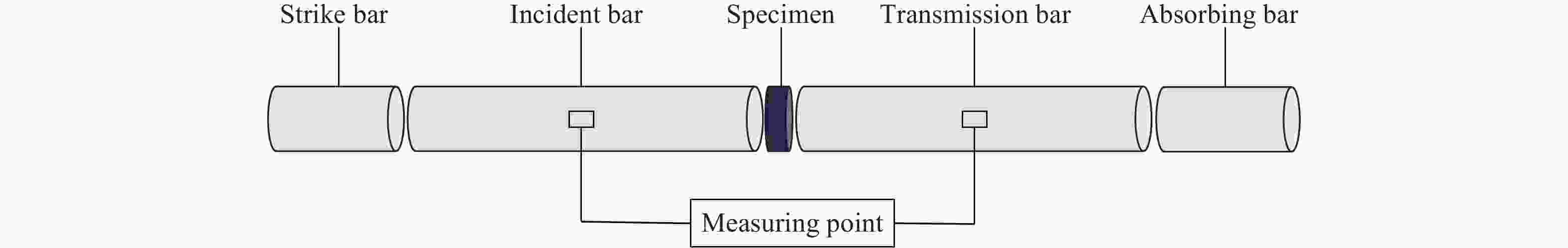
Investigation on geometric parameters effect and blast resistance of high-strength steel plates under near-field explosions
-
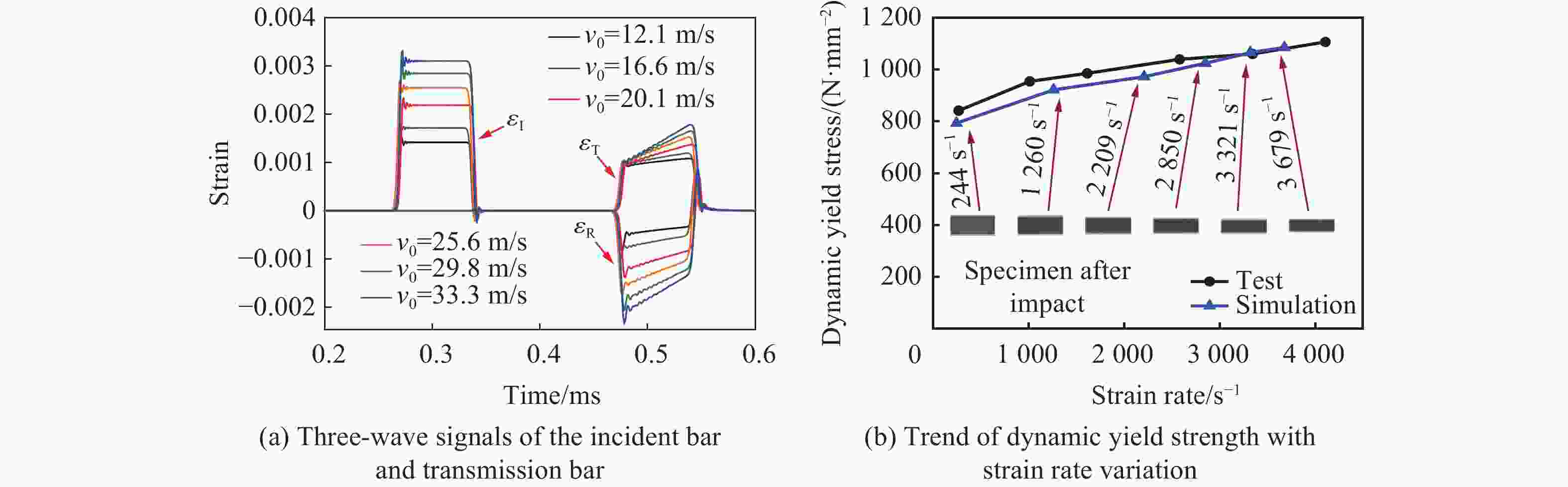
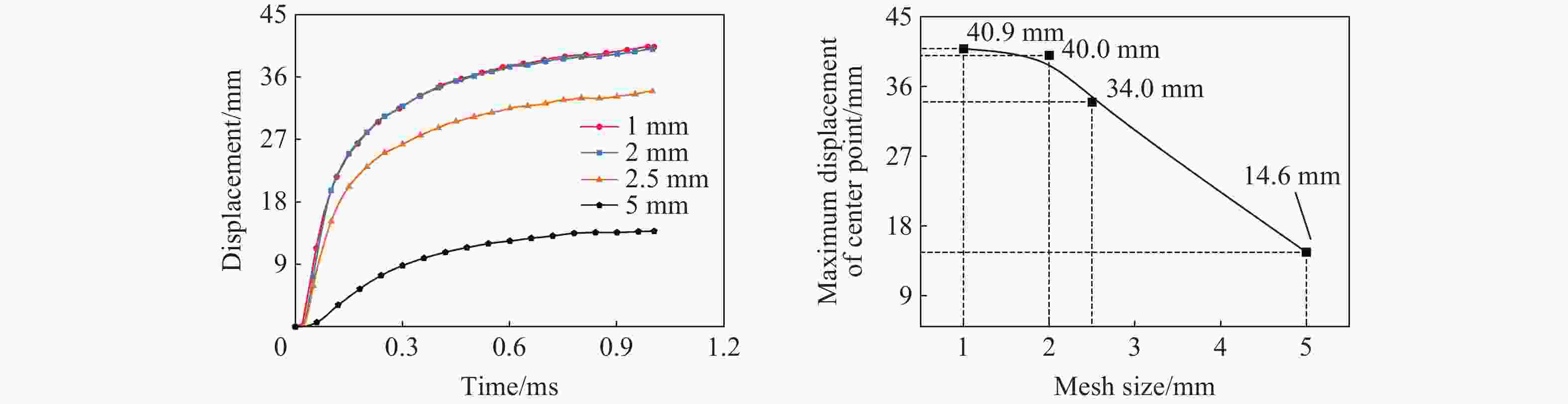
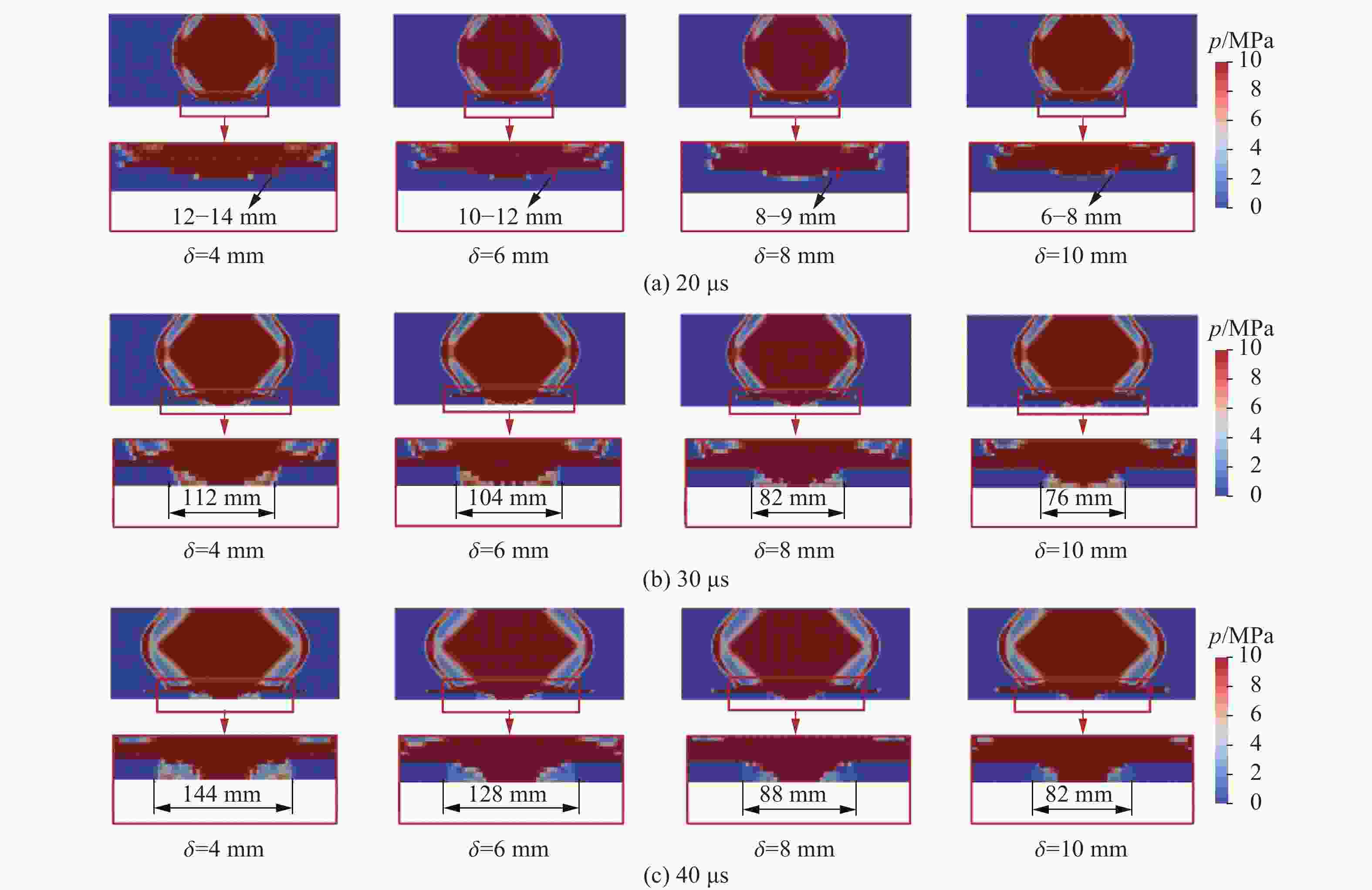
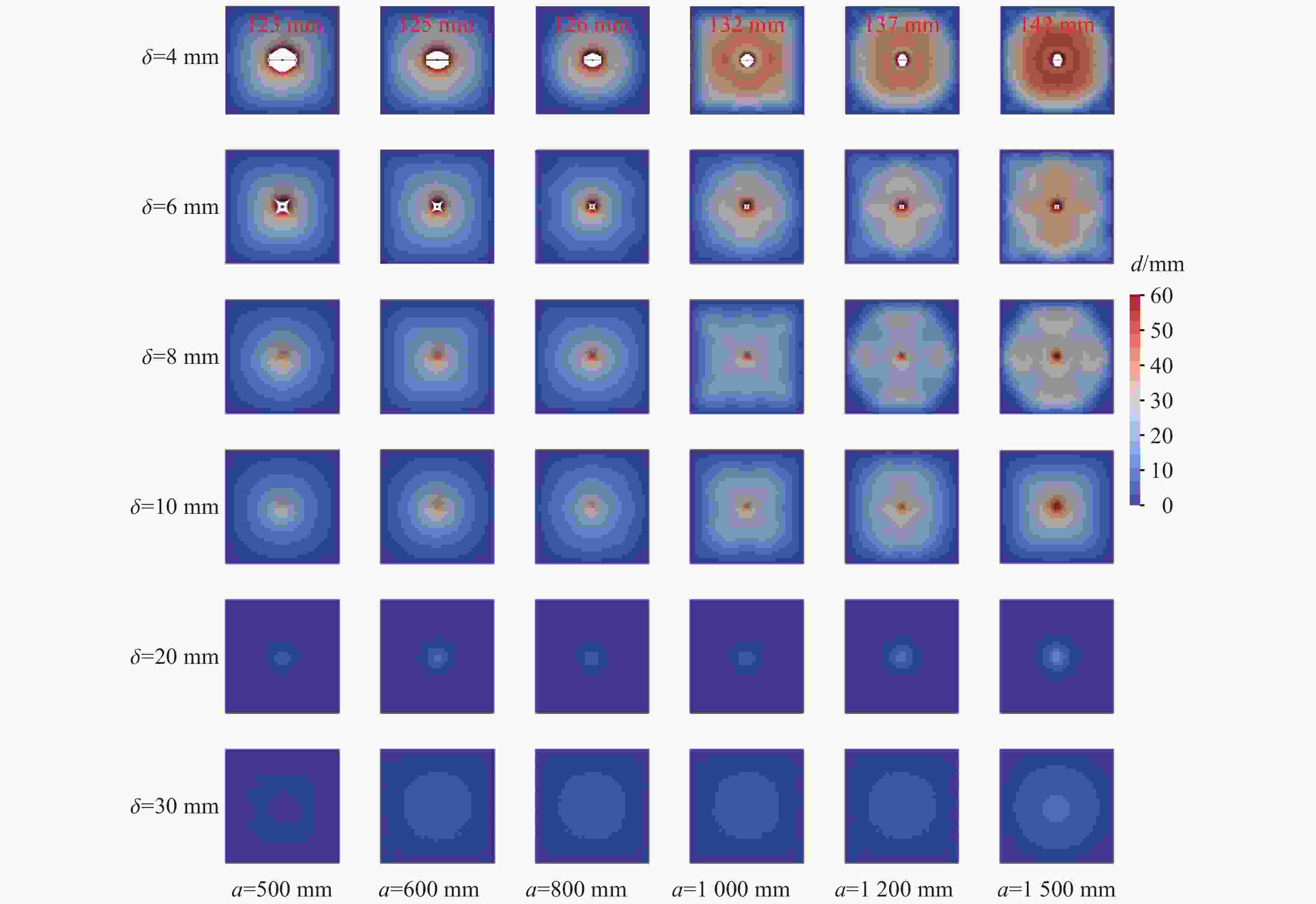
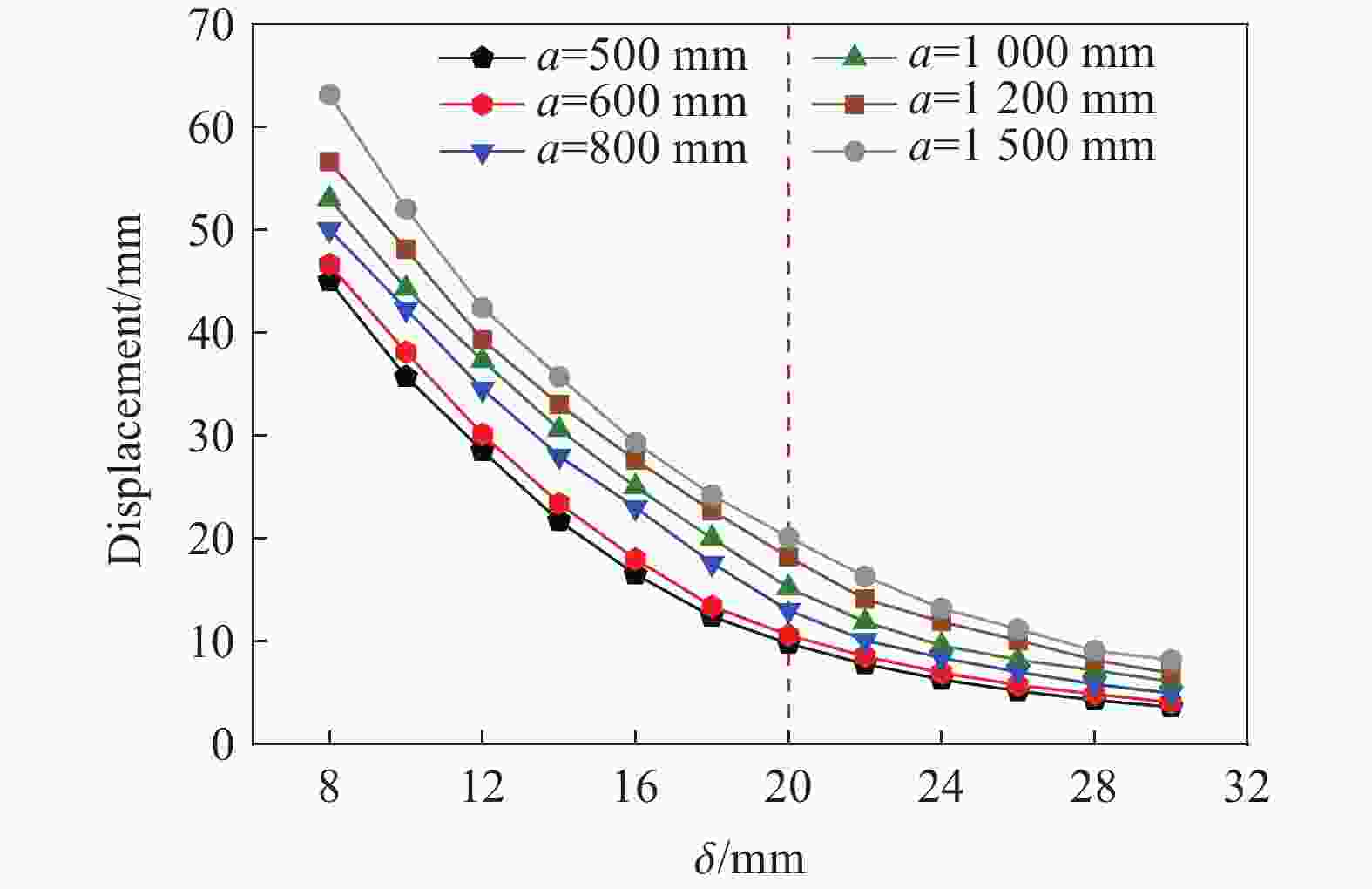
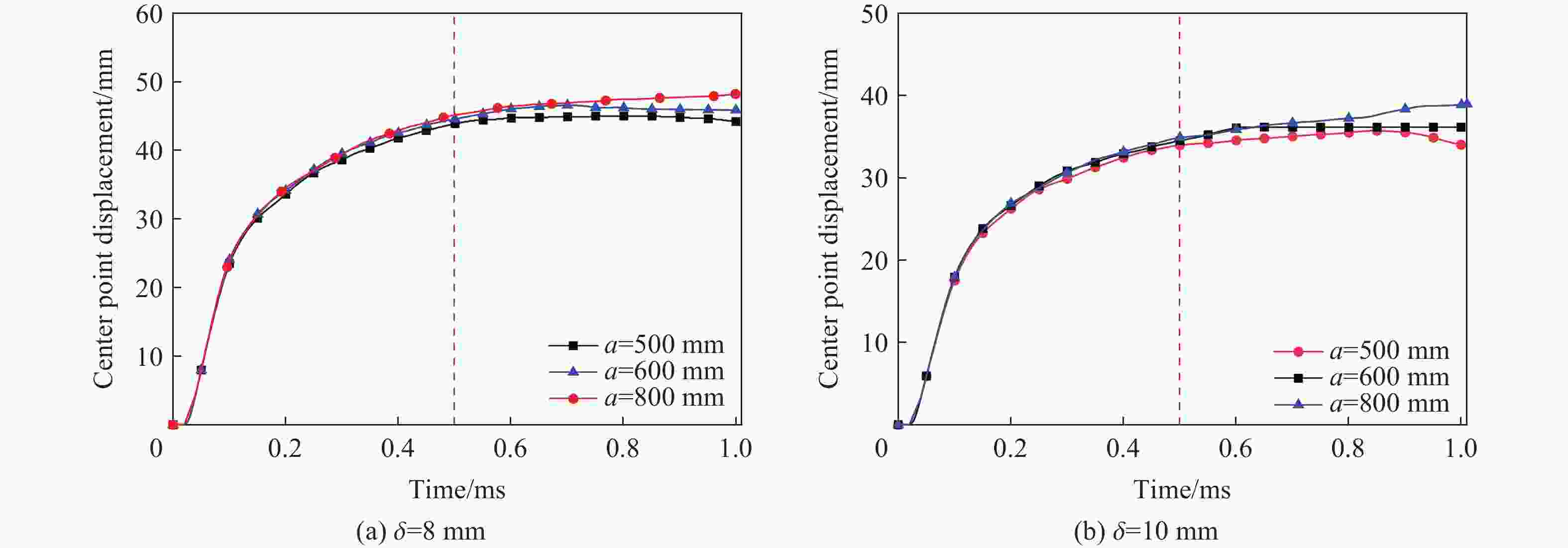
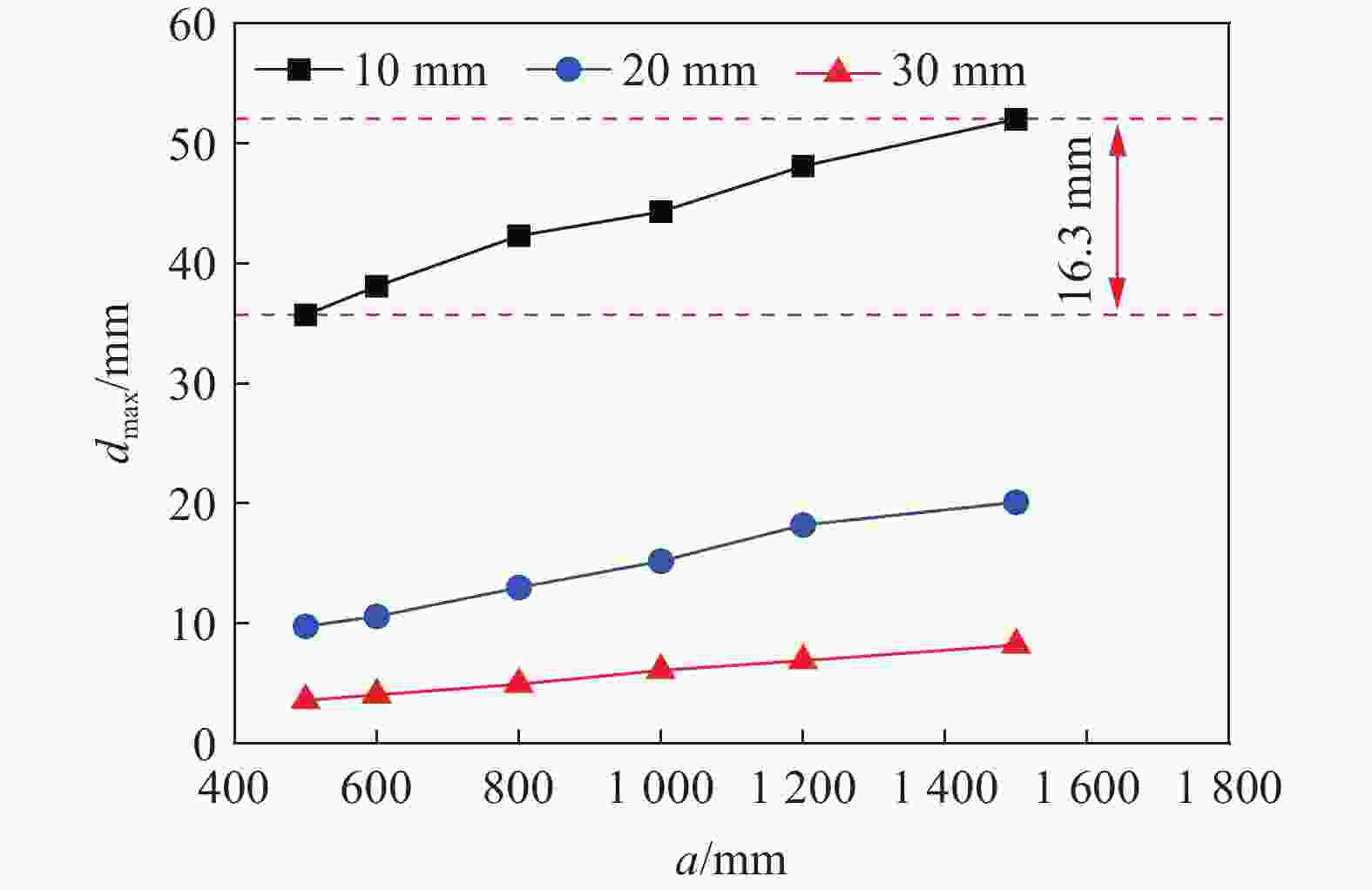
摘要: 为研究近爆载荷作用下高强钢板的抗爆性能,首先利用ANSYS/LS-DYNA软件开展了高强钢材料的SHPB冲击试验模拟,标定了表征高强钢动态本构的Johnson-Cook模型参数;基于该参数开展了84组近爆条件下高强钢板的爆炸模拟,系统分析了爆炸冲击波与钢板的相互作用过程,阐明了钢板的宽度及厚度等几何参数对其变形特征与破坏模式的影响规律。此外,通过汇总分析数值模拟结果,进一步提供了近爆作用下高强钢板最大变形位移的预测模型。研究表明:Johnson-Cook模型能有效模拟高强钢在高应变率下的力学行为;在冲击波传播方面,高强钢板厚度的增加会削弱冲击波穿透钢板后的影响范围;针对不同几何参数的高强钢板,近距离爆炸荷载会造成花瓣形破口、小破口以及大变形3种毁伤模式,且钢板厚度是决定其破坏模式的重要因素;在大变形毁伤模式下,钢板厚度的增加或边长的减小会提高其抗爆能力,宽厚比与钢板抗爆性能呈正相关。
-
关键词:
- 高强钢板 /
- Johnson-Cook模型 /
- 近距爆炸荷载 /
- 几何参数
Abstract: High-strength steel has excellent mechanical properties, which has been utilized in the fields of explosion and impact. In order to study the blast resistance of high-strength steel plates, ANSYS/LS-DYNA software was first used to simulate the impact test on high-strength steel materials. By comparing with experimental results, the Johnson-Cook model parameters characterizing the dynamic constitutive behavior of high-strength steel are determined. Based on the above model parameters, the explosion simulation of high-strength steel plates under near-field explosions is further carried out. The interaction process between the explosion shock wave and the steel plate is systematically analyzed, and the size effects of the steel plate on its deformation characteristics and failure mode are explained. The results show that the Johnson-Cook model can effectively simulate the mechanical behavior of S690 high-strength steel at high strain rates. High-strength steel plates have a weakening effect on the propagation of shock waves. With the increase of steel plate thickness, the propagation range of shock wave through steel plate decreases gradually. For high-strength steel plates of different geometric dimensions, near-field explosions will cause three damage modes: petal-shaped fracture, small fracture and large deformation. It is found that the thickness is the decisive factor to determine the failure mode of steel plates under near-field explosions. For high-strength steel plates with large deformation, the increase of thickness and decrease of width will improve the ability of resistance to near-field explosions. In addition, there is a positive correlation between the ability of shock resistance of the high-strength steel plate and the width-thickness ratio. When the proportional distance is 0.13, a model can be provided to predict the maximum displacement range of the high-strength steel plate according to the steel plate size. The above conclusions can provide some guiding significance for the optimal design and engineering application of high-strength steel structures. -
表 1 TNT炸药材料参数
Table 1. TNT material parameters
ρTNT/(kg·m−3) DCJ/(m·s−1) pCJ/GPa AJWL/GPa BJWL/GPa R1 R2 w ETNT/(J·mm−3) 1630 6930 21 371 3.231 4.15 0.95 0.35 6 注:ρTNT为炸药的密度,DCJ 和pCJ分别为CJ爆轰阶段的速度和压力. 表 2 S690的J-C模型参数
Table 2. J-C model parameters for S690
A/MPa B/MPa C n 722 400 0.21 0.57 表 3 仿真工况设置
Table 3. Simulation condition configurations
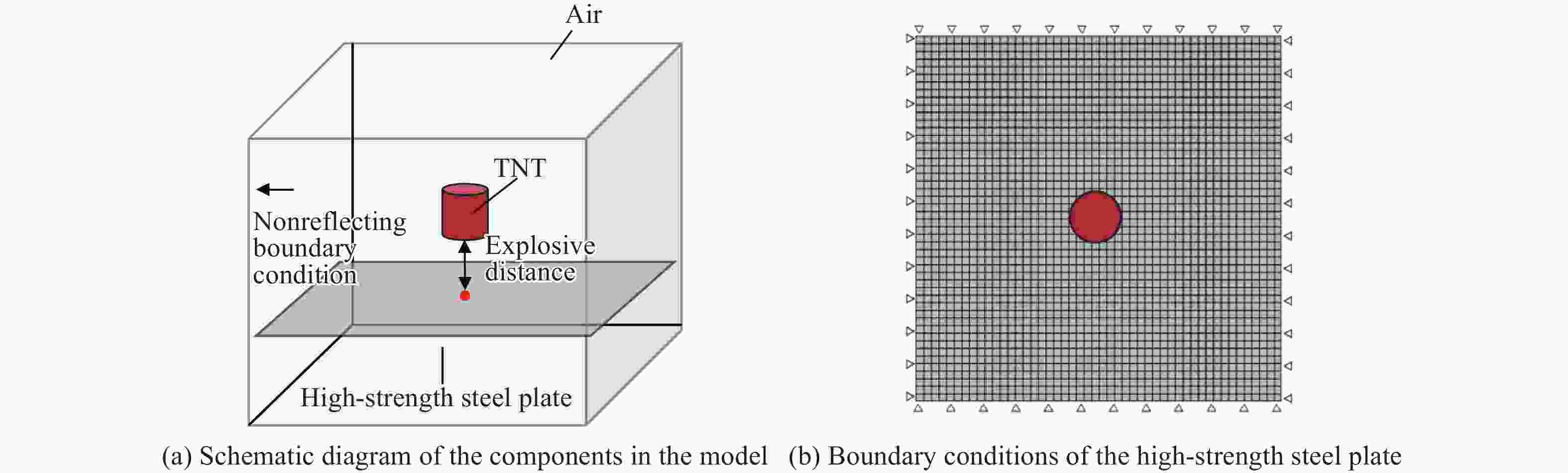
工况 a/mm m/kg 爆距/mm δ/mm 1~14 500 0.5 100 4、6、8、10、12、
14、16、18、20、
22、24、26、28、3015~28 600 0.5 100 29~42 800 0.5 100 43~56 1000 0.5 100 57~70 1200 0.5 100 71~84 1500 0.5 100 表 4 各工况高强钢板的宽厚比和最大位移
Table 4. Width-thickness ratios and maximum displacements of high-strength steel plate under different conditions
工况 a/mm δ/mm a/δ 位移/mm 工况 a/mm δ/mm a/δ 位移/mm 工况 a/mm δ/mm a/δ 位移/mm 1 500 4 125.00 - 29 800 4 200.00 - 57 1200 4 300.00 - 2 6 83.33 - 30 6 133.33 - 58 6 200.00 - 3 8 62.50 45.00 31 8 100.00 50.00 59 8 150.00 56.60 4 10 50.00 35.70 32 10 80.00 42.30 60 10 120.00 48.10 5 12 41.67 28.50 33 12 66.67 34.50 61 12 100.00 39.30 6 14 35.71 21.70 34 14 57.14 28.00 62 14 85.71 33.00 7 16 31.25 16.50 35 16 50.00 23.00 63 16 75.00 27.60 8 18 27.78 12.40 36 18 44.44 17.60 64 18 66.67 22.70 9 20 25.00 9.78 37 20 40.00 13.00 65 20 60.00 18.20 10 22 22.73 7.79 38 22 36.36 10.10 66 22 54.55 14.10 11 24 20.83 6.30 39 24 33.33 8.40 67 24 50.00 11.91 12 26 19.23 5.17 40 26 30.77 7.03 68 26 46.15 10.10 13 28 17.86 4.29 41 28 28.57 5.85 69 28 42.86 8.20 14 30 16.67 3.60 42 30 26.67 4.95 70 30 40.00 6.90 15 600 4 150.00 / 43 1000 4 250.00 / 71 1500 4 375.00 / 16 6 100.00 / 44 6 166.67 / 72 6 250.00 / 17 8 75.00 46.60 45 8 125.00 53.00 73 8 187.50 63.10 18 10 60.00 38.10 46 10 100.00 44.30 74 10 150.00 52.00 19 12 50.00 30.10 47 12 83.33 37.30 75 12 125.00 42.40 20 14 42.86 23.40 48 14 71.43 30.60 76 14 107.14 35.70 21 16 37.50 18.00 49 16 62.50 25.00 77 16 93.75 29.30 22 18 33.33 13.40 50 18 55.56 20.00 78 18 83.33 24.20 23 20 30.00 10.60 51 20 50.00 15.20 79 20 75.00 20.10 24 22 27.27 8.55 52 22 45.45 11.90 80 22 68.18 16.30 25 24 25.00 6.95 53 24 41.67 9.60 81 24 62.50 13.20 26 26 23.08 5.76 54 26 38.46 8.21 82 26 57.69 11.20 27 28 21.43 4.87 55 28 35.71 7.20 83 28 53.57 9.10 28 30 20.00 4.07 56 30 33.33 6.10 84 30 50.00 8.20 -
[1] WANG X, LIU C, ZHOU Z Q, et al. In-situ EBSD investigation of plastic damage in a 316 austenitic stainless steel and its molecular dynamics (MD) simulations [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 13: 823–833. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.05.010. [2] WANG X, CHEN J G, SU G F, et al. Application of electromagnetism method to characterize the degradation behavior in structural mild steel within the elastic range [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 241: 118011. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118011. [3] LIU J, WU C Q, LI C G, et al. Blast testing of high performance geopolymer composite walls reinforced with steel wire mesh and aluminium foam [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 197: 533–547. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.207. [4] AL-THAIRY H. A modified single degree of freedom method for the analysis of building steel columns subjected to explosion induced blast load [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 94: 120–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.04.007. [5] SUN Y X, WANG X, JI C, et al. Experimental investigation on anti-penetration performance of polyurea-coated ASTM1045 steel plate subjected to projectile impact [J]. Defence Technology, 2021, 17(4): 1496–1513. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2020.08.005. [6] CHEN A Q, LOUCA L A, ELGHAZOULI A Y. Behaviour of cylindrical steel drums under blast loading conditions [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 88: 39–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.09.007. [7] ZHOU Z Q, CHEN J G, YUAN H Y, et al. The role of Al reaction rate in the damage effect and energy output of RDX-based aluminized explosives in concrete [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2019, 44(3): 319–326. DOI: 10.1002/prep.201800093. [8] WU T Y, JIANG N, ZHOU C B, et al. Evaluate of anti-explosion for high-pressure gas steel pipeline subjected to ground explosion [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2021, 177: 106429. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2020.106429. [9] 汪维, 刘光昆, 赵强, 等. 近爆作用下方形板表面爆炸载荷分布函数研究 [J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2020, 50(2): 144–152. DOI: 10.1360/SSPMA-2019-0188.WANG W, LIU G K, ZHAO Q, et al. Study on the distribution function of blast loads on the surface of a square plate under near-explosion [J]. Science China: Physics, Mechanics, and Astronomy, 2020, 50(2): 144–152. DOI: 10.1360/SSPMA-2019-0188. [10] GAN L, ZONG Z H, CHEN Z J, et al. Differences in responses of square steel plates exposed to blast loads generated by cubic and spherical explosives [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 182: 110332. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110332. [11] 施龙, 李建平, 王川. 爆炸作用下板壳结构响应特性研究 [J]. 爆破器材, 2014, 43(5): 30–34. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2014.05.007.SHI L, LI J P, WANG C. Response characteristic research of shell structures under blasting [J]. Explosive Materials, 2014, 43(5): 30–34. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8352.2014.05.007. [12] 杨锐, 汪泉, 谢守冬, 等. 负压爆炸载荷作用下固支钢板变形研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2023, 37(5): 054102. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230685.YANG R, WANG Q, XIE S D, et al. Deformation of fixed support steel plate under explosion load in negative pressure environment [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2023, 37(5): 054102. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230685. [13] WIERZBICKI T, NURICK G N. Large deformation of thin plates under localised impulsive loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(7/8): 899–918. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(96)00027-9. [14] ZHOU Z Q, DU Z C, ZHANG Y L, et al. Microscopic defects formation and dynamic mechanical response analysis of Q345 steel plate subjected to explosive load [J]. Defence Technology, 2024, 32: 430–442. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2023.03.025. [15] 赵春风, 张利, 李晓杰. 近场爆炸下波纹双钢板混凝土组合墙板的损伤破坏及抗爆性能 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(1): 014102. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230727.ZHAO C F, ZHANG L, LI X J. Damage failure and anti-blast performance of concrete-infilled double steel corrugated-plate wall under near field explosion [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(1): 014102. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20230727. [16] GAN L, ZONG Z H, LIN J, et al. Influence of U-shaped stiffeners on the blast-resistance performance of steel plates [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2022, 188: 107046. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2021.107046. [17] 侯晓萌, 曹少俊, 郑文忠. 爆炸荷载作用下钢板-RPC抗爆门动态响应分析 [J]. 建筑结构学报, 2016, 37(S1): 219–226, 232. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2016.S1.031.HOU X M, CAO S J, ZHENG W Z. Analysis on dynamic response of steel-RPC anti-explosion doors under blast load [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2016, 37(S1): 219–226, 232. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2016.S1.031. [18] SHI G, HU F X, SHI Y J. Recent research advances of high strength steel structures and codification of design specification in China [J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2014, 14(4): 873–887. DOI: 10.1007/s13296-014-1218-7. [19] 王蕾. S690QL高强度钢材在不同应力状态下的断裂破坏研究 [J]. 机械工程师, 2019(8): 100–102.WANG L. Fracture failure investigation of S690QL high strength steel under different stress states [J]. Mechanical Engineer, 2019(8): 100–102. [20] ALABI A A, MOORE P L, WROBEL L C, et al. Tensile behaviour of S690QL and S960QL under high strain rate [J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2018, 150: 570–580. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2018.08.009. [21] CAI W Y, LI G Q. Experimental study on post-fire mechanical properties and fracture behavior of Q690 steel [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 193: 111253. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111253. [22] 张秀华, 张唯佳, 张宇. Q460高强钢柱在近爆荷载作用下的动力响应研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(3): 107–114, 147. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2022.03.013.ZHANG X H, ZHANG W J, ZHANG Y. Dynamic response of Q460 high strength steel column under near explosion load [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(3): 107–114, 147. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2022.03.013. [23] LANGDON G S, LEE W C, LOUCA L A. The influence of material type on the response of plates to air-blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 78: 150–160. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.12.008. [24] 常笑康, 罗本永, 陈长海, 等. 近距空爆载荷作用下高韧钢的抗爆性能及影响因素研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(5): 054103. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240732.CHANG X K, LUO B Y, CHEN C H, et al. Study on the blast-resistant performance and influence factors of high-toughness steel subjected to close-range air-blasts [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(5): 054103. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240732. [25] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. Fracture characteristics of three metals subjected to various strains, strain rates, temperatures and pressures [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1985, 21(1): 31–48. DOI: 10.1016/0013-7944(85)90052-9. [26] YANG X Q, YANG H, ZHANG S M. Rate-dependent constitutive models of S690 high-strength structural steel [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 198: 597–607. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.11.285. [27] KOCKS U F, MECKING H. Physics and phenomenology of strain hardening: the FCC case [J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2003, 48(3): 171–273. DOI: 10.1016/S0079-6425(02)00003-8. [28] NURICK G N, SHAVE G C. The deformation and tearing of thin square plates subjected to impulsive loads—an experimental study [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(1): 99–116. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00018-2. [29] 陈长海, 朱锡, 侯海量, 等. 近距空爆载荷作用下固支方板的变形及破坏模式 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2012, 32(4): 368–375. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)04-0368-08.CHEN C H, ZHU X, HOU H L, et al. Deformation and failure modes of clamped square plates under close-range air blast loads [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2012, 32(4): 368–375. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2012)04-0368-08. [30] 李旭东, 尹建平, 赵鹏铎, 等. 固支钢板在爆炸与均布载荷耦合作用下的破坏 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2021, 42(4): 26–30, 36. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.04.005.LI X D, YIN J P, ZHAO P D, et al. Failure of clamped steel plates under local explosion and uniformly distributed load [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2021, 42(4): 26–30, 36. DOI: 10.11809//bqzbgcxb2021.04.005. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.04.005. -






 下载:
下载: