Research progress on mechanical properties of additive manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy under static and dynamic loading
-
摘要: 增材制造凭借其高设计自由度和快速成形的特点,在制造复杂几何结构的航空航天和国防领域关键部件上具有巨大的优势。Ti-6Al-4V钛合金具有低密度、高比强度及抗蠕变性的特性,在经常承受冲击载荷的航天器、武器装备等关键部位上得到了广泛应用,深入了解增材制造Ti-6Al-4V钛合金在动静载荷作用下的力学性能及影响机制是提高构件使役性能的重要基础。为此,对增材制造Ti-6Al-4V钛合金的力学响应最新研究进展进行了系统的梳理和归纳。首先,简要概括了典型金属增材制造技术分类和工作原理。其次,梳理了增材制造Ti-6Al-4V钛合金的准静态拉伸性能和动态压缩性能,并与铸造和锻造Ti-6Al-4V构件的力学性能进行了比较。然后,对增材制造钛合金显微组织和力学行为的关联机制展开了讨论。最后,针对增材制造Ti-6Al-4V合金在静态载荷作用下的各向异性力学响应,总结了常用改善各向异性的后处理工艺。Abstract: With its high design freedom and rapid prototyping capabilities, additive manufacturing (AM) offers significant advantages in manufacturing critical components with complex geometries for the aerospace and defense industries. Ti-6Al-4V alloy, leveraging its exceptional combination of low density, high specific strength, and creep resistance, are extensively employed in critical structures that are frequently subjected to impact loading in aerospace and defense systems. A thorough understanding of the mechanical properties and underlying mechanisms of the additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy under static and dynamic loading is crucial for enhancing the service performance of these components. This paper systematically reviews and summarizes the latest advancements in the mechanical response of AM Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloys. Firstly, a brief overview of the classification and working principles of typical metal additive manufacturing (AM) technologies is provided. Subsequently, research efforts on the quasi-static tensile and dynamic compressive properties of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy are systematically reviewed, followed by a comparative analysis of its mechanical performance against cast and forged Ti-6Al-4V components. Furthermore, the mechanisms of correlation between the microstructure and mechanical behaviors of typical metal additive manufactured titanium alloys. Additionally, the commonly used post-processing techniques to mitigate the anisotropic mechanical response of AM Ti-6Al-4V alloy under static loading are summarizes.
-
Key words:
- additive manufacturing /
- Ti-6Al-4V /
- dynamic and static loading /
- mechanical properties /
- anisotropy
-
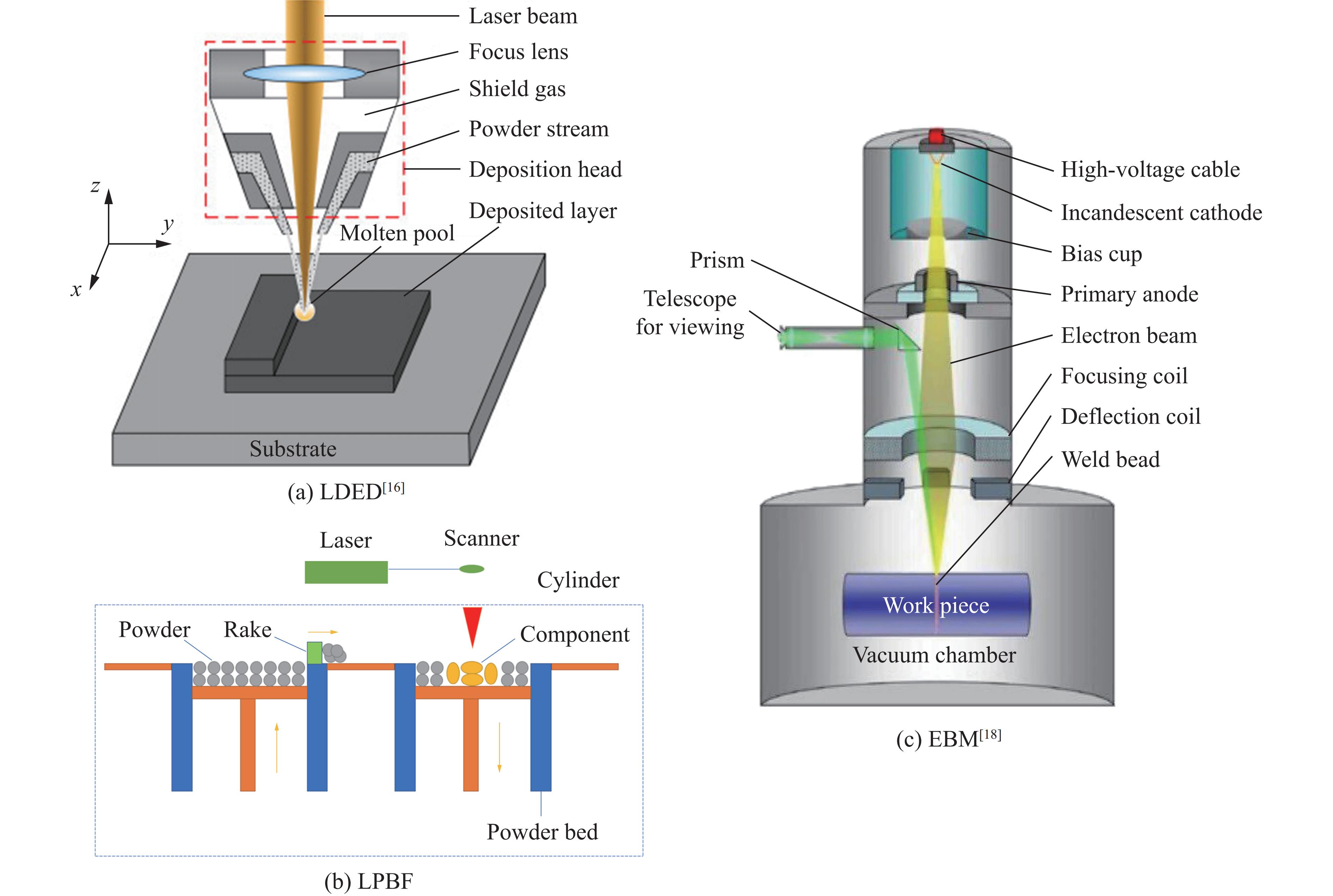
表 1 3类典型增材制造工艺的制造特点
Table 1. Manufacturing characteristics of three kinds of additive manufacturing processes
表 2 由不同制造工艺成形的Ti-6Al-4V构件的准静态拉伸力学性能[14-15, 30, 32-33, 52-53]
Table 2. Quasi-static tensile mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V components prepared by different manufacturing processes[14-15, 30, 32-33, 52-53]
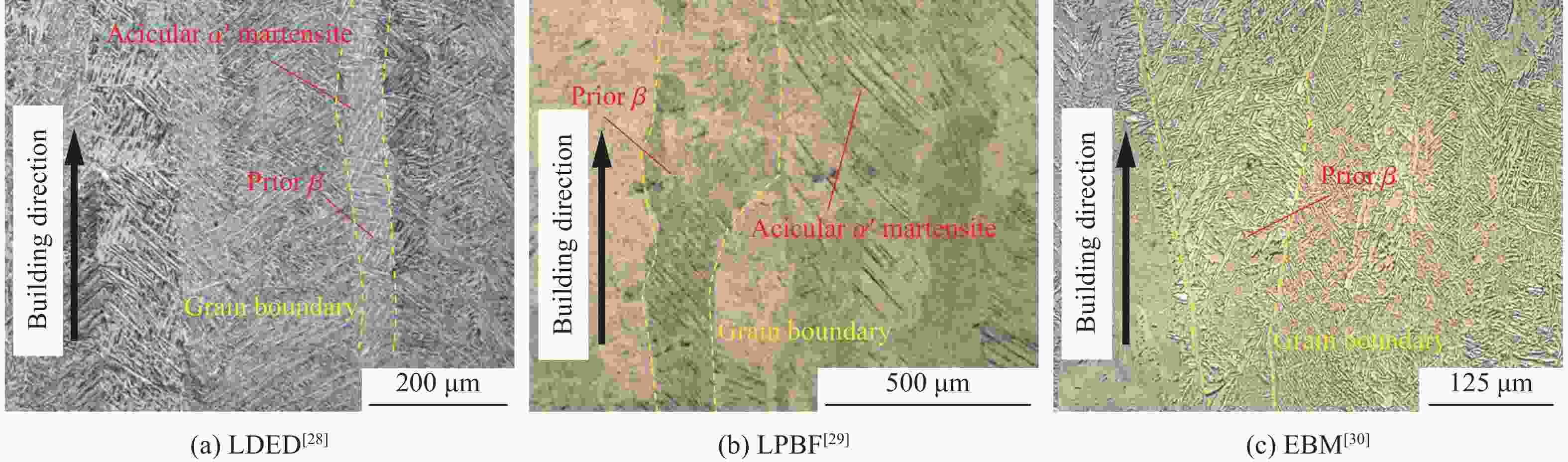
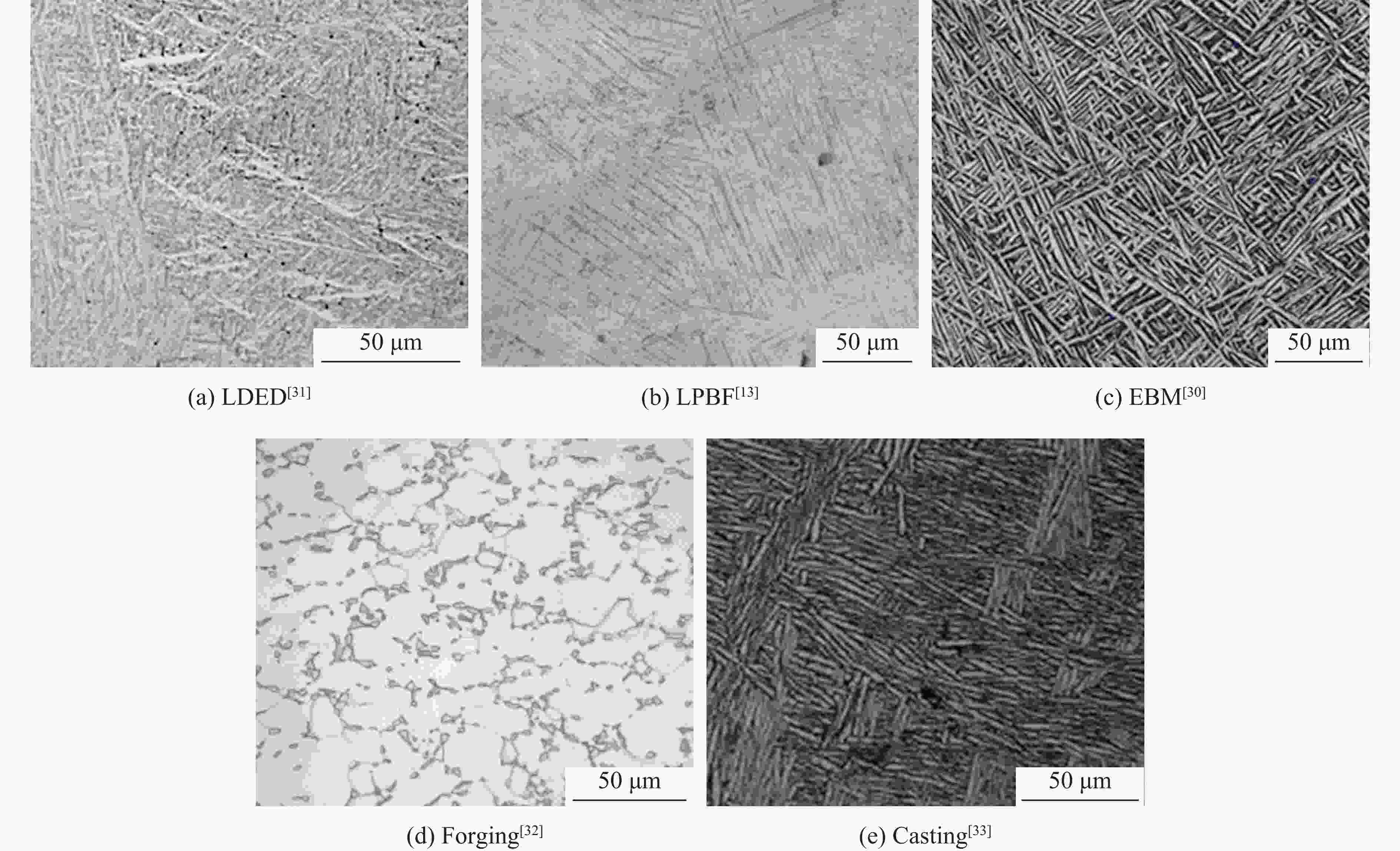
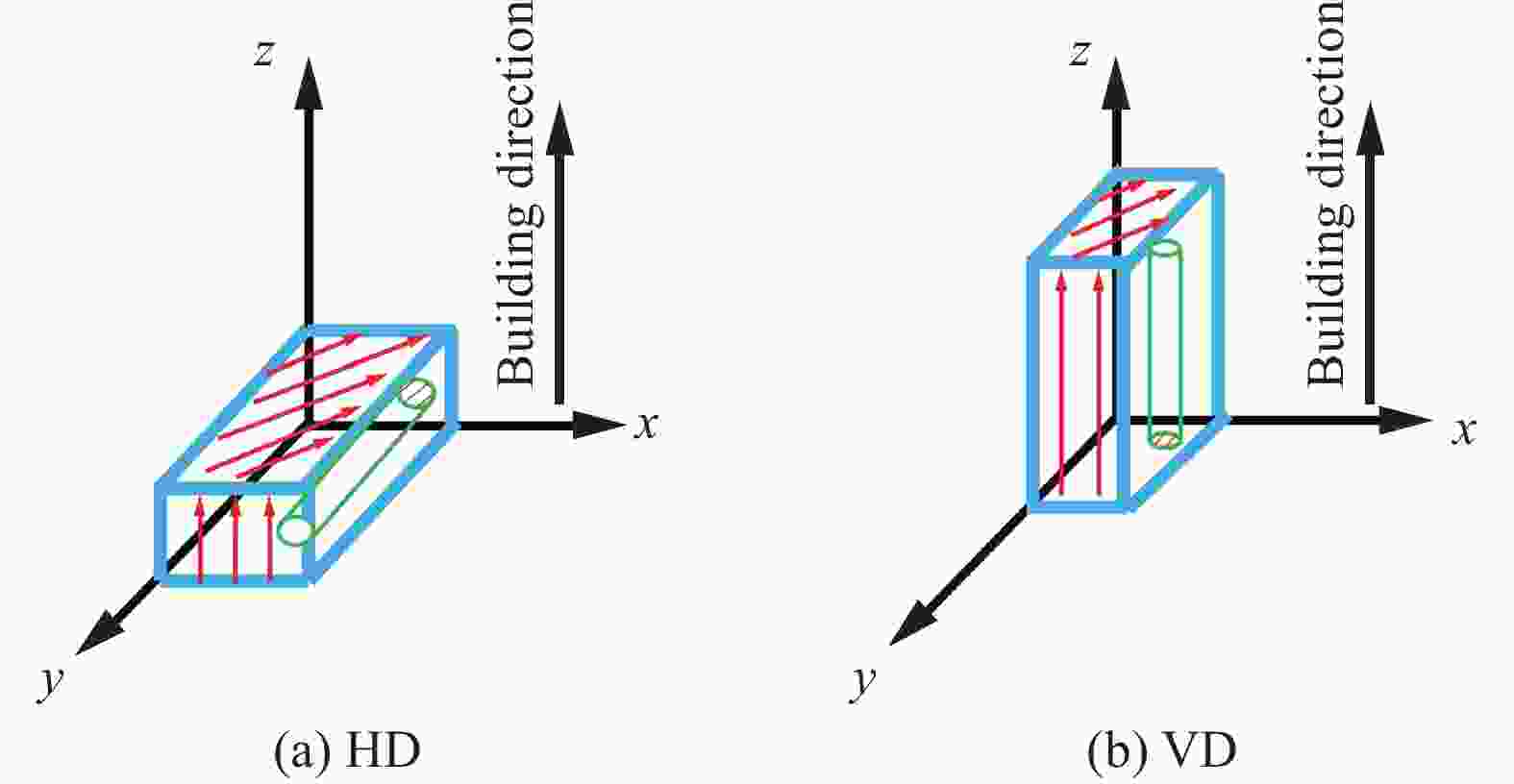
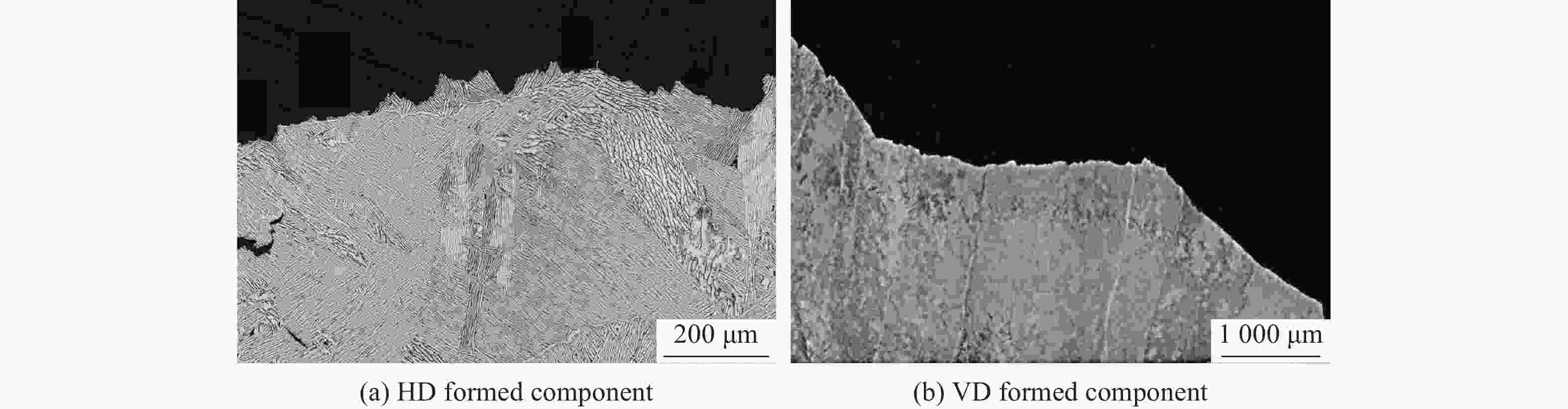
制造工艺 沉积方向 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 伸长率/% 来源 LDED 水平 1050 ± 351153 ± 155.9 ± 2.5 文献[15] 973 ± 16 1073 ± 1610 ± 0.9 文献[15] 垂直 1045 ± 171140 ± 109.2 ± 0.8 文献[15] 941 ± 6 1062 ± 1111.5 ± 1.8 文献[15] LPBF 水平 1187.80 ± 35.841307.50 ± 7.46.80 ± 1.10 文献[14] 966 ± 15 1066 ± 209.8 ± 3.3 文献[52] 垂直 1036.70 ± 133.71309.50 ± 8.28.72 ± 2.77 文献[14] 937 ± 9 1052 ± 119.6 ± 0.9 文献[52] EBM 水平 769 ± 12 867 ± 11 12.0 ± 1.5 文献[30] 846 ± 7 976 ± 11 15.0 ± 2.0 文献[53] 垂直 710 ± 1 814 ± 2.5 15 ± 0.5 文献[30] 845 ± 9 972 ± 14 14.2 ± 1.5 文献[53] 锻造 960 ± 10 1006 ± 1018.37 ± 0.88 文献[32] 铸造 837 900 6.8 文献[33] 表 3 典型增材制造工艺成形的Ti-6Al-4V构件的拉伸各向异性[1, 82-83, 88, 92]
Table 3. Anisotropic tensile behaviors of additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V specimens[1, 82-83, 88, 92]
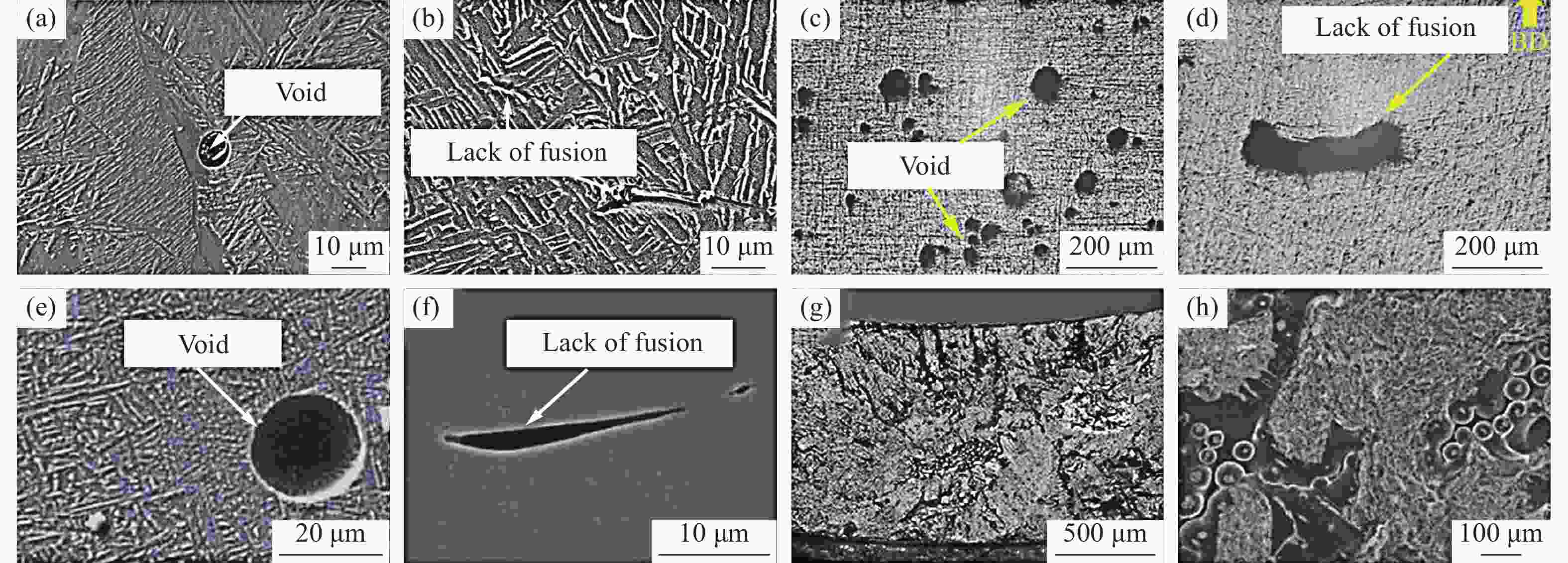
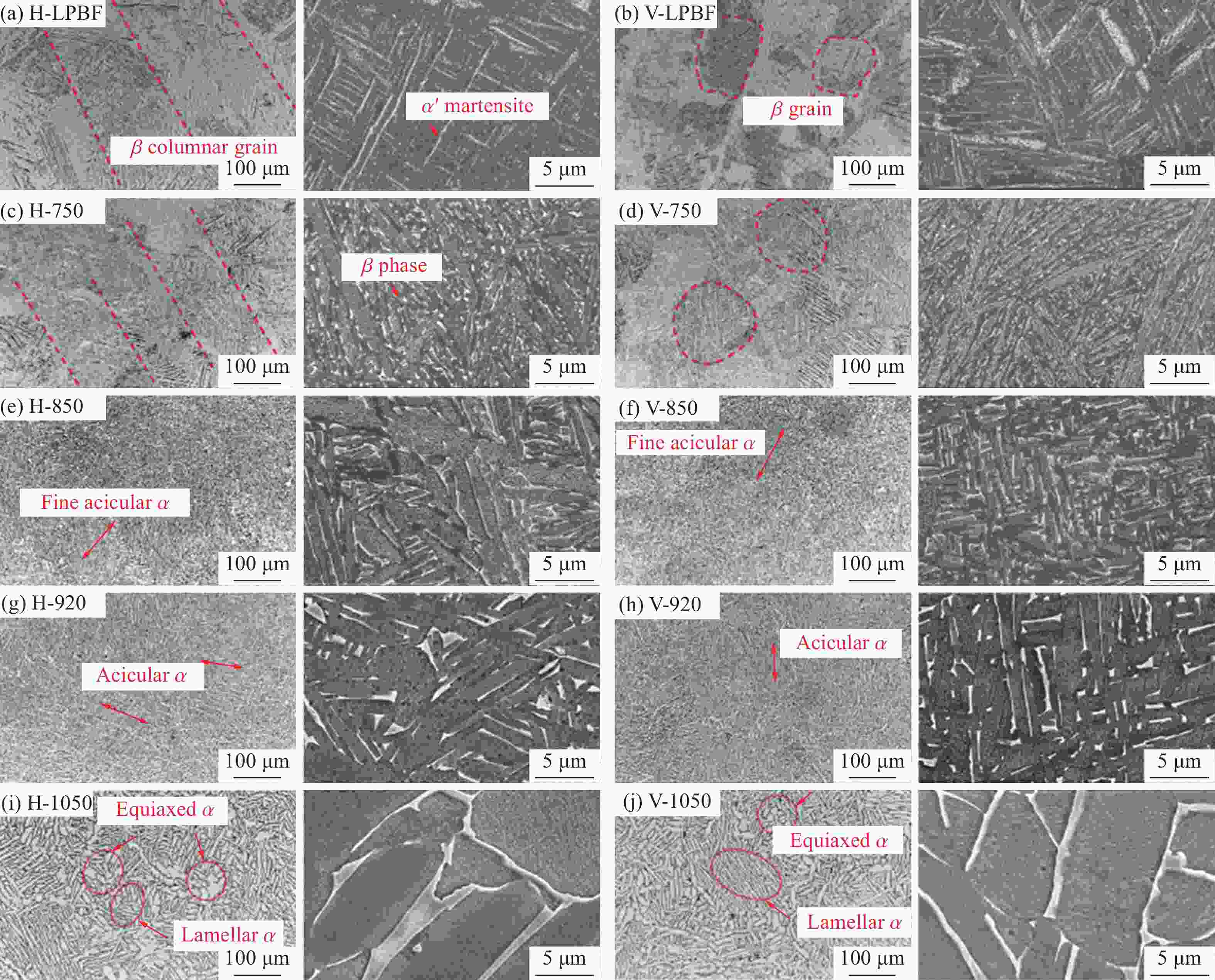
制造工艺 后处理工艺 后处理工艺制度 ry/% rt/% R/% 来源 LDED 成形态 2.7 3.8 32.62 文献[1] 固溶热处理 980 ℃下保温1 h后炉冷 4.07 2.13 21.21 LPBF 成形态 17.0 18.3 18.2 文献[82] 固溶热处理 750 ℃下保温2.5 h后炉冷 2.6 3.6 8 850 ℃下保温2.5 h后炉冷 4.3 3.4 7.5 920 ℃下保温2.5 h后炉冷 4.9 7.6 1.1 β退火 1050 ℃下保温2.5 h后炉冷1.8 0.2 2.2 成形态 11.5 9.5 19.23 文献[88] β退火 1100 ℃下保温2 h后炉冷0.8 0.5 4.7 成形态 9 14.5 42.7 文献[83] 固溶时效热处理 910 ℃下保温4 h后水淬,再于750℃下保温2 h后空淬, 11.2 4.3 30.4 成形态 28.5 45.2 文献[92] 固溶热处理 850 ℃下保温0.5 h后空冷 11.9 8.2 900 ℃下保温0.5 h后空冷 16.2 7.2 950 ℃下保温0.5 h后空冷 0.7 3.4 固溶时效热处理 850 ℃下保温0.5 h后空冷,再于600℃下保温2 h后空冷 8.7 4.1 900 ℃下保温0.5 h后空冷,再于600℃下保温2 h后空冷 21.4 5.1 950 ℃下保温0.5 h后空冷,再于600℃下保温2 h后空冷 1.5 7.5 表 4 典型制造工艺成形的Ti-6Al-4V构件的应变率敏感性[17, 46, 101, 103]
Table 4. Strain rate sensitivity of Ti-6Al-4V components formed by typical manufacturing process[17, 46, 101, 103]
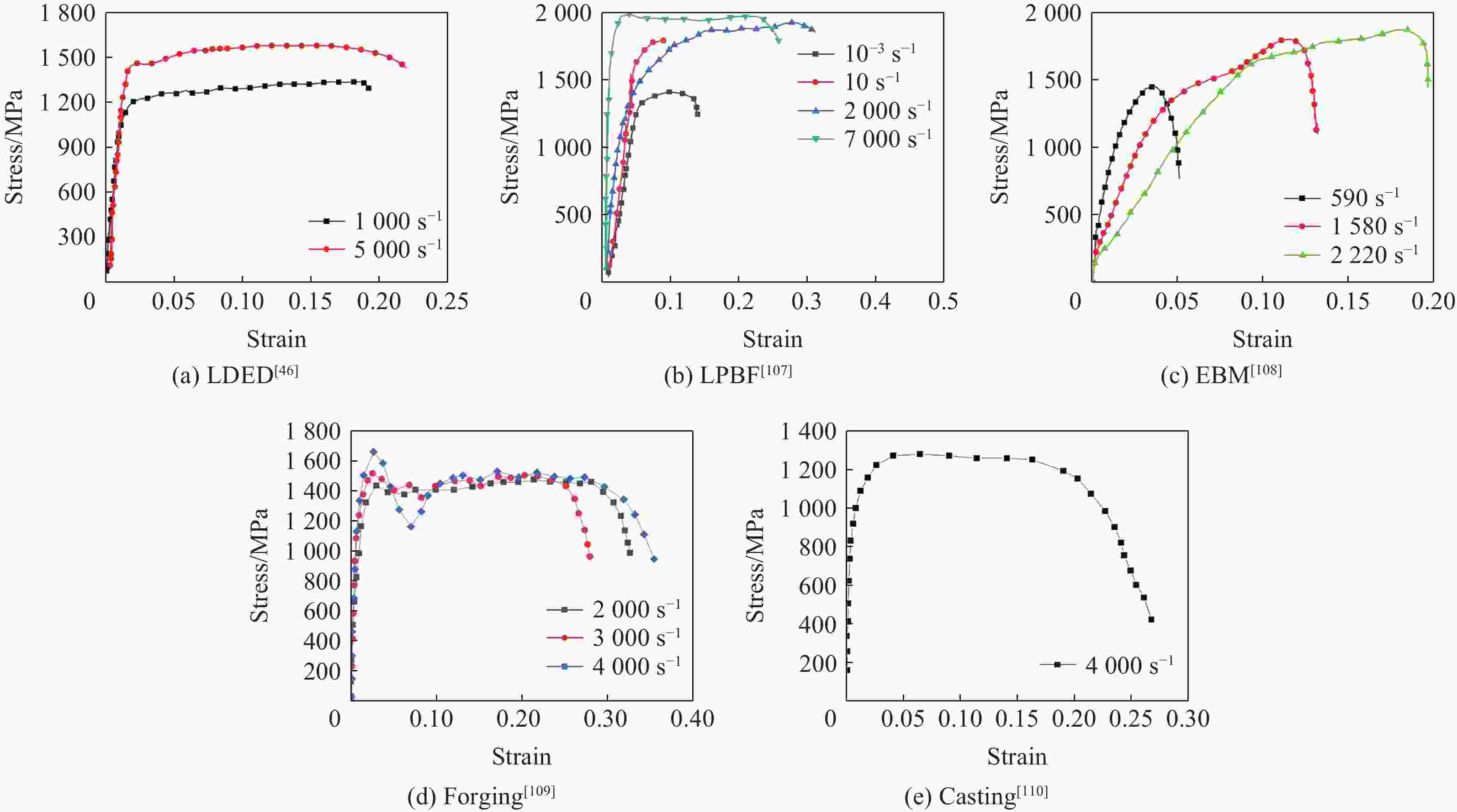
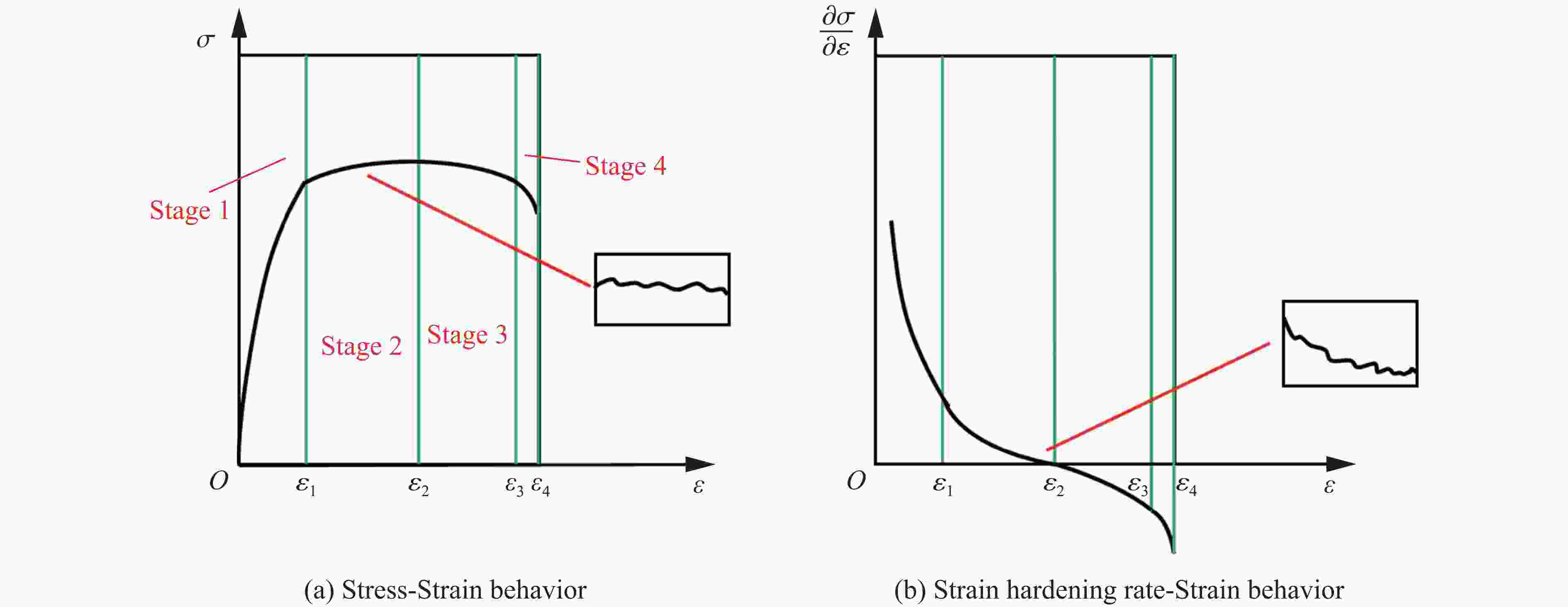
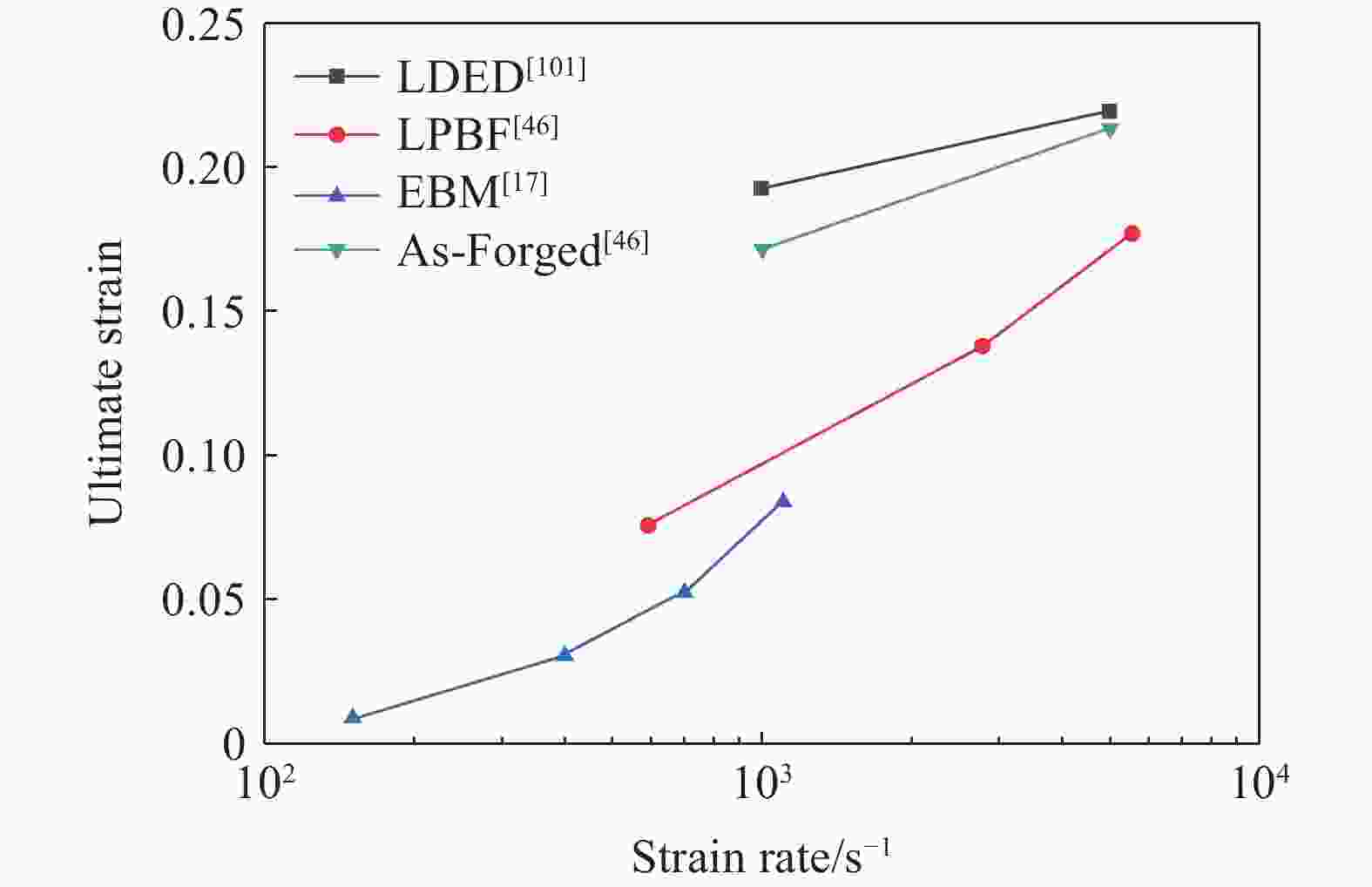
制造工艺 热处理 应变率/s−1 屈服强度/MPa m 来源 LDED 1000 (HD)1247 0.12 文献[46] 5000 (HD)1479 LDED 920 C°保温2 h+540 C°保温4 h 1000 (VD)1054 0.05 文献[101] 3000 (VD)1130 LPBF 1340 (HD)1770 0.08 文献[103] 6370 (HD)2020 380(VD) 1720 0.05 5540 (VD)2060 EBM 150(HD) 705 ± 17 0.24 文献[17] 1100 (HD)1127 ± 22150(VD) 805 ± 13 0.21 1100 (VD)1257 ± 25锻造 1000 1318 0.11 文献[46] 5000 1602 -
[1] ALCISTO J, ENRIQUEZ A, GARCIA H, et al. Tensile properties and microstructures of laser-formed Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2011, 20(2): 203–212. DOI: 10.1007/s11665-010-9670-9. [2] 周平, 郭伟国, 李鹏辉, 等. 激光立体成形TC4钛合金的力学特性与破坏机理 [J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2019, 37(1): 56–63. DOI: 10.14136/j.cnki.issn1673-2812.2019.01.011.ZHOU P, GUO W G, LI P H, et al. Mechanical properties and failure mechanism of laser solid formed TC4 Titanium Alloy [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 37(1): 56–63. DOI: 10.14136/j.cnki.issn1673-2812.2019.01.011. [3] 陈志茹, 计霞, 楚瑞坤, 等. 热处理工艺对激光熔化沉积TC4钛合金组织性能的影响 [J]. 金属热处理, 2018, 43(11): 144–149. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2018.11.030.CHEN Z R, JI X, CHU R K, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of TC4 titanium alloy by laser melting deposition [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2018, 43(11): 144–149. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2018.11.030. [4] 谢文强, 王洁琪, 庄沛林, 等. 构建方向对SLM钛合金卡环的显微结构及性能影响 [J]. 口腔疾病防治, 2019, 27(1): 17–22. DOI: 10.12016/j.issn.2096-1456.2019.01.004.XIE W Q, WANG J Q, ZHUANG P L, et al. Effect of construction orientation on the microstructure and properties of SLM Ti alloy clasps [J]. Journal of Dental Prevention and Treatment, 2019, 27(1): 17–22. DOI: 10.12016/j.issn.2096-1456.2019.01.004. [5] 辛如意, 兰亮, 何博. 选区激光熔化增材制造钛合金的疲劳性能研究进展 [J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2022, 40(4): 706–716. DOI: 10.14136/j.cnki.issn1673-2812.2022.04.025.XIN R Y, LAN L, HE B. Research progress on fatigue properties of titanium alloy fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2022, 40(4): 706–716. DOI: 10.14136/j.cnki.issn1673-2812.2022.04.025. [6] 张国栋, 张鹏, 高健时, 等. 电子束熔丝增材制造TC11钛合金组织及力学性能 [J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(4): 105–112. DOI: 10.3901/JME.2023.04.105.ZHANG G D, ZHANG P, GAO J S, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TC11 titanium alloy fabricated by wire-feed electron beam additive manufacturing [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(4): 105–112. DOI: 10.3901/JME.2023.04.105. [7] 王宁宁, 韩冬, 吴军, 等. 电子束熔丝增材制造TC11钛合金显微组织及力学性能研究 [J]. 航天制造技术, 2019(6): 36–39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5108.2019.06.009.WANG N N, HAN D, WU J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TC11 titanium alloy electron beam fuse additive manufacturing [J]. Aerospace Manufacturing Technology, 2019(6): 36–39. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5108.2019.06.009. [8] 王华明. 高性能大型金属构件激光增材制造: 若干材料基础问题 [J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(10): 2690–2698. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0174.WANG H M. Materialsʼ fundamental issues of laser additive manufacturing for high-performance large metallic components [J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(10): 2690–2698. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2014.0174. [9] ZHU J H, ZHOU H, WANG C, et al. A review of topology optimization for additive manufacturing: status and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(1): 91–110. DOI: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.09.020. [10] XU Y L, ZHANG D Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Study on topology optimization design, manufacturability, and performance evaluation of Ti-6Al-4V porous structures fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM) [J]. Materials, 2017, 10(9): 1048. DOI: 10.3390/ma10091048. [11] 刘洋, 徐怀忠, 汪小锋, 等. 冲击载荷下增材制造金属材料的动态响应及微观结构演化研究进展 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(4): 040102. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210760.LIU Y, XU H Z, WANG X F, et al. Progress in dynamic responses and microstructure evolution of the additive manufactured alloys under impact load [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(4): 040102. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20210760. [12] LIU Y, XU H Z, ZHU L, et al. Investigation into the microstructure and dynamic compressive properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy with different heating treatments [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 805: 140561. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140561. [13] LIU S Y, SHIN Y C. Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V alloy: a review [J]. Materials and Design, 2019, 164: 107552. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.107552. [14] TAO P, ZHONG J W, LI H X, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and constitutive models for Ti–6Al–4V Alloy fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM) [J]. Metals, 2019, 9(4): 447. DOI: 10.3390/met9040447. [15] AMSTERDAM E, KOOL G A. High cycle fatigue of laser beam deposited Ti-6Al-4V and inconel 718 [C]//Proceedings of the 25th Symposium of the International Committee on Aeronautical Fatigue, ICAF 2009, Bridging the Gap between Theory and Operational Practice. Rotterdam: Springer, 2009: 1261–1274. DOI: 10.1007/978-90-481-2746-7_71. [16] HU Y B, CONG W L. A review on laser deposition-additive manufacturing of ceramics and ceramic reinforced metal matrix composites [J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(17): 20599–20612. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.08.083. [17] ALAGHMANDFARD R, CHALASANI D, HADADZADEH A, et al. Dynamic compressive response of electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V under elevated strain rates: microstructure and constitutive models [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 35: 101347. DOI: 10.1016/j.addma.2020.101347. [18] KOLAMROUDI M K, ASMAEL M, ILKAN M, et al. Developments on electron beam melting (EBM) of Ti-6Al-4V: a review [J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2021, 74(4): 783–790. DOI: 10.1007/s12666-021-02230-9. [19] DOÑATE-BUENDÍA C, KÜRNSTEINER P, STERN F, et al. Microstructure formation and mechanical properties of ODS steels built by laser additive manufacturing of nanoparticle coated iron-chromium powders [J]. Acta Materialia, 2021, 206: 116566. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116566. [20] 刘晏硕, 徐诺, 徐国建, 等. Nb对激光增材制造TC4沉积态组织与性能的影响 [J]. 热加工工艺, 2024, 53(7): 41–46. DOI: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20213413.LIU Y S, XU N, XU G J, et al. Effect of Nb on microstructure and properties of laser additive manufacturing TC4 in deposited state [J]. Hot Working Technology, 2024, 53(7): 41–46. DOI: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20213413. [21] WEI B C, CHEN W G, GUO S L, et al. Study on the tribological characteristics of surface triangular textured TC4 alloy prepared by SLM technology [J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2024, 482: 130735. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2024.130735. [22] LI S J, MURR L E, CHENG X Y, et al. Compression fatigue behavior of Ti-6Al-4V mesh arrays fabricated by electron beam melting [J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(3): 793–802. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2011.10.051. [23] ARRIETA E. Comprehensive finite element modeling of Ti-6Al-4V cellular solids fabricated by electron beam melting [D]. Texas: University of Texas at El Paso, 2017: 34–35. [24] GOKULDOSS P K, KOLLA S, ECKERT J. Additive manufacturing processes: selective laser melting, electron beam melting and binder jetting: selection guidelines [J]. Materials, 2017, 10(6): 672. DOI: 10.3390/ma10060672. [25] QIU C L, KINDI M A, ALADAWI A S, et al. A comprehensive study on microstructure and tensile behaviour of a selectively laser melted stainless steel [J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 7785. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-26136-7. [26] DAS M, BALLA V K, BASU D, et al. Laser processing of SiC-particle-reinforced coating on titanium [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010, 63(4): 438–441. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.04.044. [27] AL-BERMANI S S, BLACKMORE M L, ZHANG W, et al. The origin of microstructural diversity, texture, and mechanical properties in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2010, 41(13): 3422–3434. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-010-0397-x. [28] SHIPLEY H, MCDONNELL D, CULLETON M, et al. Optimisation of process parameters to address fundamental challenges during selective laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V: a review [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2018, 128: 1–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2018.01.003. [29] ALI H, GHADBEIGI H, MUMTAZ K. Effect of scanning strategies on residual stress and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 712: 175–187. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.11.103. [30] LIU Z, ZHAO Z B, LIU J R, et al. Effect of α texture on the tensile deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced via electron beam rapid manufacturing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 742: 508–516. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.11.012. [31] HAO Y L, LI S J, YANG R. Biomedical titanium alloys and their additive manufacturing [J]. Rare Metals, 2016, 35(9): 661–671. DOI: 10.1007/s12598-016-0793-5. [32] VRANCKEN B, THIJS L, KRUTH J P, et al. Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting: microstructure and mechanical properties [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2012, 541: 177–185. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.07.022. [33] REDA R, NOFAL A, HUSSEIN A H. Effect of single and duplex stage heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of cast Ti-6Al-4V Alloy [J]. Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis, 2013, 2(6): 388–393. DOI: 10.1007/s13632-013-0103-7. [34] LIU C M, LU Y, TIAN X J, et al. Influence of continuous grain boundary α on ductility of laser melting deposited titanium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016, 661: 145–151. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.03.034. [35] SHRESTHA S, PANAKARAJUPALLY R P, KANNAN M, et al. Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties of additive repaired Ti-6Al-4V by direct energy deposition [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 806: 140604. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140604. [36] ÅKERFELDT P, ANTTI M L, PEDERSON R. Influence of microstructure on mechanical properties of laser metal wire-deposited Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016, 674: 428–437. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.07.038. [37] BANERJEE D, WILLIAMS J C. Perspectives on titanium science and technology [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(3): 844–879. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.10.043. [38] DUCATO A, FRATINI L, LA CASCIA M, et al. An automated visual inspection system for the classification of the phases of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy [C]//15th International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns. York: Springer, 2013. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-40246-3_45. [39] AHMED T, RACK H J. Phase transformations during cooling in α+β titanium alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1998, 243(1/2): 206–211. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00802-2. [40] GIL MUR F X, RODRÍGUEZ D, PLANELL J A. Influence of tempering temperature and time on the α-Ti-6Al-4V martensite [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1996, 234(2): 287–289. DOI: 10.1016/0925-8388(95)02057-8. [41] ZHAI Y W, GALARRAGA H, LADOS D A. Microstructure, static properties, and fatigue crack growth mechanisms in Ti-6Al-4V fabricated by additive manufacturing: LENS and EBM [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2016, 69: 3–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2016.05.036. [42] SAFDAR A, WEI L Y, SNIS A, et al. Evaluation of microstructural development in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 65: 8–15. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2011.12.008. [43] GALARRAGA H, LADOS D A, DEHOFF R R, et al. Effects of the microstructure and porosity on properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy fabricated by electron beam melting (EBM) [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2016, 10: 47–57. DOI: 10.1016/j.addma.2016.02.003. [44] LI J Q, LIN X, WANG J, et al. Effect of stress-relief annealing on anodic dissolution behaviour of additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V via laser solid forming [J]. Corrosion Science, 2019, 153: 314–326. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.04.002. [45] 从保强, 丁佳洛. CMT工艺对Al-Cu合金电弧增材制造气孔的影响 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2014, 43(12): 3149–3153. DOI: CNKI:SUN:COSE.0.2014-12-056.CONG B Q, DING J L. Influence of CMT process on porosity of wire arc additive manufactured Al-Cu alloy [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(12): 3149–3153. DOI: CNKI:SUN:COSE.0.2014-12-056. [46] LI P H, GUO W G, HUANG W D, et al. Thermomechanical response of 3D laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V alloy over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 647: 34–42. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.08.043. [47] 权国政, 杨焜, 盛雪, 等. 电弧熔丝增材制造残余应力控制方法综述 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2021, 28(11): 1–10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.11.001.QUAN G Z, YANG K, SHENG X, et al. A review of control method for residual stress of wire and arc additive manufacturing [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2021, 28(11): 1–10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.11.001. [48] 赵剑峰, 谢德巧, 梁绘昕, 等. 金属增材制造变形与残余应力的研究现状 [J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 51(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2019.01.001.ZHAO J F, XIE D Q, LIANG H X, et al. Review of distortion and residual stress in metal additive manufacturing [J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 51(1): 1–6. DOI: 10.16356/j.1005-2615.2019.01.001. [49] JAVIDRAD H R, GHANBARI M, JAVIDRAD F. Effect of scanning pattern and volumetric energy density on the properties of selective laser melting Ti-6Al-4V specimens [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 12: 989–998. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.03.044. [50] QIAN M, XU W, BRANDT M, et al. Additive manufacturing and postprocessing of Ti-6Al-4V for superior mechanical properties [J]. MRS Bulletin, 2016, 41(10): 775–784. DOI: 10.1557/mrs.2016.215. [51] FATEMI A, MOLAEI R, SIMSIRIWONG J, et al. Fatigue behaviour of additive manufactured materials: an overview of some recent experimental studies on Ti-6Al-4V considering various processing and loading direction effects [J]. Fatigue and Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures, 2019, 42(5): 991–1009. DOI: 10.1111/ffe.13000. [52] SIMONELLI M, TSE Y Y, TUCK C. Effect of the build orientation on the mechanical properties and fracture modes of SLM Ti-6Al-4V [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 616: 1–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.07.086. [53] WYSOCKI B, MAJ P, SITEK R, et al. Laser and electron beam additive manufacturing methods of fabricating titanium bone implants [J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(7): 657. DOI: 10.3390/app7070657. [54] LIU Y, PANG Z C, LI M, et al. Investigation into the dynamic mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy at high strain rate tensile loading [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 745: 440–449. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.01.010. [55] ZHAO Z, CHEN J, LU X F, et al. Formation mechanism of the α variant and its influence on the tensile properties of laser solid formed Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 691: 16–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.03.035. [56] ZHU Y Y, LI J, TIAN X J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hybrid fabricated Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si titanium alloy by laser additive manufacturing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 607: 427–434. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.04.019. [57] ZHOU Y G, ZENG W D, YU H Q. An investigation of a new near-beta forging process for titanium alloys and its application in aviation components [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2005, 393(1/2): 204–212. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.10.016. [58] LEI L, ZHAO Y Q, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Impact toughness and deformation modes of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with different microstructures [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 801: 140411. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140411. [59] ZHAO Z, CHEN J, TAN H, et al. Achieving superior ductility for laser solid formed extra low interstitial Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy through equiaxial alpha microstructure [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 146: 187–191. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.11.021. [60] REN H S, TIAN X J, LIU D, et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of laser melting deposited Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si titanium alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(6): 1856–1864. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63792-X. [61] MERCELIS P, KRUTH J P. Residual stresses in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting [J]. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 2006, 12(5): 254–265. DOI: 10.1108/13552540610707013. [62] LIU Y, YANG Y Q, WANG D. A study on the residual stress during selective laser melting (SLM) of metallic powder [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 87(1/2/3/4): 647–656. DOI: 10.1007/s00170-016-8466-y. [63] VRANCKEN B, CAIN V, KNUTSEN R, et al. Residual stress via the contour method in compact tension specimens produced via selective laser melting [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2014, 87: 29–32. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2014.05.016. [64] YADROITSAVA I, GREWAR S, HATTINGH D, et al. Residual stress in SLM Ti6Al4V alloy specimens [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2015, 828/829: 305–310. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.828-829.305. [65] HRABE N, GNÄUPEL-HEROLD T, QUINN T. Fatigue properties of a titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) fabricated via electron beam melting (EBM): effects of internal defects and residual stress [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 94: 202–210. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2016.04.022. [66] YANG J J, YU H C, YIN J, et al. Formation and control of martensite in Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by selective laser melting [J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 108: 308–318. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.06.117. [67] 陈欢, 孙新军, 王小江, 等. 高锰奥氏体低温钢力学性能及Hall-Petch关系的研究 [J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2018, 26(5): 11–18. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20170425.CHEN H, SUN X J, WANG X J, et al. Mechanical properties and Hall-Petch relationship of high manganese austenitic cryogenic steel [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2018, 26(5): 11–18. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20170425. [68] BAUFELD B, VAN DER BIEST O. Mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V specimens produced by shaped metal deposition [J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2009, 10(1): 015008. DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/10/1/015008. [69] WU C, ZHAO Y Q, HUANG S X, et al. Microstructure tailoring and impact toughness of a newly developed high strength Ti-5Al-3Mo-3V-2Cr-2Zr-1Nb-1Fe alloy [J]. Materials Characterization, 2021, 175: 111103. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111103. [70] SAUER C, LÜETJERING G. Processing, microstructure and properties of Ti-6246 [C]//Titanium’99: Science and Technology. Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2000: 390−397. [71] XIE Z Y, DAI Y, OU X Q, et al. Effects of selective laser melting build orientations on the microstructure and tensile performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 776: 139001. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139001. [72] XU W, BRANDT M, SUN S, et al. Additive manufacturing of strong and ductile Ti-6Al-4V by selective laser melting via in situ martensite decomposition [J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 85: 74–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.11.028. [73] XU W, LUI E W, PATERAS A, et al. In situ tailoring microstructure in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V for superior mechanical performance [J]. Acta Materialia, 2017, 125: 390–400. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.12.027. [74] 白澄岩, 兰亮, 辛如意, 等. 增材制造Ti-6Al-4V钛合金低周疲劳性能研究进展 [J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2023, 31(1): 79–90. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20220054.BAI C Y, LAN L, XIN R Y, et al. Research progress on low-cycle fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by additive manufacturing [J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2023, 31(1): 79–90. DOI: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20220054. [75] 杜子杰, 李文渊, 刘建荣, 等. CMT增材制造TC4-DT合金组织均匀性与力学性能一致性研究 [J]. 金属学报, 2020, 56(12): 1667–1680. DOI: 10.11900/0412.1961.2020.00104.DU Z J, LI W Y, LIU J R, et al. Study on the uniformity of structure and mechanical properties of TC4-DT alloy deposited by CMT process [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 56(12): 1667–1680. DOI: 10.11900/0412.1961.2020.00104. [76] CHEN R, TAN C W, YOU Z Y, et al. Effect of α phase on high-strain rate deformation behavior of laser melting deposited Ti-6.5Al-1Mo-1V-2Zr titanium alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2019, 750: 81–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.01.060. [77] ZHU Y Y, TIAN X J, LI J, et al. The anisotropy of laser melting deposition additive manufacturing Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si titanium alloy [J]. Materials and Design, 2015, 67: 538–542. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.11.001. [78] BENMESSAOUD F, CHEIKH M, VELAY V, et al. Role of grain size and crystallographic texture on tensile behavior induced by sliding mechanism in Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 774: 138835. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.138835. [79] LI H, MASON D E, BIELER T R, et al. Methodology for estimating the critical resolved shear stress ratios of α-phase Ti using EBSD-based trace analysis [J]. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(20): 7555–7567. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2013.08.042. [80] BRIDIER F, VILLECHAISE P, MENDEZ J. Analysis of the different slip systems activated by tension in a α/β titanium alloy in relation with local crystallographic orientation [J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(3): 555–567. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.09.040. [81] KISHIDA K, KIM J G, NAGAE T, et al. Experimental evaluation of critical resolved shear stress for the first-order pyramidal c + a slip in commercially pure Ti by micropillar compression method [J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 196: 168–174. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.06.043. [82] JIN N, YAN Z Y, WANG Y W, et al. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V lattice materials [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2021, 190: 106042. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2020.106042. [83] FANG M H, HU F G, HAN Y F, et al. Controllable mechanical anisotropy of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V: a new perspective into the effect of grain orientations and primary grain structure [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 827: 142031. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.142031. [84] 贺韡, 雷文杰, 彭丹迪. 去应力退火对TB15钛合金力学性能和组织的影响 [J]. 热加工工艺, 2021, 50(24): 146–148,145. DOI: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20212745.HE W, LEI W J, PENG D D. Effects of stress-relief annealing on mechanical properties and microstructure of TB15 titanium alloy [J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021, 50(24): 146–148,145. DOI: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20212745. [85] 高星, 张宁, 丁燕, 等. 热处理时间对激光选区成形TC4钛合金组织及力学性能的影响 [J]. 金属热处理, 2022, 47(9): 12–17. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2022.09.003.GAO X, ZHANG N, DING Y, et al. Effect of heat treatment time on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(9): 12–17. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2022.09.003. [86] 孙兵兵, 闫泰起, 陈冰清, 等. 选区激光熔化TC4钛合金组织性能调控热处理工艺 [J]. 焊接技术, 2023, 52(6): 1–6. DOI: 10.13846/j.cnki.cn12-1070/tg.2023.06.030.SUN B B, YAN T Q, CHEN B Q, et al. Heat treatment process for optimization of the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melting TC4 titanium alloy [J]. Welding Technology, 2023, 52(6): 1–6. DOI: 10.13846/j.cnki.cn12-1070/tg.2023.06.030. [87] 张元东, 张安, 车安达, 等. β退火的低温退火温度对TC32合金组织和性能的影响 [J]. 锻造与冲压, 2023(11): 61–66. [88] YU H C, YANG J J, YIN J, et al. Comparison on mechanical anisotropies of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy and 304 stainless steel [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 695: 92–100. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.031. [89] WU M W, NI K, YEN H W, et al. Revealing the intensified preferred orientation and factors dominating the anisotropic mechanical properties of laser powder bed fusion Ti-6Al-4V alloy after heat treatment [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 949: 169494. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169494. [90] GAO X X, TAO C H, WU S J, et al. Influence of modified microstructures and characterized defects on tensile properties and anisotropy of selective laser melting-produced Ti6Al4V alloys [J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2022, 31(9): 7705–7718. DOI: 10.1007/s11665-022-06745-0. [91] CAO S, CHEN Z E, LIM C V S, et al. Defect, microstructure, and mechanical property of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated by high-power selective laser melting [J]. JOM, 2017, 69(12): 2684–2692. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-017-2581-6. [92] HUANG W D, HE D D, WANG H, et al. The effect of heat treatment on the anisotropy of Ti-6Al-4V by selective laser melting [J]. JOM, 2022, 74(7): 2724–2732. DOI: 10.1007/s11837-022-05212-4. [93] VILARO T, COLIN C, BARTOUT J D. As-fabricated and heat-treated microstructures of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy processed by selective laser melting [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(10): 3190–3199. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-011-0731-y. [94] MEIER B, GODJA N, WARCHOMICKA F, et al. Influences of surface, heat treatment, and print orientation on the anisotropy of the mechanical properties and the impact strength of Ti 6Al 4V processed by laser powder bed fusion [J]. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 2022, 6(4): 87. DOI: 10.3390/jmmp6040087. [95] LIU J W, LIU J, LI Y X, et al. Effects of post heat treatments on microstructures and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti6AL4V alloy [J]. Metals, 2021, 11(10): 1593. DOI: 10.3390/met11101593. [96] CHANG K, WANG X, LIANG E Q, et al. On the texture and mechanical property anisotropy of Ti6Al4V alloy fabricated by powder-bed based laser additive manufacturing [J]. Vacuum, 2020, 181: 109732. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.109732. [97] AL-RUBAIE K S, MELOTTI S, RABELO A, et al. Machinability of SLM-produced Ti6Al4V titanium alloy parts [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 57: 768–786. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.07.035. [98] 冉春, 陈鹏万, 李玲, 等. 中高应变率条件下TC18钛合金动态力学行为的实验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(9): 1723–1728. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.09.008.RAN C, CHEN P W, LI L, et al. Experimental research on dynamic mechanical behavior of TC18 titanium alloy under medium and high strain rates [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(9): 1723–1728. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.09.008. [99] CHENG F, WANG H M, LI Z, et al. Dynamic compression deformation behavior of laser directed energy deposited α+β duplex titanium alloy with basket-weave morphology [J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2023, 61: 103336. DOI: 10.1016/j.addma.2022.103336. [100] LU G, YU T X. Energy absorption of structures and materials[M]. London: Elsevier Science, 2003: 19-22. [101] ZHAO S H, YUAN K B, GUO W G, et al. A comparative study of laser metal deposited and forged Ti-6Al-4V alloy: uniaxial mechanical response and vibration fatigue properties [J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2020, 136: 105629. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105629. [102] 张世进, 李凯, 易丹青, 等. 冷轧TA5钛合金退火过程的再结晶行为及织构演变 [J]. 金属热处理, 2022, 47(2): 1–8. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2022.02.001.ZHANG S J, LI K, YI D Q, et al. Recrystallization behavior and texture evolution of cold rolled TA5 titanium alloy during annealing [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(2): 1–8. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2022.02.001. [103] WAYMEL R F, CHEW H B, LAMBROS J. Loading orientation effects on the strength anisotropy of additively-manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloys under dynamic compression [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2019, 59(6): 829–841. DOI: 10.1007/s11340-019-00506-2. [104] RODRIGUEZ O L, ALLISON P G, WHITTINGTON W R, et al. Strain rate effect on the tension and compression stress-state asymmetry for electron beam additive manufactured Ti6Al4V [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 713: 125–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.12.062. [105] JIANG X J, CHEN G Y, MEN X L, et al. Grain refinement and excellent mechanical properties of a Ti-based alloy via laser melting and subsequent low temperature annealing [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 737: 182–187. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.09.042. [106] PANG Z C, LIU Y, LI M, et al. Influence of process parameter and strain rate on the dynamic compressive properties of selective laser-melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J]. Applied Physics A, 2019, 125(2): 90. DOI: 10.1007/s00339-018-2359-x. [107] DIXIT T, SAHU P K, JONNALAGADDA K, et al. Effect of powder layer thickness and scan orientation on the deformation and failure of selectively laser melted Ti-6Al-4V alloy over six decades of strain rates [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 822: 141656. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141656. [108] ALAGHMANDFARD R, CHALASANI D, ODESHI A G, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V parts fabricated by electron beam melting under dynamic compression tests [C]//Canadian Society for Mechanical Engineering International Congress. Charlottetown, Canada, 2020. DOI: 10.32393/csme.2020.1190. [109] 陈钰浩, 闵小华, 张海洋, 等. TC17和TC4合金锻件的动态响应及绝热剪切行为 [J]. 航空材料学报, 2023, 43(5): 39–49. DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2023.000105.CHEN Y H, MIN X H, ZHANG H Y, et al. Dynamic responses and adiabatic shear behaviors of TC17 and TC4 alloy forgings [J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2023, 43(5): 39–49. DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2023.000105. [110] 余东辉, 范群波, 王富耻, 等. 铸造态钛合金力学性能及抗弹性能研究 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(8): 2234–2239.YU D H, FAN Q B, WANG F C, et al. Mechanical properties and ballistic performance of as-cast titanium alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(8): 2234–2239. [111] 黄均毅, 杨扬. 选区电子束熔炼Ti-6Al-4V钛合金的绝热剪切各向异性 [J]. 矿冶工程, 2022, 42(5): 143–147. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2022.05.033.HUANG J Y, YANG Y. Anisotropic behavior of adiabatic shear band in Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy fabricated by selected electron beam melting [J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2022, 42(5): 143–147. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2022.05.033. [112] PU B, LI W B, ZHANG Q, et al. Research on the dynamic compressive deformation behavior of 3D-printed Ti6Al4V [J]. Metals, 2021, 11(8): 1327. DOI: 10.3390/met11081327. [113] WANG S Q, LIU J H, CHEN D L. Effect of strain rate and temperature on strain hardening behavior of a dissimilar joint between Ti-6Al-4V and Ti17 alloys [J]. Materials and Design, 2014, 56: 174–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.003. [114] RODRIGUEZ O L, ALLISON P G, WHITTINGTON W R, et al. Dynamic tensile behavior of electron beam additive manufactured Ti6Al4V [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2015, 641: 323–327. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.06.069. [115] TREVISAN F, CALIGNANO F, LORUSSO M, et al. On the selective laser melting (SLM) of the AlSi10Mg alloy: process, microstructure, and mechanical properties [J]. Materials (Basel), 2017, 10(1): 76. DOI: 10.3390/ma10010076. [116] 张斌, 郭玲梅, 汪洋, 等. TA7钛合金拉伸和压缩加载时的孪生变形行为 [J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2021, 31(9): 2427–2435. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39781.ZHANG B, GUO L M, WANG Y, et al. Deformation twinning behavior of TA7 titanium alloy under tension and compression [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2021, 31(9): 2427–2435. DOI: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2021-39781. [117] 闫辰侃, 曲寿江, 冯艾寒, 等. 钛及钛合金形变孪晶的研究进展 [J]. 稀有金属, 2019, 43(5): 449–460. DOI: 10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.xy18040028.YAN C K, QU S J, FENG A H, et al. Recent advances of deformation twins in titanium and titanium alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2019, 43(5): 449–460. DOI: 10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.xy18040028. [118] ALAGHMANDFARD R, DHARMENDRA C, ODESHI A G, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and failure characteristics of electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V under high strain rate impact loadings [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 793: 139794. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139794. [119] 陈冠方, 张金勇, 钟艺, 等. 相变/孪晶诱发塑性的β钛合金加工硬化行为研究 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020, 49(1): 297–303.CHEN G F, ZHANG J Y, ZHONG Y, et al. Stain-hardening behavior of a ductile beta Ti-alloy with transformation induced plasticity and twinning induced plasticity [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020, 49(1): 297–303. -






 下载:
下载: