GPa-level slow-front ramp wave loading technology driven by non-shock initiation reaction
-
摘要: 为研究在吉帕、十微秒级缓前沿斜波作用下压装PBX炸药基体中微介观热点点火行为,设计了一种强约束压装PBX炸药非冲击点火反应驱动的斜波加载装置,基于炸药层流燃烧的燃速模型和自编的二维轴对称有限差分程序对装置输出的压力波形特性进行了分析,讨论了燃烧过程中加载炸药破碎程度和装置结构参数(壳体和隔层厚度)对输出波形的影响。计算结果表明,加载炸药破碎形成的燃烧比表面积大小是影响非冲击点火反应压力演化的关键因素,燃烧比表面积越大,输出的斜波压力越大,峰值压力可达吉帕以上,对应的压力上升前沿可从数十微秒降至数微秒。加载炸药外部壳体厚度即约束强度对非冲击点火反应产生的压力大小影响显著,壳体越厚输出的斜波压力越大。加载炸药与受试炸药之间的隔层厚度直接关系到输出至受试炸药处的斜波压力大小,随着隔层厚度的增大,输出的斜波压力以近似指数的关系衰减。参考计算结果完成了装置的结构设计,对受试PBX炸药进行了斜波加载实验,采用PVDF测得受试炸药入射界面处的压力为1.6 GPa、前沿宽度为25 μs,初步证明了采用强约束压装PBX炸药非冲击点火反应实现吉帕、十微秒级斜波压力输出的可行性。Abstract: To study the ignition behavior of micro-mesoscopic hot spots in the matrix of pressed PBXs under GPa and 10 μs-level slow-front ramp wave loading, a ramp wave loading device driven by non-shock initiation reaction of pressed PBX with heavy constraint was designed. With the help of the output pressure from the explosion reaction of the donor explosive, the acceptor explosive was loaded by a ramp wave. A two-dimensional axisymmetric finite difference program was developed based on the burn rate equation of laminar combustion on the explosive surface to guide the structural design of the device. The pressure history during the combustion process of the explosive crack surface formed by the explosive fragmentation in the late stage of the non-shock initiation reaction of the donor explosive in the device configuration and the pressure waveform acting on the acceptor explosive are analyzed. And the influence of crushing degree of donor explosive and device structure parameters (thickness of case and interlayer) on output pressure waveform during the combustion process is discussed. The calculation results show that the specific combustion surface area formed by the crushing of the donor explosive is the key factor affecting the pressure evolution of the non-shock initiation reaction. The larger the specific combustion surface area, the greater the ramp wave pressure is. The ramp wave pressure can reach above GPa, and the corresponding rising front of the pressure wave can be reduced from tens of milliseconds to several milliseconds. The thickness of the case of the donor explosive, namely the constraint strength, has a significant effect on the pressure during the non-shock initiation reaction. As the thickness of the interlayer increases, the output ramp wave pressure decays approximately exponentially. The structural design of the device was completed according to the calculation results, and the ramp wave loading experiment was carried out on the tested PBX. The pressure at the incident interface of the tested explosive measured by PVDF is 1.6 GPa, and the front of the ramp wave is 25 μs, which preliminarily proved the feasibility of realizing GPa and 10 μs-level ramp wave pressure output by using the non-shock initiation reaction of heavily constrained pressed PBX explosives.
-
压装PBX炸药非冲击点火剧烈爆炸能否发展为爆轰是炸药安全性研究中关注的重点问题。非冲击点火反应[1]指意外事故条件刺激(如低速撞击、摩擦以及火烧等)下炸药局部位置能量沉积温升点火,以及点火后由热传导机制主导的发生在炸药表面以亚声速推进的燃烧过程。对于压装PBX炸药,非冲击点火反应过程通常涉及产物气体驱动裂纹传播和裂纹、结构缝隙表面的层流燃烧等复杂过程[2-5]。在强约束条件下,炸药表面裂纹扩展形成的大比表面积燃烧会导致压力急剧增长,对应的压力剖面通常为吉帕、十微秒级的斜波[6-7],外在表现为壳体快速膨胀破坏的剧烈爆炸现象。此类剧烈反应过程中,燃烧阵面前的炸药基体会受到吉帕级高幅值、宽前沿的压力脉冲作用,炸药基体中微介观热点反应能否被大规模激活(像典型冲击波载荷作用下那样发生SDT),答案并不清楚,是研究非冲击点火反应能否转爆轰即DDT的核心问题。
Salisbury等[8]和Winter等[9]为研究复杂加载条件下炸药的起爆特性,对EDC37进行了系列双冲击加载实验,发现相较于单次冲击加载,双冲击加载下转爆轰距离更长。Salisbury等[8]和Winter等[9]认为:较低幅值的预压缩波使炸药被压实,炸药基体中的孔洞大大减少,因此在预压缩区域更难以引发SDT,即存在“冲击钝化”效应。对于本文关注的非冲击点火剧烈爆炸中表现出的高幅值、缓前沿压力历程,燃烧表面相邻炸药基体在受到吉帕级压力脉冲前会经历毫秒级(包括毫秒级、100 MPa以下的压力缓慢增长和数十微秒历程的压力急剧增长)的低幅值压缩过程,其是否会产生类似的预压缩“钝化”效应甚至无法激活热点反应还没有系统的进行研究。Garcia等[10]测量了烤燃反应在临近炸药中产生的压力波,观测到相邻的PBX9501炸药在1.2 GPa、数十微秒前沿斜波压力作用下,随着应力波在炸药中传播,压力峰值快速降低,炸药四处飞散,Garcia等[10]认为此类宽前沿吉帕级载荷作用下受试PBX不会发生爆轰。目前有关此类高幅值、缓前沿斜波载荷下炸药准冲击起爆特性的实验研究较少,缺乏相应的实验数据,炸药基体中微介观热点点火行为与加载压力的前沿之间的关联机制并不清楚。
现有斜波加载技术如磁驱动准等熵加载和密度梯度飞片冲击加载,产生的斜波前沿宽度(亚微秒级)和压力幅值(10~100 GPa)不符合本文关注的非冲击点火剧烈爆炸表现出的微秒特征宽前沿斜波压力特征。受李涛等[7]臼炮实验装置的启发,本文设计一种强约束压装PBX炸药的非冲击点火反应驱动的吉帕级斜波加载装置,并借助该装置研究斜波载荷下受试炸药基体中微介观热点点火行为:采用炸药层流燃烧的燃速模型和自编的二维轴对称有限差分程序对装置输出的压力波形特性进行分析,讨论燃烧过程中加载炸药破碎程度、加载炸药外部壳体厚度以及加载炸药与受试炸药之间隔层厚度对输出压力波形的影响;并基于数值计算结果进行装置结构设计,通过实验对斜波加载装置的可行性进行验证。
1. 斜波加载装置的结构设计
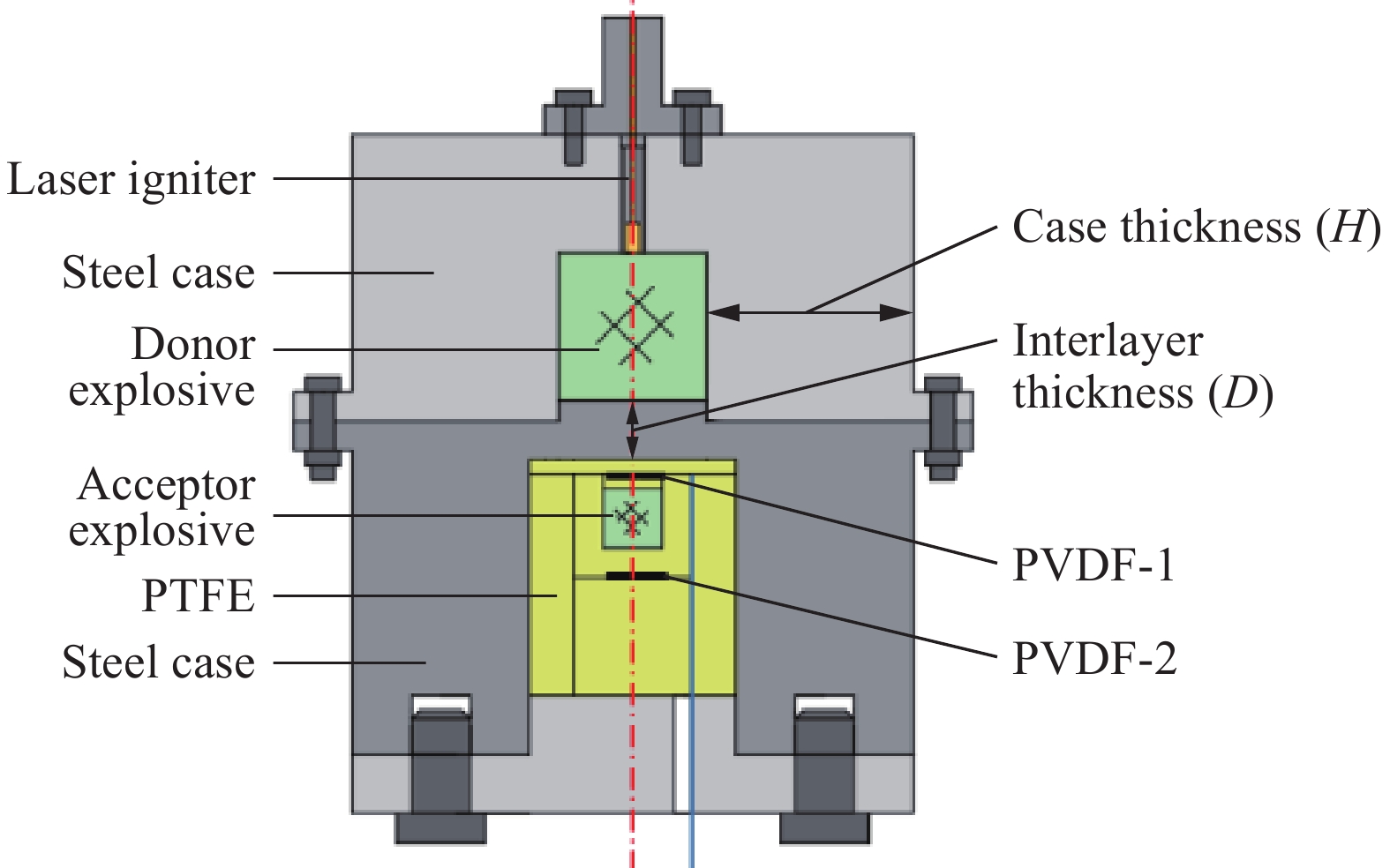
实验装置示意图如图1所示。装置为轴对称结构(除底端的引线槽),由两部分组成,包括上端的载荷发生器和下端的受试炸药容腔。实验中,通过装置上端的激光点火头引发加载炸药的非冲击点火燃烧反应,借助加载炸药非冲击点火进而剧烈爆炸产生的斜波压力实现对下端受试炸药的斜波加载。受试炸药用PTFE(聚四氟乙烯)内壳包裹以缓解容腔边界反射波的影响。其中,H为壳体厚度,D为加载炸药与受试炸药之间的隔层厚度。测试系统上,采用PVDF(聚偏二氟乙烯)压力传感器对受试炸药前后界面处的压力波形进行测量。同时,还设计了经雷管起爆借助加载炸药底端数毫米间隙调节加载压力幅值及前沿宽度的爆轰产物驱动的斜波加载装置作为对比设计[11]。
2. 斜波压力输出的数值计算分析
由于炸药的非冲击点火反应演化过程与约束强度相互关联,并且加载炸药反应产生的压力脉冲在作用于受试炸药前会在传播过程中发生衰减。因此在装置结构设计前,为分析作用于受试炸药的斜波压力载荷能否满足设计要求(吉帕、十微秒级特征),基于压装PBX炸药非冲击点火的炸药表面层流燃烧机制和层流燃烧的燃速模型,采用自编的二维轴对称有限差分程序对装置构型下非冲击点火反应输出的压力波形进行分析,重点讨论加载炸药的破碎程度、加载炸药外部壳体厚度H和加载炸药与受试炸药之间隔层厚度D对输出压力波形的影响。
根据壳体约束下压装PBX炸药非冲击点火反应演化机制,加载炸药非冲击点火后的反应演化过程需经历早期的缓慢层流燃烧过程(包括产物气体在裂纹和结构缝隙间的对流传播、燃烧产物驱动炸药裂纹扩展等)以及中后期破碎炸药大比表面积燃烧的压力剧烈增长过程。因反应早期过程复杂,燃烧压力通常不超过100 MPa[12-13],不会对装置结构产生明显影响,因此本文模拟仅计算反应中后期大比表面积裂纹表面燃烧时的压力演化历程。
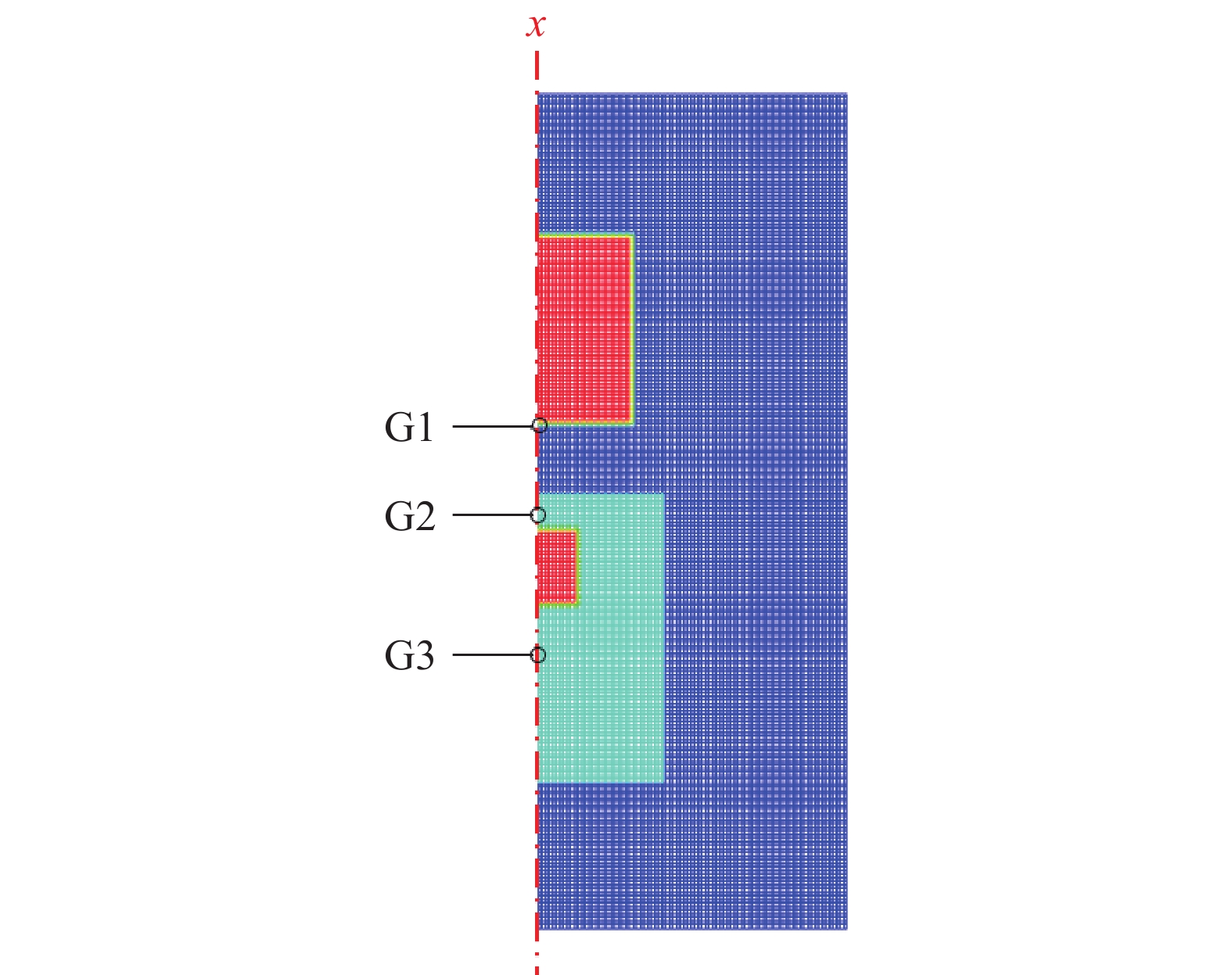
计算模型如图2所示,为便于计算处理,将加载炸药裂纹和结构缝隙表面的燃烧过程,以相对燃烧面积S/S0(其中,S为燃烧总面积,S0为炸药外表面的面积)的形式等效处理为炸药外表面的包覆燃烧过程。考虑到非冲击点火反应过程中吉帕级高幅值压力形成时间仅数十微秒,此时壳体尚未发生明显变形,加载炸药的燃烧产物不会经壳体连接处泄漏,因此计算中忽略了加载炸药外壳和受试炸药容腔之间的界面的滑移,将加载炸药外壳和受试炸药容腔作为一个整体进行计算。监测单元G1、G2、G3分别位于加载炸药燃烧容腔内以及受试炸药前、后界面处。采用由炸药表面层流燃烧的燃速压力关系确定的炸药燃耗量以及释放的燃烧热,来描述燃烧阵面处未反应炸药和燃烧产物之间的质量、能量交换:
re=apμ (1) 式中:re为层流燃烧速率,mm/s;a为燃烧速率常数,mm/(s·MPa);p为压力,MPa;
为压力指数。选取的炸药参数为a=2.16, =1.08[14]。 在燃烧阵面处,考虑到产物气体占据的空间小,且气体中压力传播速度远大于亚声速推进的层流燃烧速度,可近似认为产物气体中无压力梯度即产物气体处于压力平衡状态,且燃烧产物气体与相邻的炸药表面也处于压力平衡状态。在一个时间步长中,燃烧阵面处产物气体网格中质量m、体积V和内能E变化可描述为
mk+1−mk=ρedVr,Vk+1−Vk=dV+dVr,Ek+1−Ek=ρedV⋅Qc (2) 式中:下标k和k+1代表两个相邻的时刻;ρe为未反应炸药的密度;Qc为单位质量未反应炸药的燃烧热,取为 5.5 MJ/kg;dV为未反应炸药体积压缩产生的气体网格体积变化;dVr为一个时间步长中燃烧消耗的炸药体积
dVr=reΔt⋅Sc (3) 式中:Δt为计算时间步长,Sc为燃烧阵面处炸药网格的横截面积。
炸药和PTFE采用Mie-Grüneisen状态方程。产物气体采用Abel余容状态方程:
p=νρRT/[1−ρα(ρ)] (4) 式中:p为压力;
ν 为产物气体的物质的量;R为摩尔气体常数;ρ为产物气体的密度;T为温度;α为气体分子体积修正量,α(ρ)=e−0.4ρ 。结合式(2)和式(4),可确定产物气体的密度和压力,至此构成一个产物气体状态更新的计算循环。
壳体材料为45钢,采用Mie-Grüneisen状态方程和Johnson-Cook本构模型。由于计算结果仅关注输出的斜波压力波形及其在受试炸药中的传播衰减,计算中不考虑对受试炸药发生反应的模型描述。各材料参数见表1和表2,并以加载炸药容腔中40 MPa作为计算时的起始压力。
表 2 壳体材料Johnson-Cook本构模型参数Table 2. Parameters of Johnson-Cook constitutive model for case materialsA/MPa B/MPa C n m Tm/K ε*/s−1 350 275 0.022 0.36 1.0 1811 1.0 注:A、B、C、n、m为材料常数,Tm为材料熔点,ε*为无量纲塑性应变率。 2.1 加载炸药破碎程度对输出波形的影响
非冲击点火反应过程中,炸药破碎形成的燃烧比表面积大小与反应过程的压力演化密切相关。计算中在其他条件不变的情况下(H=60 mm,D=20 mm),讨论了相对燃烧面积S/S0分别为25、50、100等三种燃烧比表面积下的压力演化历程,来分析加载炸药燃烧过程中的破碎程度对输出压力波形的影响。
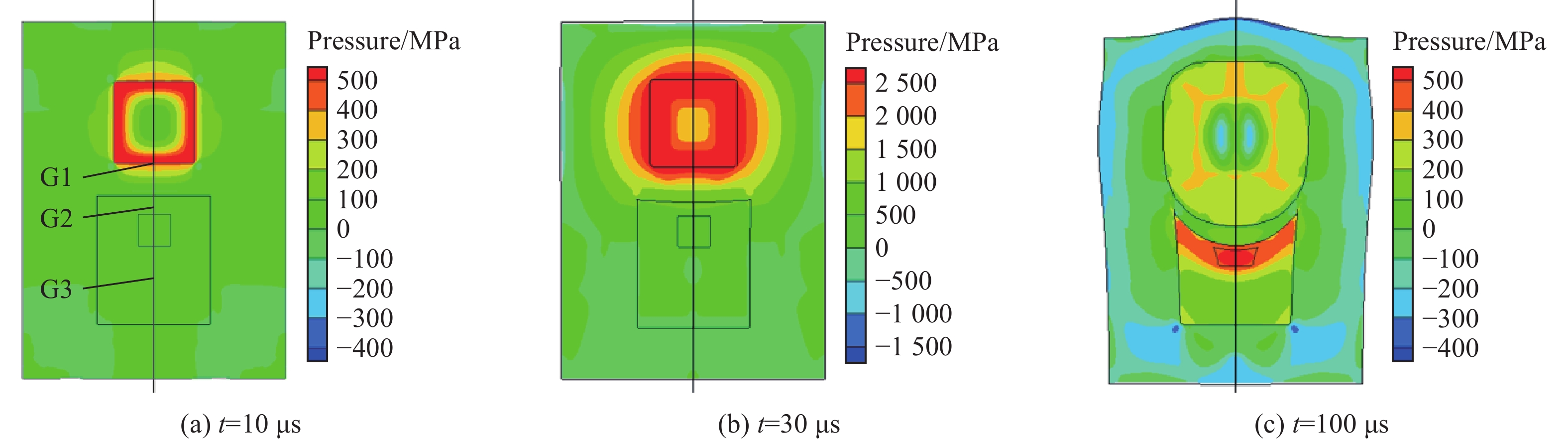
图3为相对燃烧面积S/S0=50情况下不同时刻的压力云图,在反应的早期过程中(对应图3(a)和图3(b)),装置壳体未发生明显变形,加载炸药燃烧容腔内的压力持续增长,并达到约3 GPa。随着压力的逐渐增大,壳体开始发生膨胀变形,燃烧容腔的体积增大限制了压力的持续增长,加载炸药燃烧容腔内的压力迅速下降至吉帕以下。下端受试炸药在加载炸药非冲击点火反应产生的压力载荷下发生变形。
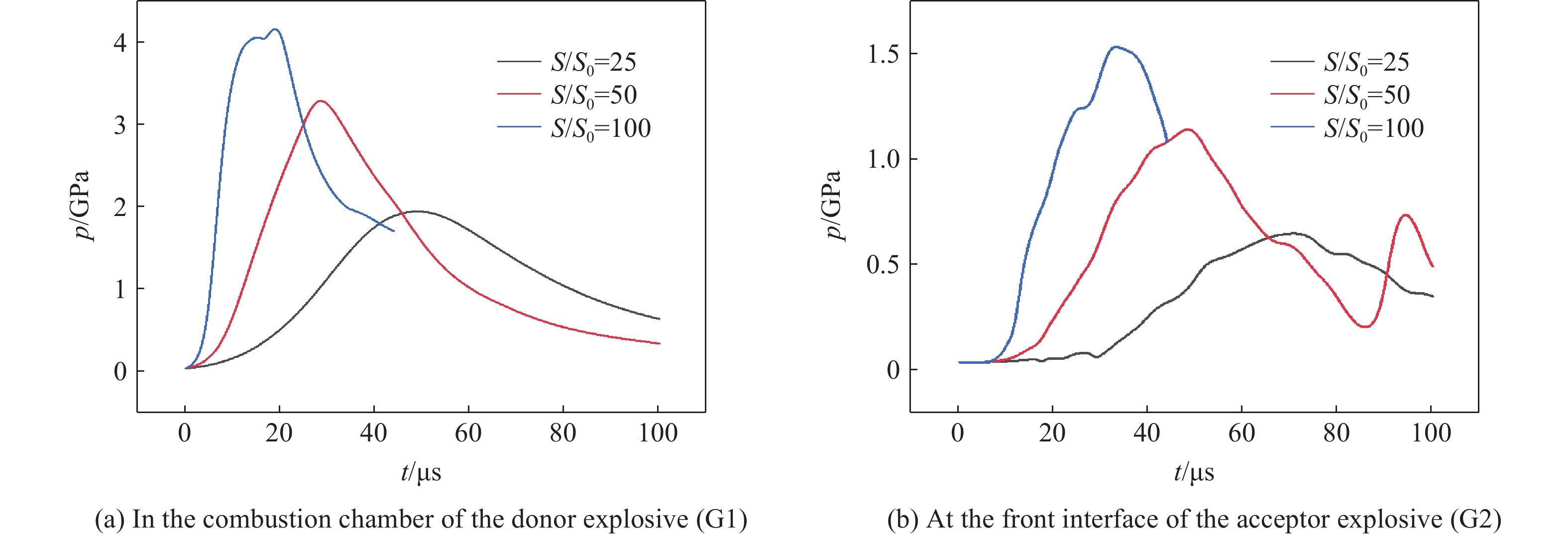
图4为三种相对燃烧面积S/S0下加载炸药燃烧容腔内以及受试炸药前界面处的压力波形。从图4(a)可以看出,随着S/S0的增大,加载炸药燃烧产生的压力峰值增大,而压力上升前沿宽度减小。在S/S0为25~100的范围内,加载炸药燃烧产生的压力峰值为2~4 GPa,压力上升沿宽度为20~50 μs。反应产生的斜波压力经壳体传播到受试炸药处的压力波形(见图4(b))与燃烧容腔内的压力特征基本一致,在S/S0为25~100的范围内,作用于受试炸药的压力峰值为0.6~1.5 GPa,斜波前沿宽度为20~50 μs。炸药燃烧过程中的破碎程度对压力演化历程影响显著,实验中为达到吉帕级的斜波压力输出,需采用低粘接剂的脆性易碎的炸药,以满足压力剧烈增长所需的燃烧比表面积条件。
2.2 壳体厚度对输出波形的影响
除炸药本身的燃烧特性、脆性特征外,壳体的约束强度同样对非冲击点火反应的压力演化历程具有重要影响。计算中,在相对燃烧面积S/S0为50的情况下,讨论了20、40、60 mm和无限厚四种壳体厚度H下燃烧过程的压力历程,以分析约束强度对输出压力脉冲的影响。其中无限厚壳体情况采用壳体外壁固壁条件近似处理。
图5为不同壳体厚度下加载炸药燃烧容腔内以及受试炸药前界面处的压力波形。从图5(a)中加载炸药燃烧压力历程可以看出,在压力增长的早期(<1 GPa),不同壳体厚度下压力增长历程近似一致。这是由于在压力较低时壳体未发生明显膨胀变形,相同的燃烧比表面积下燃烧增压速率基本一致。当压力继续增长时,壳体开始发生膨胀变形,壳体约束强度对压力增长的影响逐渐体现出来,壳体厚度越大,燃烧所能达到的峰值压力也越大。但根据无限厚壳体情况的压力历程,即使提供足够强的约束条件,燃烧所能达到的峰值压力仅为3.4 GPa。这是由于加载炸药与受试炸药之间的薄壁壳体是结构约束的弱环,限制了燃烧压力的持续增长(见图3(c))。图5(b)为受试炸药前界面处的压力波形,不同壳体厚度下的应力波形与加载炸药燃烧容腔内压力特征基本一致,壳体厚度越大,装置输出的斜波压力也越大,在30 mm到无限厚壳体范围内,输出的斜波压力峰值在0.6~1.8 GPa范围。需要注意的是,虽然壳体足够厚时加载炸药燃烧容腔内的压力峰值增长并不明显,但高压维持的时间更长,从而使得输出到受试炸药处的压力峰值明显增大。因此,为达到吉帕级斜波压力输出,需尽量增大壳体厚度。对应该计算条件下,壳体厚度需在60 mm以上。
2.3 隔层厚度对输出波形的影响
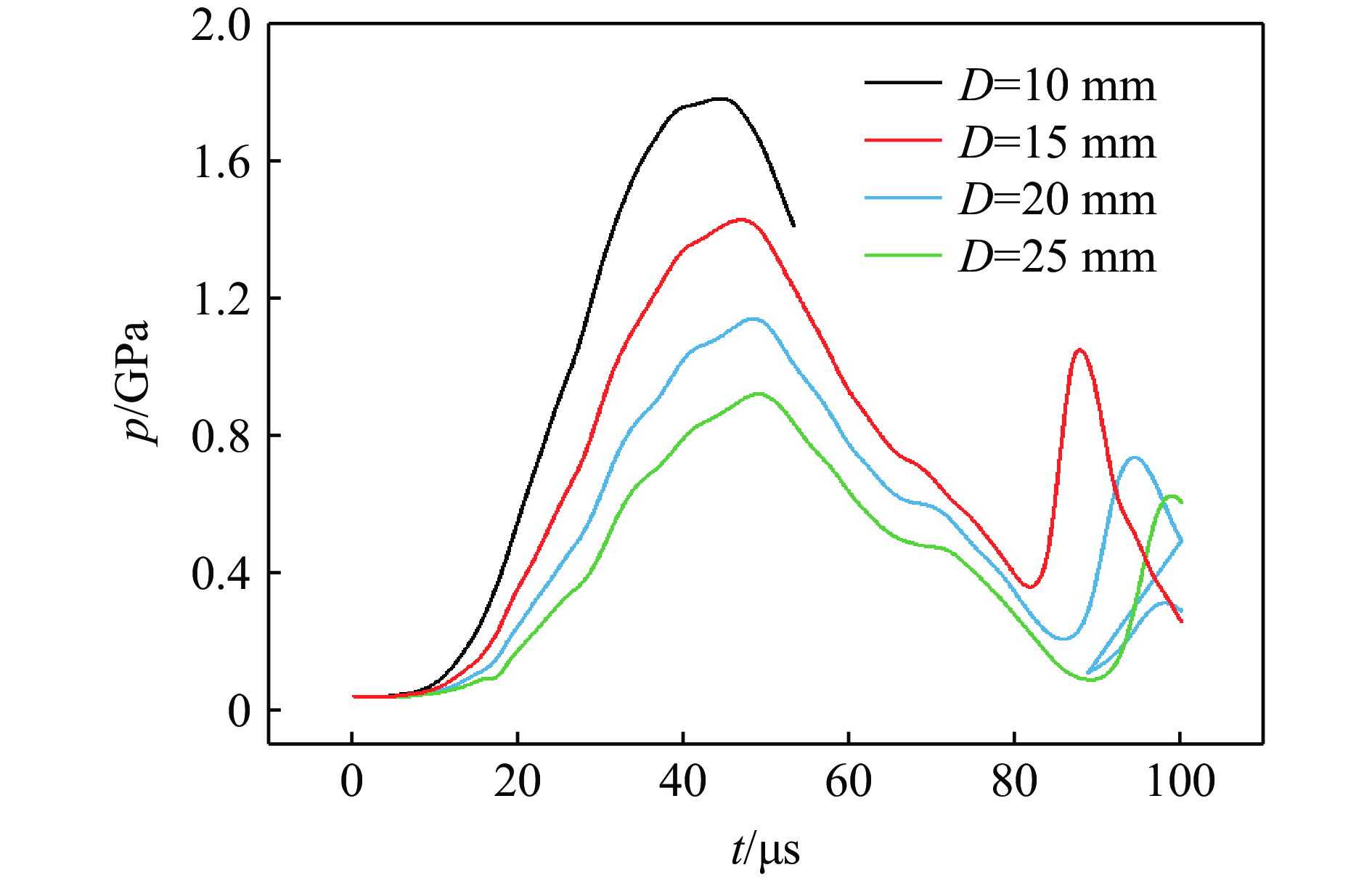
考虑到加载炸药与受试炸药之间的隔层厚度直接关系到斜波载荷的输出,在相同计算条件下(S/S0=50,H=60 mm),讨论了10、15、20和25 mm四种隔层厚度D下反应输出的斜波压力特征。
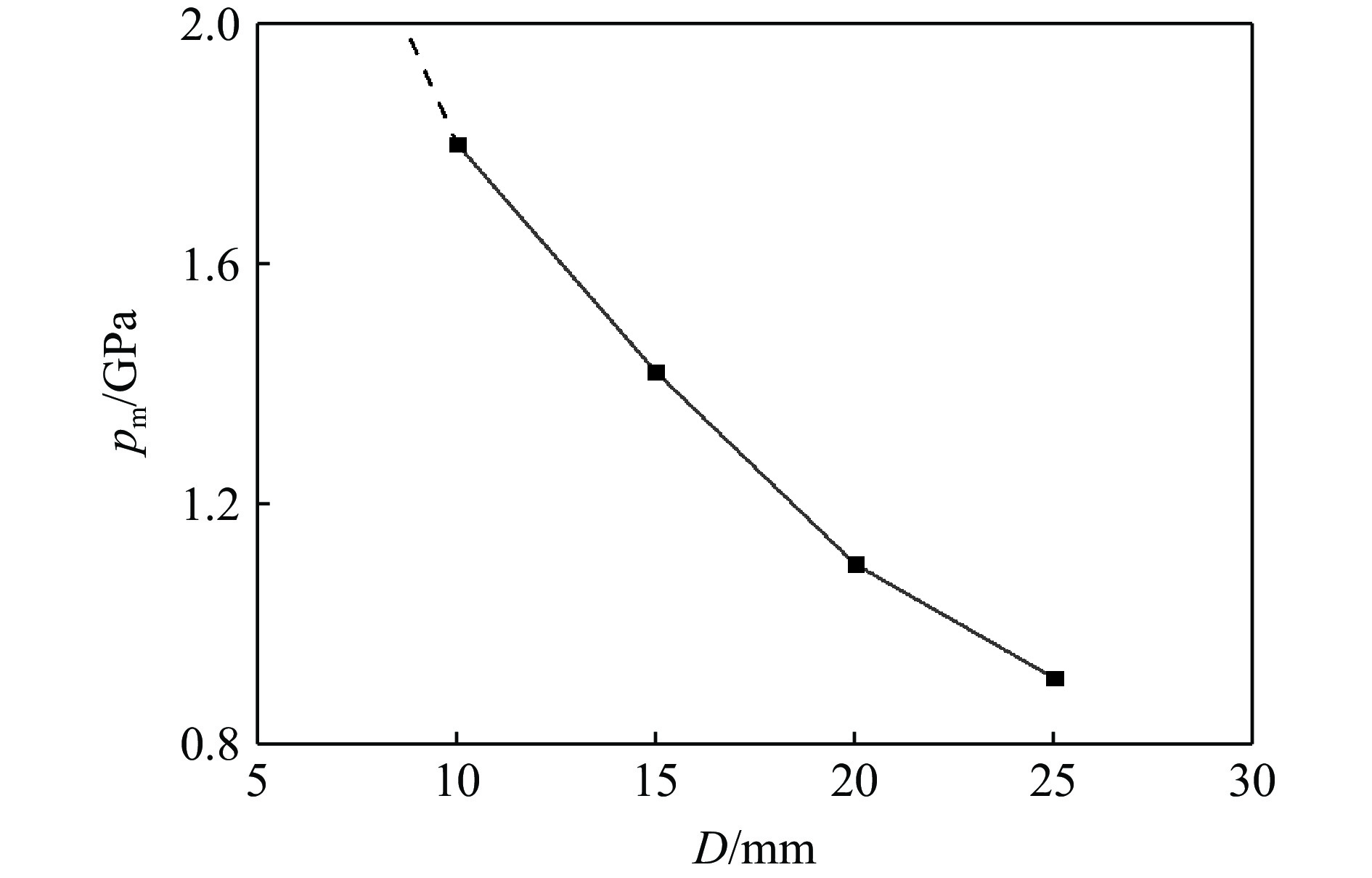
图6为四种隔层厚度下受试炸药前界面处(G2)的压力波形对比。可以看出:不同隔层厚度下斜波上升沿宽度基本一致(约为30 μs),但斜波压力峰值随着隔层厚度的增大而减小。图7给出了斜波压力峰值pm与隔层厚度D之间的关系,压力峰值关于隔层厚度近似呈指数衰减关系,在隔层厚度D为25~10 mm范围内,输出的斜波压力峰值为0.9~1.8 GPa。因此,为使得输出的斜波压力较高,隔层的厚度不宜太厚。对应计算条件下,斜波压力输出在1 GPa以上时,需控制隔层厚度在20 mm以内。
3. 斜波加载装置的实验验证
基于上述分析,完成斜波加载装置的结构设计。为满足吉帕级高幅值的斜波压力输出要求,加载炸药选取为燃速压力敏感且脆性特征明显即易碎的压装PBX炸药,设定H=80 mm,以提供反应压力增长的必要条件,设定D=20 mm。此外,为避免非冲击点火反应早期,燃烧产物气体泄漏导致压力下降,在激光点火头和壳体连接处做密封处理。测试系统上,采用光子多普勒测速仪(photon doppler velocimeter, PDV)测量壳体外部的膨胀速度历史,采用PVDF(聚偏二氟乙烯)测量受试炸药前、后界面处的压力波。
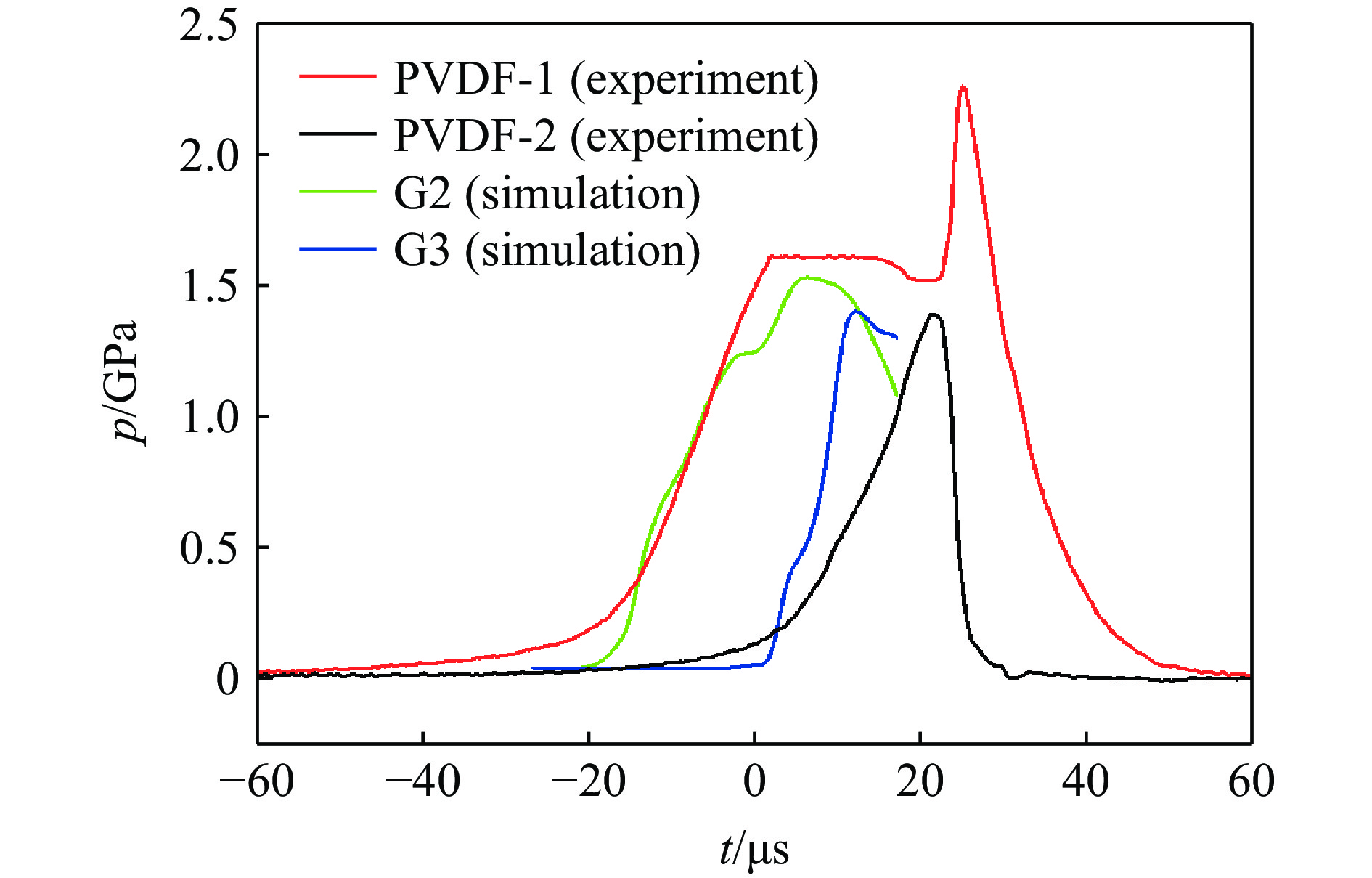
图8为PVDF所测受试炸药前、后界面处的压力波形:受试炸药前界面处的斜波压力为1.6 GPa、上升沿宽度约为25 μs,较好地满足了斜波加载装置的设计要求;其中在22 μs时刻,受试炸药前、后界面处压力信号的异常增长和下降可能为结构变形挤压测试电路引线导致的PDVF测量失效。图8中还给出了实验装置结构下S/S0=100时的计算结果,主要区别在于实验中低压段压力增长更加平缓,而计算中压力为快速上升。这是由于实际反应过程中,燃烧比表面积是随裂纹扩展而不断增长变化的过程,而计算中并未考虑此类因素的影响,但从压力波形的整体趋势上来看计算结果与实验测得数据大致吻合。
4. 结 论
(1) 设计了一种强约束压装PBX炸药非冲击点火反应驱动的吉帕、十微秒级斜波加载装置,采用层流燃烧速率模型和二维有限差分程序对斜波压力输出特征进行了分析。加载炸药破碎形成的燃烧比表面积的大小直接关系到非冲击点火反应的压力输出,燃烧比表面积越大,输出至受试炸药处的斜波压力越大,峰值压力可达吉帕以上,对应的压力上升前沿可从数十微秒降至数微秒。为获取较高幅值的斜波压力,需选用低粘接剂脆性易碎的炸药。加载炸药外部的壳体厚度也是影响斜波压力输出的关键因素,壳体厚度越大,输出的斜波压力峰值越大。为达到吉帕级斜波压力输出,壳体厚度需在60 mm以上。加载炸药与受试炸药之间的隔层厚度直接影响到受试样品受到的斜波压力大小,斜波压力峰值与隔层厚度之间近似呈指数衰减关系,隔层厚度越大,斜波峰值压力越小。
(2) 参考数值计算结果,完成了斜波加载装置的结构设计,在加载炸药选取为PBX-1,壳体厚度为80 mm以及隔层间隔为20 mm的情况下,经PDVF测得受试炸药前界面处的斜波压力为1.6 GPa、上升沿宽度约为25 μs,可较好地满足的斜波加载装置的设计要求。若不考虑对受试炸药的保护和回收,可减小加载炸药与受试炸药之间的隔层厚度,进一步提高作用于受试炸药处的斜波压力幅值,以开展2~4 GPa斜波加载实验研究。
-
表 1 Mie-Grüneisen状态方程参数
Table 1. Parameters of Mie-Grüneisen equation of state
表 2 壳体材料Johnson-Cook本构模型参数
Table 2. Parameters of Johnson-Cook constitutive model for case materials
A/MPa B/MPa C n m Tm/K ε*/s−1 350 275 0.022 0.36 1.0 1811 1.0 注:A、B、C、n、m为材料常数,Tm为材料熔点,ε*为无量纲塑性应变率。 -
[1] ASAY B W. Shock wave science and technology reference library, Vol. 5: non-shock initiation of explosives [M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2010: 1–14. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-87953-4. [2] 郭应文, 胡海波, 李涛, 等. 压装PBX炸药DDT管实验初始反应演化过程分析 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2017, 40(3): 77–79, 89. DOI: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2017.03.014.GUO Y W, HU H B, LI T, et al. Analysis of initial reaction evolution process of experiment of DDT tube filled with pressed PBX explosives [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives & Propellants, 2017, 40(3): 77–79, 89. DOI: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.2017.03.014. [3] HU H B, GUO Y W, LI T, et al. Reactive behavior of explosive billets in deflagration tube of varied confinements [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2018, 1979(1): 150020. [4] 胡海波, 傅华, 李涛, 等. 压装密实炸药装药非冲击点火反应传播与烈度演化实验研究进展 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(1): 011401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0346.HU H B, FU H, LI T, et al. Progress in experimental studies on the evolution behaviors of non-shock initiation reaction in low porosity pressed explosive with confinement [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(1): 011401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0346. [5] 邱天, 文尚刚, 李涛, 等. 长管强约束条件下压装PBX炸药点火实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(1): 011405. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0360.QIU T, WEN S G, LI T, et al. Experimental study on initiated reaction evolution of pressed explosives in long thick wall cylinder confinement [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(1): 011405. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0360. [6] 李涛, 胡海波, 尚海林, 等. 强约束球形装药反应裂纹传播和反应烈度表征实验 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(1): 011402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0348.LI T, HU H B, SHANG H L, et al. Propagation of reactive cracks and characterization of reaction violence in spherical charge under strong confinement [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(1): 011402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0348. [7] 李涛, 程赋, 胡海波, 等. 一种单向柱壳约束反应烈度量化诊断装置和诊断方法: CN201910955979.0 [P]. 2019-10-10.LI T, CHENG F, HU H B, et al. One-way cylindrical shell constraint reaction intensity quantitative diagnosis device and diagnosis method: CN201910955979.0 [P]. 2019-10-10. [8] SALISBURY D A, TAYLOR P, WINTER R E, et al. Single and double shock initiation of EDC37 [J]. Dimensions, 2002, 2000(10): 150. [9] WINTER R E, SORBER S S, SALISBURY D A, et al. Experimental study of the shock response of an HMX-based explosive [J]. Shock Waves, 2006, 15(2): 89–101. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-006-0010-9. [10] GARCIA F, FORBES J W, TARVER C M, et al. Pressure wave measurements from thermal cook-off of an HMX based high explosive PBX 9501 [J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2002, 620(1): 882–885. [11] 杨天昊. 炸药非冲击点火爆炸事故反应主控因素及GPa级斜波作用下PBX基体中微介观热点响应行为研究 [D]. 绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院, 2022.YANG T H. Study on main controlling factors of explosive non-shock initiation explosion accident reaction and the response behavior of micro-mesoscopic hot spots in PBX under the GPa-level ramp wave [D]. Mianyang, China: China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2022. [12] 尚海林, 杨洁, 胡秋实, 等. 炸药裂缝中的对流燃烧现象实验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(1): 99–106. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.01.012.SHANG H L, YANG J, HU Q S, et al. Experimental research on convective burning in explosive cracks [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(1): 99–106. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.01.012. [13] 尚海林, 胡秋实, 李涛, 等. 炸药裂缝燃烧增压过程的一维理论 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(1): 011403. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0345.SHANG H L, HU Q S, LI T, et al. One-dimensional theory for pressurization process in explosive crack burning [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(1): 011403. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0345. [14] 姚奎光, 赵学峰, 樊星, 等. 高压下PBX-1炸药的燃速-压力特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(1): 011404. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0347.YAO K G, ZHAO X F, FAN X, et al. Burn rate-pressure characteristic for PBX-1 explosive at high pressures [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(1): 011404. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0347. [15] 王延飞, 刘杰, 张旭, 等. 未反应炸药JOB-9003的JWL状态方程 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2016, 30(5): 387–391. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2016.05.007.WANG Y F, LIU J, ZHANG X, et al. JWL equation of state of unreacted JOB-9003 explosive [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2016, 30(5): 387–391. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2016.05.007. -








 下载:
下载:

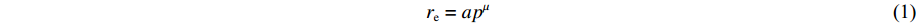
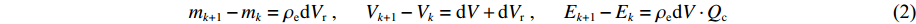


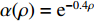







 下载:
下载: