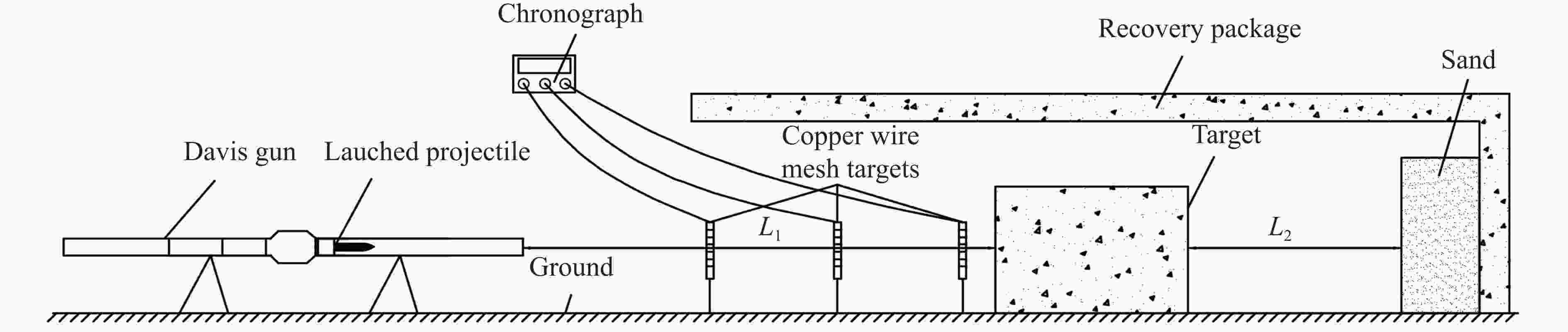
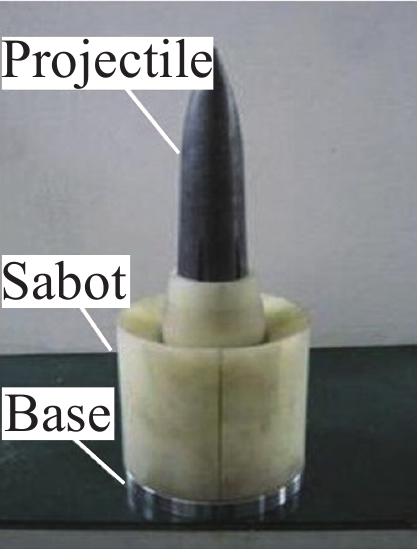
Experimental study on high-speed penetration of reinforced concrete targets by structural projectiles made of two types of materials
-
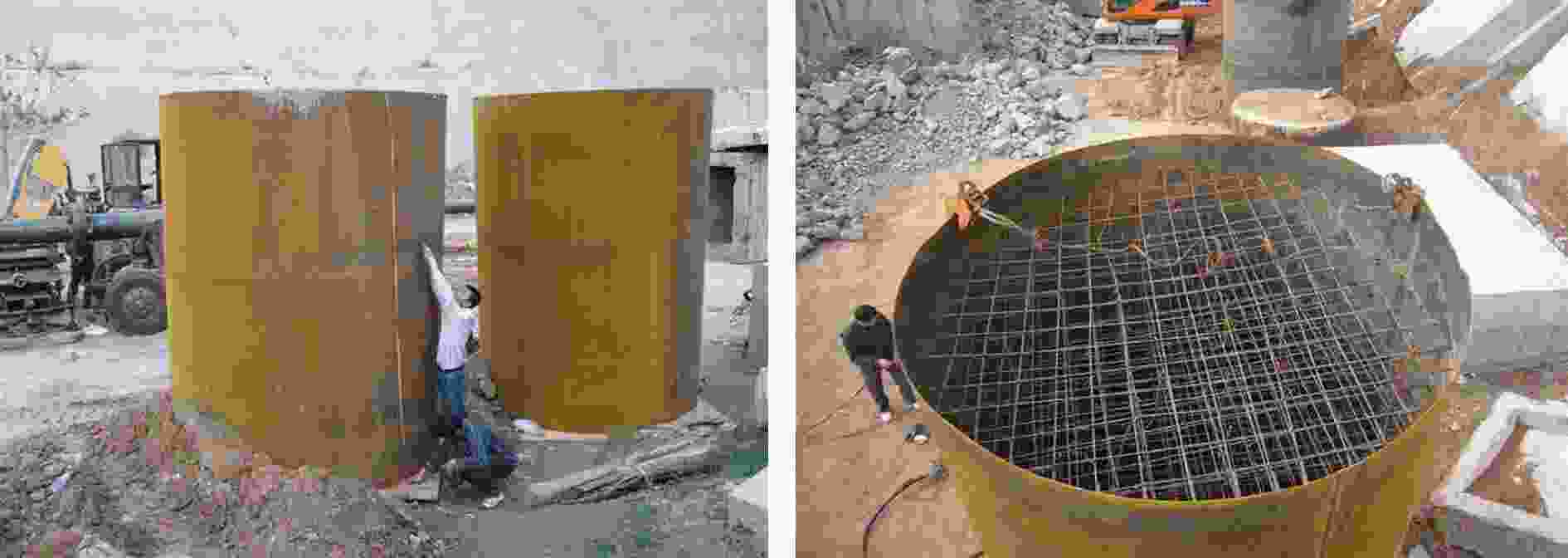
摘要: 设计了2种不同材料的结构弹,以203 mm平衡炮为发射平台,开展了11 kg级弹体在
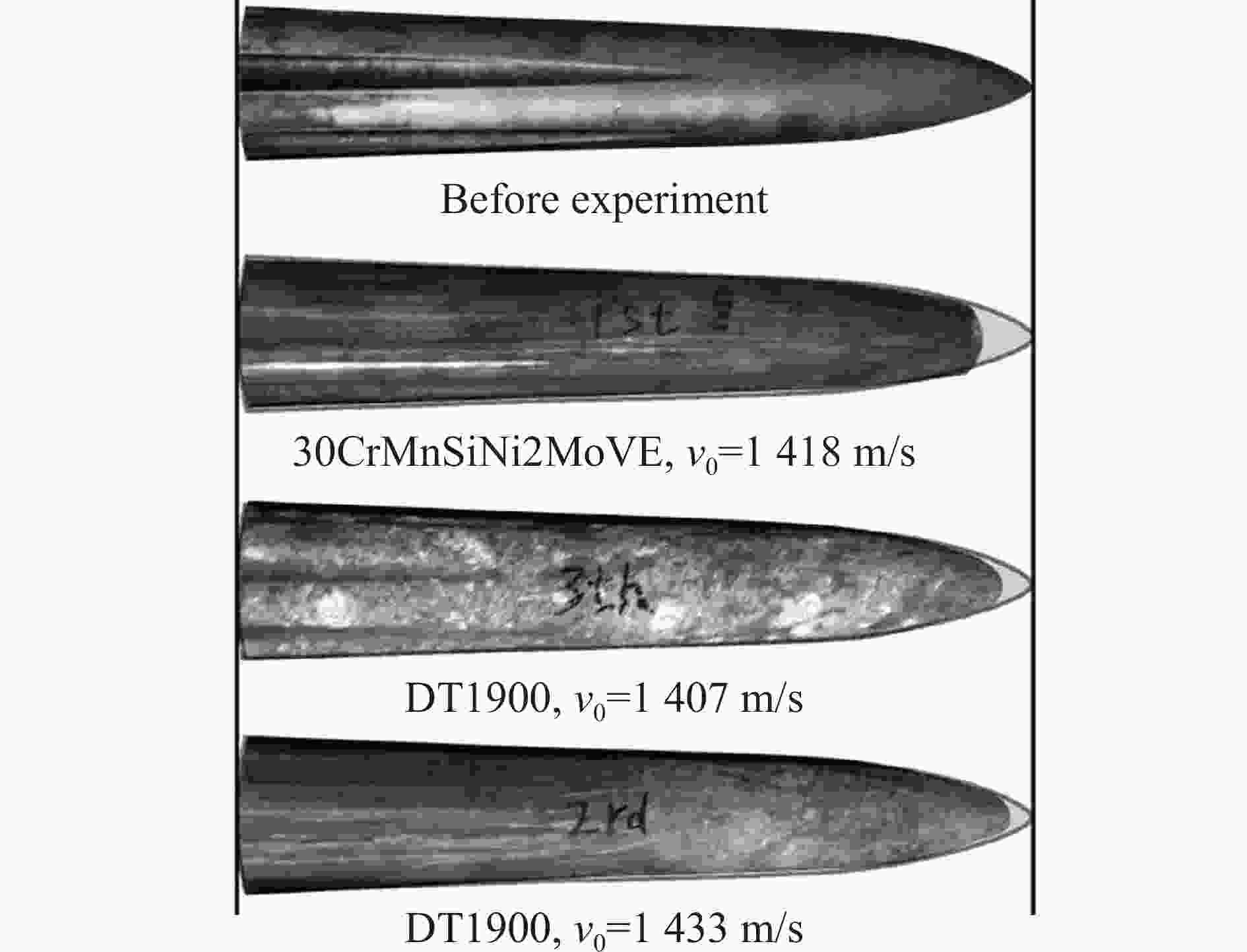
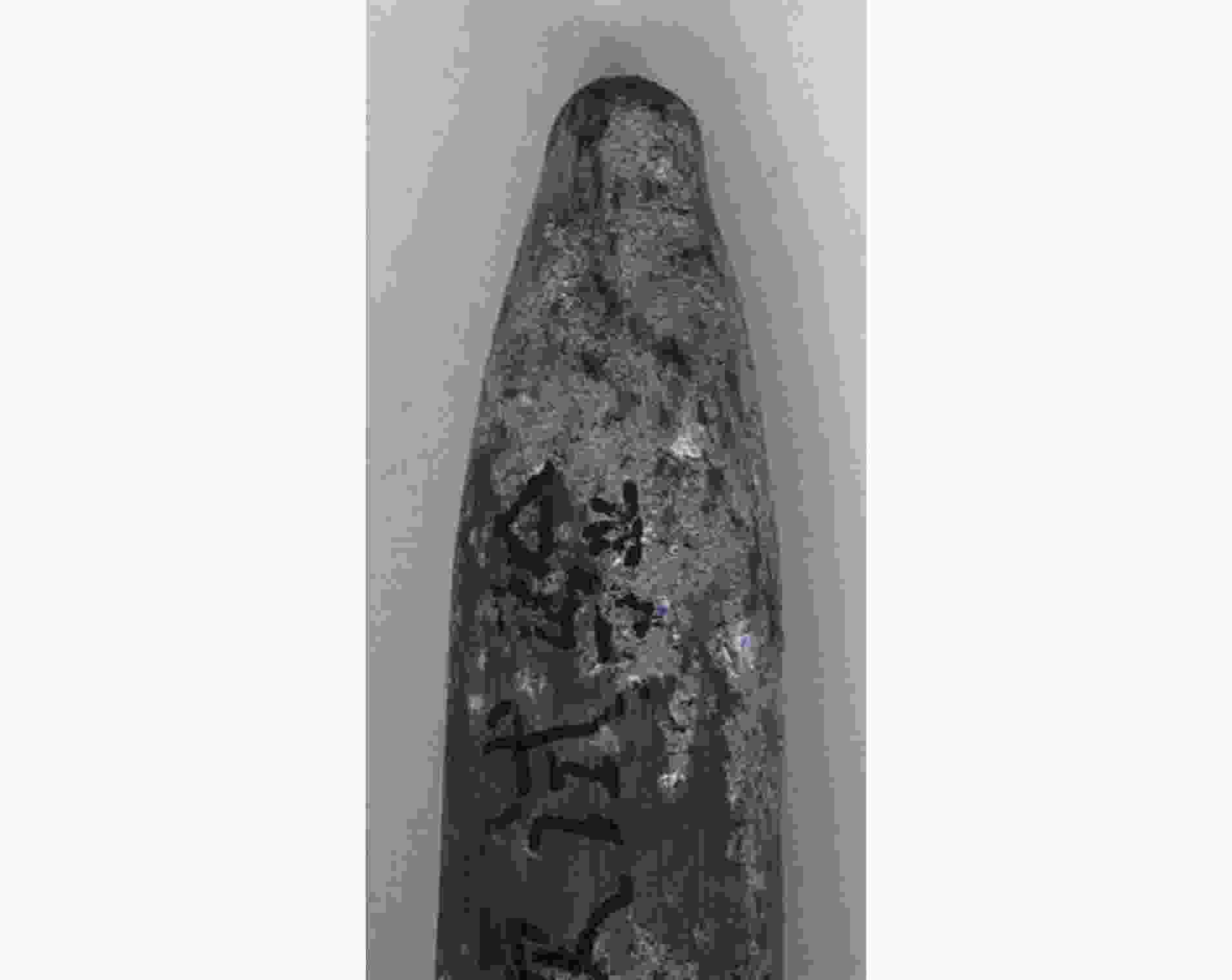
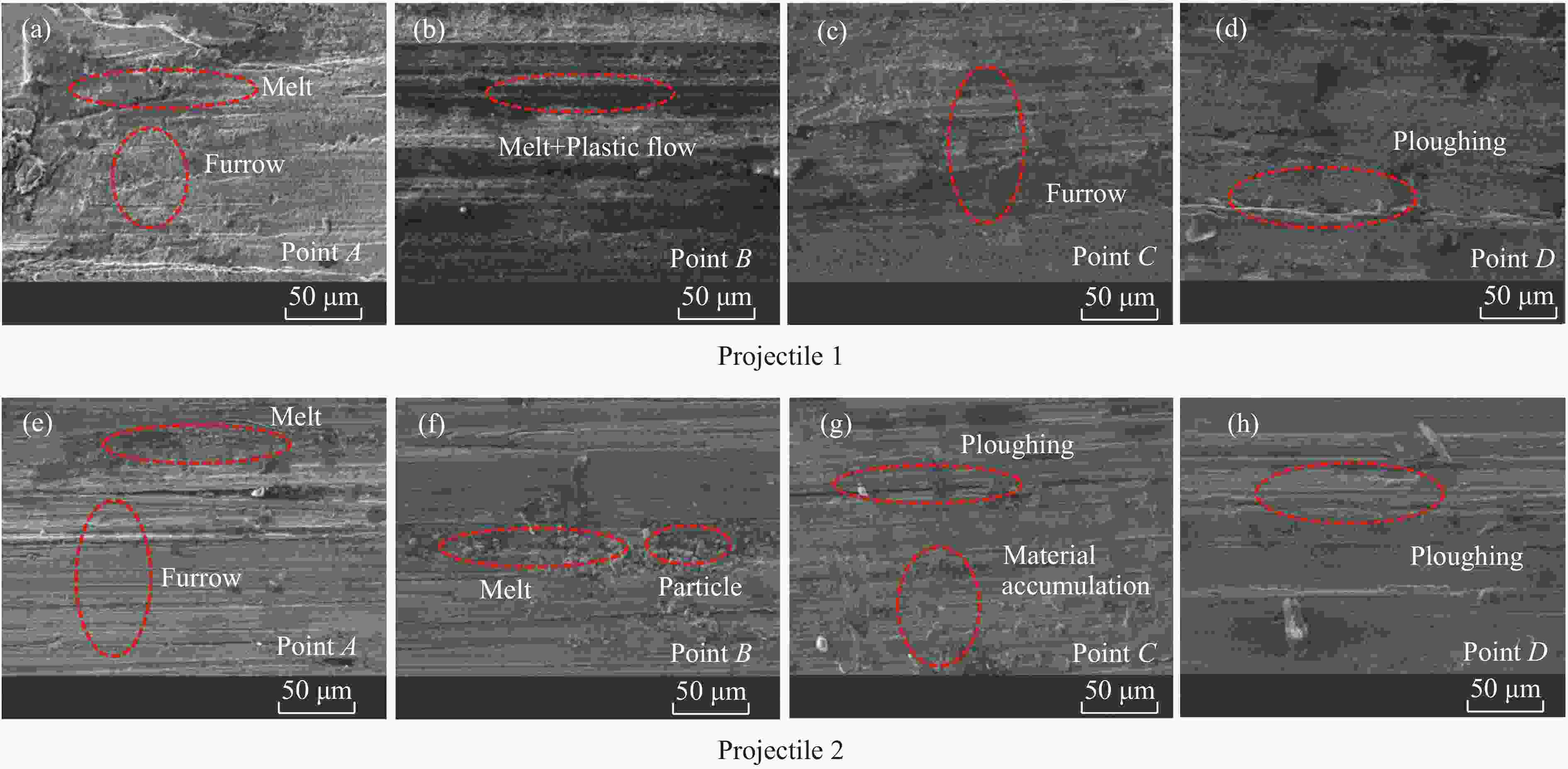
1400 m/s速度段侵彻钢筋混凝土靶的实验研究。基于实验结果,对侵彻弹体进行了宏微观结构表征,探究了不同材料弹体在高速侵彻下的侵蚀机理,分析了壳体材料对弹体侵彻效应的影响。结果表明:在实验速度段,弹体材料主导弹体的侵蚀变形,材料强度越高,抗冲击压缩性能越强,弹体头部的侵蚀越小;材料的抗剪和耐磨性越好,弹身的磨蚀越少。高速侵彻条件下,锥形结构弹体的质量损失主要集中在弹身部分。弹体头部的侵蚀和墩粗在一定程度上会降低弹体的侵彻深度,弹体头部侵蚀程度越低,侵彻深度越高,其中,DT1900实验弹的极限侵彻深度可达9倍弹长。Abstract: Two kinds of structural projectiles made of two different materials were designed in this paper. An experimental study of 11 kg projectiles penetrating the reinforced concrete target at 1400 m/s was carried out using a 203 mm Davis gun. Based on the experimental results, the structural response, penetration capability and related engineering issues of the projectile are discussed. The results show that when the reinforced concrete target is penetrated at a velocity of1400 m/s, the heads of projectiles made of two different materials experienced erosion and were mushroomed. This was caused by high temperatures resulting from friction between the projectile and the concrete during penetration, which significantly softened the surface of the projectile. Furthermore, the contact pressure between the projectile and the target exceeded the yield strength of the projectile material near the surface, causing the material to enter a state of plastic flow and ultimately leading to the erosion and mushrooming of the projectile head. Additionally, the surface material of the projectile was stripped due to the cutting action of the hard aggregates in the concrete, resulting in severe abrasion of the projectile body. When comparing the structural responses of projectiles made of different materials, it was evident that material properties influenced their behavior. Compared to 30CrMnSiNi2MoVE, DT1900, known for its higher strength, hardness and better resistance to impact compression, showed less erosion at the projectile head. However, the inferior shear resistance and wear resistance of DT1900 led to severe abrasion on the projectile body. The mass loss pattern of a conical projectile is different from that of a solid long-rod projectile, with the latter concentrated mainly in the projectile body. The conical flared tail design, while suppressing ballistic deflection, increased the contact area between the projectile body and the target, enhancing the abrasive and cutting actions of aggregates and steel. Moreover, under high-speed penetration conditions, the erosion and mushrooming of the projectile head could reduce the penetration depth; the less erosion at the head, the greater the penetration depth. In experiments, the maximum penetration depth of DT1900 projectiles could reach up to nine times the length of the projectile.-
Key words:
- structural projectile /
- high-speed penetration /
- reinforced concrete /
- eroding /
- penetration depth
-
表 1 热处理后弹体材料的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of projectile materials after heat treatment
材料 序号 ${\sigma _{0.2}}$/MPa ${\sigma _{\mathrm{b}}}$/MPa δ/% Ψ/% KIC/(MPa·m1/2) HRC 30CrMnSiNi2MoVE 1 1326 1656 12.8 45 110 48.6 2 1356 1680 10.9 45 107 48.5 3 1390 1713 10.5 43 101 48.8 DT1900 1 1770 1960 14.0 64.5 118 52.5 2 1790 1970 14.0 69.0 110 51.6 3 1770 2000 14.0 65.5 103 52.2 表 2 实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results
弹体编号 弹体质量/kg 靶板强度/MPa 撞靶速度/(m·s−1) 等效侵彻深度/m 剩余弹体尺寸/mm 剩余弹体质量/kg 长度 直径 1 11.27 32.5 1418 3.6 415.85 87.03 10.18 2 11.30 30.7 1433 3.8 432.16 86.04 10.11 3 11.40 30.7 1407 4.2 433.07 86.04 10.29 表 3 靶体材料参数
Table 3. Material parameter of target
靶体材料 E/GPa φ/(˚) Y/MPa A 沙 0.75 3 7 3.68 混凝土 30 5 30 5.74 表 4 实验弹的几何尺寸变化及质量损失
Table 4. The variation of the projectile size and mass
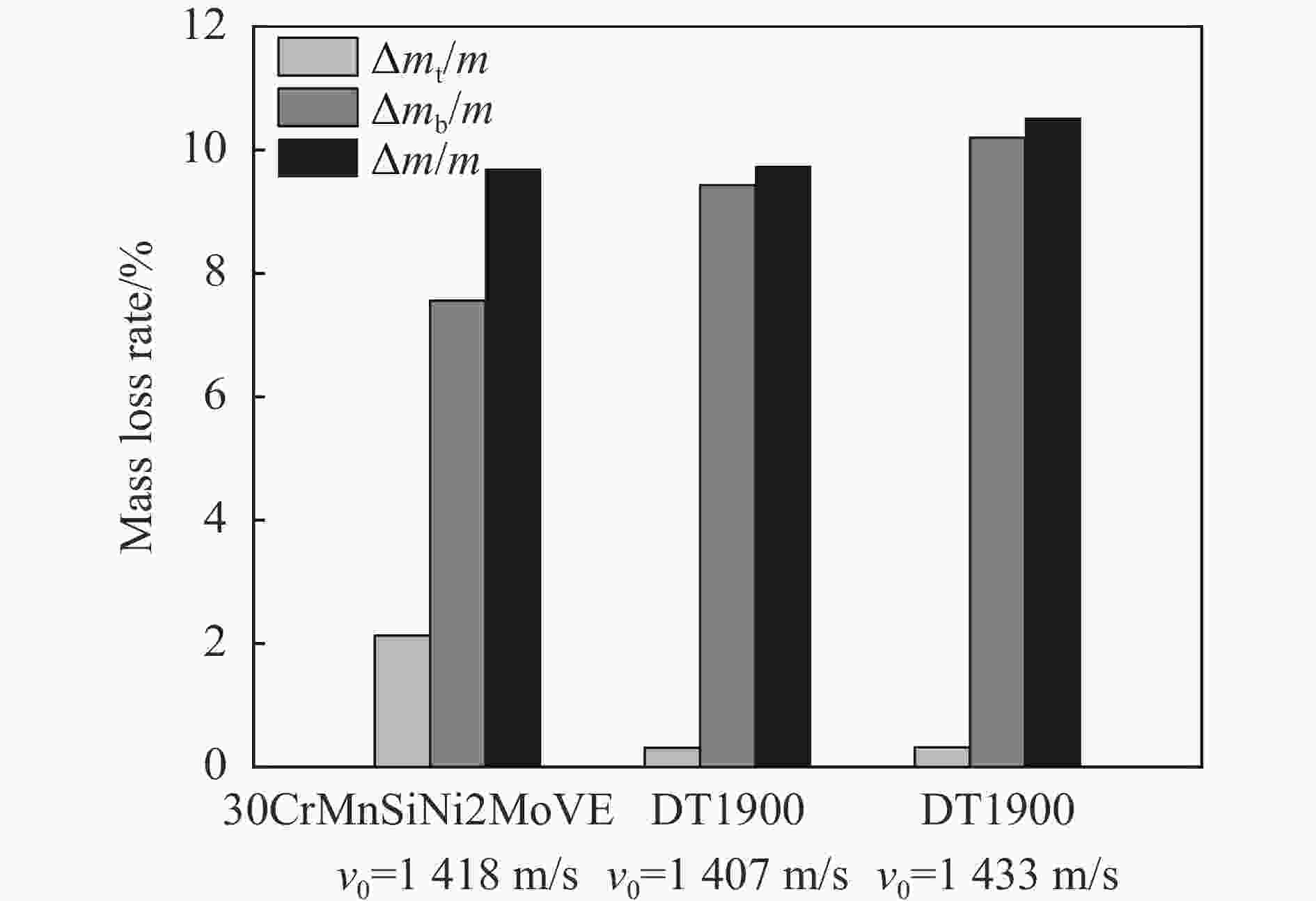
弹体材料 v0/(m·s−1) (ΔL/L)/% (ΔD/D)/% (Δmt/m)/% (Δmb/m)/% (Δm/m)/% 30CrMnSiNi2MoVE 1418 8.2 3.3 2.13 7.56 9.69 DT1900 1407 4.4 4.4 0.31 9.43 9.74 1433 4.6 4.4 0.32 10.20 10.52 表 5 实验弹的无量纲侵彻深度
Table 5. Dimensionless penetration depths of experimental projectiles
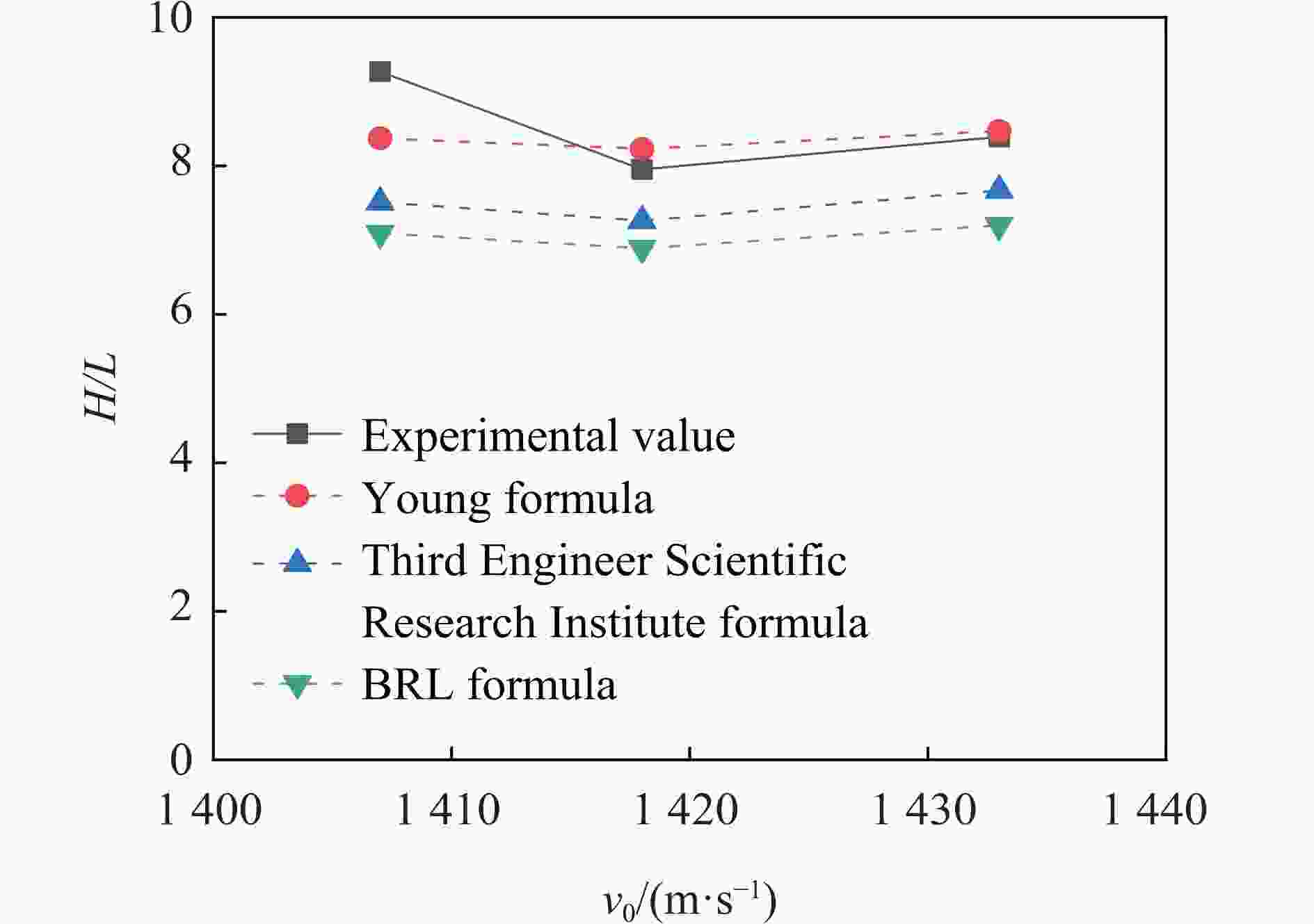
弹体材料 撞靶速度/(m·s−1) 靶板强度/MPa 靶板厚度 H/L 30CrMnSiNi2MoVE 1418 32.5 有限靶 7.95 DT1900 1407 30.7 有限靶 9.27 1433 30.7 8.39 -
[1] 杨建超, 左新建, 何翔, 等. 弹体高速侵彻混凝土质量侵蚀实验研究 [J]. 实验力学, 2012, 27(1): 122–127.YANG J C, ZUO X J, HE X, et al. Experimental study of projectile mass loss in high velocity penetration of concrete target [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2012, 27(1): 122–127. [2] DONG H, LIU Z H, WU H J, et al. Study on penetration characteristics of high-speed elliptical cross-sectional projectiles into concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 132: 103311. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.025. [3] ZHANG X Y, WU H J, ZHANG S, et al. Projectile penetration of reinforced concrete considering the effect of steel reinforcement: experimental study and theoretical analysis [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 144: 103653. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103653. [4] WANG J, WU H J, DONG H, et al. Flow field analysis of long rod hypervelocity penetration into semi-infinite concrete target [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2023, 179: 104564. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2023.104564. [5] GUO L, HE Y, ZHANG X F, et al. Thermal-mechanical analysis on the mass loss of high-speed projectiles penetrating concrete targets [J]. European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids, 2017, 65: 159–177. DOI: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2017.03.011. [6] GUO L, HE Y, ZHANG X F, et al. Study mass loss at microscopic scale for a projectile penetration into concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2014, 72: 17–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2014.05.001. [7] 周忠彬, 马田, 赵永刚, 等. 不同材料弹体超声速侵彻钢筋混凝土靶的结构破坏对比实验 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(2): 025101. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190841.ZHOU Z B, MA T, ZHAO Y G, et al. Comparative experiment on structural damage of supersonic projectiles with different metal materials penetrating into reinforced concrete targets [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(2): 025101. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20190841. [8] DENG Y J, CHEN X W, SONG W J. Dynamic cavity-expansion penetration model of elastic-cracked-crushed response for reinforced-concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 157: 103981. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103981. [9] LU Y Y, ZHANG Q M, XUE Y J, et al. Hypervelocity penetration of concrete targets with long-rod steel projectiles: experimental and theoretical analysis [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 148: 103742. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103742. [10] KAMAL I M, ELTEHEWY E M. Projectile penetration of reinforced concrete blocks: test and analysis [J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2012, 60(1): 31–37. DOI: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2012.06.005. [11] MU Z C, ZHANG W, WANG W, et al. Revising the penetration behavior of concrete-like and metal-like materials against the rigid projectile impact [J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2020, 142: 103274. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2019.103274. [12] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HICKERSON J P, et al. Penetration of concrete targets with deceleration-time measurements [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(5): 479–497. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00108-2. [13] FREW D J, FORRESTAL M J, CARGILE J D. The effect of concrete target diameter on projectile deceleration and penetration depth [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 32(10): 1584–1594. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.01.012. [14] 武海军, 黄风雷, 王一楠, 等. 高速侵彻混凝土弹体头部侵蚀终点效应实验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2012, 33(1): 48–55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2012.01.009.WU H J, HUANG F L, WANG Y N, et al. Experimental investigation on projectile nose eroding effect of high-velocity penetration into concrete [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2012, 33(1): 48–55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2012.01.009. [15] 何翔, 徐翔云, 孙桂娟, 等. 弹体高速侵彻混凝土的效应实验 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0001-06.HE X, XU X Y, SUN G J, et al. Experimental investigation on projectiles’ high-velocity penetration into concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010, 30(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)01-0001-06. [16] 戴湘晖, 周刚, 沈子楷, 等. 高速弹体对钢筋混凝土靶的侵彻/贯穿效应实验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2019, 33(5): 055101. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180672.DAI X H, ZHOU G, SHEN Z K, et al. Experimental study of high-speed projectile penetration/perforation into reinforced concrete targets [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2019, 33(5): 055101. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20180672. [17] FENG J, SONG M L, SUN W W, et al. Thick plain concrete targets subjected to high speed penetration of 30CrMnSiNi2A steel projectiles: tests and analyses [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 122: 305–317. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.09.005. [18] 郭磊, 何勇, 潘绪超, 等. 高速侵彻弹体表层侵蚀效应理论计算 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(15): 51–58. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2018.15.007.GUO L, HE Y, PAN X C, et al. Theoretical calculation for surface abrasion effect of projectiles penetrating in to concrete targets with a high speed [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(15): 51–58. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2018.15.007. [19] 梁斌, 陈小伟, 姬永强, 等. 先进钻地弹概念弹的次口径高速深侵彻实验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008, 28(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)01-0001-09.LIANG B, CHEN X W, JI Y Q, et al. Experimental study on deep penetration of reduced-scale advanced earth penetrating weapon [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008, 28(1): 1–9. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)01-0001-09. [20] ZHAO J, CHEN X W, JIN F N, et al. Depth of penetration of high-speed penetrator with including the effect of mass abrasion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(9): 971–979. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2010.03.008. [21] 王可慧, 周刚, 李明, 等. 弹体高速侵彻钢筋混凝土靶试验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(11): 113302. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0463.WANG K H, ZHOU G, LI M, et al. Experimental research on the mechanism of a high-velocity projectile penetrating into a reinforced concrete target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(11): 113302. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0463. [22] 任辉启. 精确制导武器侵彻效应与工程防护 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.REN Q H. The penetration effect of precision guided weapons and engineering protection [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [23] 武海军, 张爽, 黄风雷. 钢筋混凝土靶的侵彻与贯穿研究进展 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(1): 182–208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.01.020.WU H J, ZHANG S, HUANG F L. Research progress in penetration/perforation into reinforced concrete targets [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(1): 182–208. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.01.020. [24] GWALTNEY R C. Missile generation and protection in light-water-cooled power reactor plants: ORNL-NSIC-22 [R]. Oak Ridge: Oak Ridge National Laboratory, 1968. [25] 邓佳杰, 张先锋, 刘闯, 等. 头部非对称刻槽弹体侵彻混凝土目标性能研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(7): 1249–1258. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.07.001.DENG J J, ZHANG X F, LIU C, et al. Research on penetration of asymmetrically grooved nose projectile into concrete target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(7): 1249–1258. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.07.001. [26] 王可慧, 段建, 李明, 等. 降低终点弹道偏转效应弹体结构设计 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2015, 35(3): 50–52,98. DOI: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2015.03.014.WANG K H, DUAN J, LI M, et al. Penetrator design to reduce trajectory deflexion effect [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2015, 35(3): 50–52,98. DOI: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2015.03.014. -







 下载:
下载: