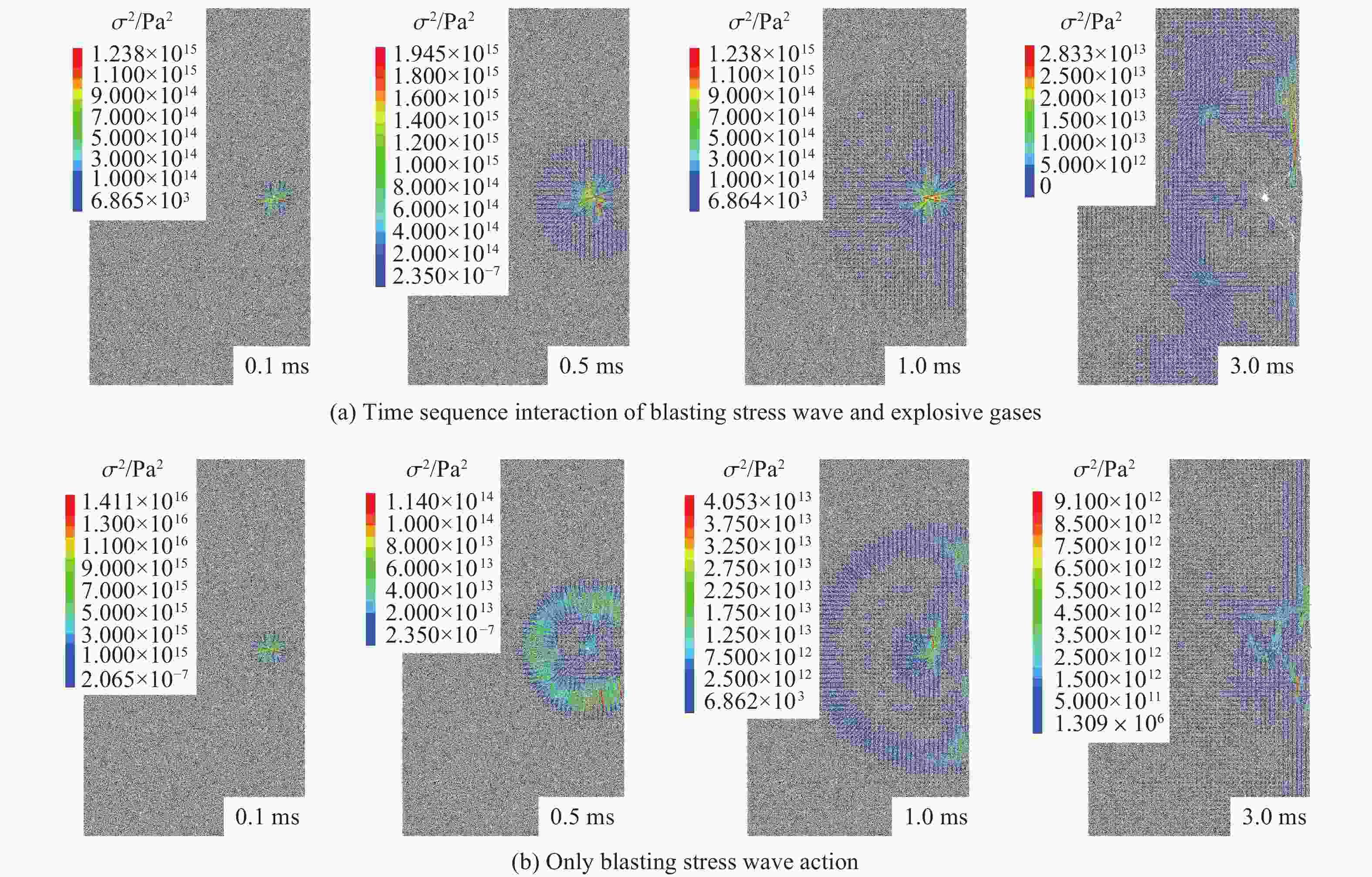
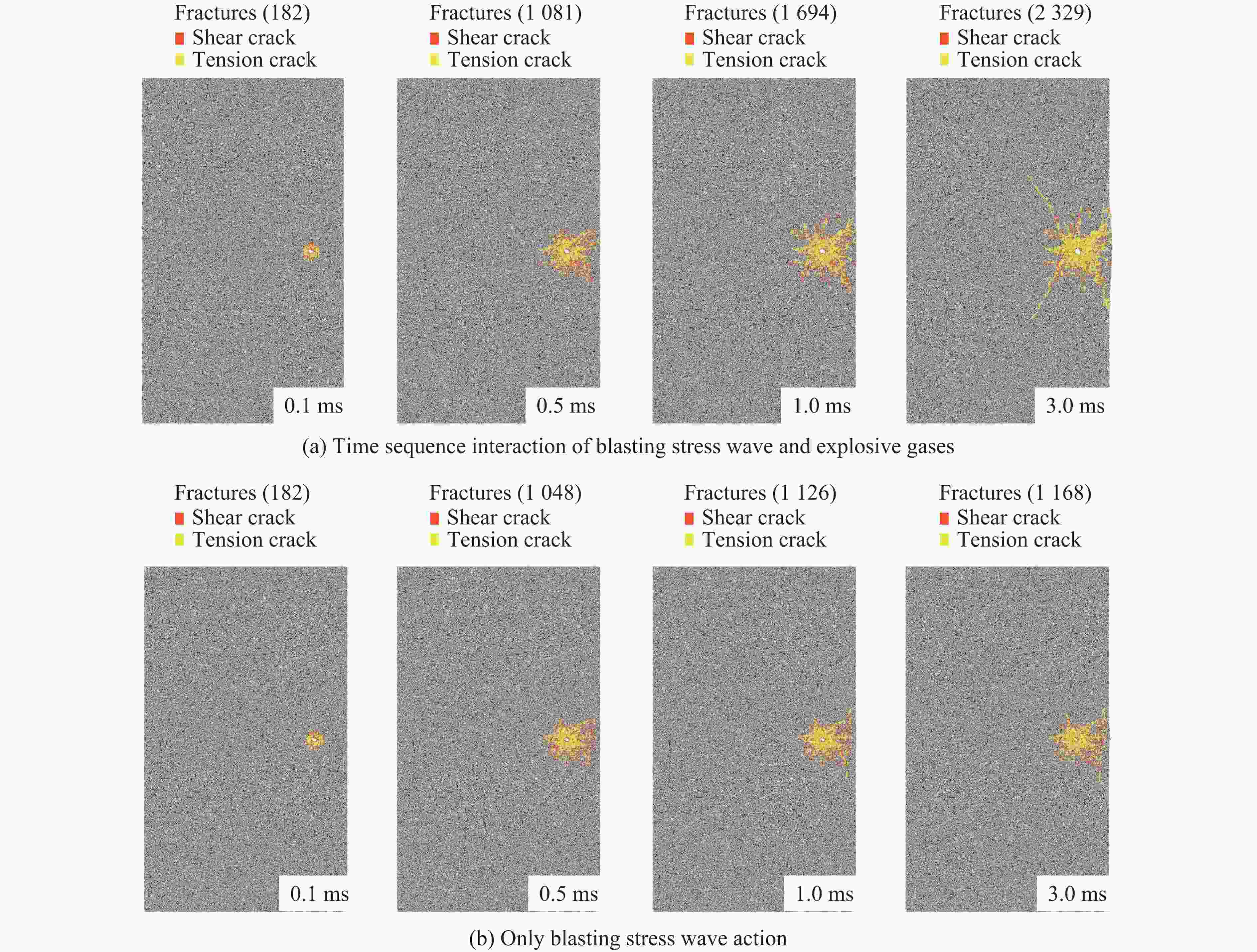
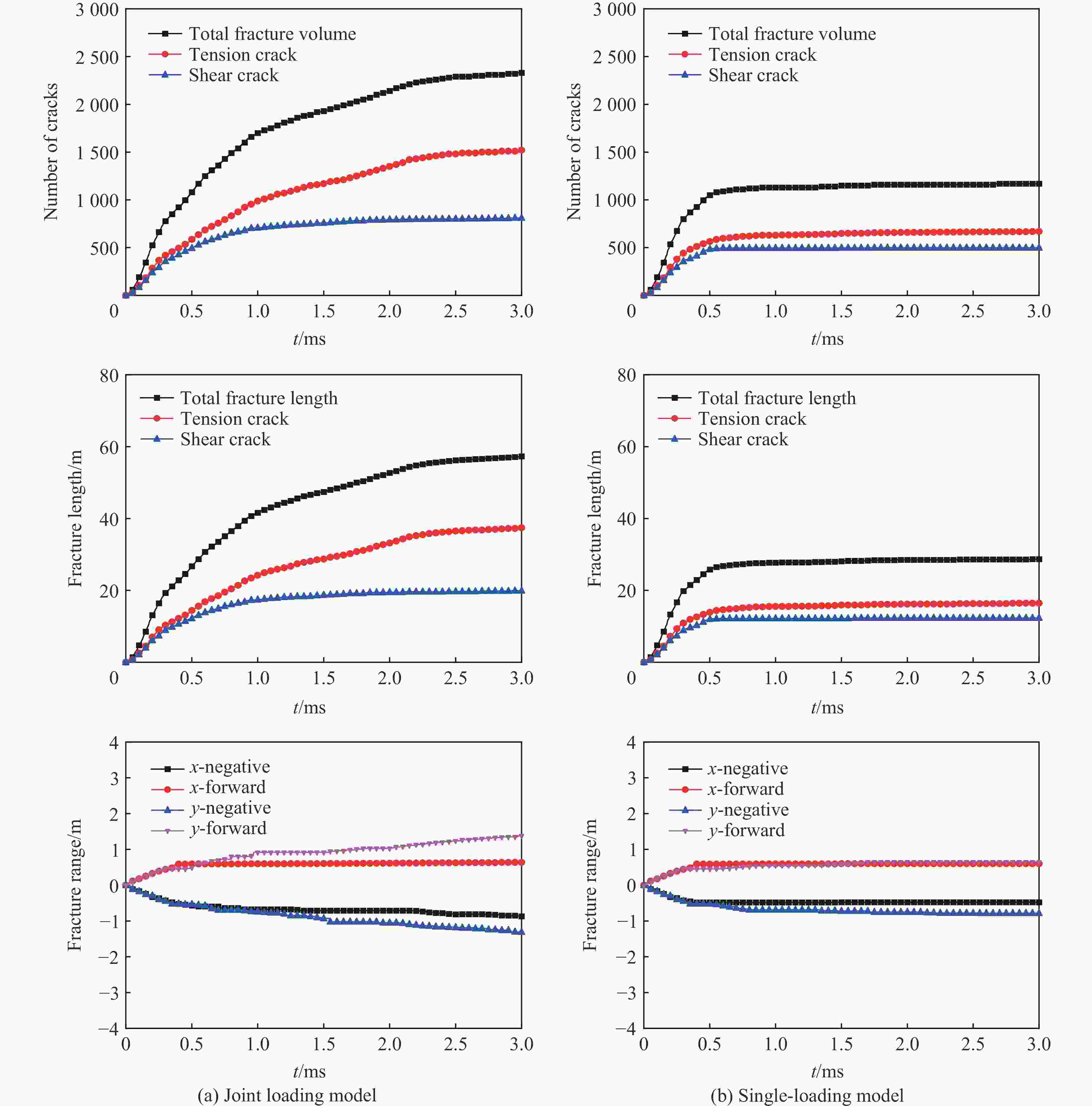
Formation mechanism of blasting crater considering the dynamic-static sequential action of blasting
-
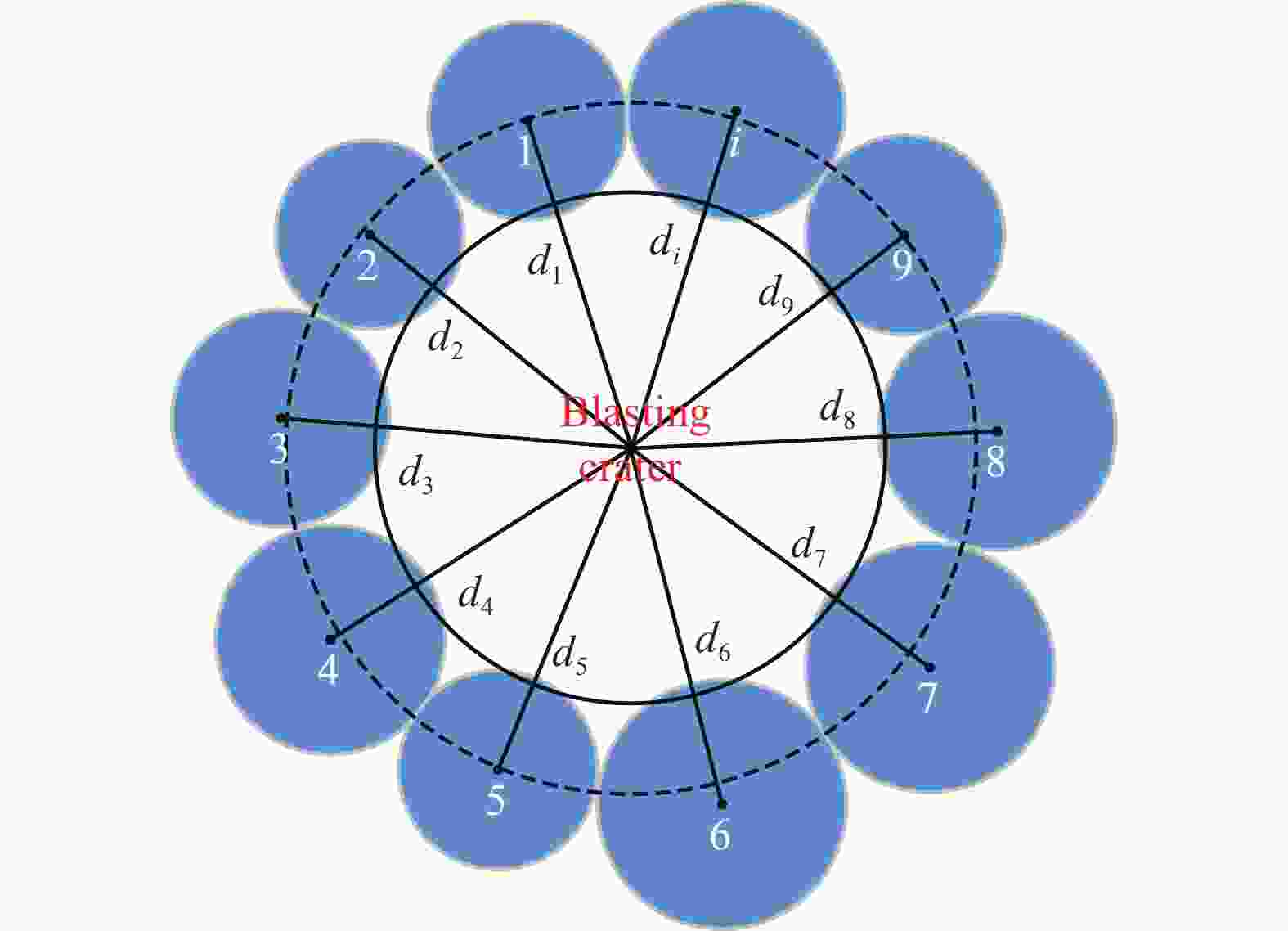
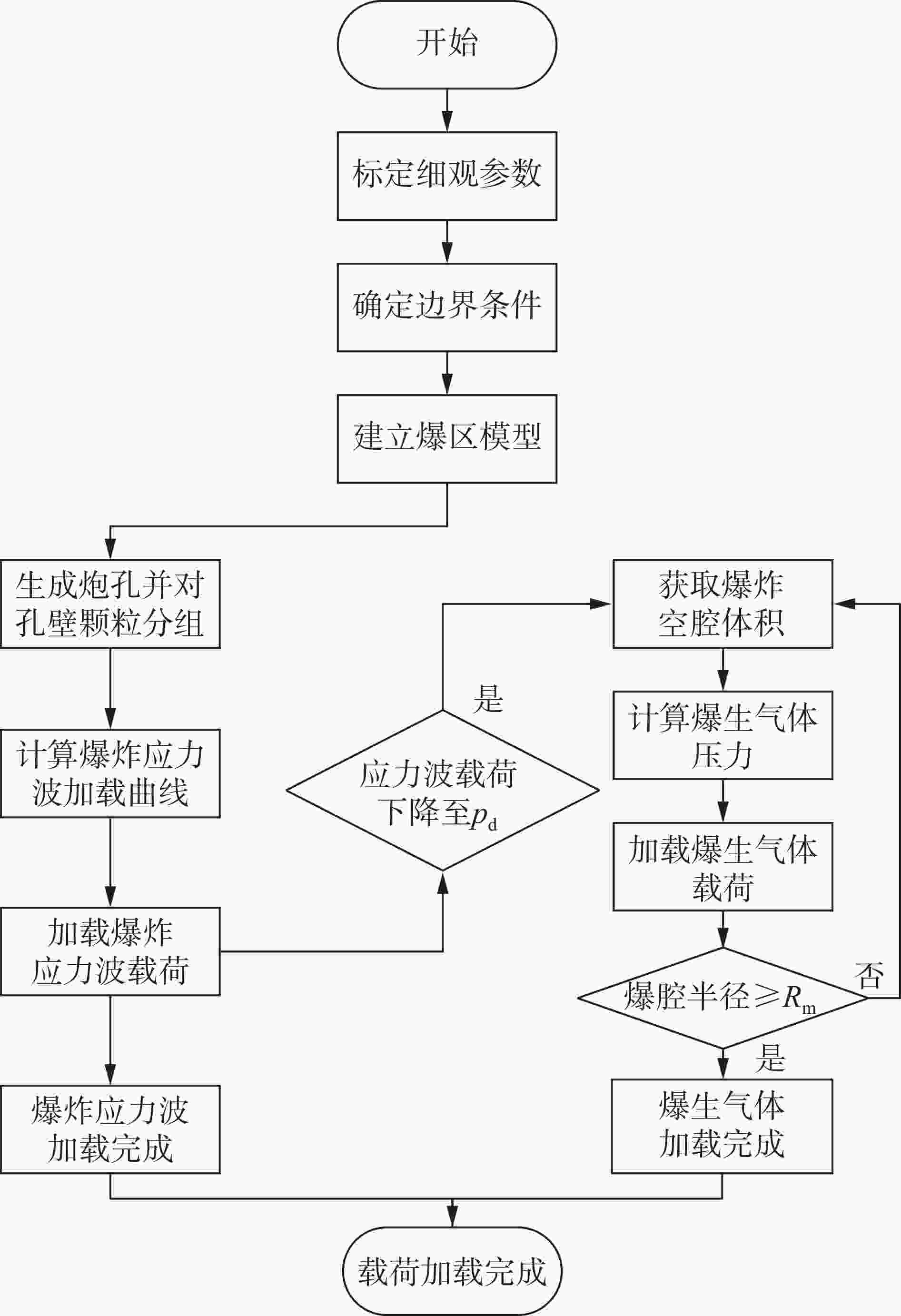
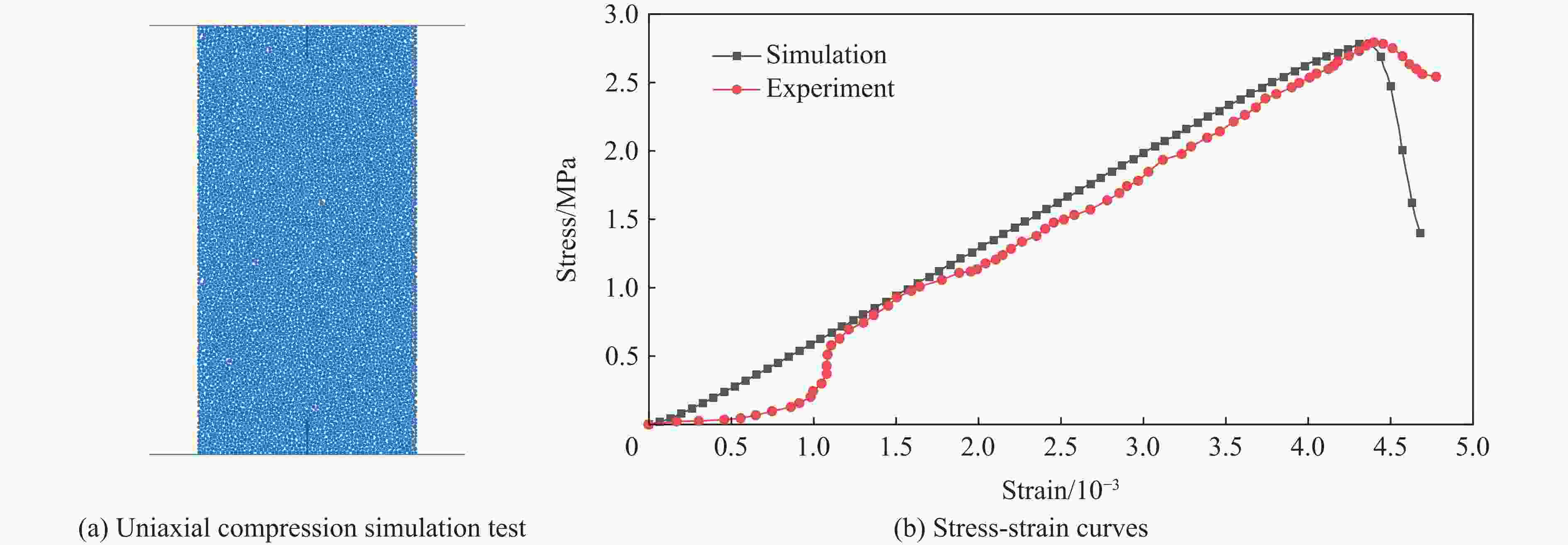
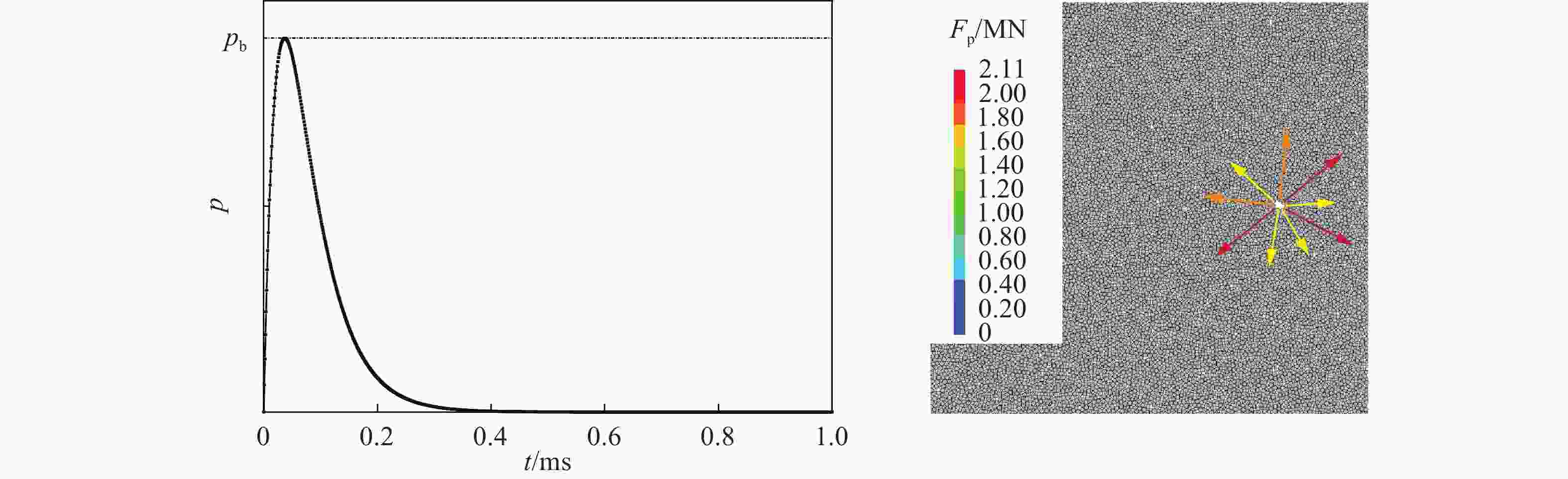
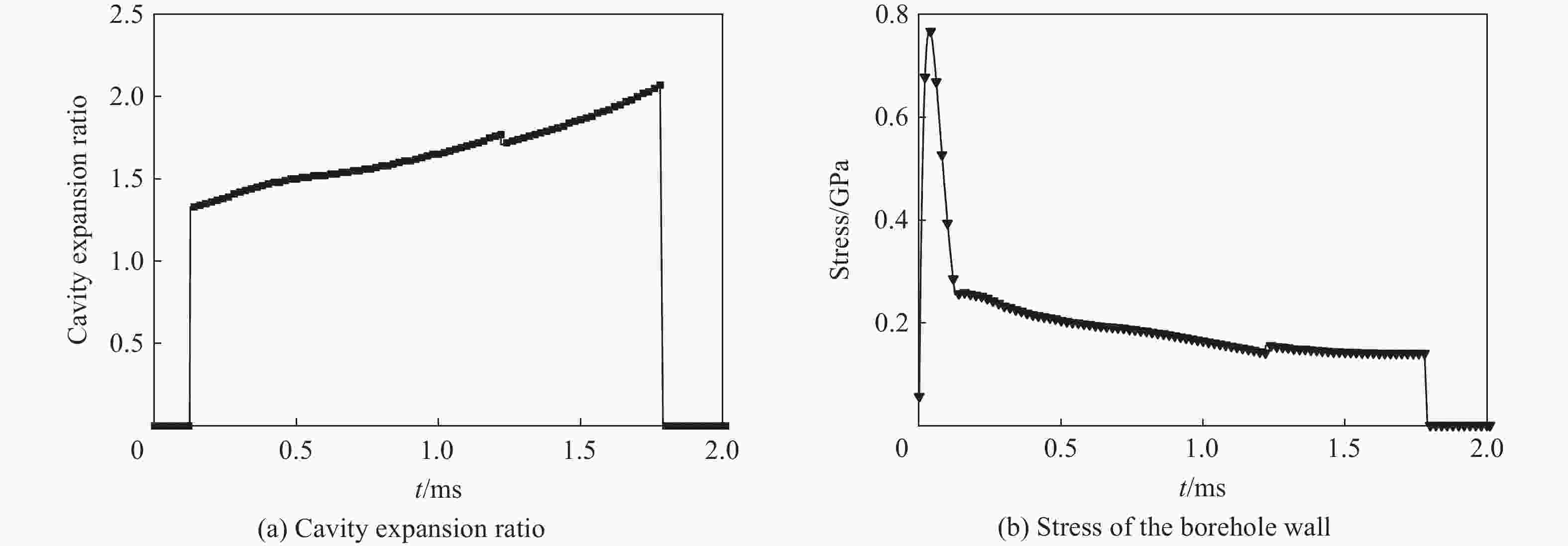
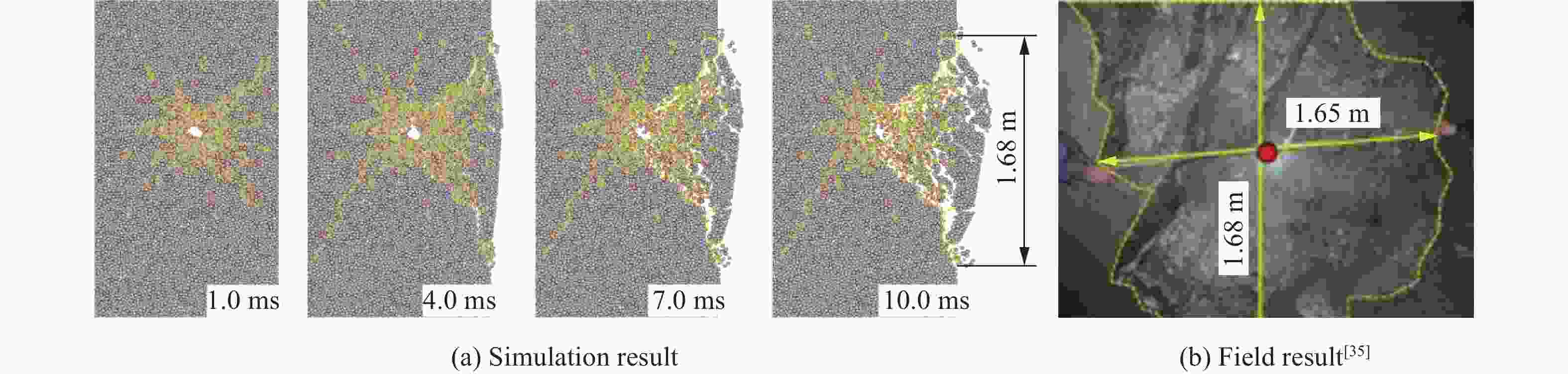
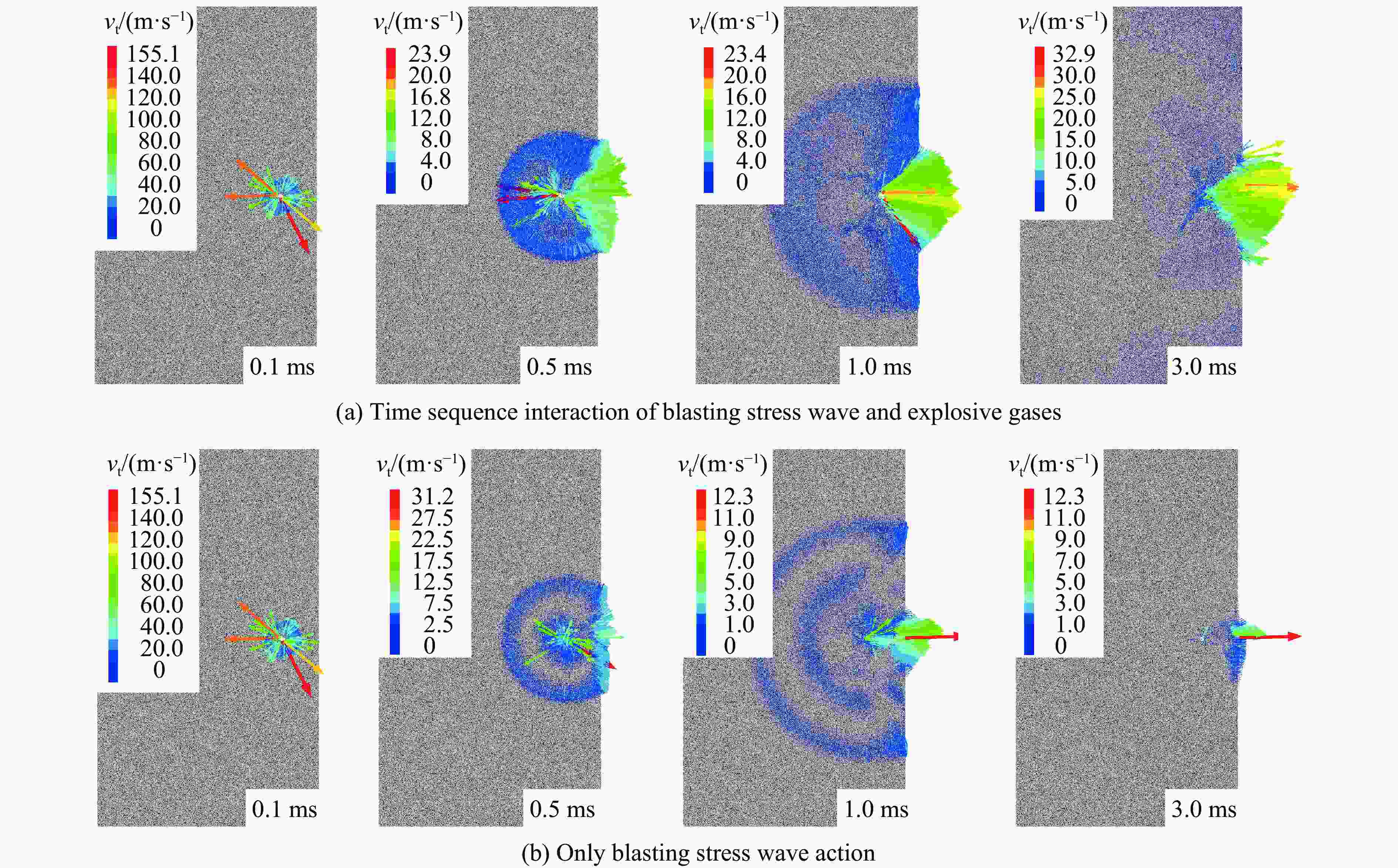
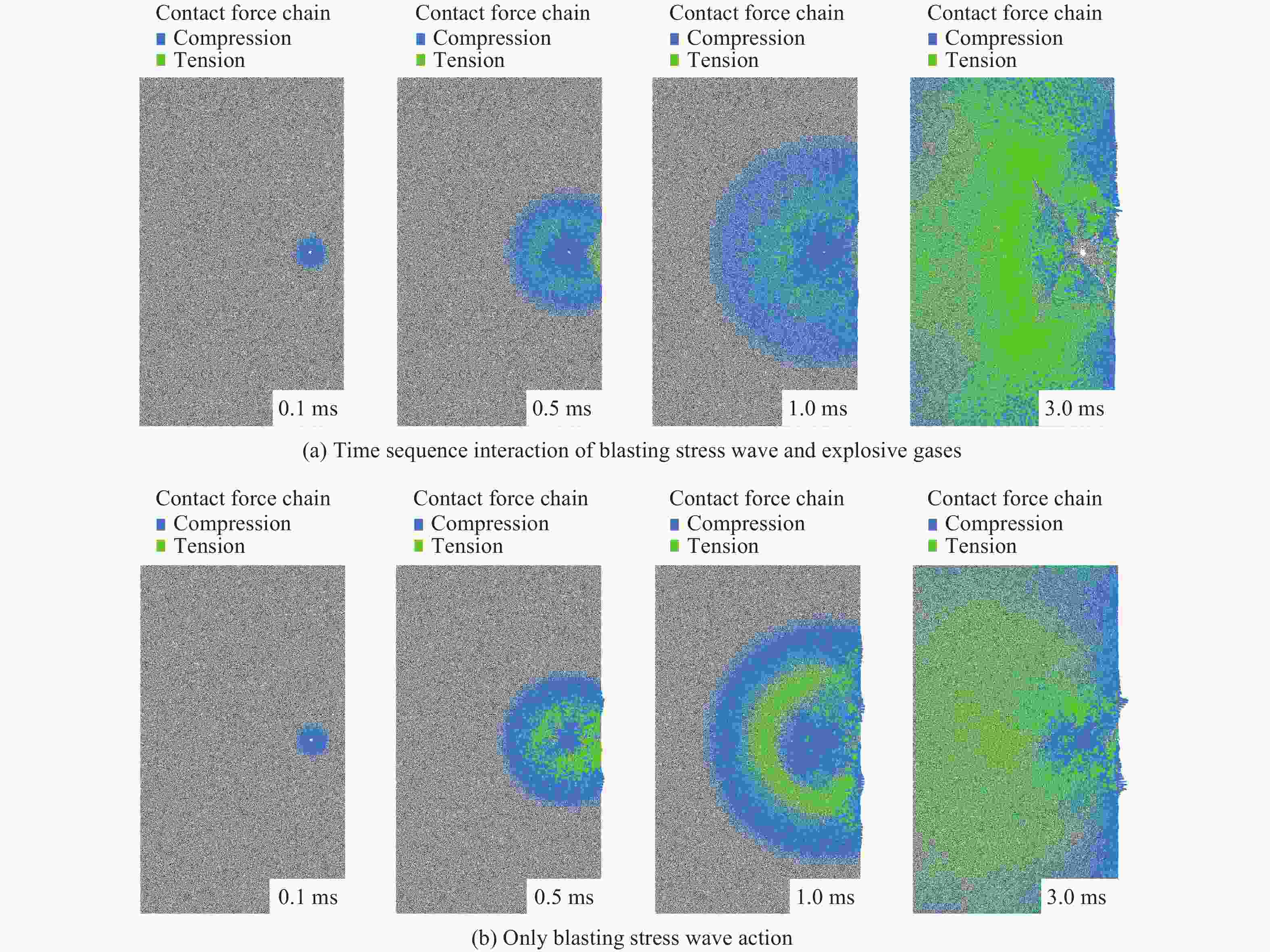
摘要: 为研究爆破漏斗的形成过程和机理,并探究该过程中爆炸应力波与爆生气体的破岩作用,基于双指数型爆炸载荷函数和爆生气体压力状态方程,构建了考虑药包爆破动-静时序作用的爆炸载荷加载模型,结合爆炸应力波和爆生气体的加载特点,建立了爆破漏斗离散元数值模型,并开展了被爆岩体的裂隙发育及破碎抛掷过程的模拟研究,对比了加载和不加载爆生气体的模拟结果,探讨了爆破漏斗形成过程中爆炸应力波和爆生气体的不同作用。结果表明:考虑药包爆破动-静时序作用的爆炸载荷加载模型模拟的爆破漏斗尺寸与现场试验结果基本吻合,可以较好地反映爆破岩体区域内裂隙的形成与演化规律及破碎岩体的抛掷效果。爆炸应力波加载率较大是引起爆源近区环状微裂隙的主要原因,同时,它会在自由面处发生反射拉伸,形成“片落”破坏;而爆生气体则是爆源远区径向长裂隙形成的主要原因,此外,它会推动破碎岩体以较大速度向外抛掷。爆生气体不仅具有准静态作用,也存在一定的动态作用,延长了爆破振动的作用时间,加强了爆破振动的速度峰值。漏斗形成过程中的裂隙发育可大致分为爆炸应力波加载致裂、爆生气体加载致裂以及变形能释放致裂3个阶段。Abstract: Research on blasting craters is one of the most fundamental studies in blasting engineering. To elucidate the formation process and mechanisms of blasting craters and to investigate the roles of blasting stress waves and explosion gases in rock fragmentation during this process, a blasting load model was developed. This model is based on a double-exponential explosive load function and the equation of state for explosion gas pressure, incorporating the dynamic-static sequential effects of blasting. By combining the distinct loading characteristics of blasting stress waves and explosion gases, a discrete element numerical model of the blasting crater was established to simulate the development of fractures, rock fragmentation, and ejection of blasted rock. Simulations were performed both with and without the inclusion of explosion gas loading to explore the respective contributions of blasting stress waves and explosion gases to crater formation. The results show that the blasting crater dimensions simulated with the dynamic-static sequential loading model align closely with field test results, accurately capturing the formation and evolution of fractures in the blasting zone and the ejection behavior of fragmented rock. The high loading rate of blasting stress waves is the primary cause of ring-shaped microfractures in the near-field region of the explosion source, which can also induce reflective tensile damage, forming “slice drop” failure at free surfaces. Explosion gases, on the other hand, are the main drivers of radially extensive fractures in the far-field region of the explosion source and propel fragmented rock outward at a high velocity. Explosion gases exhibit not only quasi-static effects but also dynamic effects, extending the duration of blasting vibrations and amplifying the peak vibration velocity. The development of fractures during crater formation can be broadly categorized into three stages: stress wave-induced fracturing, explosion gas-induced fracturing, and deformation energy release-induced fracturing.
-
表 1 平行黏结模型的细观参数
Table 1. Fine-scale parameters of the parallel bonding model
颗粒密度/
(kg·m−3)颗粒最大半径
Rmax/mm颗粒最小半径
Rmin/mm颗粒摩擦
因数颗粒接触弹性
模量/GPa颗粒
刚度比平行黏结弹性
模量/GPa黏结
刚度比平行黏结抗拉
强度/MPa平行黏结
黏聚力/MPa2 730 16.6 10.0 0.54 3.79 4.0 16.2 4.0 53.5 19.8 表 2 模型各监测点的主要数据
Table 2. Main data of each monitoring point of the model
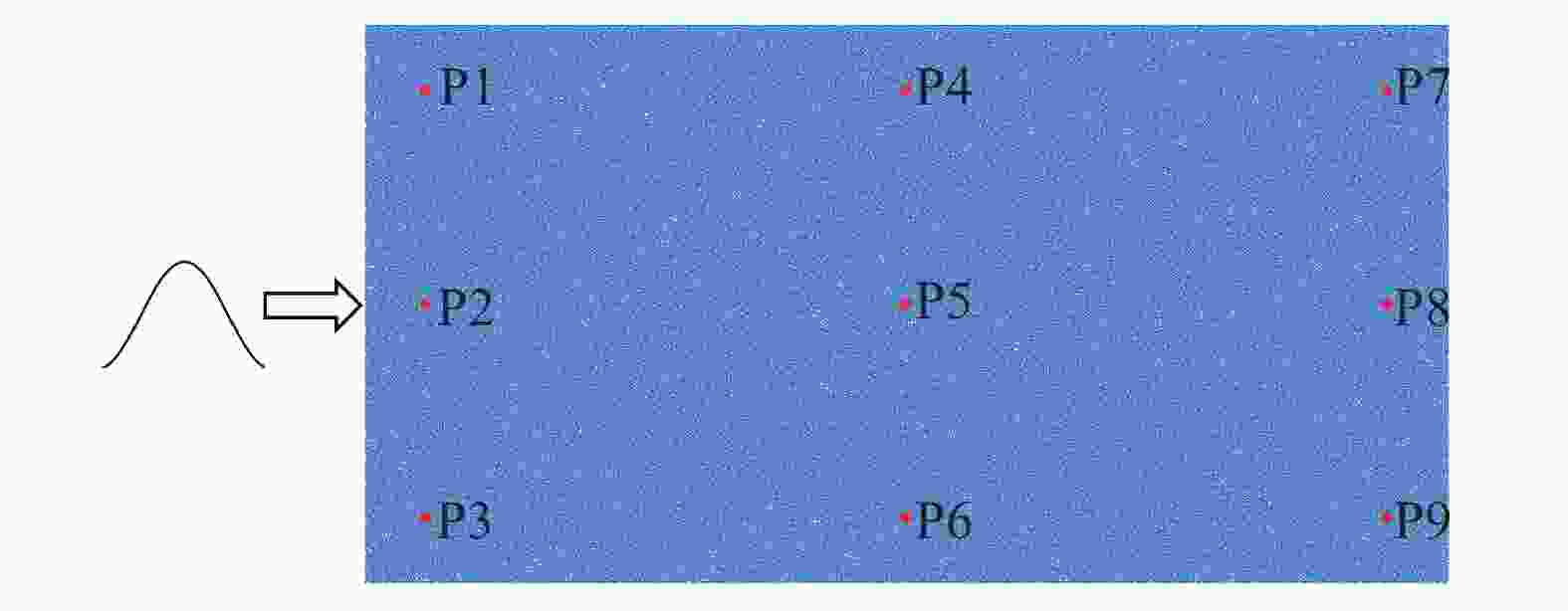
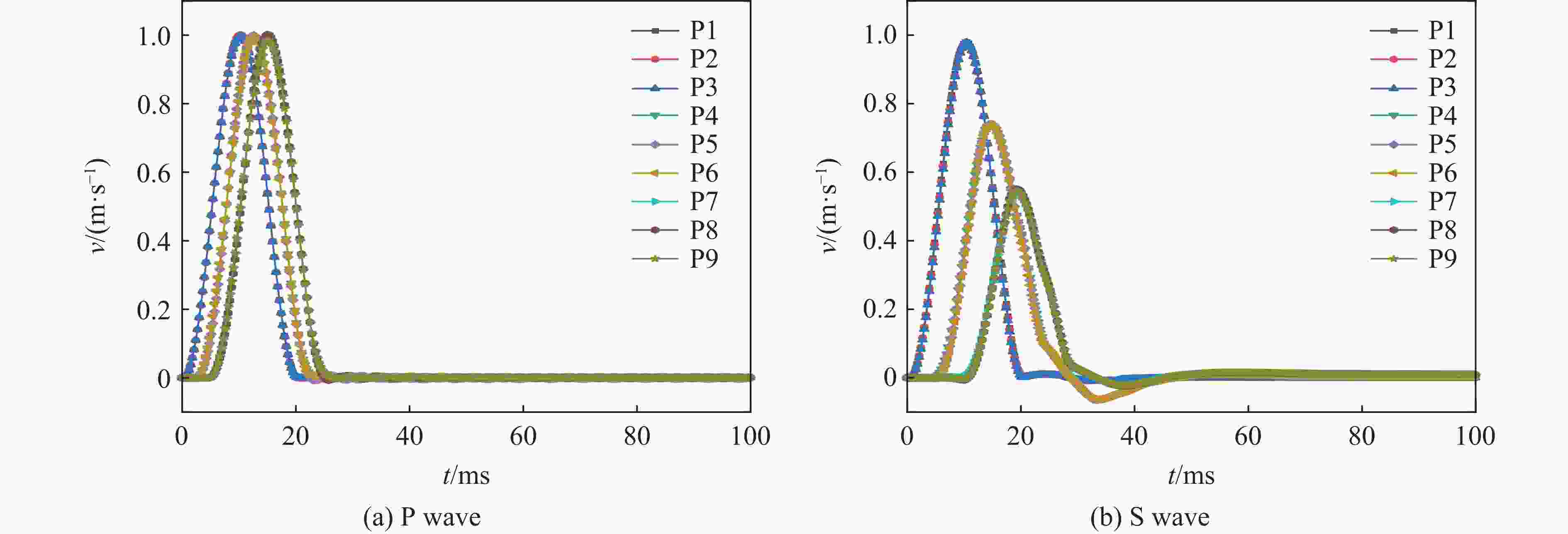
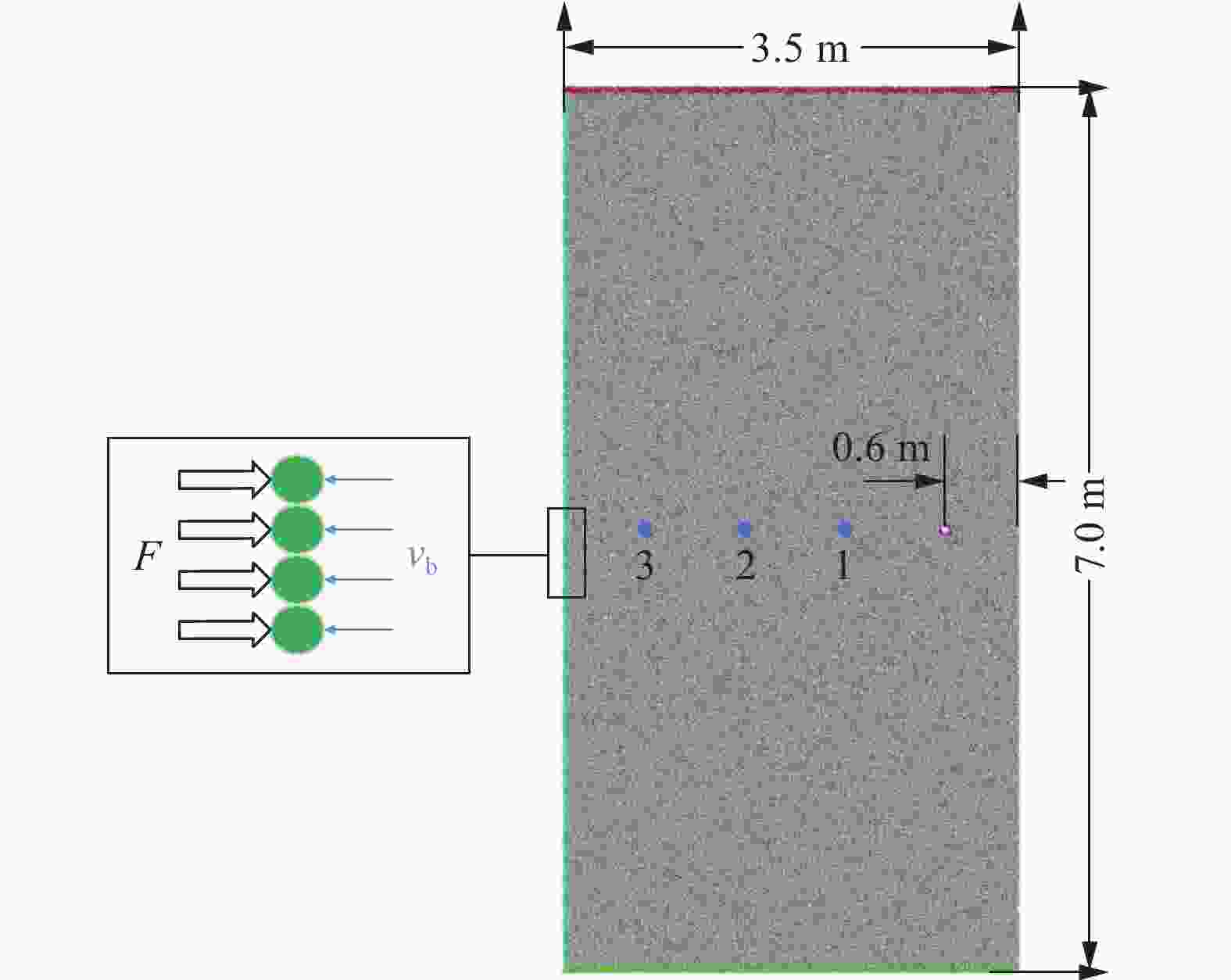
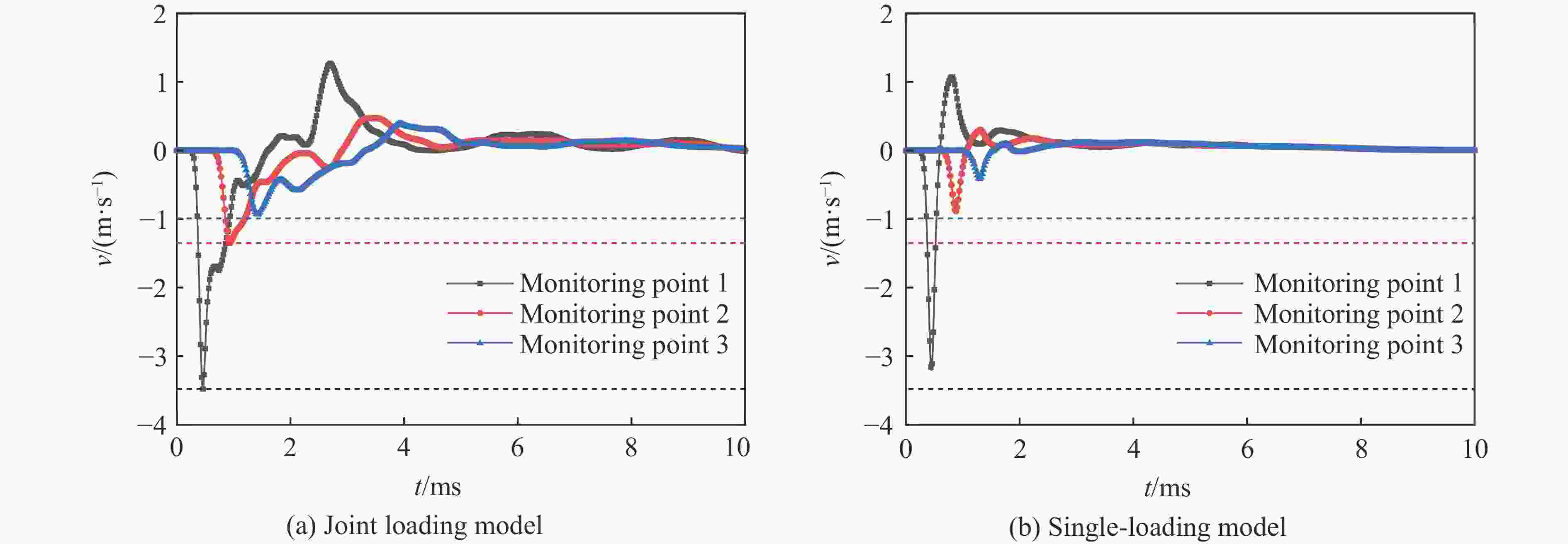
模型 监测点 速度峰值/(m·s−1) 到达峰值时间/μs 第一次归零时间/μs 联合加载模型 1 3.48 234 1144 2 1.35 346 1500 3 0.93 438 1876 单一加载模型 1 3.20 224 146 2 0.89 288 192 3 0.41 316 222 -
[1] 高启栋, 靳军, 王亚琼, 等. 孔内起爆位置对爆破振动场分布的影响作用规律 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(10): 105201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0352.GAO Q D, JIN J, WANG Y Q, et al. Acting law of in-hole initiation position on distribution of blast vibration field [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(10): 105201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0352. [2] 高峰, 李新, 罗增武, 等. 爆破漏斗体积测量方法比较与应用研究 [J]. 矿冶工程, 2023, 43(3): 38–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2023.03.009.GAO F, LI X, LUO Z W, et al. Comparison of different ways of volume measurement for explosion-produced crater [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2023, 43(3): 38–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2023.03.009. [3] 范勇, 吴进高, 冷振东, 等. 爆破漏斗岩石破碎块度实验与仿真 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(9): 2125–2139. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2022.0869.FAN Y, WU J G, LENG Z D, et al. Experiment and simulation of rock fragmentation size of blasting crater [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(9): 2125–2139. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2022.0869. [4] 齐金铎. 现代爆破理论的发展阶段 [J]. 爆破, 1996, 13(4): 7–10.QI J D. Stages in the development of modern blasting theory [J]. Blasting, 1996, 13(4): 7–10. [5] 史涵虚, 周传波, 张升, 等. 基于CWM和CM的长滩露天矿深孔台阶爆破岩体可爆性评价 [J]. 爆破, 2024, 41(1): 51–59, 119. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.01.008.SHI H X, ZHOU C B, ZHANG S, et al. Evaluation on rock mass blastability of deep hole bench blasting in Changtan open-pit mine based on CWM and CM [J]. Blasting, 2024, 41(1): 51–59, 119. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.01.008. [6] 张智宇, 陈春超, 黄永辉, 等. 爆破漏斗鼓包运动模型的构建及验证 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2020, 40(8): 810–817. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.219.ZHANG Z Y, CHEN C C, HUANG Y H, et al. Construction and validation for the model of bulging movement in explosion [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2020, 40(8): 810–817. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2019.219. [7] 李祥龙, 胡涛, 张智宇, 等. 基于高速摄影技术爆破鼓包运动规律的研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2015, 35(12): 1228–1232. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.12.004.LI X L, HU T, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Bulging movement in explosion based on high speed photography technology [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(12): 1228–1232. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.12.004. [8] ZHANG F P, YAN G L, YANG Q B, et al. Strain field evolution characteristics of free surface during crater blasting in sandstone under high stress [J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(18): 6285. DOI: 10.3390/app10186285. [9] YAN G L, ZHANG F P, KU T, et al. Experimental study on failure mechanism and geometric parameters of blasting crater under uniaxial static compressive stresses [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2022, 81(6): 251. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-022-02714-y. [10] PAN D, ZHOU K P, LI N, et al. The optimization research on large-diameter longhole blasting parameters of underground mine based on artificial neural network [C]//Proceedings of 2009 Second International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation. Changsha: IEEE, 2009, 1: 419–422. DOI: 10.1109/ICICTA.2009.109. [11] 冯春, 李世海, 郑炳旭, 等. 基于连续-非连续单元方法的露天矿三维台阶爆破全过程数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(2): 024201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0393.FENG C, LI S H, ZHENG B X, et al. Numerical simulation on complete process of three-dimensional bench blasting in an open-pit mine based on CDEM [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(2): 024201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0393. [12] HU Y G, LU W B, CHEN M, et al. Numerical simulation of the complete rock blasting response by SPH-DAM-FEM approach [J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2015, 56: 55–68. DOI: 10.1016/j.simpat.2015.04.001. [13] YU R G, ZHANG Z H, GAO W L, et al. Numerical simulation of rock mass blasting vibration using particle flow code and particle expansion loading algorithm [J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2023, 122: 102686. DOI: 10.1016/j.simpat.2022.102686. [14] GAO W L, ZHANG Z H, LI B J, et al. Study on numerical simulation of geometric elements of blasting funnel based on PFC5.0 [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2021, 2021(1): 8812964. DOI: 10.1155/2021/8812964. [15] ZHANG Z H, GAO W L, LI K P, et al. Numerical simulation of rock mass blasting using particle flow code and particle expansion loading algorithm [J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2020, 104: 102119. DOI: 10.1016/j.simpat.2020.102119. [16] 傅鹏. 岩体结构面对台阶爆破效果影响研究 [J]. 爆破, 2023, 40(1): 77–84. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.01.011.FU P. Influence of rock mass structure on bench blasting effect [J]. Blasting, 2023, 40(1): 77–84. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.01.011. [17] 赵毅波, 苏都都, 范勇, 等. 群孔起爆不同短延迟时间岩石破裂过程仿真与块度分析 [J]. 爆破, 2023, 40(3): 92–100, 122. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.013.ZHAO Y B, SU D D, FAN Y, et al. Simulation of rock fracture process and fragmentation analysis with different short delays for group hole blasting [J]. Blasting, 2023, 40(3): 92–100, 122. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.013. [18] XIA M, ZHOU K P. Particle simulation of the failure process of brittle rock under triaxial compression [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2010, 17(5): 507–513. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-010-0350-4. [19] POTYONDY D O. Simulating stress corrosion with a bonded-particle model for rock [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2007, 44(5): 677–691. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.10.002. [20] YANG J X, SHI C, YANG W K, et al. Numerical simulation of column charge explosive in rock masses with particle flow code [J]. Granular Matter, 2019, 21(4): 96. DOI: 10.1007/s10035-019-0950-2. [21] AN L, SUORINENI F T, XU S, et al. A feasibility study on confinement effect on blasting performance in narrow vein mining through numerical modelling [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 112: 84–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.10.010. [22] HAGAN T N. Rock breakage by explosives [M]//OPPENHEIM A K. Gasdynamics of Explosions and Reactive Systems. Oxford: Pergamon, 1980: 329–340. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-08-025442-5.50034-2. [23] CLARK J A, DURELLI A J. An introduction to dynamic photoelasticity: discussion [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1983, 23(1): 42–48. DOI: 10.1007/BF02328680. [24] 王家来, 徐颖. 应变波对岩体的损伤作用和爆生裂纹传播 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1995, 15(3): 212–216. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1995)03-0212-5.WANG J L, XU Y. Damaging effects of strain waves on rock masses and explosive crack propagation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1995, 15(3): 212–216. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1995)03-0212-5. [25] 苏都都, 严鹏, 卢文波, 等. 露天台阶爆破爆堆形态的PFC模拟 [J]. 爆破, 2012, 29(3): 35–41. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2012.03.009.SU D D, YAN P, LU W B, et al. Prediction of muckpile profile for open bench blasting with PFC [J]. Blasting, 2012, 29(3): 35–41. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2012.03.009. [26] 黄尘, 李江腾, 赵远, 等. 基于PFC2D的冬瓜山铜矿爆破参数优化 [J]. 矿冶工程, 2022, 42(1): 1–4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2022.01.001.HUANG C, LI J T, ZHAO Y, et al. Optimization of blasting parameters for Dongguashan copper mine based on PFC2D [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2022, 42(1): 1–4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2022.01.001. [27] JEON S S, KIM D S, JANG Y W. Stability assessment of concrete lining and rock bolts of the adjacent tunnel by blast-induced vibration [J]. Journal of the Korean Geotechnical Society, 2007, 23(10): 33–45. DOI: 10.7843/kgs.2007.23.10.33. [28] 冷振东, 刘亮, 周旺潇, 等. 起爆位置对台阶爆破爆堆形态影响的离散元分析 [J]. 爆破, 2018, 35(2): 50–55, 100. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2018.02.009.LENG Z D, LIU L, ZHOU W X, et al. Numerical investigation of initiation points on muckpile profile in bench blasting [J]. Blasting, 2018, 35(2): 50–55, 100. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2018.02.009. [29] YE Z W, YANG J H, YAO C, et al. Attenuation characteristics of shock waves in drilling and blasting based on viscoelastic wave theory [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2023, 171: 105573. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2023.105573. [30] 杜俊林, 罗强, 宗琦. 空气不耦合装药爆破孔壁冲击压力分析 [J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2005, 25(3): 306–310. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2005.03.009.DU J L, LUO Q, ZONG Q. Analysis on preliminary shock pressure on borehole of air-de-coupling charging [J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2005, 25(3): 306–310. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9315.2005.03.009. [31] 陈士海, 李玉民, 林从谋, 等. 条形装药硐室爆破研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1995, 15(4): 363–373. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1995)04-0363-11.CHEN S H, LI Y M, LIN C M, et al. Explosive blast studies of strip-charged chambers [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1995, 15(4): 363–373. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1995)04-0363-11. [32] 田浩帆, 雷振, 包太, 等. 初始地应力作用下岩石爆破裂纹扩展研究 [J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(3): 138–146, 159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.03.018.TIAN H F, LEI Z, BAO T, et al. Study on rock blasting crack growth under initial in-situ stress [J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2022, 12(3): 138–146, 159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.03.018. [33] NING Y J, YANG J, MA G W, et al. Modelling rock blasting considering explosion gas penetration using discontinuous deformation analysis [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2011, 44(4): 483–490. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-010-0132-3. [34] 于成龙, 王仲琦. 球形装药爆腔预测的准静态模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(2): 249–254. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)02-0249-06.YU C L, WANG Z Q. Quasi-static model for predicting explosion cavity with spherical charges [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(2): 249–254. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)02-0249-06. [35] 吴再海, 安龙, 齐兆军, 等. 基于LS-DYNA与PFC联合的岩体爆破数值模拟方法分析 [J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2021, 38(3): 609–614. DOI: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2020.0133.WU Z H, AN L, QI Z J, et al. The numerical simulation method of rock mass blasting based on PFC combined with LS-DYNA [J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2021, 38(3): 609–614. DOI: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2020.0133. [36] LYSMER J, KUHLEMEYER R L. Finite dynamic model for infinite media [J]. Journal of the engineering mechanics division, 1969, 95(4): 859–877. DOI: 10.1061/JMCEA3.0001144. [37] 石崇, 张强, 王盛年. 颗粒流(PFC5.0)数值模拟技术及应用 [M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2018: 353–360.SHI C, ZHANG Q, WANG S N. Numerical simulation technology and application with particle flow code (PFC 5.0) [M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2018: 353–360. [38] 许彪. 基于PFC的岩石控制爆破技术研究 [D]. 淮南: 安徽理工大学, 2018: 29–30. DOI: 10.7666/d.Y3396161.XU B. Research on controlled blasting technology of rock based on PFC [D]. Huainan: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2018: 29–30. DOI: 10.7666/d.Y3396161. [39] 雷涛, 康普林, 叶海旺, 等. 柱状药包爆破过程中应力波叠加与岩体裂隙分布的方向效应研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2024, 43(2): 399–411. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2023.0476.LEI T, KANG P L, YE H W, et al. Study on the direction effect of stress wave superposition and fracture distribution in rock mass during cylindrical charge blasting [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2024, 43(2): 399–411. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2023.0476. [40] 冷振东, 卢文波, 陈明, 等. 岩石钻孔爆破粉碎区计算模型的改进 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2015, 35(1): 101–107. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)01-0101-07.LENG Z D, LU W B, CHEN M, et al. Improved calculation model for the size of crushed zone around blasthole [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2015, 35(1): 101–107. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2015)01-0101-07. -






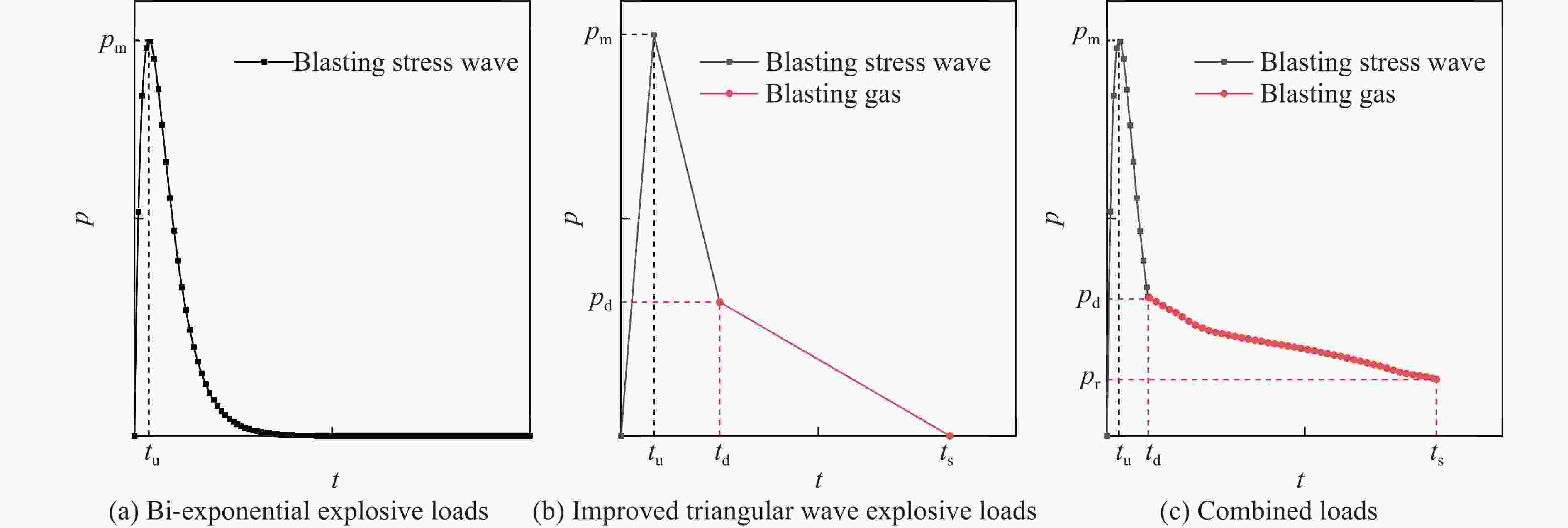
 下载:
下载: