Research progress on hydrogen gas explosion suppression materials and their suppression mechanisms
-
摘要: 氢气在全球清洁能源转型中扮演着关键角色,但其可燃性和高爆炸危害性也使得氢气安全成为研究热点。聚焦氢气抑爆领域的最新研究成果,对不同种类抑爆材料及抑爆机理进行了综合评述。首先,介绍了气体、液体、固体以及多相复合抑爆材料的研究进展,对比分析了抑爆效果、关键参数及其变化规律。其次,探讨了抑爆材料影响氢气爆炸的物理、化学以及物理化学综合的作用过程,以揭示各类材料的抑爆机理。最后,展望了氢气抑爆材料的未来发展趋势,强调对高效能抑爆材料探索和机理研究的深化以及在实际应用中所面临的诸多挑战。Abstract: Hydrogen is crucial in the global shift towards clean energy and is gaining significance in the energy industry, while its high flammability and explosive hazard make its safety a research hotspot. It is crucial to thoroughly investigate and assess the safety of hydrogen as it progresses toward commercialization in the energy sector. This article reviews the latest advancements in hydrogen explosion suppression conducted by researchers around the world, aiming at offering a scientific foundation and technical approach to efficiently manage and reduce the damaging impacts of hydrogen explosion incidents. The article focuses on the study of hydrogen explosion suppression materials and their suppression mechanisms, so as to provide scientific understanding and technical support for the safe application of hydrogen. Firstly, it systematically introduces the research progress in hydrogen explosion suppression by discussing four significant categories, i.e., gas, liquid, solid, and multiphase composite explosion suppression materials. By comparing and analyzing the effects, key performance parameters, and the variation rules of these materials, the current research status and effectiveness of various explosion suppression materials are sorted out, helping to deepen the understanding of the explosion suppression effects of these materials. Secondly, focusing on the suppression mechanism, the research delves into the vital role of explosion suppression materials in suppressing hydrogen explosions. Starting from three dimensions, i.e., physical suppression, chemical suppression, and physicochemical comprehensive suppression, it elucidates the mechanisms of action of explosion suppression materials in the suppression process, contributing to a deeper understanding of the role of explosion suppression materials in suppressing or mitigating hydrogen explosions. Finally, the article looks forward to the future development directions of hydrogen explosion suppression materials, especially emphasizing the importance of further studies on the high-efficiency explosion suppression materials and the challenges faced in practical applications. This review is aimed to provide scientific reference and inspiration for the research, development, and application of new hydrogen explosion suppression materials.
-
表 1 近年氢气泄漏爆炸事故
Table 1. Recent hydrogen gas leak explosion incidents
事故时间 事故地点 事故原因 事故后果 2018年3月12日 中国江西省九江市一石化企业 柴油加氢装置原料缓冲罐超压爆炸着火 2人死亡,1人受伤
直接经济损失约338万元2019年5月23日 韩国江原道江陵市 在水电解氢气试验的过程中,因操作失误而导致爆炸 2人死亡,6人受伤 2019年6月1日 美国加州圣塔克拉拉一化工厂 储氢罐发生泄漏爆炸 无人伤亡,经济损失数万美元,
当地氢燃料供应被迫中断2019年6月 挪威桑维卡一合营加氢站 高压储氢罐一特殊插头装配错误 2人受伤
经济损失约2亿欧元2019年12月 威斯康星州沃基工厂 储氢区发生爆炸起火 1人受伤 2020年1月14日 中国珠海长炼石化设备有限公司 重整加氢装置预加单元发生闪爆 无人伤亡
直接经济损失198万元2020年4月 美国北卡州朗维尤一氢燃料工厂 加氢站爆炸 无人伤亡,损失数百美元 2021年8月4日 中国辽宁沈阳经济开发区
一企业院加氢站内卸车柱上软管破裂导致氢气罐爆燃 无人伤亡
直接经济损失1475 万元2021年9月11日 湖南省永兴镇马田镇 个人私自利用液化石油气钢瓶制氢,
导致其制氢罐发生爆炸1人死亡,1人受伤
直接经济损失超93万元2022年4月24日 中国石化齐鲁石化胜利炼油厂 氢气泄漏着火 无人伤亡
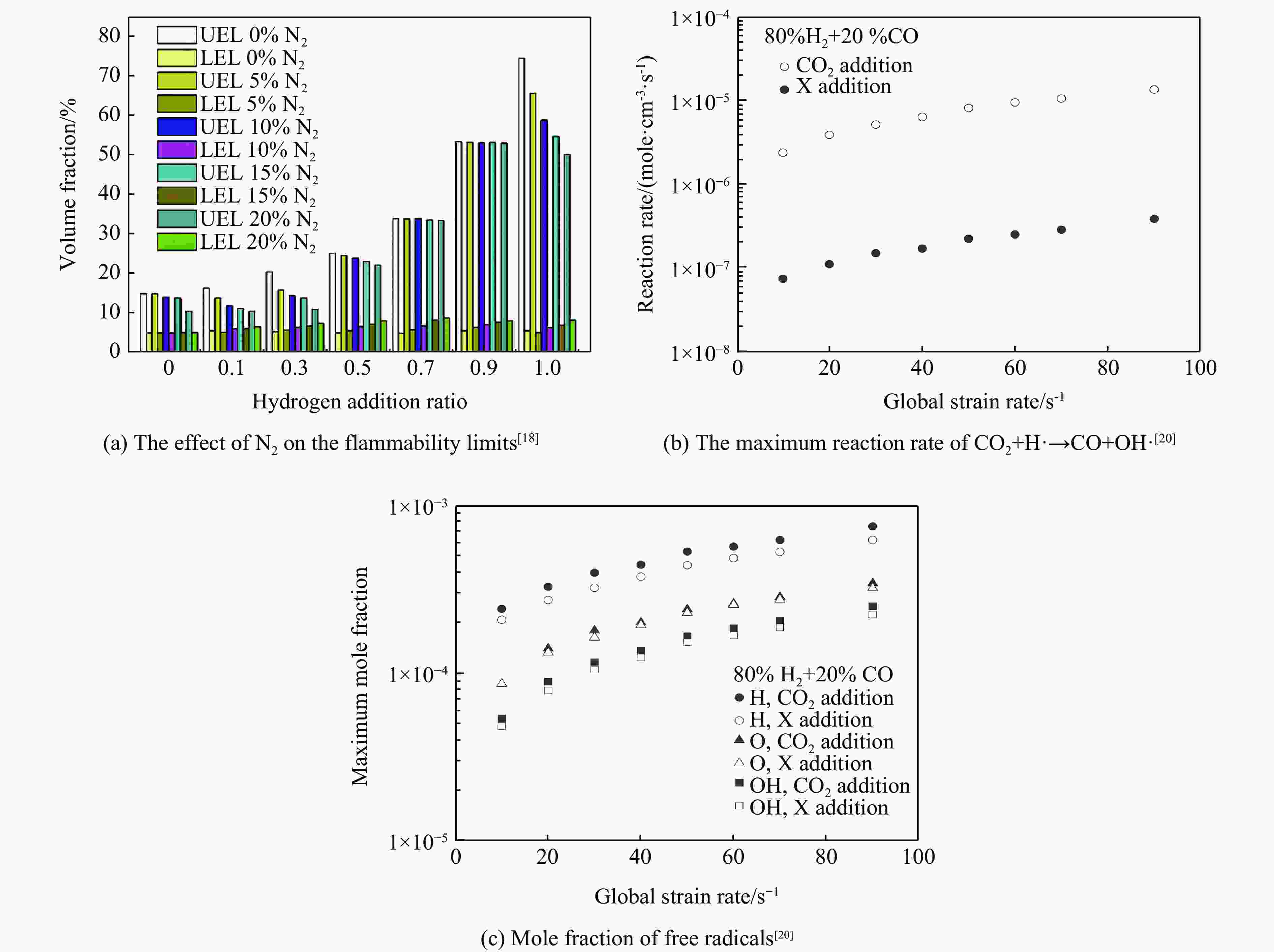
直接经济损失180万元研究人员 研究对象 实验装置 抑爆剂 结论 刘原一等[21] H2/CO 2 m长不锈钢
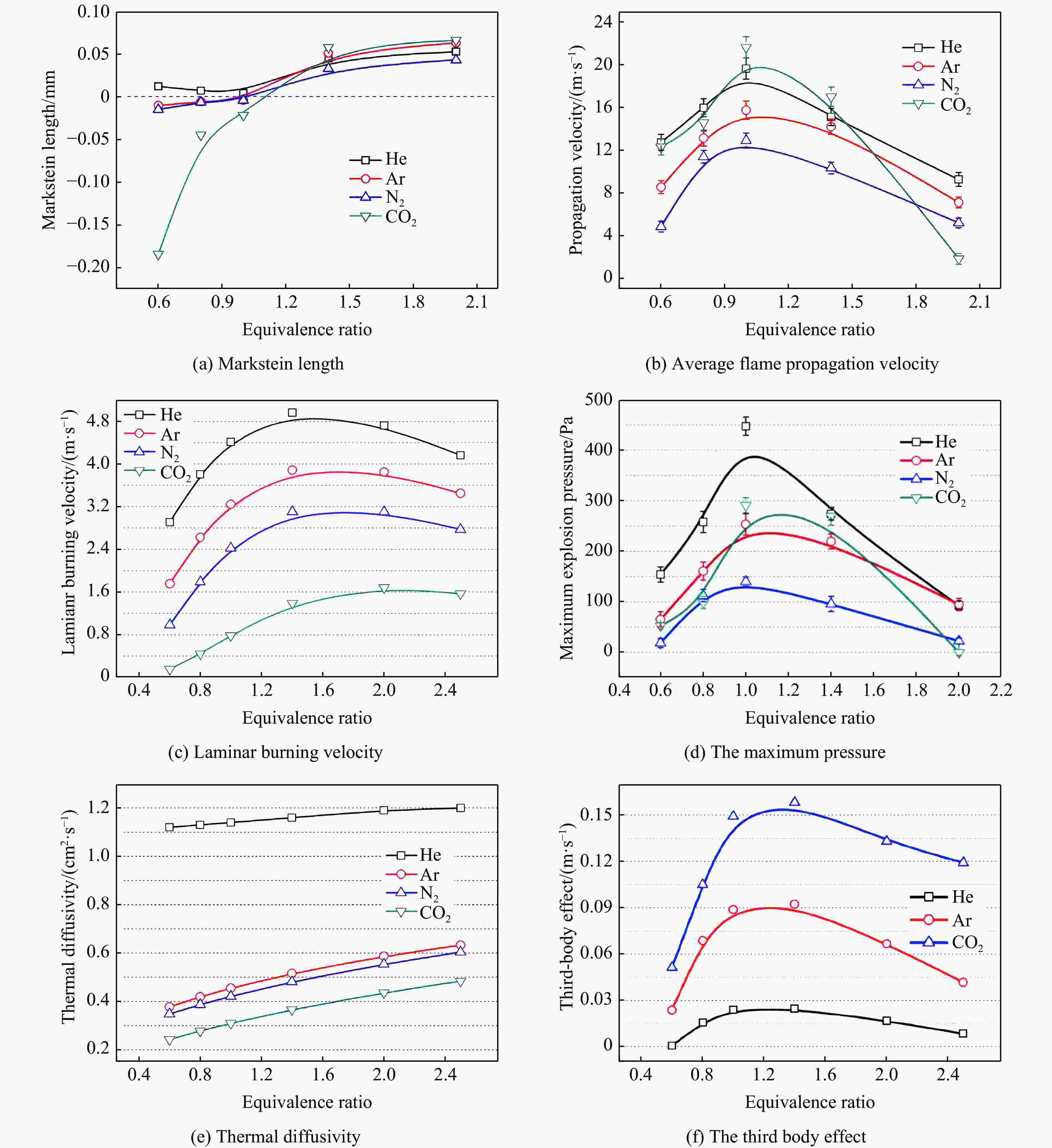
管道N2、CO2 CO2对混合气爆燃特性的影响强于N2,主要表现在燃爆下限和压力波传播上 Yan等[22] H2/CO 球形爆炸室 N2、CO2 随着CO2和N2含量的增加,绝热火焰温度、热扩散系数和活性自由基摩尔分数不断降低,
使层流燃烧速度降低。其次,CO2抑制氢气爆炸压力比N2更有效Li等[23] H2 肥皂泡装置 He、Ar、
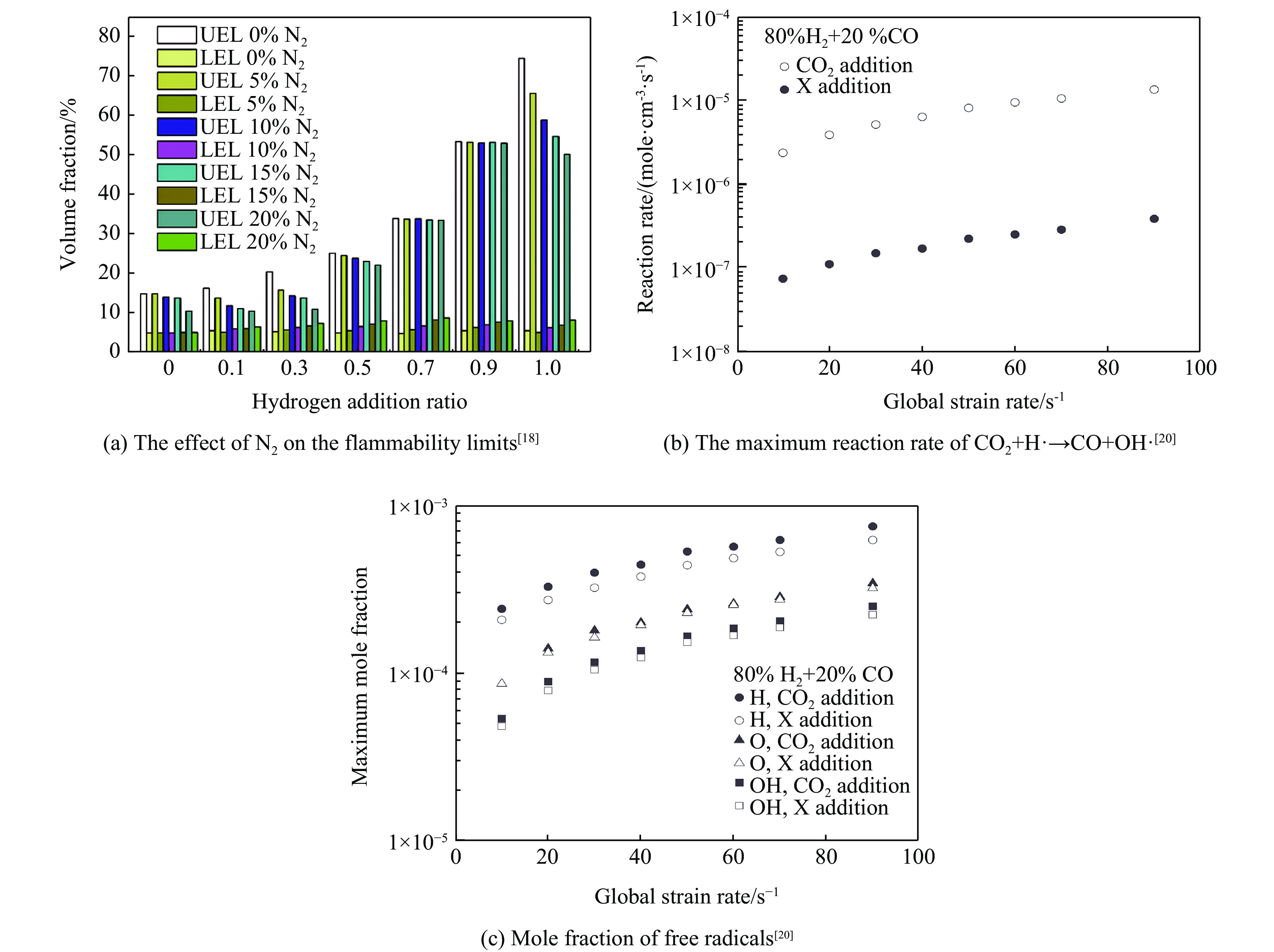
N2、CO2影响热扩散系数、绝热火焰温度、层流燃烧速度和热膨胀率的降低排序:He>Ar>N2>CO2,且N2不存在第三体效应,第三体效应:CO2>Ar>He,因此,CO2是缓解氢气爆炸较有效的添加物 Wei等[24] H2 定容燃烧弹 Ar、N2、CO2 不活泼气体的稀释减缓了火焰在燃烧室中的传播。抑制作用由小到大依次是Ar、N2、CO2 Wang等[25] H2 7.3 L圆筒
封闭容器Ar、N2、CO2 CO2比热高于N2和Ar,且CO2对能量损失的增加最显著,N2和Ar次之,
因此CO2的抑制效果优于Ar和N2邹颖等[26] H2 20L爆炸球 N2、CO2 CO2在爆炸压力及压力增长率方面的抑制效果优于N2 Wang等[27] H2/LPG 20L爆炸球 N2、CO2 比较了爆炸压力、自由基的摩尔分数和产生速率,得出CO2抑制作用优于N2。
其中N2主要起到了物理抑制作用,而CO2还发挥了化学抑制作用Chang等[28] H2 20 L标准球形
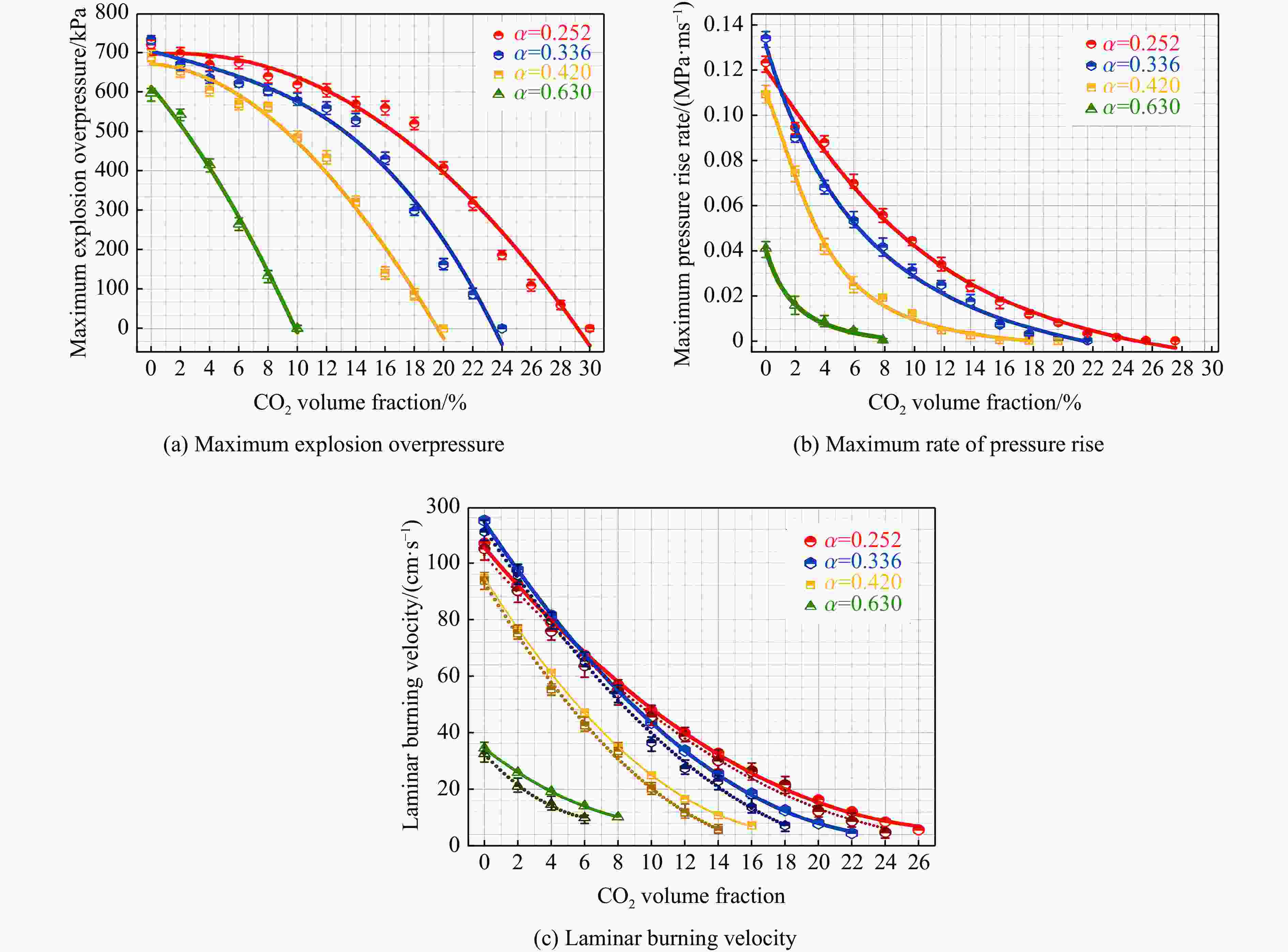
爆炸容器中N2、CO2 N2、CO2气体稀释的抑制作用可以平衡湍流的促进作用。在某些情况下,由于CO2的分子量较大,其对爆炸行为的增强作用比N2射流更明显 Wu等[29] H2 圆柱形停滞室 N2、CO2 从火焰长度减速比的比较可知,CO2与N2的减缓效果非常接近 Zhang等[30] H2 爆炸管道 N2、CO2 比较了爆炸压力、燃烧持续时间和火焰传播等爆炸参数,验证了CO2比N2抑制效果强。
此外,多层爆炸抑制对不同侧缓蚀剂的抑制效果最好当量比 绝热火焰温度/K He Ar N2 CO2 0.6 2764.9 2764.9 2222.5 1645.6 0.8 2988.8 2988.8 2566.2 1955.6 1.0 3090.1 3090.1 2760.8 2464.1 1.4 3069.8 3069.8 2705.8 2076.7 2.0 2853.0 2853.0 2478.2 1865.4 表 4 卤代烃与活化中心化学反应参数对比[77]
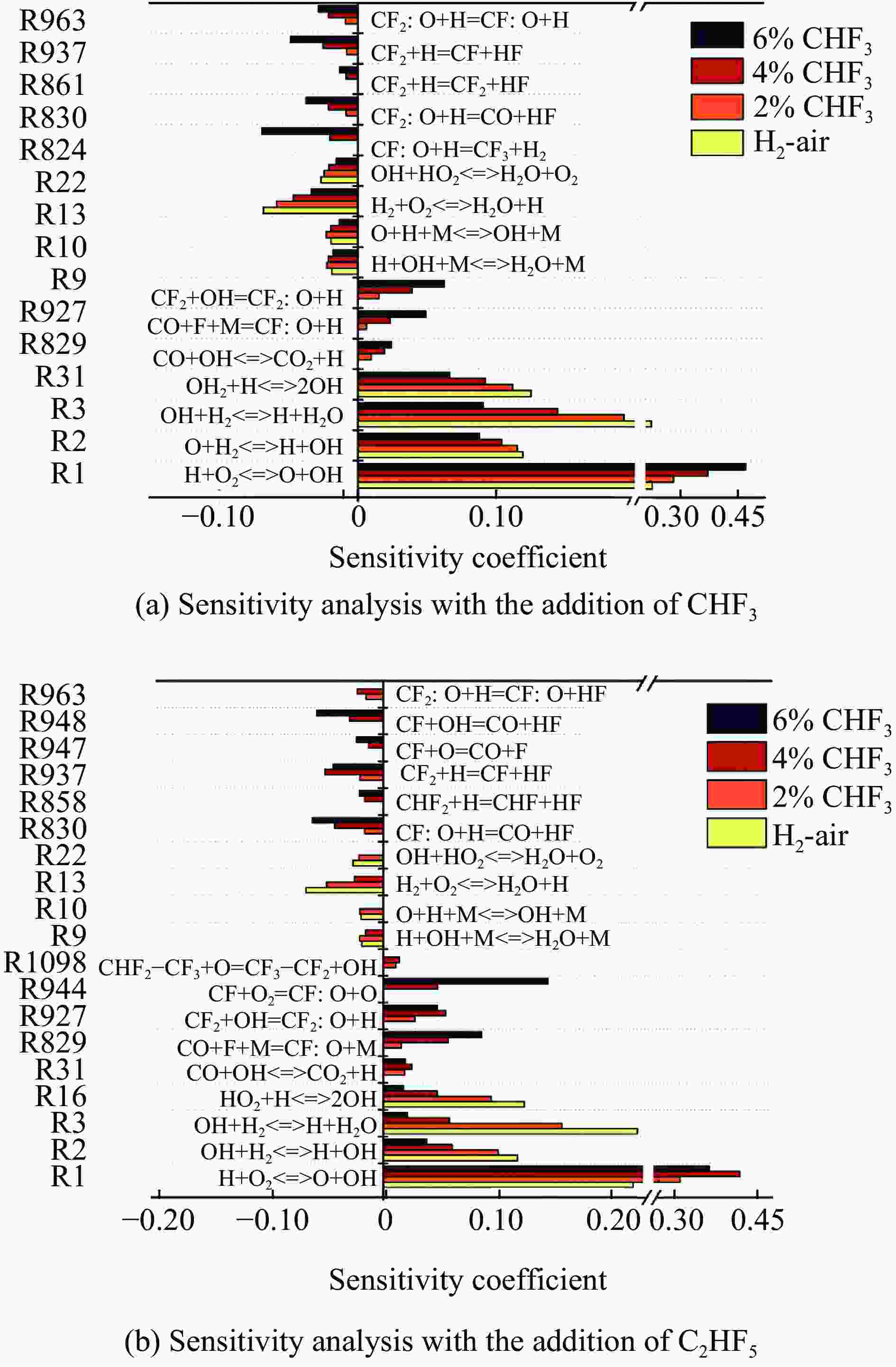
Table 4. Comparison of halogenated hydrocarbons and activation center chemical reaction parameters[77]
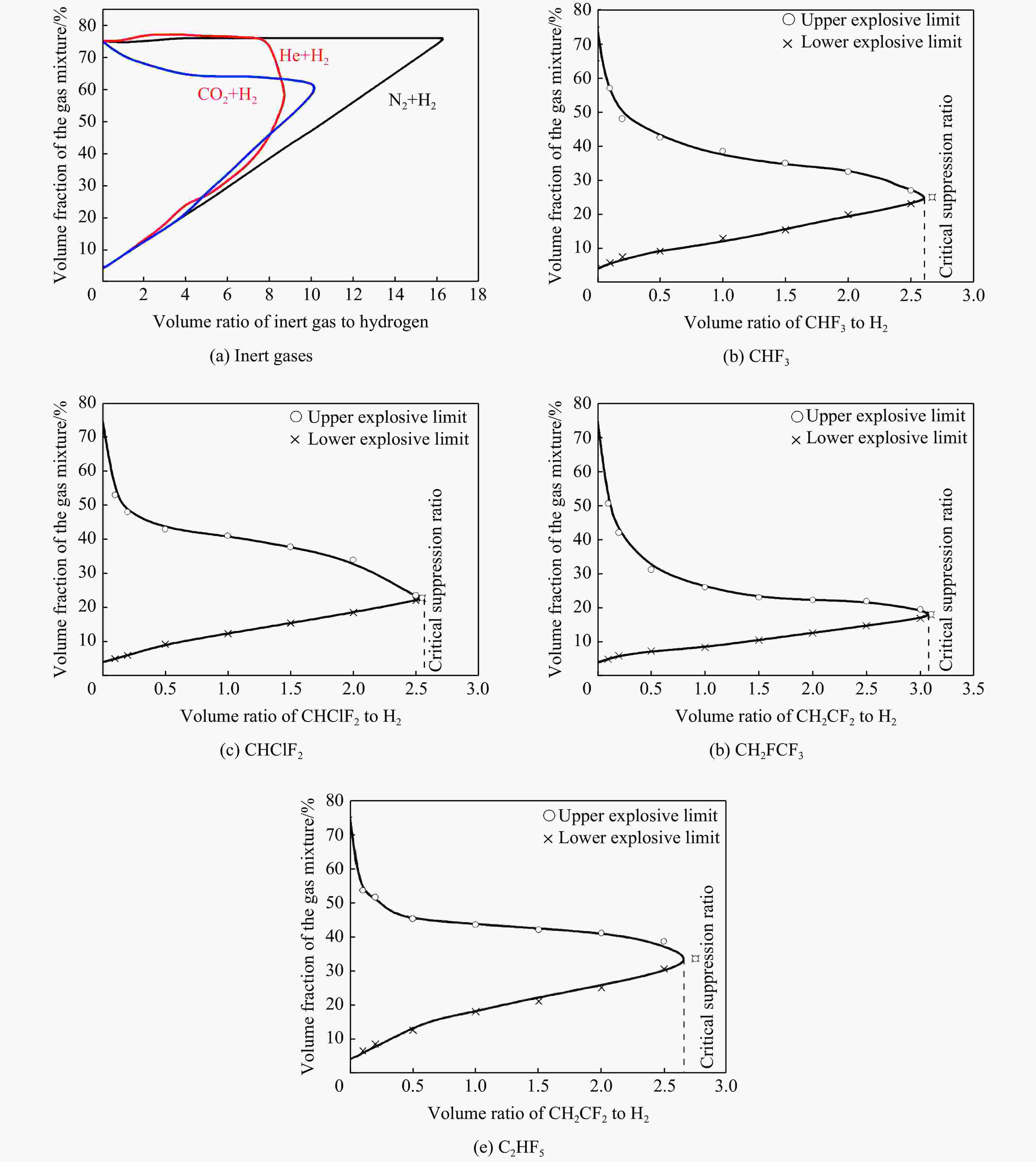
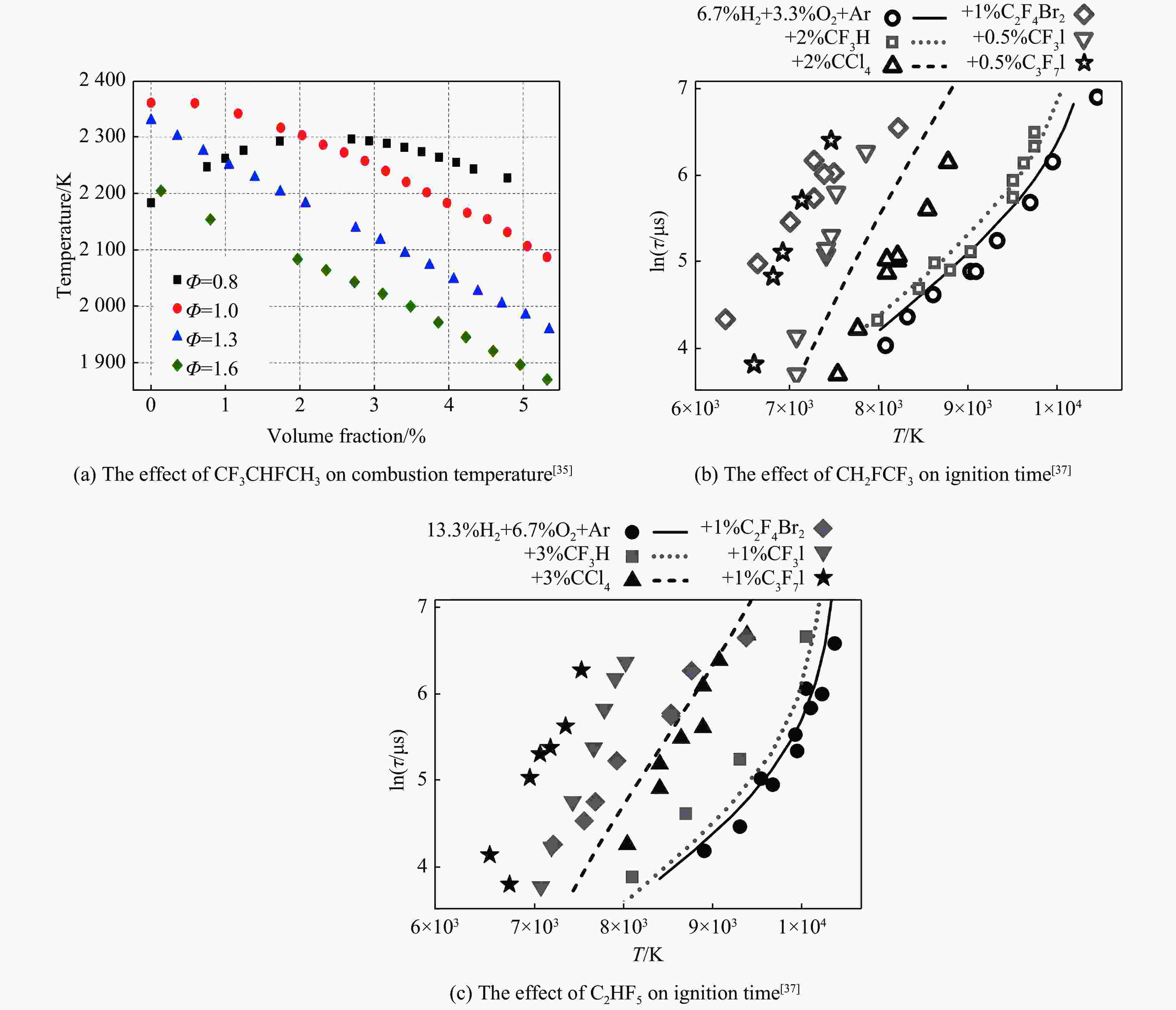
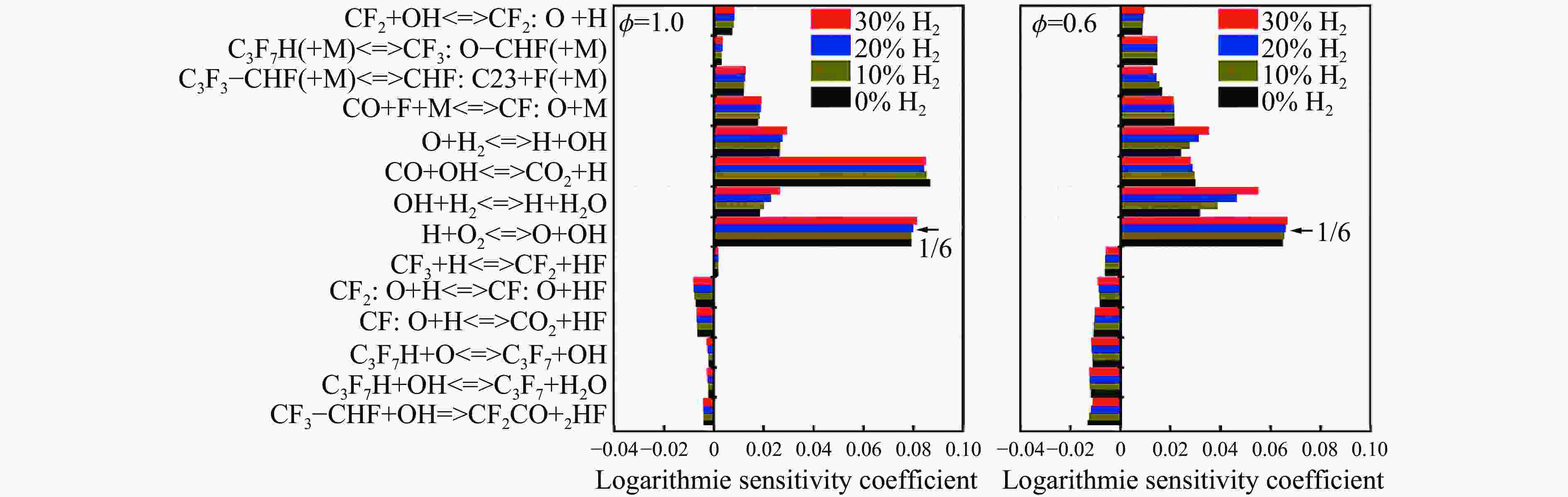
反应过程 活化能$ {E}_{\mathrm{a}} $/(kJ∙mol−1) 反应速率常数$ K $/(cm³∙mol−1∙s−1) CHF3+OH·→CF3+H2O 19.10 2.71×10-16 CHClF2+OH·→CClF2+ H2O 12.72 4.60×10-15 CH2FCF3+OH·→CHFCF3+H2O 12.80 4.16×10-15 C2HF5+OH·→C2F5+H2O 13.80 1.90×10-15 -
[1] RICCI M, BELLABY P, FLYNN R. What do we know about public perceptions and acceptance of hydrogen ? : a critical review and new case study evidence [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(21): 5868–5880. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.07.106. [2] TANG C L, ZHANG Y J, HUANG Z H. Progress in combustion investigations of hydrogen enriched hydrocarbons [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 30: 195–216. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.10.005. [3] ACAR C, DINCER I. The potential role of hydrogen as a sustainable transportation fuel to combat global warming [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(5): 3396–3406. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.10.149. [4] SINGH S, JAIN S, PS V, et al. Hydrogen: A sustainable fuel for future of the transport sector [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 51: 623–633. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.06.040. [5] MAYRHOFER M, KOLLER M, SEEMANN P, et al. Assessment of natural gas/hydrogen blends as an alternative fuel for industrial heat treatment furnaces [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(41): 21672–21686. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.03.228. [6] MORADI R, GROTH K M. Hydrogen storage and delivery: review of the state of the art technologies and risk and reliability analysis [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(23): 12254–12269. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.03.041. [7] 林言训, 秦家俊. 小型氮肥厂的爆炸事故及預防措施 [J]. 劳动, 1963(5): 32–33.LIN Y X, QIN J J. Explosion accidents and preventive measures in small nitrogen fertilizer plants [J]. Labor, 1963(5): 32–33. [8] 汪德山. 氢气燃爆现象种种 [J]. 甘肃消防, 1999(8): 17.Wang D S. Various hydrogen explosion phenomena [J]. Gansu Fire Protection, 1999(8): 17. [9] LAHNAOUI A, WULF C, HEINRICHS H, et al. Optimizing hydrogen transportation system for mobility via compressed hydrogen trucks [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(35): 19302–19312. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.10.234. [10] SAZALI N. Emerging technologies by hydrogen: a review [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(38): 18753–18771. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.05.021. [11] AARSKOG F G, HANSEN O R, STRØMGREN T, et al. Concept risk assessment of a hydrogen driven high speed passenger ferry [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(2): 1359–1372. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.05.128. [12] 郑凯. 管道中氢气/甲烷混合燃料爆燃预混火焰传播特征研究 [D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2017.ZHENG K. Study on the propagation characteristics of premixed flame of hydrogen/methane deflagration in ducts [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2017. [13] 高玉刚. 管道中可燃气体燃爆特性研究 [D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2011.GAO Y G. Study on burning explosion characteristics of flammable gas in tube [D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science & Technology, 2011. [14] 孙占强, 余磊. 长输管道合于使用评价常见问题总结 [J]. 云南化工, 2023, 50(6): 163–165. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-275X.2023.06.44.SUN Z Q, YU L. Summary of common problems in the evaluation of suitability for use of long-distance pipelines [J]. Yunnan Chemical Technology, 2023, 50(6): 163–165. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-275X.2023.06.44. [15] CROWL D A, JO Y D. The hazards and risks of hydrogen [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2007, 20(2): 158–164. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2007.02.002. [16] NG H D, LEE J H S. Comments on explosion problems for hydrogen safety [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2008, 21(2): 136–146. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2007.06.001. [17] 李一鸣. 七氟丙烷抑制甲烷-空气爆炸的实验研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018.LI Y M. Experimental study of suppressing the methane/air explosion by heptafluoropropane [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. [18] SU Y, LUO Z M, WANG T, et al. Effect of nitrogen on deflagration characteristics of hydrogen/methane mixture [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(15): 9156–9168. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.01.013. [19] RAZUS D, MITU M, GIURCAN V, et al. Numerical study of pressure and composition influence on laminar flame propagation in nitrogen-diluted H2-O2 mixtures [J]. Revue Roumaine de Chimie, 2020, 65(6): 529–537. DOI: 10.33224/rrch.2020.65.6.02. [20] PARK J, KIM J S, CHUNG J O, et al. Chemical effects of added CO2 on the extinction characteristics of H2/CO/CO2 syngas diffusion flames [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(20): 8756–8762. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.08.046. [21] 刘原一, 朱轶铭, 熊英莹, 等. N2/CO2气氛对CO/H2爆燃特性的影响 [J]. 燃烧科学与技术, 2014, 20(5): 383–387. DOI: 10.11715/rskxjs.R201404011.LIU Y Y, ZHU Y M, XIONG Y Y, et al. Influence of N2/CO2 on deflagration characteristics of CO/H2 [J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2014, 20(5): 383–387. DOI: 10.11715/rskxjs.R201404011. [22] YAN C C, BI M S, LI Y C, et al. Effects of nitrogen and carbon dioxide on hydrogen explosion behaviors near suppression limit [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2020, 67: 104228. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2020.104228. [23] LI Y C, BI M S, HUANG L, et al. Hydrogen cloud explosion evaluation under inert gas atmosphere [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 180: 96–104. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.08.015. [24] WEI H Q, XU Z L, ZHOU L, et al. Effect of hydrogen-air mixture diluted with argon/nitrogen/carbon dioxide on combustion processes in confined space [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(31): 14798–14805. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.06.038. [25] WANG L Q, MA H H, SHEN Z W. Explosion characteristics of hydrogen-air mixtures diluted with inert gases at sub-atmospheric pressures [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(40): 22527–22536. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.059. [26] 邹颖, 董冰岩, 查裕学, 等. 密闭受限空间内N2、CO2对H2/Air混合气体的抑爆效果研究 [J]. 科技与创新, 2022(17): 87–92. DOI: 10.15913/j.cnki.kjycx.2022.17.028.ZOU Y, DONG B Y, ZHA Y X, et al. Study on the explosion suppression effect of N2 and CO2 on H2/air mixed gas in confined enclosed spaces [J]. Science and Innovation, 2022(17): 87–92. DOI: 10.15913/j.cnki.kjycx.2022.17.028. [27] WANG J Y, LIANG Y T, ZHAO Z Z. Effect of N2 and CO2 on explosion behavior of H2-liquefied petroleum gas-air mixtures in a confined space [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(56): 23887–23897. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.05.152. [28] CHANG X Y, BAI C H, ZHANG B. The effect of gas jets on the explosion dynamics of hydrogen-air mixtures [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 162: 384–394. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.04.032. [29] WU Y, YU X, WANG Z C, et al. The flame mitigation effect of N2 and CO2 on the hydrogen jet fire [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 165: 658–670. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.07.027. [30] ZHANG S Y, WEN X P, GUO Z D, et al. Experimental study on the multi-level suppression of N2 and CO2 on hydrogen-air explosion [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 169: 970–981. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.11.069. [31] 邹颖. 密闭空间内H2爆炸及CO2、N2抑爆过程的数值模拟及实验研究 [D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2022. DOI: 10.27176/d.cnki.gnfyc.2022.000560.ZOU Y. Numerical simulation and experimental study of H2 explosion and SUPPR ESSION of CO2 and N2 explosion in confined space [D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2022. DOI: 10.27176/d.cnki.gnfyc.2022.000560. [32] TROPIN D. Numerical modeling of suppression of detonation waves in hydrogen-air mixture by system of inert particles clouds [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(66): 28699–28709. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.06.169. [33] 姜程山. 氢气的爆炸极限抑制研究 [D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2017.JIANG C S. Inhibition of hydrogen's explosion limits [D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2017. [34] 马文丽. 哈龙灭火剂替代产品的分类及特点研究 [J]. 忻州师范学院学报, 2008, 24(4): 132–134. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1491.2008.04.047.MA W L. Study on classification and characteristics of Halon fire extinguishing agent substitute products [J]. Journal of Xinzhou Teachers University, 2008, 24(4): 132–134. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1491.2008.04.047. [35] FAN R J, WANG Z R, GUO W J, et al. Experimental and theoretical study on the suppression effect of CF3CHFCF3 (FM-200) on hydrogen-air explosion [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(26): 13191–13198. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.02.062. [36] DRAKON A, EREMIN A, MATVEEVA N, et al. The opposite influences of flame suppressants on the ignition of combustible mixtures behind shock waves [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2017, 176: 592–598. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2016.11.001. [37] DRAKON A, EREMIN A. On relative effectiveness of halogenated hydrocarbons for suppression of hydrogen-oxygen mixture autoignition [J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2018, 190(3): 550–555. DOI: 10.1080/00102202.2017.1402011. [38] GAO M D, BI M S, YE L L, et al. Suppression of hydrogen-air explosions by hydrofluorocarbons [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 145: 378–387. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.08.036. [39] SHANG S, BI M S, ZHANG K, et al. Suppression of hydrogen-air explosions by isobutene with special molecular structure [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(61): 25864–25875. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.06.012. [40] SHANG S, BI M S, ZHANG Z L, et al. Synergistic effects of isobutene and carbon dioxide on suppressing hydrogen-air explosions [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(60): 25433–25442. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.05.256. [41] 李卓然, 夏远辰, 张彬, 等. 细水雾对置障管内预混气体抑爆机理研究 [J]. 消防科学与技术, 2021, 40(6): 884–887. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2021.06.024.LI Z R, XIA Y C, ZHANG B, et al. Study on the suppression mechanism of water mist on the deflagration of premixed methane gas in a barrier tube [J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 884–887. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2021.06.024. [42] 汪剑辉, 刘飞, 薛一江. 可燃气云抑爆技术初探 [J]. 工程爆破, 2011, 17(2): 19–22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2011.02.005.WANG J H, LIU F, XUE Y J. Preliminary discuss on explosion suppression technique of flammable gas cloud [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2011, 17(2): 19–22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2011.02.005. [43] ZALOSH R G, BAJPAI S N. Effect of water fogs on the deliberate ignition of hydrogen. Final report: EPRI-NP-2637 [R]. Norwood: Factory Mutual Research Corp. , 1982. [44] LUANGDILOK W, BENNETT R B. Fog inerting effects on hydrogen combustion in a PWR ice condenser containment [J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1995, 117(2): 502–507. DOI: 10.1115/1.2822550. [45] BUTZ J R, FRENCH P. Application of fine water mists to hydrogen deflagrations [C]//Proceedings of the Halon Alternatives Technical Working Conference. Albuquerque, NM. 1993: 345-356. [46] JONES S J, AVERILL A F, INGRAM J M, et al. Mitigation of hydrogen-air explosions using fine water mist sprays [C]// Symposium on Hazards: Process Safety and Environmental Protection. Manchester, UK: IChemE Symposium Series No. 151, 2006: 1-10. [47] INGRAM J M, AVERILL A F, BATTERSBY P N, et al. Suppression of hydrogen–oxygen–nitrogen explosions by fine water mist: Part 1. Burning velocity [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(24): 19250–19257. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.09.092. [48] MODAK A U, ABBUD-MADRID A, DELPLANQUE J P, et al. The effect of mono-dispersed water mist on the suppression of laminar premixed hydrogen–, methane–, and propane–air flames [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 144(1/2): 103–111. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.07.003. [49] XIA Y C, ZHANG B, ZHANG J N, et al. Experimental research on combined effect of obstacle and local spraying water fog on hydrogen/air premixed explosion [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(94): 40099–40115. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.09.152. [50] 胡耀元, 钟依均, 应桃开, 等. H2, CO, CH4多元爆炸性混合气体支链爆炸阻尼效应 [J]. 化学学报, 2004, 62(10): 956–962. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2004.10.006.HU Y Y, ZHONG Y J, YING T K, et al. Damping effect on the branch-chain explosion of polybasic explosive mixture gas containing H2, CO and CH4 [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2004, 62(10): 956–962. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0567-7351.2004.10.006. [51] WEI S M, YU M G, PEI B, et al. Experimental and numerical study on the explosion suppression of hydrogen/dimethyl ether/methane/air mixtures by water mist containing NaHCO3 [J]. Fuel, 2022, 328: 125235. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125235. [52] WANG Z R, XU H, LU Y W, et al. Experimental and theoretical study on the suppression effect of water mist containing dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP) on hydrogen jet flame [J]. Fuel, 2023, 331: 125813. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125813. [53] 夏煜, 程扬帆, 胡芳芳, 等. 典型固体抑爆剂对乙炔-空气的抑爆特性 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2022, 36(6): 065201. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220580.XIA Y, CHENG Y F, HU F F, et al. Inhibition characteristics of typical solid explosion suppressors on acetylene-air explosion [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2022, 36(6): 065201. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220580. [54] LUO Z M, SU Y, CHEN X K, et al. Effect of BC powder on hydrogen/methane/air premixed gas deflagration [J]. Fuel, 2019, 257: 116095. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116095. [55] 田莉. 受限空间内氢气/甲烷/空气混合物爆炸特性及抑爆研究 [D]. 杭州: 中国计量大学, 2019. DOI: 10.27819/d.cnki.gzgjl.2019.000072.TIAN L. Study on characteristics and suppression of hydrogen/methane/air mixture explosion in enclosed space [D]. Hangzhou: China Jiliang University, 2019. DOI: 10.27819/d.cnki.gzgjl.2019.000072. [56] TSAI Y T, FU T, ZHOU Q. Explosion characteristics and suppression of hybrid Mg/H2 mixtures [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(78): 38934–38943. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.09.145. [57] LI Y, CHEN X F, YUAN B H, et al. Synthesis of a novel prolonged action inhibitor with lotus leaf-like appearance and its suppression on methane/hydrogen/air explosion [J]. Fuel, 2022, 329: 125401. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125401. [58] LI Y, ZHAO Q, LIU L J, et al. Investigation on the flame and explosion suppression of hydrogen/air mixtures by porous copper foams in the pipe with large aspect ratio [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2022, 76: 104744. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2022.104744. [59] BIVOL G Y, GOLOVASTOV S V. Suppression of hydrogen-air detonation using porous materials in the channels of different cross section [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(24): 13471–13483. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.01.052. [60] SONG X Z, ZUO X C, YANG Z K, et al. The explosion-suppression performance of mesh aluminum alloys and spherical nonmetallic materials on hydrogen-air mixtures [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(56): 32686–32701. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.08.197. [61] 段玉龙, 王硕, 贺森, 等. 多孔材料下气体爆炸转扩散燃烧的特性研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(9): 095401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0009.DUAN Y L, WANG S, HE S, et al. Characteristics of gas explosion to diffusion combustion under porous materials [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(9): 095401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0009. [62] HOLBORN P G, BATTERSBY P, INGRAM J M, et al. Estimating the effect of water fog and nitrogen dilution upon the burning velocity of hydrogen deflagrations from experimental test data [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(16): 6882–6895. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.063. [63] BATTERSBY P N, AVERILL A F, INGRAM J M, et al. Suppression of hydrogen-oxygen-nitrogen explosions by fine water mist: part 2: mitigation of vented deflagrations [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(24): 19258–19267. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.10.029. [64] 苏洋, 罗振敏, 王涛. CO2/海泡石抑爆剂对氢气/甲烷爆炸特性参数的影响 [J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(11): 5731–5736. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-0044.SU Y, LUO Z M, WANG T. Effect of CO2/sepiolite explosion suppressant on hydrogen/methane deflagration characteristic parameters [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(11): 5731–5736. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2022-0044. [65] YANG Z K, ZHAO K, SONG X Z, et al. Effects of mesh aluminium alloys and propane addition on the explosion-suppression characteristics of hydrogen-air mixture [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(70): 34998–35013. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.08.035. [66] 程方明, 南凡, 罗振敏, 等. 瓦斯抑爆材料及机理研究进展与发展趋势 [J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(8): 114–124. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.08.015.CHENG F M, NAN F, LUO Z M, et al. Research progress and development trend of gas explosion suppression materials and mechanism [J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(8): 114–124. DOI: 10.13199/j.cnki.cst.2021.08.015. [67] 陈硕, 路长, 苏振国, 等. 煤矿瓦斯爆炸发展规律及防治的综述及展望 [J]. 火灾科学, 2021, 30(2): 63–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2021.02.01.CHEN S, LU C, SU Z G, et al. Review on development and prevention of coal mine gas explosion [J]. Fire Safety Science, 2021, 30(2): 63–79. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2021.02.01. [68] MOORE P E. Suppressants for the control of industrial explosions [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 1996, 9(1): 119–123. DOI: 10.1016/0950-4230(95)00045-3. [69] 王任伟. N2/CO2/Ar稀释气体对甲烷预混层流火焰速度影响的物理与化学效应研究 [D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021. DOI: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2021.002801.WANG R W. A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of master of engineering [D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2021. DOI: 10.27157/d.cnki.ghzku.2021.002801. [70] 左前明, 程卫民, 汤家轩. 粉体抑爆剂在煤矿应用研究的现状与展望 [J]. 煤炭技术, 2010, 29(11): 78–80.ZUO Q M, CHENG W M, TANG J X. Current status and prospects of application and research of powder coal mine explosion suppression agent [J]. Coal Technology, 2010, 29(11): 78–80. [71] 李艳超. 氢气火焰失稳传播与爆炸压力的耦合影响机制研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019. DOI: 10.26991/d.cnki.gdllu.2019.003558.LI Y C. Dynamic couplings of unstable hydrogen flame propagation and explosion pressure evolution [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. DOI: 10.26991/d.cnki.gdllu.2019.003558. [72] SU B, LUO Z M, WANG T, et al. Chemical kinetic behaviors at the chain initiation stage of CH4/H2/air mixture [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123680. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123680. [73] 闫彩彩. 近抑爆极限氢气爆炸动力学行为研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020. DOI: 10.26991/d.cnki.gdllu.2020.000377.YAN C C. Study on hydrogen explosion dynamics near explosion suppression limit [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020. DOI: 10.26991/d.cnki.gdllu.2020.000377. [74] LI Y C, BI M S, ZHOU Y H, et al. Hydrogen cloud explosion suppression by micron-size water mist [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(55): 23462–23470. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.05.132. [75] 张天巍. 含钾盐添加剂细水雾的灭火有效性及机理研究 [D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2017. DOI: 10.26948/d.cnki.gbjlu.2017.000014.ZHANG T W. Fire-extinguishing performance and mechanism study on water mist with potassium additives [D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2017. DOI: 10.26948/d.cnki.gbjlu.2017.000014. [76] 夏远辰, 张彬, 王博乔, 等. 超细水雾对氢气-甲烷预混气体爆燃抑制机理的实验研究 [J]. 大连海事大学学报, 2022, 48(4): 127–134. DOI: 10.16411/j.cnki.issn1006-7736.2022.04.015.XIA Y C, ZHANG B, WANG B Q, et al. Experimental research on suppression mechanism of ultrafine water mist on deflagration of hydrogen-methane premixed gas [J]. Journal of Dalian Maritime University, 2022, 48(4): 127–134. DOI: 10.16411/j.cnki.issn1006-7736.2022.04.015. [77] ATKINSON R, BAULCH D L, COX R A, et al. Evaluated kinetic, photochemical and heterogeneous data for atmospheric chemistry: supplement V. IUPAC subcommittee on gas kinetic data evaluation for atmospheric chemistry [J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1997, 26(3): 521–1011. DOI: 10.1063/1.556011. [78] WILLIAMS B A, L’ESPÉRANCE D M, FLEMING J W. Intermediate species profiles in low-pressure methane/oxygen flames inhibited by 2-H heptafluoropropane: comparison of experimental data with kinetic modeling [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2000, 120(1/2): 160–172. DOI: 10.1016/S0010-2180(99)00081-4. [79] XU W, JIANG Y, QIU R, et al. Influence of halon replacements on laminar flame speeds and extinction limits of hydrocarbon flames [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2017, 182: 1–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2017.03.029. [80] KATTA V R, TAKAHASHI F, LINTERIS G T. Fire-suppression characteristics of CF3H in a cup burner [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 144(4): 645–661. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2005.09.006. [81] ZHANG X, YANG Z, HUANG X, et al. Combustion enhancement and inhibition of hydrogen-doped methane flame by HFC-227ea [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(41): 21704–21714. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.03.250. [82] PAGLIARO J L, LINTERIS G T, SUNDERLAND P B, et al. Combustion inhibition and enhancement of premixed methane–air flames by halon replacements [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2015, 162(1): 41–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2014.07.006. [83] 左前明, 程卫民, 邹冠贵, 等. 协同增效原理在煤尘抑爆剂中的应用实验 [J]. 重庆大学学报, 2012, 35(1): 105–109,116. DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2012.01.020.ZUO Q M, CHENG W M, ZOU G G, et al. Applied experiments on coal dust inhibitor based on the theory of synergistic effect [J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2012, 35(1): 105–109,116. DOI: 10.11835/j.issn.1000-582X.2012.01.020. [84] LI Y C, BI M S, YAN C C, et al. Inerting effect of carbon dioxide on confined hydrogen explosion [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(40): 22620–22631. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.04.181. [85] LI J, HUANG H Y, KOBAYASHI N, et al. Numerical study on laminar burning velocity and ignition delay time of ammonia flame with hydrogen addition [J]. Energy, 2017, 126: 796–809. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.03.085. [86] AZATYAN V V, SAIKOVA G R, BALAYAN G V, et al. Dependence of the flammability of hydrogen-air mixtures on the chemical and physical properties of admixtures [J]. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2015, 89(3): 369–371. DOI: 10.1134/S0036024415030048. [87] 王志荣. 受限空间气体爆炸传播及其动力学过程研究 [D]. 南京: 南京工业大学, 2005.WANG Z R. Study on the dynamics of gas explosion process in confined space [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Tech University, 2005. [88] CAO X Y, WANG Z R, LU Y W, et al. Numerical simulation of methane explosion suppression by ultrafine water mist in a confined space [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 109: 103777. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103777. [89] DOUNIA O, VERMOREL O, POINSOT T. Theoretical analysis and simulation of methane/air flame inhibition by sodium bicarbonate particles [J]. Combustion and Flame, 2018, 193: 313–326. DOI: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2018.03.033. -






 下载:
下载: