Blast mitigation performance of porous polyurethane-basedcomposite explosion-proof barrier
-
摘要: 针对削弱爆炸恐怖袭击危害这一公共安全领域的热点难题,开展新型削/防爆结构的研究刻不容缓。聚氨酯泡沫具有密度低、微观结构易设计、在爆炸载荷作用下不会产生二次杀伤性破片等优点,在新型削爆结构方面具有良好的应用前景。基于削弱爆炸危害的研究背景,搭建了定向冲击波流场装置对聚氨酯平板进行爆炸加载实验,并通过流固耦合数值模拟对实验进行了验证。在此基础上,利用已验证的模拟方法针对聚氨酯(polyurethane, PU)、水体环形复合屏障面向内爆炸载荷的削弱效应进行了模拟分析。以屏障的总体积相等作为设计前提,对比了PU/水、水、水/PU这3种屏障的冲击波削弱性能,并分析了聚氨酯密度对性能的影响规律。结果表明:削爆屏障的存在迫使冲击波发生反射、绕射、透射以及波与波之间的相互作用。相比于纯水屏障,PU/水屏障在自重下降32%的同时,依然能够有效削减冲击波峰值(可达13.3%),主要利用了内侧聚氨酯波的低阻抗来降低冲击波的反射强度。Abstract: In view of the hot problem of reducing the harm of explosive terrorist attacks in public security field, the research on explosion-proof structures is urgent. Polyurethane foam has the advantages of being lightweight, has excellent mechanical properties, and can avoid secondary debris damage. It has a good application prospect in the new explosive disposal equipment. Based on the research background of explosion hazard reduction, the mechanism and effectiveness of shock wave weakening of polyurethane foam and polyurethane-based composite barriers need to be investigated. The microstructure and mechanical properties of porous polyurethane were tested firstly. It was to obtain the basic parameters and contribute to construct the simulation model of the samples with different densities (100-300 kg/m3). A directional flow field device was set up to impact the polyurethane plate and the feasibility of the corresponding numerical model was analyzed to study its protective performance against the plane shock wave. On this basis, the weakening effect of the polyurethane-water annular composite barrier under internal explosive loading was analyzed numerically by using the verified numerical model. The design premise was that the total volume of barriers was equal, and the shockwave weakening performances of PU/water, pure water and water/PU barriers were compared. The influence of polyurethane density on shock wave weakening performance was analyzed. The results show that the existence of a barrier forces the shock wave to reflect, diffract, transmit and interact with each other. Compared with a pure water barrier, the PU/water barrier can effectively reduce shock wave peak (up to 13.3%) when the total mass decreases by 32%. This is mainly because of the lower impedance of the inner polyurethane foam, which can reduce the strength of the shock wave reflected back from the barrier wall. Under current simulation conditions, it is more effective for the protection of corresponding barrier when the density of PU is 200 kg/m3 in the PU/water barrier.
-
Key words:
- polyurethane foam /
- explosion-proof barrier /
- explosion impact /
- shock wave weakening
-
安全快速地处置公共场合发现的疑似爆炸物是安全领域的研究热点和难点,其中先进防爆材料和结构的设计是削弱爆炸危害的关键。在重要场合配备或搭建削/防爆屏障是抵御爆炸突袭的常用方法之一。目前的削/防爆屏障主要分为:(1) 基于混凝土、合金等高强度材料制成的刚性防爆结构,如固定式的防爆墙[1]和钢制防爆桶[2],这些结构的设计要求其受到爆炸作用后不发生破坏和大变形;(2) 基于液体、细沙、聚合物颗粒、聚合物多孔材料及纤维织物等结构薄弱材料[3]的柔性削/防爆结构,这些结构自重轻而机动性好、造价低廉、几乎不产生二次杀伤性破片并可在爆炸后发生碎裂。削爆屏障对爆炸冲击波的削弱效应主要依靠迫使来袭冲击波发生反射和绕射,进而避免了冲击波直接传播并作用到屏障后方脆弱的人员或设备上[4-5]。当面临超过自身额定防护能力的大当量爆炸时,刚性防爆结构可能会发生破裂和解体,进而产生具有更大威胁的二次杀伤新碎片,即具有潜在附带伤害威胁。相比之下,柔性削/防爆结构因所用材料质地柔软,密度低,且不会产生二次杀伤性碎片,因而柔性削/防爆结构具有更高的安全性和工程应用价值。
已有的研究验证了一些基于柔性削/防爆材料的屏障具有较好的冲击波削弱性能[6-10],其中基于纯水的防爆结构得到了大量的关注。但是大多数研究中的防爆结构多基于单种材料,即很少研究柔性复合结构,且很少关注基于聚合物泡沫的防爆结构。聚氨酯(polyurethane,PU)泡沫材料因其材质软、密度低和特有的三维网状结构,在爆炸及冲击波防护领域具有比其他材料更出色的性能[11],多孔聚氨酯材料常作为抗冲击防护的能量吸收结构的组分而被广泛应用于军事领域[12],例如导弹防护罩、复合装甲的组成结构[13]、水下兵器冲击控制器[14]等。相比于液体和细沙等材料,在爆炸冲击加载作用下,聚氨酯泡沫可发生明显的压缩塑性变形直至密实状态,因此具有可观的能量吸收性能。同时,聚氨酯泡沫中包含的大量空气孔隙在爆炸载荷作用下(可视为绝热压缩过程)会吸收一部分能量转换成自身的内能,造成内部温度的大幅度提升。另外,聚氨酯泡沫具有更低的波阻抗,可能会有效地降低反射冲击波,进而削弱屏障后方或外部的冲击波载荷。然而,因为聚氨酯泡沫密度很低,纯聚氨酯泡沫的削爆屏障可能需要非常厚的用料才能避免冲击波直接冲垮防护结构而泄露到其后方。因此,可考虑设计一种基于聚氨酯泡沫和纯水的复合结构,用于搭建环形削爆屏障。
本文中首先对多孔聚氨酯进行微观表征及力学性能测试,然后采用爆炸冲击平板实验研究多孔聚氨酯对爆炸冲击波的防护作用,并通过数值模拟对实验进行详细的分析和验证,随后利用验证后的数值模型分析多孔聚氨酯/水双层环形复合结构对削爆屏障的冲击波削弱性能,并考察材料排布顺序以及聚氨酯泡沫密度对复合结构的防护性能的影响。
1. 多孔聚氨酯平板的爆炸冲击实验
1.1 多孔聚氨酯的微观表征及力学性能
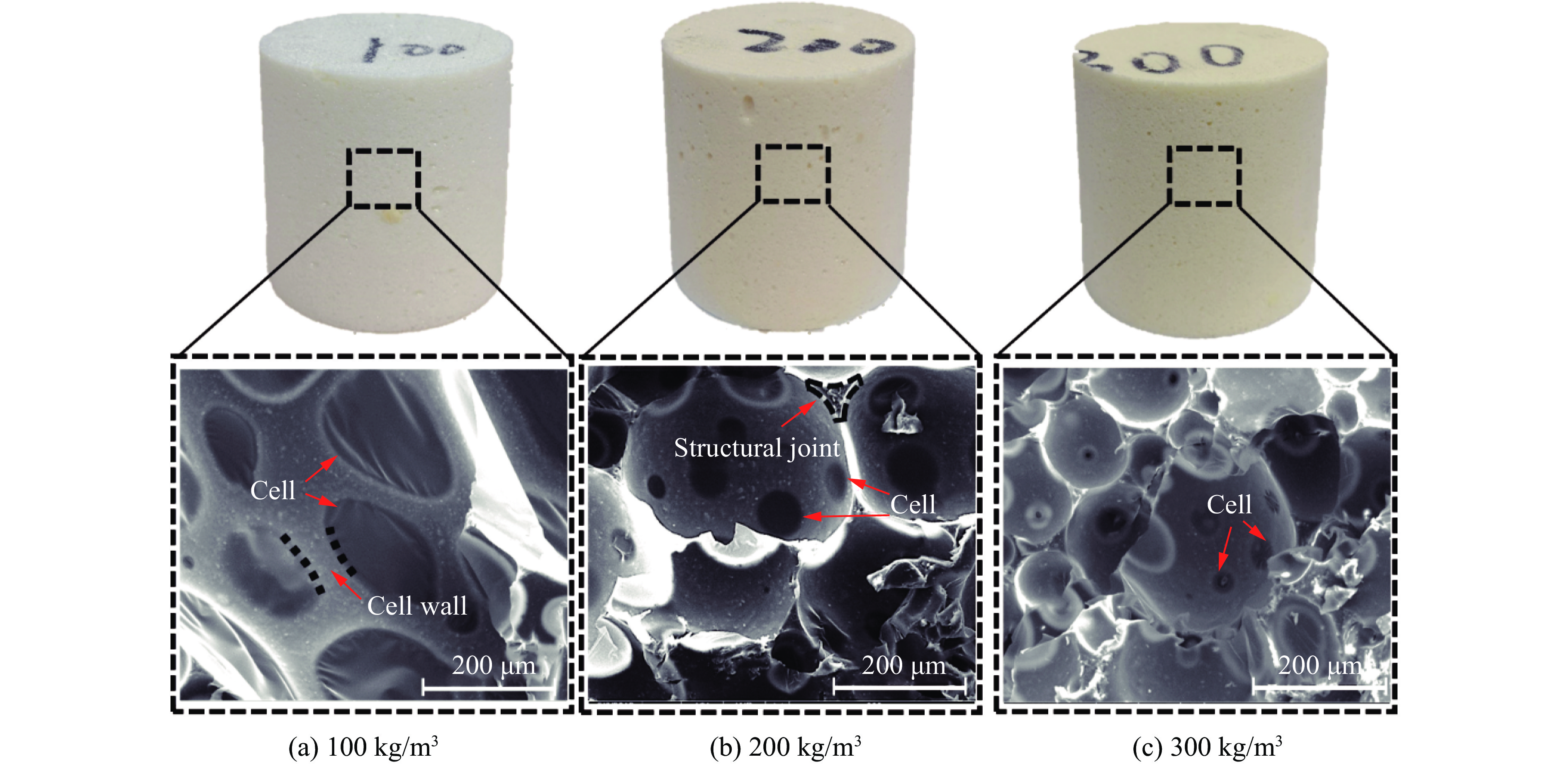
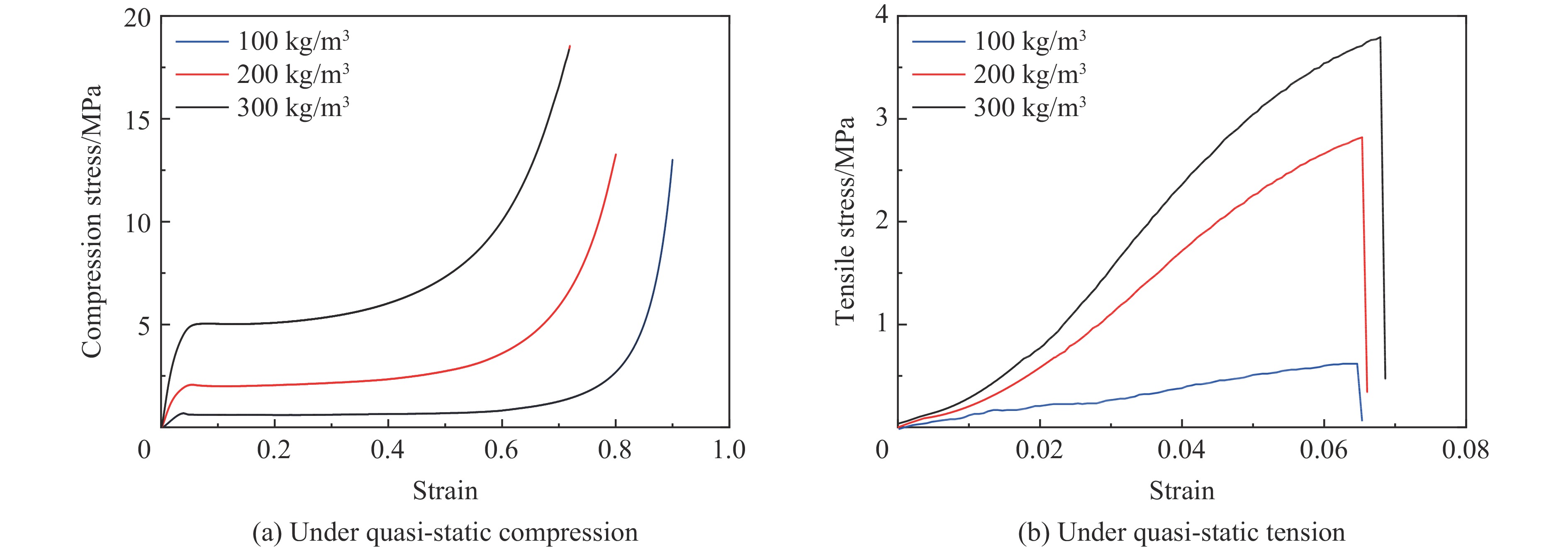
采用的多孔聚氨酯试样由北京理工大学鲁南研究院提供,研究表明,聚氨酯的密度及孔隙度对其中形成的初始冲击波压力及传播衰减效应有显著的影响[13],因而选取了3种试样,密度分别为100、200和300 kg/m3。利用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM)扫描不同试样的微观结构(图1)进行对比,观察试样内部胞体尺寸,沿着发泡方向L(长轴)较长,垂直于发泡的方向W(短轴)较短,定义孔形系数α=L/W,其中α会随着泡沫体密度的增加(100、200和300 kg/m3)而减小(分别对应1.7、1.2和1.1),最终趋近于1,即泡孔形状由椭圆球形转变为球形。试样胞孔的尺寸随密度的提升有降低的趋势,胞孔平均直径由142、82 μm降至22 μm,对应的开孔率分别为8.6%、29.8%、22.1%。如图2所示,微观特征也体现在材料力学性能中,泡沫的平台应力随密度增加而提升的效果明显[15](压缩和拉伸实验对应的工程应变率分别为0.0010和0.0016 s−1),从低密度(100 kg/m3)试样对应的抗压强度0.64 MPa提升至较高密度(300 kg/m3)对应的5.04 MPa。
1.2 实验设置及结果分析
平面冲击波对材料的加载行为在材料动态特性的研究、材料的缓冲吸能和防护性能等相关领域有着广泛的应用。一般平面冲击波加载技术包括炸药爆轰加载技术和轻气炮(激波管)驱动加载技术,为了更接近在实际削/抗爆防护中的应用场景,搭建了炸药爆轰加载的定向冲击波流场装置对聚氨酯材料的防护性能(压力峰值衰减率)进行探究。
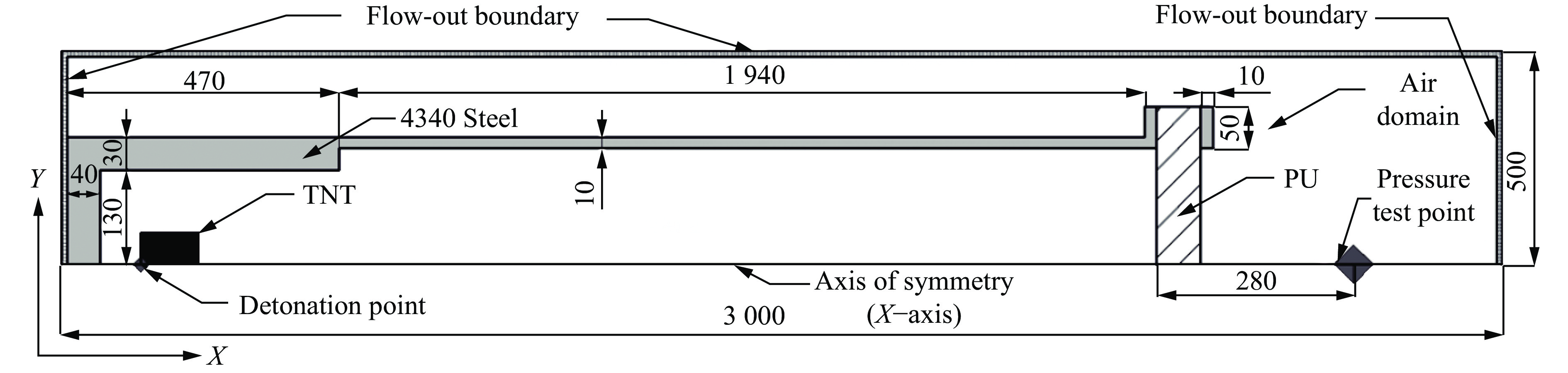
实验中采用20 g压装炸药TNT作为爆炸源(尺寸
∅ 25 mm×26 mm,压药密度1.58 g/cm3),放置于装置中心轴上,其中心距离爆炸室钢板垂直面83 mm,用8#雷管起爆(图3)。采用的聚氨酯试样的横向截面尺寸为405 mm×405 mm,实验中选取了3种密度的试样,分别为100 kg/m3(厚度40 mm)、200 kg/m3(厚度60 mm)、300 kg/m3(厚度20 mm,60 mm)。试样两侧利用钢板夹持(边长405 mm,中心有∅ 300 mm的圆形缺孔),通过对角线上的4个螺栓将两者固定,试样的冲击波受载面即为中心处∅ 300 mm的圆形区域。在相同药量的TNT在爆炸冲击波定向流场装置中引起的近似平面冲击波作用下,通过测量冲击波经过泡沫板后的靶后压力值(靶后压力值可为靶板后方的人员及建筑物的损伤等级评估提供数据支撑[3]),利用高速摄影仪记录聚氨酯泡沫板的变形破坏形态,对比研究不同密度及厚度的聚氨酯硬质泡沫的削爆隔爆能力。
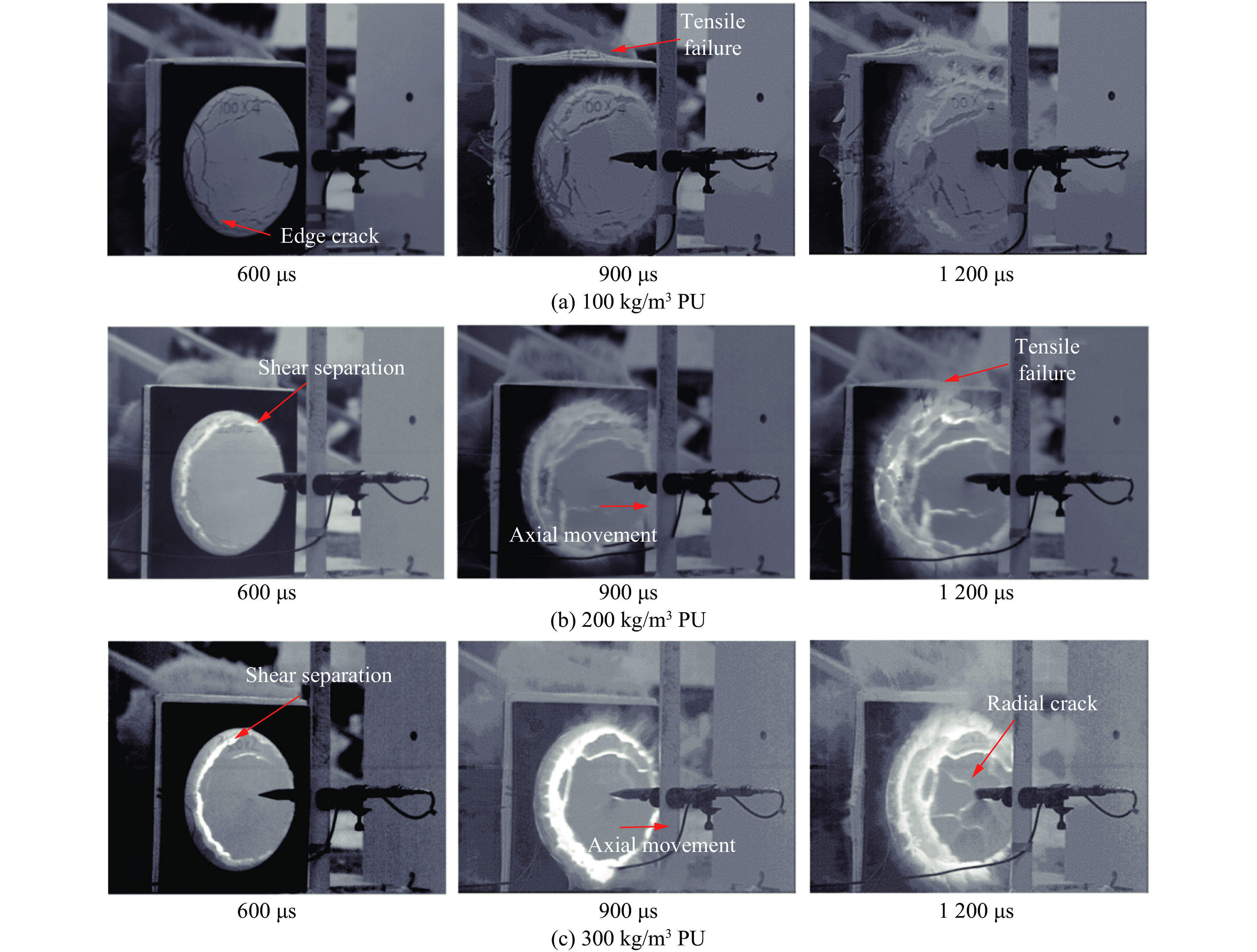
不同密度下的泡沫试样受到冲击的响应形态如图4所示:起爆后600 μs时,3种密度的聚氨酯试样都以近似平面的整体形态从试样端的夹持窗口处向传感器方向运动,即试样受到近似平面波的加载作用而做出了相应的响应;对比900和1200 μs的画面可以观察到,聚氨酯试样的受载区域(与定向流场装置内径尺寸匹配的部分)除了与夹持边缘之间发生分离,其在到达传感器尖端之前几乎保持了完整的平面形貌,在与传感器接触之后,由于应力集中导致试样表面出现了明显的径向裂纹。
密度为100 kg/m3的聚氨酯泡沫试样在沿着轴向运动的同时,在棱边中点处的径向变形也非常明显,推测这样的现象是由于冲击波进入试样之后,应力波传播到试样与空气的接触边界,由于自由面上试样与空气2种介质的密度和波速都有较大的差异,因此造成一部分压缩应力波在界面处反射为方向相反的拉伸应力波;结合霍金逊现象,可以表述为当反射拉伸应力与入射的压缩应力叠加之后的拉应力大于材料的抗拉强度时,临近自由面的试样会被拉断破坏[16];虽然本实验注意控制试样的横向尺寸与纵向尺寸的比值(大于6),但侧面稀疏波对应力波沿纵向传播的影响仍不可忽略。由此可以推测,聚氨酯试样沿轴向的运动及破碎现象除了冲击波加载压缩、爆轰气体及产物的驱动,也包括反射拉伸波的影响。考虑到聚氨酯泡沫的抗压强度远高于抗拉强度,因而在爆炸防护中,应当尽量减少边界稀疏波对聚氨酯材料的影响,避免反射的拉应力对泡沫体造成过早的破坏,同时利用其较高的抗压比强度作为防护材料的优势,所以一般聚氨酯可用于削/抗爆复合结构的前板或夹芯层[17];因而在下文中,通过设计聚氨酯与水这2种典型的易碎性柔性材料的组合方式和性能研究,以达到凸显聚氨酯优势、减少稀疏波提前破坏的目的。
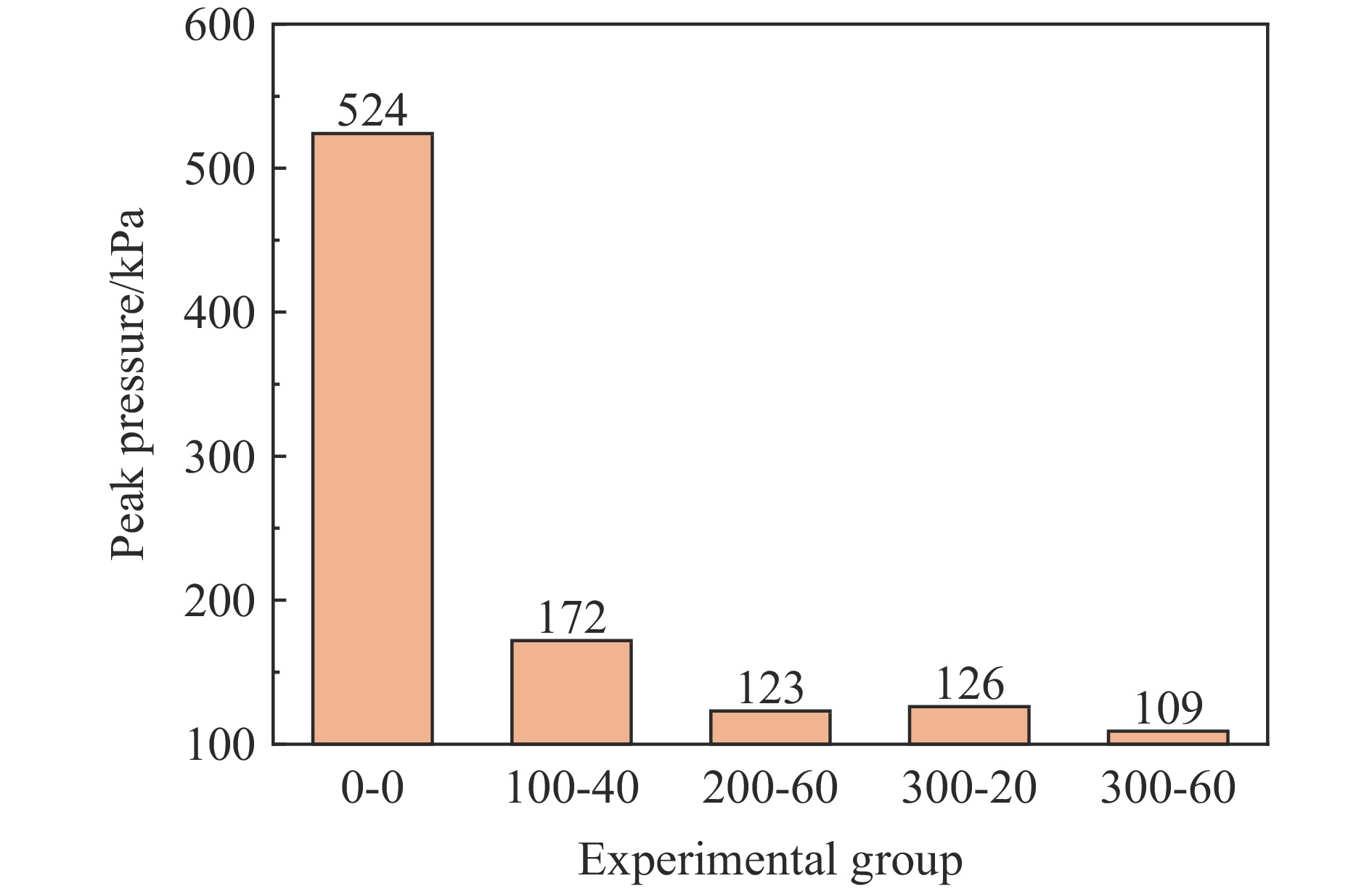
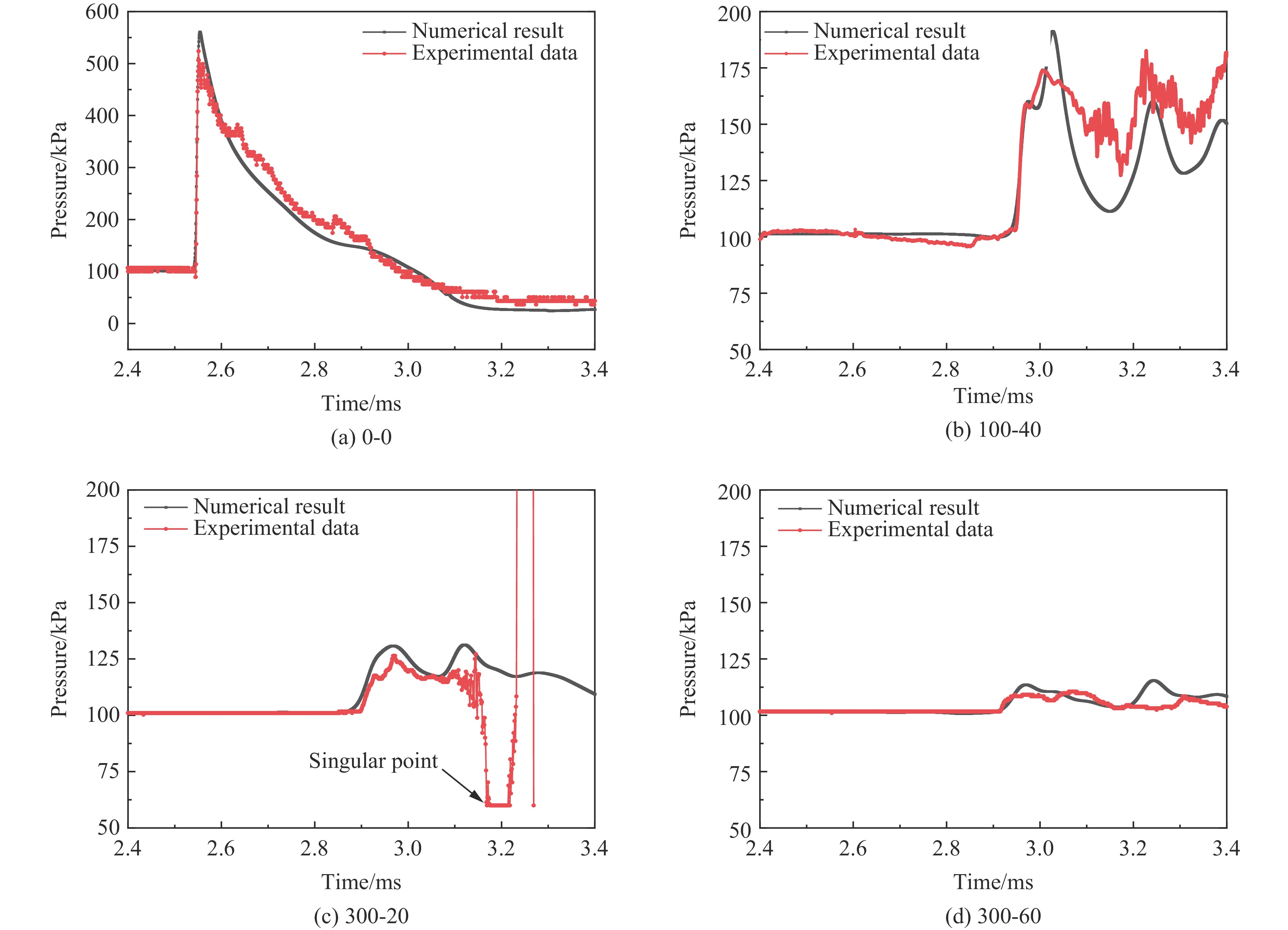
实验中测得的靶后压力峰值如图5所示(x-y中的x表示试样密度,y表示试样厚度;其中0-0表示无泡沫防护)。结果表明,聚氨酯泡沫对冲击波的削减作用明显,不同实验组的压力峰值衰减率均可达到67%以上。参考冲击波超压对有生力量的破坏作用等级(表1),可认为当峰值超压小于0.02 MPa时,冲击波超压对有生力量几乎无威胁。结合平板冲击实验结果,可以得到空爆对应的靶后超压峰值(0.42 MPa)远高于Ⅴ级(0.10 MPa,大部分死亡)的最低阈值,泡沫试样的加入可以大幅降低靶后超压的破坏作用等级,除了密度为100 kg/m3试样以外,其余聚氨酯泡沫试样均可将靶后超压破坏等级大幅降至Ⅱ级(轻伤)甚至Ⅰ级(无杀伤作用),实现对冲击波的有效削减作用。比较可知,200-60和300-20这2种结构对应的靶后压力峰值相近,但后者的面密度仅为前者的50%,因此可认为泡沫密度对冲击波削减作用的积极影响较厚度更明显。对比相同厚度下的试样200-60和300-60以及相同密度下的试样300-20和300-60对应的压力峰值,可知密度或厚度的提升[18]与结构的削波性能正相关。
2. 平板屏障冲击实验的数值模拟
2.1 数值模型及材料参数
参照爆炸冲击平板实验,建立AUTODYN-2D的二维轴对称模型、采用欧拉多物质算法,建立的模型与实验实物比例为1∶1(图6)。空气域完全覆盖实验装置及试样,尺寸为3 000 mm×500 mm;爆炸定向流场装置采用与实验一致的4340钢和对应的尺寸;聚氨酯试样则根据实验条件建立相应尺寸的几何模型;考虑到拉格朗日算法对于流体计算时,很可能由于材料的大变形导致网格畸变,造成计算难以维持的问题,所以TNT炸药和空气采用欧拉算法,钢和聚氨酯泡沫采用拉格朗日算法。考虑到夹持端的螺栓直径略小于试样穿孔,夹持主要约束X轴即冲击方向,基本不会造成试样的面内预应力,试件与夹持端之间采用Lagrange/Lagrange Interaction接触,试件与空气之间采用Euler/Lagrange Interaction流固耦合接触。为了模拟无限的空气流场(即用有限的空间范围模拟无限的空间[20]),分别在空气域的三侧添加流出边界条件,从而允许物质从边界流出而不发生反射。
数值模型中的材料包括:TNT炸药、空气、4340钢以及聚氨酯泡沫,材料模型均来自AUTODYN内置材料库。欧拉域内的材料均采用状态方程表征其动态响应行为,其中TNT炸药的状态方程采用JWL(Jones-Wilkins-Lee)状态方程[21],空气采用理想气体状态方程[10,21],钢采用线性状态方程[22]进行描述。
聚氨酯泡沫采用Crushable foam模型来模拟泡沫在冲击波压缩加载条件下的力学行为。开展了3种不同密度的聚氨酯泡沫准静态压缩、拉伸实验,获得了如图2所示的工程应力-应变曲线,材料参数如表2所示。另外考虑到在爆炸冲击加载条件下,部分材料单元容易发生严重的扭曲畸变,造成计算成本急剧增加甚至难以进行,因此采用侵蚀准则,用于删除一些畸变的拉格朗日单元,即当网格的瞬时几何应变极限超过2时[23],删除对应的畸变网格。
表 2 泡沫材料参数Table 2. Material parameters for PU foams密度/(kg·m−3) 体积模量/MPa 剪切模量/MPa 最大拉伸应力/MPa 泊松比 100 5.53 8.30 0.69 0.12 200 11.27 16.90 2.77 0.13 300 37.35 56.02 3.64 0.18 2.2 模型验证与结果分析
数值模拟的验证主要通过实验和数值模拟测得的压力峰值差异来定量判断,如图7所示,提取测试信号较完整的4次实验数据与数值模拟的压力时程曲线进行对比。其中需要注意的是,实验中无法准确地确定起爆时刻,因而将实验数据沿时间轴进行调整,使得实验与数值模拟的冲击波到达观测点的起始时刻相同。对比结果表明,两者吻合程度整体较好,数值模拟基本可以再现实验中冲击波压力特征(其中300-20实验中的传感器由于受到振动或撞击,测得的超压曲线在3.1 ms后出现了基线漂移和大幅振动的现象,因而此段数据暂不作为对比依据)。通过比较得到:数值模拟与实验测得的靶后压力峰值差异均低于12%(表3)。表3中列举的x-y中的x表示试样密度,y表示试样厚度。此外,由于数值模拟中的炸药参数和冲击波成长过程更为理想,为减少实验测试引起的系统误差对数值模型验证带来的影响,对比这2种方式的压力峰值衰减率也具有参考价值;除去无试样时靶后压力的测试实验(0-0),其余4次有效实验的压力峰值的衰减率差异均在2%以内。这在一定程度上可认为数值模拟方法可以为聚氨酯泡沫试样在爆炸加载下削波能力的预测提供参考。
表 3 实验与数值模拟的靶后压力峰值及对比Table 3. Comparison between experimental and numerical simulation on peak pressure behind target工况 靶后压力峰值/kPa 衰减率/% 实验 数值模拟 相对误差/% 实验 数值模拟 相对误差/% 0-0 524 560 6.9 0 0 0 100-40 172 191 11.1 67.2 65.9 1.9 200-60 123 126 2.4 76.5 77.5 1.0 300-20 126 129 2.4 75.9 76.9 1.3 300-60 109 113 3.7 79.2 79.8 0.8 爆炸冲击平板实验揭示了聚氨酯泡沫对冲击波载荷的有效削弱效果(压力峰值衰减率均可达67%以上),因而可以进一步考虑将其作为冲击波防护屏障的组成部分。接下来针对简易爆炸物的防护,设计了以聚氨酯泡沫为基础的复合削爆屏障,运用数值模拟进行防护效能评估和参数分析,从而为爆炸冲击波的区域防护提供参考。
3. 聚氨酯基环形屏障内爆炸防护性能
使用单一材料或单纯依靠增加防护结构的厚度可能导致成本急剧提高、体积和质量过大,因而目前关于多层复合结构的设计已成为防爆研究的热点[24-25]。通过聚氨酯平板试样的爆炸冲击实验已明确其具有较优的削波性能,但聚氨酯泡沫作为一种易燃性材料[26],无法消除爆炸燃烧的高温火焰会对周围环境、装备及人员造成热辐射、损伤致死等威胁,因而有必要利用复合结构设计来弥补这一劣势。考虑到水具有较高的比热容,可通过相变吸收燃烧中的热量[27];而且已有研究表明,与聚氨酯泡沫相似,水屏障在冲击波削弱方面较混凝土等硬质材料有质量轻、无二次伤害等优势[28],但为了进一步提升柔性结构的削爆效能,在液体屏障的基础上,可结合聚氨酯泡沫多孔可压缩结构特点和高比强度的力学特征,设计聚氨酯-液体复合环形屏障,以期取得削波、熄焰等爆炸防护的综合优势。
3.1 结构模型参数
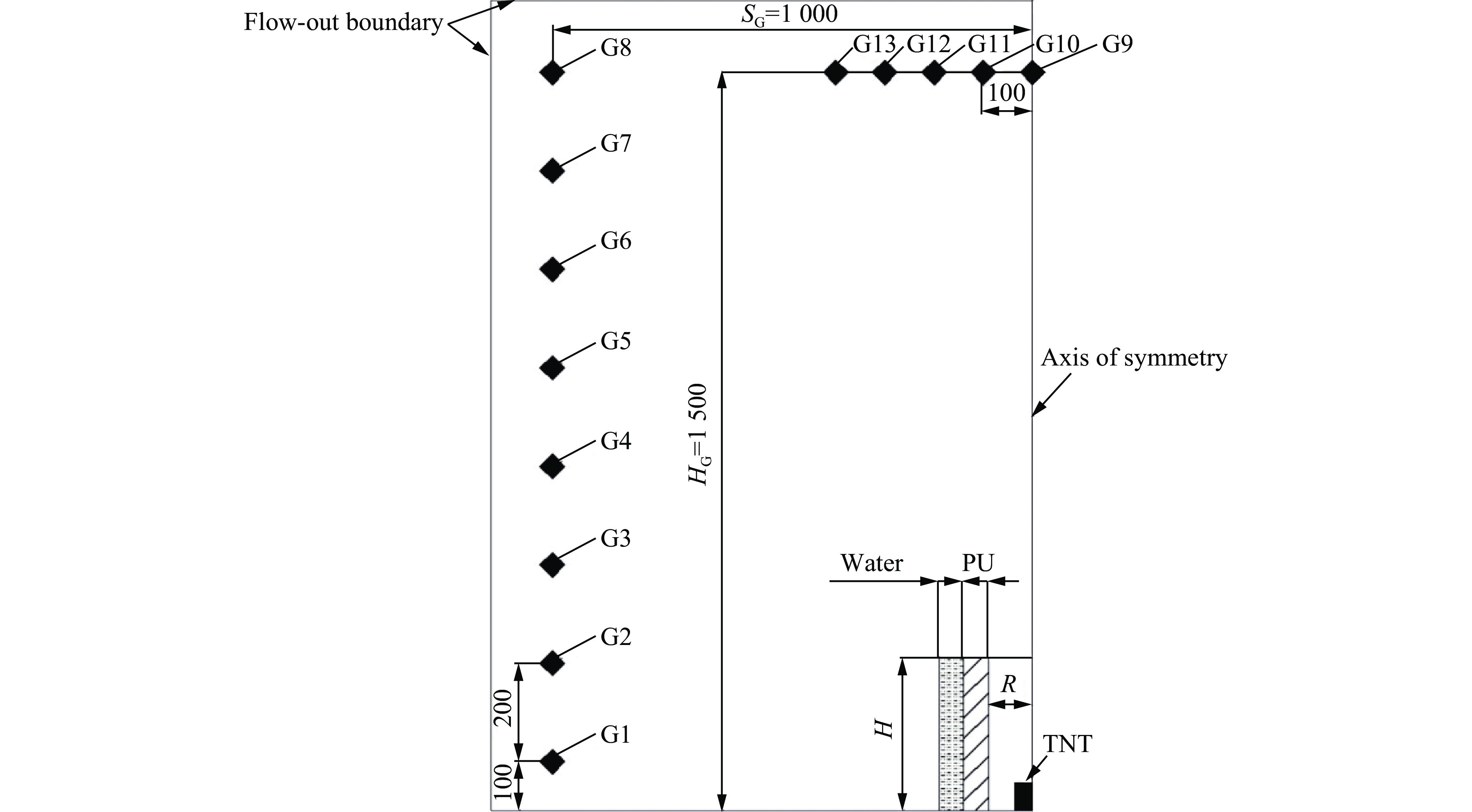
本文中采用的数值计算模型均为轴对称结构,且对称轴位于同一直线上,参考Chapman等[29]运用AUTODYN 二维(2D)轴对称简化模型,所预测的冲击波压力历程与实验测量结果吻合性较好,因此可采用AUTODYN 2D轴对称模型进行模拟计算。数值模型示意图如图8所示,其中,TNT炸药、空气以及水采用欧拉算法模拟[30],聚氨酯泡沫采用拉格朗日算法模拟。欧拉域尺寸为1100 mm×1600 mm,底部边线采用固定边界,用于模拟刚性地面;侧面和顶部边线采用流出边界,用于模拟无限大的空气域。所使用的炸药为500 g 圆柱状TNT,尺寸为
∅ 80 mm×61 mm,放置于刚性地面上,位于削爆屏障的中心轴处;屏障均为环形,3种不同结构的具体几何尺寸见表4。在对比分析PU泡沫和液体的排布顺序对削波性能的影响时,所采用的均为密度200 kg/m3的PU泡沫;在对比分析PU泡沫密度影响时,所采用的PU泡沫密度分别为100、200和300 kg/m3。在屏障侧向和顶部设置冲击波观测点,其位置参数见图8,其中SG表示观测点与爆炸中心轴的水平距离,HG表示观测点与刚性地面的竖直距离。观测点G1~G8距爆心的水平距离与SG相同,均为1 m,用于评估削爆屏障对侧向冲击波的削弱性能。观测点G9~G13离地高度与HG相同,均为1.5 m,用于评估削爆屏障对顶部冲击波的削弱性能。选取的观测点均位于冲击波稳定传播的区域内,从而确保观测点测得的冲击波压力可对结构防护性能进行表征。表4中的屏障名称:比如PU/水、水/PU结构中先出现的材料位于屏障内侧,即迎爆材料;例如PU/水结构中PU位于屏障内侧。模型中使用的材料参数与2.1节一致,此外水采用线性状态方程进行描述[22]。表 4 数值模型中不同防护结构的几何参数Table 4. Geometrical parameters of different protective structures in the numerical model屏障名称 壁厚
A1/mm壁厚
A2/mm迎爆面内圆
半径R/mm屏障高度
H/mm水 0 100 90 310 PU/水 50 50 90 310 水/PU 50 50 90 310 3.2 冲击波传播过程分析
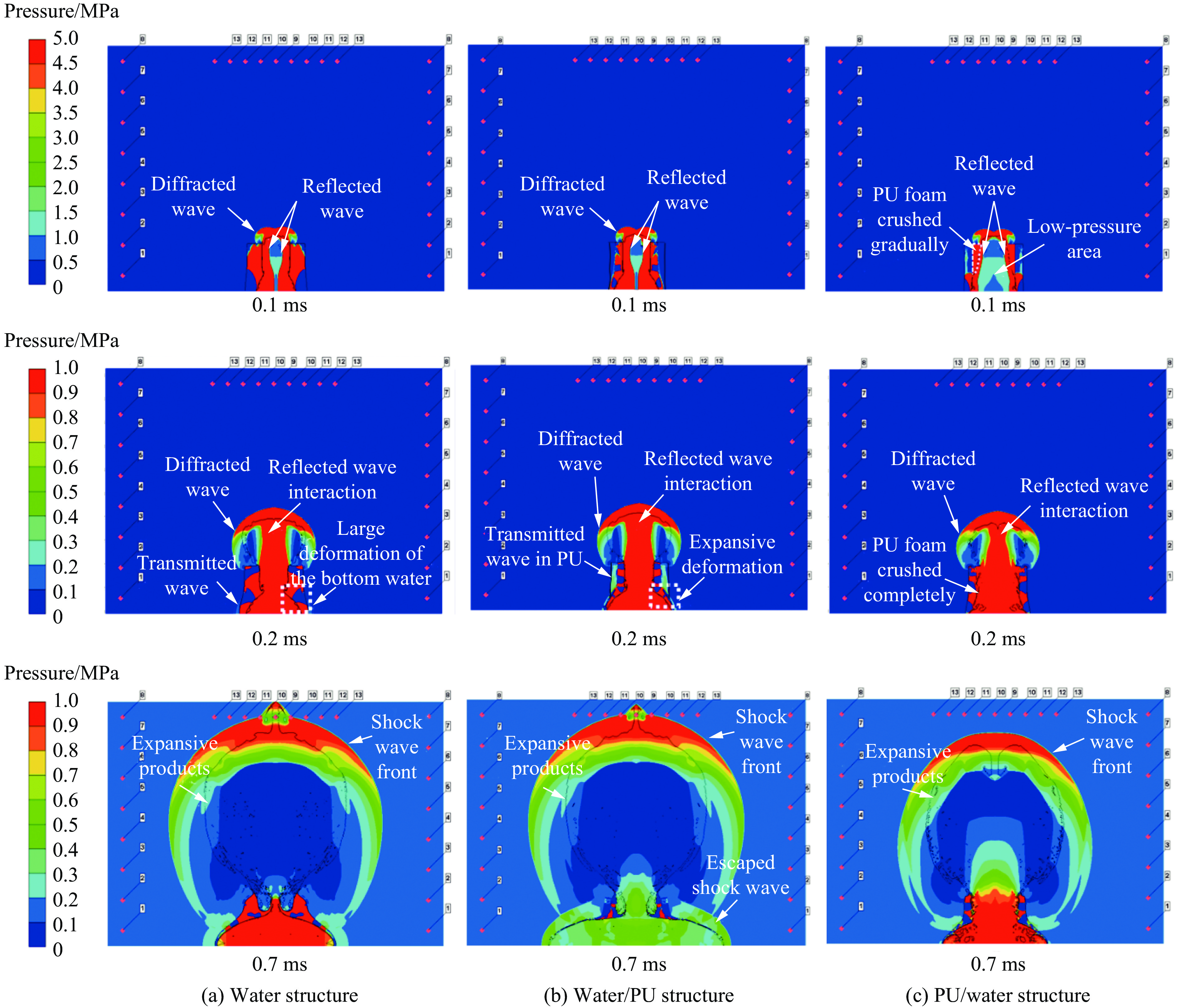
基于数值模拟结果,以典型的水屏障(W)作为对比基准,分析聚氨酯与水组成的复合结构PU/水、水/PU(后续简称为PW、WP)在特征时刻的冲击波压力云图及结构动态响应(图9),从而得到环形复合结构的主要爆炸防护机理,提出性能更具优势的柔性削爆结构。
起爆后0.1 ms:相比于液体位于内侧的W和WP结构,传入PW结构液体层中的爆炸冲击波载荷范围和强度都明显降低。由于PW结构中的PU与空气的阻抗不匹配程度远低于其他2种结构中液体与空气的不匹配度,所以在W或WP结构中,从空气/液体界面上反射回来的冲击波强度更高,并有逐渐向结构中心轴处传播进而与对侧反射回来的冲击波相互作用的趋势。当冲击波沿竖直方向向上传播到达防护结构的高度时,开始沿着结构顶部向外侧发生绕射。相比之下,同一时刻的PW结构的内部依然保持一个较大的低压区,推测因为空气/泡沫界面处反射回来的冲击波强度和速度较W、WP结构更低,从而延长了防护结构对爆炸载荷的约束以及冲击波与结构相互作用的时间,有利于增强防护效果。
起爆后0.2 ms:W结构液体底部沿径向扩展、厚度减小、变形严重;部分冲击波透射至液体层的外侧,这是因为炸药在地面起爆的工况下,爆心与液体屏障根部距离更近,爆炸冲击波与其接触时间更早、强度更高并且作用时间更长。WP结构的响应与之相似,由于其中的液体厚度降为W结构的1/2,其惯性效应降低、膨胀变形的程度提高,而且外侧的PU层中出现了均匀的透射波。相比之下,PW结构的整体变形较小,并且几乎未在结构外侧观测到透射波,分析认为是以下原因导致的:(1) 冲击波首先对PU形成压垮,所以作用到液体的冲击波被PU层吸收削弱,并且PU自身的延展性很低,在受到冲击压垮的过程中不会提前破坏液体层的形态位置,为接下来冲击波与液体的相互作用提供了良好的前提环境;(2) 冲击波与液体层接触界面(内径280 mm)相比于W结构(内径180 mm)更远,可能由于距离的延长造成冲击波自身的能量和强度衰减。另外,结构内部的低压区在逐渐减小,一方面是因为反射冲击波逐渐朝向环形屏障中心轴运动,另一方面是因为PU层被逐渐压实,空气与结构的接触界面随之转变为空气与压实的PU材料,即界面的阻抗不匹配程度有所提高,导致冲击波反射强度随之增加。与此同时,3种结构的绕射冲击波的辐射区域继续扩展。
起爆后0.7 ms:W和WP结构顶部的冲击波阵面已经到达观测点(G9),在中心轴处发生碰撞交汇的冲击波及爆炸产物相比于两侧的传播速度更快,并且结构外侧的绕射波与结构中部、底部对应的透射波发生交汇及相互作用。以G9~G13顶部观测点的高度作为参考,PW结构的冲击波阵面的竖直最高点与参考观测点仍有一定的距离,并且高压区相比于其他2种结构明显减小,位于中心轴两侧的爆炸产物的扩散速度高于中心轴区域。WP结构中的泡沫大部分变形失效,这是因为泡沫本身的拉伸失效应变十分有限(小于压缩失效应变的12%),无法承受内侧水膨胀引起的环向拉伸以及沿轴向的不均匀载荷引起的弯曲大变形[31],提前破坏失效,不利于泡沫对爆炸冲击能量的充分吸收;进而在结构外侧泄露了大量冲击波,这也是3.3节定量分析中WP结构对于外侧底部区域的削波效应较其他结构较弱的主要原因。另外与W结构类似,PW在结构1/2高度处也逐渐出现透射波并沿径向传播,如图9(c)所示。
结合特征时刻的压力云图,总结得到:爆炸冲击波主要经历了反射、绕射、透射及相互交汇等模式。比较W、WP与PW这3种结构,主要区别在于冲击波初始传播界面从空气/液体转变为空气/聚氨酯,由于阻抗不匹配程度的降低,界面反射的冲击波速度减小、强度降低,因而在中心轴处与对侧反射回来的冲击波发生汇聚的时刻推迟、相互作用形成的强度也会随之降低,造成冲击波阵面沿着远离地面的竖直方向获得的上升速度减小,延长了冲击波到达观测点之前与周围介质交换能量的时间。PW结构内侧的PU泡沫受到冲击波产生的压垮变形延迟了冲击波与液体的作用时刻,使得结构底端由于阻抗不匹配形成透射波的时刻较W、WP结构更晚、且强度更低;并且在整个分析过程中(0~0.7 ms),其外层的液体除底端变形外仍能保持初始形态。因而,综合冲击波削减性能和结构形态变化,PW屏障的防护能力更具有优势。
3.3 参数影响分析
以无屏障时的冲击波压力峰值作为参考标准,对防护结构的削波能力进行定量评估[10],首先定义无量纲超压峰值参数Mp,其为有防护和无防护时对应的压力峰值的比值:
Mp=pbpno\_b (1) 式中:pb、pno_b分别表示有防护和无屏障时的压力峰值。
定义无量纲测点位置参数MH、MS,对削爆屏障径向外侧、顶部不同位置的超压观测点进行描述:
MH=HGSG (2) MS=SGHG (3) 式中:HG为观测点距离地面的竖直距离,SG为观测点距离爆心的水平距离。
3.3.1 聚氨酯相对位置的影响
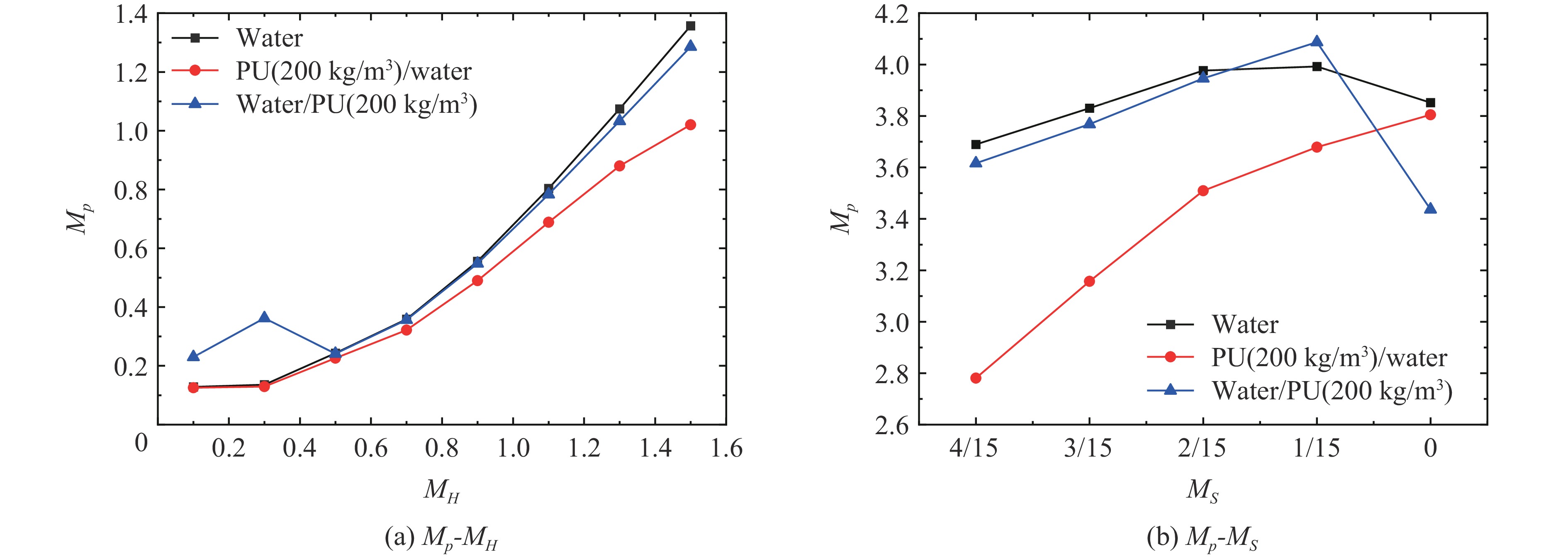
图10对比了纯液体W、PW和WP复合结构对应的Mp值,以确定聚氨酯的相对位置对屏障的冲击波削弱性能的影响;其中复合结构中采用的聚氨酯泡沫的密度均为200 kg/m3。基于无量纲的冲击波峰值参量MP在3种防护结构下随MH、MS的变化,可以得到:同体积条件下,PW结构比其他2种结构,对爆炸冲击波超压峰值的削弱效果更为明显;相比于W结构,PW结构(内侧PU密度为液体的1/5)在总体质量降低32.9%的条件下,其对超压峰值的削弱程度仍然高于W结构。与WP结构相比, PW结构的Mp随不同观测点的变化曲线更为平缓(除在MS趋近于0时PW对应Mp高于WP结构),定量说明了将聚氨酯泡沫放在内侧具有更好的冲击波削弱性能。另外,在侧向底部区域(MH=0.1~0.5),WP结构相比于其他2种结构出现了明显的压力提升、性能削弱的现象。需要注意的是,数值结果表明:3种结构对应的工况下,均存在较高位置的观测点对应的无量纲超压峰值Mp超过1的现象,即由于冲击波的绕射作用及遮蔽效应,与无削爆屏障时相比,削爆屏障对应的冲击波均在较高位置发生了明显的增强效应[32]。
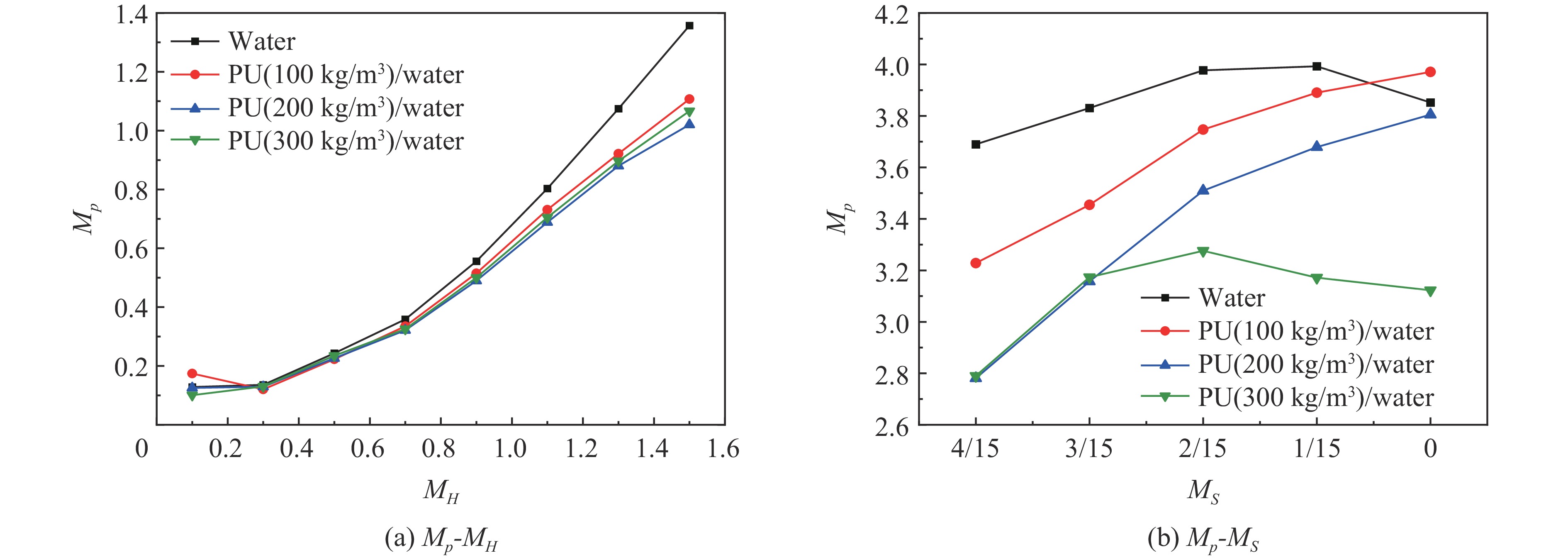
3.3.2 聚氨酯密度的影响
图11~12给出了不同密度(100、200和300 kg/m3)聚氨酯的PW、WP复合结构和W结构对应的Mp结果。如图11(a)所示,在MH<0.3时,PW复合结构对超压峰值的削弱性能与PU密度正相关,并且PU密度为200 kg/m3时与W结构达到相同的作用效果,将此作为PU与W结构防护能力相当的临界密度。在MH>0.3后,这种削弱性能与PU密度并不再成简单正相关的关系,整体上来看,密度200 kg/m3的PU/水结构对超压峰值削弱性能最为优异。图11(b)显示了屏障顶部的冲击波超压峰值结果,相比于W结构,3种不同密度PU对应的PW结构几乎均能够明显改善冲击波增强的状况;且PU密度越大,对冲击波增强效应的缓解效果更加明显。因而,兼顾防护屏障自重和削波性能,优选的PW结构采用密度约200 kg/m3的PU比较合适。
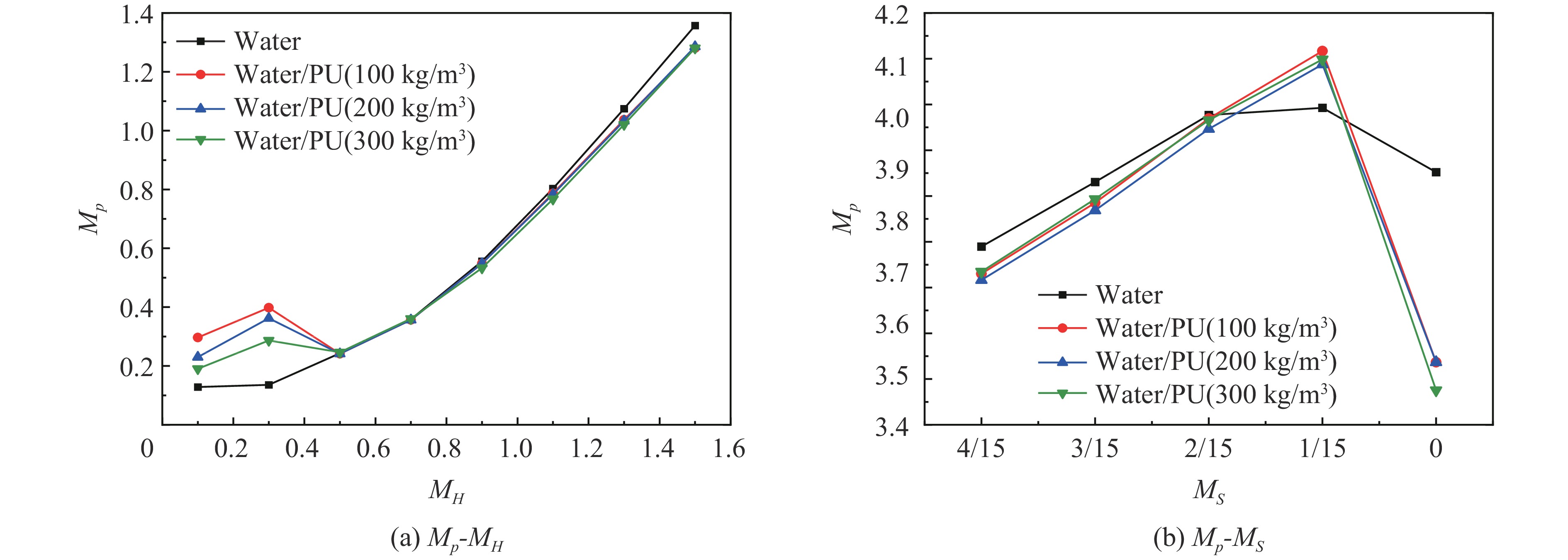
相比之下,将聚氨酯置于液体的外侧时(图12(a)~(b)),WP复合结构相比于相同体积下的纯液体(W结构)对冲击波削弱效果并不明显,在0.1
⩽ MH⩽ 0.5或者1/15⩽ MS⩽ 2/15时,水/PU的超压峰值甚至明显高于纯液体。另外,3种不同密度PU对应的WP结构在MH>0.5的区域内的Mp-MH、Mp-MS曲线几乎重合,即改变PU的密度对于水/PU结构的削波能力并无明显的影响。4. 结 论
本文中以安全处置简易爆炸装置的设计为研究背景,利用定向冲击波流场装置对聚氨酯泡沫平板进行爆炸加载实验;随后沿用已验证的流固耦合方法对环形复合结构在内爆炸冲击波作用下的响应进行模拟,分析了相对位置、聚氨酯密度对复合结构的冲击波削弱性能的影响,主要结论如下。
(1) 在聚氨酯泡沫密度和厚度的研究范围内,聚氨酯平板对爆炸冲击波压力峰值的衰减率均在67%以上,密度和厚度与削波能力呈现正相关,其中密度较厚度的提升对冲击波削弱能力的增益更大。
(2) 对于聚氨酯基复合削爆屏障,PU/水复合环形屏障(聚氨酯泡沫放置于结构内侧)优于水/PU结构,且与同体积的纯水结构相比,PU/水结构在总体质量降低32%的前提下,依然具有更优异的冲击波超压峰值削弱性能。
(3) 聚氨酯泡沫密度对水/PU复合环形屏障的冲击波削弱性能的影响不明显。相比之下,聚氨酯泡沫密度对PU/水结构的冲击波削弱性能影响较为明显;兼顾防护屏障自重和削波性能,优选的PU/水结构采用密度200 kg/m3的PU较为合适。
通过材料排序、密度择优等优化设计提出的复合柔性削爆屏障(如PU/水)对内爆炸载荷的削波效应有明显增益。在对简易爆炸物处置、弹药的隔爆与销毁中,这种复合结构可以发挥其自重轻、削波效能高且无二次杀伤的优势。
-
表 1 冲击波超压对有生力量的破坏作用阈值[19]
Table 1. Threshold value of destructive effect ofshockwave overpressure on effectives[19]
等级 超压峰值范围/MPa 破坏作用 Ⅰ < 0.02 没有杀伤作用 Ⅱ 0.02~0.03 轻伤(轻微的挫伤) Ⅲ 0.03~0.05 中等损伤(听觉器官损伤、
中等挫伤、骨折等)Ⅳ 0.05~0.10 重伤、甚至死亡(内脏严重挫伤) Ⅴ > 0.10 大部分死亡 表 2 泡沫材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters for PU foams
密度/(kg·m−3) 体积模量/MPa 剪切模量/MPa 最大拉伸应力/MPa 泊松比 100 5.53 8.30 0.69 0.12 200 11.27 16.90 2.77 0.13 300 37.35 56.02 3.64 0.18 表 3 实验与数值模拟的靶后压力峰值及对比
Table 3. Comparison between experimental and numerical simulation on peak pressure behind target
工况 靶后压力峰值/kPa 衰减率/% 实验 数值模拟 相对误差/% 实验 数值模拟 相对误差/% 0-0 524 560 6.9 0 0 0 100-40 172 191 11.1 67.2 65.9 1.9 200-60 123 126 2.4 76.5 77.5 1.0 300-20 126 129 2.4 75.9 76.9 1.3 300-60 109 113 3.7 79.2 79.8 0.8 表 4 数值模型中不同防护结构的几何参数
Table 4. Geometrical parameters of different protective structures in the numerical model
屏障名称 壁厚
A1/mm壁厚
A2/mm迎爆面内圆
半径R/mm屏障高度
H/mm水 0 100 90 310 PU/水 50 50 90 310 水/PU 50 50 90 310 -
[1] 毛益明, 方秦, 张亚栋, 等. 水体与混凝土防爆墙消波减爆作用对比研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(S2): 84–89.MAO Y M, FANG Q, ZHANG Y D, et al. Comparison investigation on mitigation effect of water and concrete explosion proof walls [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(S2): 84–89. [2] ZHU W H, XUE H L, ZHOU G Q, et al. Dynamic response of cylindrical explosive chambers to internal blast loading produced by a concentrated charge [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(9): 831–845. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)00022-5. [3] DOUGLAS K, ANDREW A, KATHERINE H, et al. A comparison of the blast & fragment mitigation performance of several structurally weak materials [C]// AIP Conference Proceedings 2007. Waikoloa: American Institute of Physics, 2007, 955(1): 951–954. DOI: 10.1063/1.2833286. [4] 宁建国, 王仲琦, 赵衡阳, 等. 爆炸冲击波绕流的数值模拟研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 1999, 19(5): 543–547. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.1999.05.003.NING J G, WANG Z Q, ZHAO H Y, et al. Study on the flow of the explosive shock wave around the wall numerical simulation [J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 1999, 19(5): 543–547. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.1999.05.003. [5] SHEN Y L, NING J G. Numberical simulation of the 2-d explosion field for the effect of protective wall’s shape [J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (English Edition), 2001(1): 39–44. [6] GELFAND B E, SILNIKOV M V, CHERNYSHOV M V. Modification of air blast loading transmission by foams and high density materials[C]// HANNEMANN K, SEILER F. In Proceeding of the 26th International Symposium on Shock Waves. Germany: Springer, 2007: 103–108. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-85168-4_15. [7] BAILEY J L, LINDSAY M S, SCHWER D A, et al. Blast mitigation using water mist: NRL/MR/6180-06-8933 [R]. Washington DC: Naval Research Laboratory, 2006. [8] BORNSTEIN H, PHILLIPS P, ANDERSON C. Evaluation of the blast mitigating effects of fluid containers [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 75: 222–228. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.08.014. [9] ZHAO H Z, LAN K Y, CHONG O Y . Water mitigation effects on the detonations in confined chamber and tunnel system [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2001, 8(6): 349–355. DOI: 10.1155/2001/124019. [10] ZHU W, HUANG G Y, LIU C M, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of a hollow cylindrical water barrier against internal blast loading [J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 172: 789–806. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.06.062. [11] 蔡军锋, 傅孝忠, 易建政. 超高分子量聚乙烯-聚氨酯泡沫复合材料的抗爆实验与数值模拟 [J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2013, 29(11): 79–83. DOI: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.2013.11.019.CAI J F, FU X Z, YI J Z. Anti-explosion experiment and numerical simulation of UHMWPE-PUF composite [J]. Analysis of Polymers Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2013, 29(11): 79–83. DOI: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.2013.11.019. [12] 石少卿, 张湘冀, 刘颖芳, 等. 硬质聚氨酯泡沫塑料抗爆炸冲击作用的研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2005, 24(5): 56–59. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2005.05.017.SHI S Q, ZHANG X Y, LIU Y F, et al. Studies on the properties of anti-detonation and anti-penetration of rigid polyurethane foam [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2005, 24(5): 56–59. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2005.05.017. [13] 王海福, 冯顺山. 爆炸载荷下聚氨酯泡沫材料中冲击波压力特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1999, 19(1): 78–83.WANG H F, FENG S S. Properties of shock pressure caused by explosion loads in polyurethane foam [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1999, 19(1): 78–83. [14] 陈网桦, 彭金华, 葛桂兰, 等. 聚氨酯泡沫塑料抗冲击性能的实验研究 [J]. 弹道学报, 1997(4): 88–92.CHEN W H, PENG J H, GE G L, et al. The experimental investigation of the shock-resistant properties of polyurethane foam plastics [J]. Journal of Ballistics, 1997(4): 88–92. [15] 卢子兴, 袁应龙. 高应变率加载下复合泡沫塑料的吸能特性及失效机理研究 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2002, 19(5): 114–117. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2002.05.022.LU Z X, YUAN Y L. Investigation into the energy absorption and failure characteristics of syntactic foams at high strain rates [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2002, 19(5): 114–117. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2002.05.022. [16] ZHOU T Y, ZHANG P, XIAO W, et al. Experimental investigation on the performance of PVC foam core sandwich panels under air blast loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 226: 111081. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111081. [17] 曾祥, 刘彦, 许泽建, 等. 爆炸载荷作用下玻璃钢/硬质聚氨酯泡沫夹层结构抗冲击性能实验研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2021, 41(11): 1145–1153. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.036.ZENG X, LIU Y, XU Z J, et al. Experimental study on impact resistance of glass fiber reinforced plastic/rigid polyurethane foam sandwich structures under air blast loading [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(11): 1145–1153. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2021.036. [18] 张勇. 聚氨酯泡沫铝复合结构抗爆吸能试验及数值模拟分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(4): 045101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0182.ZHANG Y. Testing the antiknock energy absorption of polyurethane foam aluminum composite structure and numerical simulation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(4): 045101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0182. [19] 李剑. 爆炸与防护 [M]. 第1版. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2014: 258. [20] 闫伟杰. 水下爆炸数值模拟研究 [D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2007: 17–21. [21] CHEN L, ZHANG L, FANG Q, et al. Performance based investigation on the construction of anti-blast water wall [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 81: 17–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.03.003. [22] 年鑫哲, 严东晋, 张耀, 等. 水体防爆墙和混凝土防爆墙对爆炸冲击波的消减效应 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(18): 214–220. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2014.18.035.NIAN X Z, YAN D J, ZHANG Y, et al. Mitigation effects of explosion-proof water walls and explosion-proof concrete walls on blast shock wave [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(18): 214–220. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2014.18.035. [23] CHENG Y, ZHOU T, WANG H, et al. Numerical investigation on the dynamic response of foam-filled corrugated core sandwich panels subjected to air blast loading [J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures and Materials, 2019, 21(3): 838–864. DOI: 10.1177/1099636217700350. [24] 王宇新, 顾元宪, 孙明, 等. 冲击载荷作用下多孔材料复合结构防爆理论计算 [J]. 兵工学报, 2006, 27(2): 375–379. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2006.02.042.WANG Y X, GU Y X, SUN M, et al. Blast-resistant calculation of compound structure with porous material under impact load [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2006, 27(2): 375–379. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2006.02.042. [25] 宋博, 胡时胜, 王礼立. 分层材料的不同排列次序对透射冲击波强度的影响 [J]. 兵工学报, 2000, 21(3): 272–274. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2000.03.021.SONG B, HU S S, WANG L L. Influence on the transmitted intensity of shock wave through different tactic orders of layered materials [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2000, 21(3): 272–274. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2000.03.021. [26] 刘秀, 刘国胜, 郝建薇, 等. 阻燃硬质聚氨酯泡沫燃烧热值对阻燃性能的影响 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2015, 35(2): 197–202. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.02.017.LIU X, LIU G S, HAO J W, et al. Effect of heat of combustion on flame retardancy of rigid polyurethane foams [J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(2): 197–202. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.02.017. [27] RESNYANSKY A, DELANEY T. Experimental study of blast mitigation in a water mist: DSTO technical report: DSTO-TR-1944 [R]. Australia: Defence Science and Technology Organisation Weapons Systems Division, 2006. [28] 洪武, 徐迎, 金丰年. 水体防爆机理研究进展 [J]. 防护工程, 2011, 33(3): 73–78.HONG W, XU Y, JIN F N. Development of blast-resistant water walls [J]. Protective Engineering, 2011, 33(3): 73–78. [29] CHAPMAN T C, ROSE T A, SMITH P D. Blast wave simulation using AUTODYN 2D: a parametric study [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1995, 16(5): 777–787. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00012-Y. [30] CHENG M, HUNG K C, CHONG O Y. Numerical study of water mitigation effects on blast wave [J]. Shock Waves, 2005, 14(3): 217–223. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-005-0267-4. [31] YANG Y F, HE J M. Mechanical characterization of phenolic foams modified by short glass fibers and polyurethane prepolymer [J]. Polym Composite, 2015, 36(9): 1584–1589. DOI: 10.1002/pc.23066. [32] JIN M, HAO Y F, HAO H. Numerical study of fence type blast walls for blast load mitigation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 131: 238–255. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.007. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 曾浩,袁鹏程,杨婷,徐慎春,吴成清. 地聚物超高性能混凝土复合板抗接触爆炸试验与数值模拟. 爆炸与冲击. 2024(06): 105-121 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 胡俊华,董奇,胡八一,任逸飞,黄广炎. 抗爆容器的内部爆炸效应和动态力学行为研究进展. 含能材料. 2024(09): 986-1008 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-








 下载:
下载:























 下载:
下载:











 百度学术
百度学术