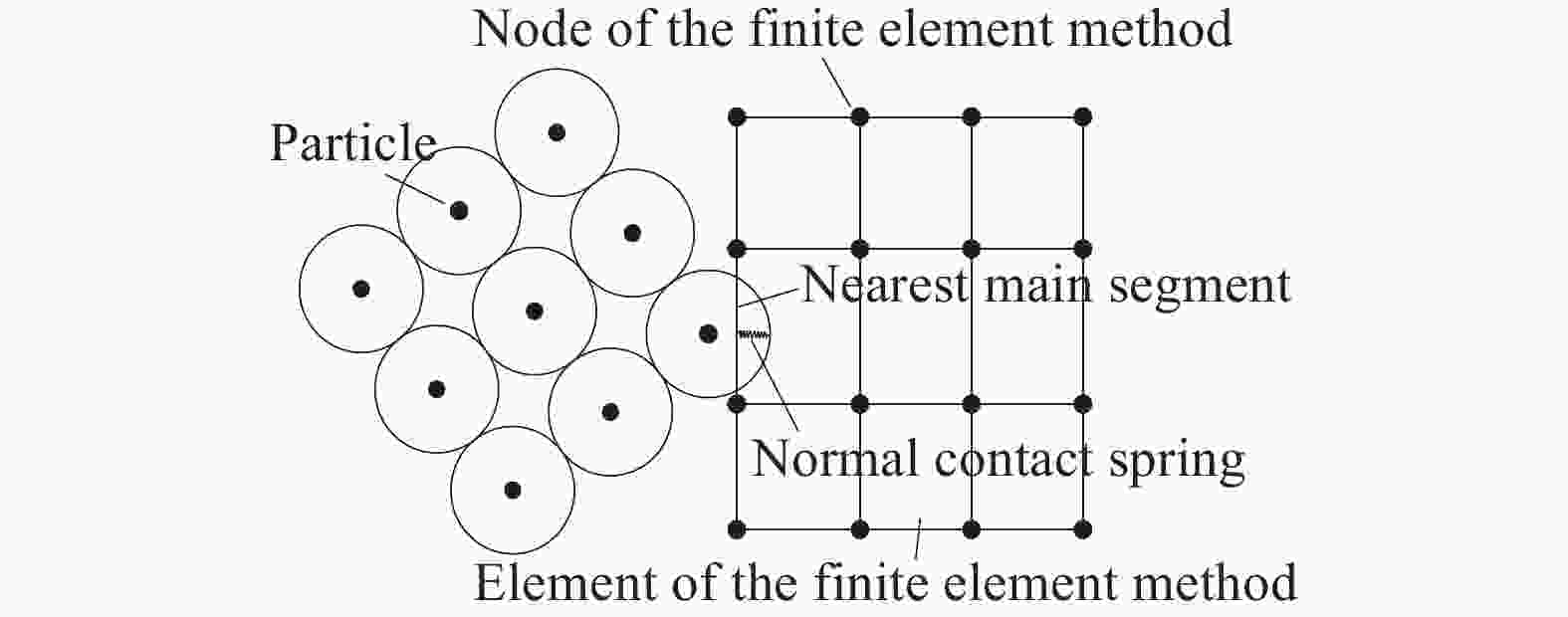
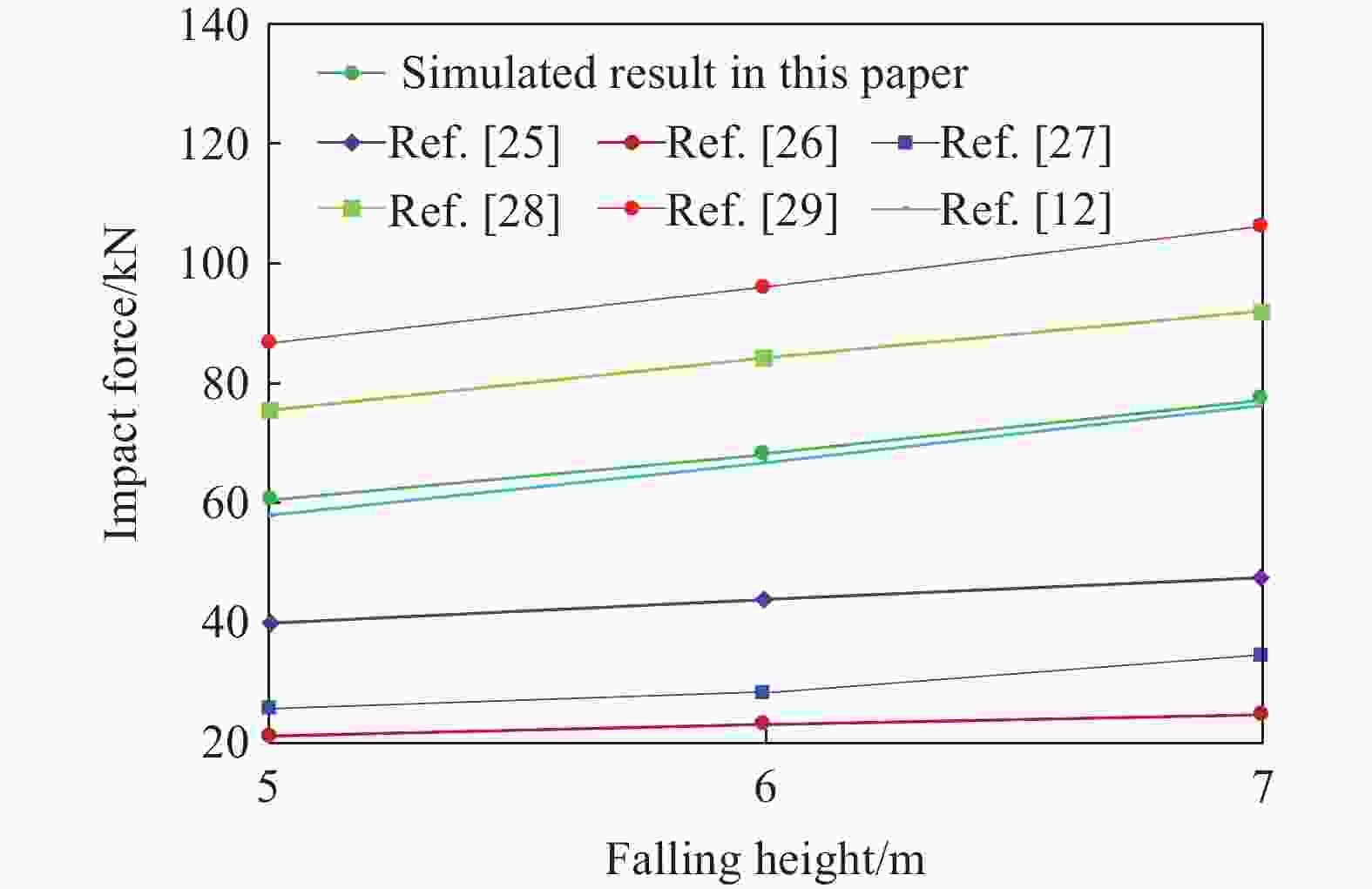
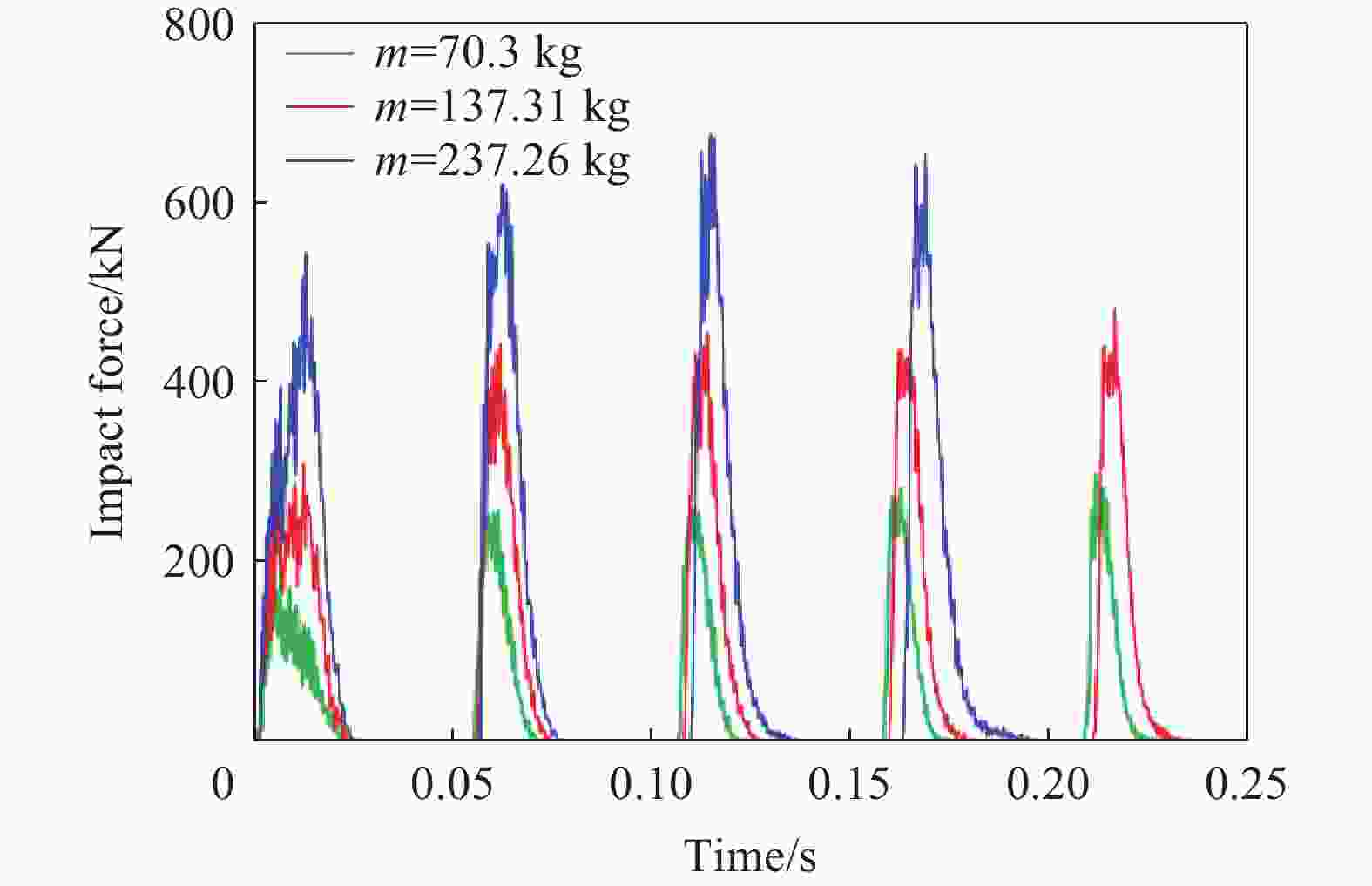
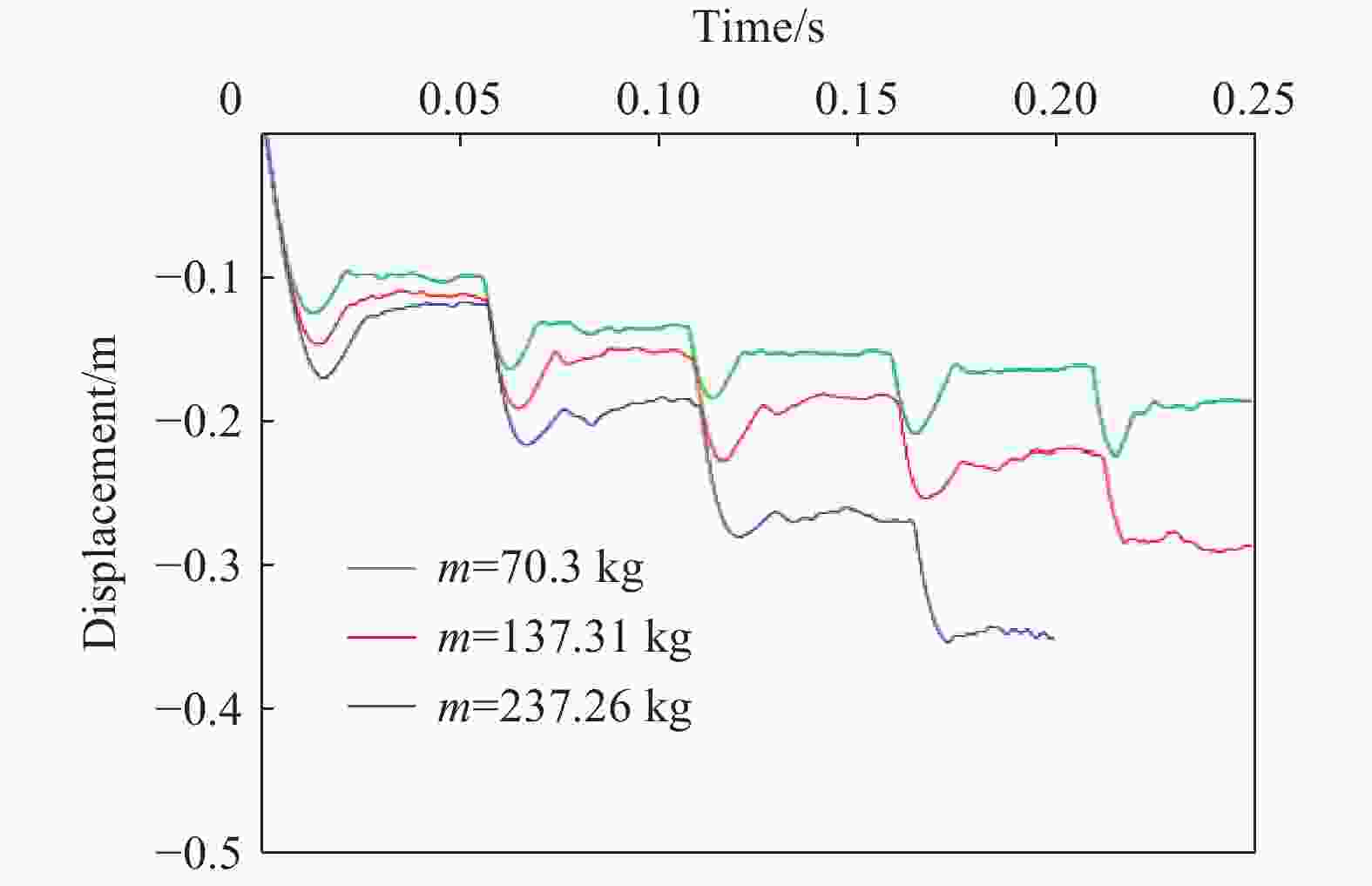
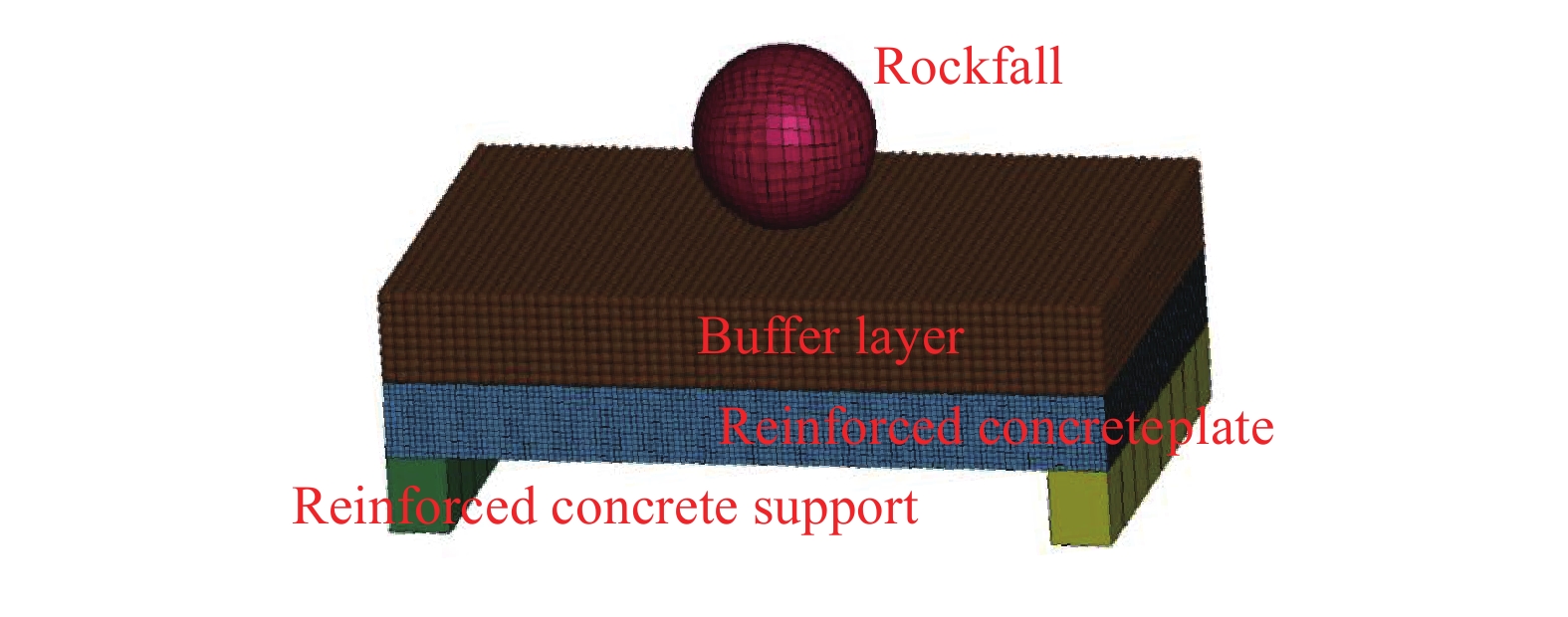
Numerical simulation on dynamic response of the shed-tunnel structure under multiple rockfall impacts
-
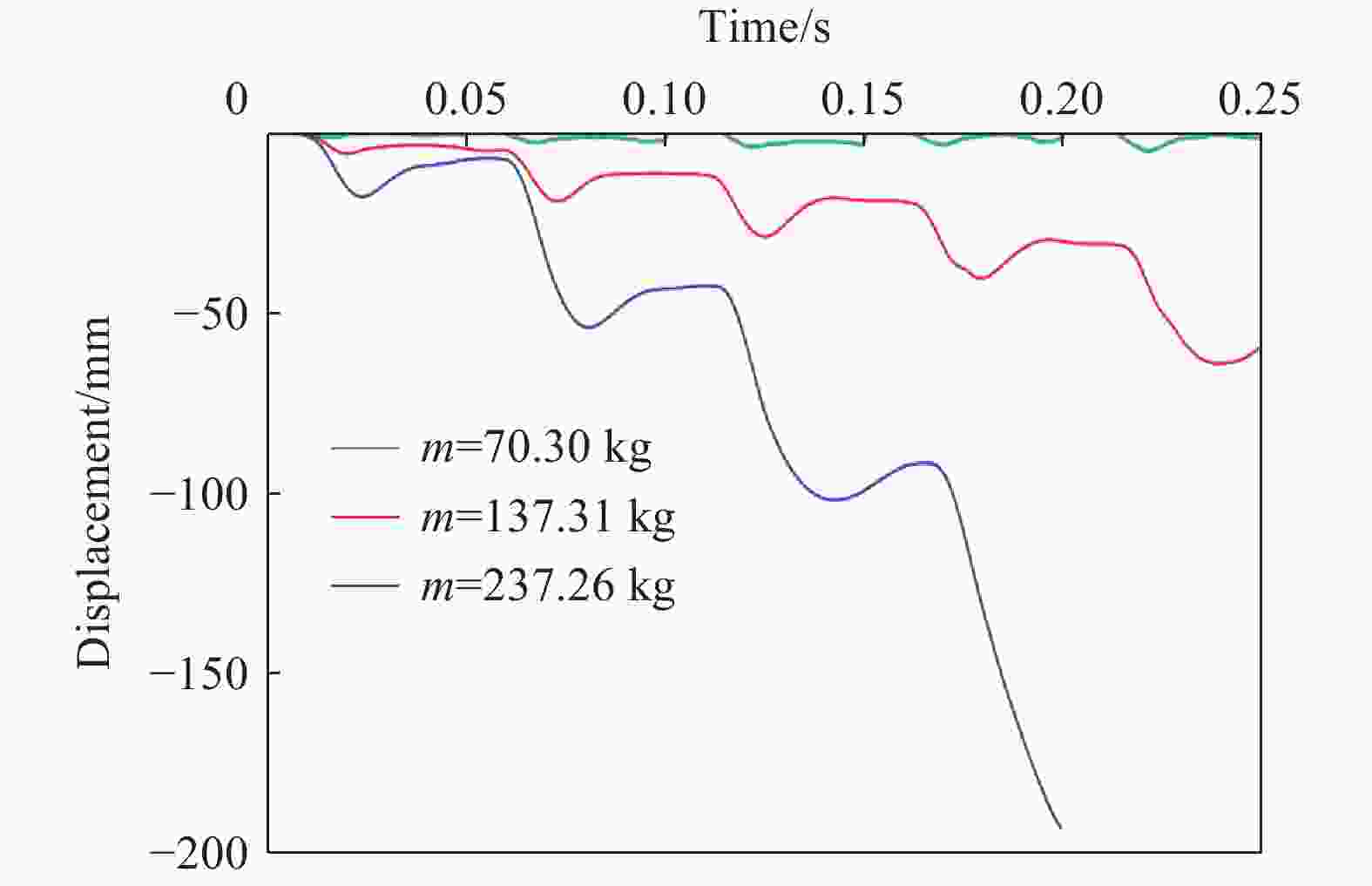
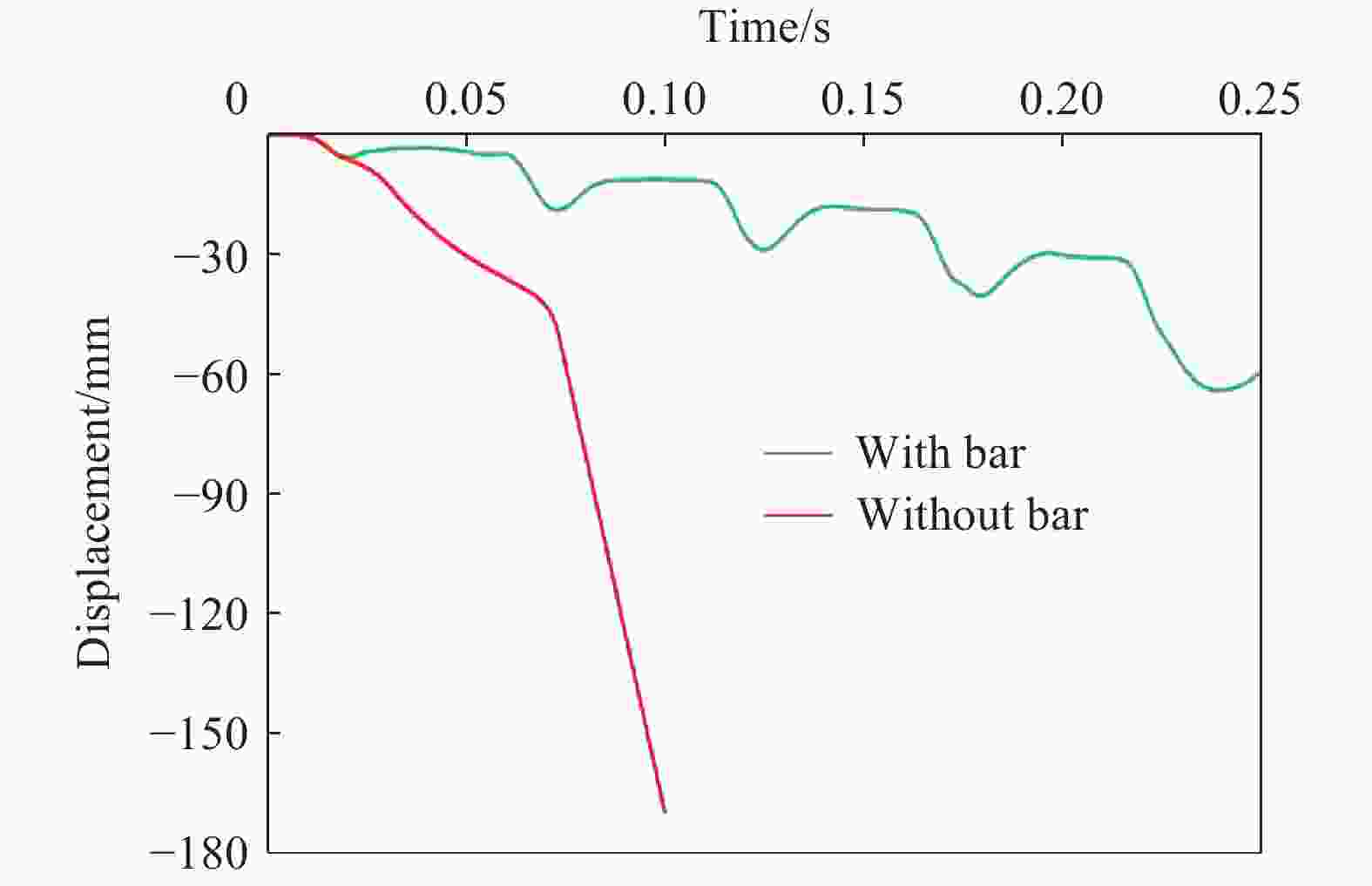
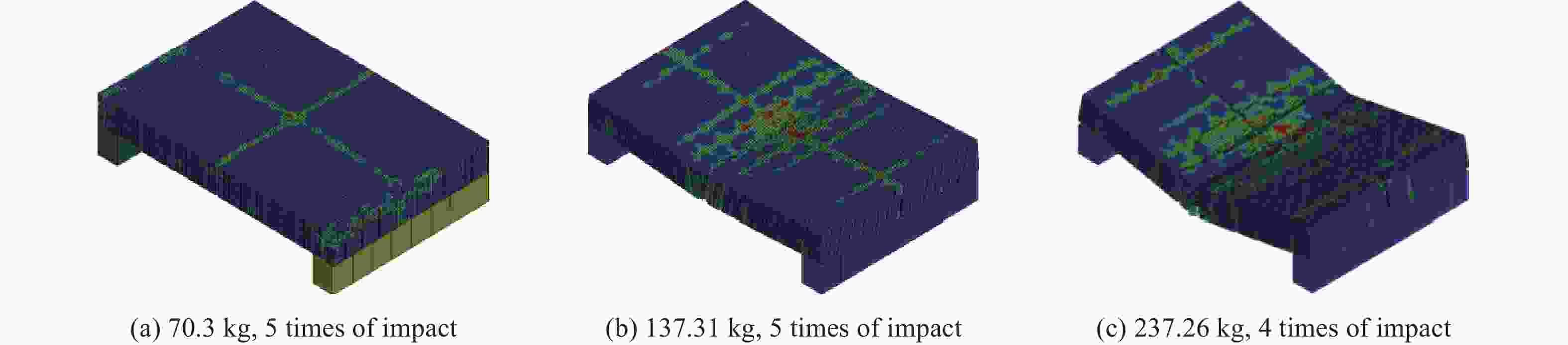
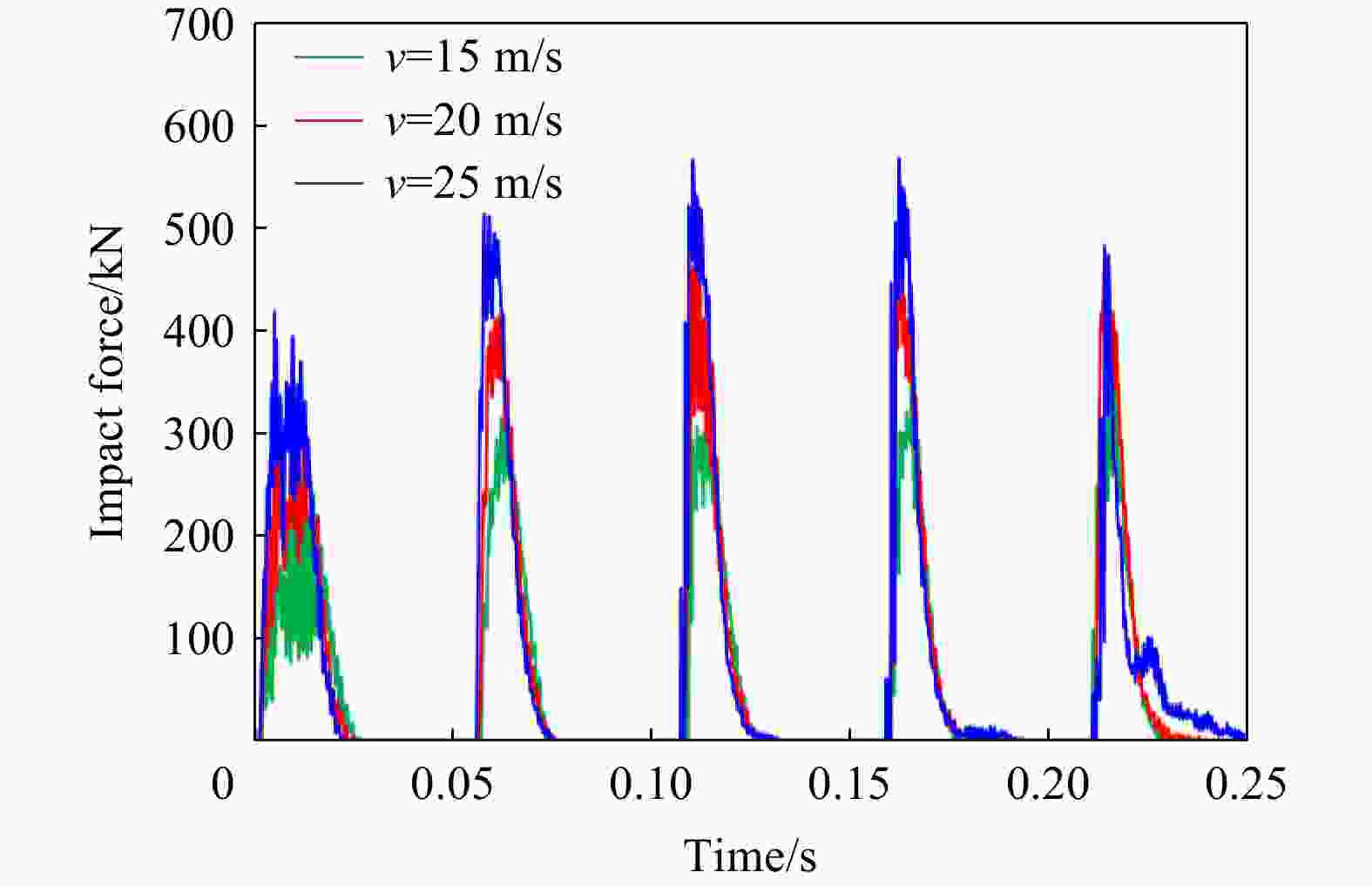
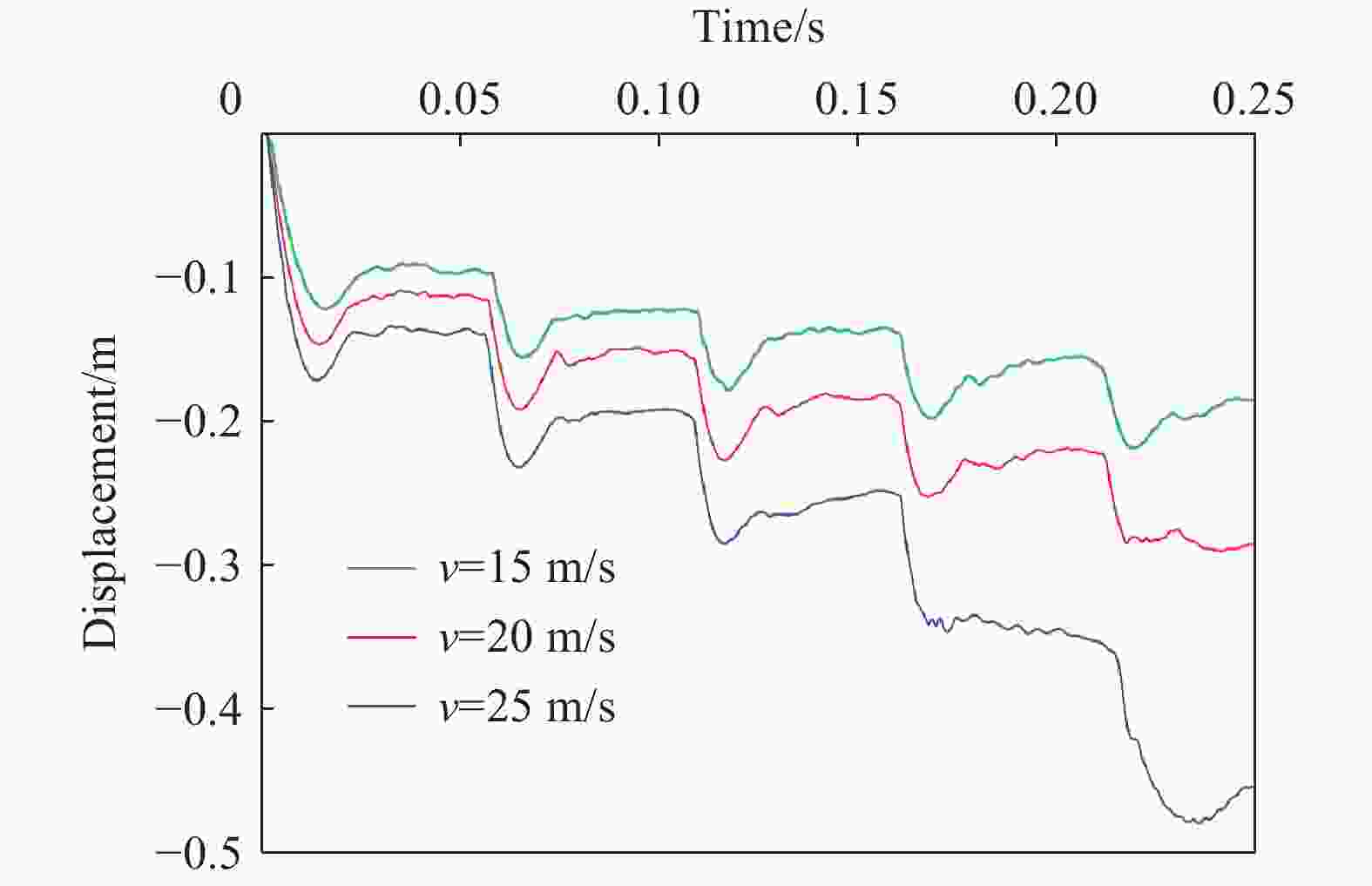
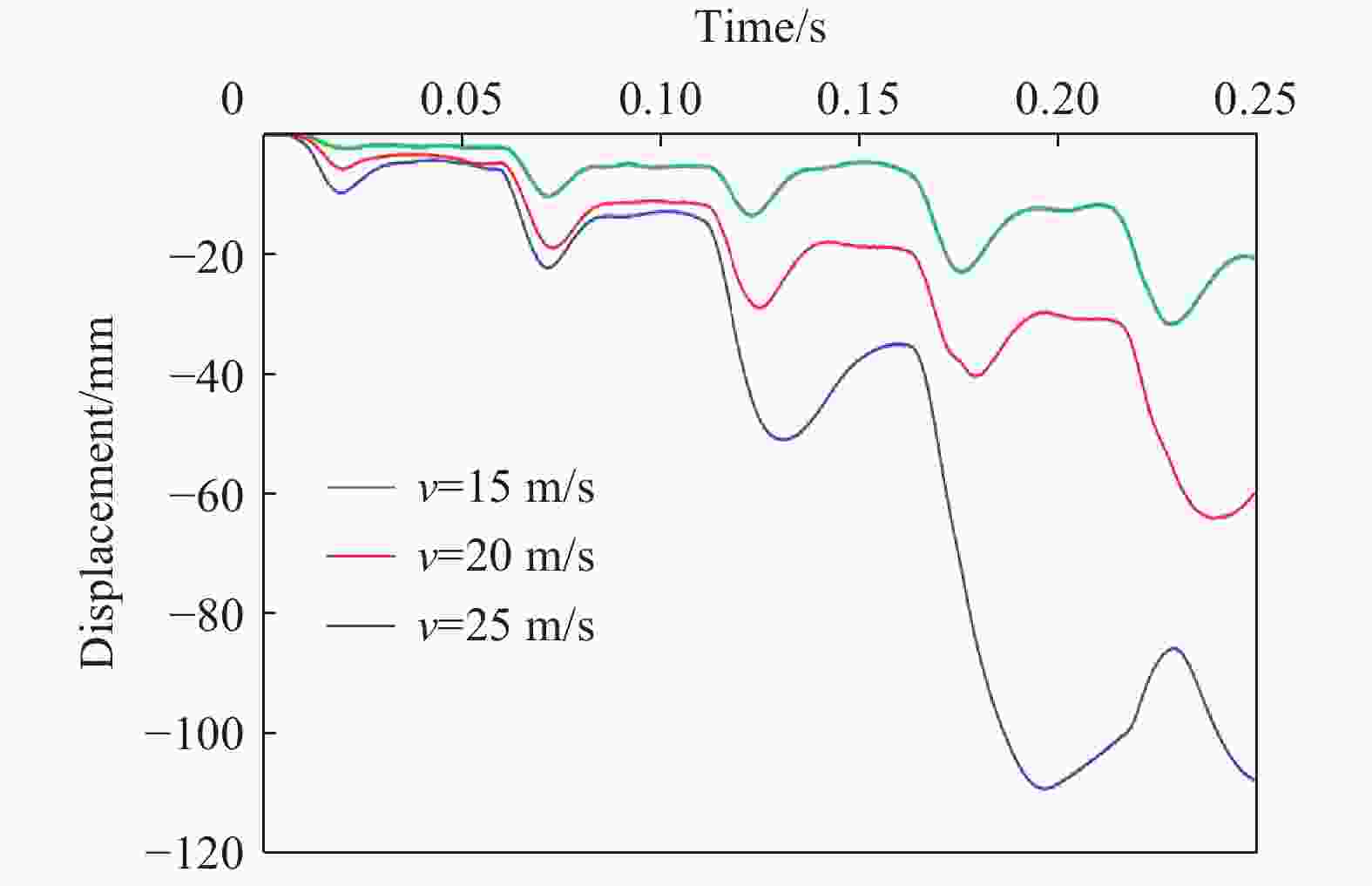
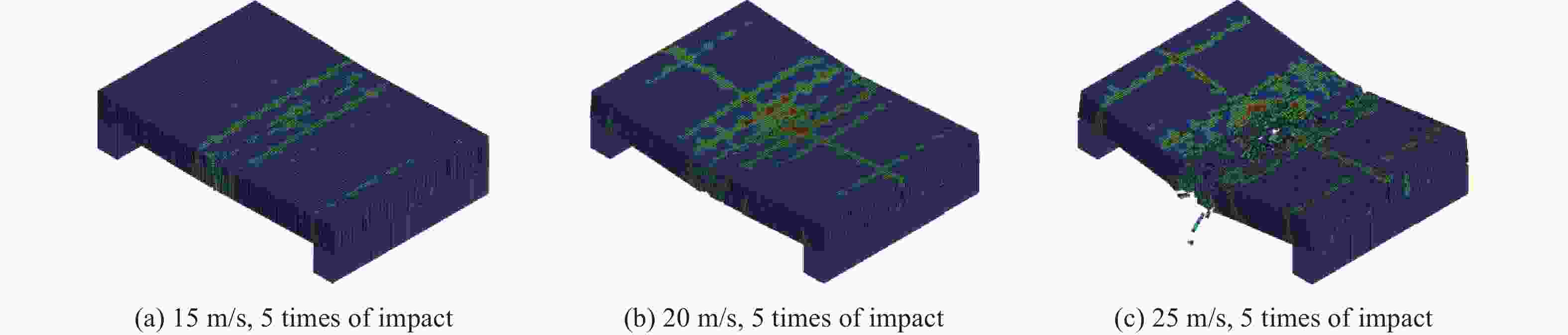
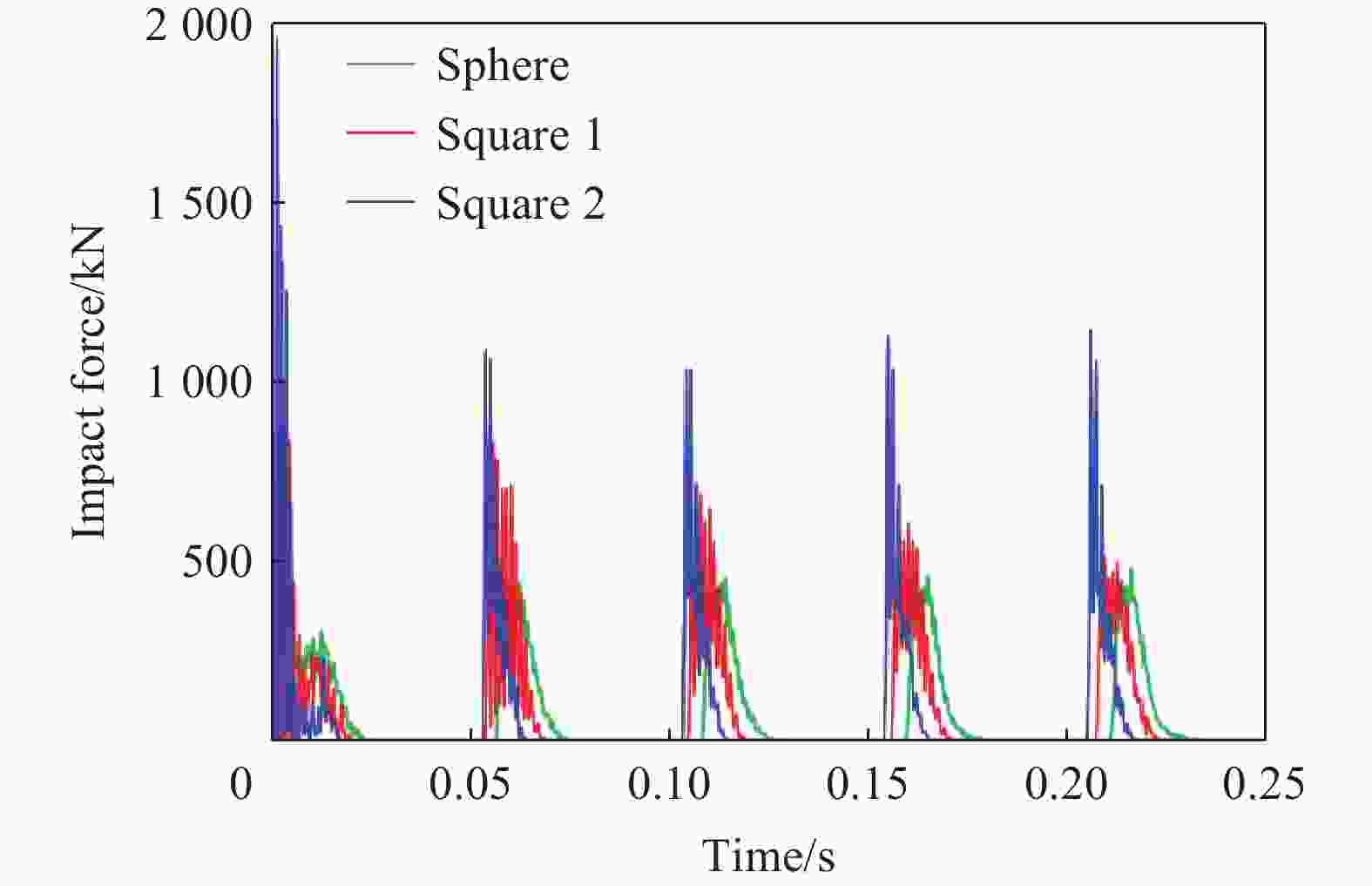
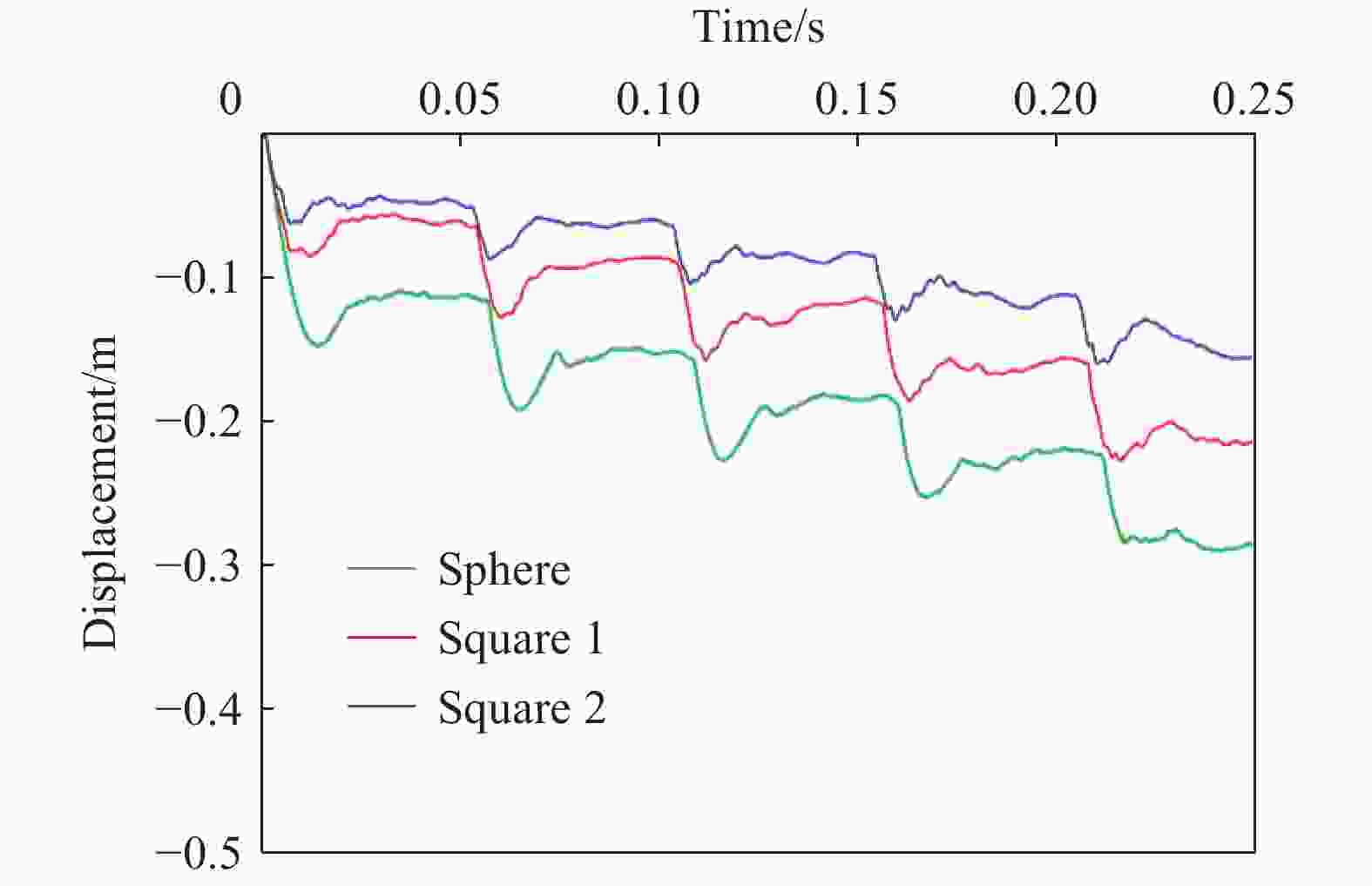
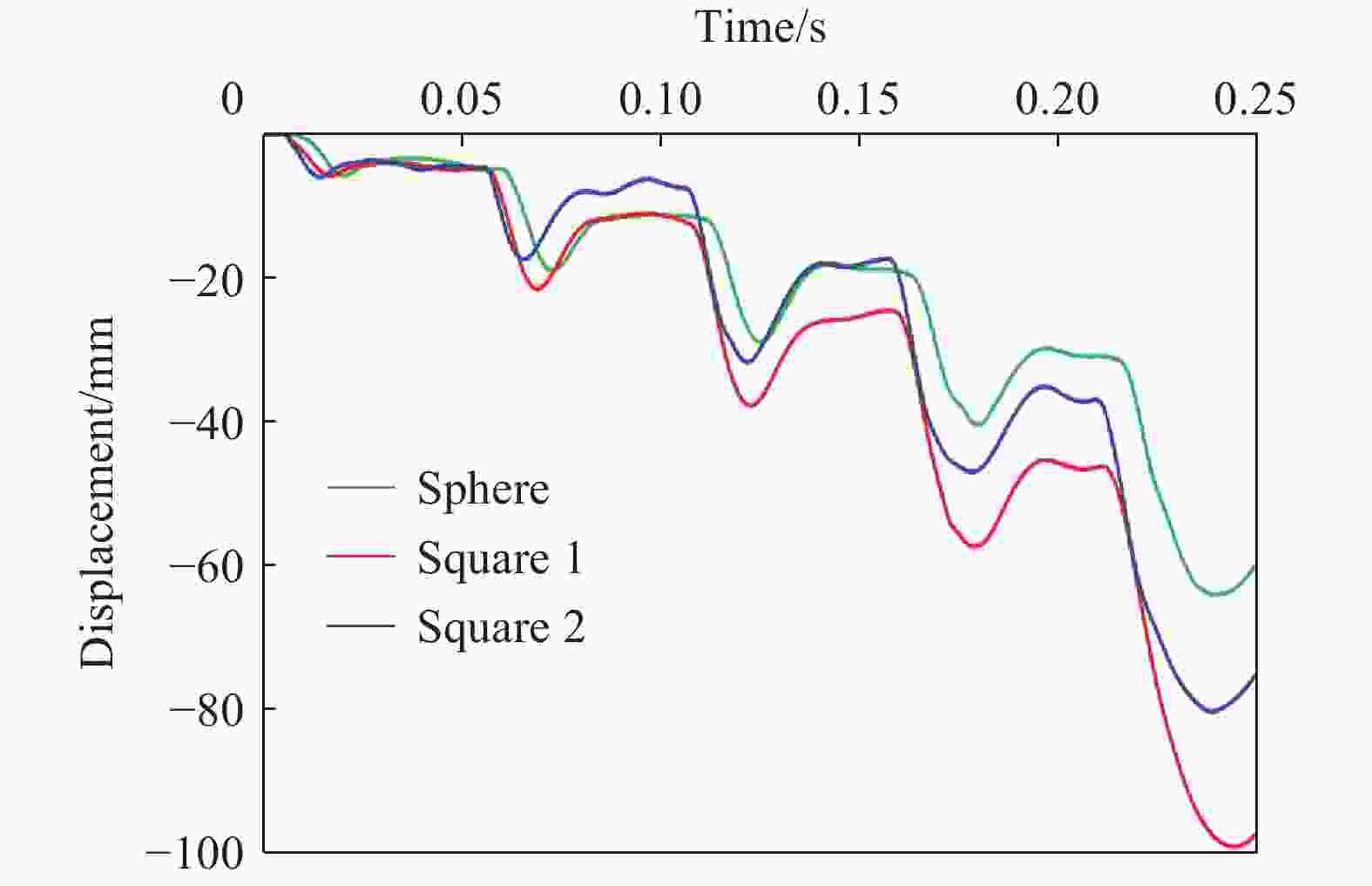
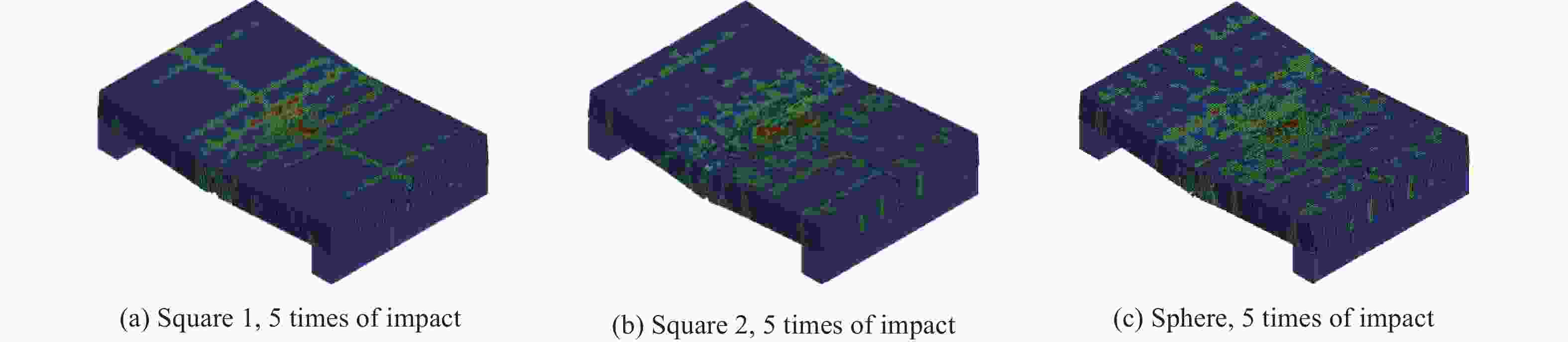
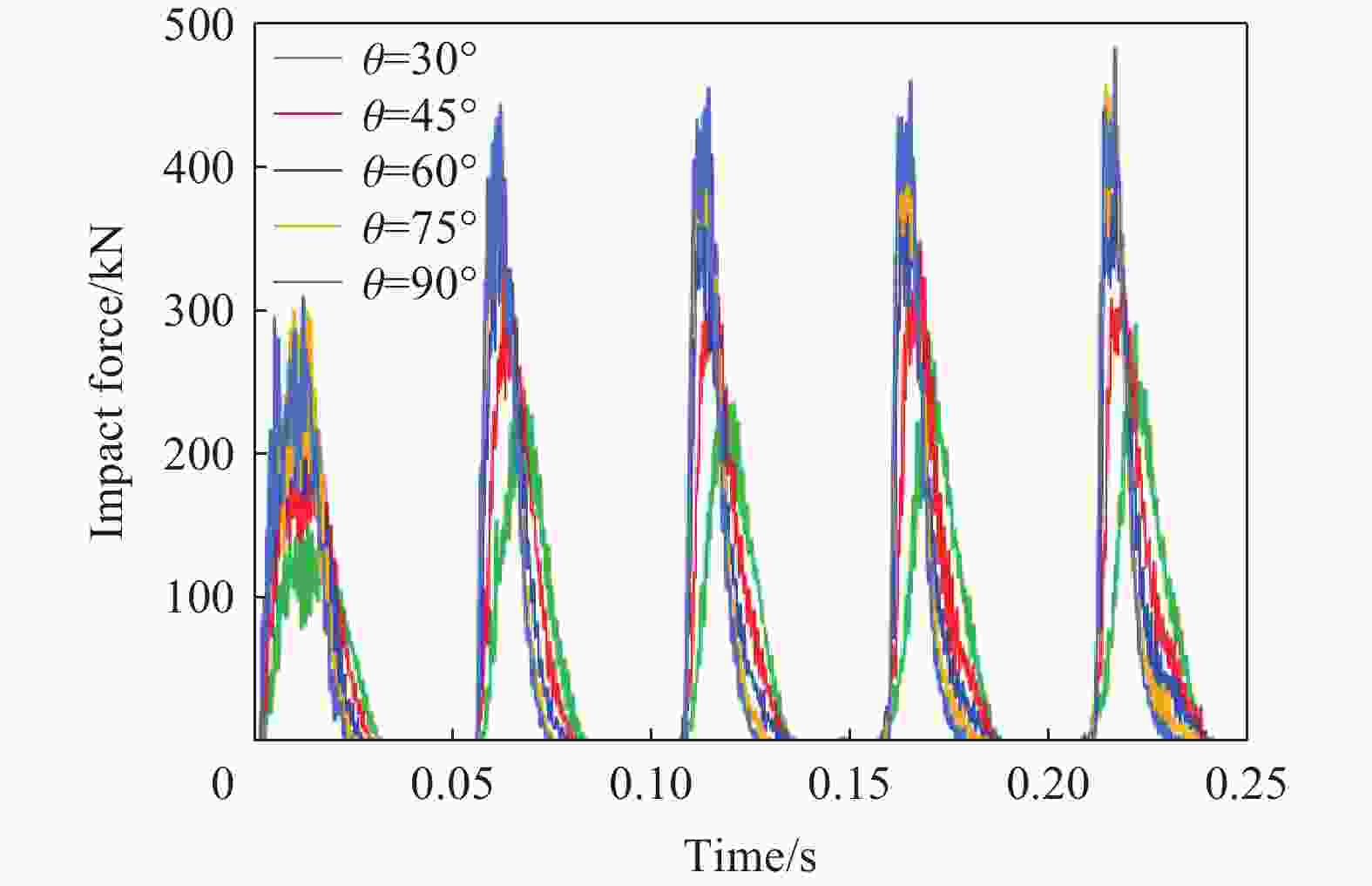
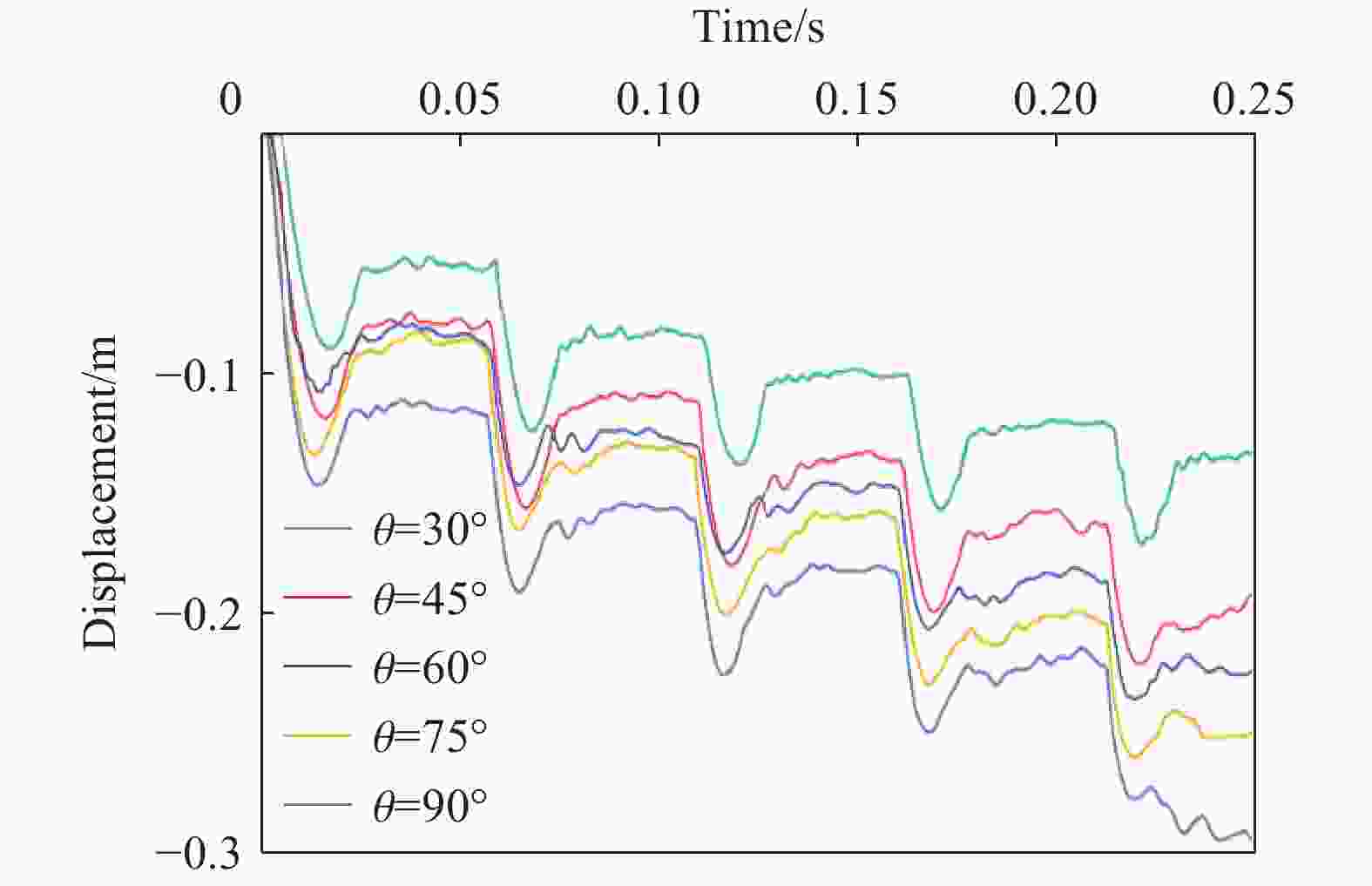
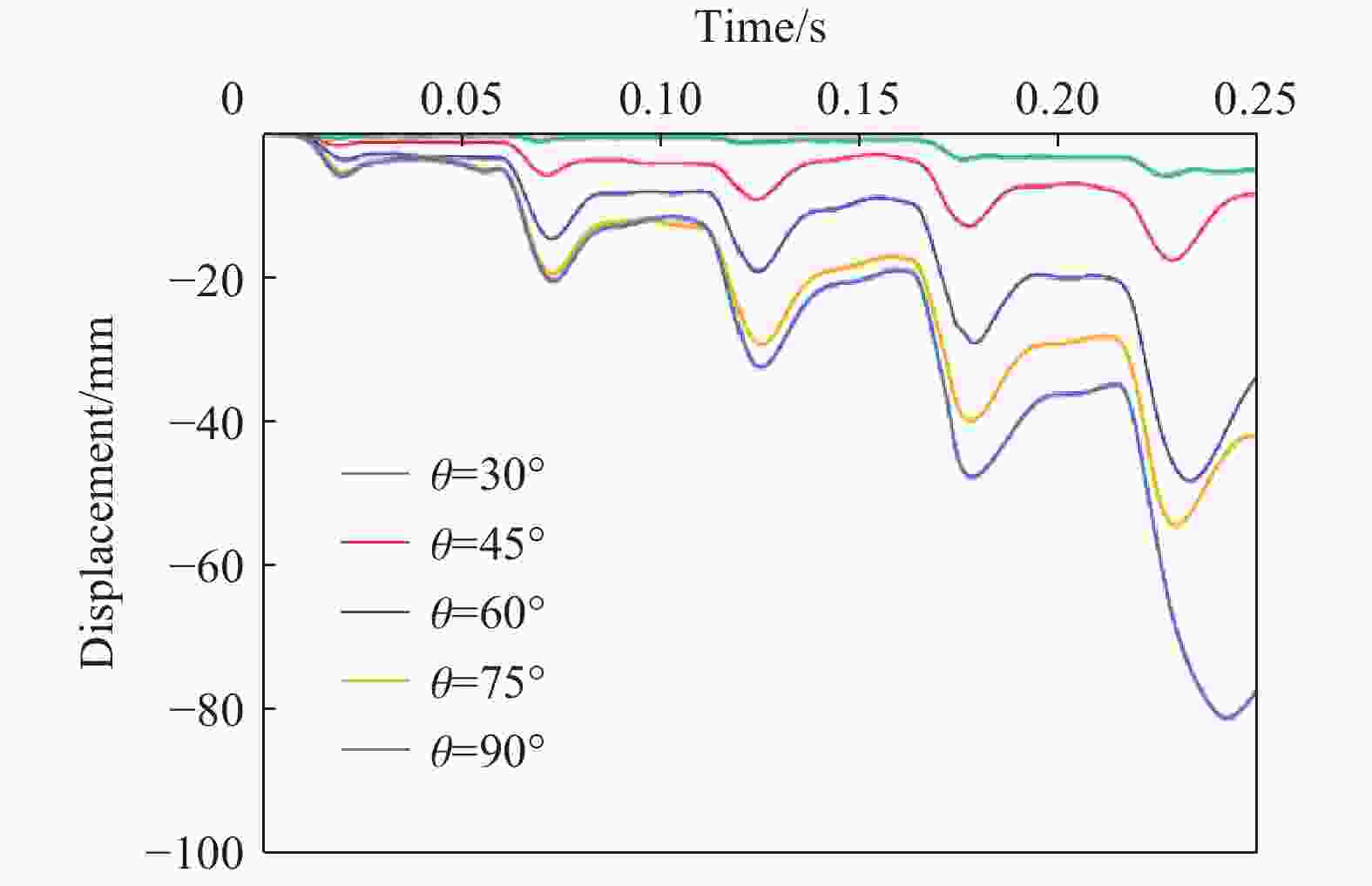
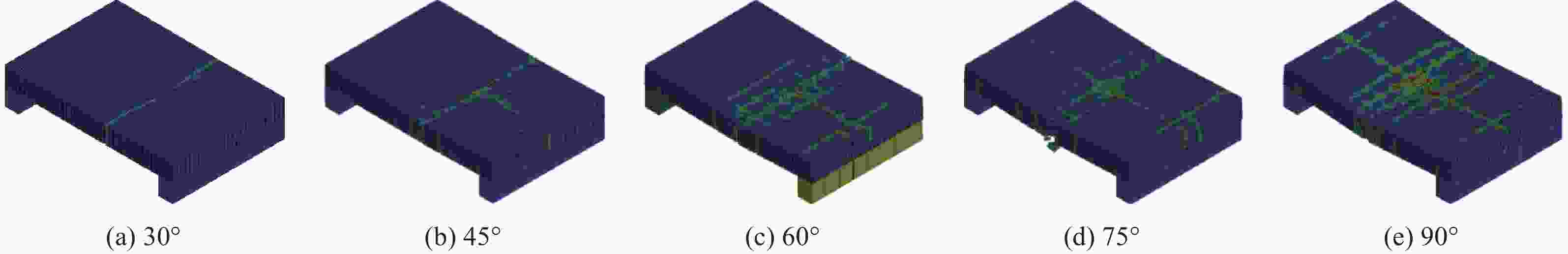
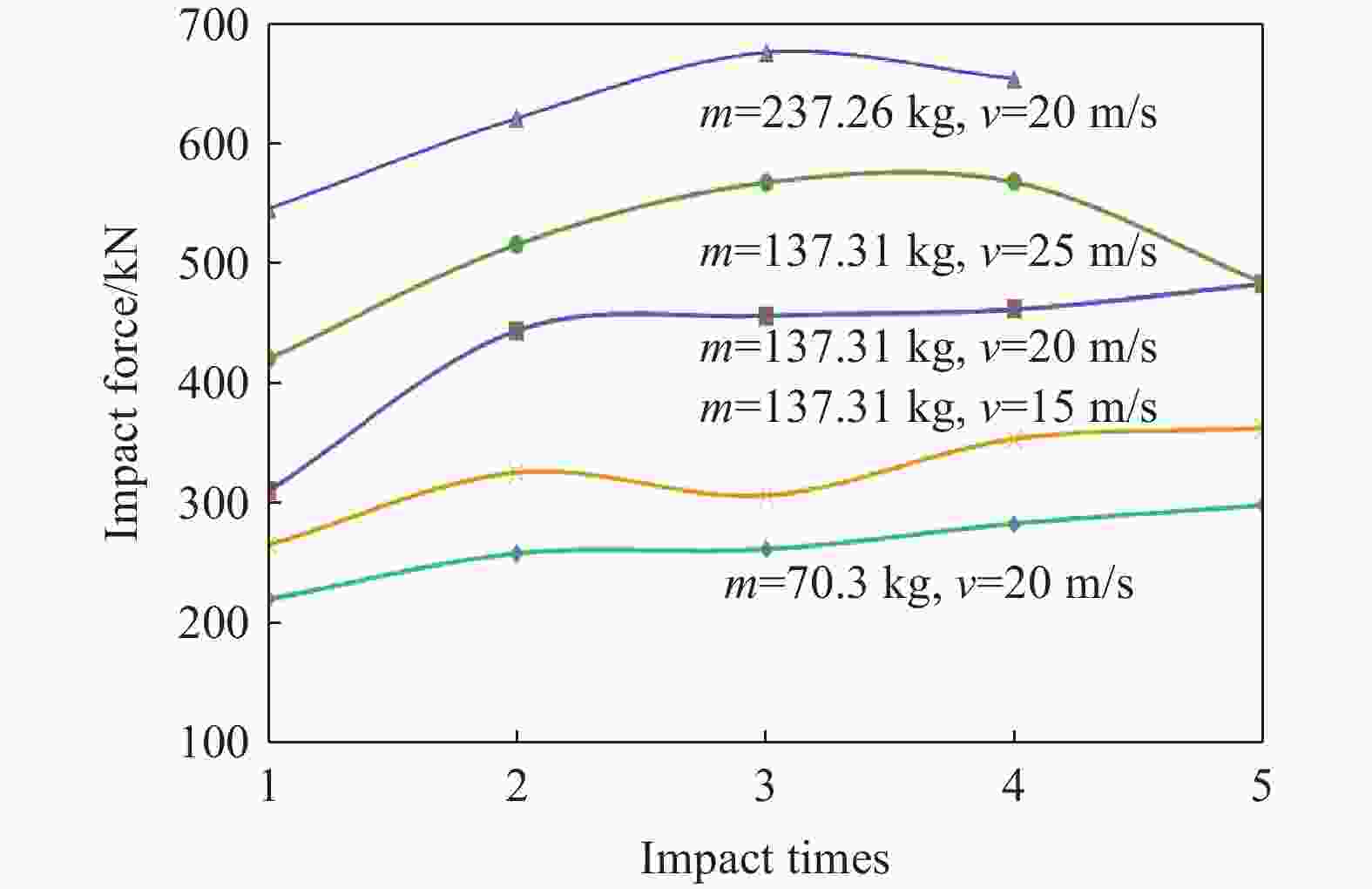
摘要: 为探究多次落石冲击下棚洞结构的动力响应特征,建立并验证了基于ANSYS/LS-DYNA有限元软件的落石冲击棚洞FEM-SPH耦合数值模型,并结合LS-DYNA完全重启动技术,研究了落石冲击速度、质量、冲击角度、形状等4个因素对多次落石冲击棚洞结构动力响应的影响。结果表明:冲击力、缓冲层顶部冲击位移、棚顶位移、棚洞塑性应变均与落石质量、速度、冲击方向与棚洞平面的夹角呈正相关;长方体落石冲击产生的冲击力、棚顶位移和塑性应变均大于球体落石,球体落石产生的冲击位移大于长方体;对于长方体落石,冲击位移、棚顶位移、塑性应变与接触面积呈负相关;随着落石冲击次数的增加,峰值冲击力通常会先增大而后趋于稳定。
-
关键词:
- 棚洞结构 /
- 动力响应 /
- FEM-SPH耦合数值模型 /
- 冲击力 /
- 多次落石
Abstract: To exploring the dynamic response characteristics of the shed-tunnel structure under multiple rockfall impacts, an FEM-SPH coupled numerical model is established based on ANSYS/LS-DYNA and is also tested with the data before. Then, the model is combined with the full restart technique to study the effects of the shed-tunnel structure dynamic response under multiple rockfall impacts by considering four factors, e.g., rockfall impact velocity, rockfall mass, impact angle and rockfall shape. The results show that the impact force, buffer top impact displacement, roof displacement and plastic strain of the shed-tunnel are positively correlated with the rockfall mass, velocity and angle. The impact force, roof displacement and plastic strain of the shed-tunnel structure generated by the cuboid rockfall impact are all larger than those of the spherical rockfall, and the impact displacement generated by the spherical rockfall impact is larger than that of the cuboid. For the cuboid rockfall, the impact displacement, roof displacement and plastic strain are negatively correlated with the contact area. Under the multiple rockfall impacts, the peak impact force usually increases firstly and then tends to be stable. -
表 1 材料物理力学参数表
Table 1. Material physical and mechanical parameters
材料 弹性模量/MPa 密度/(kg·m−3) 泊松比 内摩擦角/(°) 粘聚力/kPa 抗压强度/MPa 屈服强度/MPa 落石 33500 2097.86 0.3 − − − − 缓冲垫层 15 1540 0.27 30 20 − − 混凝土 30000 2400 0.167 − − 30 − 钢筋 200000 7850 0.3 − − − 335 -
[1] DORREN L K A. A review of rockfall mechanics and modelling approaches [J]. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 2003, 27(1): 69–87. DOI: 10.1191/0309133303pp359ra. [2] LI L P, LAN H X. Probabilistic modeling of rockfall trajectories: a review [J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2015, 74(4): 1163–1176. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-015-0718-9. [3] 吴长, 丁金伟, 黄贵武. 滚石冲击下新型组合棚洞结构的动力响应分析 [J]. 建筑结构, 2018, 48(S2): 546–549. DOI: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2018.S2.110.WU C, DING J W, HUANG G W. Dynamic response analysis of a new composite shed-tunnel structure under the rockfall impact [J]. Building Structure, 2018, 48(S2): 546–549. DOI: 10.19701/j.jzjg.2018.S2.110. [4] HERTZ H. Über die Berührung fester elastischer körper [J]. Journal fur die Reine und Angewandte Mathematik, 1882, 92: 156–171. [5] 何思明, 李新坡, 吴永. 考虑弹塑性变形的泥石流大块石冲击力计算 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(8): 1664–1669. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.08.017.HE S M, LI X P, WU Y. Calculation of impact force of outrunner blocks in debris flow considering elastoplastic deformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(8): 1664–1669. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.08.017. [6] 陈颖骐, 王全才. 基于Hertz弹性理论和Thornton弹塑性假设的滚石冲击力的修正计算 [J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(13): 37–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.13.006.CHEN Y Q, WANG Q C. Correction calculation of impact force of rockfall based on Hertz contact theory and Thornton elastoplasticity hypothesis [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(13): 37–41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.13.006. [7] THORNTON C. Coefficient of restitution for collinear collisions of elastic – perfectly plastic spheres [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics-Transactions of the ASME, 1997, 64: 383–386. DOI: 10.1115/1.2787319. [8] ZHENG D, BINIENDA W K. Effect of permanent indentation on the delamination threshold for small mass impact on plates [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44(25/26): 8143–8158. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2007.06.005. [9] 陈泰江, 章广成, 向欣. 落石冲击混凝土棚洞力学特性研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(1): 277–285, 298. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2021.0890.CHEN T J, ZHANG G C, XIANG X. Investigations on mechanical characteristics of rockfall impact on concrete shed cave [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(1): 277–285, 298. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2021.0890. [10] 刘红岩. 落石冲击下钢筋混凝土桩板墙的动态响应 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 53(6): 2290–2299. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2022.06.029.LIU H Y. Dynamic damage model for reinforced concrete pile-plate retaining wall under rockfall impact [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(6): 2290–2299. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2022.06.029. [11] 闫鹏, 方秦, 张锦华, 等. 不同典型形状落石冲击砂垫层试验与量纲分析 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(7): 073303. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0219.YAN P, FANG Q, ZHANG J H, et al. Experimental study of different typical shape falling-rocks impacting on the sand cushion and dimensionless analysis [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(7): 073303. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0219. [12] WU J L, MA G T, ZHOU Z H, et al. Experimental investigation of impact response of RC slabs with a sandy soil cushion layer [J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2021, 2021(1): 1562158. DOI: 10.1155/2021/1562158. [13] NAKAJIMA S, ABE K, SHINODA M, et al. Experimental study on impact force due to collision of rockfall and sliding soil mass caused by seismic slope failure [J]. Landslides, 2021, 18(1): 195–216. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-020-01461-z. [14] 苏宇宸, 王媛, 唐辉明, 等. 落石连续冲击下废弃混凝土垫层宏细观缓冲机制研究 [J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(10): 2698–2706. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2021.1709.SU Y C, WANG Y, TANG H M, et al. Macro-mesoscopic investigation of cushioning mechanism of recycled concrete aggregate under successive rockfall impacts [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(10): 2698–2706. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2021.1709. [15] SHEN W G, ZHAO T, DAI F, et al. DEM analyses of rock block shape effect on the response of rockfall impact against a soil buffering layer [J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 249: 60–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.011. [16] OUYANG C J, LIU Y, WANG D P, et al. Dynamic analysis of rockfall impacts on geogrid reinforced soil and eps absorption cushions [J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2019, 23(1): 37–45. DOI: 10.1007/s12205-018-0704-4. [17] 王爽, 周晓军, 姜波, 等. 落石冲击下隧道大跨度棚洞的动力响应数值分析与抗冲击研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2016, 36(4): 548–556. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0548-09.WANG S, ZHOU X J, JIANG B, et al. Numerical analysis of dynamic response and impact resistance of a large-span rock shed in a tunnel under rockfall impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2016, 36(4): 548–556. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)04-0548-09. [18] ZHONG H Q, LYU L, YU Z X, et al. Study on mechanical behavior of rockfall impacts on a shed slab based on experiment and SPH-FEM coupled method [J]. Structures, 2021, 33: 1283–1298. DOI: 10.1016/j.istruc.2021.05.021. [19] WANG H B, GUO C C, WANG F M, et al. Peridynamics simulation of structural damage characteristics in rock sheds under rockfall impact [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2022, 143: 104625. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104625. [20] 黄福有, 张路青, 周剑, 等. 落石冲击作用下棚洞垫层动力响应的颗粒级配效应耦合数值模拟研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(2): 413–428. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2022.0519.HUANG F Y, ZHANG L Q, ZHOU J, et al. Coupled numerical simulation study on particle gradation effect of the dynamic response of shed cushion under rockfall impact [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(2): 413–428. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2022.0519. [21] OLSSON R. Analytical model for delamination growth during small mass impact on plates [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2010, 47(21): 2884–2892. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.06.015. [22] 王东坡, 刘洋, 裴向军, 等. 滚石冲击钢筋混凝土板的弹塑性动力响应研究 [J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(6): 1147–1153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.06.014.WANG D P, LIU Y, PEI X J, et al. Elasto-plastic dynamic responses of reinforced concrete slabs under rockfall impact [J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(6): 1147–1153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.06.014. [23] 王东坡, 刘浩, 裴向军, 等. 基于离散元-有限差分耦合的滚石冲击棚洞垫层动力响应研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(19): 246–253. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.19.031.WANG D P, LIU H, PEI X J, et al. Dynamic response of shed tunnel cushion under rolling stone impact based on discrete element-finite difference coupling [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(19): 246–253. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.19.031. [24] PHAM A T, TAN K H, YU J. Numerical investigations on static and dynamic responses of reinforced concrete sub-assemblages under progressive collapse [J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 149: 2–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.07.042. [25] 铁道部第二勘测设计院. 铁路工程设计技术手册·隧道(修订版) [M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1999: 141–191. [26] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 公路路基设计规范: JTG D30-2015 [S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2015.Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for design of highway subgrades: JTG D30-2015 [S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2015. [27] 杨其新, 关宝树. 落石冲击力计算方法的试验研究 [J]. 铁道学报, 1996, 18(1): 101–106. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1996.01.017.YANG Q X, GUAN B S. Test and research on calculating method of falling stone impulsive force [J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 1996, 18(1): 101–106. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8360.1996.01.017. [28] LABIOUSE V, DESCOEUDRES F, MONTANI S. Experimental study of rock sheds impacted by rock blocks [J]. Structural Engineering International, 1996, 6(3): 171–176. DOI: 10.2749/101686696780495536. [29] 日本道路协会. 落石对策便览[M]. 东京: 丸善株式会社出版事业部, 2000. -






 下载:
下载: