Prediction of blast loads on bridge girders based on PCA-BPNN
-
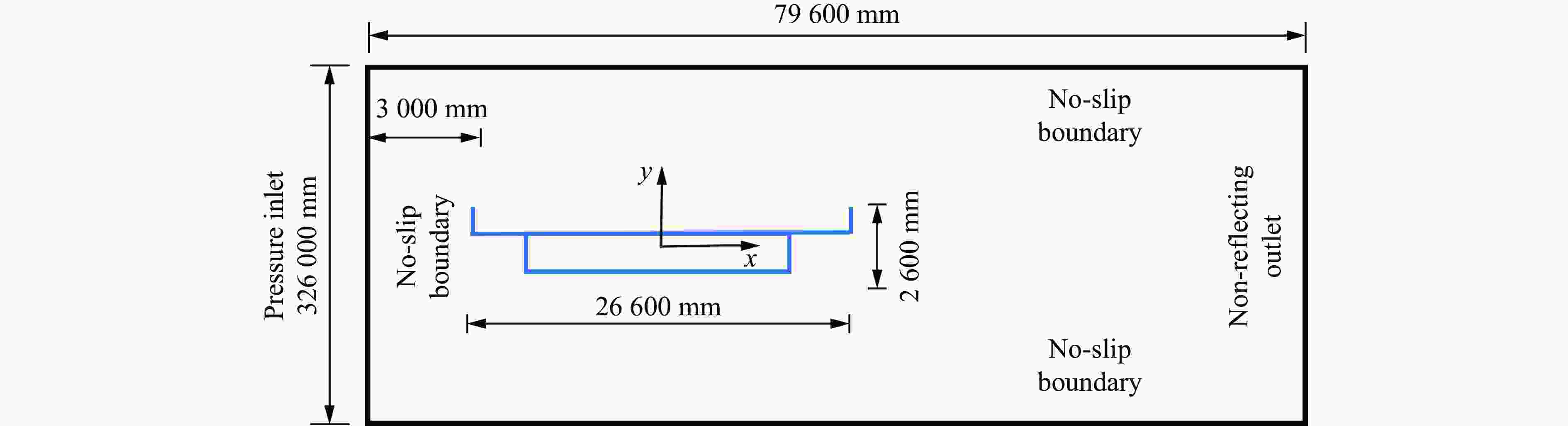
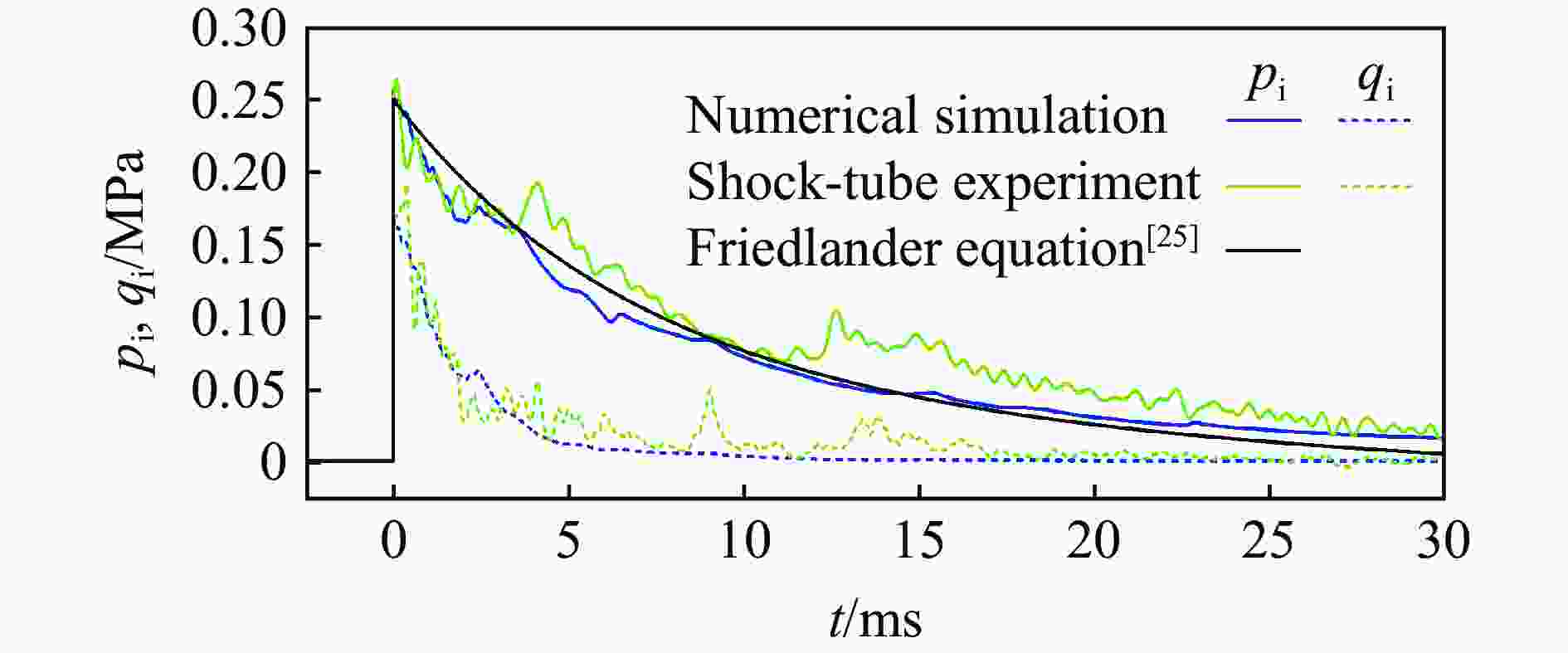
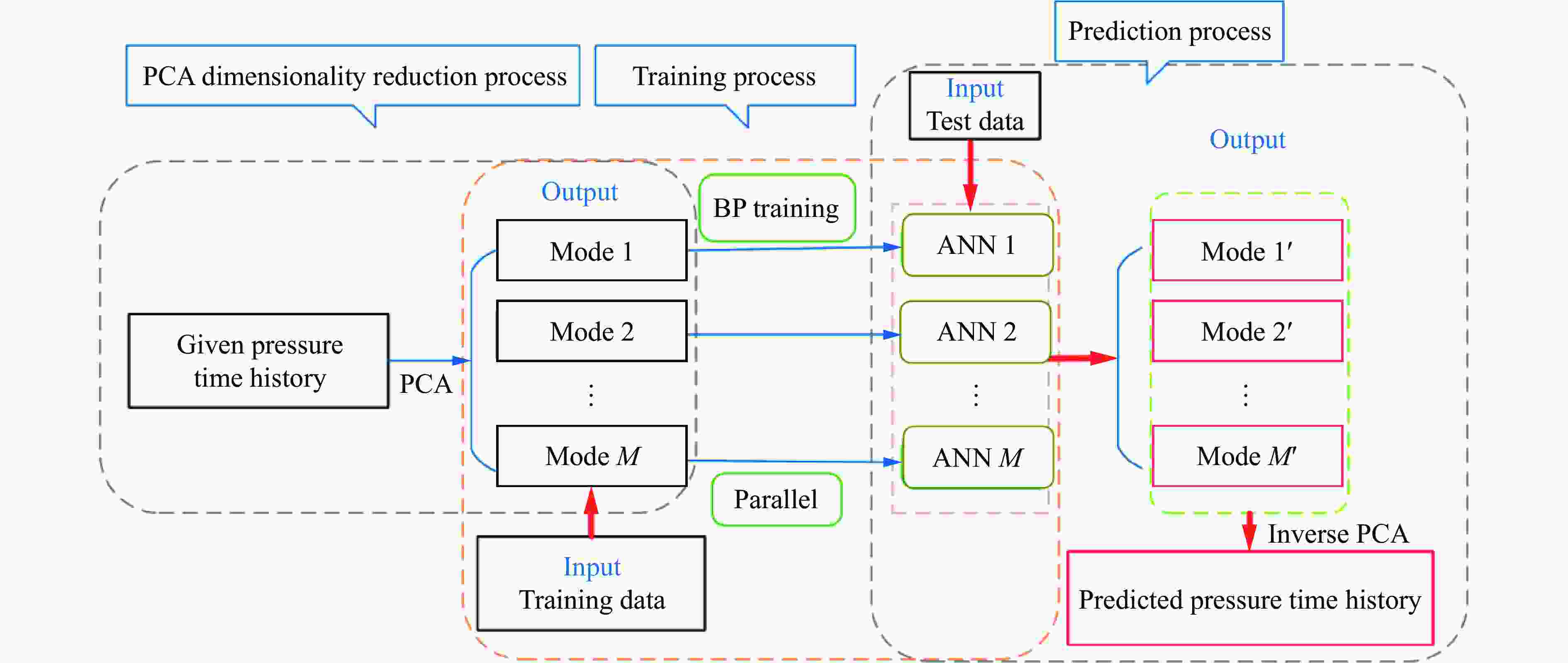
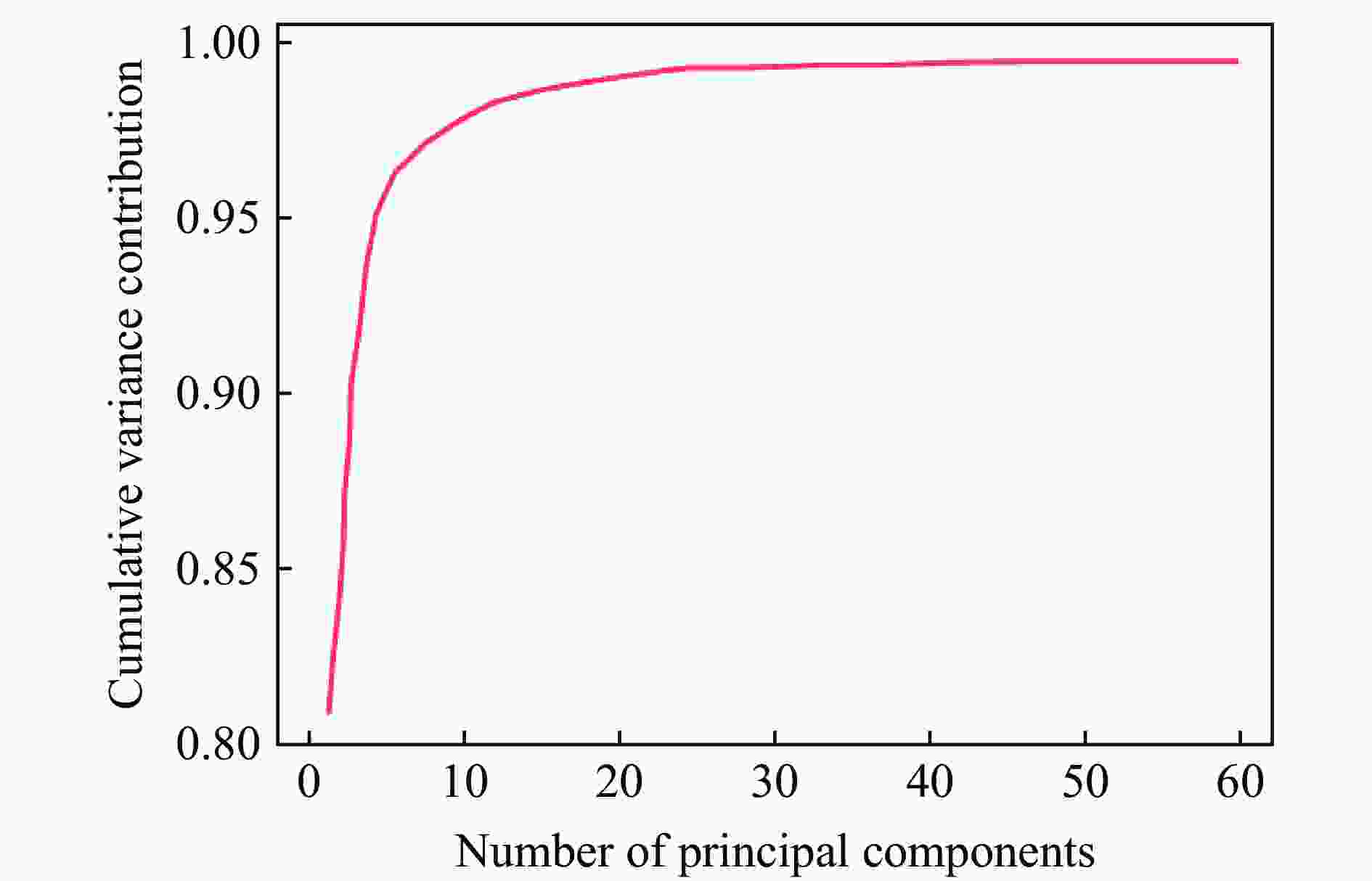
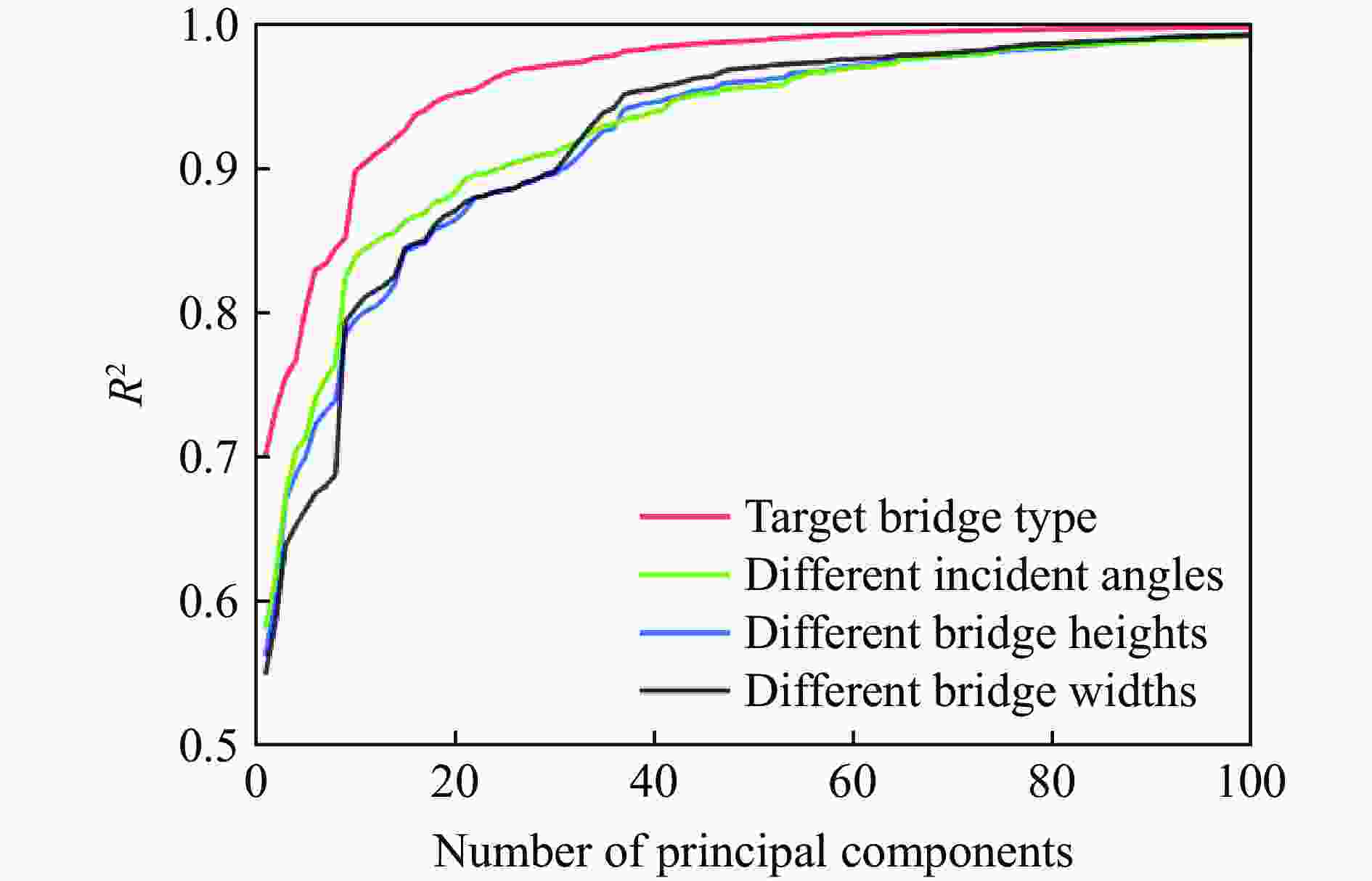
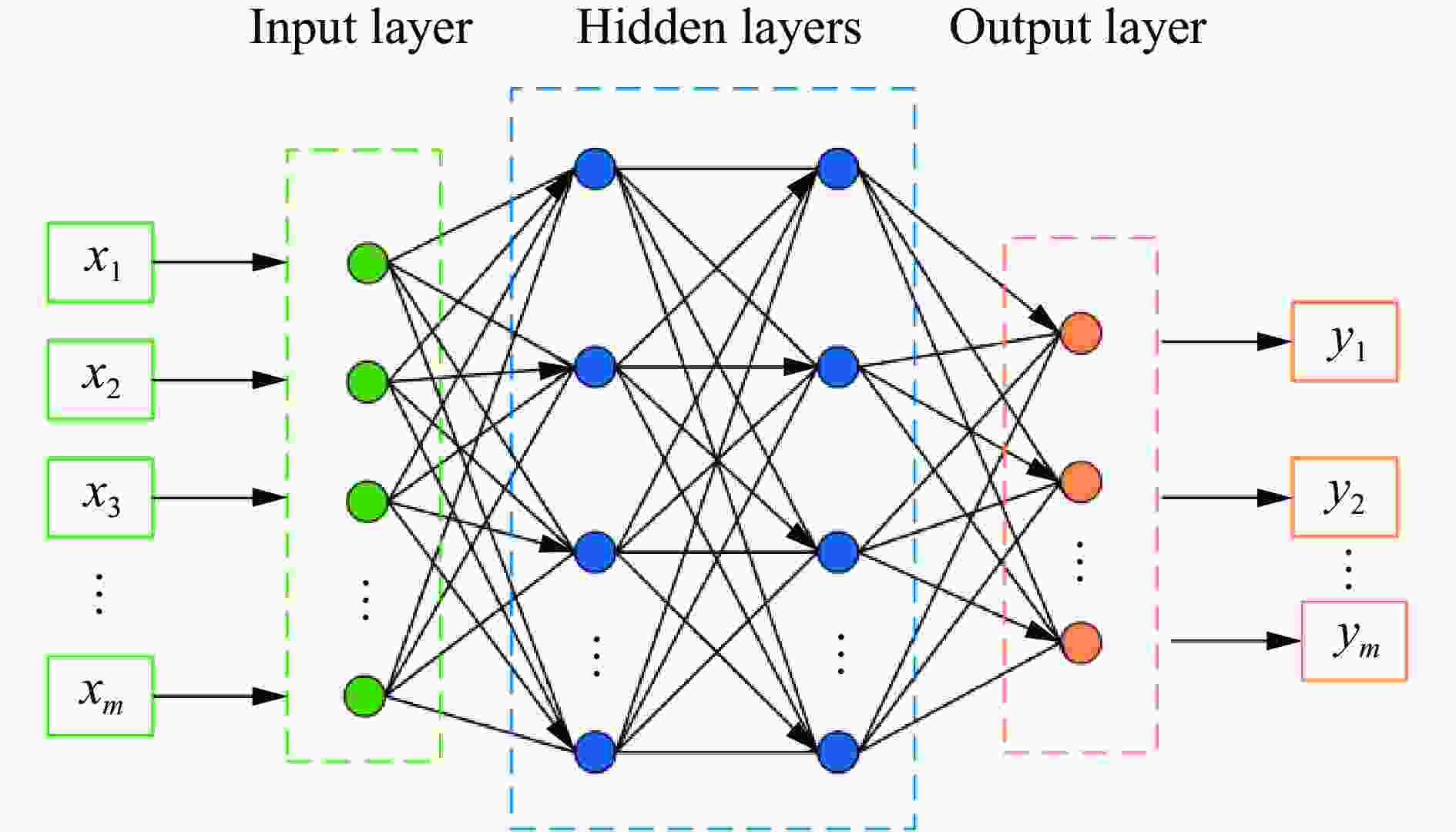
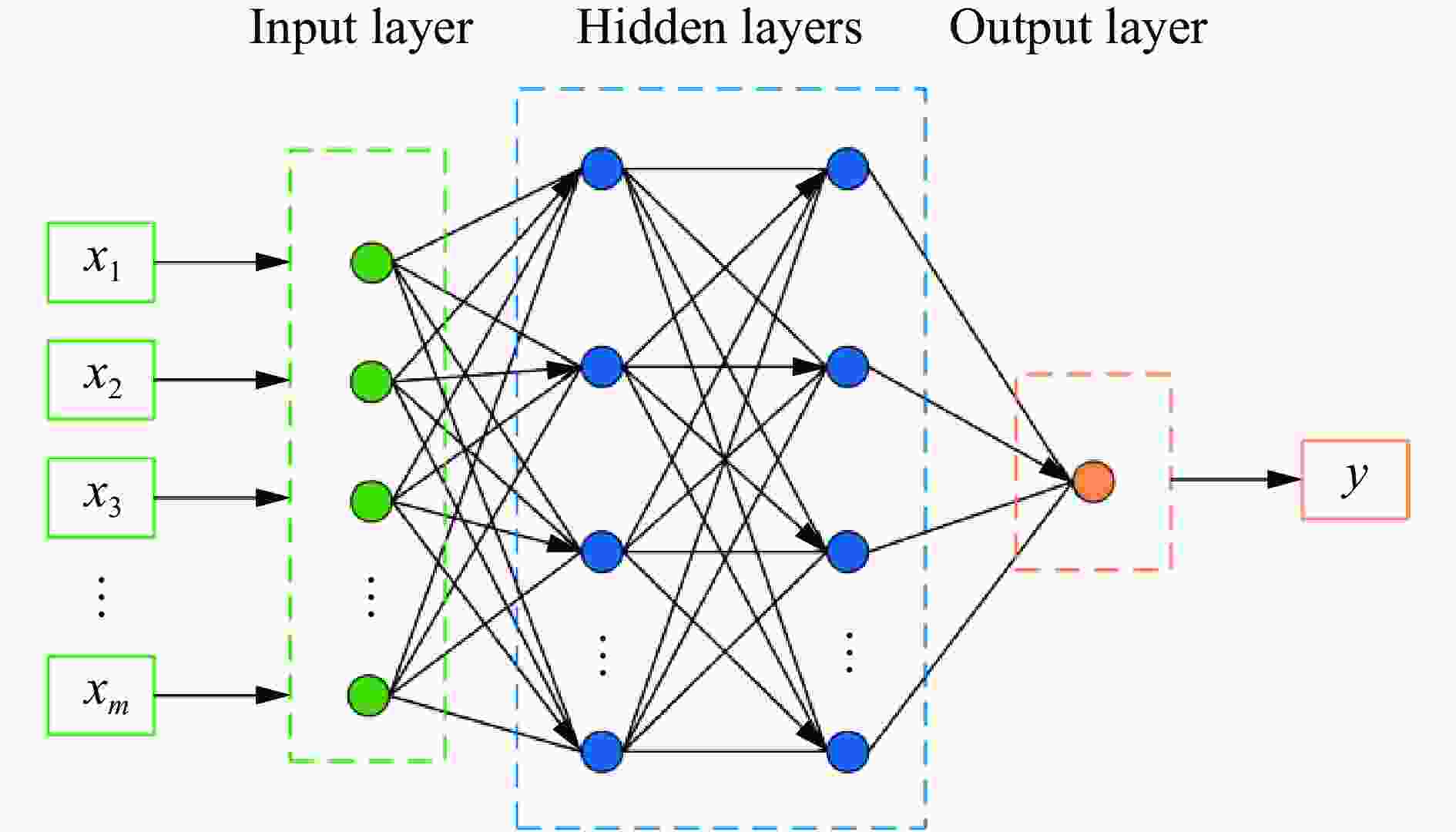
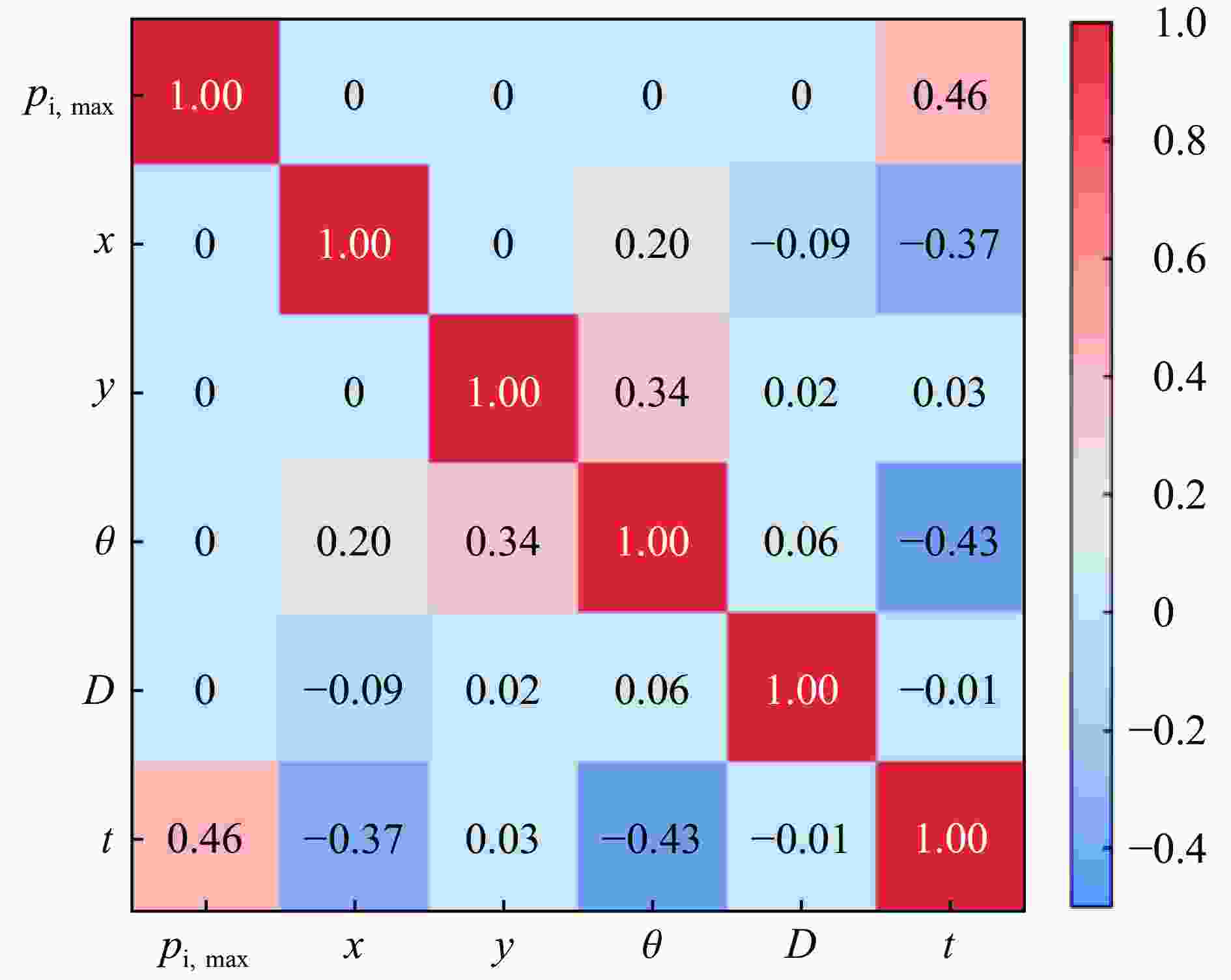
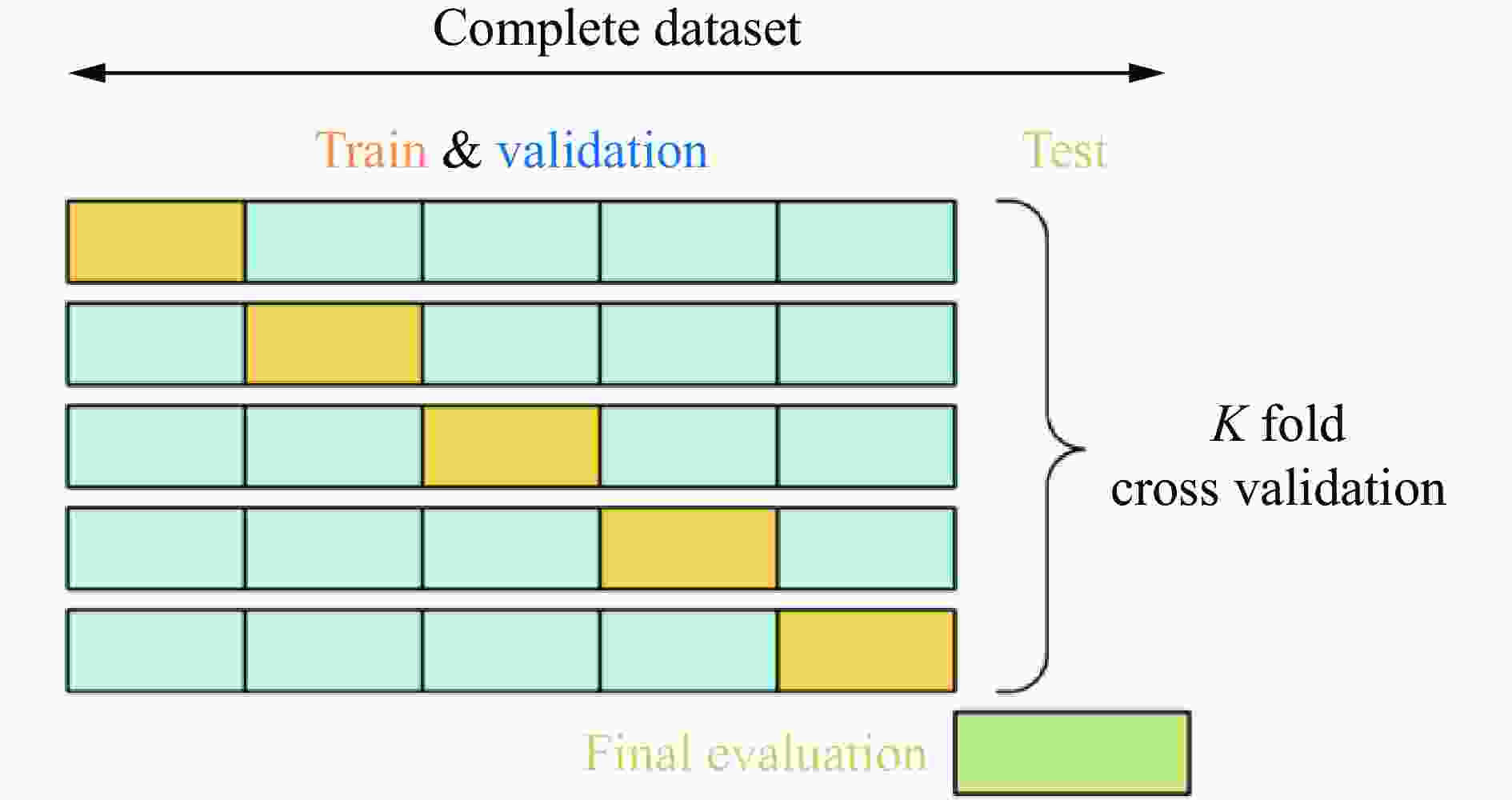
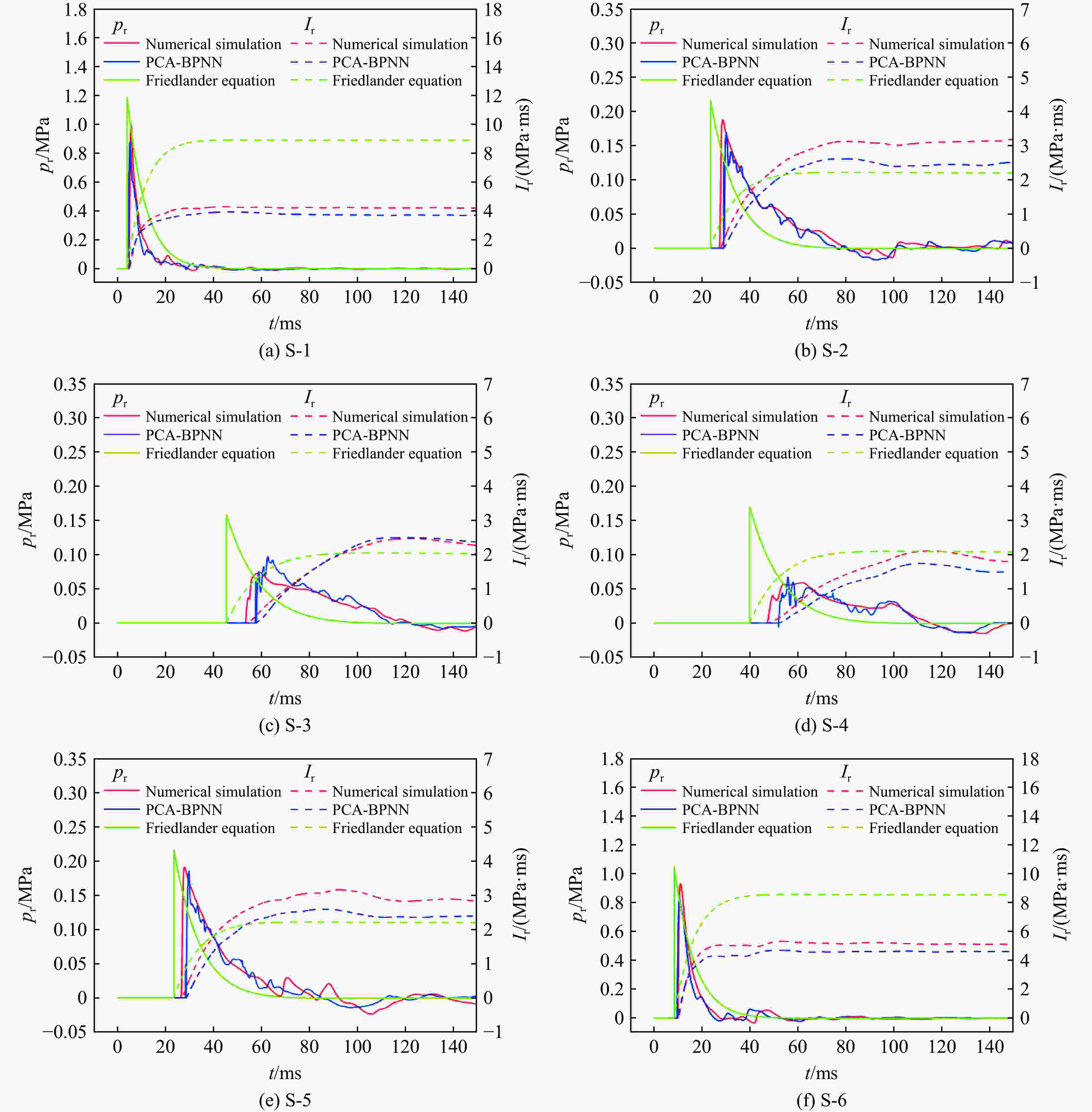
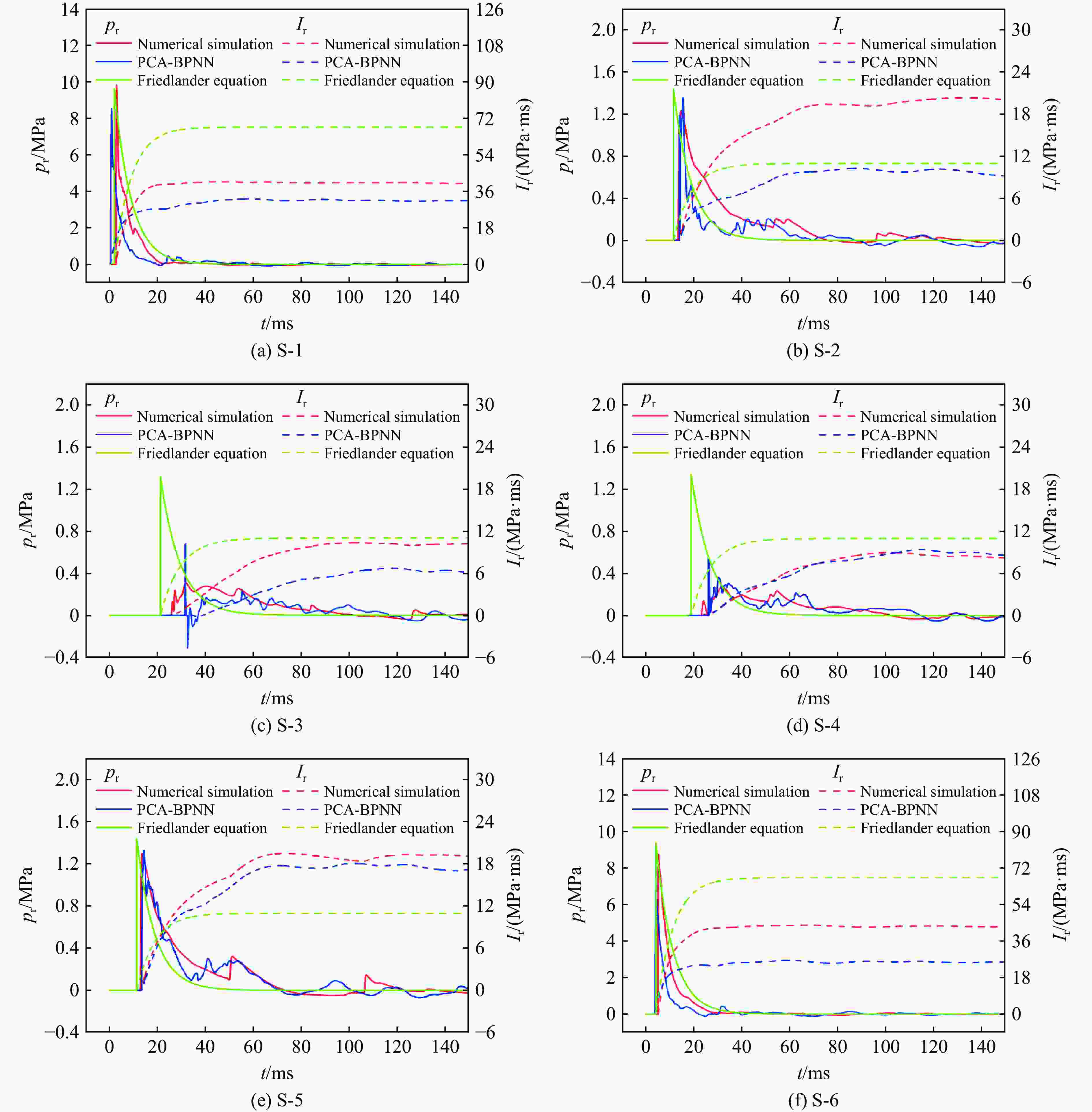
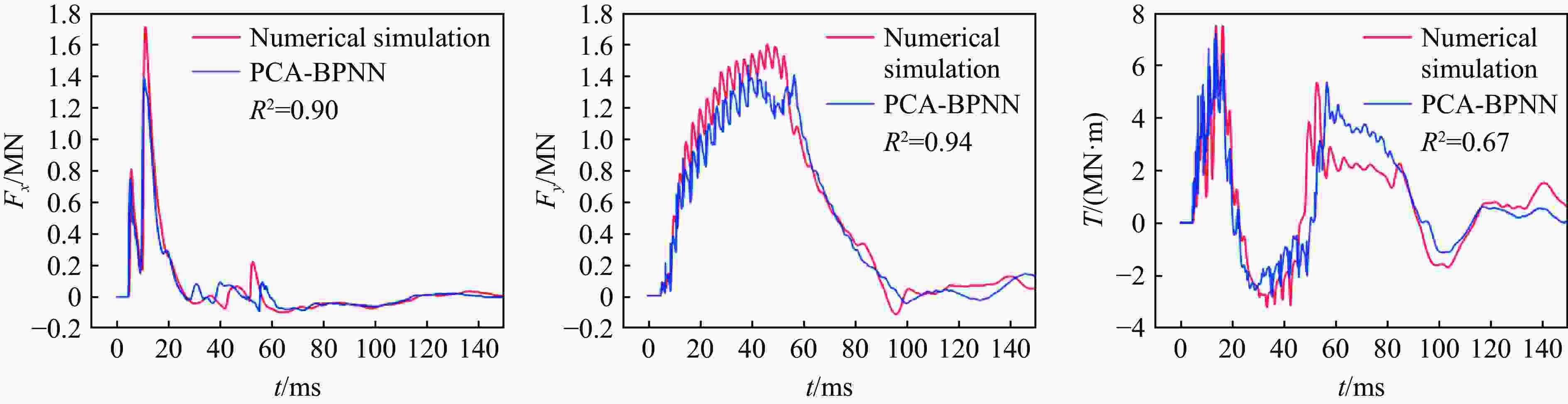
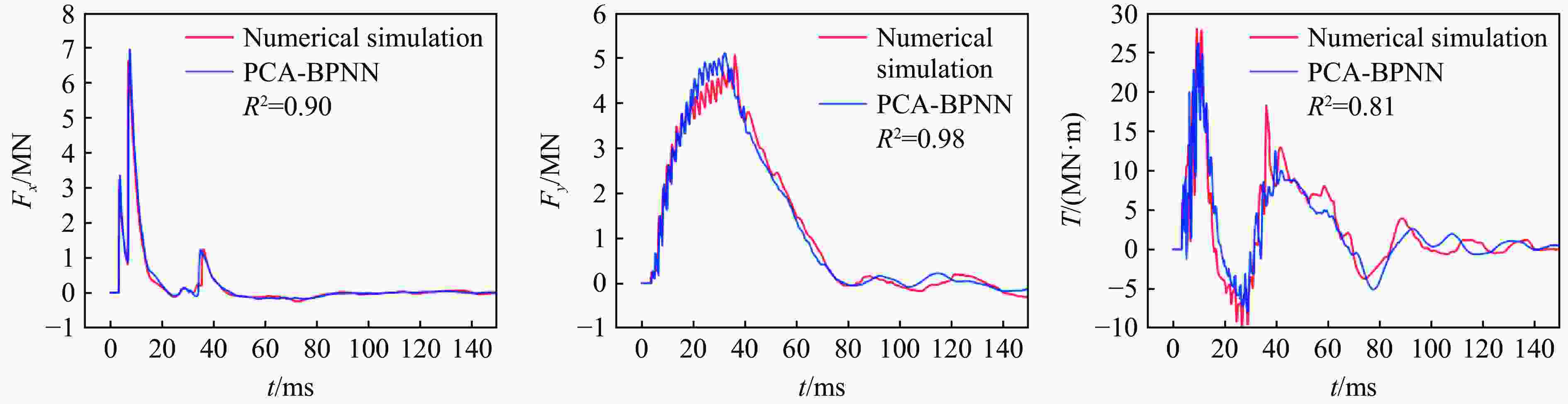
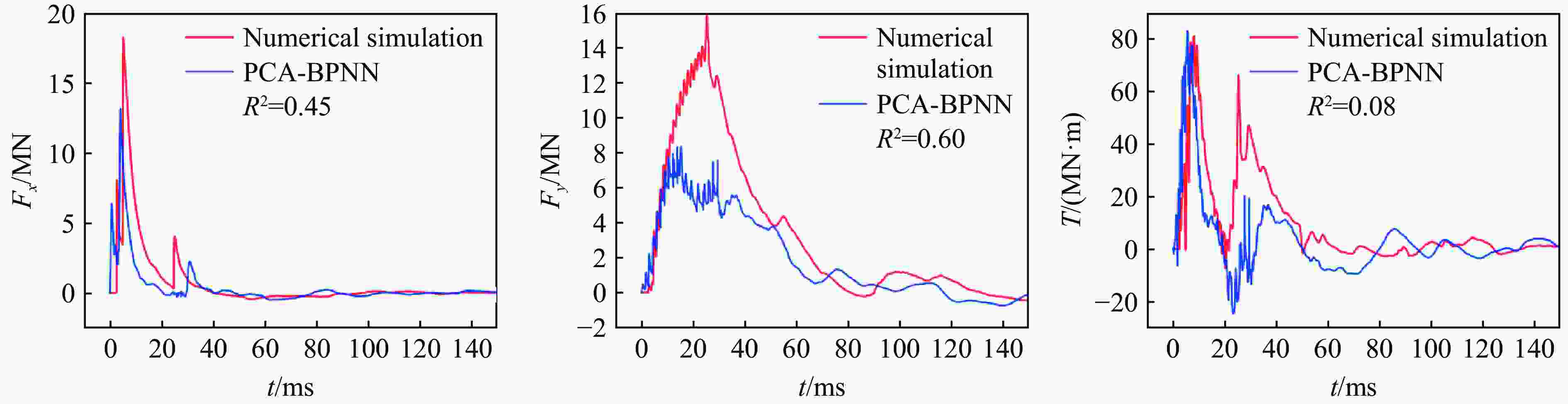
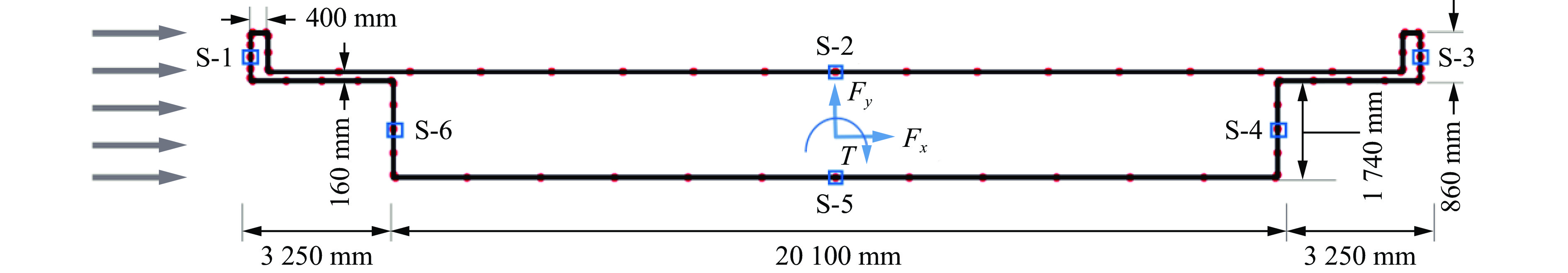
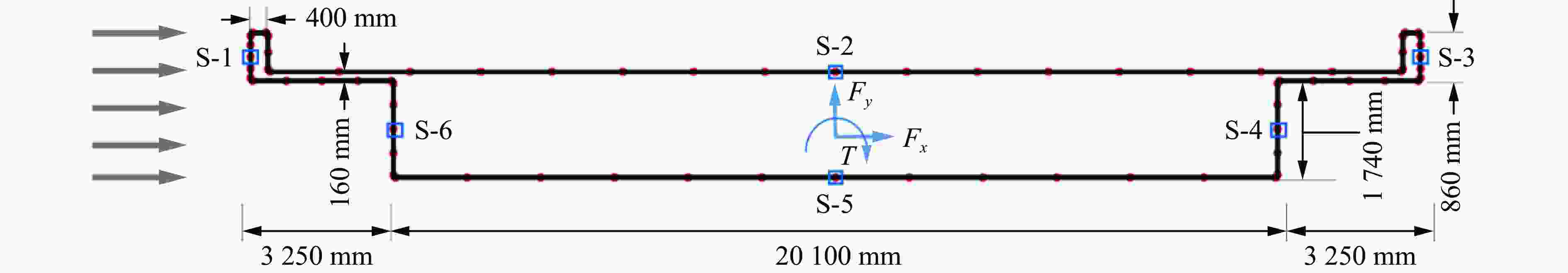
摘要: 人工智能方法是预测爆炸荷载的新手段,但现有方法主要用于预测爆炸冲击波的超压峰值或冲量,而用于预测反射超压时程的研究不多。针对这一问题,以平面冲击波绕射桥梁主梁为对象,提出了一种基于主成分分析(principal components analysis, PCA)和误差反向传播神经网络(backpropagation neural network, BPNN)的桥梁爆炸冲击波反射超压时程预测模型。该预测模型利用PCA降维处理时程数据,基于多任务学习的BPNN算法,提出了考虑超压峰值和冲量峰值影响的损失函数,使模型能有效预测不同入射超压下的桥梁冲击波荷载时程。通过分析多任务学习模型、多输入单输出模型和多输入多输出模型等3种BPNN模型,发现多任务学习模型的预测精度最高,而多输入多输出模型难以有效适应当前预测任务需求。采用多任务学习模型预测得到的桥梁表面各测点位置的反射超压时程、超压峰值精度较高,决定系数R2分别为0.792和0.987,作用在箱梁上的合力时程和扭矩时程预测值也与数值模拟值较为吻合。同时,该模型对内插值预测的表现优于外推值预测,但其在预测外推值方面同样展现出了一定的能力。
-
关键词:
- 爆炸荷载预测 /
- 反射超压时程 /
- 误差反向传播神经网络 /
- 主成分分析 /
- 多任务学习
Abstract: Facing the challenges on the accurate and effective prediction under extreme loads, machine learning has gradually demonstrated its potential to replace traditional methods. Existing approaches primarily focus on predicting the peak overpressure or impulse of explosive shock waves, with limited research on predicting the reflected overpressure time history. Load-time history prediction encompasses not only the peak overpressure but also embraces various multi-dimensional information including duration, waveform, and impulse, thereby offering a more comprehensive depiction of the dynamic temporal and spatial characteristics of shock waves. To address this issue, a prediction model for bridge surface reflected overpressure time history is proposed, targeting a planar shock wave diffracting around a bridge section. This model is based on principal component analysis (PCA) and back propagation neural network (BPNN) algorithm with multi-task learning. A loss function considering the impact of peak overpressure and maximum impulse is introduced to fully consider the potential correlations between different modes after PCA dimension reduction. This enables the model to effectively predict bridge shock wave load time histories under varying incident overpressure. Through the analysis of three types of BPNN models, multi-task learning model, multi-input single-output model, and multi-input multi-output model. It was found that the multitask learning model has the highest prediction accuracy, while the multi-input multi-output model struggles to effectively adapt to the current predictive task requirements. The multitask learning model, used for predicting, achieves high precision in forecasting the time history of reflected overpressure at various measurement points on the bridge surface and the peak overpressure values, with R2 values of 0.792 and 0.987. It also closely matches the simulation values in predicting the time history of combined forces and torque acting on the box girder. Additionally, this model performs better in interpolative value prediction than in extrapolative value prediction, but it also demonstrates a certain capability in predicting extrapolative values. -
表 1 超压峰值的各模型预测评价指标
Table 1. Evaluation metrics for peak overpressure prediction models
预测模型 RMSE MAE MAPE R2 多输出模型 1.089 0.788 3.105 −0.386 单输出模型 0.152 0.092 0.220 0.976 多任务模型 0.115 0.074 0.180 0.987 表 2 冲量峰值的各模型预测评价指标
Table 2. Evaluation metrics for peak impulse prediction models
预测模型 RMSE MAE MAPE R2 多输出模型 3.970 2.822 0.554 −0.403 单输出模型 0.866 0.646 0.133 0.934 多任务模型 0.693 0.542 0.109 0.958 表 3 超压时程曲线的各模型预测评价指标
Table 3. Evaluation metrics of overpressure time-history prediction models
预测模型 RMSE MAE MAPE R2 多输出模型 0.173 0.068 − −5.466 单输出模型 0.069 0.015 − 0.753 多任务模型 0.065 0.014 − 0.792 表 4 模型预测误差及经验公式计算误差对比
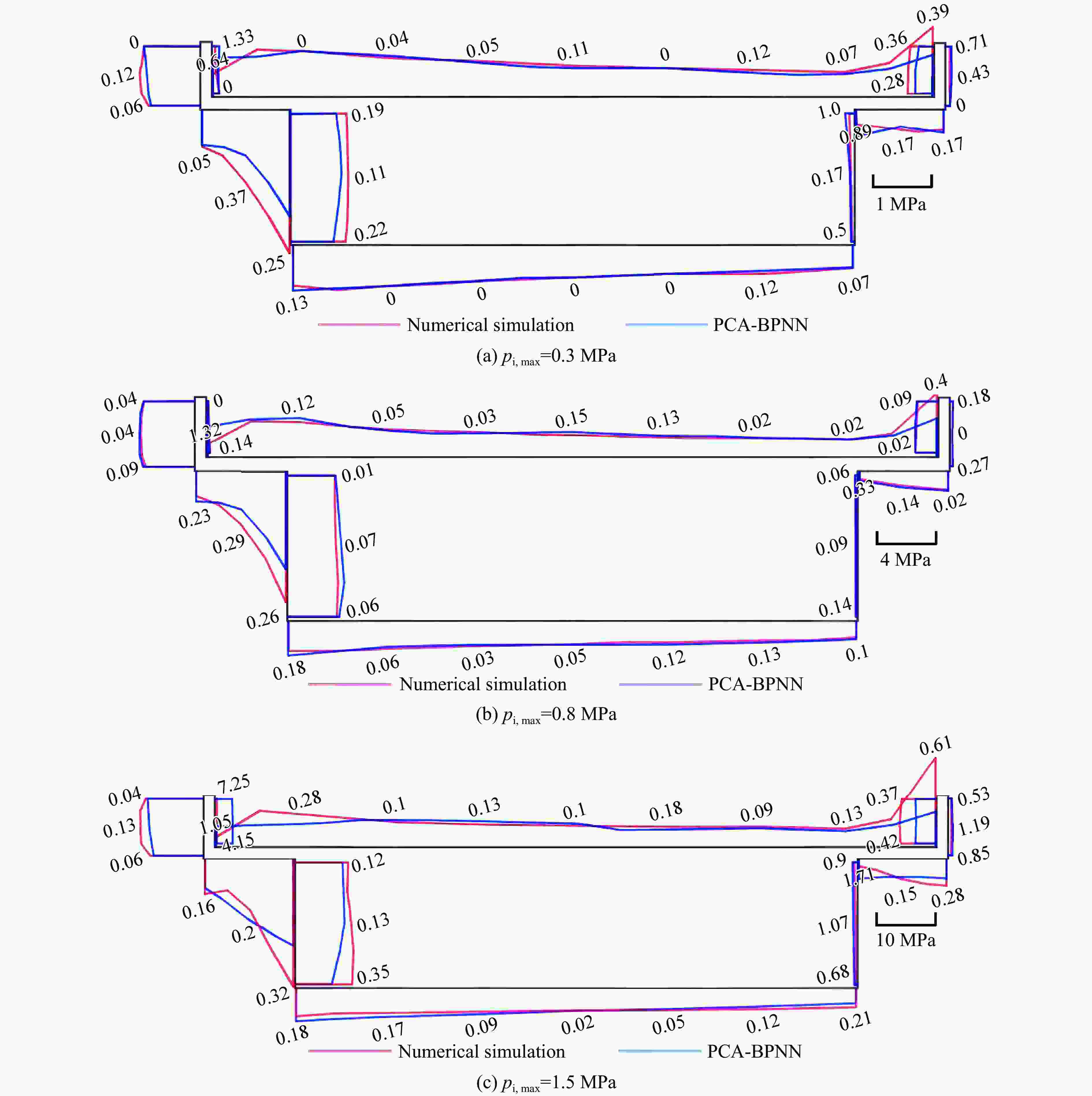
Table 4. Comparison of model prediction error and empirical formula calculation error
方法 pi,max=0.3 MPa pi,max=0.8 MPa pi,max=1.5 MPa 超压时程的R2 最大冲量的MAPE 超压时程的R2 最大冲量的MAPE 超压时程的R2 最大冲量的MAPE PCA-BPNN 0.81 0.124 0.92 0.052 0.46 0.262 经验公式 −0.33 0.410 −2.05 0.573 −1.42 0.396 -
[1] CLUBLEY S K. Non-linear long duration blast loading of cylindrical shell structures [J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 59: 113–126. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2013.10.030. [2] DENNY J W, CLUBLEY S K. Long-duration blast loading & response of steel column sections at different angles of incidence [J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 178: 331–342. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.10.019. [3] JIANG Y X, ZHANG B Y, WANG L, et al. Dynamic response of polyurea coated thin steel storage tank to long duration blast loadings [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 163: 107747. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2021.107747. [4] SAKURAI A. Blast wave theory [M]. Mathematics Research Center, United States Army, University of Wisconsin, 1964. [5] RIGBY S E, AKINTARO O I, FULLER B J, et al. Predicting the response of plates subjected to near-field explosions using an energy equivalent impulse [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 128(1): 24–36. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.01.014. [6] KINGERY C N, BULMASH G. Airblast parameters from TNT spherical air burst and hemispherical surface burst [R]. US Army Armament and Development Center, Ballistic Research Laboratory, 1984. [7] RIGBY S E, TYAS A, FAY S D, et al. Validation of semiempirical blast pressure predictions for far field explosions: is there inherent variability in blast wave parameters? [C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Protection of Structures Against Hazards. Sheffield, 2014. [8] LARCHER M, CASADEI F. Explosions in complex geometries: a comparison of several approaches [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2010, 1(2): 169–195. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.1.2.169. [9] DENNIS A A, PANNELL J J, SMYL D J, et al. Prediction of blast loading in an internal environment using artificial neural networks [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2021, 12(3): 287–314. DOI: 10.1177/2041419620970570. [10] HANSEN O R, HINZE P, ENGEL D, et al. Using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) for blast wave predictions [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2010, 23(6): 885–906. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2010.07.005. [11] REMENNIKOV A M, ROSE T A. Modelling blast loads on buildings in complex city geometries [J]. Computers & Structures, 2005, 83(27): 2197–2205. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2005.04.003. [12] SOHAIMI A S M, RISBY M S. Using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) for blast wave propagation under structure [J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 80: 1202–1211. DOI: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.05.463. [13] HASTIE T, TIBSHIRANI R, FRIEDMAN J H, et al. The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction [M]. New York: Springer, 2009. [14] FLOOD I, BEWICK B T, DINAN R J, et al. Modeling blast wave propagation using artificial neural network methods [J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2009, 23(4): 418–423. DOI: 10.1016/j.aei.2009.06.005. [15] REMENNIKOV A M, ROSE T A. Predicting the effectiveness of blast wall barriers using neural networks [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(12): 1907–1923. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.11.003. [16] BEWICK B, FLOOD I, CHEN Z. A neural-network model-based engineering tool for blast wall protection of structures [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2011, 2(2): 159–176. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.2.2.159. [17] ALSHAMMARI O G, ISAAC O S, CLARKE S D, et al. Mitigation of blast loading through blast-obstacle interaction [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2023, 14(3): 357–389. DOI: 10.1177/20414196221115869. [18] PANNELL J J, RIGBY S E, PANOUTSOS G. Physics-informed regularisation procedure in neural networks: an application in blast protection engineering [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2022, 13(3): 555–578. DOI: 10.1177/20414196211073501. [19] PANNELL J J, RIGBY S E, PANOUTSOS G. Application of transfer learning for the prediction of blast impulse [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2023, 14(2): 242–262. DOI: 10.177/20414196221096699. [20] LI Q L, WANG Y, SHAO Y D, et al. A comparative study on the most effective machine learning model for blast loading prediction: from GBDT to transformer [J]. Engineering Structures, 2023, 276: 115310. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.115310. [21] LI Q L, WANG Y, LI L, et al. Prediction of BLEVE loads on structures using machine learning and CFD [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 171: 914–925. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2023.02.008. [22] HUANG Y, ZHU S J, CHEN S W. Deep learning-driven super-resolution reconstruction of two-dimensional explosion pressure fields [J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 78: 107620. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107620. [23] 孙传猛, 裴东兴, 陈嘉欣, 等. 基于深度学习的爆炸冲击波信号重构模型 [J]. 计测技术, 2022, 42(2): 57–67. DOI: 10.11823/j.issn.1674-5795.2022.02.07.SUN C M, PEI D X, CHEN J X, et al. Model for reconstruction of explosion shock wave signals based on deep learning [J]. Measurement Technology, 2022, 42(2): 57–67. DOI: 10.11823/j.issn.1674-5795.2022.02.07. [24] QIU T, CHENG S, DU X Q, et al. Spacing effects on blast loading characteristics of two tandem square columns under planar shock waves [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(12): 127116. DOI: 10.1063/5.0177869. [25] KARLOS V, LARCHER M, SOLOMOS G. Analysis of the blast wave decay coefficient in the Friedlander equation using the Kingery-Bulmash data [R]. Joint Research Center, European Commission, 2015. [26] ZHOU Z H. Machine learning [M]. Springer Nature, 2021. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-15-1967-3. [27] MISRA D. Mish: a self-regularized non-monotonic activation function[R]. British Machine Vision Conference, 2019. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1908.08681. -






 下载:
下载: