Design of shield based on integrated effect of penetration and moving charge explosion of warheads
-
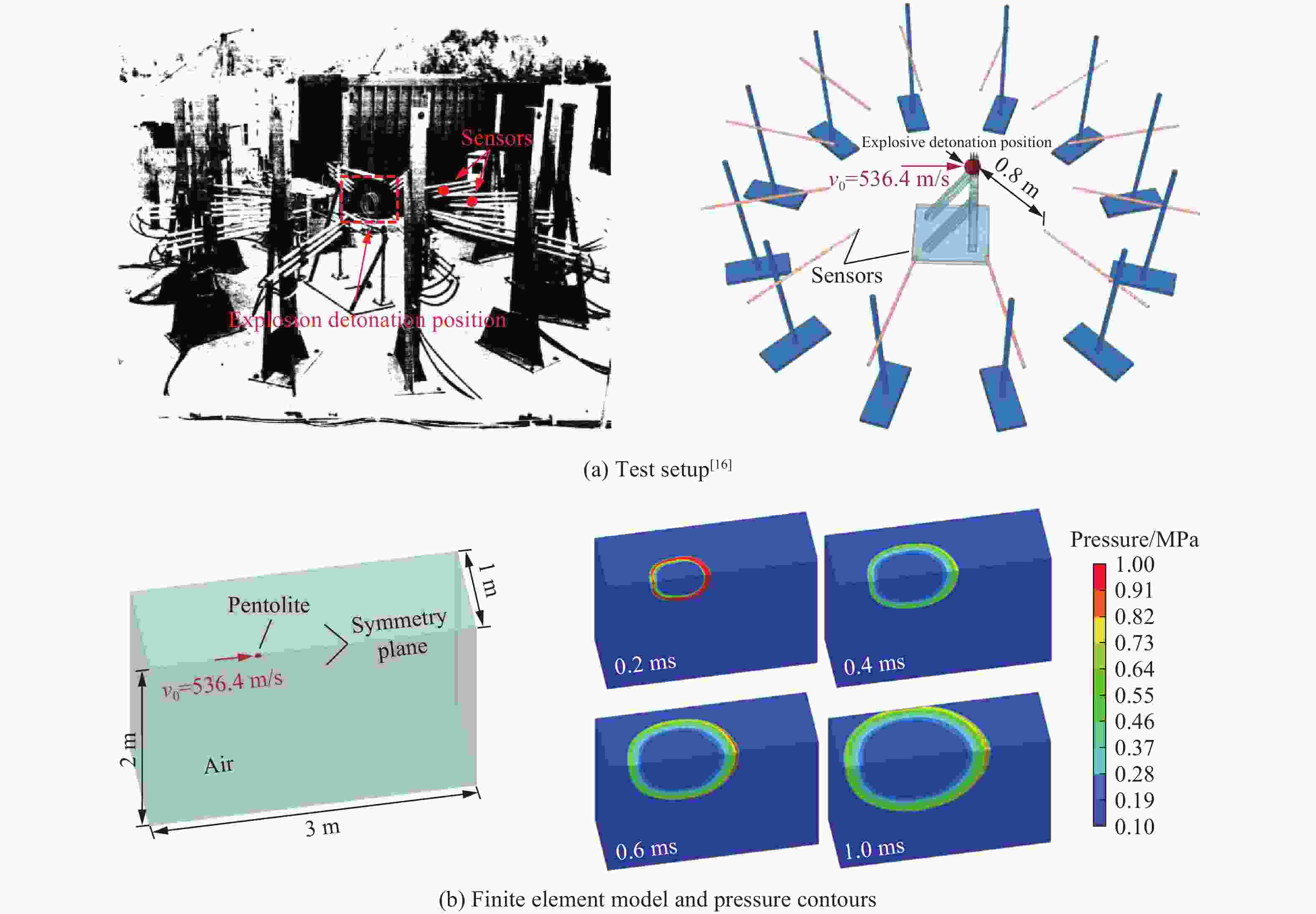
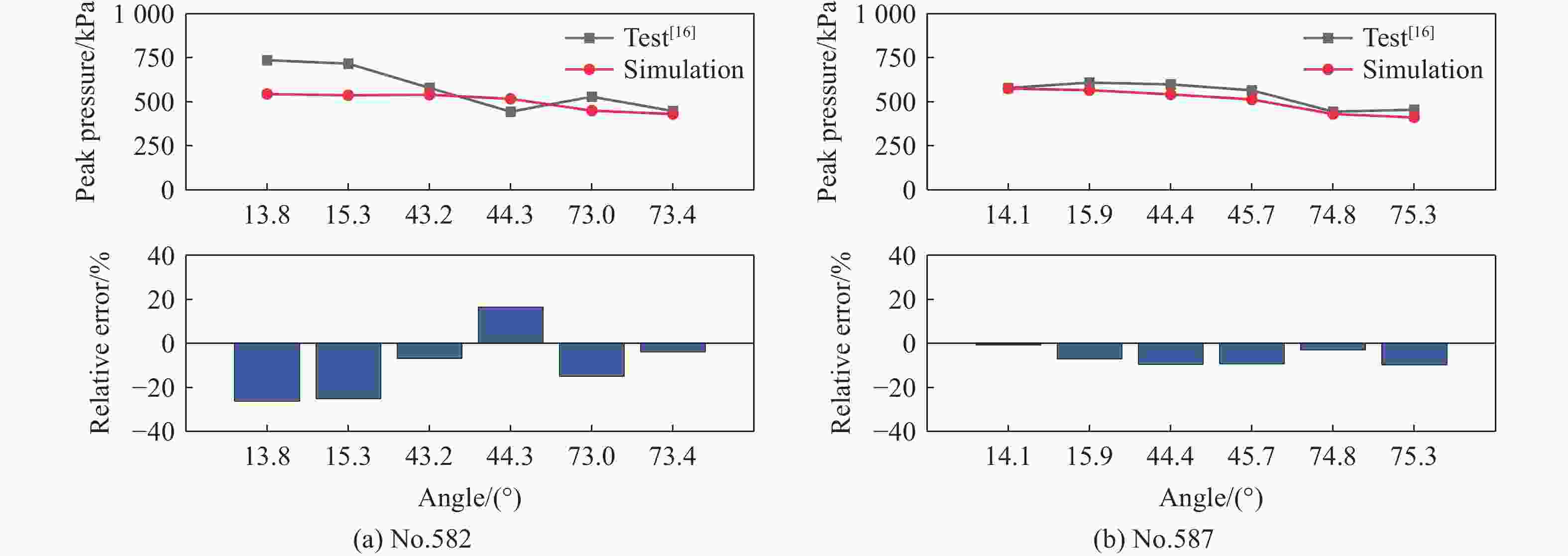
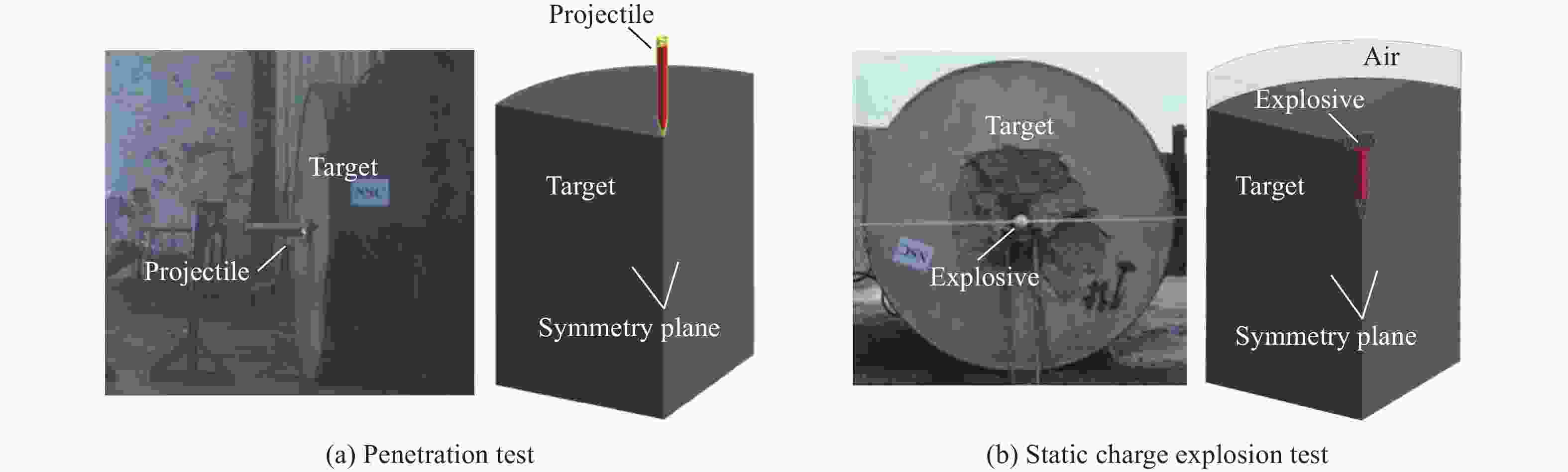
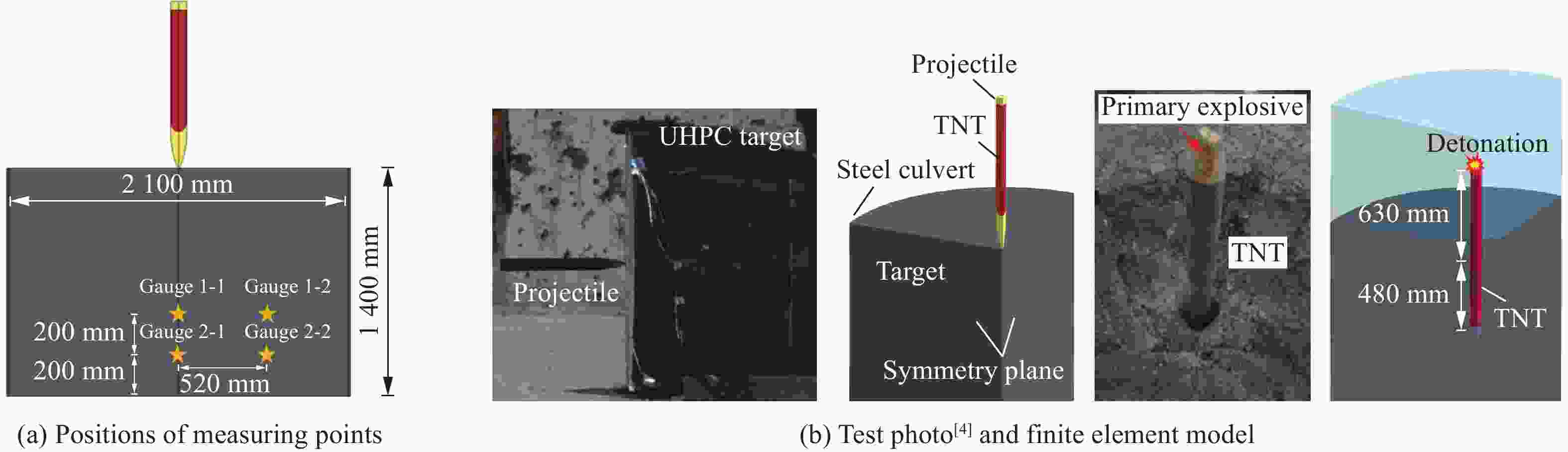
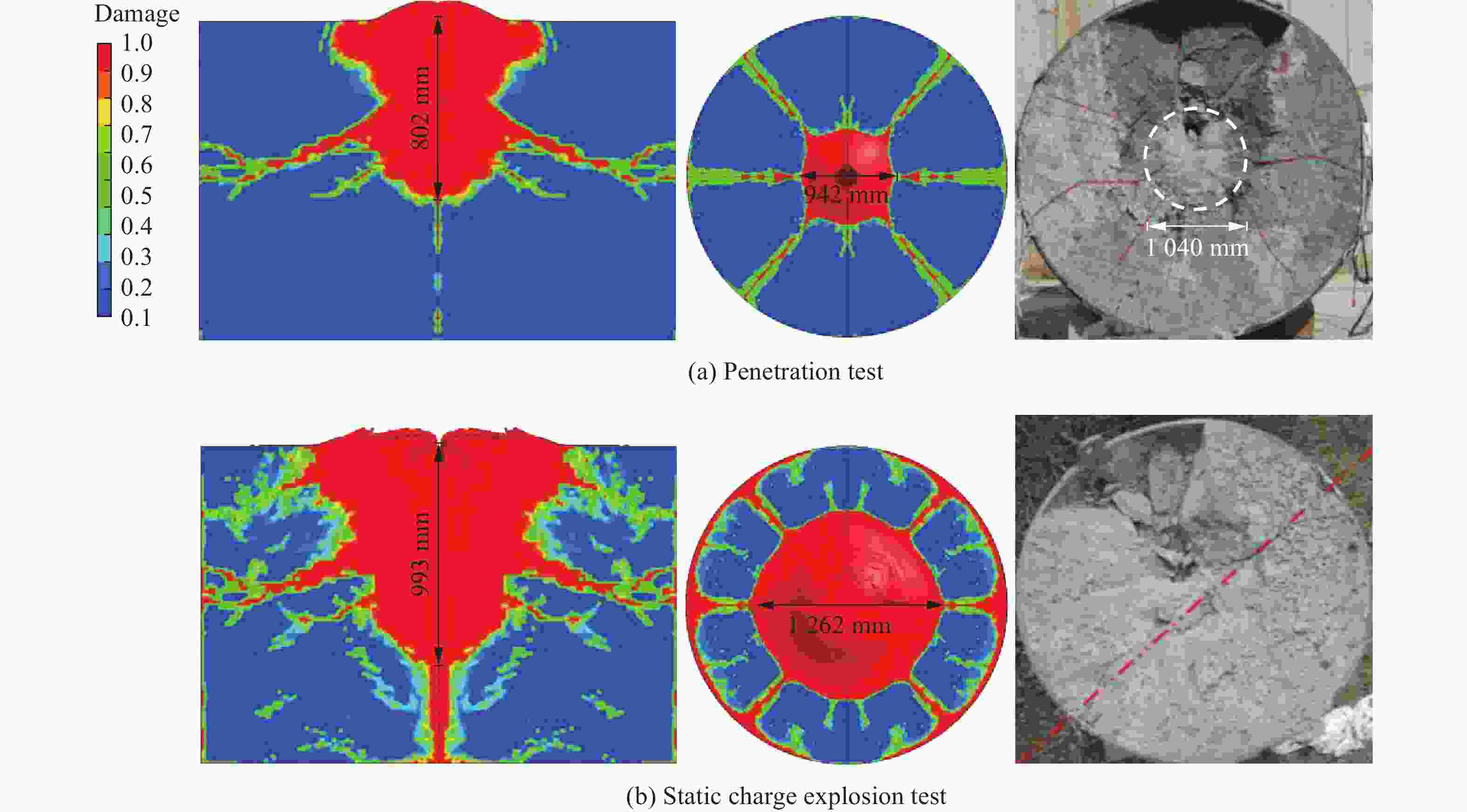
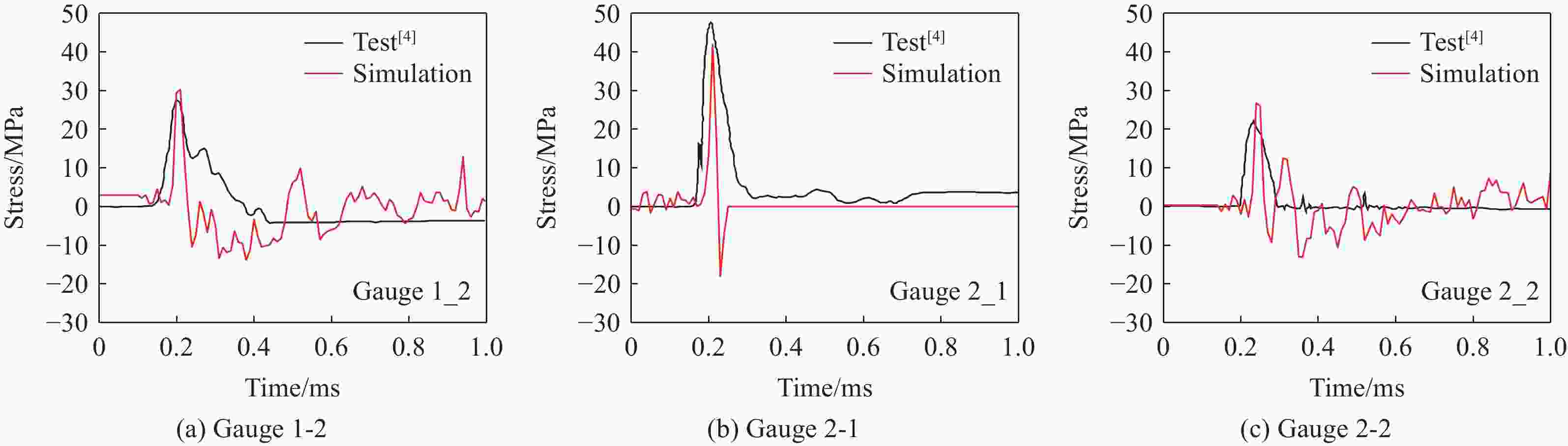
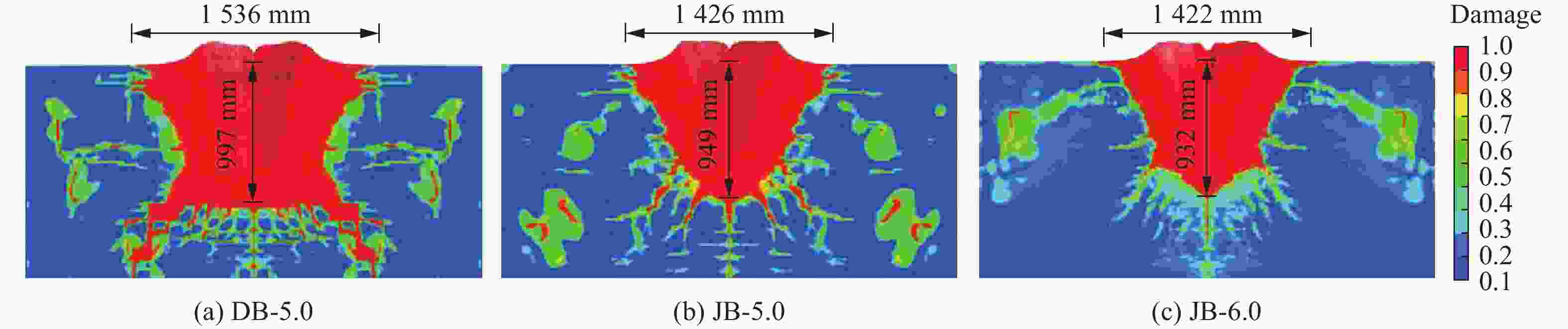
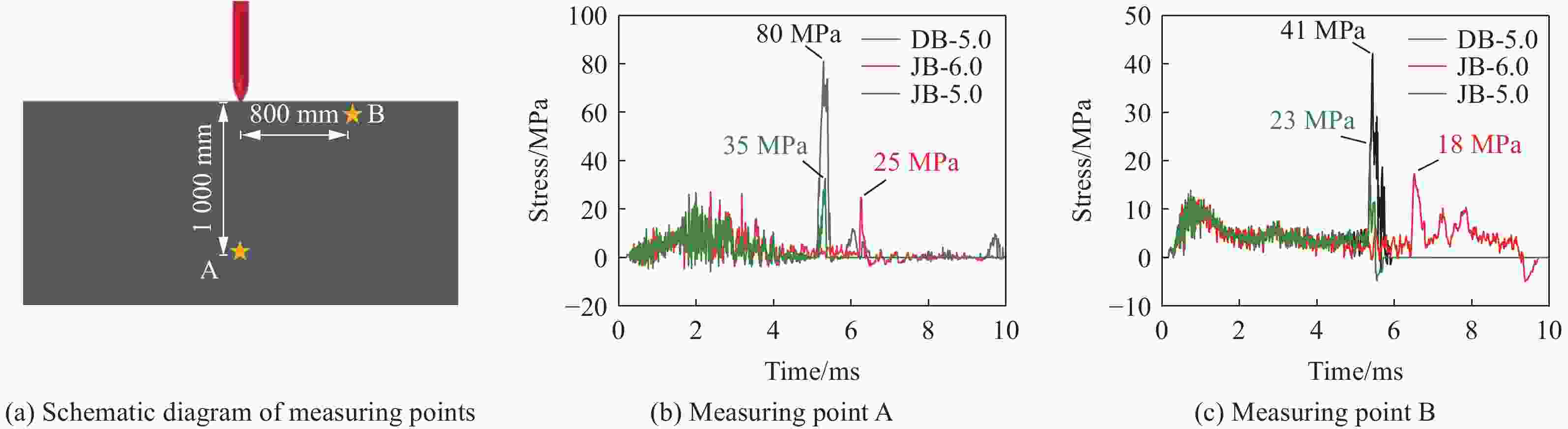
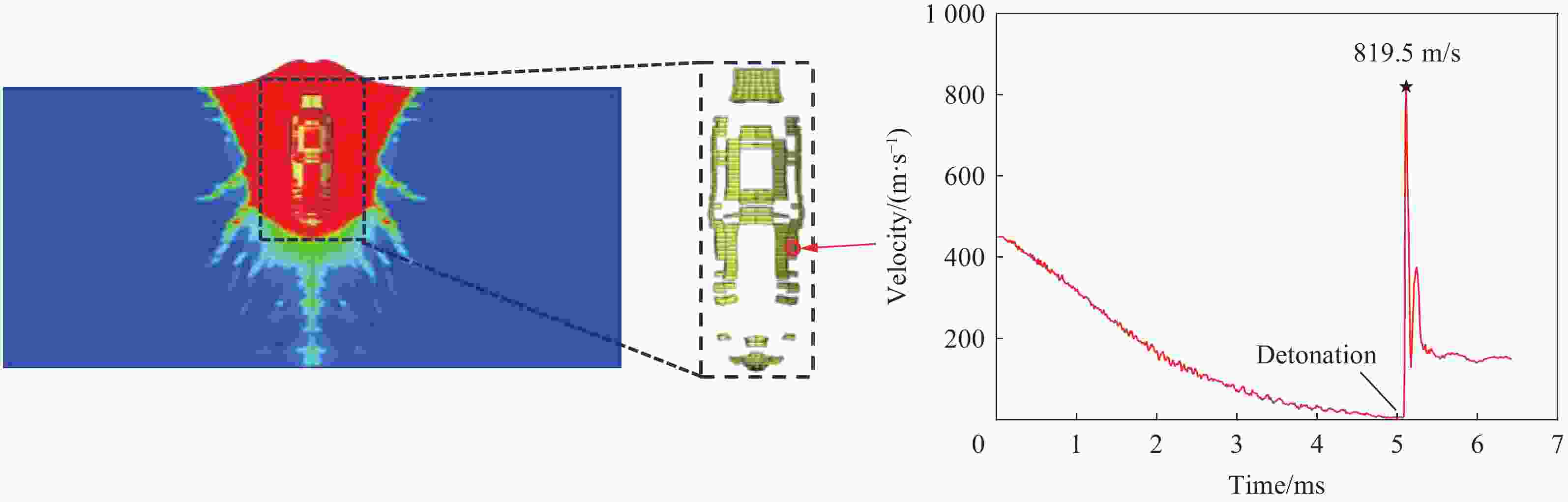
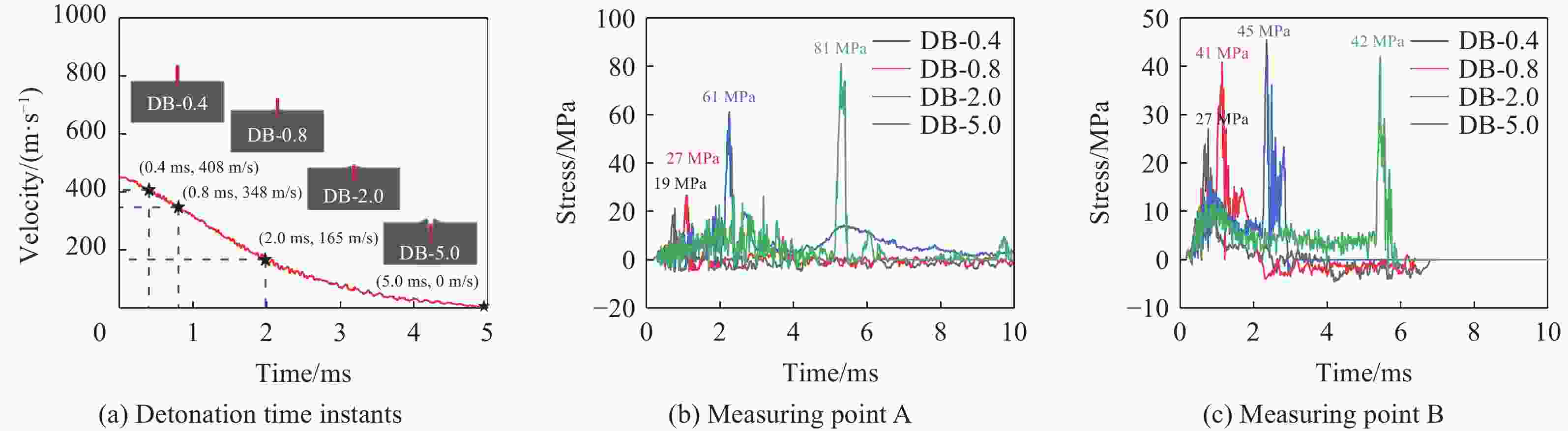
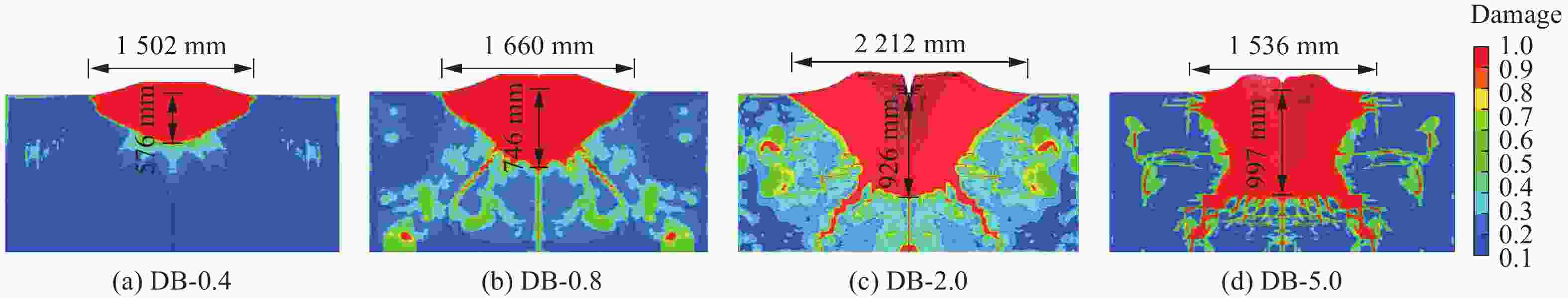
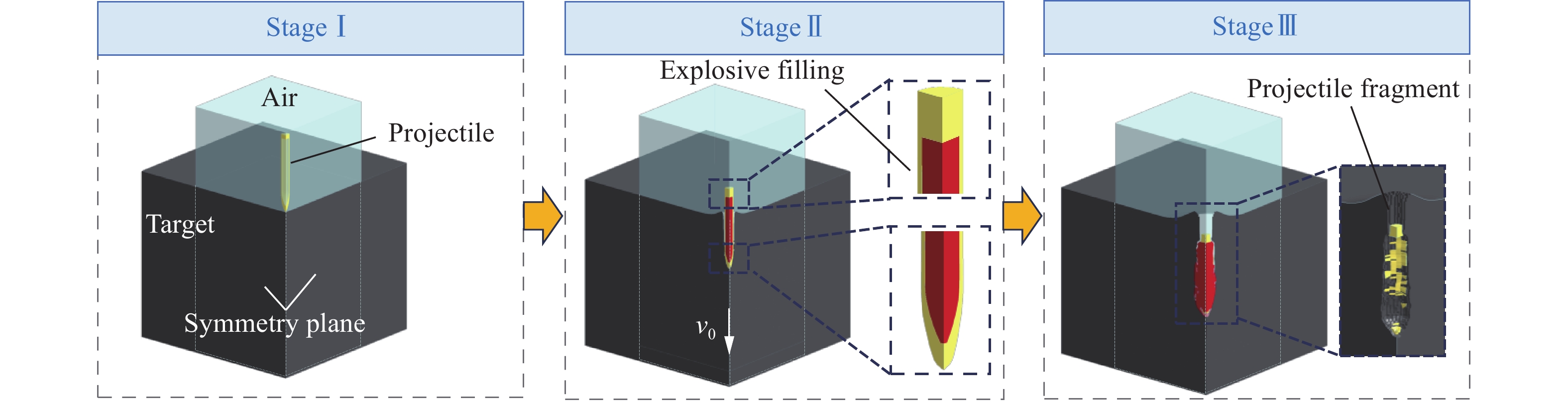
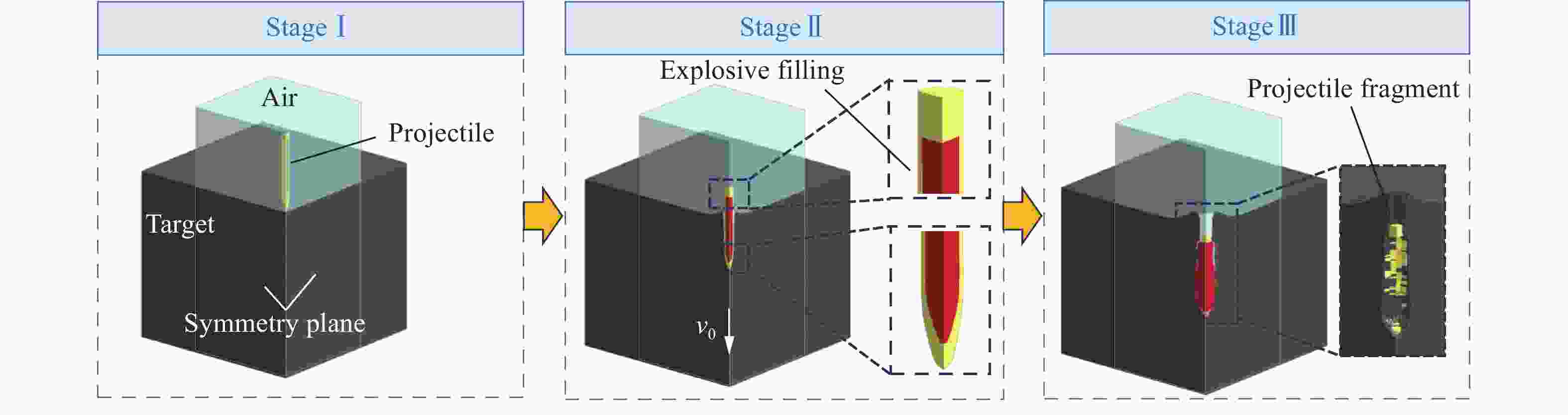
摘要: 准确评估钻地武器战斗部侵彻和装药运动爆炸(侵彻动爆)的连续作用是对防护结构遮弹层进行可靠设计的前提。首先,基于装药体积填充和侵彻爆炸分步耦合技术,提出了三阶段弹体侵彻动爆一体化有限元分析方法,通过与已有的装药运动爆炸试验以及普通混凝土(normal strength concrete,NSC)和超高性能混凝土(ultra-high performance concrete,UHPC)靶体的侵彻静爆试验结果进行对比,充分验证了所提出方法对侵彻爆炸过程中爆炸波传播、靶体内应力峰值和开裂行为及其损伤演化描述的准确性。然后,基于105 mm口径缩比弹体打击NSC靶体工况,对比了所提出方法与传统侵彻静爆法预测靶体损伤破坏的差异,分析了侵彻爆炸应力场的叠加效应以及弹壳约束和断裂破片的影响,并基于弹载装药在不同时刻起爆下靶体的破坏特征,确定了战斗部最不利起爆时刻。最后,针对SDB、WDU-43/B和BLU-109/B等3种原型战斗部打击工况开展数值模拟,其侵彻动爆作用下的NSC和UHPC遮弹层破坏深度分别为1.33、2.70、2.35 m和0.79、1.76、1.70 m,进一步给出了相应的遮弹层临界震塌厚度和临界贯穿厚度。结果表明,采用侵彻动爆一体化方法计算得到的破坏深度、临界震塌厚度和临界贯穿厚度较传统侵彻静爆法计算结果增大约5%~30%。Abstract: Accurately evaluating the continuous effect of penetration and moving charge explosion of earth penetrating weapons is the premise of reliable design of shield on the protective structure. Firstly, a three-stage integrated projectile penetration and moving charge explosion finite element analysis method was proposed based on the technologies of volume filling of explosive and the two-step coupling in penetration and explosion processes. By conducting the numerical simulations of the existing tests of moving charge explosion, penetration and static charge explosion of normal strength concrete (NSC) and ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) targets, the accuracy of the proposed method in describing the propagation of explosive waves, peak stress, cracking behavior and damage evolution of target under the penetration and explosion was fully verified. Besides, for the scenario of an NSC target against a 105 mm-caliber scaled projectile, the differences of target damage predicted by the proposed finite element analysis method and traditional penetration and static charge explosion method were compared. Meanwhile, the superimposed effect of the penetration and explosion stress field and the influence of shell constraint and fracture fragment were analyzed. Based on the damage characteristics of targets at different detonation time instants of explosive, the most unfavorable detonation time instant of the warhead was determined. Finally, numerical simulations were conducted for the scenarios of three prototype warheads: SDB, WDU-43/B and BLU-109/B. The destructive depths of NSC and UHPC shields subjected to the penetration and moving charge explosion loadings are 1.33, 2.70, 2.35 m and 0.79, 1.76, 1.70 m, respectively. The corresponding scabbing and perforation limits of shields were further given. The results show that the destructive depths, scabbing limits and perforation limits calculated by the finite element analysis method with considering integrated penetration and moving charge explosion are about 5%–30% higher than those calculated by the traditional penetration and static charge explosion method.
-
表 1 炸药材料模型和状态方程参数
Table 1. Parameters for material model and equation of state of explosives
表 2 NSC的RHT模型和状态方程参数[21]
Table 2. Parameters for RHT material model and equation of state of NSC[21]
σc/MPa G/GPa $\sigma_{\mathrm{t}}^{*} $ $\sigma_{\mathrm{s}}^{*} $ $ g_{\text{c}}^{\text{*}} $ $ g_{\text{t}}^{\text{*}} $ $\xi $ A 32 16.546 0.1 0.18 0.53 0.7 0.5 1.6 n Q0 B Af nf D1 D2 $ \varepsilon _{\text{p}}^{\text{m}} $ 0.61 0.680 5 0.010 5 1.6 0.61 0.04 1.0 0.01 ρ0/(kg·m−3) α0 pE/MPa pC/MPa N A1/GPa A2/GPa A3/GPa 2 300 1.191 2 21.3 6 000 3 35.27 39.58 9.04 B0 B1 T1/GPa T2/GPa $ \dot \varepsilon _{\text{0}}^{\text{c}} $/s−1 $ \dot \varepsilon _{\text{0}}^{\text{t}} $/s−1 βc βt 1.22 1.22 35.27 0 3×10−5 3×10−6 0.034 0.038 表 3 NSC靶体试验[3]与数值模拟破坏深度和开坑直径对比
Table 3. Comparisons of test[3] and simulated destructive depths and cracking diameters of NSC target
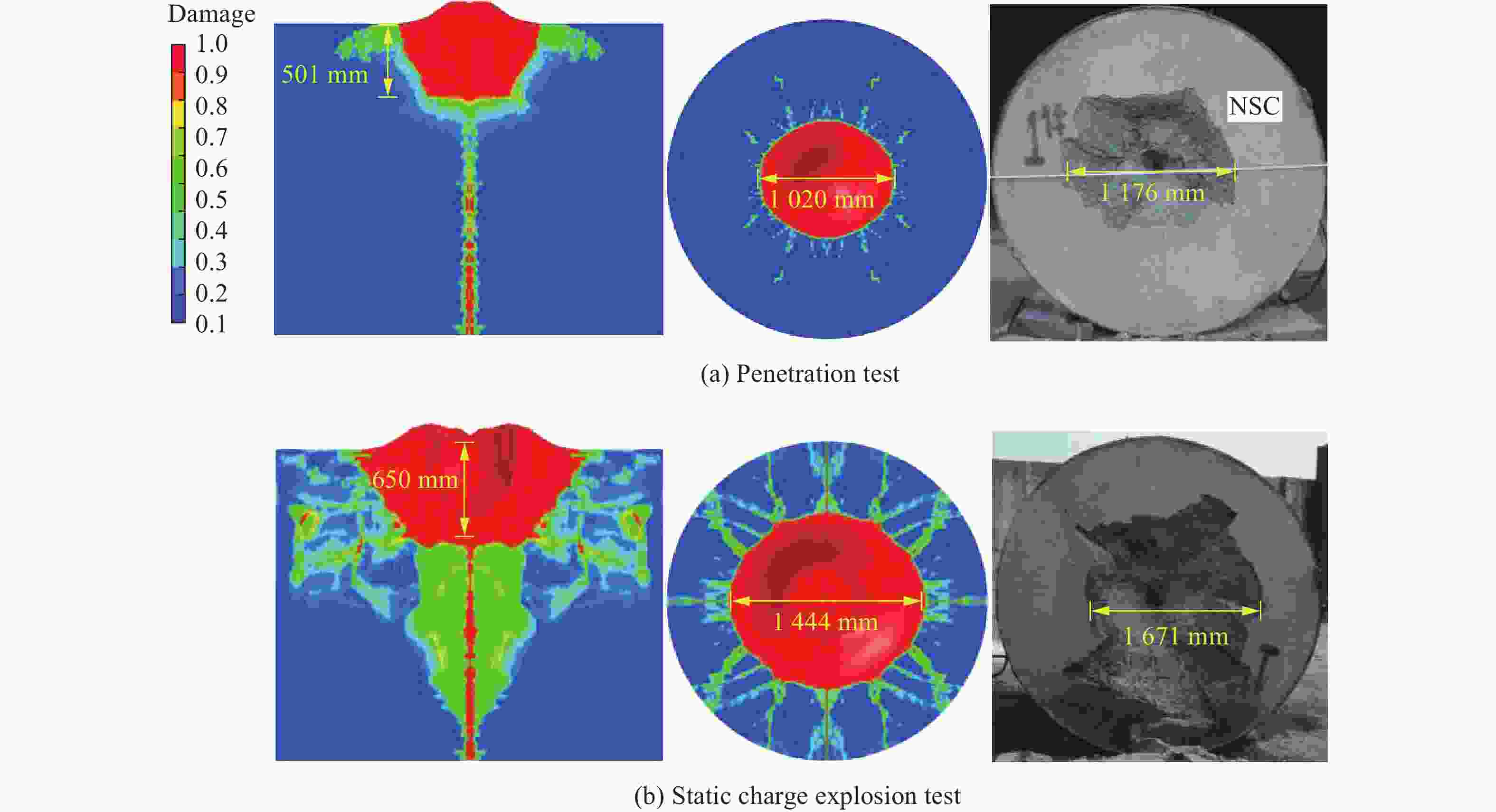
试验 破坏深度 开坑直径 试验/mm 模拟/mm 相对误差/% 试验/mm 模拟/mm 相对误差/% 侵彻阶段 515 501 −2.72 1 176 1 020 −13.27 静爆阶段 680 650 −4.41 1 671 1 444 −13.58 表 4 UHPC的RHT模型和状态方程参数[21]
Table 4. Parameters for RHT material model and equation of state of UHPC[21]
σc/MPa G/GPa $\sigma_{\mathrm{t}}^{*} $ $\sigma_{\mathrm{s}}^{*} $ $ g_{\text{c}}^{\text{*}} $ $ g_{\text{t}}^{\text{*}} $ $\xi $ A 123.5 20.9 0.070 7 0.267 0.53 0.7 0.67 1.6 n Q0 B Af nf D1 D2 $ \varepsilon _{\text{p}}^{\text{m}} $ 0.61 0.681 0.010 5 1.75 0.52 0.04 1.0 0.08 ρ0/(kg·m−3) α0 pE/MPa pC/MPa N A1/GPa A2/GPa A3/GPa 2 500 1.191 2 46.6 6 000 4 44 29.58 11.28 B0 B1 T1/GPa T2/GPa $ \dot \varepsilon _{\text{0}}^{\text{c}} $/s−1 $ \dot \varepsilon _{\text{0}}^{\text{t}} $/s−1 βc βt 1.22 1.22 44 0 3×10−5 3×10−6 0.012 5 0.014 3 表 5 30CrMnSiNi2MoVE钢的Johnson-Cook模型参数[22]
Table 5. Johnson-Cook model parameters of 30CrMnSiNi2MoVE steel[22]
ρ/(kg·m−3) G/GPa A0/MPa B0/MPa N0 C M Tm/K Tr/K cV/(J·kg−1·K−1) $ {\dot \varepsilon _0} $/s−1 7 800 81 1 300 2 483 0.474 0.009 1.07 1 793 289 477 1×10−4 ε0 D0 D3 D4 D5 C0/(m·s−1) S1 S2 S3 γ0 α 0.692 1.581 −3.053 −0.042 2.98 4 569 1.49 0 0 2.17 0.46 表 6 3种原型战斗部参数
Table 6. Parameters of three prototypical warheads
战斗部 直径/mm 总质量/kg 长度/mm 弹壳壁厚/mm 头部曲径比 装药类型 装药质量/kg 等效TNT质量/kg SDB 152 113 1 800 10.8 3 HMX 15.3 23 WDU-43/B 234 454 2 400 41.5 9 HMX 66.7 100 BLU-109/B 368 874 2 510 25.4 3 PBXN-109 238 324 表 7 3种原型战斗部打击NSC和UHPC遮弹层计算结果
Table 7. Calculation results of NSC and UHPC shields against three prototypical warheads
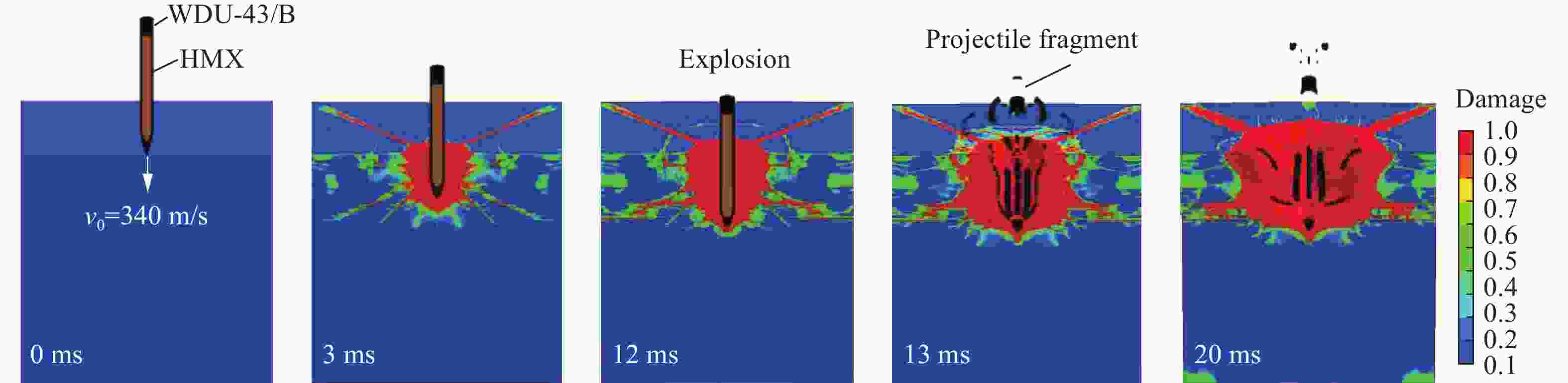
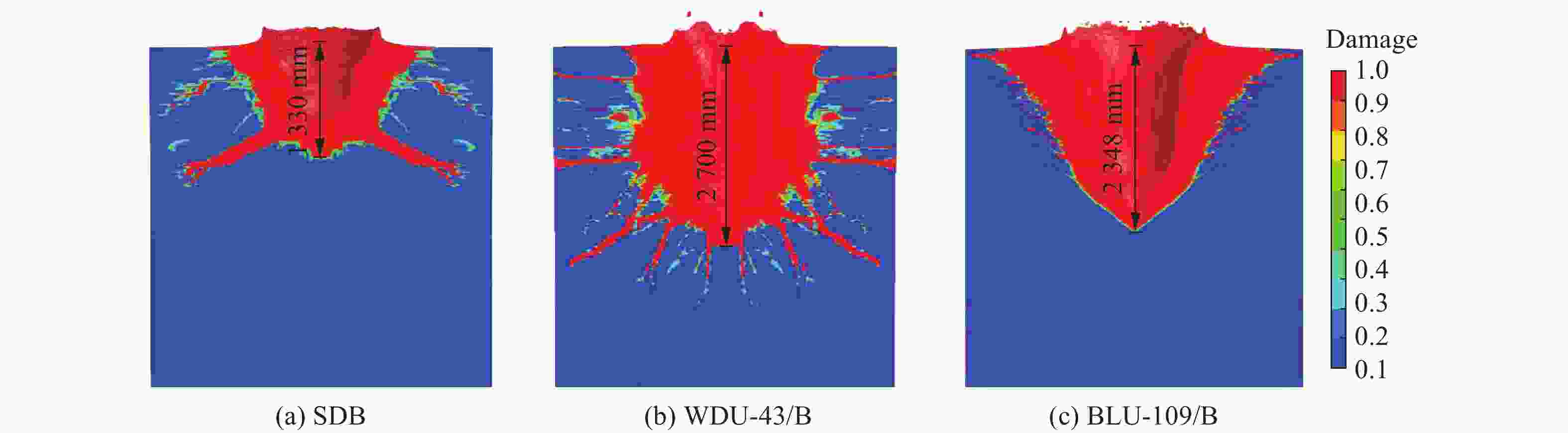
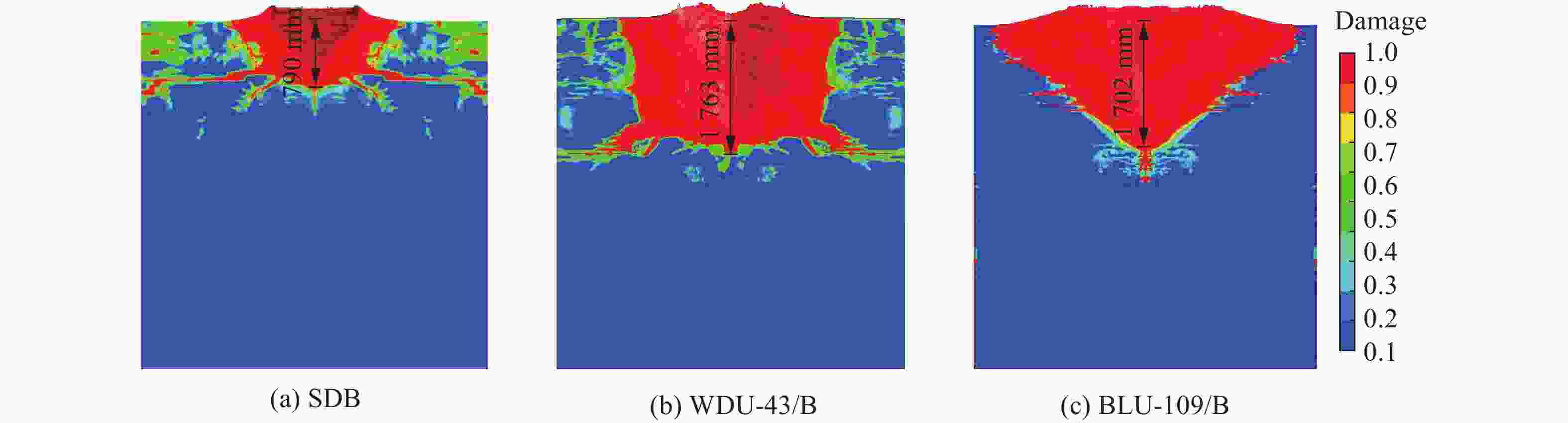
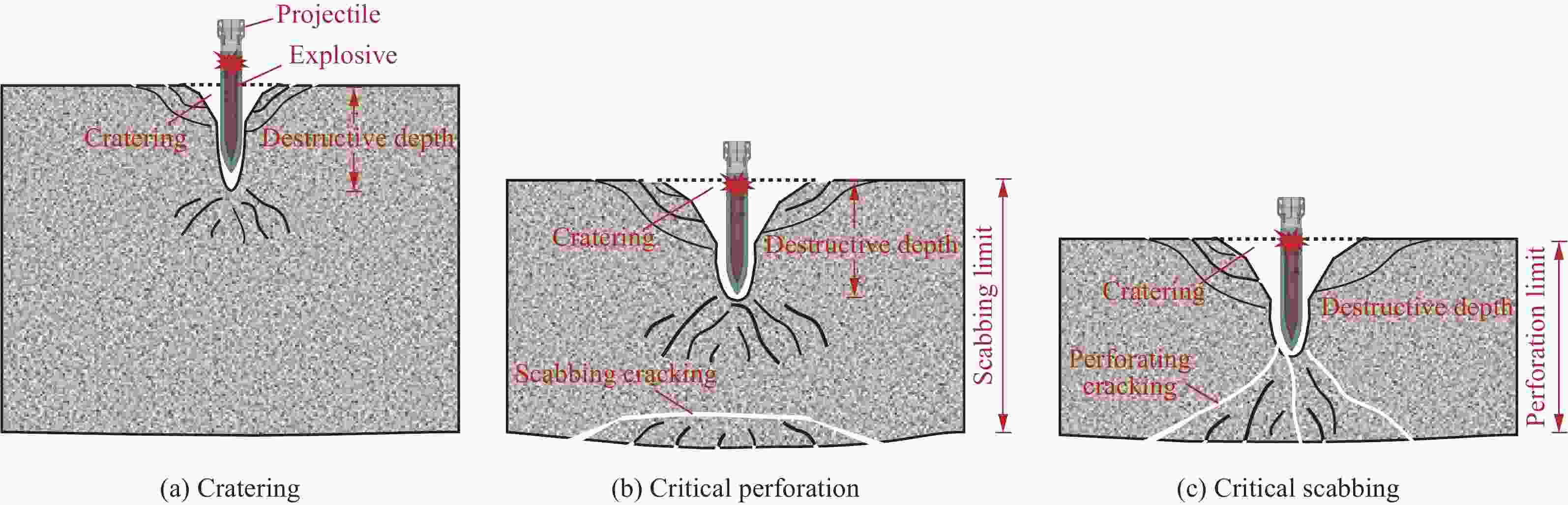
战斗部 遮弹层类型 侵彻爆炸破坏深度/m 相对差值/% 临界震塌厚度/m 临界贯穿厚度/m 侵彻静爆法[3, 26] 侵彻动爆法 系数[3, 26] 侵彻静爆法[3, 26] 侵彻动爆法 系数[3, 26] 侵彻静爆法[3, 26] 侵彻动爆法 SDB NSC 1.03 1.33 29.13 3.50 3.60 4.66 1.36 1.40 1.81 UHPC 0.74 0.79 6.76 2.30 1.70 1.82 1.76 1.30 1.39 WDU-43/B NSC 2.45 2.70 10.20 2.57 6.30 6.94 1.39 3.40 3.75 UHPC 1.61 1.76 9.50 2.36 3.80 4.16 1.58 2.55 2.79 BLU-109/B NSC 2.18 2.35 7.71 3.81 8.30 8.95 1.74 3.80 4.09 UHPC 1.62 1.70 5.06 3.09 5.00 5.26 1.60 2.60 2.72 -
[1] FAN Y, CHEN L, YU R Q, et al. Experimental study of damage to ultra-high performance concrete slabs subjected to partially embedded cylindrical explosive charges [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 168: 104298. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104298. [2] LAI J Z, GUO X J, ZHU Y Y. Repeated penetration and different depth explosion of ultra-high performance concrete [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 84: 1–12. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.05.006. [3] 程月华, 周飞, 吴昊. 抗战斗部侵彻爆炸作用的混凝土遮弹层设计 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(4): 045101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0346.CHENG Y H, ZHOU F, WU H. Design of concrete shield against the combination of penetration and explosion of warheads [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(4): 045101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0346. [4] YANG Y Z, FANG Q, KONG X Z. Failure mode and stress wave propagation in concrete target subjected to a projectile penetration followed by charge explosion: experimental and numerical investigation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 177: 104595. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104595. [5] 赖建中, 尹雪祥, 李宏基, 等. 基于功能梯度原理的超高性能混凝土抗侵彻爆炸性能 [J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(8): 1188–1200. DOI: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20200231.LAI J Z, YIN X X, LI H J, et al. Anti-penetration and explosion performance of ultra-high performance concrete based on the principle of functional gradient [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 48(8): 1188–1200. DOI: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20200231. [6] CHENG Y H, ZHOU F, WU H, et al. Resistance of composite target against combined effects of large caliber projectile penetration and successive charge explosion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 168: 104288. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104288. [7] 李述涛, 魏万里, 陈叶青, 等. 基于体积填充法的弹体侵爆一体毁伤效应研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2023, 42(12): 194–204. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.012.022.LI S T, WEI W L, CHEN Y Q, et al. A study on damage effect of projectile penetration and explosion integration based on a volume filling method [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2023, 42(12): 194–204. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2023.012.022. [8] WEI W L, CHEN Y Q, WANG Z Q, et al. Research on damage effect of the concrete target under the penetration and explosion integration [J]. Structures, 2023, 47: 1511–1523. DOI: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.11.083. [9] WEI W L, CHEN Y Q, WANG Z Q, et al. Research on damage effect of penetration and explosion integration based on volume filling method [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 177: 104591. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104591. [10] FORRESTAL M J, FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, et al. Penetration of grout and concrete targets with ogive-nose steel projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1996, 18(5): 465–476. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(95)00048-F. [11] 孙传杰, 卢永刚, 张方举, 等. 新型头形弹体对混凝土的侵彻 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2010, 30(3): 269–275. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)03-0269-07.SUN C J, LU Y G, ZHANG F J, et al. Penetration of cylindrical-nose-tip projectiles into concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2010, 30(3): 269–275. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2010)03-0269-07. [12] 王可慧, 周刚, 李明, 等. 弹体高速侵彻钢筋混凝土靶试验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(11): 113302. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0463.WANG K H, ZHOU G, LI M, et al. Experimental research on the mechanism of a high-velocity projectile penetrating into a reinforced concrete target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(11): 113302. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0463. [13] GAO C, KONG X Z, FANG Q. Experimental and numerical investigation on the attenuation of blast waves in concrete induced by cylindrical charge explosion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 174: 104491. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104491. [14] 高矗, 孔祥振, 方秦, 等. 混凝土中爆炸应力波衰减规律的数值模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(12): 123202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0041.GAO C, KONG X Z, FANG Q, et al. Numerical study on attenuation of stress wave in concrete subjected to explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(12): 123202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0041. [15] 王银, 孔祥振, 方秦, 等. 弹体对混凝土材料先侵彻后爆炸损伤破坏效应的数值模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(1): 013301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0132.WANG Y, KONG X Z, FANG Q, et al. Numerical investigation on damage and failure of concrete targets subjected to projectile penetration followed by explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(1): 013301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0132. [16] ARMENDT B F, SPERRAZZA J. Air blast measurements around moving explosive charges, part Ⅲ: AD0114950 [R]. Aberdeen: Army Ballistics Research Laboratory, 1956. [17] MARRS F, HEIGES M. Soil modeling for mine blast simulation [C]//13th International LS-DYNA Users Conference. Dearborn: Schwer Engineering and Consulting Services, 2014. [18] DOBRATZ B M. LLNL explosives handbook: properties of chemical explosives and explosives and explosive simulants: UCRL-52997 [R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 1981. [19] LEE L, FINGER M, COLLINS W. JWL Equation of state coefficients for high explosive: UCID-16189 [R]. Livermore: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, 1973. [20] LU J P, LOCHERT I J, KENNEDY D L, et al. Simulation of sympathetic reaction tests for PBXN-109 [C]//Proceedings of 13th International Symposium on Detonation. New York: ISB, 2006: 1338–1349. [21] RIEDEL W, THOMA K, HIERMAIER S, et al. Penetration of reinforced concrete by BETA-B-500, numerical analysis using a new macroscopic concrete model for hydrocodes [C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Interaction of the Effects of Munitions with Structures. Berlin: ISIEMS, 1999: 315–322. [22] CHENG Y H, WU H, JIANG P F, et al. Ballistic resistance of high-strength armor steel against ogive-nosed projectile impact [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 183: 110350. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2022.110350. [23] 刘彦, 段卓平, 王新生, 等. 不同厚度壳体装药在混凝土中爆炸的实验研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2010, 30(7): 771–773, 848. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2010.07.008.LIU Y, DUAN Z P, WANG X S, et al. Experiments on explosion of explosives with different thickness shells in concrete [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2010, 30(7): 771–773, 848. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2010.07.008. [24] 陈龙明, 李志斌, 陈荣. 装药动爆冲击波特性研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(1): 013201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0029.CHEN L M, LI Z B, CHEN R. Characteristics of dynamic explosive shock wave of moving charge [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(1): 013201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0029. [25] 欧育湘. 炸药学 [M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014: 213–230.OU Y X. Explosives [M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 213–230. [26] 程月华, 吴昊, 岑国华, 等. 侵彻爆炸联合作用下超高性能混凝土遮弹层设计 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2025, 45(1): 013301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0061.CHENG Y H, WU H, CEN G H, et al. Design of ultra-high performance concrete shield against combined penetration and explosion of warheads [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2025, 45(1): 013301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0061. [27] 吴昊, 张瑜, 程月华, 等. 典型战斗部侵彻爆炸下块石混凝土的遮弹层设计 [J/OL]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024[2024-07-08] https://www.bzycj.cn/article/doi/ 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0136. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0136.WU H, ZHANG Y, CHENG Y H, et al. Design of rock-rubble concrete shield against the combination of penetration and explosion of warheads [J/OL]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024[2024-07-08] https://www.bzycj.cn/article/doi/ 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0136. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0136. -






 下载:
下载: