On formation mechanism of perforation channel during rock breaking by abrasive water jet
-
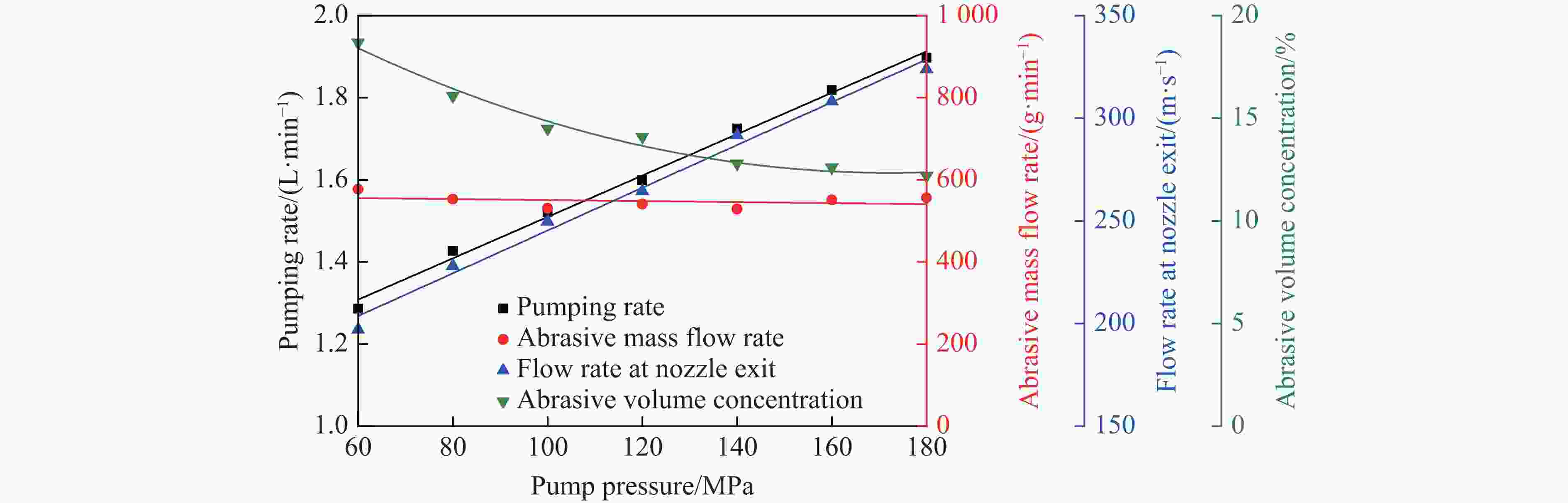
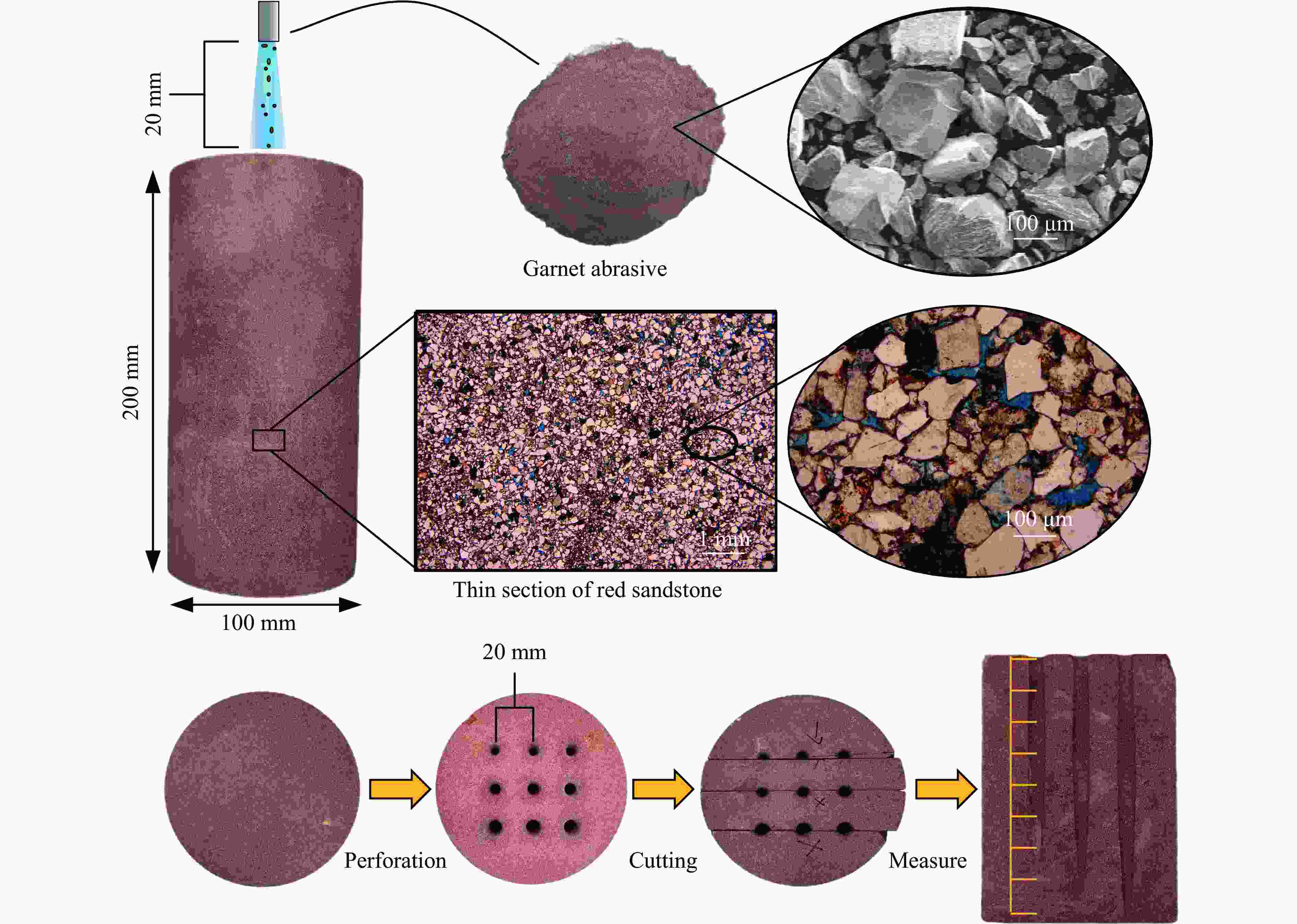
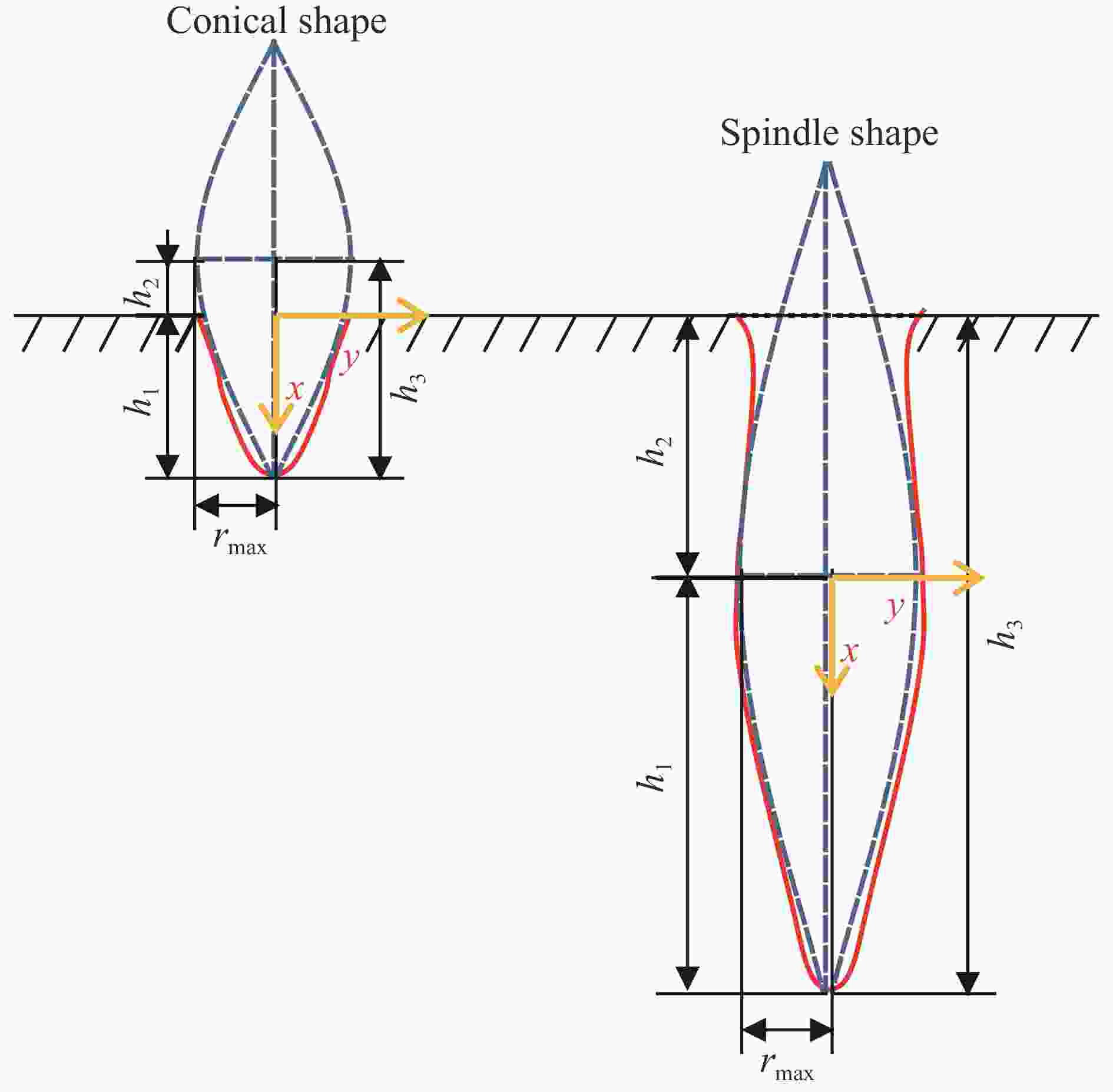
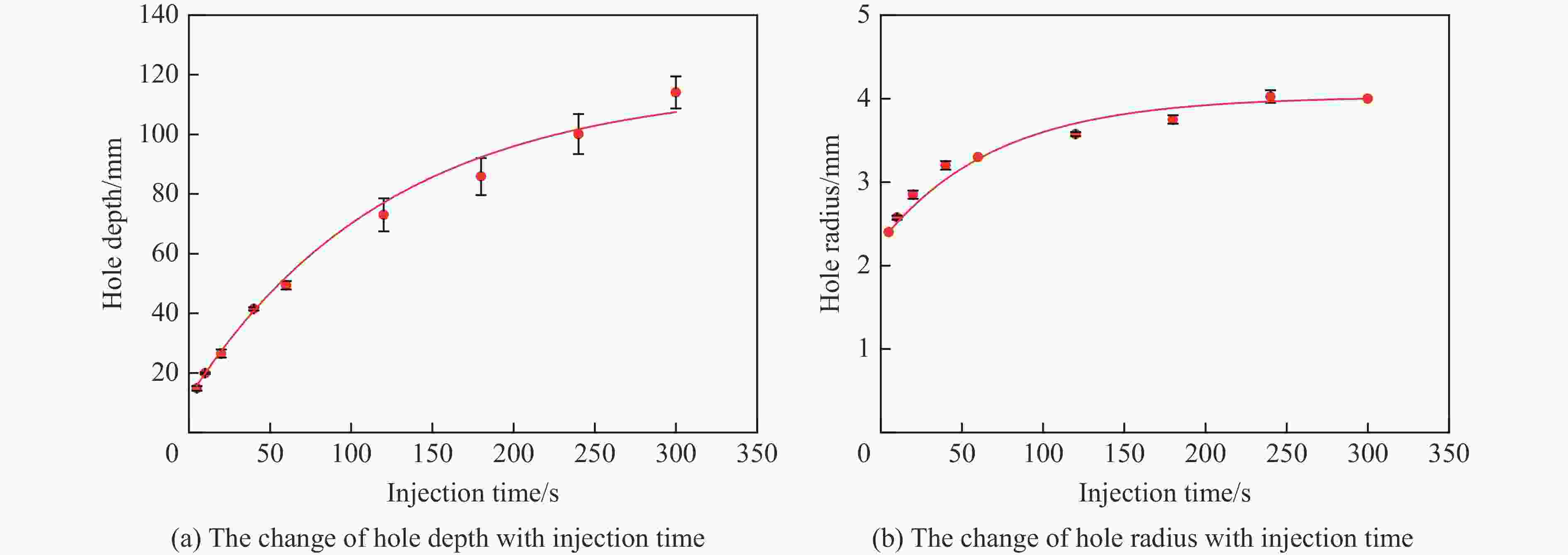
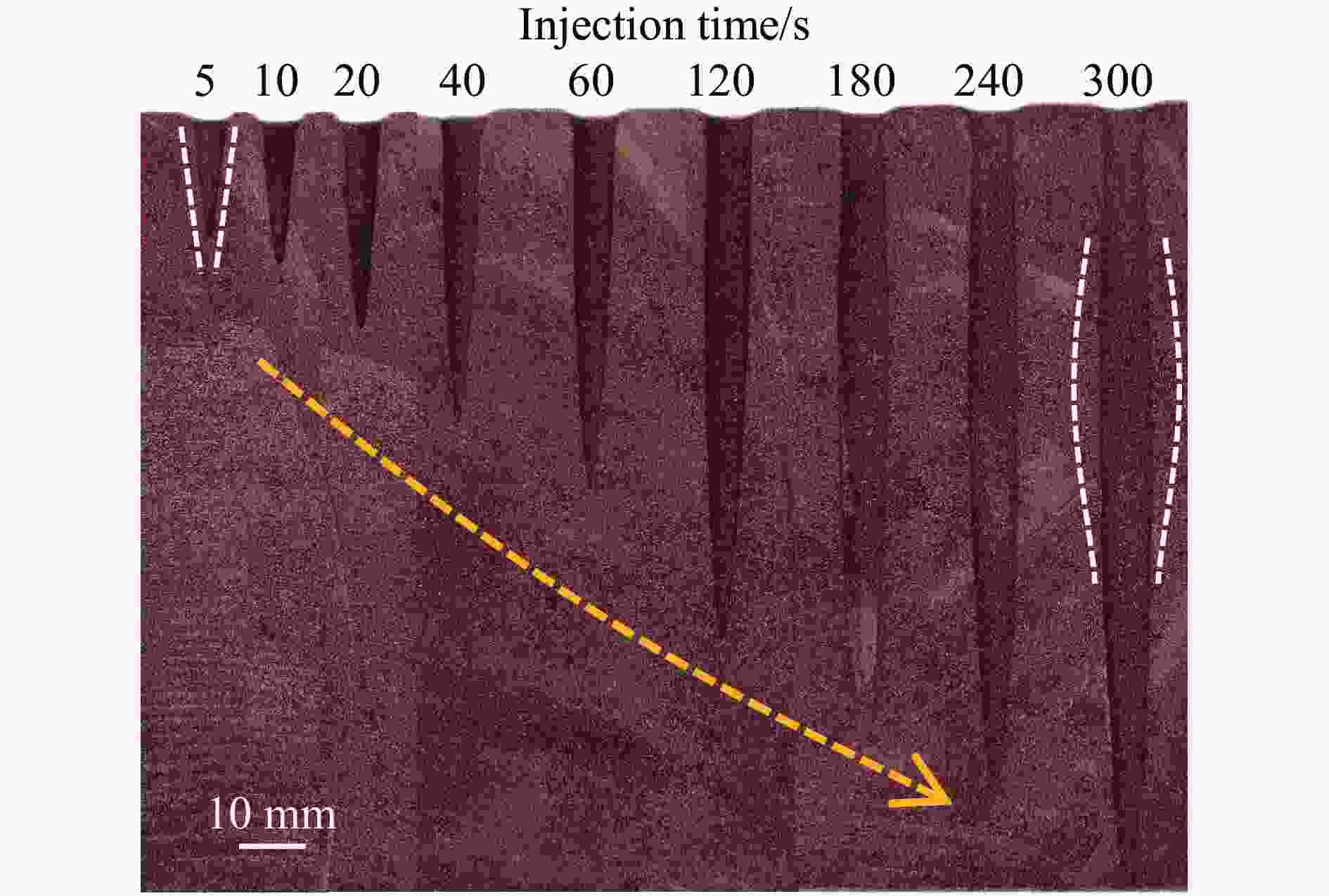
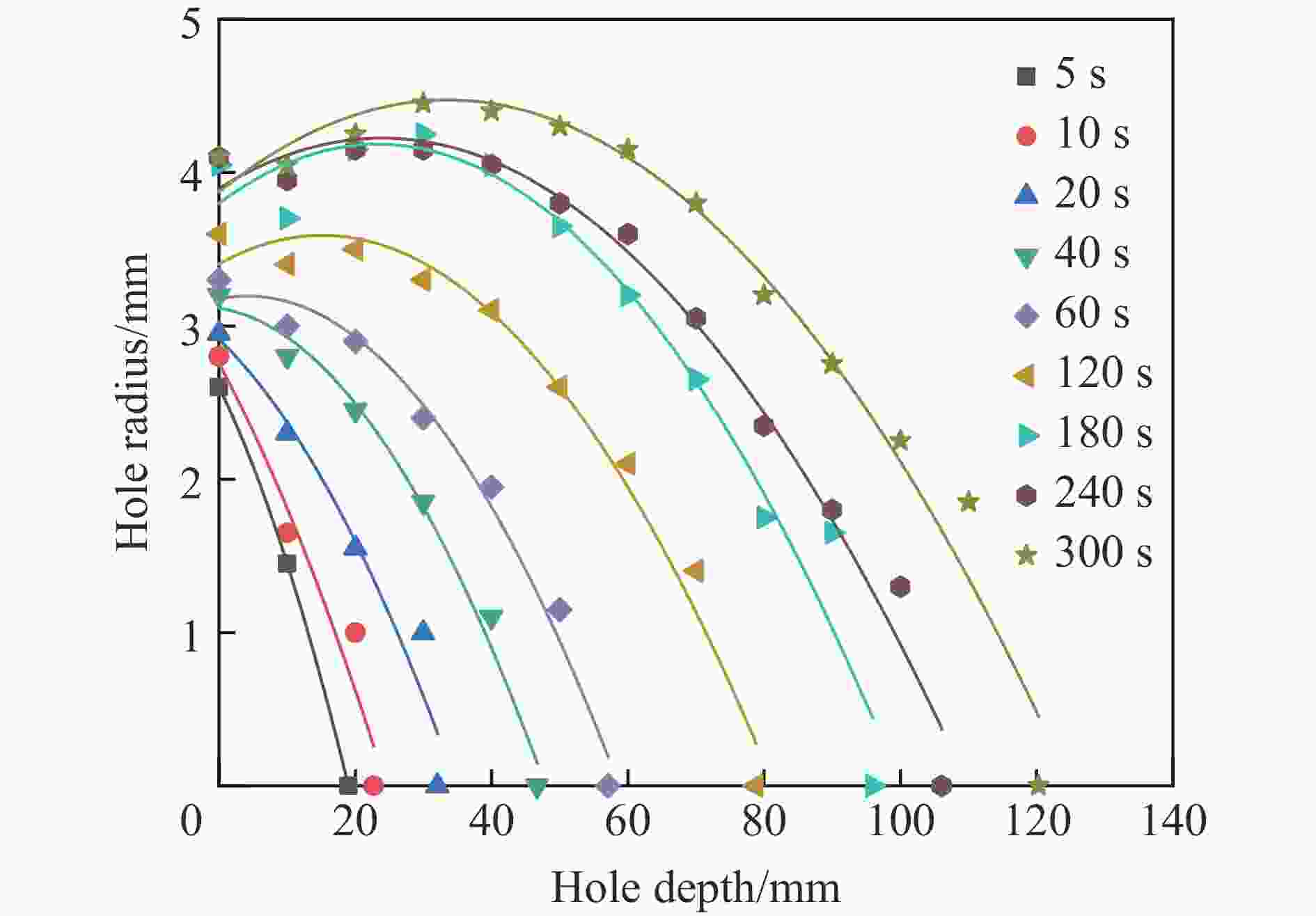
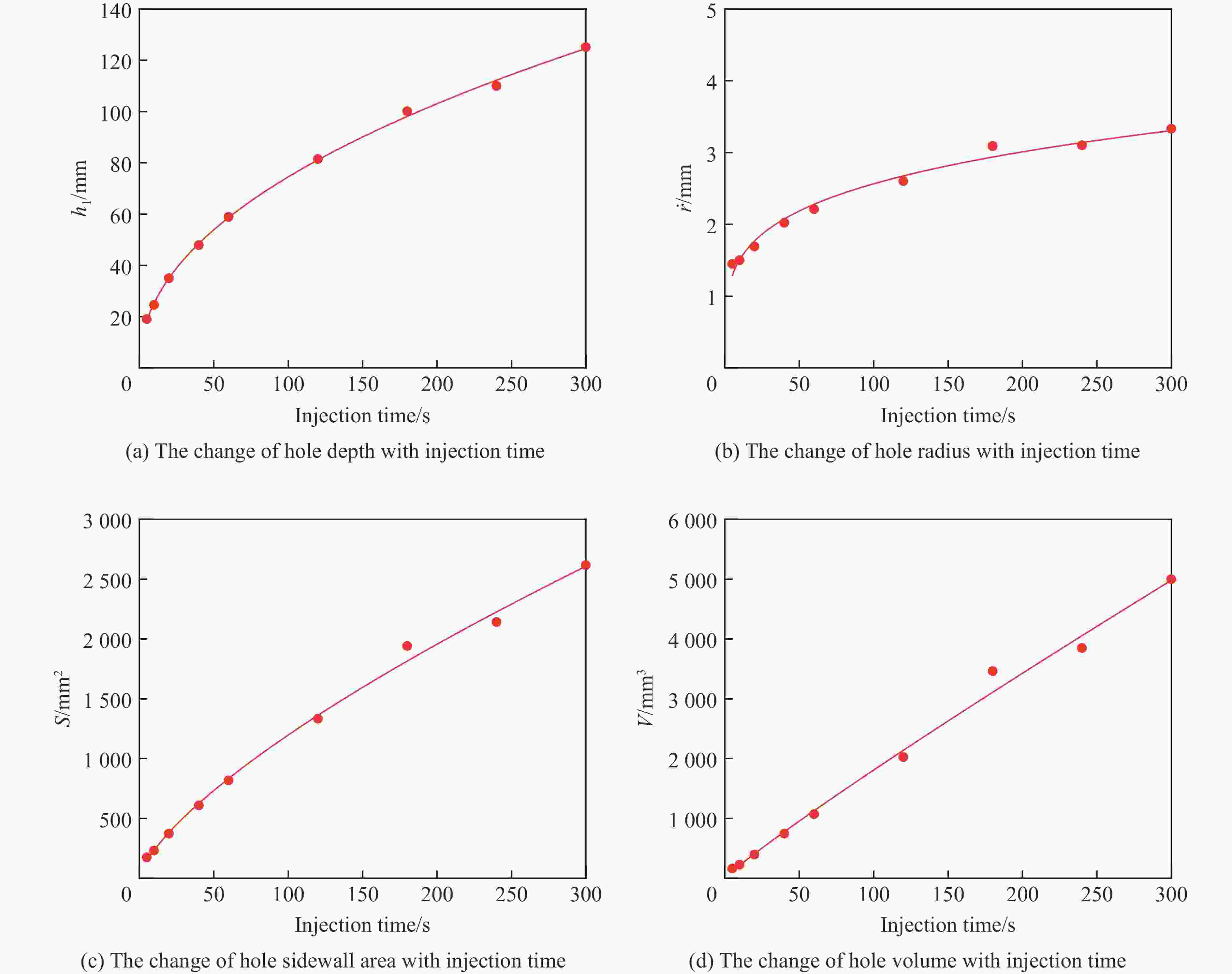
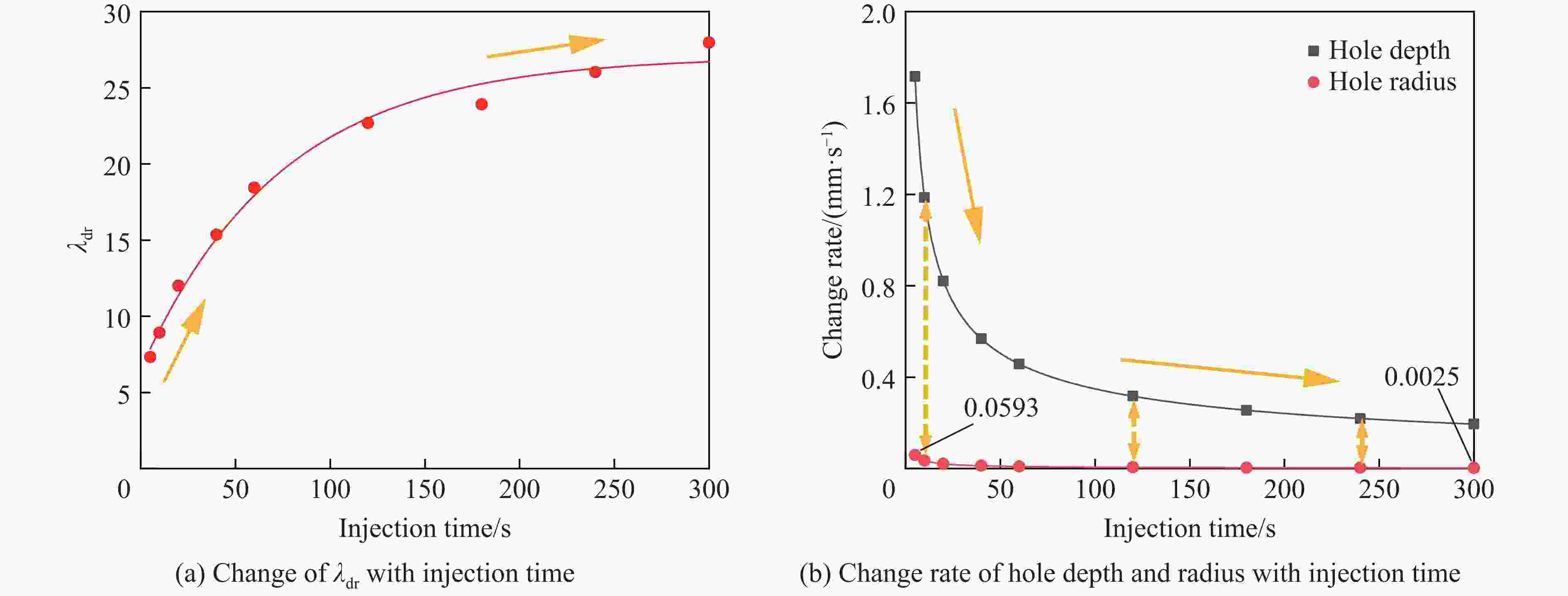
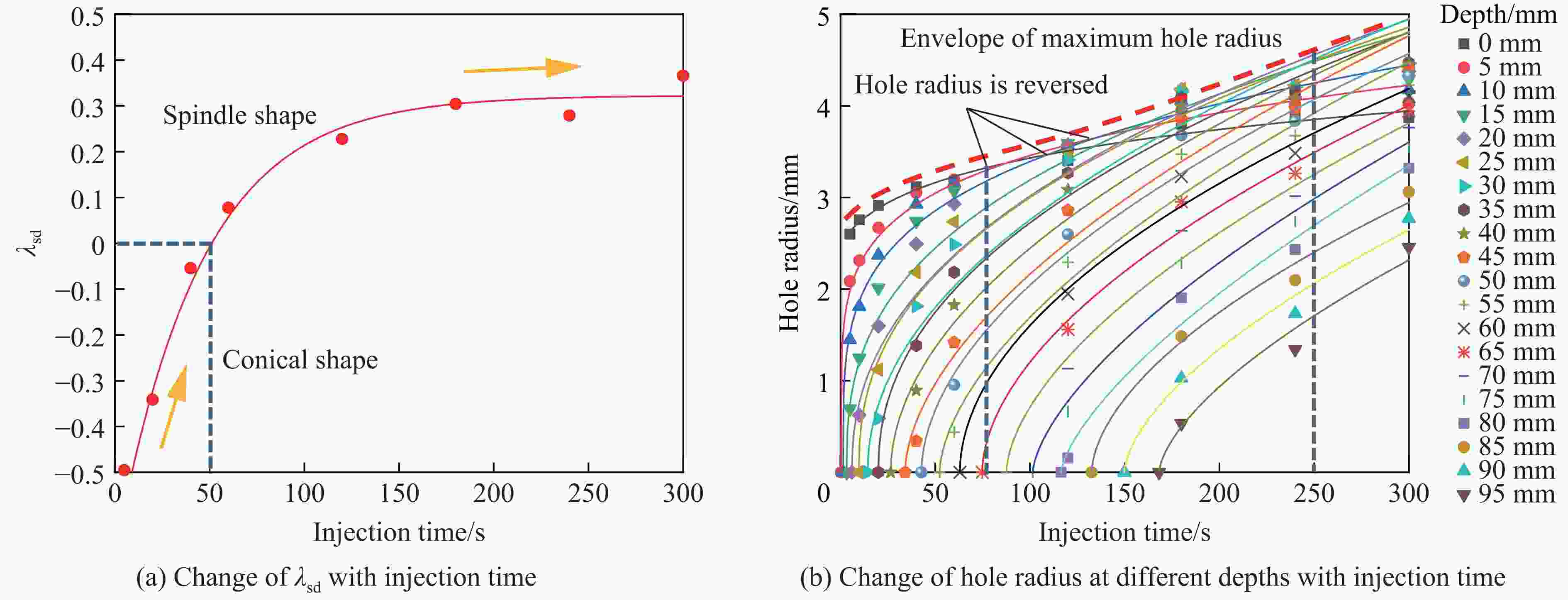
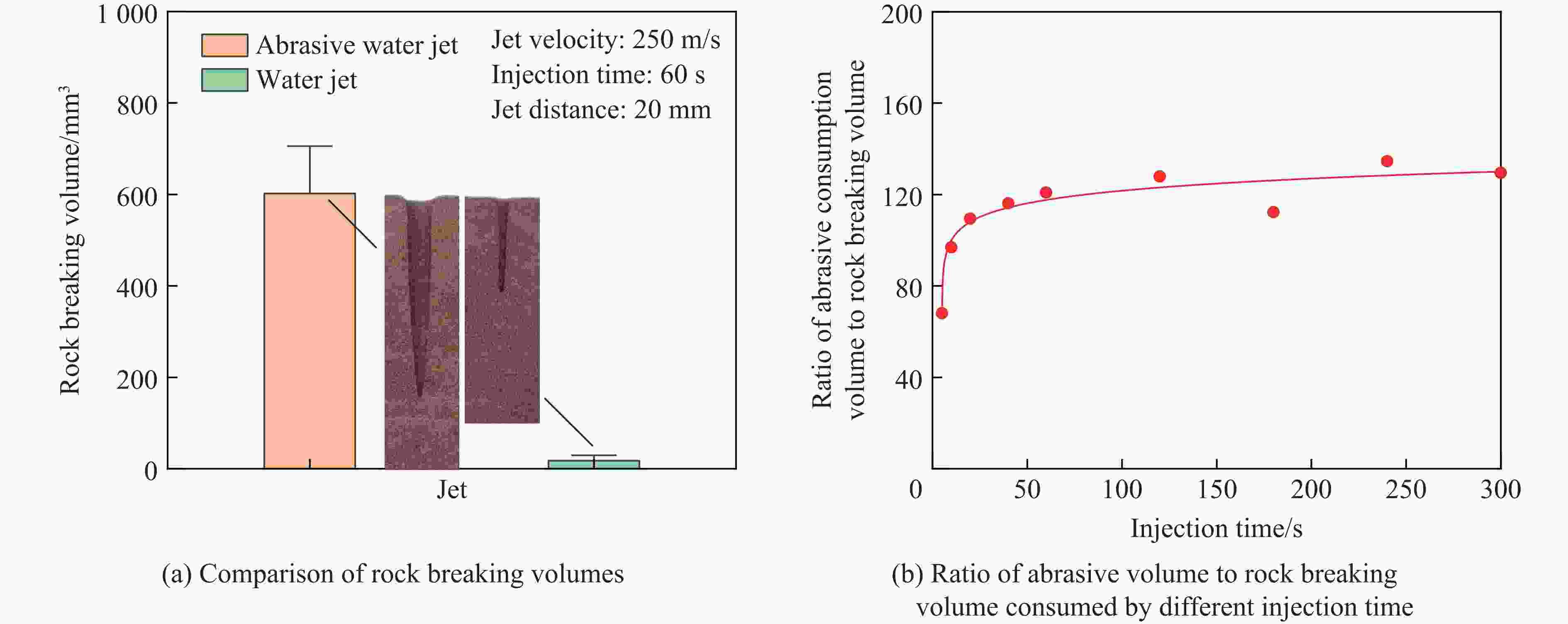
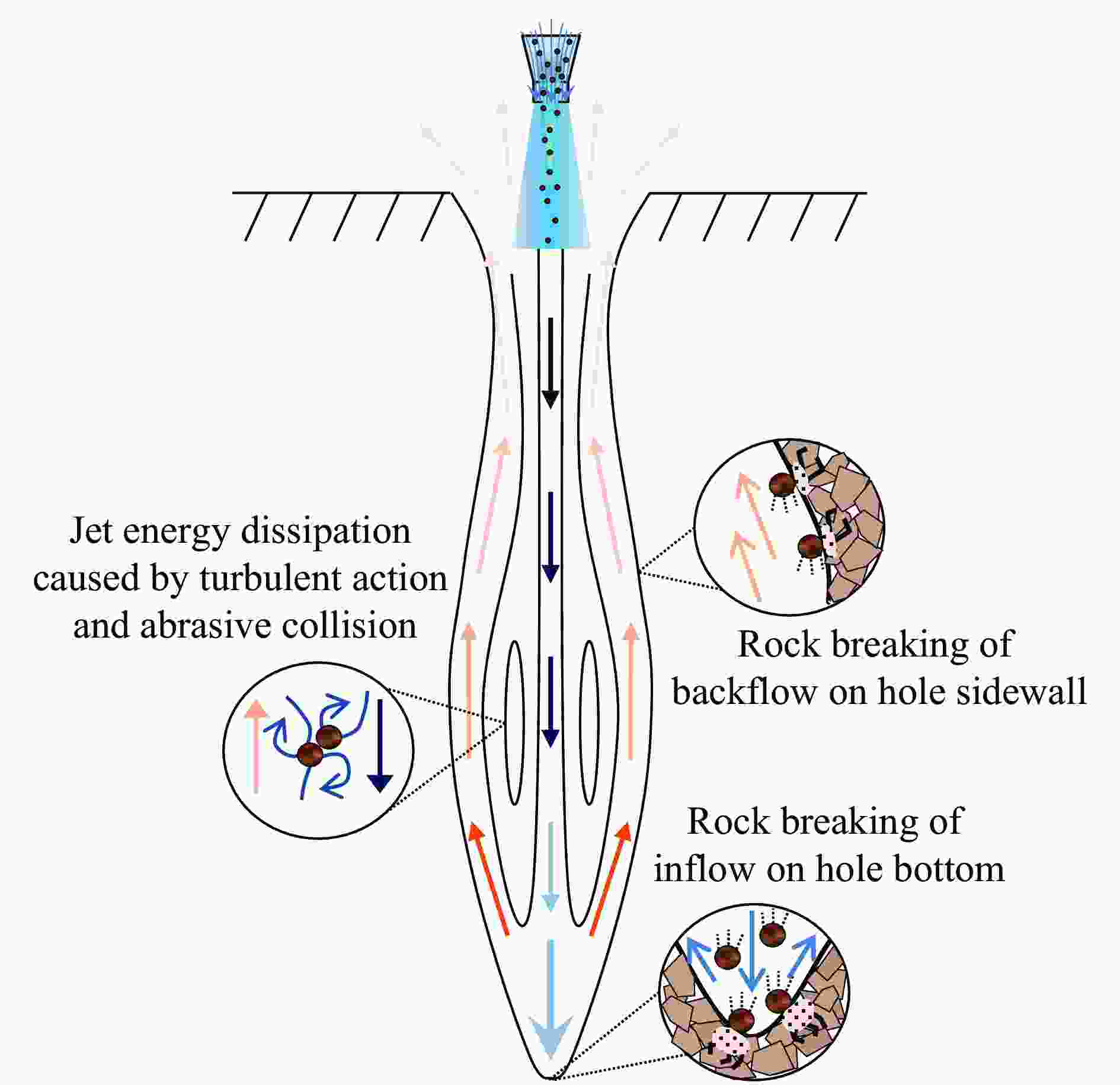
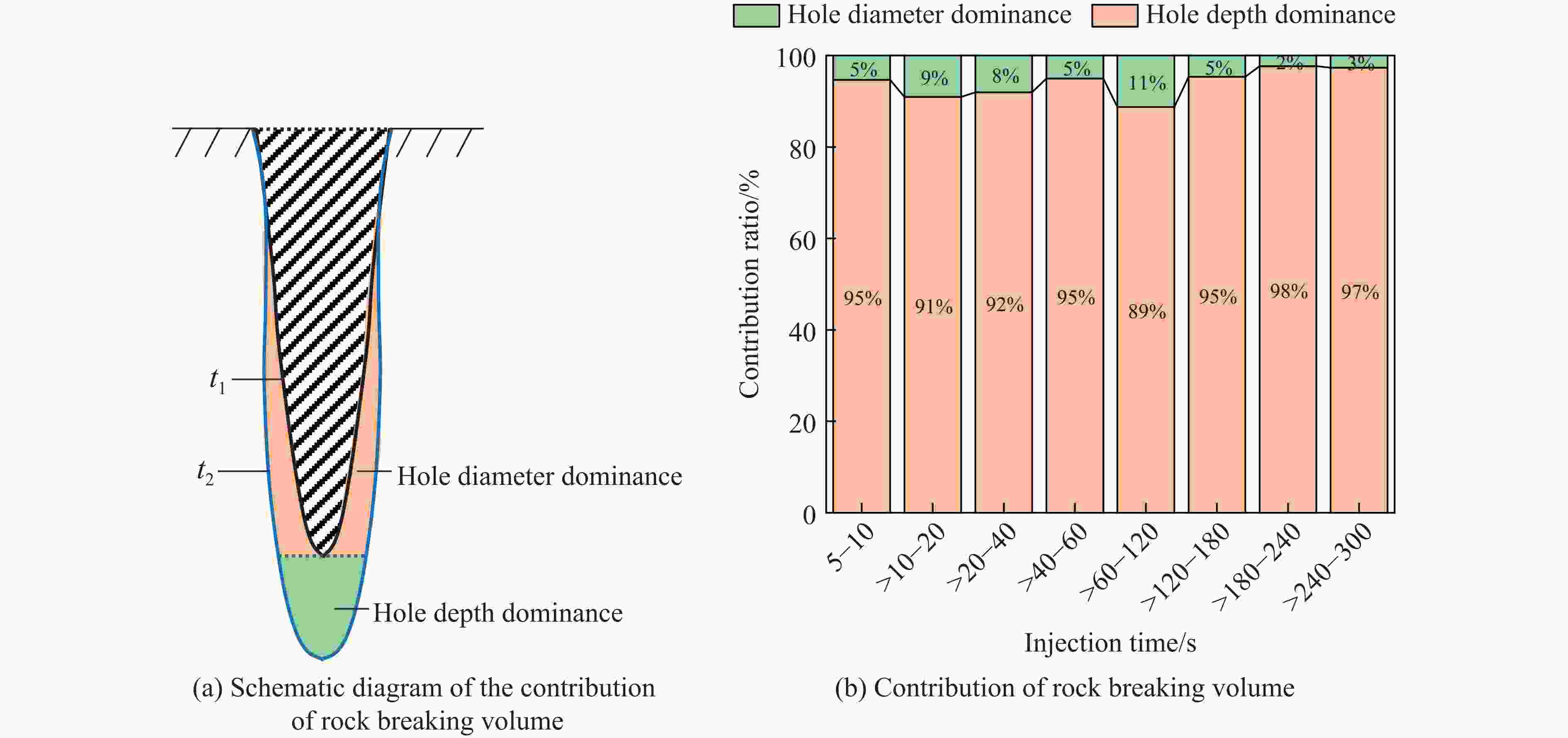
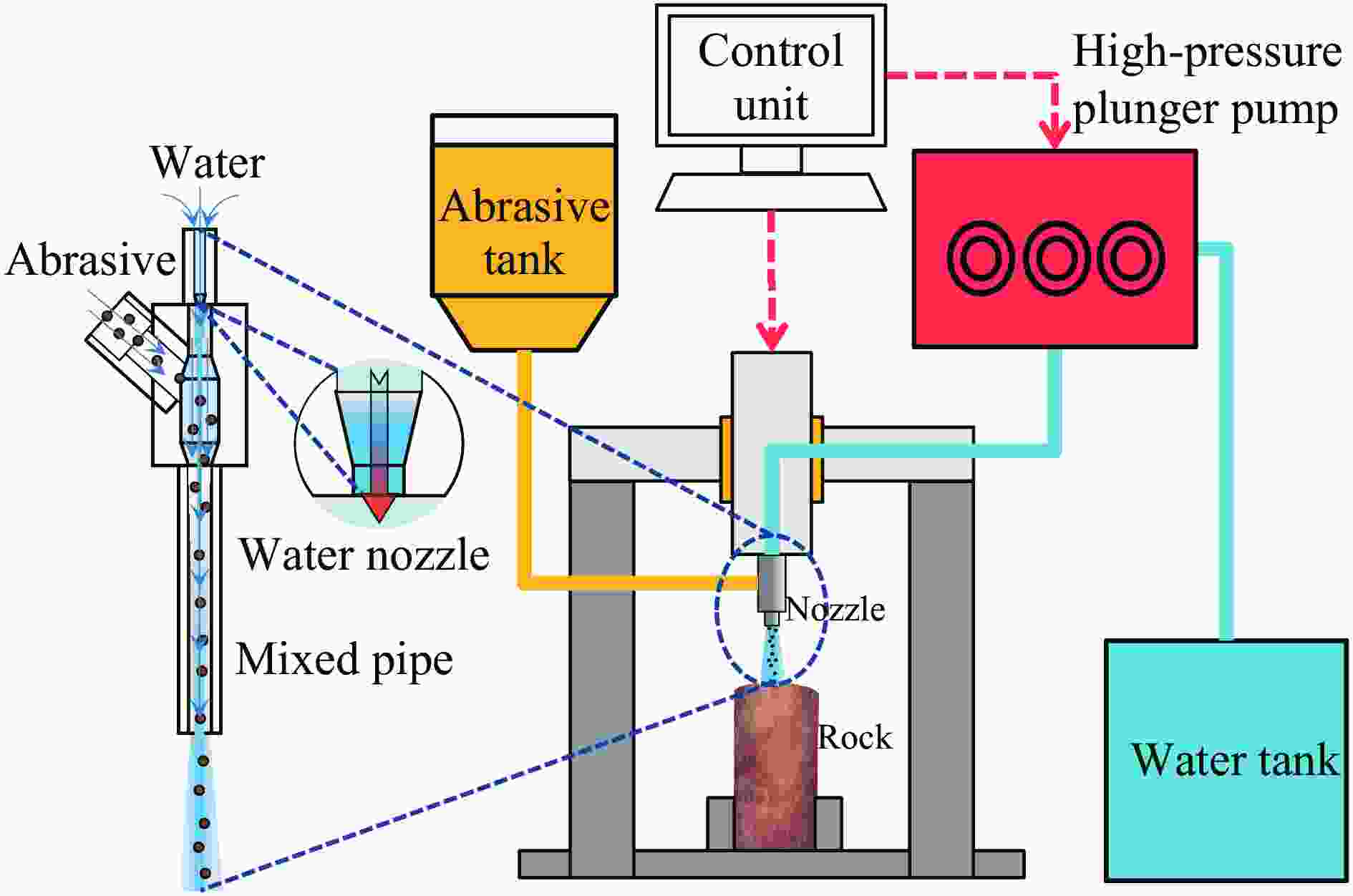
摘要: 磨料水射流射孔是一种有效的油气井射孔增产手段,然而,孔道形成机制及其参数调控规律仍是亟待解决的问题之一。鉴于此,设计并开展了磨料水射流射孔实验。结果表明,孔道形成过程是3种物理作用耦合的结果,即:入流垂直冲蚀孔尖岩石加深孔道;返流以小角度冲蚀孔壁岩石达到扩径作用;沿程流体机械能耗散使得射孔后期孔道演化变缓。由于入流破岩能力远强于返流破岩能力,磨料水射流射孔孔道的孔深和孔径的比随喷射时间的延长而增大,喷射5~300 s,孔深与孔径的比由7增大到28。返流的破岩能力由孔尖到孔口递减,返流对孔壁岩石的累积作用时间由孔尖到孔口递增,二者的共同影响使孔道由圆锥状向纺锤状演化。随着喷射时间的延长,孔深增大,沿程流体机械能耗散加剧,孔深变化率降低至11.3%,孔径变化率降低至4.3%,孔形演化变缓。Abstract: Abrasive water jet (AWJ) perforation is an effective mean for stimulation in oil and gas wells. However, the mechanism of perforation formation and the regulation of its parameter remain poorly understood. This study investigates the variation in hole shape during AWJ perforation through a series of experimental designs and analyses. By analyzing the variation in perforation shape with injection time, the rock-breaking damage caused by AWJ and the flow characteristics in the perforation were quantitatively characterized. The results show that the process of perforation formation is governed by the coupling of three physical effects. The inflow increases the hole depth by vertically impacting the hole tip, while the backflow enlarges the hole diameter by eroding the hole wall. As the fluid mechanical energy dissipates along the path, the evolution of the perforation slows down during the later perforation period. Because the rock breaking ability of inflow is stronger than that of backflow, the ratio of hole depth to hole diameter of AWJ perforation increases with the increase of injection time. Specifically, when the injection time ranges from 5 s to 300 s, the ratio increases from 7 to 28. The rock breaking ability of the backflow decreases from the tip to the orifice, whereas the duration of the backflow's action on the hole wall increases in the same direction. Under the combined influence of rock breaking ability and rock breaking time, the hole evolves from a conical shape to a spindle shape, and the degree of spindle increases. With the increase of injection time and hole depth, the fluid mechanical energy loss becomes more severe. The change rate of hole depth decreased to 11.3% and the change rate of hole diameter decreased to 4.3%. The evolution of the AWJ perforation became slow.
-
Key words:
- abrasive water jet /
- rock breaking /
- perforation /
- fluid-structure interaction /
- experiment research
-
表 1 不同喷射时间孔深-孔径拟合函数参数
Table 1. Fitting function parameters for relationship between hole depth and hole radius at different injection times
喷射时间/s a1/mm−1 b1 c1/mm R2 喷射时间/s a1/mm−1 b1 c1/mm R2 5 − 0.0024 −0.09 2.60 1.00 120 − 0.0008 0.02 3.40 0.98 10 − 0.0012 −0.08 2.76 0.94 180 − 0.0007 0.03 3.80 0.96 20 − 0.0012 −0.04 2.91 0.94 240 − 0.0006 0.03 3.90 0.98 40 − 0.0012 −0.01 3.12 0.99 300 − 0.0005 0.04 3.87 0.97 60 − 0.0011 0.01 3.18 0.98 表 2 不同深度的孔径-喷射时间拟合函数参数
Table 2. Fitting function parameters of the hole radius with injection time at different depths
深度/mm a2/(mm·s−1) b2/s c2 R2 深度/mm a2/(mm·s−1) b2/s c2 R2 0 1.82 0.00 0.13 0.98 50 0.23 42.69 0.54 0.98 5 1.50 0.31 0.18 0.99 55 0.17 52.33 0.59 0.98 10 1.12 1.37 0.24 0.99 60 0.25 63.01 0.52 0.99 15 0.60 3.26 0.36 0.96 65 0.20 74.76 0.55 0.99 20 0.42 6.03 0.43 0.94 70 0.16 87.58 0.59 0.99 25 0.47 9.71 0.41 0.97 75 0.12 101.49 0.65 0.99 30 0.32 14.34 0.49 0.96 80 0.09 116.49 0.69 0.99 35 0.37 19.93 0.45 0.98 85 0.16 132.59 0.57 0.99 40 0.27 26.50 0.51 0.97 90 0.12 149.81 0.62 0.99 45 0.20 34.09 0.57 0.97 95 0.10 168.14 0.64 0.98 -
[1] 李根生, 沈忠厚. 高压水射流理论及其在石油工程中应用研究进展 [J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2005, 32(1): 96–99. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.01.026.LI G S, SHEN Z H. Advances in researches and applications of water jet theory in petroleum engineering [J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2005, 32(1): 96–99. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.01.026. [2] 黄中伟, 李根生, 唐志军, 等. 水力喷射侧钻径向微小井眼技术 [J]. 石油钻探技术, 2013, 41(4): 37–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.04.009.HUANG Z W, LI G S, TANG Z J, et al. Technology of hydra-jet sidetracking of horizontal micro-radial laterals [J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2013, 41(4): 37–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2013.04.009. [3] 田守嶒, 李根生, 黄中伟, 等. 水力喷射压裂机理与技术研究进展 [J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2008, 30(1): 58–62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2008.01.016.TIAN S Z, LI G S, HUANG Z W, et al. Research on hydrajet fracturing mechanisms and technologies [J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2008, 30(1): 58–62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2008.01.016. [4] 黄中伟, 李根生. 水力射孔参数对起裂压力影响的实验研究 [J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 31(6): 48–50, 54. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.2007.06.011.HUANG Z W, LI G S. Experimental study on effects of hydrau-perforation parameters on initial fracturing pressure [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 2007, 31(6): 48–50. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.2007.06.011. [5] LI H, HUANG Z W, LI J B, et al. Effect of nozzle structure on rock drilling performances of abrasive waterjet [C]//57th U. S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium. Atlanta: ARMA, 2023: ARMA-2023-0252. [6] XUE Y Z, SI H, XU D Y, et al. Experiments on the microscopic damage of coal induced by pure water jets and abrasive water jets [J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 332: 139–149. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.03.051. [7] SURJAATMADJA J B, BAILEY A, SIERRA S. HydraJet testing under deep well conditions defines new requirements for hard-rock perforating [C]//SPE Rocky Mountain Petroleum Technology Conference. Denver: SPE, 2009: SPE-122817-MS. DOI: 10.2118/122817-MS. [8] EAST L, ROSATO J, FARABEE M, et al. Packerless multistage fracture-stimulation method using CT perforating and annular path pumping [C]//SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. Dallas: SPE, 2005: SPE-96732-MS. DOI: 10.2118/96732-MS. [9] 李根生, 牛继磊, 刘泽凯, 等. 水力喷砂射孔机理实验研究 [J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, 26(2): 31–34. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.2002.02.009.LI G S, NIU J L, LIU Z K, et al. Experimental study on mechanisms of hydraulic sand blasting perforation for improvement of oil production [J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2002, 26(2): 31–34. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-5870.2002.02.009. [10] NAKHWA A D, LOVING S W, FERGUSON A, et al. Oriented perforating using abrasive fluids through coiled tubing [C]//SPE/ICoTA Coiled Tubing and Well Intervention Conference and Exhibition. The Woodlands: SPE, 2007: SPE-107061-MS. DOI: 10.2118/107061-MS. [11] 李宪文, 赵振峰, 付钢旦, 等. 水力喷砂射孔孔道形态研究 [J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2012, 34(2): 55–58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2012.02.015.LI X W, ZHAO Z F, FU G D, et al. Research on channel pattern of hydraulic sand blasting perforation [J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2012, 34(2): 55–58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7393.2012.02.015. [12] 汤积仁, 卢义玉, 孙惠娟, 等. 基于CT方法的磨料射流冲蚀损伤岩石特性研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(2): 297–302. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0881.TANG J R, LU Y Y, SUN H J, et al. Study of erosion and damage characteristics of rock by abrasive water jet using CT [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 297–302. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0881. [13] HUANG F, ZHAO Z Q, LI D, et al. Investigation of the breaking manifestations of bedded shale impacted by a high-pressure abrasive water jet [J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 397: 117021. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.11.065. [14] LI Z T, GE Z L, ZHOU Z, et al. Micro-failure behaviors of mineral crystals in reservoir rocks impacted by abrasive water jet [J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2024, 241: 213170. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoen.2024.213170. [15] MI J Y, TANG J R, LIU W C, et al. Investigation of fracturing in heterogeneous rocks with cracks under abrasive water jet impact using pixel method [J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 443: 119900. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2024.119900. [16] SHANGGUAN J M, GE Z L, ZHOU Z, et al. Damage and fracture characteristics of thermal-treated granite subjected to ultra-high pressure jet [J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2024, 241: 213174. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoen.2024.213174. [17] KAYA S, AYDIN G, KARAKURT I. An experimental study on the cutting depth produced by abrasive waterjet: how do abrasive and rock properties affect the cutting process? [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2023, 125(9): 4811–4823. DOI: 10.1007/s00170-023-11053-5. [18] 牛继磊, 李根生, 宋剑, 等. 水力喷砂射孔参数实验研究 [J]. 石油钻探技术, 2003, 31(2): 14–16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2003.02.006.NIU J L, LI G S, SONG J, et al. An experimental study on abrasive water jet perforation parameters [J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2003, 31(2): 14–16. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2003.02.006. [19] QU H, TANG S M, SHENG M, et al. Experimental investigation of the damage characteristics and breaking process of shale by abrasive waterjet impact [J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 211: 110165. DOI: 10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110165. [20] QU H, WU X G, LIU Y, et al. Effect of shale mineralogy characteristics on the perforation performance and particle fragmentation of abrasive waterjet [J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 367: 427–442. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.03.068. [21] CAI C, WANG X C, YUAN X H, et al. Experimental investigation on perforation of shale with ultra-high pressure abrasive water jet: shape, mechanism and sensitivity [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 67: 196–213. DOI: 10.1016/j.jngse.2019.05.002. [22] LI Z T, GE Z L, ZHOU Z, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of heterogeneous granite impacted by abrasive water jet based on SPH-FEM coupling algorithm [J]. Powder Technology, 2023, 416: 118233. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2023.118233. [23] XUE Y Z, SI H, CHEN G H. The fragmentation mechanism of coal impacted by water jets and abrasive jets [J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 361: 849–859. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.11.018. [24] 薛胜雄. 高压水射流技术与应用 [J]. 中国安全科学学报, 1999, 9(S1): 92–92. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.1999.z1.028.XUE S X. High pressure water jet technology and application [J]. China Safety Science Journal, 1999, 9(S1): 92–92. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.1999.z1.028. [25] 薛永志. 高压水射流冲击下煤岩损伤诱导机制及分布特性研究 [D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018.XUE Y Z. Study on the inducement and distribution of damage in coal impacted by high pressure water jets [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018. [26] VAN GIJTENBEEK K A, SURJAATMADJA J B, HEITMAN C. Unique hydrajet tool provides cost savings and improved performance in placing many perforations and proppant fractures in horizontal wellbores [C]//Tight Gas Technology Symposium. San Antonio: SPE, 2010: SPE-130255-MS. DOI: 10.2118/130255-MS. [27] STOCKHAUSEN H W, GARCÍA SANCHEZ D G, LUONGO S A, et al. In-depth evaluation of deep-rock hydrajet results shows unique jetted rock surface characteristics [C]//SPE Europec/EAGE Annual Conference. Copenhagen: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2012. DOI: 10.2118/153333-MS. -






 下载:
下载: