Study on load reduction characteristics of porous foam buffer for high-speed water entry vehicle
-
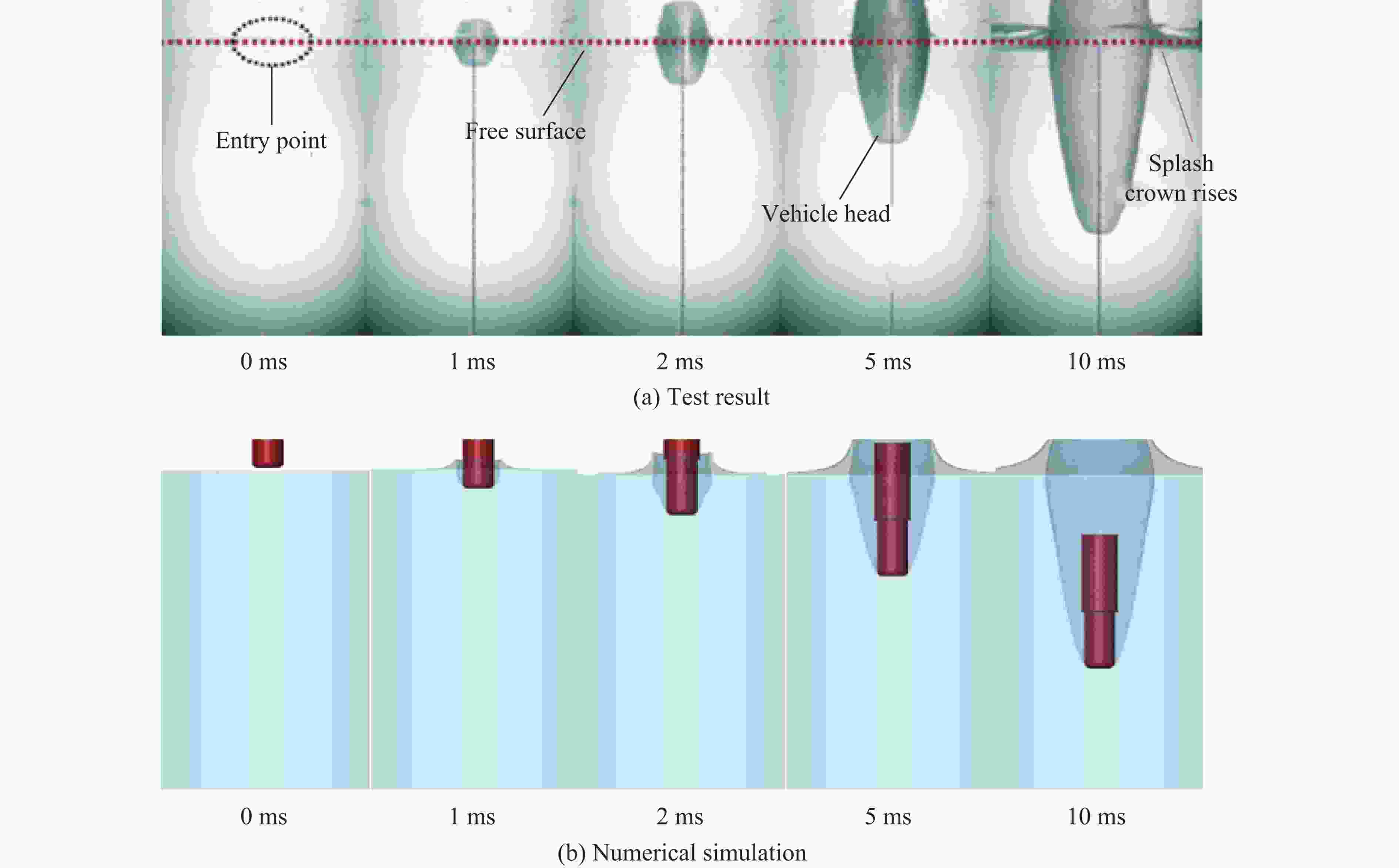
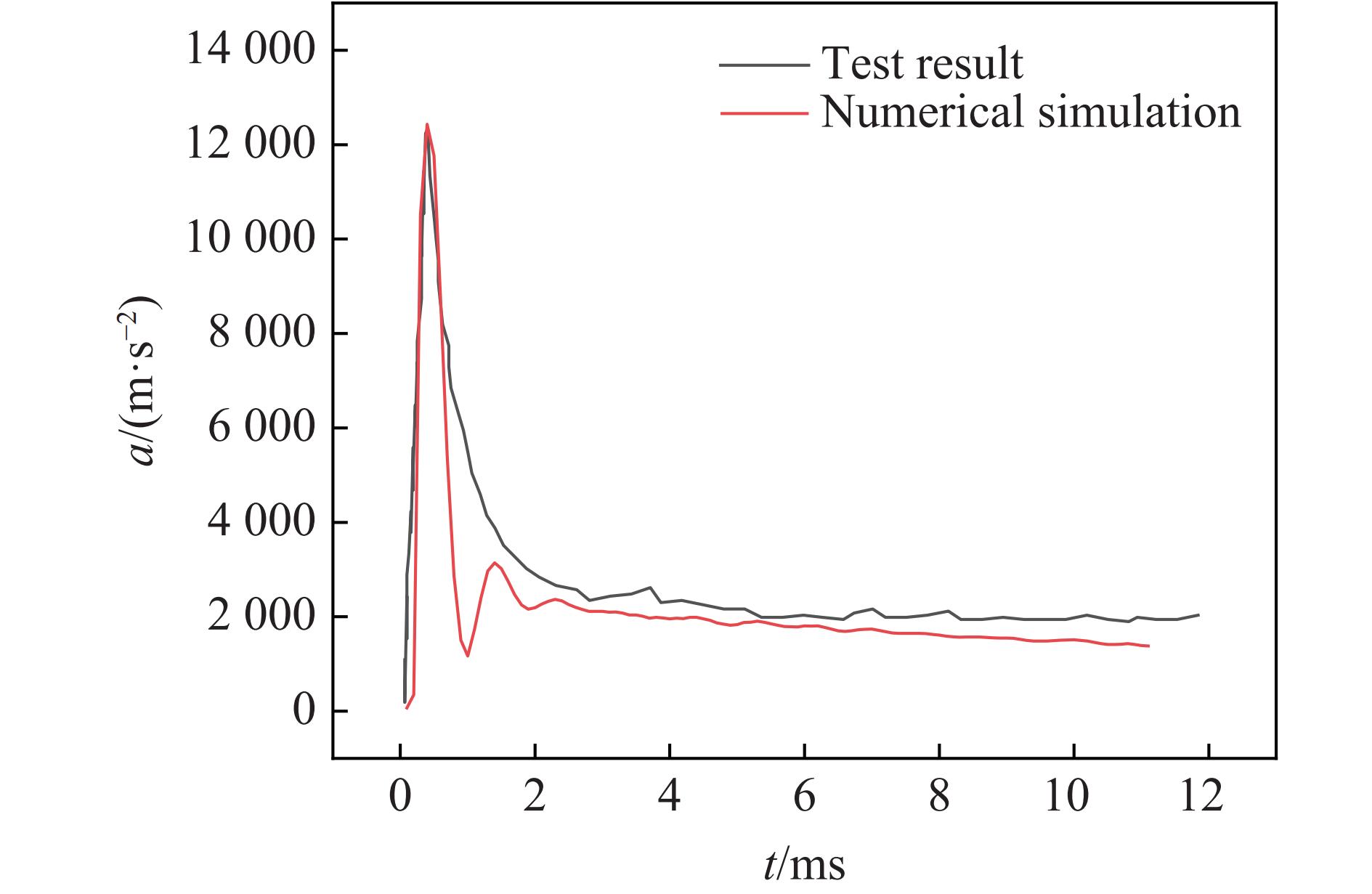
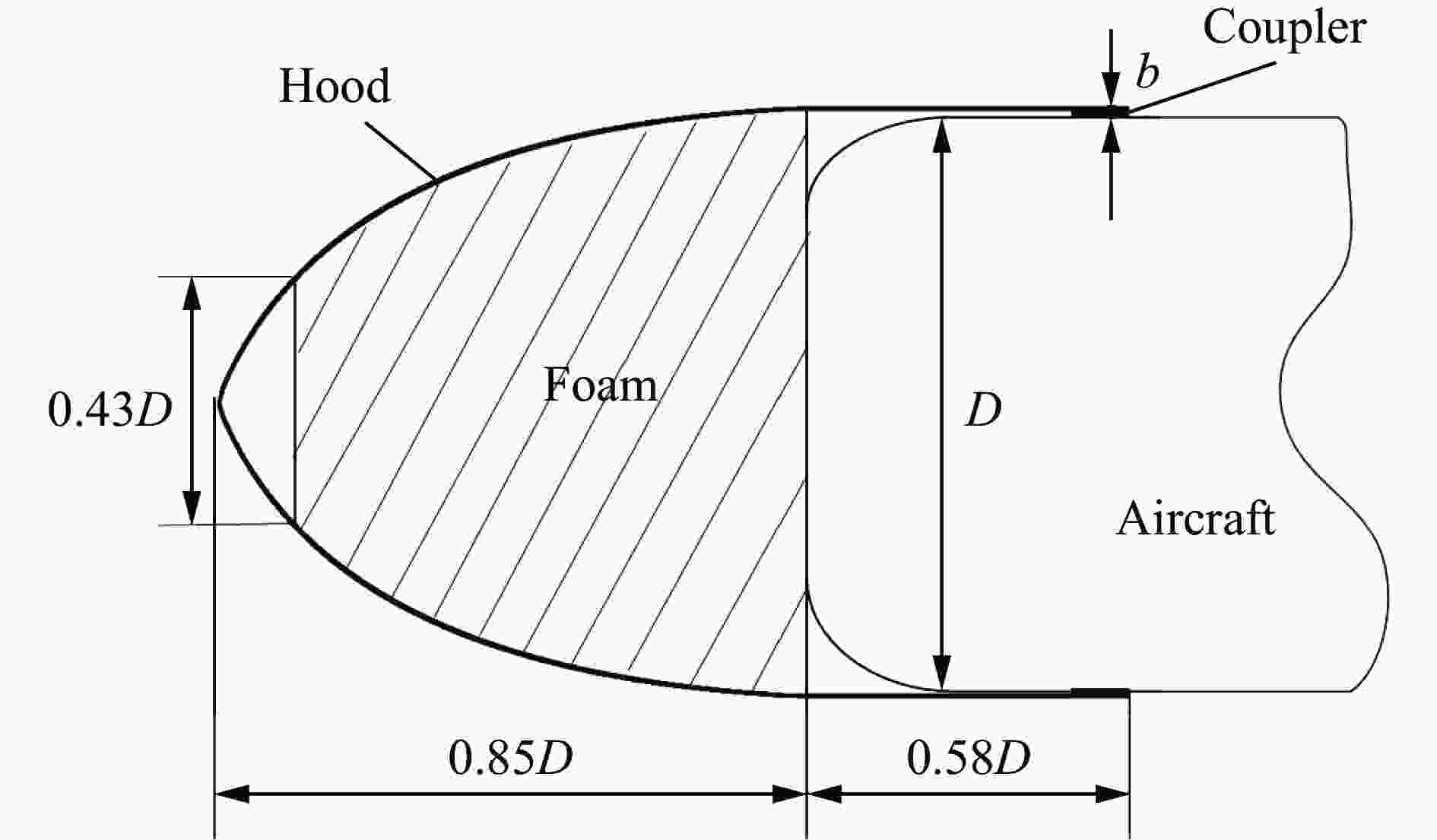
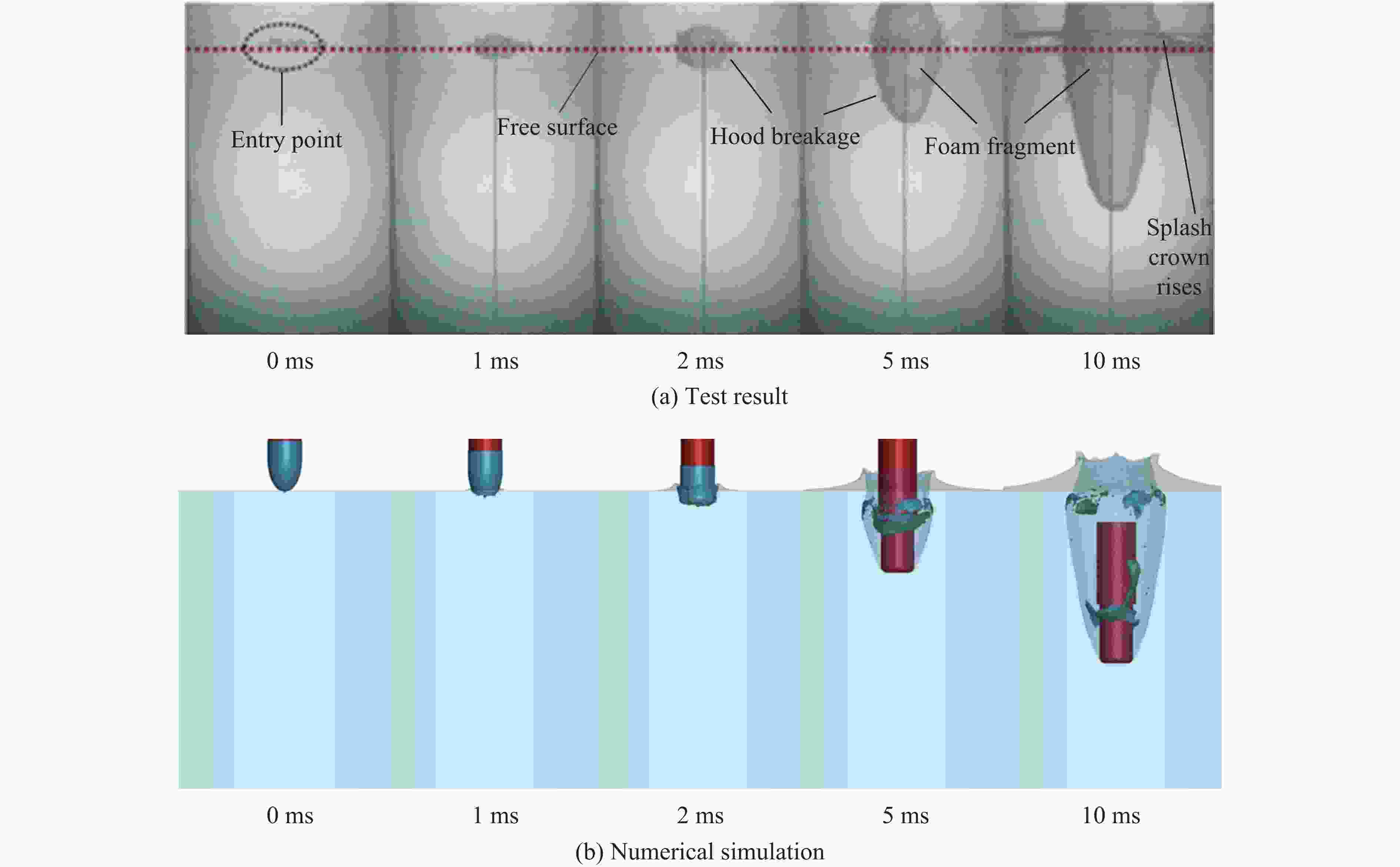
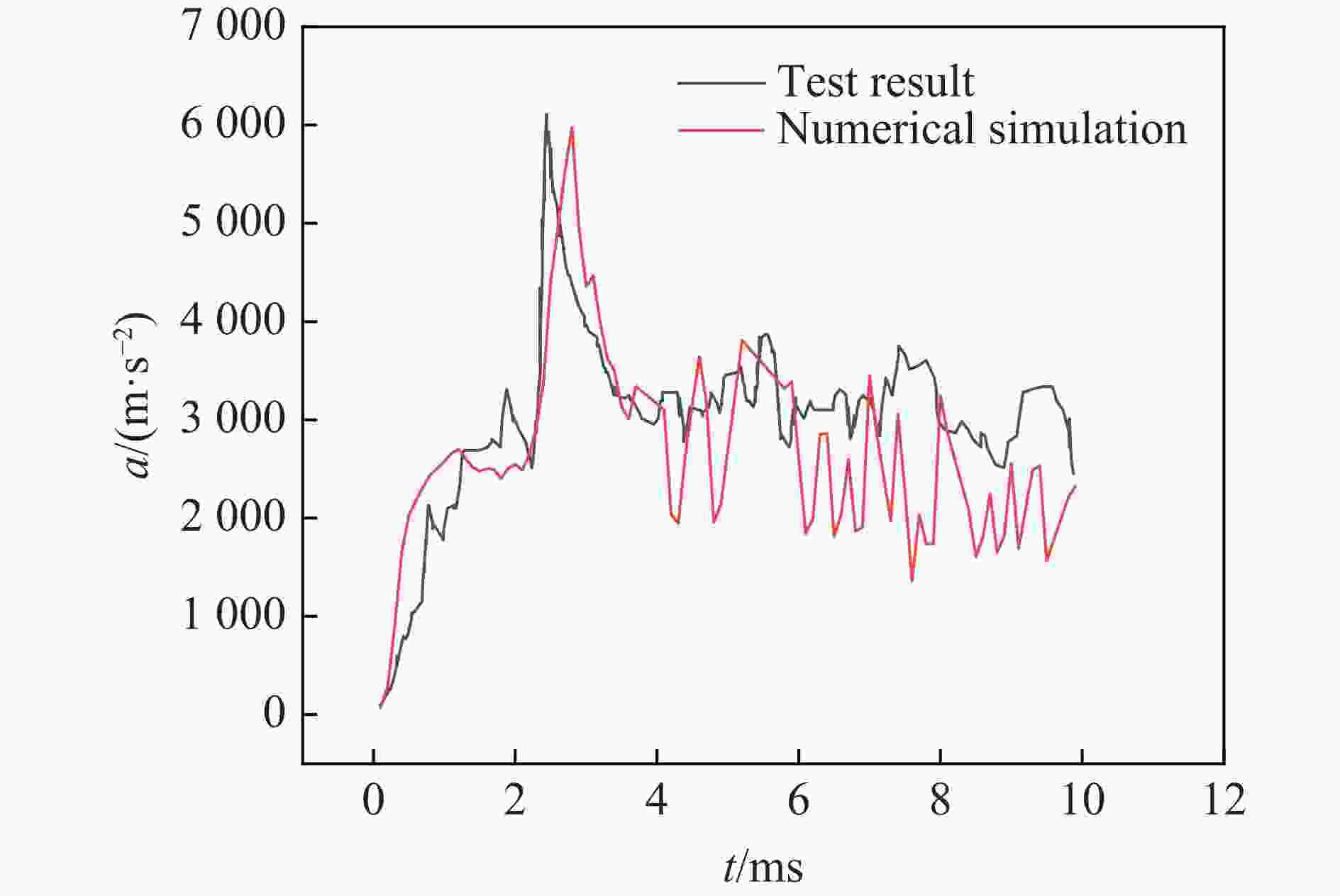
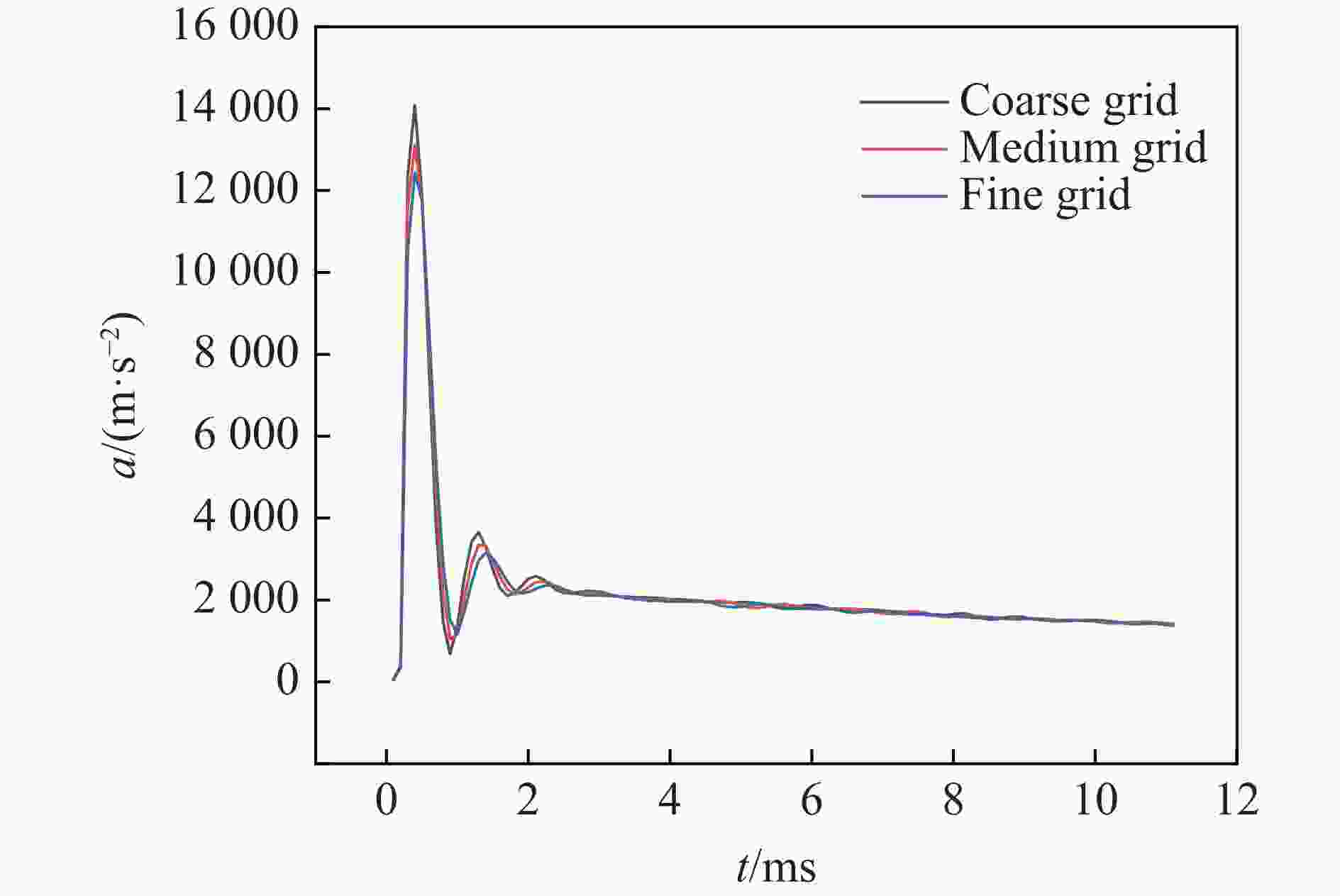
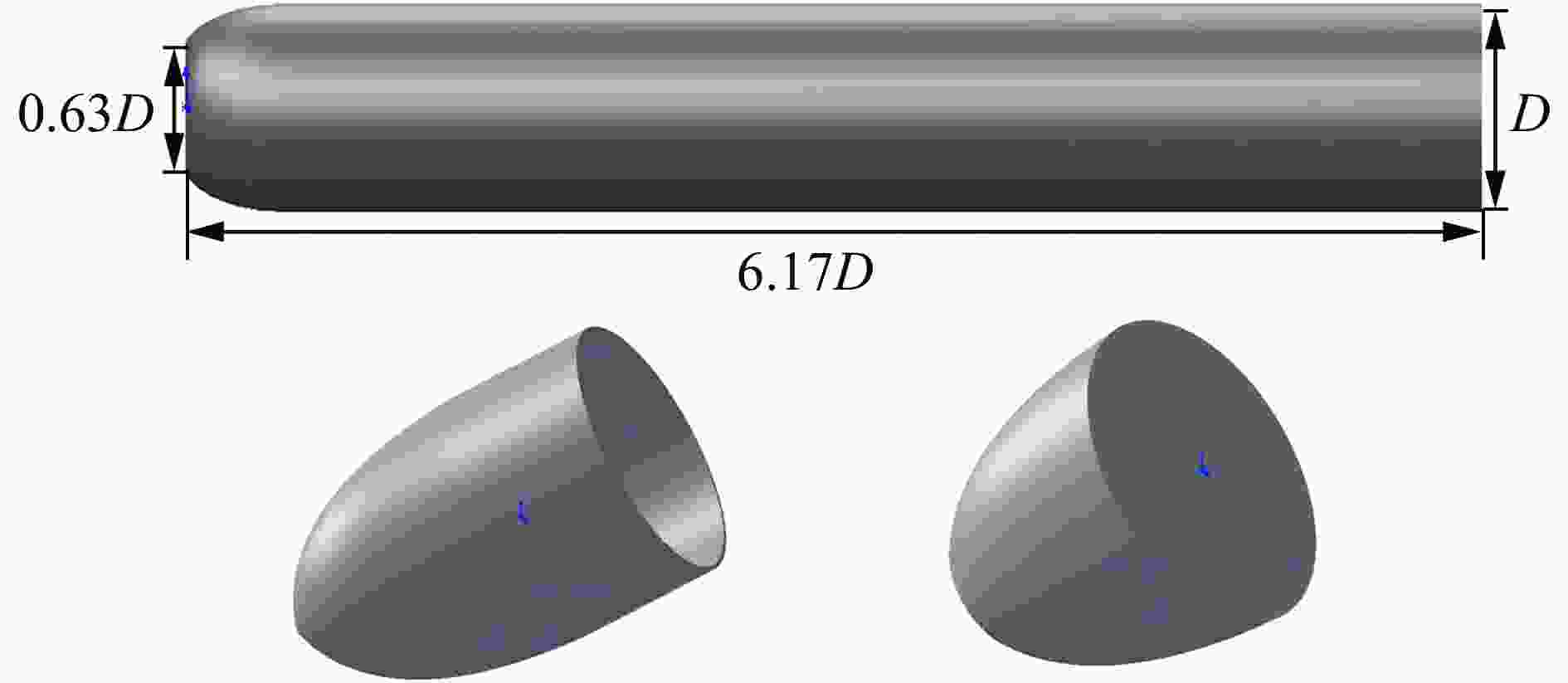
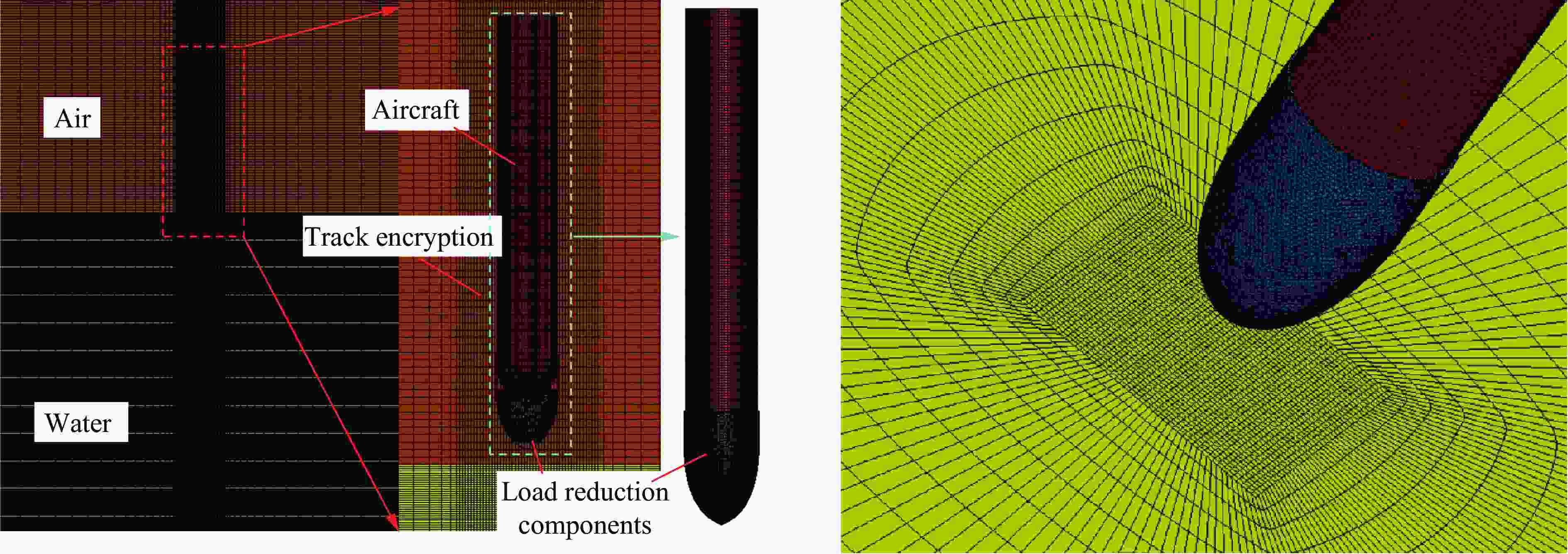
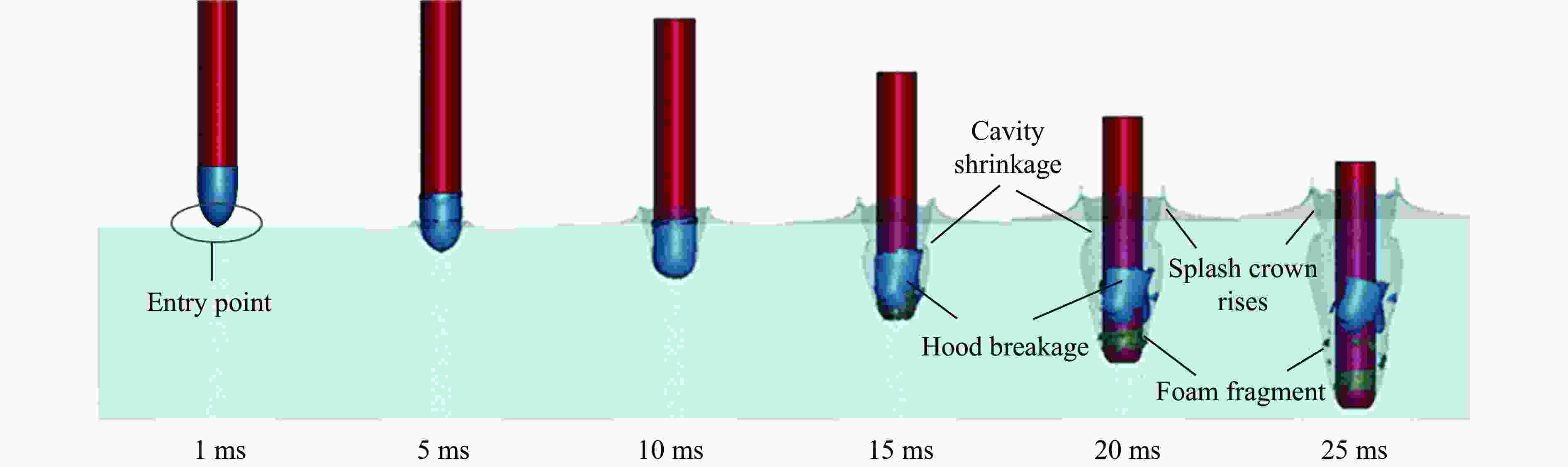
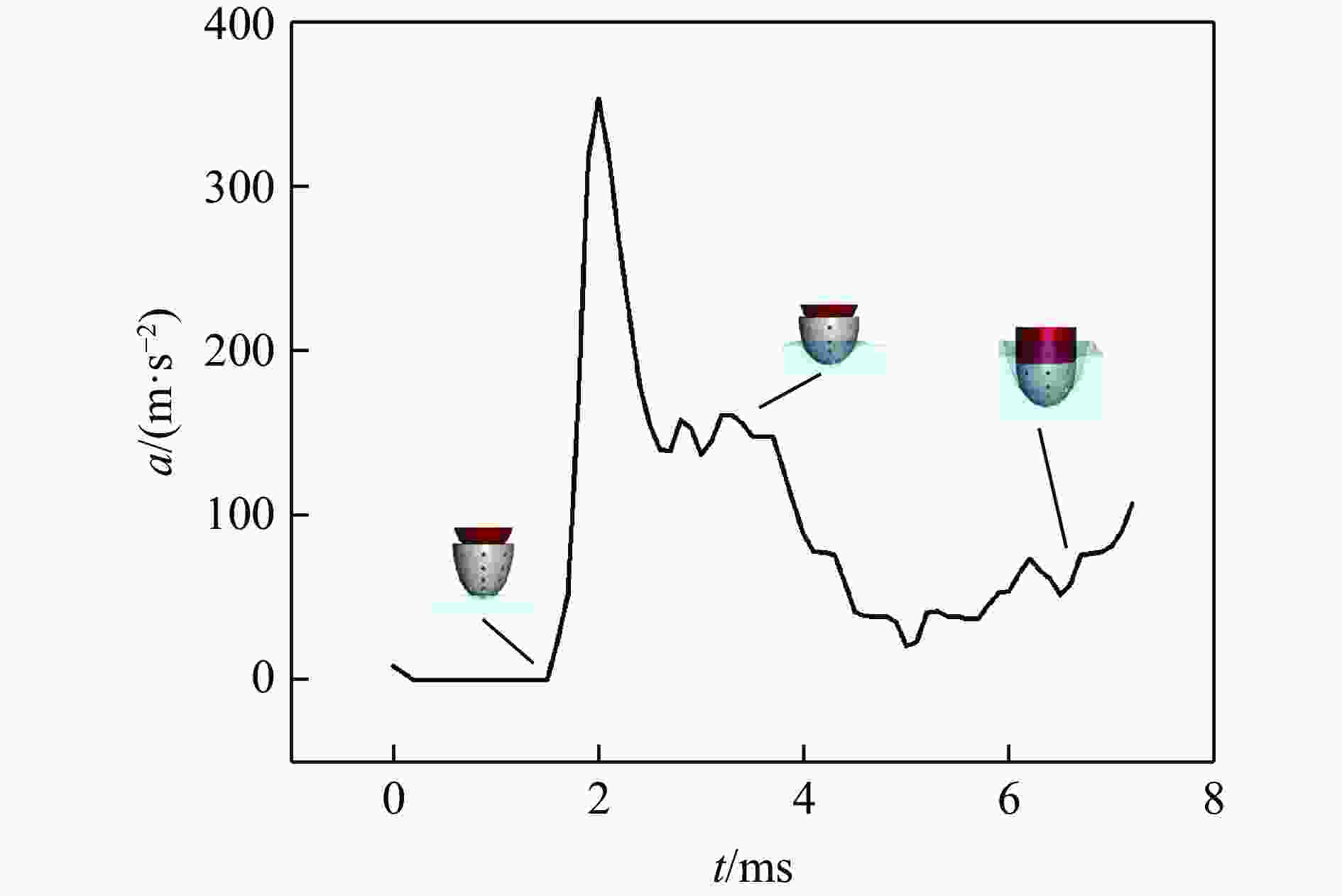
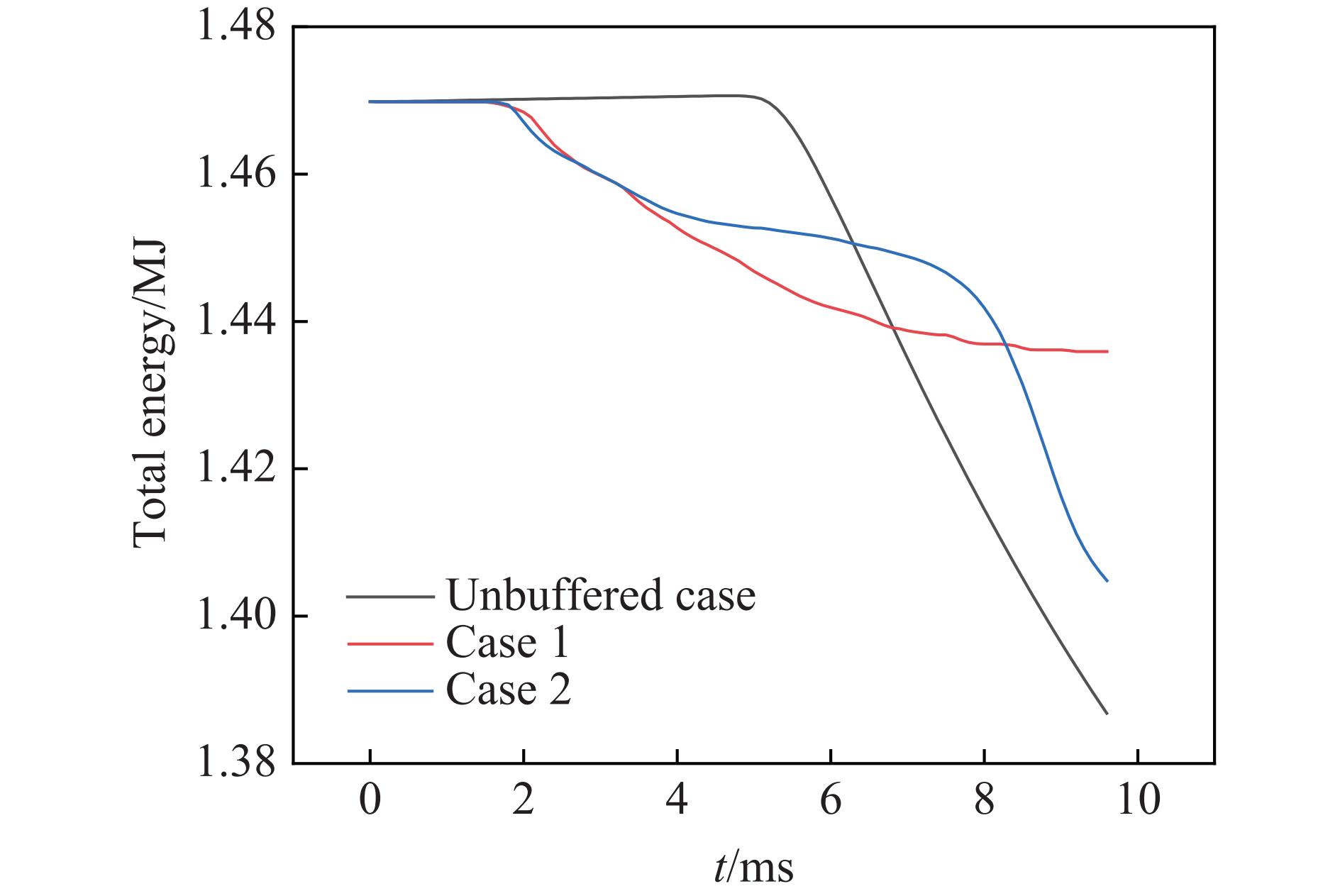
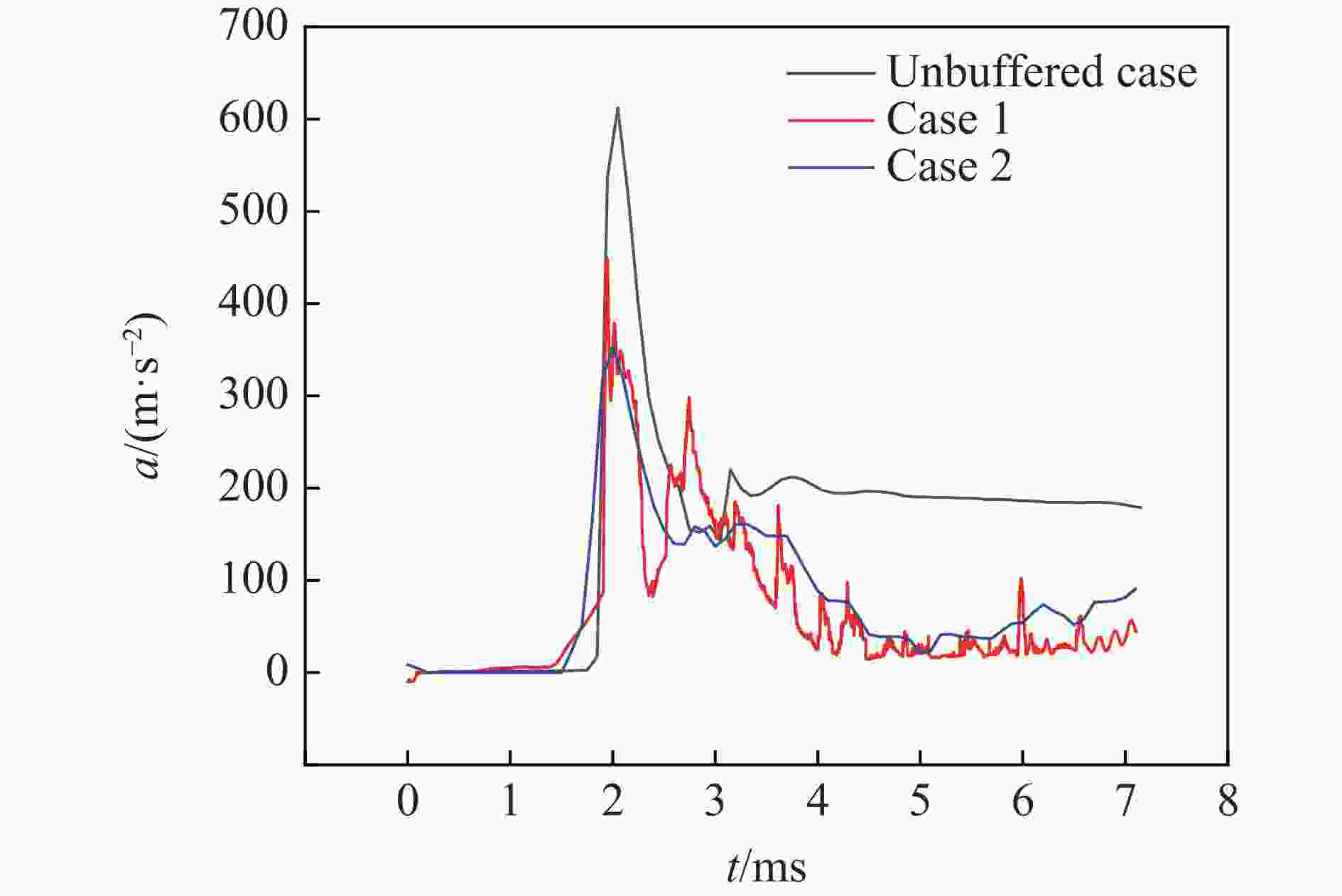
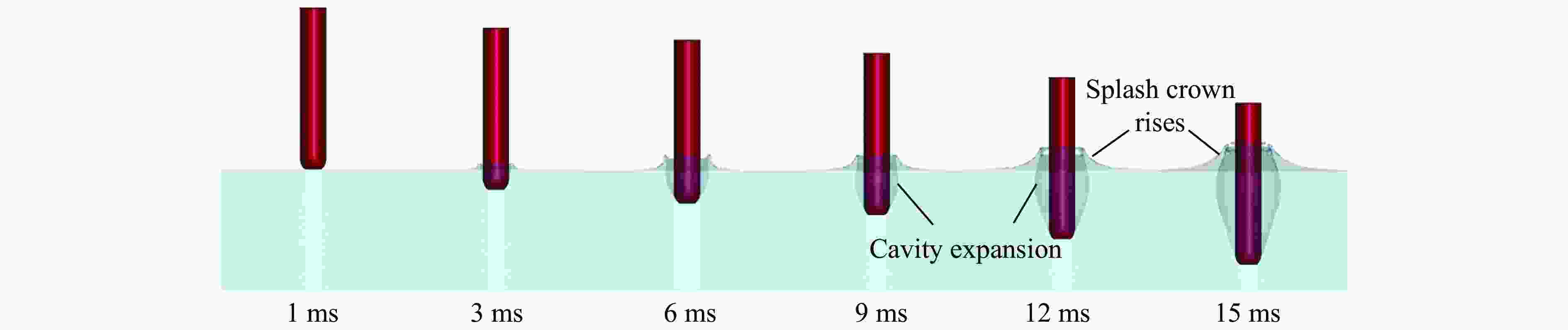
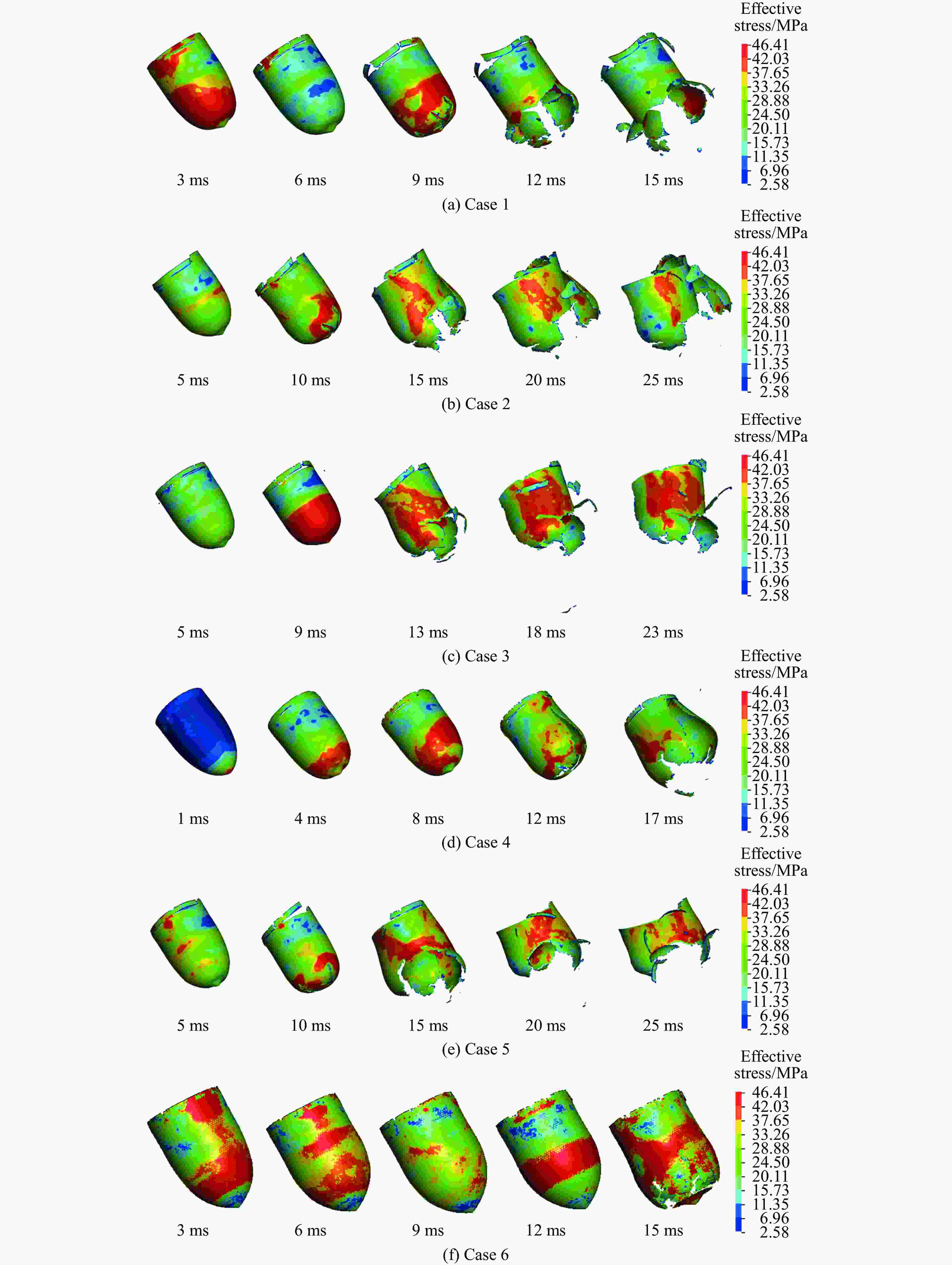
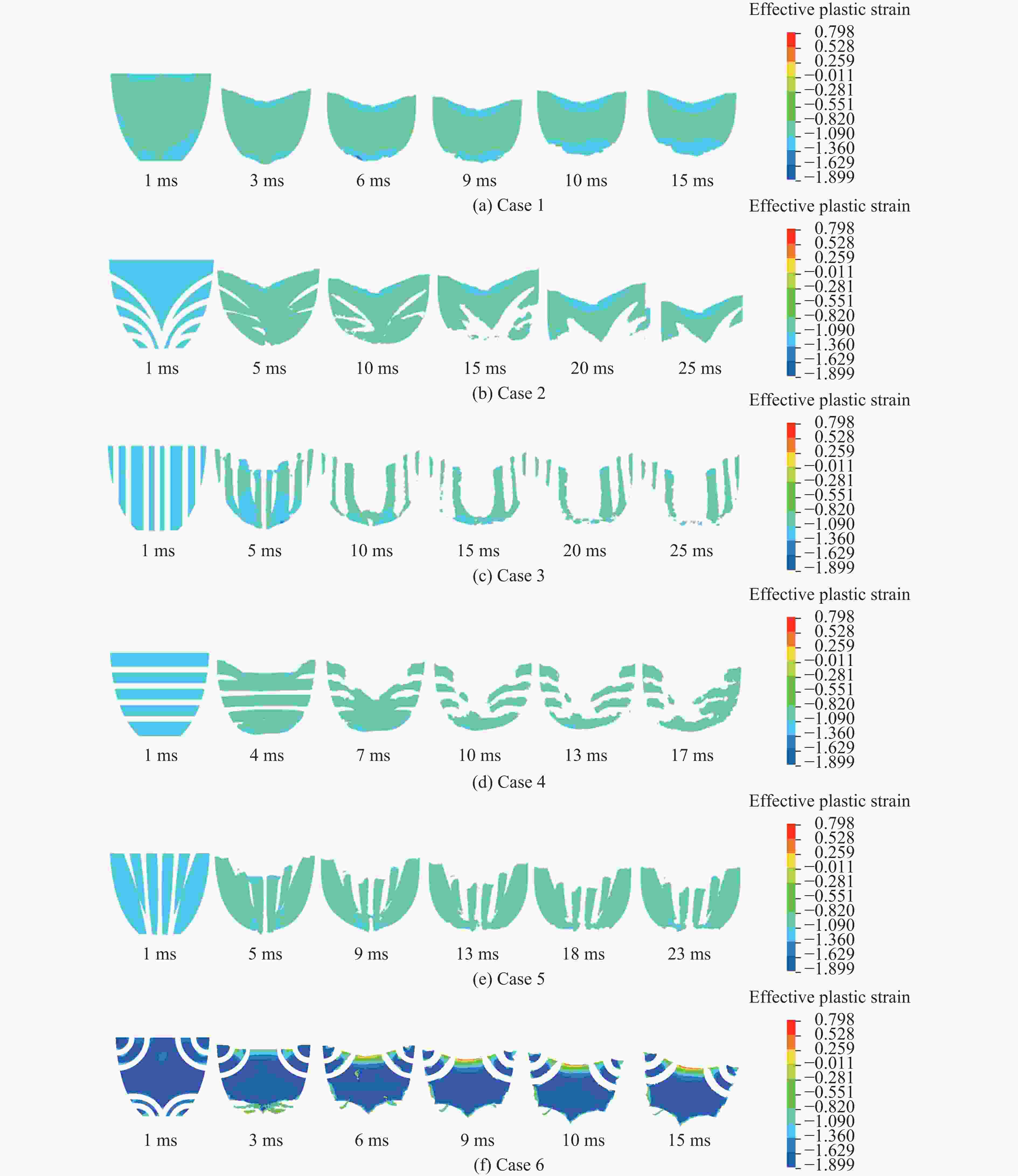
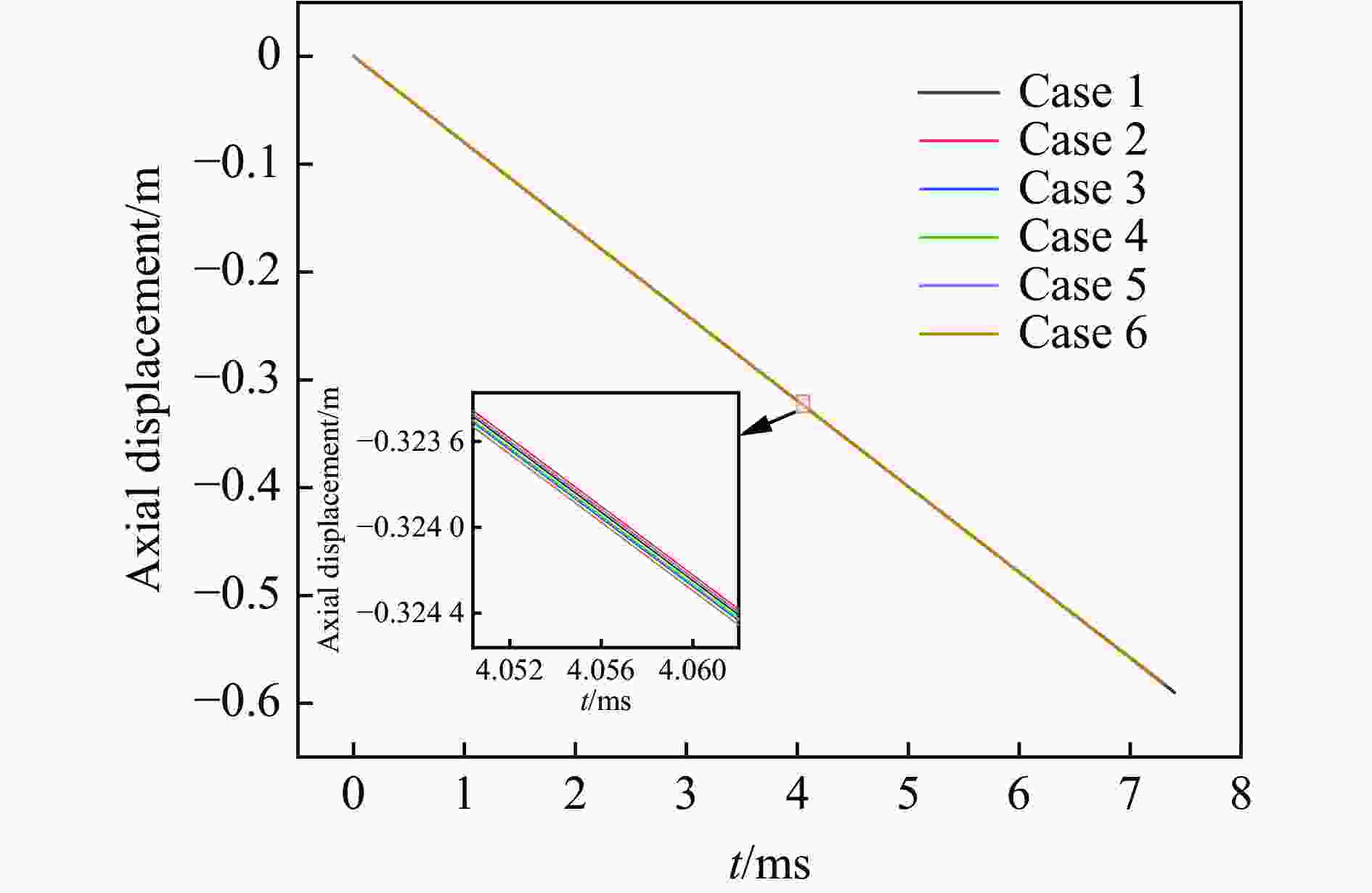
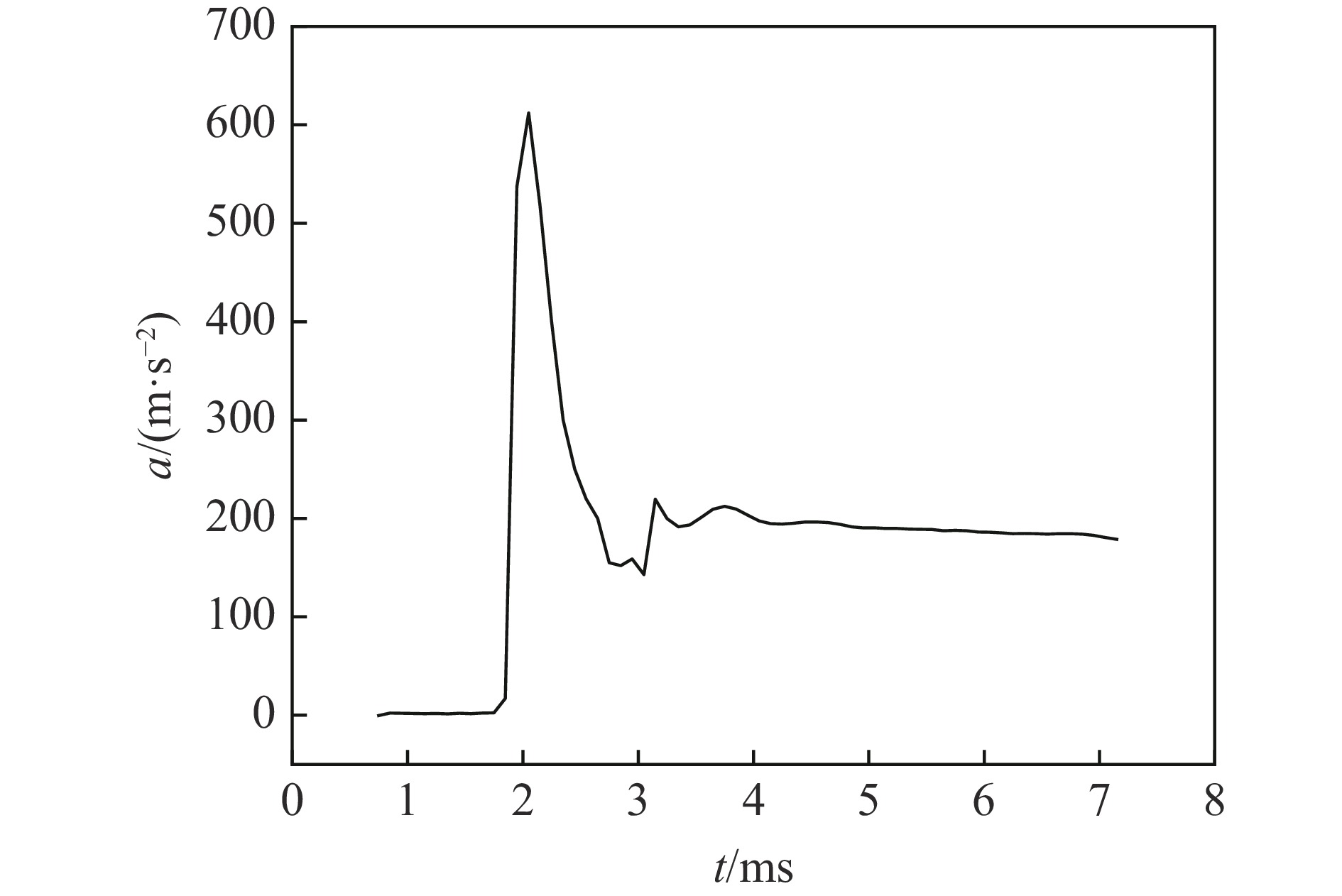
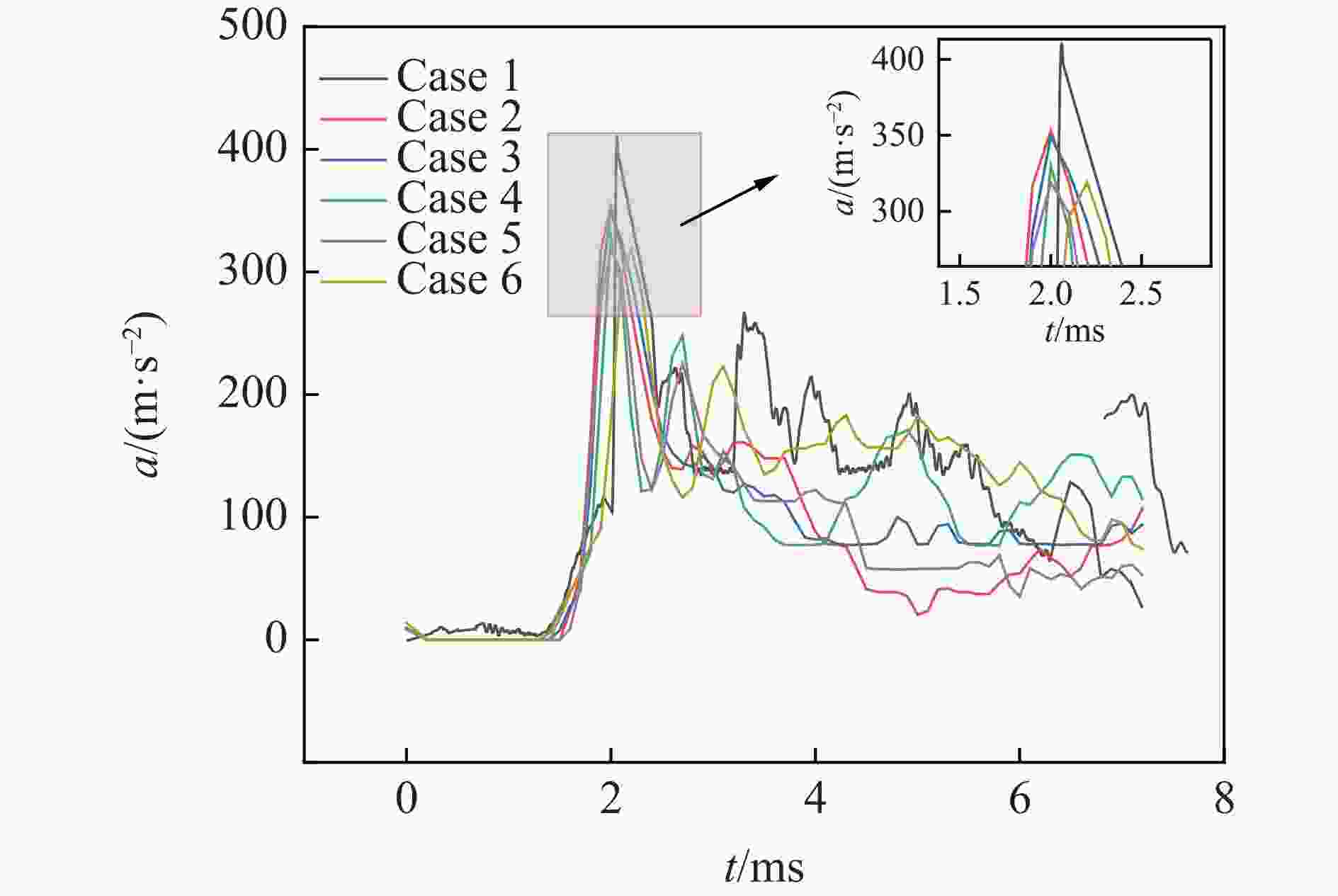
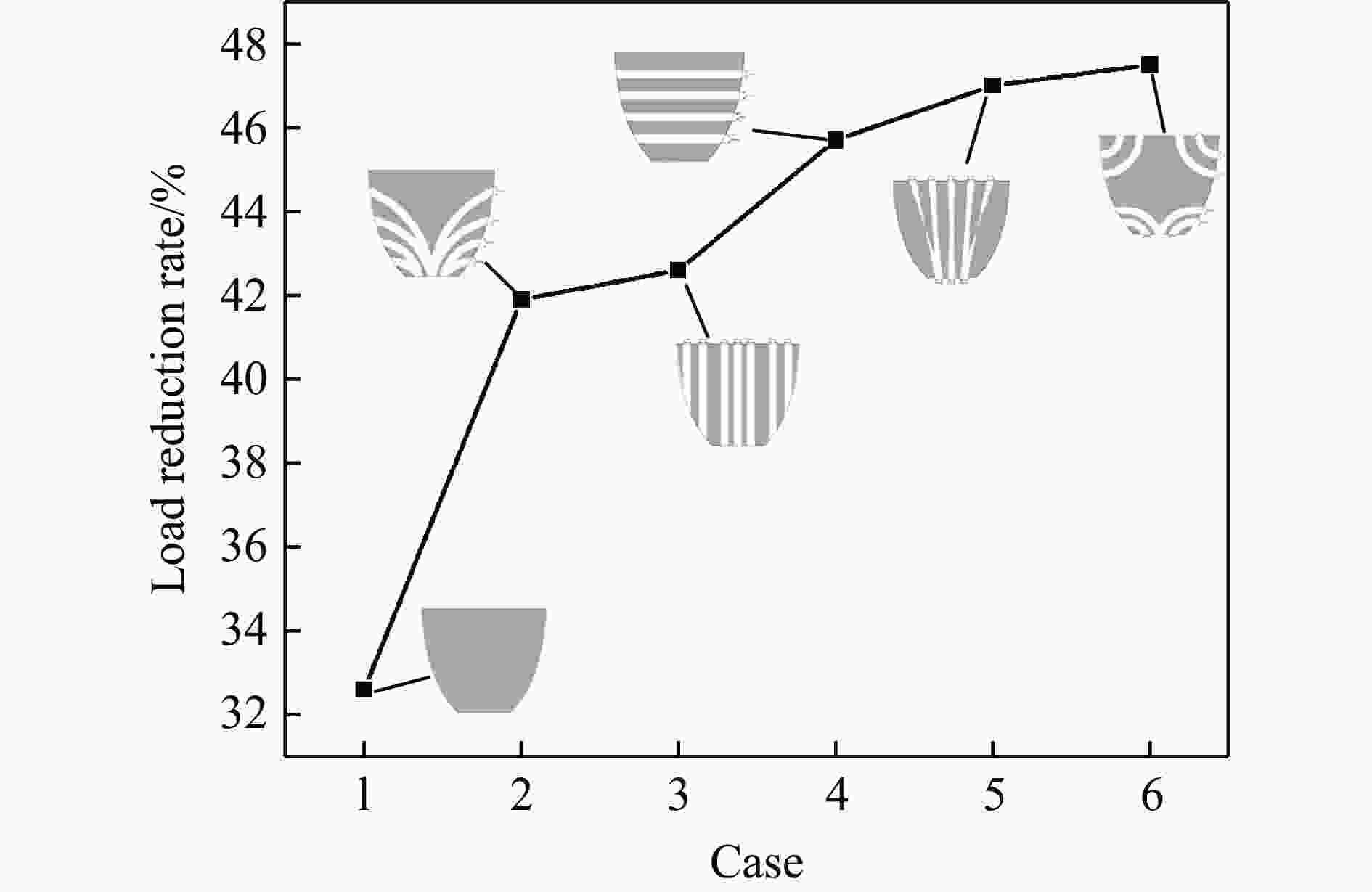
摘要: 针对航行体高速入水时的缓冲降载问题,设计了适用的缓冲头罩及多种开孔形式的缓冲泡沫构型,基于任意拉格朗日-欧拉方法,建立了航行体高速入水缓冲降载数值计算模型,并通过数值模拟对不同开孔形式的缓冲泡沫的降载性能进行了深入研究。结果表明:多孔缓冲泡沫在分散航行体入水冲击力及吸收冲击能量方面表现出显著优势,具有更好的缓冲效果;同时,缓冲头罩在入水时会发生局部渐进破碎,缓冲罩壳与航行体之间的连接器处的缓冲头罩外壁面的变形和破裂是由于撞水时产生的应力集中分布引起的;多孔泡沫接触水面时,前端部分会进入坍塌阶段,吸收大量能量并产生塑性变形,孔隙减少,此阶段为缓冲泡沫的主要能量吸收阶段;相比之下,不开孔泡沫的降载性能较差。因此,采用多孔泡沫是一种更优的航行体高速入水缓冲降载方案。Abstract: Applicable buffer-head covers and various open-cell foam buffer configurations were designed to meet the buffering and load reduction challenges during high-speed water entry vehicles. In the arbitrary Lagrangian-Euler method, the grid can move as the material flows within the spatial grid. This unique feature allows the arbitrary Lagrangian-Euler method to harness the advantages of both the Lagrangian and Euler methods. It not only overcomes numerical calculation challenges stemming from element distortion but also facilitates accurate computation of large deformations and displacements in solids and fluids. This makes it particularly well-suited for addressing high-speed water buffer load reduction problems. Based on the arbitrary Lagrangian-Euler method and considering the large deformation of the buffer foam and the hood, a numerical calculation model for buffering and load reduction during high-speed water entry of navigational bodies was established. Through numerical simulations, an in-depth study was conducted on the load reduction performance of buffer foams with different open-cell patterns. The results indicate that open-cell buffer foam exhibits significant advantages in dispersing the impact force and absorbing impact energy during water entry of navigational bodies, offering better buffering effects. Simultaneously, the buffer head cover experiences local progressive fragmentation upon water entry. The deformation and rupture of the outer wall surface of the buffer head cover at the connector between the buffer shell and the navigational body are caused by the stress concentration distribution generated during water impact. When the open-cell foam contacts the water surface, the front part enters the collapse stage, absorbing a large amount of energy and undergoing plastic deformation, resulting in a reduction of pores. This stage is the primary energy absorption phase for the buffer foam. In comparison, closed-cell foam exhibits poorer load reduction performance. Therefore, the adoption of open-cell foam represents a superior solution for buffering and load reduction during high-speed water entry of navigational bodies.
-
Key words:
- high-speed water entry /
- buffer and load reduction /
- energy absorption /
- porous foam
-
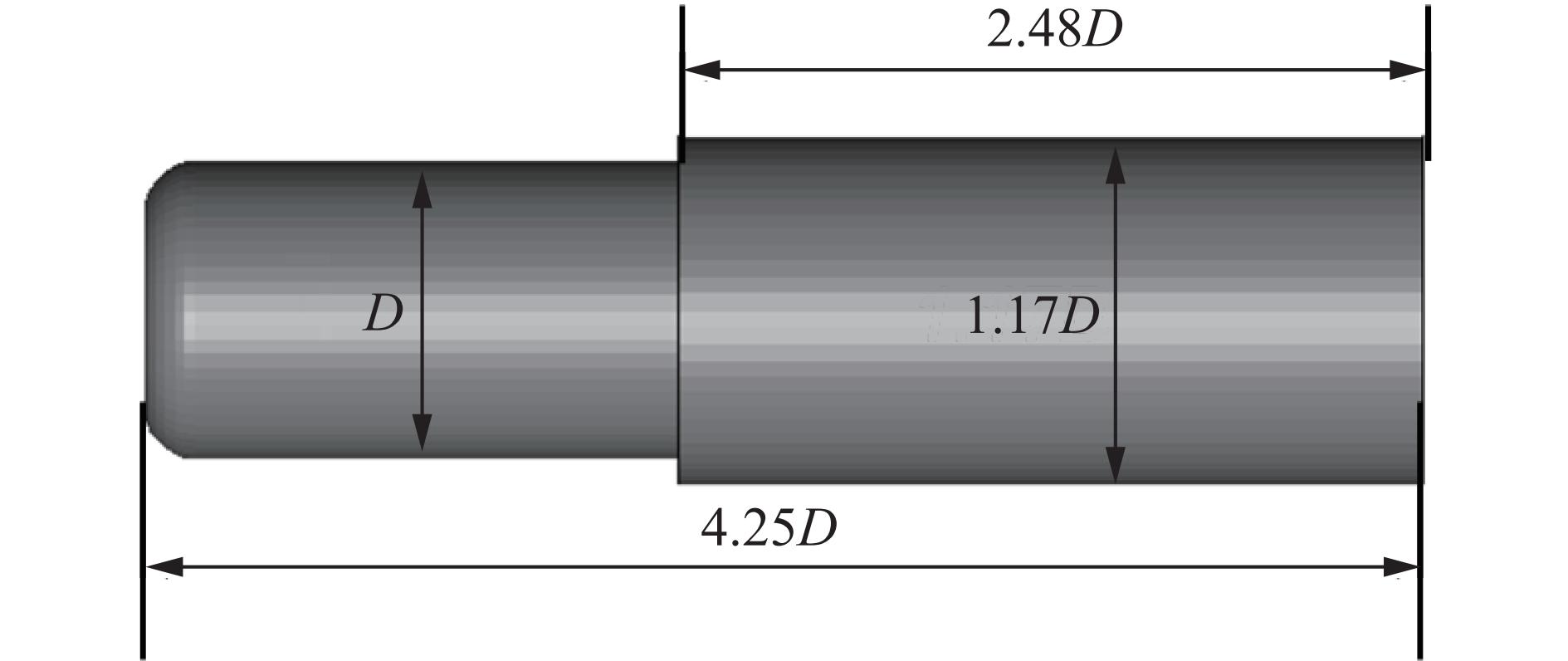
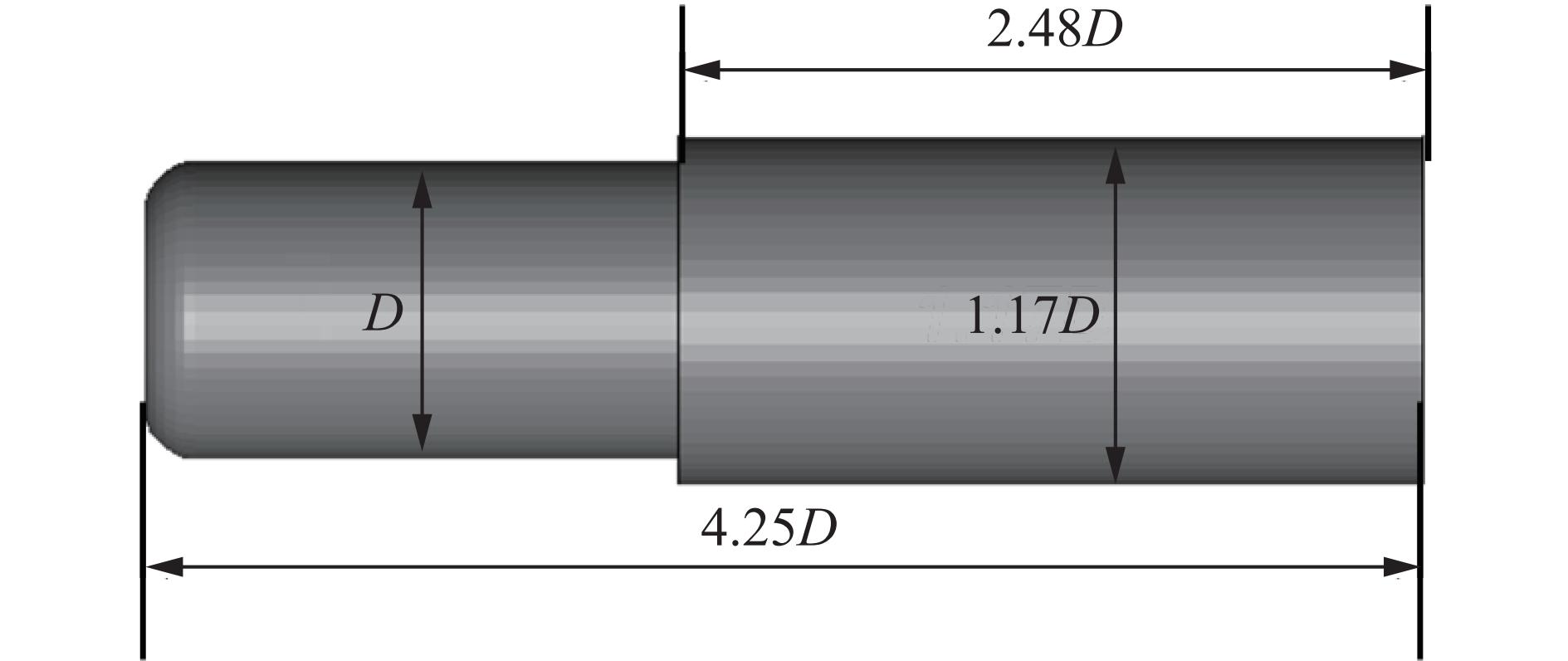
表 1 材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters
材料 密度/
(kg·m−3)杨氏模量/
GPa泊松比 屈服应力/
MPa切线模量/
MPa缓冲头帽 1 200 8.5 0.33 45.0 9 缓冲泡沫 100 1.0 0.24 1.4 表 2 数值模拟工况
Table 2. Simulation cases
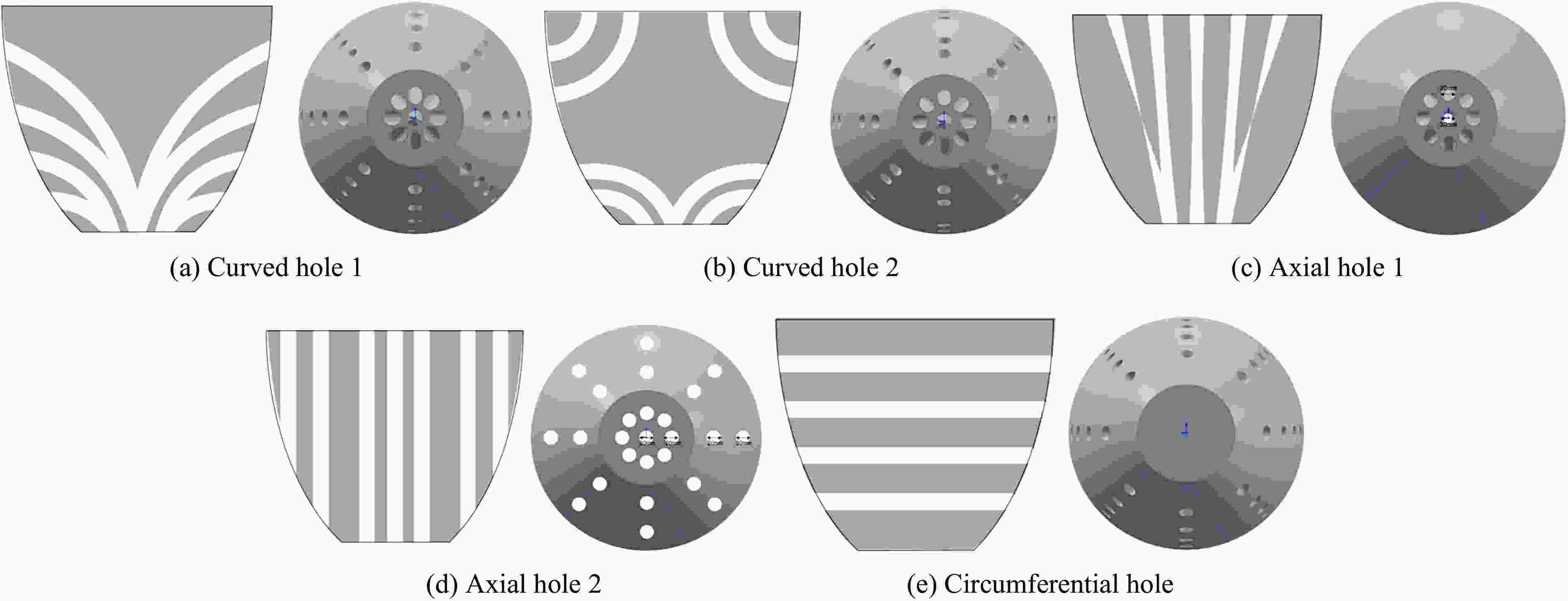
工况 速度/(m·s−1) 缓冲泡沫 工况 速度/(m·s−1) 缓冲泡沫 1 80 不开孔 4 80 周向孔 2 80 弯孔1 5 80 轴向孔1 3 80 轴向孔2 6 80 弯孔2 -
[1] 吕红庆, 许磊, 王振清. 不同头型旋成体入水初期流场特性数值分析 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(12): 34–42. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.12.006.LYU H Q, XU L, WANG Z Q. Numerical research on flow field characteristics of axisymmetric bodies with different head shapes during initial water entry [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(12): 34–42. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.12.006. [2] TANG S Q, ZHANG Y, SUN S L, et al. Experimental investigation on the air-cushion effect during free fall of a trimaran section using an air escape control method [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 254: 111417. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111417. [3] WU S Y, SHAO Z Y, FENG S S, et al. Water-entry behavior of projectiles under the protection of polyurethane buffer head [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 197: 106890. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106890. [4] KUBOTA Y, MOCHIZUKI O. Influence of head shape of solid body plunging into water on splash formation [J]. Journal of Visualization, 2011, 14(2): 111–119. DOI: 10.1007/s12650-011-0071-4. [5] 石汉成, 蒋培, 程锦房. 头部形状对水雷入水载荷及水下弹道影响的数值仿真分析 [J]. 舰船科学技术, 2010, 32(10): 104–107. DOI: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2010.10.027.SHI H C, JIANG P, CHENG J F. Research on numerical simulation of mine water-entry impact acceleration and underwater ballistic trajectory under the different mine’s head shape [J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2010, 32(10): 104–107. DOI: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2010.10.027. [6] SHI Y, PAN G, YIM S C, et al. Numerical investigation of hydroelastic water-entry impact dynamics of AUVs [J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2019, 91: 102760. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2019.102760. [7] GUO Z T, ZHANG W, XIAO X K, et al. An investigation into horizontal water entry behaviors of projectiles with different nose shapes [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 49(2): 43–60. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2012.04.004. [8] 潘龙, 王焕然, 姚尔人, 等. 头部喷气平头圆柱体人水缓冲机制研究 [J]. 工程热物理学报, 2015, 36(8): 1691–1695.PAN L, WANG H R, YAO E R, et al. Mechanism research on the water-enter impact of the head-jetting flat cylinder [J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2015, 36(8): 1691–1695. [9] SUN T Z, WANG S S, BAI P Y, et al. Cavity dynamics of water entry for a head-ventilated cylinder [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34(7): 073302. DOI: 10.1063/5.0094249. [10] 王峻, 刘珑翔, 陈瑛. 头部喷气圆柱高速入水空泡与降载特性的数值模拟研究 [J]. 水动力学研究与进展A辑, 2023, 38(2): 195–204. DOI: 10.16076/j.cnki.cjhd.2023.02.005.WANG J, LIU L X, CHENG Y. Numerical investigation on the high-speed water entry cavity and load reduction of air-jetting cylinder [J]. Chinese Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2023, 38(2): 195–204. DOI: 10.16076/j.cnki.cjhd.2023.02.005. [11] 赵海瑞, 施瑶, 潘光. 头部喷气航行器高速入水空泡特性数值分析 [J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2021, 39(4): 810–817. DOI: 10.1051/jnwpu/20213940810.ZHAO H R, SHI Y, PAN G. Numerical analysis of cavitation characteristics for high speed water entry of headjet vehicle [J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2021, 39(4): 810–817. DOI: 10.1051/jnwpu/20213940810. [12] 宣建明, 宋志平, 严忠汉. 鱼雷入水缓冲保护头帽解体试验研究 [J]. 鱼雷技术, 1999, 7(2): 41–46.XUAN J M, SONG Z P, YAN Z H. Experimental study on disintegration of torpedo nose cap during water entry [J]. Torpedo Technology, 1999, 7(2): 41–46. [13] HORTON D M. Shock-mitigating nose for underwater vehicles: U. S. Patent 6536365 [P]. 2003. [14] AVALLE M, BELINGARDI G, MONTANINI R. Characterization of polymeric structural foams under compressive impact loading by means of energy-absorption diagram [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 25(5): 455–472. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(00)00060-9. [15] 曾斐, 潘艺, 胡时胜. 泡沫铝缓冲吸能评估及其特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2002, 22(4): 358–362. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2002)04-0358-5.ZENG F, PAN Y, HU S S. Evaluation of cushioning properties and energy-absorption capability of foam aluminium [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2002, 22(4): 358–362. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2002)04-0358-5. [16] SHI Y, GAO X, PAN G. Design and load reduction performance analysis of mitigator of AUV during high speed water entry [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 181: 314–329. DOI: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.03.062. [17] 孙龙泉, 王都亮, 李志鹏, 等. 基于CEL方法的航行体高速入水泡沫铝缓冲装置降载性能分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(20): 80–88. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.20.011.SUN L Q, WANG D L, LI Z P, et al. Analysis on load reduction performance of foamed aluminum buffer device for high-speed water entry of vehicle based on a CEL method [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(20): 80–88. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2021.20.011. [18] 魏海鹏, 史崇镔, 孙铁志, 等. 基于ALE方法的航行体高速入水缓冲降载性能数值研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(10): 104201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0461.WEI H P, SHI C B, SUN T Z, et al. Numerical study on load-shedding performance of a high-speed water-entry vehicle based on an ALE method [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(10): 104201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0461. [19] HENNEAUX D, SCHROOYEN P, CHATELAIN P, et al. High-order enforcement of jumps conditions between compressible viscous phases: an extended interior penalty discontinuous Galerkin method for sharp interface simulation [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 415: 116215. DOI: 10.1016/j.cma.2023.116215. [20] LI Y, ZONG Z, SUN T Z. Classification of the collapse of a composite fairing during the oblique high-speed water entry [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 182(12): 110260. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110260. [21] 魏洪亮, 赵静, 徐志程, 等. 基于流固耦合的航行体高速入水规律研究 [J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 2020(2): 33–37. DOI: 10.7654/j.issn.1004-7182.20200207.WEI H L, ZHAO J, XU Z C, et al. Study on high-speed water entry law of trans-media vehicle based on fluid solid coupling [J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 2020(2): 33–37. DOI: 10.7654/j.issn.1004-7182.20200207. [22] 孙琦, 周军, 林鹏. 基于LS-DYNA的弹体撞水过程流固耦合动力分析 [J]. 系统仿真学报, 2010, 22(6): 1498–1501. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2010.06.005.SUN Q, ZHOU J, LIN P. Dynamic analysis of fluid-structure interaction for water impact of projectile using LS-DYNA [J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2010, 22(6): 1498–1501. DOI: 10.16182/j.cnki.joss.2010.06.005. [23] 李尧. 航行体高速入水缓冲头帽的降载机制与行为特性研究 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2023: 23–25, 53–56.LI Y. Load reduction mechanism and behavior characteristics of the buffering cap for the vehicle during the high-speed water entry [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2023: 23–25, 53–56. -






 下载:
下载: