否 615.47 566.04 是 561.80 否 518.13 是 569.26 否 466.56 否 608.52 否 495.05 是 622.41 是 20 574.71 是 485.85 607.45 是 483.09 否 8 20 728.16 是 624.52 488.60 是 702.58 是 40 468.02 否 619.68 692.84 是 636.94 是 614.75 否 602.41 否 560.75 否 6.23 11.06 0 361.01 否 376.91 563.27 否 371.75 否 634.29 是 369.46 否 40 649.35 否 798.02 406.50 是 755.67 否 20 427.96 是 389.13 821.92 是 355.03 否 808.63 是 404.31 是 740.74 否 363.2 否 787.40 否 390.63 是 8.27 11.06 0 459.49 是 444.00 40 574.71 是 481.74 428.57 否 460.12 否 473.19 是 503.36 是 20 549.45 是 475.87 452.49 否 461.54 否 510.20 是 490.20 是 40 606.06 是 575.6 561.80 否 589.39 是 表 4 弹靶材料Johnson-Cook模型参数
Table 4. Johnson-Cook model parameters of 22SiMn2TiB steel and 93W4Ni3Fe
材料 ρ/(g·cm−3) G/GPa A/GPa B/GPa C M n 22SiMn2TiB 7.78 81.8 1.086 0.51 0.014 1.03 0.26 93W4Ni3Fe 17.7 160 0.731 1.67 0.03 0.82 0.91 材料 c/(m·s−1) S1 S2 S3 γ0 A 22SiMn2TiB 4600 1.730 0 0 1.67 0.46 93W4Ni3Fe 4046 1.268 0 0 1.58 0.46 表 6 撞击靶板贯穿极限速度的数值模拟与试验值对比
Table 6. Comparison of ultimate penetration velocity between simulation and test
θ/(°) 钨球初速/(m·s−1) 是否穿透 v50/(m·s−1) 数值模拟 试验 相对误差/% 0 480 是 475 480.8 1.14 470 否 20 490 是 485 485.8 0.16 480 否 40 625 是 619.5 619.6 0.02 614 否 表 7 钨球撞击靶板过程能量变化
Table 7. Energy change during tungsten ball impacting target plate
θ/(°) E0/kJ E1/kJ E2/kJ (ΔE1-0/E0)/% (ΔE2-1/E0)/% 0 2.72 1.03 0.74 62.13 10.51 10 2.78 1.13 0.72 59.35 14.86 20 2.84 1.20 0.58 57.75 21.83 30 3.54 1.54 1.05 56.50 13.84 40 4.62 2.32 1.03 49.78 27.92 50 6.39 4.26 2.05 33.33 34.59 表 8 撞击靶板贯穿极限速度的试验与理论值对比
Table 8. Comparison of ultimate penetration velocity between experimental and theoretical value
钨球直径/mm 靶板厚度/mm 着角/(°) v50/(m·s−1) 误差/% 试验 理论 8.00 6.23 20 485.85 474.03 −3.69 11.06 8.27 40 575.60 592.01 2.85 6.84 6.75 0 610.00 604.94 −0.83 8.12 6.75 0 520.30 513.08 −1.39 表 9 撞击靶板贯穿极限速度的计算值与理论值对比
Table 9. Comparison of ultimate penetration velocity between numberical and theoretical value
钨球直径/mm 靶板厚度/mm 着角/(°) v50/(m·s−1) 误差/% 计算 理论 8.00 4.00 0 309.50 309.89 0.12 8.00 3.00 0 195.00 235.11 20.57 8.00 2.00 0 193.00 159.30 17.46 8.00 6.00 10 480.00 464.26 −3.28 8.00 6.00 30 542.00 526.51 −2.86 8.00 6.00 50 730.00 704.89 −3.44 -
[1] AWERBUCH J, BODNER S R . Analysis of the mechanics of perforation of projectiles in metallic plates [J]. International Journal of Solids & Structures, 1974, 10(6): 671–684. [2] 陈志斌, 刘志刚. 球形弹垂直碰撞金属靶板的实验研究 [J]. 弹道学报, 1991, 7(1): 66–70.CHEN Z B, LIU Z G. Experimental investigation on the mental target by normal impact of spherical shell [J]. Journal of Ballistics, 1991, 7(1): 66–70. [3] 任杰, 徐豫新, 王树山. 超高强度平头圆柱形弹体对低碳合金钢板的高速撞击实验 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(4): 629–636. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0629-08.REN J, XU Y X, WANG S S. High-speed impact of low-carbon alloy steel plates by ultra-high strength blunt projectiles [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(4): 629–636. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)04-0629-08. [4] 陈材, 石全, 尤志锋, 等. 预制破片侵彻靶板临界跳飞角变化规律 [J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2021, 46(5): 29–34. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.05.006.CHEN C, SHI Q, YOU Z F, et al. Change law of critical ricochet angle of prefabricated fragment penetrating target plate [J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2021, 46(5): 29–34. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2021.05.006. [5] 姚熊亮, 王治, 叶墡君, 等. 球头弹体侵彻舰船板架加强筋时的攻角变化简化理论模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(3): 033301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0092.YAO X L, WANG Z, YE S J, et al. A simplified theoretical model for attack angle change of a hemispherically-nosed projectile while penetrating the stiffener of a ship plate frame [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(3): 033301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0092. [6] 午新民. 钨合金球体对有限厚靶板侵彻的理论与试验研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 1999. [7] 胡邓平, 赵利平, 伍先明, 等. 616装甲防弹钢动态冲击下的性能研究 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2017, 40(2): 96–99. DOI: 10.19822/j.cnki.1671-6329.20210032.HU D P, ZHAO L P, WU X M, et al. Study on the performance of 616 armored ballistic steel under dynamic impact [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2017, 40(2): 96–99. DOI: 10.19822/j.cnki.1671-6329.20210032. [8] XU Y X, HAN X G, ZHAO X X, et al. Experimentation research on failure behavior of tungsten alloy penetrating low carbon steel plate at high velocity [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(1): 122–126. [9] 赵荣贵, 陈林恒, 左秀荣. 超高强度装甲钢抗弹失效机理研究 [J]. 宽厚板, 2020, 26(5): 11–14. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7864.2020.05.003.ZHAO R G, CHEN L H, ZUO X R. Research on the ballistic failure mechanism of ultra-high strength armored steel [J]. Wide and Heavy Plate, 2020, 26(5): 11–14. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7864.2020.05.003. [10] 程瑶, 赵太勇, 陈智刚, 等. 低中速钨球变形与速度关系计算模型 [J]. 爆破器材, 2019, 48(5): 52–56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2019.05.010.CHENG Y, ZHAO T Y, CHEN Z G, et al. Calculation model of the relationship between deformation and velocity of low and medium speed tungsten ball [J]. Explosive Materials, 2019, 48(5): 52–56. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2019.05.010. [11] 曹柏桢, 凌玉崑, 蒋浩征, 等. 飞航导弹战斗部与引信[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 1995: 140-141. [12] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain-rates and high temperatures [C]// Proceeding of the Seventh International Symposium on Ballistics. Hague, Netherlands, 1983: 541−547. [13] 刘铁, 史洪刚, 程新, 等. 钨合金帽型试样的绝热剪切带数值模拟研究 [J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2008(2): 75–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2008.02.020.LIU T, SHI H G, CHENG X, et al. Numerical simulations for adiabatic shear bands of WHA in hat specimen [J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2008(2): 75–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2008.02.020. -









 下载:
下载: