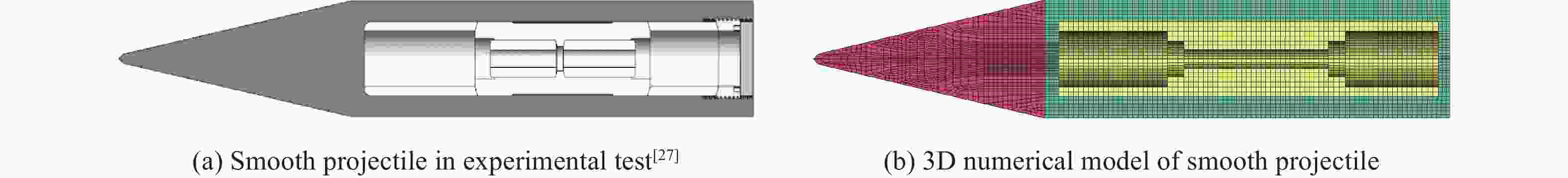
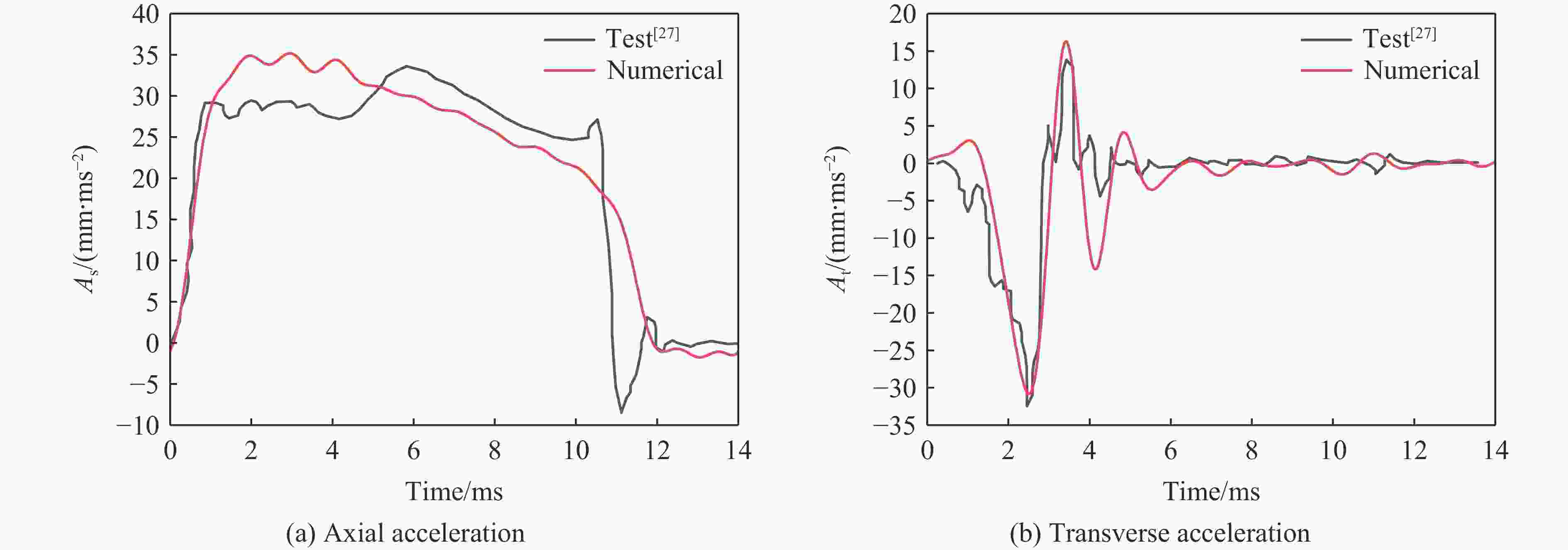
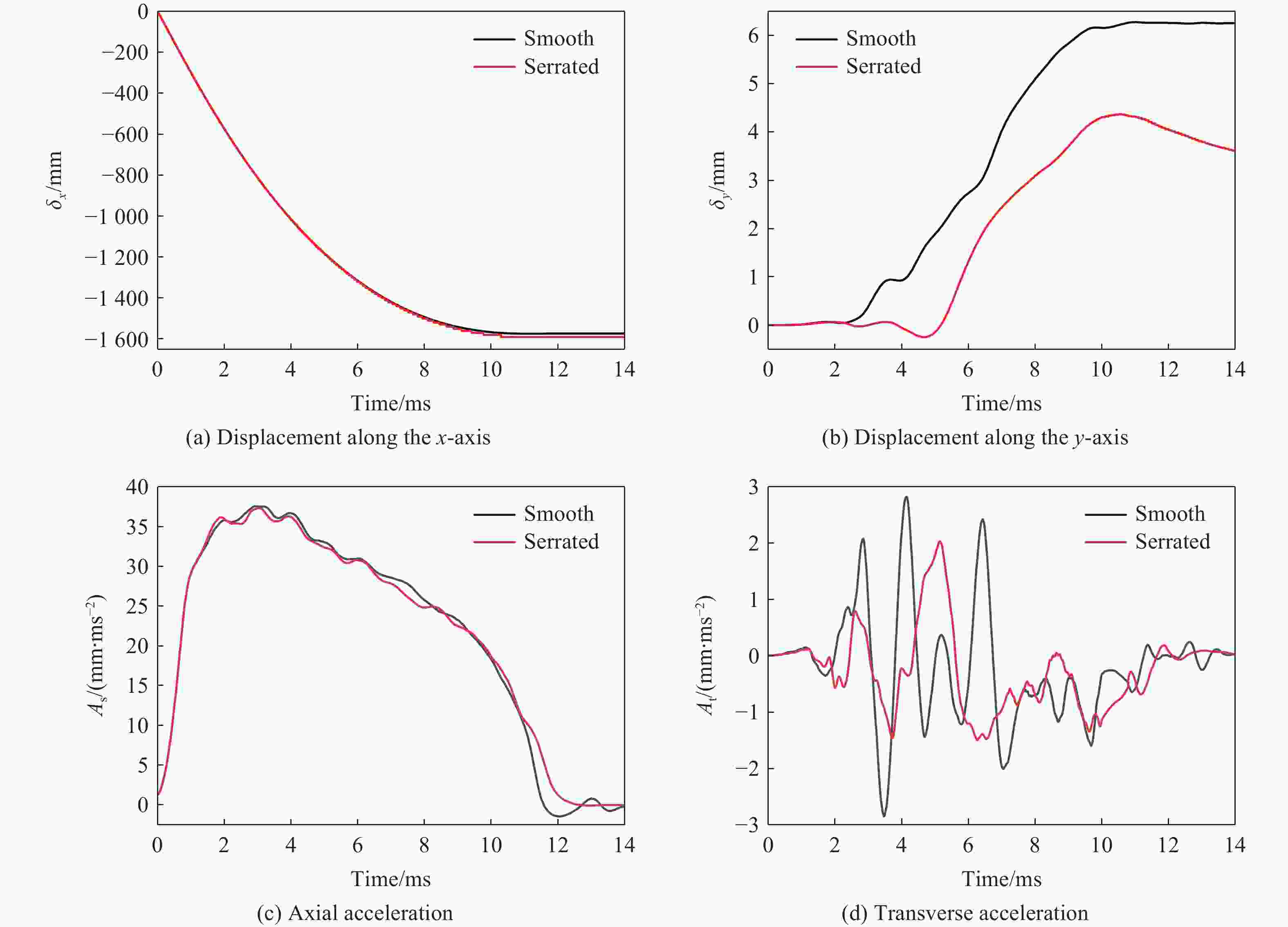
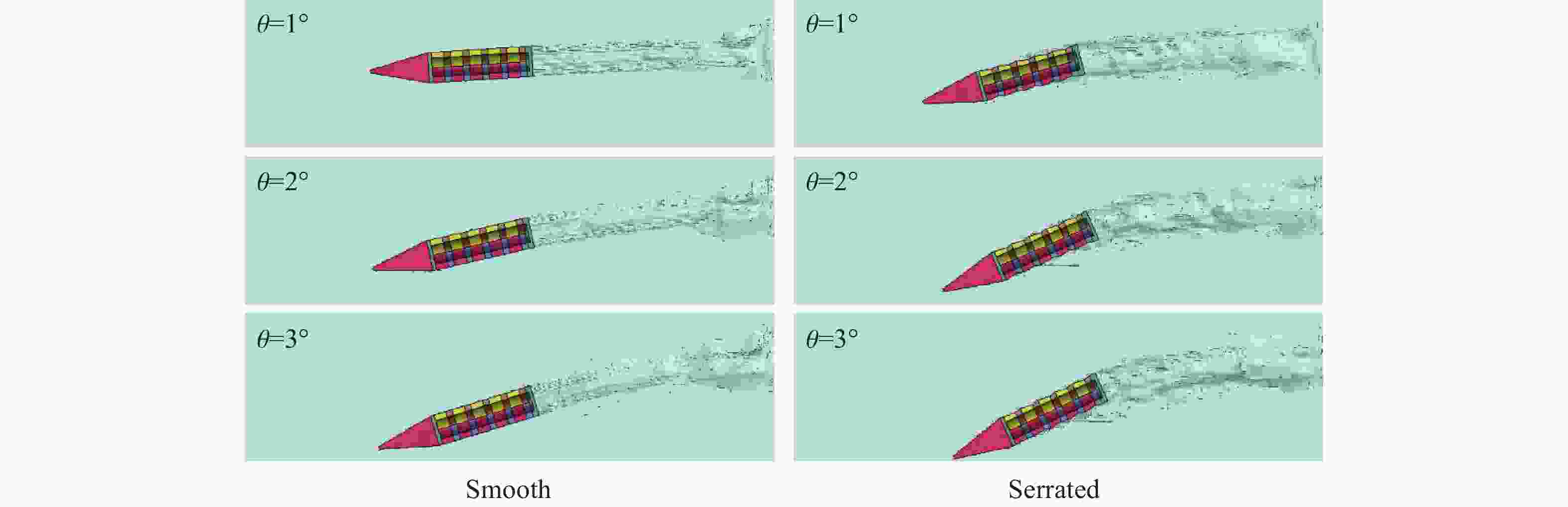
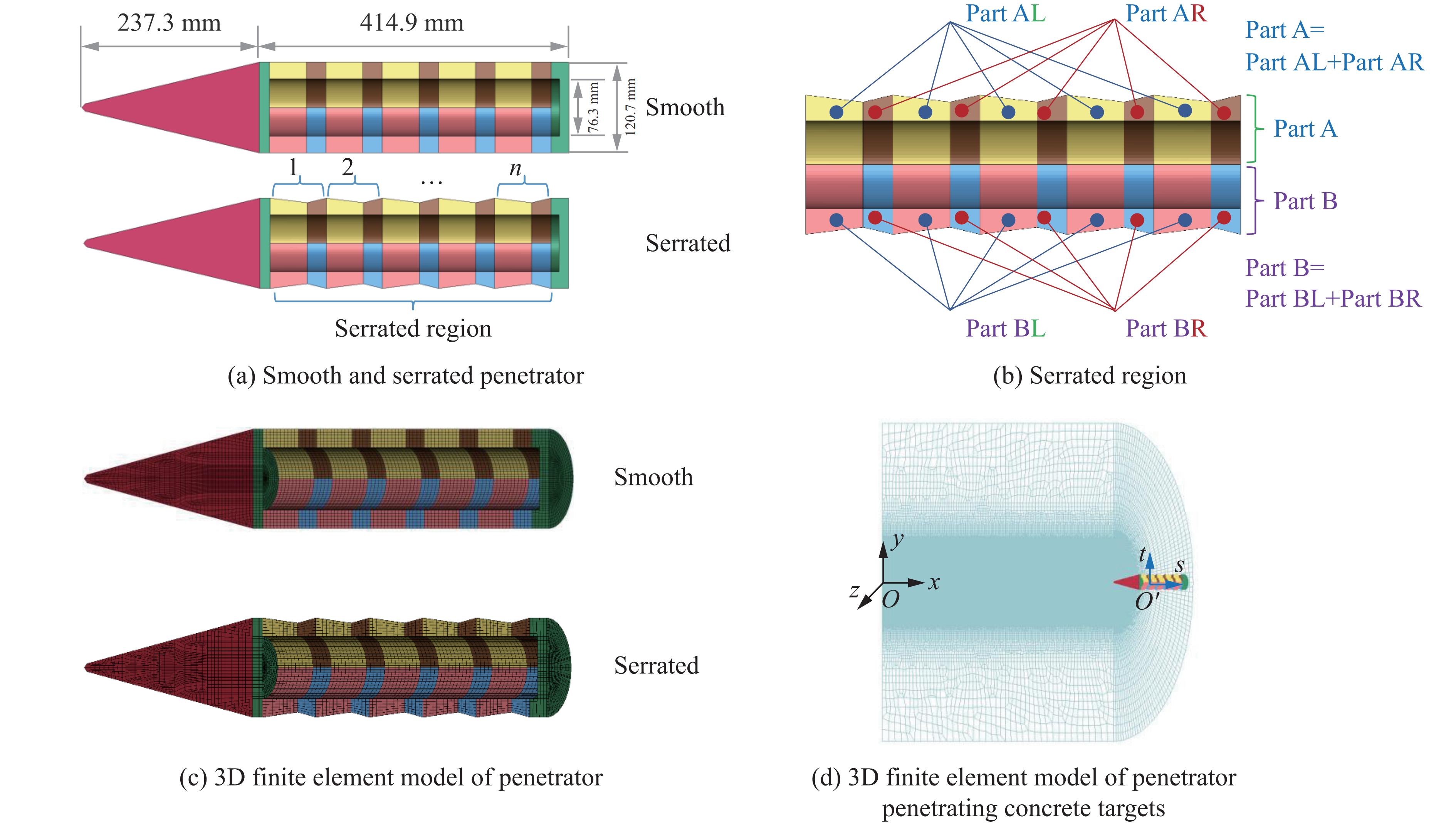
Influence of serrated configuration on transverse overload ofthe projectile penetrating with a small attack angle
-
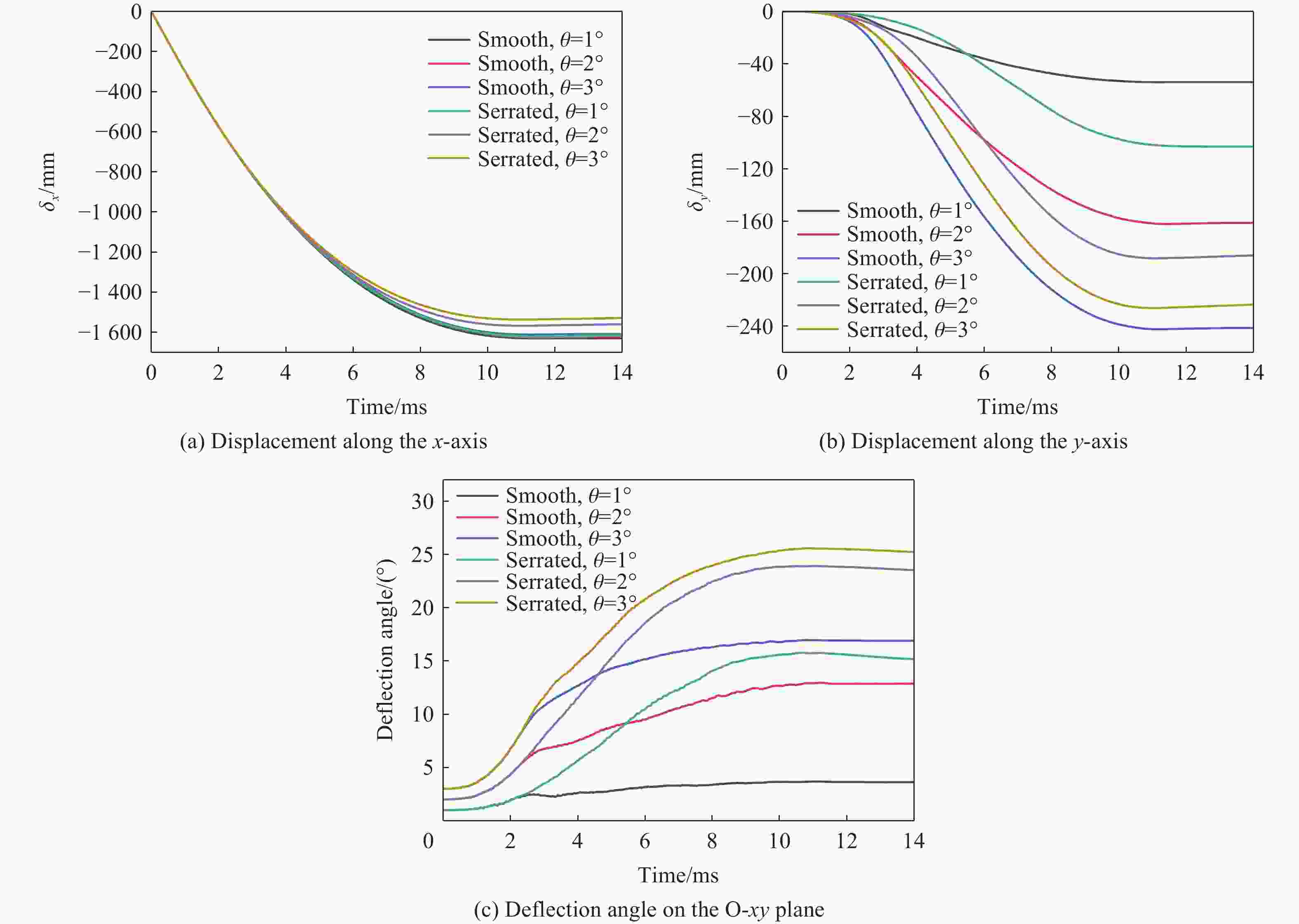
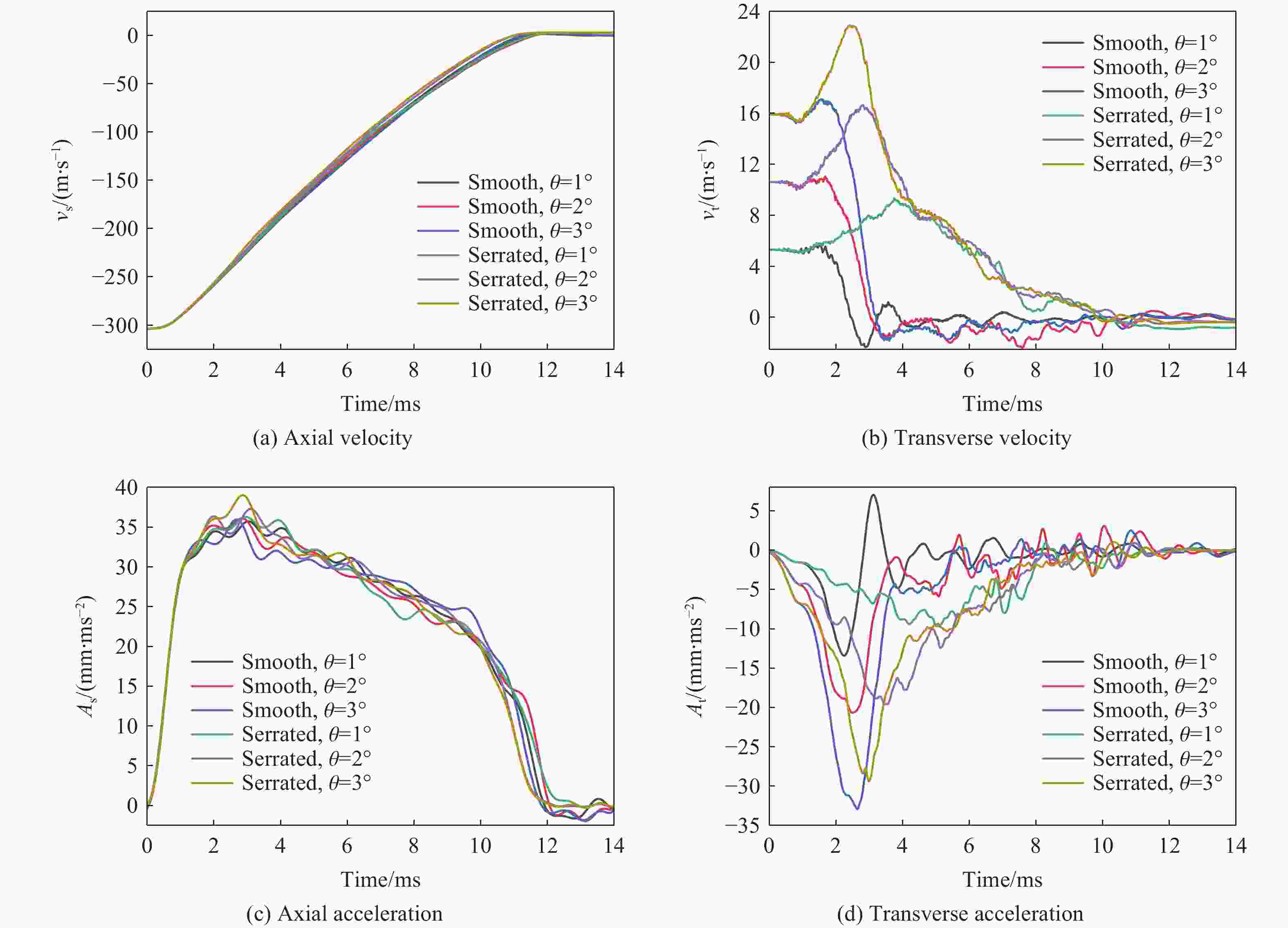
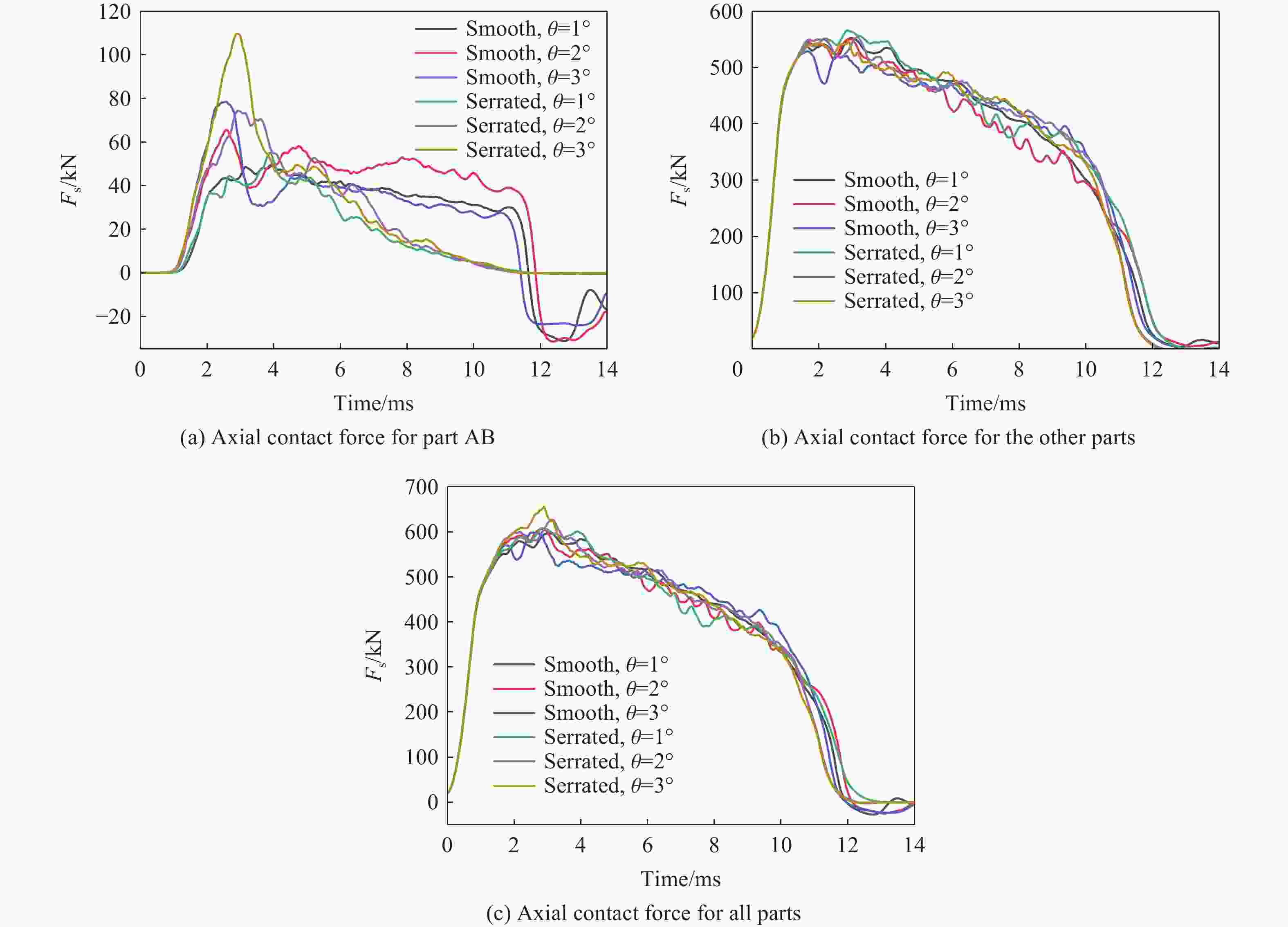
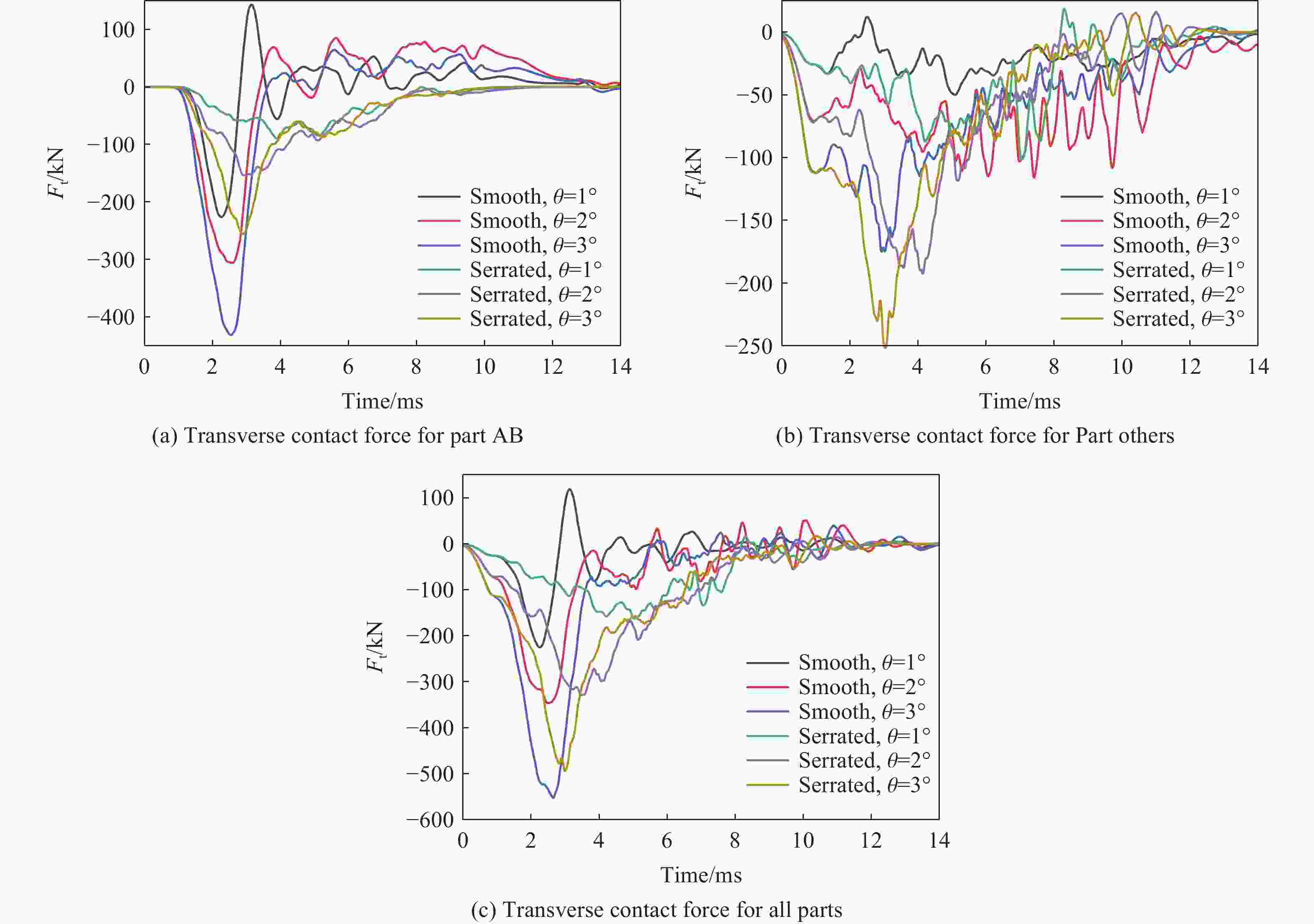
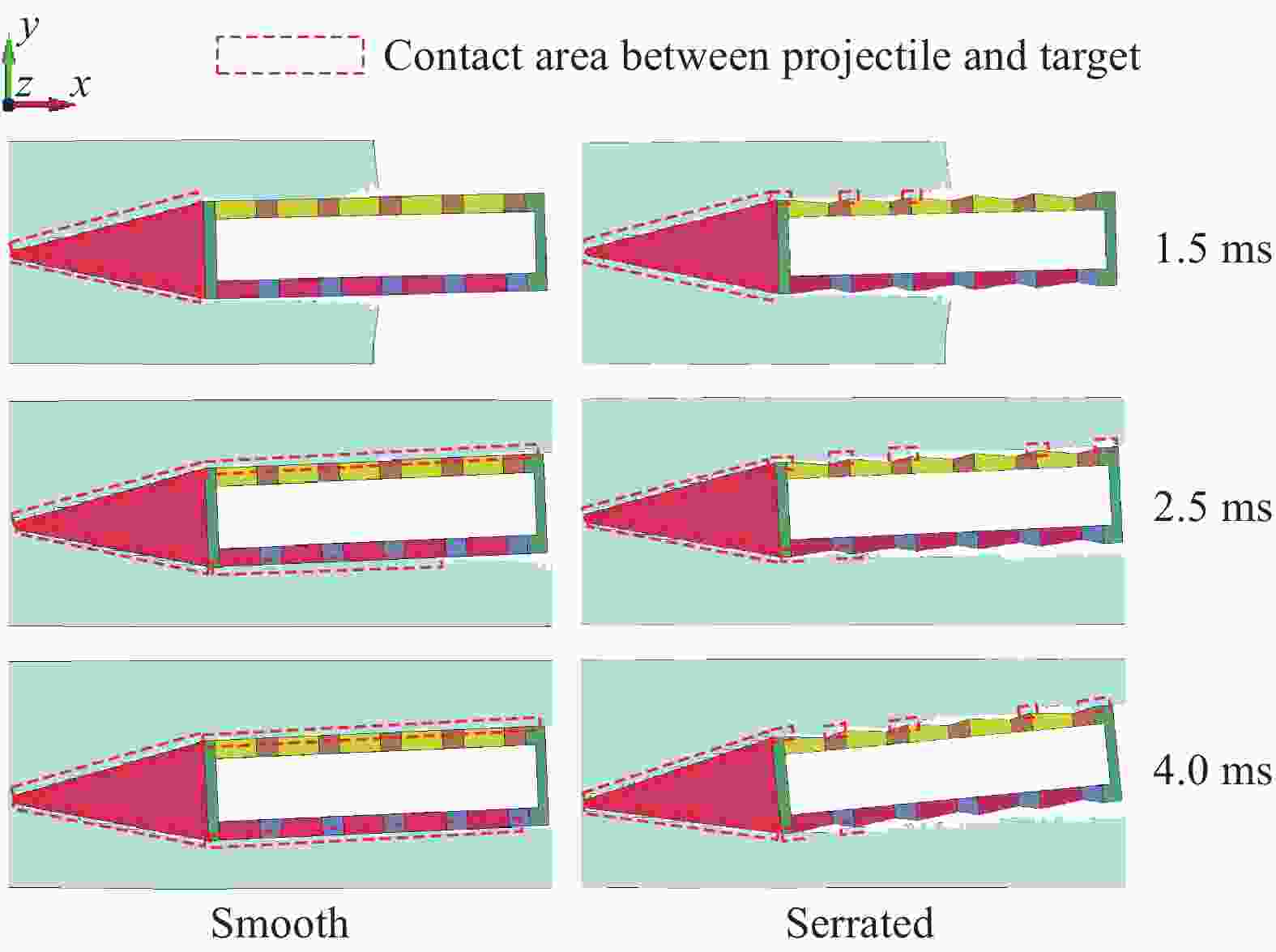
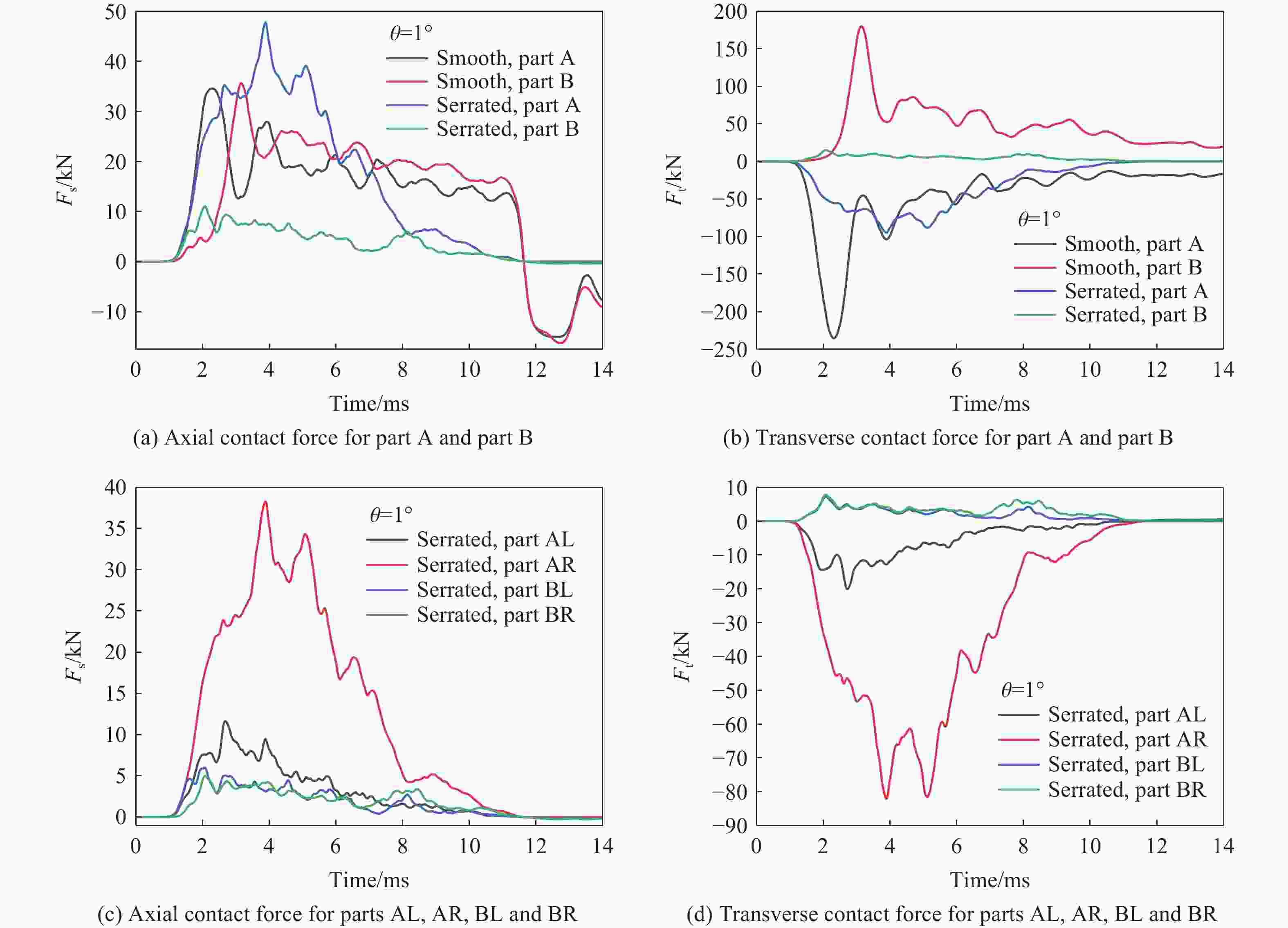
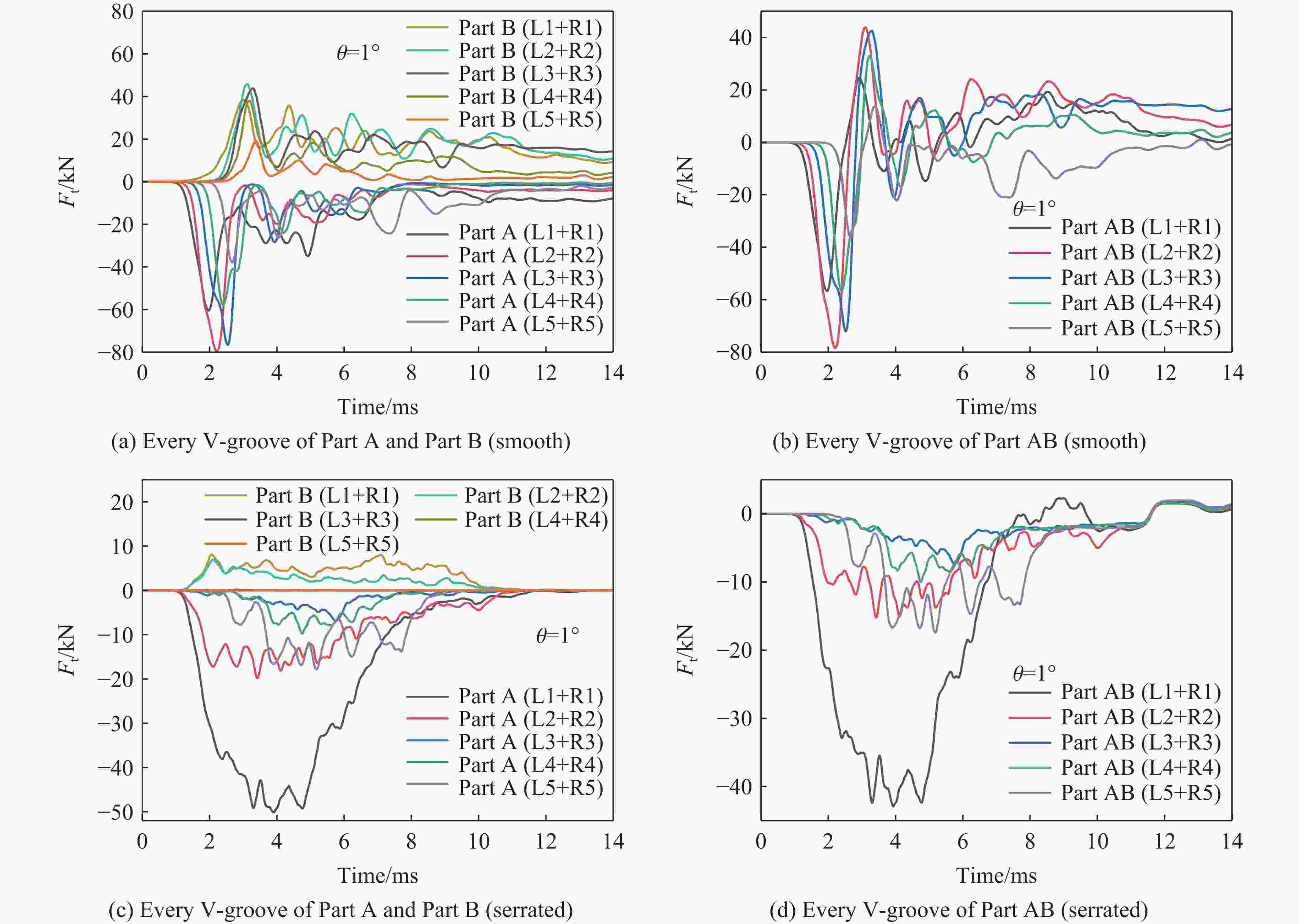
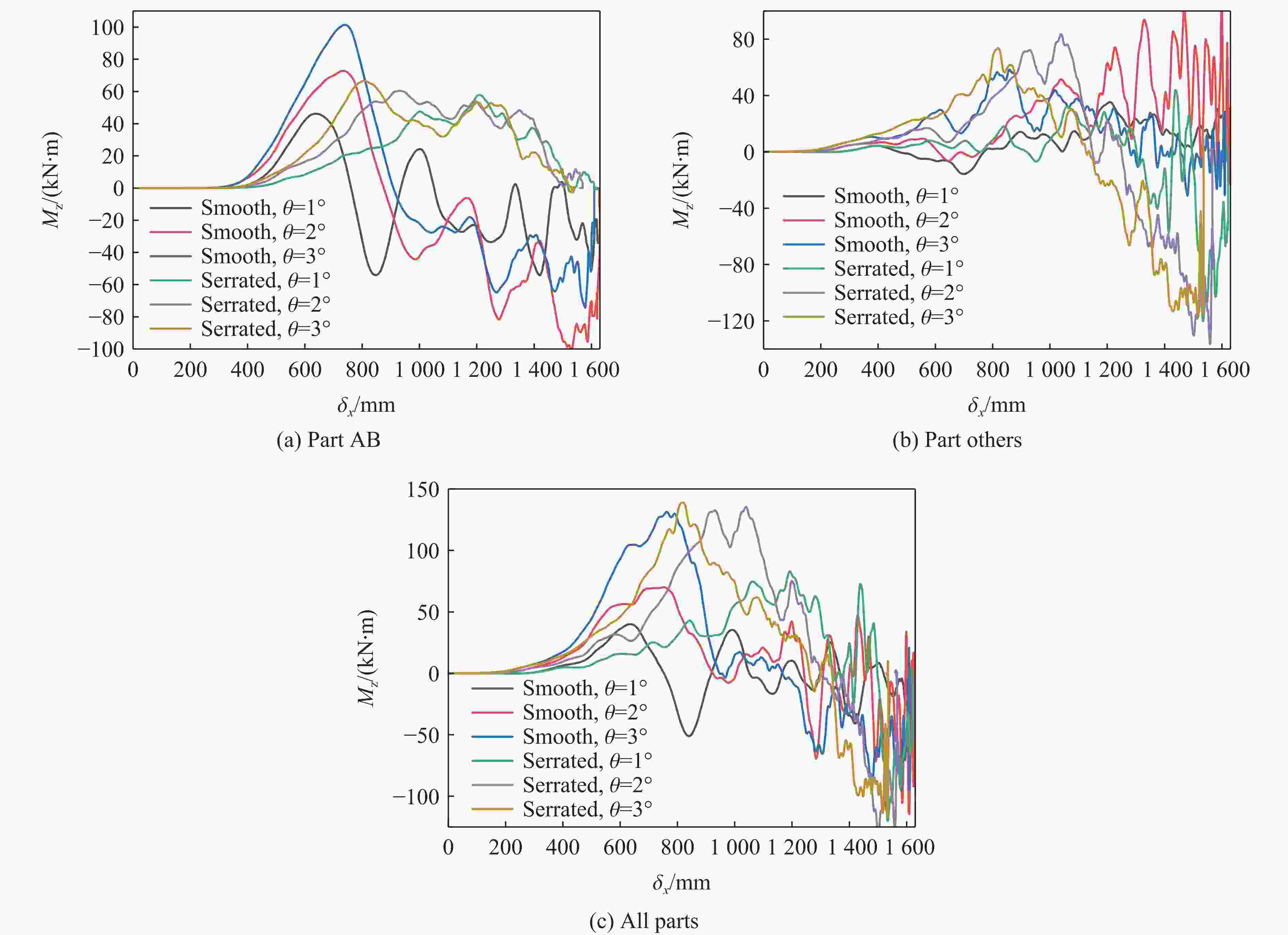
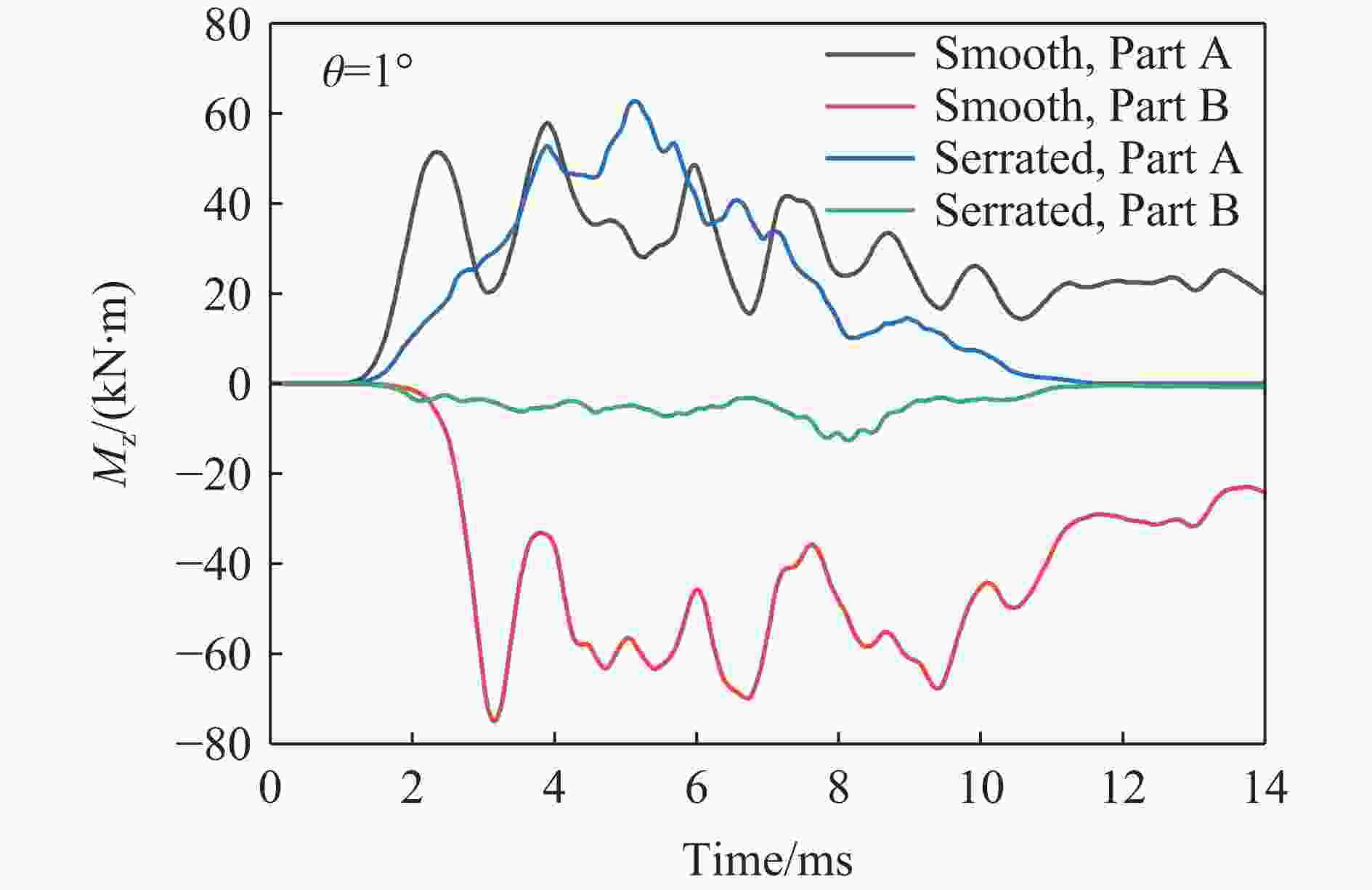
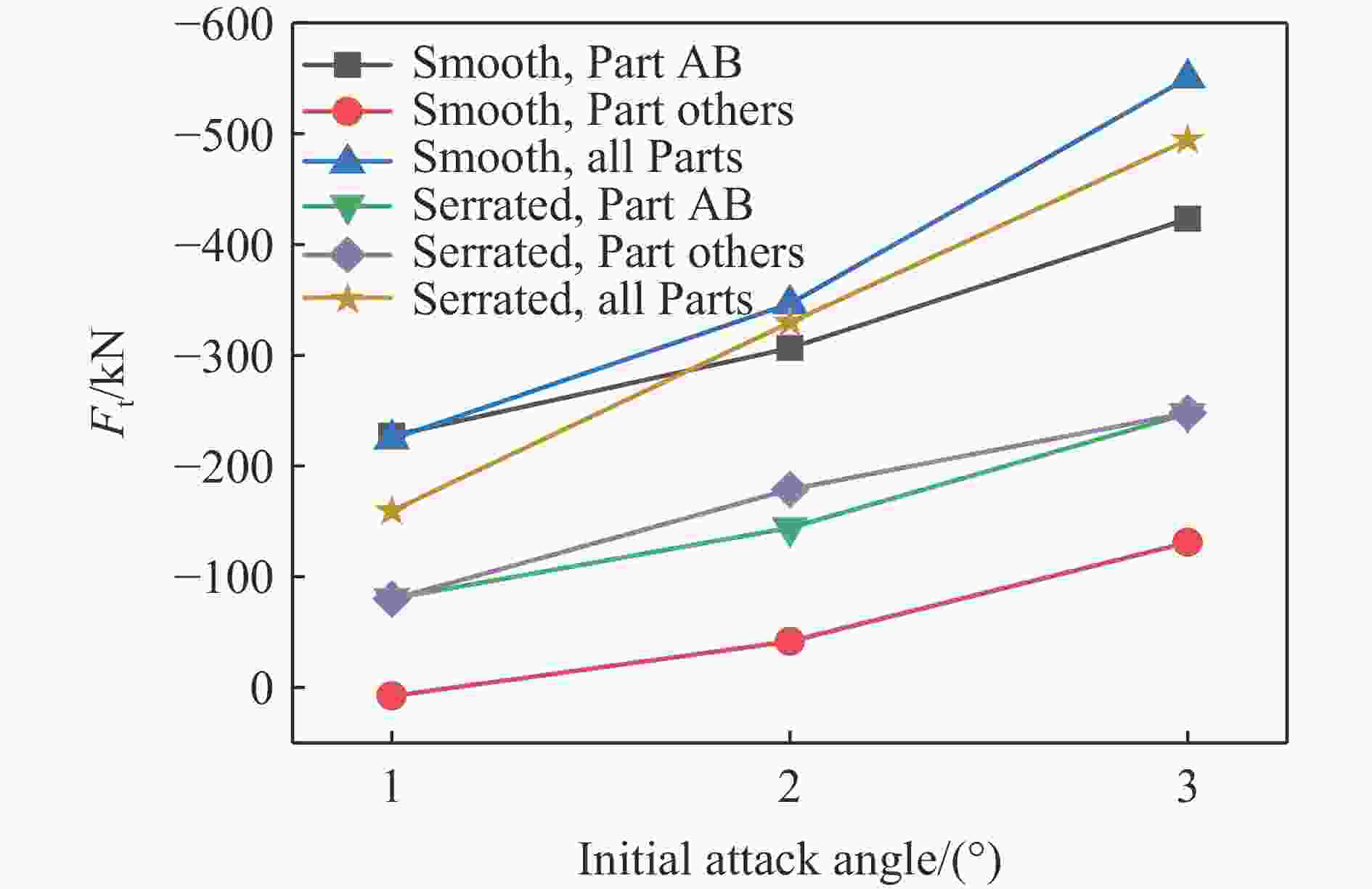
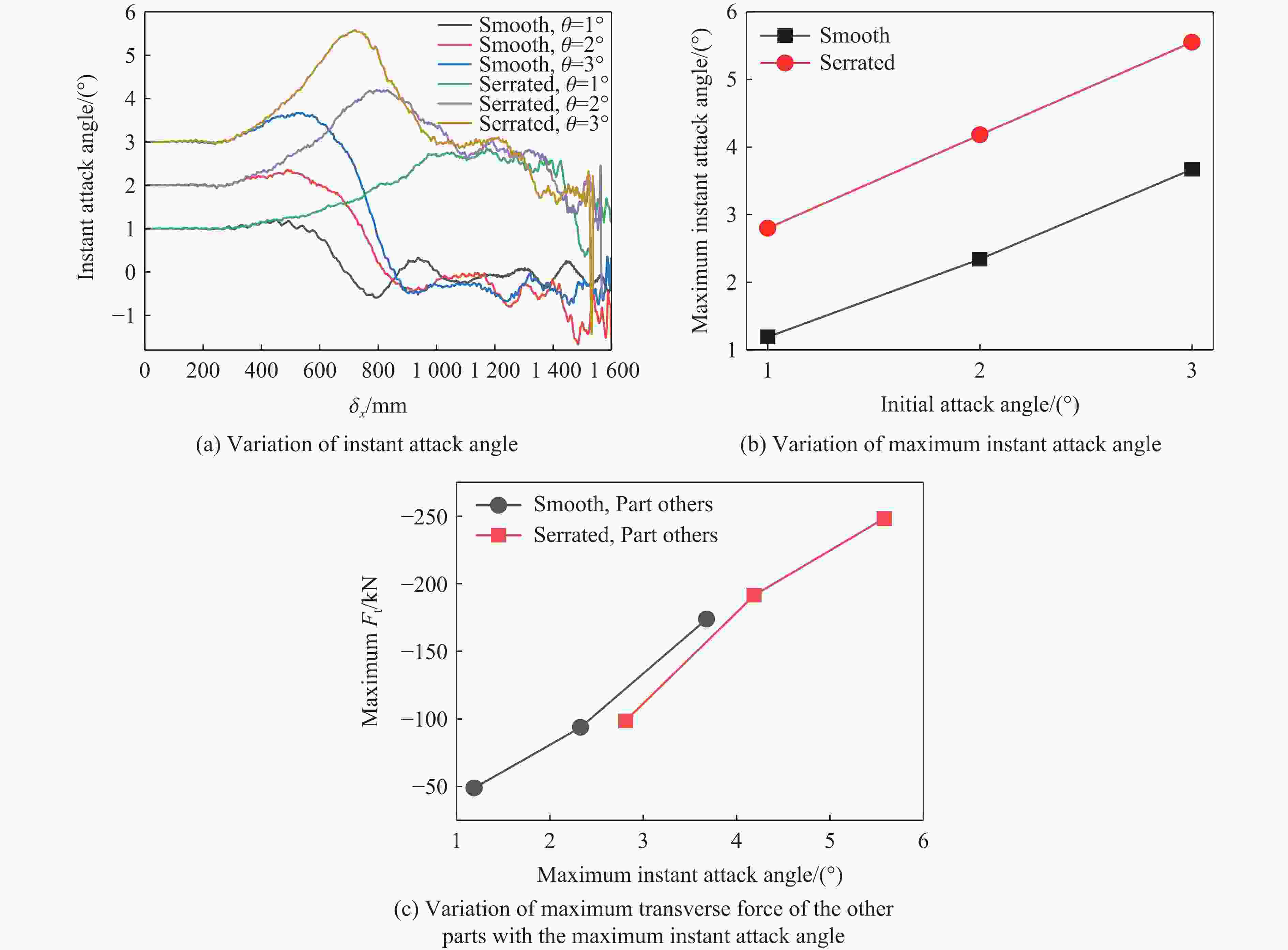
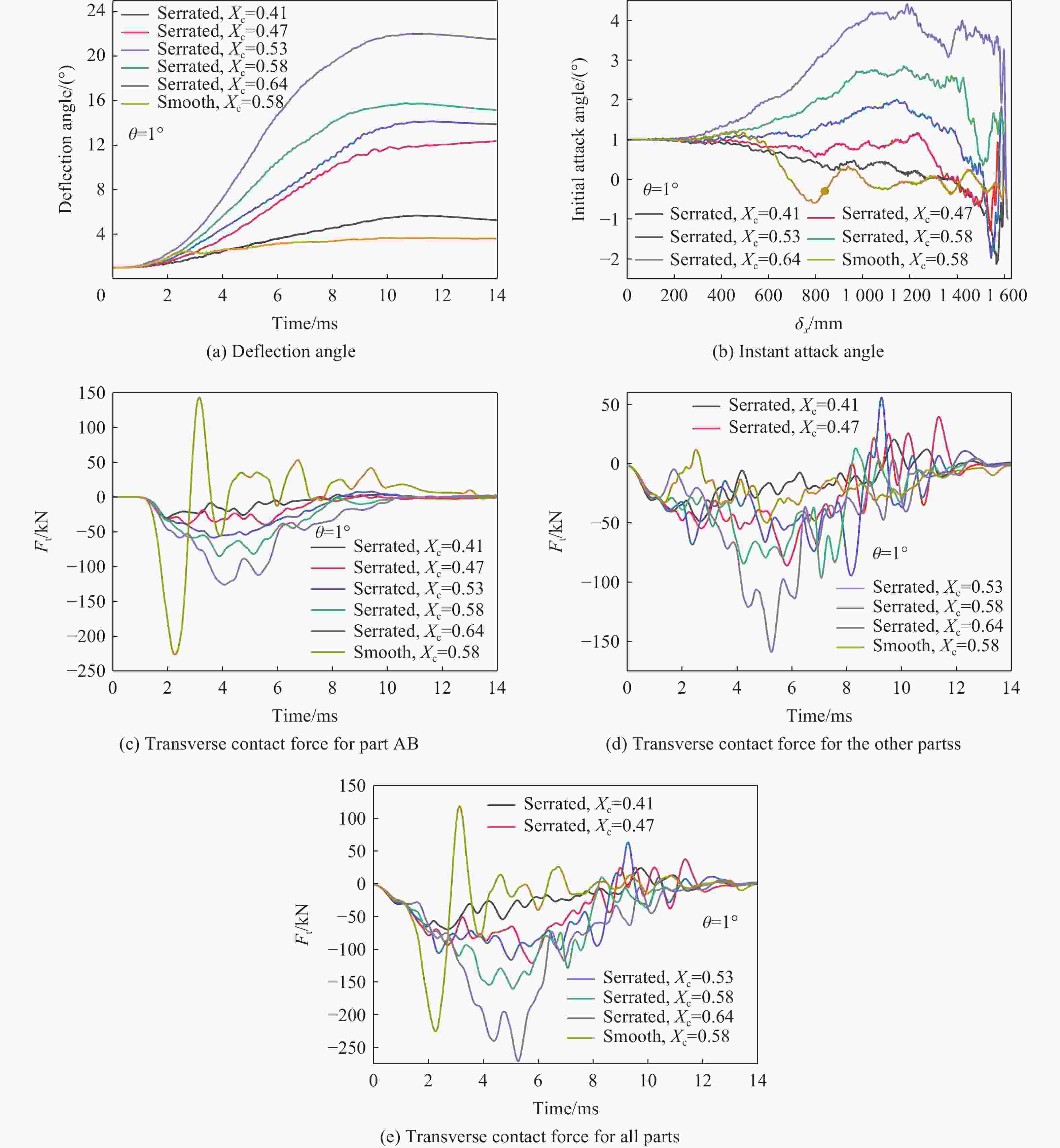
摘要: 为降低具有初始攻角的弹体在侵彻时产生的横向过载峰值,采用数值模拟方法,研究了一种带锯齿弹身的新型钻地弹以非零攻角姿态侵彻混凝土靶体时其特有的横向降载效应和机理。考虑初始攻角、质心系数等的影响,以常规光滑弹作为对比对象,分析了弹体运动规律、弹靶接触力、接触力矩、接触面积等。结果表明,在1°、2°和3°的小初始攻角范围内,锯齿弹较光滑弹分别降低横向过载峰值约30.6%、5.2%和11.3%,但相应的接触力矩的峰值和脉宽、偏转角度等均有所增大。研究结果揭示了锯齿弹的横向降载机理:锯齿弹身减小了弹靶的接触面积,横向接触力主要集中在弹身锯齿区靠近头部的前两个锯齿环槽的右锯齿上,使得锯齿弹身与靶的横向接触力减小,而非锯齿区(主要是弹体头部)与靶的横向接触力增大,二者的竞争可增强锯齿弹整体的横向降载效果。通过结构设计等手段抑制锯齿弹的弹道偏转后,可有效提升锯齿弹的横向降载效率。Abstract: In the process of deep penetration of the earth penetration weapon (EPW) attacking the underground target, the non-ideal penetration attitude with an initial attack angle is inevitable, which will introduce transverse overload with a large peak value for the earth penetrator. It could damage some important components of the earth-penetrating projectile and reduce the penetration efficiency of the projectile. Therefore, it is necessary to study the methodology of reducing the transverse overload peak value of the earth-penetrating projectile. However, the previous research on the earth-penetrating projectile seldom considered the influence of transverse overload, making it difficult to effectively reduce the transverse overload. In order to overcome this problem, a numerical simulation method was used to study the special transverse overload shedding effect and its mechanism of a new type of earth-penetrating projectile with a serrated configuration penetrating concrete targets at non-zero attack angles. The influences of the initial attack angle and the coefficient of the center of mass of the projectile were studied, and the motion, contact force, contact moment, and contact area of the projectile were analyzed using a conventional smooth projectile for comparison. The results show that for small initial attack angles of 1°, 2° and 3°, the peak value of transverse overload of the serrated projectile is reduced by about 30.6%, 5.2%, and 11.3%, respectively, compared to the smooth projectile but the peak value of contact moment, pulse width, and deflection angle are increased. The research reveals the mechanical mechanism to reduce transverse overload: the serrated body of the projectile reduces the contact area between the projectile and the target, and the transverse contact force is mainly concentrated on the upper surface of the right serrated parts of the first two serrated grooves near the head of the projectile; the transverse contact force between the serrated body and the target decreases, while the transverse contact force between the non-serrated parts (mainly the head of the projectile) and the target increases. Therefore, these two parts of the projectile compete and control the reduction effects of the transverse overload of the whole projectile in the process of deep penetration with an initial attack angle. When optimizations of structural design are used to suppress the ballistic deflection of the serrated projectile, the transverse overload shedding efficiency of serrated projectiles can be effectively improved.
-
表 1 G50钢与7075铝合金弹塑性本构模型参数
Table 1. Elastoplastic constitutive parameters of G50 steel and 7075 aluminum alloy
材料 密度/
(g·cm−3)弹性模量/
GPa泊松比 屈服应力/
MPa切线模量/
MPaG50钢 7.8 200 0.3 1800 1000 7075 铝合金2.7 70 0.3 520 477 密度/(g·cm−3) 剪切模量/GPa a b C N fc/MPa T/MPa $ {\dot \varepsilon _0} $/s−1 εe, min 1.604 1.15 0.28 1.85 0.006 0.84 12.3 1.8 1 0.01 Fmax pc/MPa εc pl/MPa εl D1 D2 K1/GPa K2/GPa K3/GPa 15.0 13.8 0.0075 1210 0.15 0.04 1.0 12 135 698 表 3 不同攻角时光滑弹与锯齿弹的侵彻工况设计
Table 3. Penetration condition of smooth and serrated projectiles at different attack angles
工况 弹体类型 初始攻角$ \theta $/(°) 质心系数$ {X}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 左锯齿密度/(g·cm−3) 右锯齿密度/(g·cm−3) 其他区域密度/(g·cm−3) 1 光滑弹 0 0.58 8.525 8.525 8.525 2 锯齿弹 0 0.58 9.800 11.000 8.525 3 光滑弹 1 0.58 8.525 8.525 8.525 4 锯齿弹 1 0.58 9.800 11.000 8.525 5 光滑弹 2 0.58 8.525 8.525 8.525 6 锯齿弹 2 0.58 9.800 11.000 8.525 7 光滑弹 3 0.58 8.525 8.525 8.525 8 锯齿弹 3 0.58 9.800 11.000 8.525 表 4 不同质心位置构型弹体侵彻工况
Table 4. Penetration conditions of configurations of projectiles with different mass centers
工况 弹体类型 初始攻角$ \theta $/(°) 质心系数Xc 左锯齿密度/(g·cm−3) 右锯齿密度/(g·cm−3) 其他区域密度/(g·cm−3) 9 锯齿弹 1 0.41 0.479 0.479 24.200 10 锯齿弹 1 0.47 3.721 3.721 18.985 11 锯齿弹 1 0.53 6.965 6.965 13.756 4 锯齿弹 1 0.58 11.000 11.000 9.800 12 锯齿弹 1 0.64 13.454 13.454 3.295 3 光滑弹 1 0.58 8.525 8.525 8.525 -
[1] 余同希, 卢国兴, 张雄. 能量吸收: 结构与材料的力学行为和塑性分析 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 303–330. [2] 诺曼·琼斯. 结构冲击 [M]. 许骏, 蒋平, 译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2018: Ⅹ–Ⅺ.JONES N. Structural impact [M]. Translated by XU J, JIANG P. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2018: Ⅹ–Ⅺ. [3] WANG S, XU F, ZHANG X Y, et al. A directional framework of similarity laws for geometrically distorted structures subjected to impact loads [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 161: 104092. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104092. [4] 陈小伟. 穿甲/侵彻力学的理论建模与分析 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 281–470.CHEN X W. Modelling on the perforation and penetration [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 281–470. [5] BEN-DOR G, DUBINSKY A, ELPERIN T. 高速侵彻动力学: 工程模型和方法 [M]. 武海军, 黄风雷, 皮爱国, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 241–298.BEN-DOR G, DUBINSKY A, ELPERIN T. High-speed penetration dynamics: engineering models and methods [M]. Translated by WU H J, HUANG F L, PI A G. Beijing: Science Press, 2020: 241–298. [6] JONES S E, RULE W K, JEROME D M, et al. On the optimal nose geometry for a rigid penetrator [J]. Computational Mechanics, 1998, 22(5): 413–417. DOI: 10.1007/s004660050373. [7] BEN-DOR G, DUBINSKY A, ELPERIN T. Shape optimization of impactor penetrating into concrete or limestone targets [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2003, 40(17): 4487–4500. DOI: 10.1016/S0020-7683(03)00212-9. [8] 刘坚成, 黄风雷, 皮爱国, 等. 异型头部弹体增强侵彻性能机理研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(4): 409–414. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)04-0409-06.LIU J C, HUANG F L, PI A G, et al. On enhanced penetration performance of modified nose projectiles [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(4): 409–414. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)04-0409-06. [9] 柴传国, 武海军, 皮爱国, 等. 异形头部弹体中低速侵彻混凝土的实验研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2015, 35(8): 787–791. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.08.004.CHAI C G, WU H J, PI A G, et al. Experimental study on nose headed penetrator penetrating to concrete target with middle and low speed [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(8): 787–791. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2015.08.004. [10] 张欣欣, 武海军, 黄风雷, 等. 刻槽弹侵彻混凝土受力模型研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2016, 36(1): 75–80. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)01-0075-06.ZHANG X X, WU H J, HUANG F L, et al. Mechanical model of the grooved-tapered projectile penetrating concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2016, 36(1): 75–80. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2016)01-0075-06. [11] 皮爱国, 黄风雷. 大长细比动能弹体弹塑性动力响应数值模拟 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2007, 27(8): 666–670. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0645.2007.08.003.PI A G, HUANG F L. Numerical simulation of the elastic-plastic dynamic response of a slender kinetic energy penetrator [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2007, 27(8): 666–670. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0645.2007.08.003. [12] CHEN X W, LI Q M. Deep penetration of a non-deformable projectile with different geometrical characteristics [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27(6): 619–637. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00005-2. [13] 高旭东, 李庆明. 带攻角斜侵彻混凝土的弹道偏转分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2014, 35(S2): 33–39.GAO X D, LI Q M. Trajectory analysis of projectile obliquely penetrating into concrete target at attack angle [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(S2): 33–39. [14] 尹放林, 王明洋, 钱七虎, 等. 弹丸斜入射对侵彻深度的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1998, 18(1): 69–76. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1998)01-0069-8.YIN F L, WANG M Y, QIAN Q H, et al. Penetration depth of projectile oblique into target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1998, 18(1): 69–76. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1998)01-0069-8. [15] 闪雨, 黄风雷, 武海军, 等. 动能弹非正侵彻弹道稳定性研究 [C]//第六届全国强动载效应及防护学术会议暨2014年复杂介质/结构的动态力学行为创新研究群体学术研讨会论文集. 北京: 中国力学学会爆炸力学专业委员会, 2014: 450–459. [16] 段卓平, 李淑睿, 马兆芳, 等. 刚性弹体斜侵彻贯穿混凝土靶的姿态偏转理论模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(6): 063302. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0411.DUAN Z P, LI S R, MA Z F, et al. Analytical model for attitude deflection of rigid projectile during oblique perforation of concrete targets [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(6): 063302. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0411. [17] 何丽灵, 郭虎, 陈小伟, 等. 结构变形对深侵彻弹体偏转的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(9): 091404. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0068.HE L L, GUO H, CHEN X W, et al. Influence of structural deformation on the deflection of penetrator into concrete target with deep penetration [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(9): 091404. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0068. [18] WARREN T L, HANCHAK S J, POORMON K L. Penetration of limestone targets by ogive-nosed VAR 4340 steel projectiles at oblique angles: experiments and simulations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2004, 30(10): 1307–1331. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2003.09.047. [19] 马爱娥, 黄风雷, 初哲, 等. 弹体攻角侵彻混凝土数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2008, 28(1): 33–37. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)01-0033-05.MA A E, HUANG F L, CHU Z, et al. Numerical simulation on yawed penetration into concrete [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2008, 28(1): 33–37. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2008)01-0033-05. [20] BERNARD R S, CREIGHTON D C. Projectile penetration in soil and rock: analysis for non-normal impact: SL-79-15 [R]. USA: Vicksbury: Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station Strutures Laboratory, 1979. [21] 吕中杰, 徐钰巍, 黄风雷. 弹体斜侵彻混凝土过程中的方向偏转 [J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(S2): 301–304.LYU Z J, XU Y W, HUANG F L. Transverse deflection of projectile obliquely penetrating into concrete [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(S2): 301–304. [22] 王可慧, 宁建国, 李志康, 等. 高速弹体非正侵彻混凝土靶的弹道偏转实验研究 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2013, 27(4): 561–566. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2013.04.015.WANG K H, NING J G, LI Z K, et al. Ballistic trajectory of high-velocity projectile obliquely penetrating concrete target [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2013, 27(4): 561–566. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2013.04.015. [23] 武海军, 黄风雷, 王一楠. 高速弹体非正侵彻混凝土试验研究 [C]//第八届全国爆炸力学学术会议论文集. 吉安: 中国力学学会爆炸力学专业委员会, 2007: 488–494. [24] 康海峰, 代廷静, 沈培辉, 等. 弹体形状对侵彻弹道的影响分析 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2012, 32(2): 73–76. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2012.02.020.KANG H F, DAI T J, SHEN P H, et al. The analysis of the influence of projectile’s shape on penetration trajectory [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2012, 32(2): 73–76. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2012.02.020. [25] 郭松林, 高世桥, 李泽章, 等. 弹引系统攻角侵彻混凝土仿真与试验研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2022, 43(1): 135–139, 205. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.01.021.GUO S L, GAO S Q, LI Z Z, et al. Experiment and simulation of projectile obliquely penetrating into concrete target at attack angle [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2022, 43(1): 135–139, 205. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2022.01.021. [26] 郭虎, 何丽灵, 陈小伟, 等. 球形颗粒遮弹层对高速侵彻弹体的作用机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(10): 103301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0428.GUO H, HE L L, CHEN X W, et al. Penetration mechanism of a high-speed projectile into a shelter made of spherical aggregates [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(10): 103301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0428. [27] SPAWN C M. Field testing of earth penetrators: LA-UR-23-21935 [R]. Los Alamos: Los Alamos National Laboratory, 2023. DOI: 10.2172/1958976. [28] HOLMQUIST T J, JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A computational constitutive model for concrete subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high pressures [C]//The 14th International Symposium on Ballistic. Quebec, 1993: 591–600. [29] 任根茂, 吴昊, 方秦, 等. 普通混凝土HJC本构模型参数确定 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(18): 9–16. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2016.18.002.REN G M, WU H, FANG Q, et al. Determinations of HJC constitutive model parameters for normal strength concrete [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(18): 9–16. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2016.18.002. -






 下载:
下载: