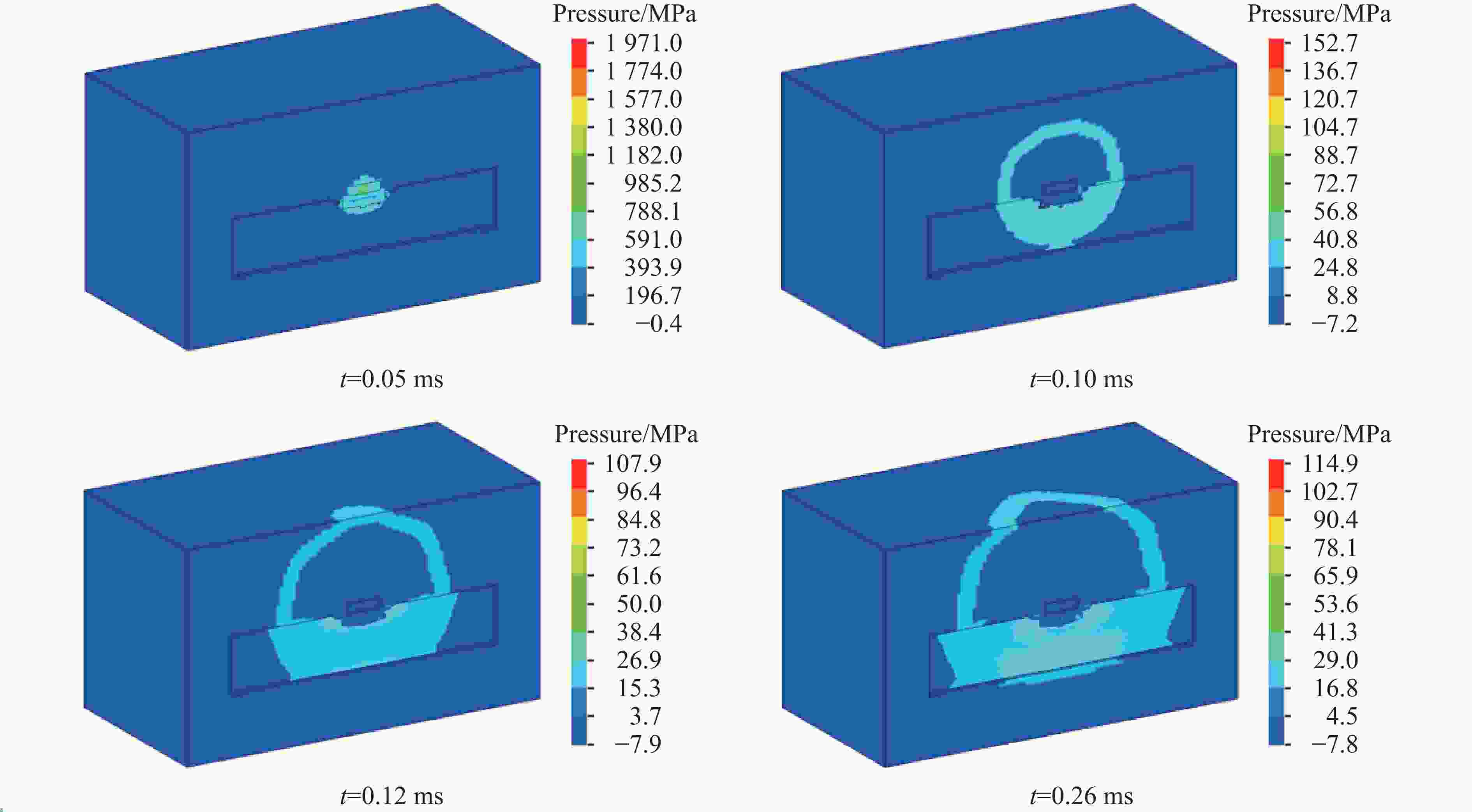
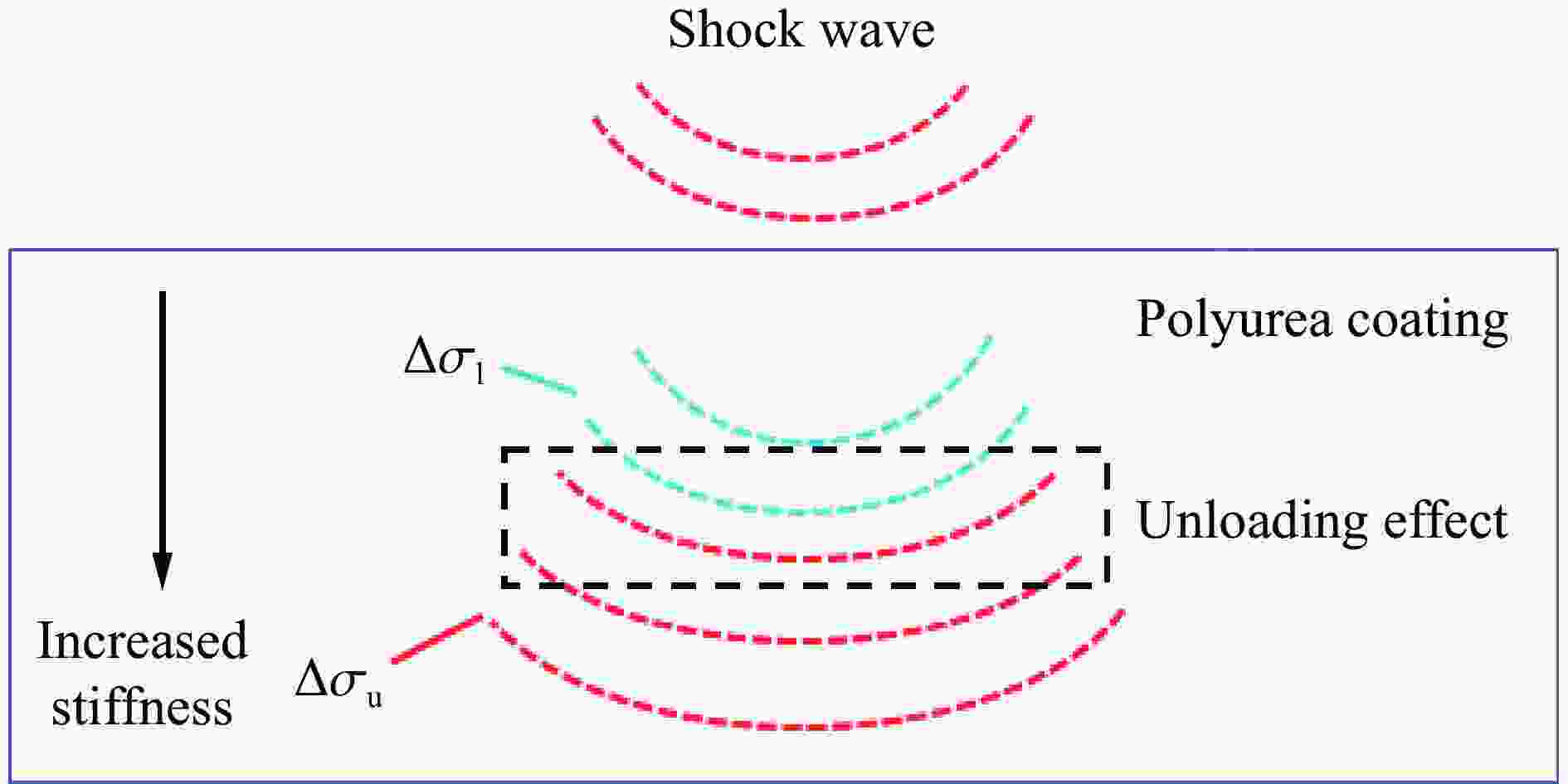
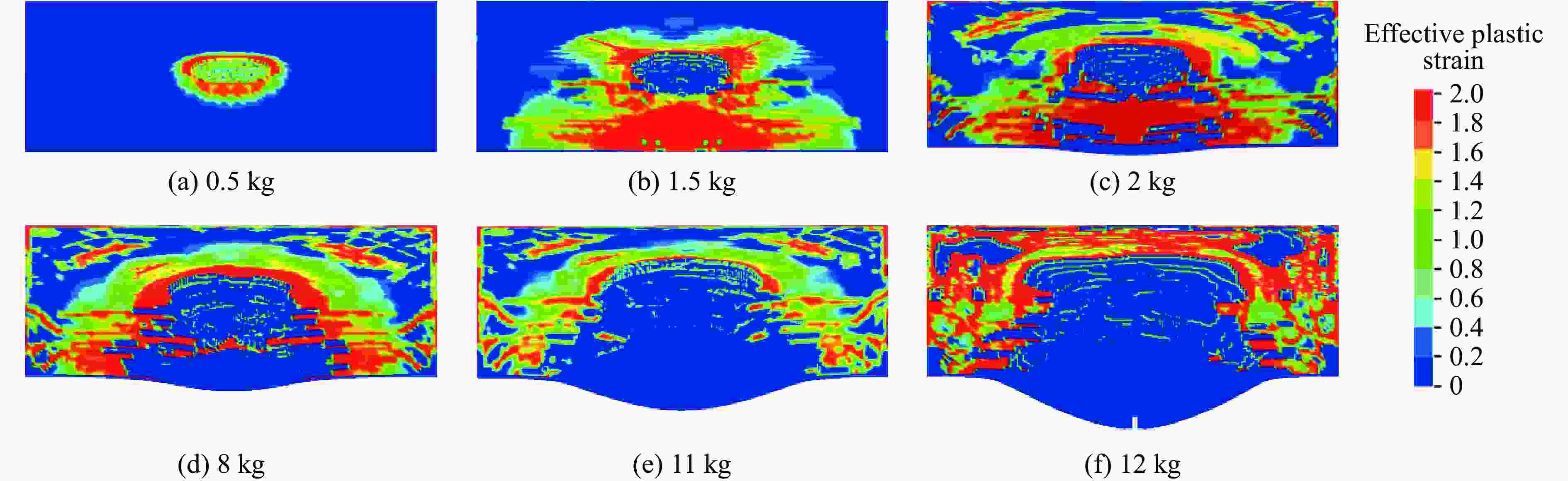
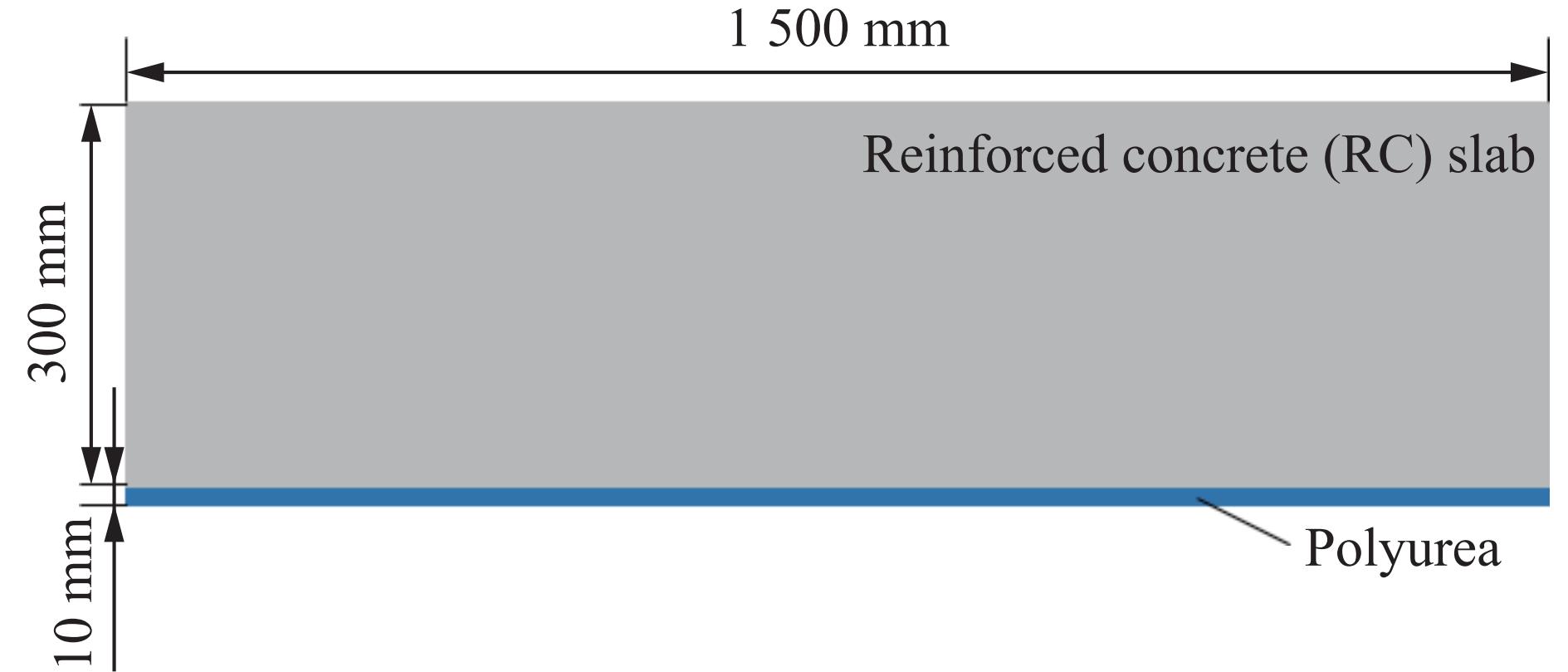
Blast resistance of polyurea/reinforced concrete thick slab composite structures under contact explosion
-
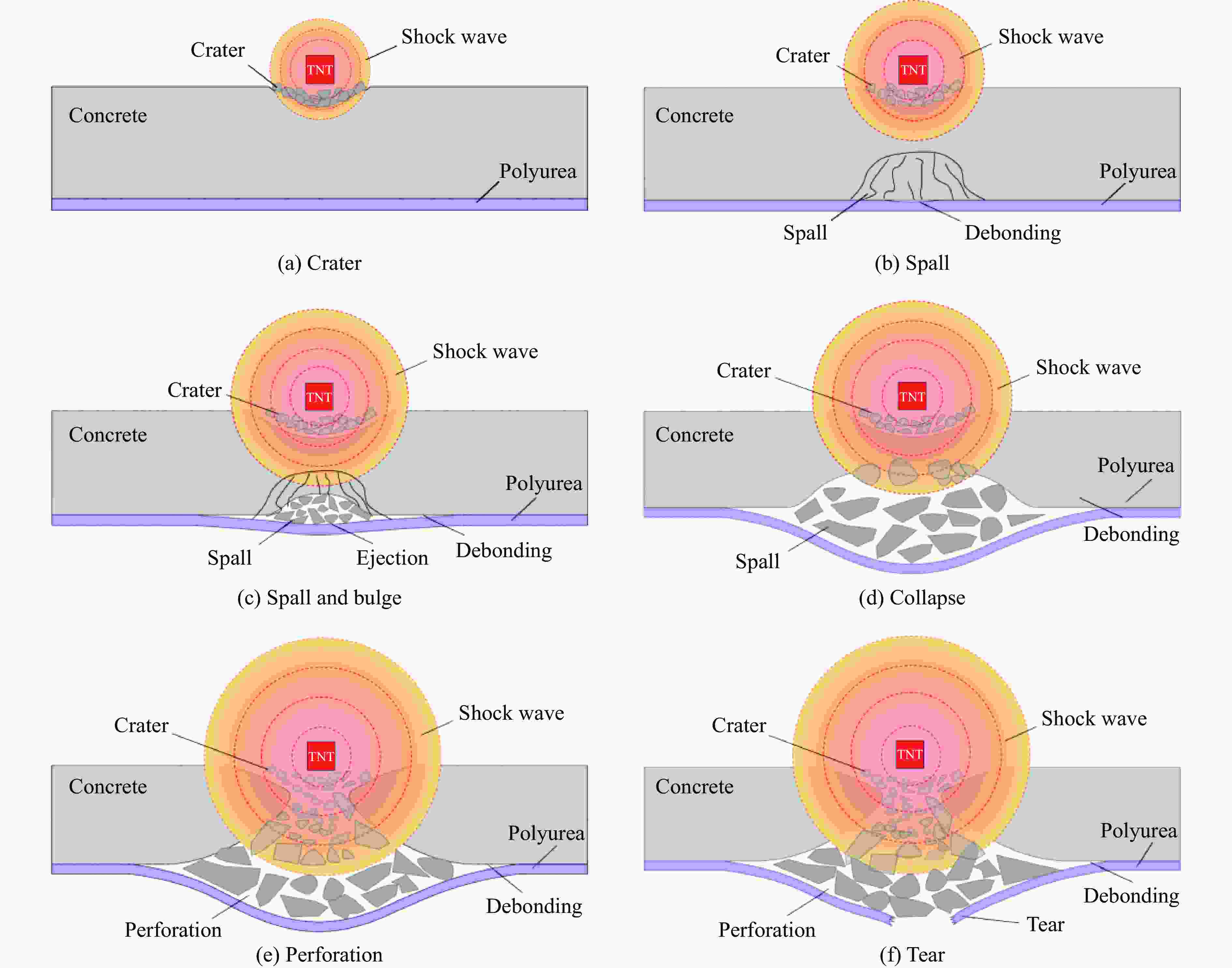
摘要: 为了研究聚脲/钢筋混凝土厚板复合结构的抗爆性能,对聚脲/钢筋混凝土厚板复合结构开展不同装药量下的接触爆炸实验,并对其整体及局部的破坏特征进行分析。利用LS-DYNA有限元仿真软件探究了聚脲/钢筋混凝土厚板复合结构的损伤过程及机理,并进一步分析了聚脲/钢筋混凝土厚板复合结构的破坏模式及特征。实验及有限元结果表明:接触爆炸载荷作用下的聚脲/钢筋混凝土厚板复合结构呈现6种破坏模式,即正面成坑;层裂破坏;层裂鼓包;震塌破坏,聚脲涂层鼓包大变形;爆炸贯穿,聚脲涂层严重鼓包变形;贯穿和撕裂破坏。在钢筋混凝土厚板背面涂覆聚脲有效增强了复合结构的抗爆性能。Abstract: Reinforced concrete slabs, as the main load-bearing components in the structure of construction projects, are very likely to suffer serious damage in explosive accidents, while polyurea elastomers, with their better anti-blast and anti-impact properties, have been widely used in the field of protective engineering. It is well known that the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms of thin slabs in the range from 100 mm to 250 mm and thick concrete slabs above 250 mm are not the same, and the thickness of reinforced concrete substrates studied so far is generally concentrated in the range from 100 mm to 250 mm, and there are relatively few studies on thick slabs of polyurea-coated reinforced concrete with a slab thickness of 250 mm or more. In order to study the anti-blast performance of the polyurea/reinforced concrete thick slab composite structure, firstly, the contact explosion experiments were carried out on the polyurea/reinforced concrete thick slab composite structure with different charges, while the overall and local damage characteristics were analyzed. Secondly, numerical simulations were carried out using LS-DYNA finite element simulation software to verify the correctness of the numerical model by comparing with the experimental results. Based on LS-DYNA finite element simulations, the damage process of polyurea/reinforced concrete thick plate composite structure and the evolution of shock wave inside the polyurea/reinforced concrete thick plate were investigated, which revealed the anti-blast mechanism of the polyurea coating, and further analyzed the damage mode and damage characteristics of the polyurea/reinforced concrete thick plate composite structure. The experimental and finite element results showed that the polyurea/steel-reinforced concrete composite structure exhibited six damage modes under the contact explosion load (i.e., crate; spall; spall and bulge; threshold spall, bulging deformation of the polyurea coating; severe spall, serious bulging deformation of the polyurea coating; perforation). The investigation also demonstrated that the backside polyurea-coated reinforced concrete thick slabs effectively improved the anti-blast performance of the composite structure. The results of the study can provide a basis and reference for the design of blast resistance of polyurea/reinforced concrete thick slab composite structures.
-
表 1 实验工况
Table 1. Experimental conditions
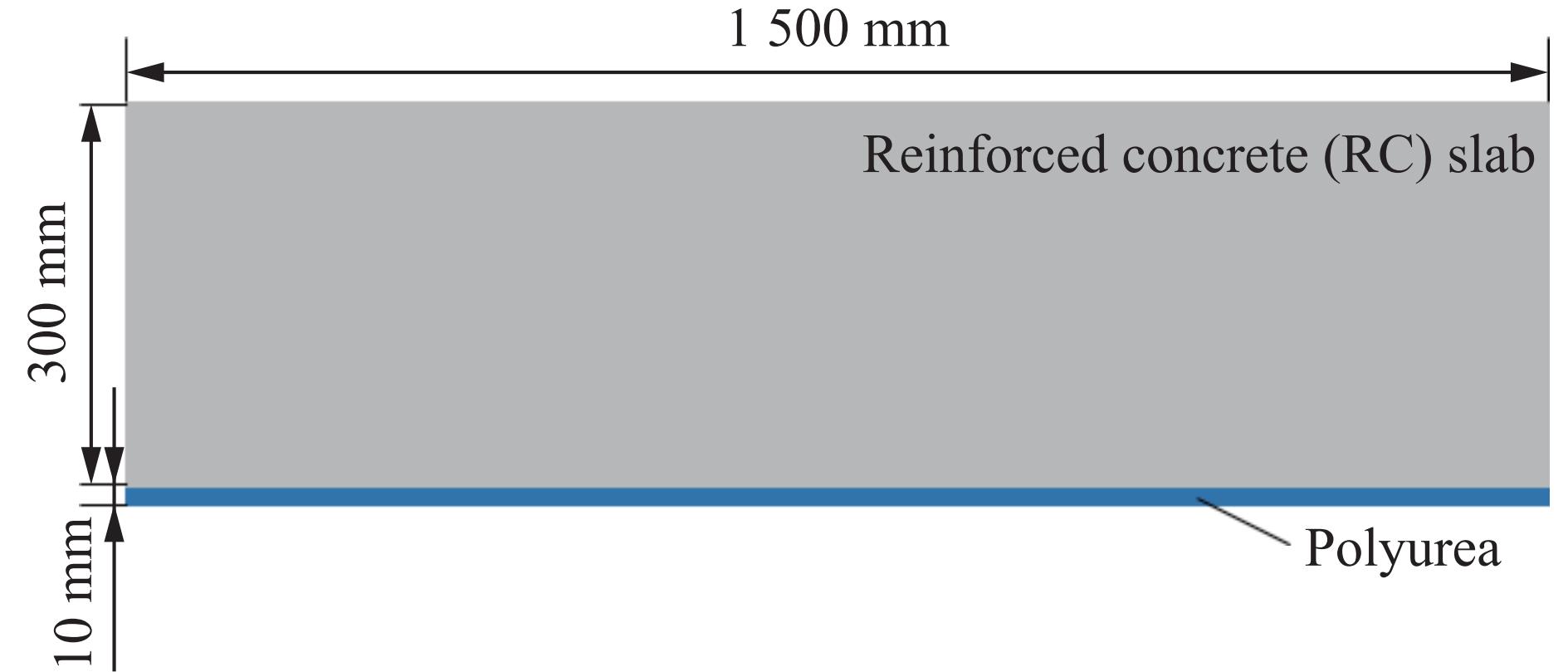
工况 模型 TNT药量/kg 聚脲涂层厚度/mm 涂覆位置 破坏形态 1 RCP1 3 10 背面 未贯穿,背面最大鼓起高度90 mm 2 RCP2 5 10 背面 未贯穿,背面最大鼓起高度172 mm 表 2 实验与数值计算结果的对比
Table 2. Comparison of experimental and numerical calculation results
模型 实验 模拟 模拟结果与实验结果的相对误差/% D/mm H/mm d/mm h/mm D/mm H/mm d/mm h/mm D H d h RCP1 738 170 1250 90 700 160 1200 84 5.15 5.88 4.00 6.67 RCP2 760 210 1270 172 720 190 1250 164 5.26 9.52 1.57 4.65 表 3 数值结果
Table 3. Numerical results
工况编号 装药量/kg 聚脲厚度/mm 比例厚度/(m∙kg−1/3) 破坏模式 RCP-1 0.5 10 0.378 正面成坑 RCP-2 1.0 10 0.300 正面成坑 RCP-3 1.5 10 0.262 层裂破坏 RCP-4 2.0 10 0.238 层裂鼓包 RCP-5 2.5 10 0.221 层裂鼓包 RCP-6 3.0 10 0.208 层裂鼓包 RCP-7 3.5 10 0.198 层裂鼓包 RCP-8 4.0 10 0.189 层裂鼓包 RCP-9 4.5 10 0.182 层裂鼓包 RCP-10 5.0 10 0.175 层裂鼓包 RCP-11 5.5 10 0.170 层裂鼓包 RCP-12 6.0 10 0.165 层裂鼓包 RCP-13 6.5 10 0.161 层裂鼓包 RCP-14 7.0 10 0.157 层裂鼓包 RCP-15 7.5 10 0.153 层裂鼓包 RCP-16 8.0 10 0.150 层裂鼓包 RCP-17 8.5 10 0.147 震塌破坏 RCP-18 9.0 10 0.144 震塌破坏 RCP-19 9.5 10 0.142 震塌破坏 RCP-20 10.0 10 0.139 震塌破坏 RCP-21 10.5 10 0.137 震塌破坏 RCP-22 11.0 10 0.135 爆炸贯穿 RCP-23 11.5 10 0.133 爆炸贯穿 RCP-24 12.0 10 0.131 贯穿和撕裂 -
[1] ZHAO C F, HE K C, ZHI L H, et al. Blast behavior of steel-concrete-steel sandwich panel: experiment and numerical simulation [J]. Engineering Structures, 2021, 246: 112998. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112998. [2] 杨光瑞, 汪维, 杨建超, 等. POZD涂覆波纹钢加固钢筋混凝土板抗爆性能 [J]. 兵工学报, 2023, 44(5): 1374–1383. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0024.YANG G Y, WANG W, YANG J C, et al. Blast resistance of reinforced concrete slabs strengthened with POZD coated corrugated steel [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2023, 44(5): 1374–1383. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2022.0024. [3] HONG J, FANG Q, CHEN L, et al. Numerical predictions of concrete slabs under contact explosion by modified K&C material model [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 155: 1013–1024. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.08.060. [4] REBELO H B, CISMASIU C. Robustness assessment of a deterministically designed sacrificial cladding for structural protection [J]. Engineering Structures, 2021, 240: 112279. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112279. [5] LI J, WU C Q, HAO H. Investigation of ultra-high performance concrete slab and normal strength concrete slab under contact explosion [J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 102: 395–408. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2015.08.032. [6] 蔡路军, 曾成林, 陈少杰, 等. 塑钢纤维混凝土板抗爆性能的试验研究及数值模拟 [J]. 混凝土, 2022(11): 6–10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2022.11.002.CAI L J, ZENG C L, CHEN S J, et al. Experimental study and numerical simulation of anti-blast performance of plastic steel fiber concrete slab [J]. Concrete, 2022(11): 6–10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2022.11.002. [7] LEE M J, KWAK H G. Numerical simulations of blast responses for SFRC slabs using an orthotropic model [J]. Engineering Structures, 2021, 238: 112150. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.112150. [8] 姜天华, 王威, 杨云锋, 等. 钢纤维混凝土箱梁在爆炸荷载作用下的动态响应 [J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2019(9): 50–53. DOI: 10.19761/j.1000-4637.2019.09.050.04.JIANG T H, WANG W, YANG Y F, et al. Dynamic response of the steel fiber reinforced concrete box girders under blast loading [J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2019(9): 50–53. DOI: 10.19761/j.1000-4637.2019.09.050.04. [9] HE J T, LEI D, SHE Z S, et al. Flexural performance and damage evaluation on basalt fiber reinforced polymer (BFRP) sheet reinforced concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 395: 132321. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132321. [10] LI S S, HE H G, YANG D P, et al. Blast responses of BFRP-bar reinforced AAC panels [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 365: 129655. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129655. [11] GAO Y J, ZHOU Y Z, ZHOU J N, et al. Blast responses of one-way sea-sand seawater concrete slabs reinforced with BFRP bars [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 232: 117254. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117254. [12] YANG F, FENG W H, LIU F, et al. Experimental and numerical study of rubber concrete slabs with steel reinforcement under close-in blast loading [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 198: 423–436. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.248. [13] YU J, LIANG S L, REN Z P, et al. Structural behavior of steel-concrete-steel and steel-ultra-high-performance-concrete-steel composite panels subjected to near-field blast load [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2023, 210: 108108. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2023.108108. [14] ZHAO C F, LU X, WANG Q, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of steel-concrete (SC) slabs under contact blast loading [J]. Engineering Structures, 2019, 196: 109337. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.109337. [15] 王逸平, 汪维, 杨建超, 等. 钢板/POZD复合结构在近距空爆载荷下的抗爆性能 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2023, 37(1): 014104. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220650.WANG Y P, WANG W, YANG J C, et al. Blast resistant performance of steel/POZD composite structures under close-range air blast loading [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2023, 37(1): 014104. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20220650. [16] ZHANG H, CHANG B X, PENG K F, et al. Anti-blast analysis and design of a sacrificial cladding with graded foam-filled tubes [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 182: 110313. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110313. [17] KOSTOPOULOS V, KALIMERIS G D, GIANNAROS E. Blast protection of steel reinforced concrete structures using composite foam-core sacrificial cladding [J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2022, 230: 109330. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2022.109330. [18] 王大江, 李鑫, 朱健. 爆炸载荷下蜂窝/波纹夹芯方板的动力学行为研究 [J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2018, 49(6): 881–885. DOI: 10.16355/j.cnki.issn1007-9432tyut.2018.06.012.WANG D J, LI X, ZHU J. Dynamic behavior of honeycomb/corrugated sandwich plates under blast loading [J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018, 49(6): 881–885. DOI: 10.16355/j.cnki.issn1007-9432tyut.2018.06.012. [19] KUMAR R, PATEL S. Failure analysis on octagonal honeycomb sandwich panel under air blast loading [J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 46: 9667–9672. DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.525. [20] CHEN Y S, WANG B, ZHANG B, et al. Polyurea coating for foamed concrete panel: an efficient way to resist explosion [J]. Defence Technology, 2020, 16(1): 136–149. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2019.06.010. [21] RAMAN S N, NGO T, MENDIS P, et al. Elastomeric polymers for retrofitting of reinforced concrete structures against the explosive effects of blast [J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2012, 2012: 754142. DOI: 10.1155/2012/754142. [22] 汪维, 杨建超, 汪剑辉, 等. POZD涂层方形钢筋混凝土板抗接触爆炸试验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(12): 121402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0180.WANG W, YANG J C, WANG J H, et al. Experimental research on anti-contact explosion of POZD coated square reinforced concrete slab [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(12): 121402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0180. [23] 杨建超, 汪剑辉, 王幸, 等. 聚异氰氨酸脂噁唑烷弹性涂层钢筋混凝土板抗震塌机理 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(4): 1338–1343. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.04.005.YANG J C, WANG J H, WANG X, et al. Anti-collapsing mechanism of reinforced concrete slab with polyisocyanate-oxazodone elastic coating [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(4): 1338–1343. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2022.04.005. [24] 彭培, 李展, 张亚栋, 等. 燃气爆炸作用下蒸压加气混凝土砌体墙的加固性能 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(3): 035101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0252.PENG P, LI Z, ZHANG Y D, et al. Performance of retrofitted autoclaved aerated concrete masonry walls subjected to gas explosions [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(3): 035101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0252. [25] WANG W, ZHANG D, LU F Y, et al. Experimental study on scaling the explosion resistance of a one-way square reinforced concrete slab under a close-in blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 49: 158–164. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2012.03.010. [26] 陈锐林, 李康, 董琪, 等. CFRP加固钢筋混凝土板爆炸冲击作用下动力响应分析的数值模拟 [J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020, 17(6): 1517–1527. DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20180143.CHEN R L, LI K, DONG Q, et al. Numerical simulation of dynamic response analysis of reinforced concrete slabs strengthened with CFRP under blast load [J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020, 17(6): 1517–1527. DOI: 10.19713/j.cnki.43-1423/u.T20180143. [27] 王喜梦, 刘均, 陈长海, 等. 近距空爆载荷下钢板/聚脲复合结构动响应特性仿真 [J]. 中国舰船研究, 2021, 16(2): 116–124. DOI: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01833.WANG X M, LIU J, CHEN C H, et al. Simulation on dynamic response characteristics of steel/polyurea composite structures under close-range air blast loading [J]. Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2021, 16(2): 116–124. DOI: 10.19693/j.issn.1673-3185.01833. [28] ZHAO C F, CHEN J Y. Damage mechanism and mode of square reinforced concrete slab subjected to blast loading [J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2013, 63/64: 54–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2013.03.006. [29] TAO C, JI C, TU J, et al. Protection mechanism of liquid-filled welded square steel container with polyurea elastomer subjected to small-arms bullet [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 198: 111668. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2024.111668. [30] 赵苏政, 葛文璇. 聚脲涂层防护下钢筋混凝土柱的抗爆性能研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2022, 28(6): 85–91. DOI: 10.19931/j.EB.20210253.ZHAO S Z, GE W X. Study on anti-detonation performance of reinforced concrete columns protected by polyurea coating [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2022, 28(6): 85–91. DOI: 10.19931/j.EB.20210253. [31] 张鹏. 聚脲涂覆结构抗弹抗爆防护性能与机制研究 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2020.ZHANG P. Protection performance and mechanism of polyurea coated structures under ballistic and blast loading conditions [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2020. [32] 张天锡. 工程爆破中卸载波与加载波互相作用的初步讨论 [J]. 爆破, 2010, 27(2): 18–21. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2010.02.005.ZHANG T X. Discussion on interaction between unloading wave and loading wave in blasting [J]. Blasting, 2010, 27(2): 18–21. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2010.02.005. [33] ZHU W Q, XIAO Y, YU J H, et al. Damage modes and mechanism of steel-concrete composite bridge slabs under contact explosion [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2024, 212: 108223. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2023.108223. [34] MCVAY M K. Spall damage of concrete structures [R]. USA: Mississippi State University. 1988: 204–209. [35] YU X, ZHOU B K, HU F, et al. Experimental investigation of basalt fiber-reinforced polymer (BFRP) bar reinforced concrete slabs under contact explosions [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 144: 103632. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103632. -






 下载:
下载: