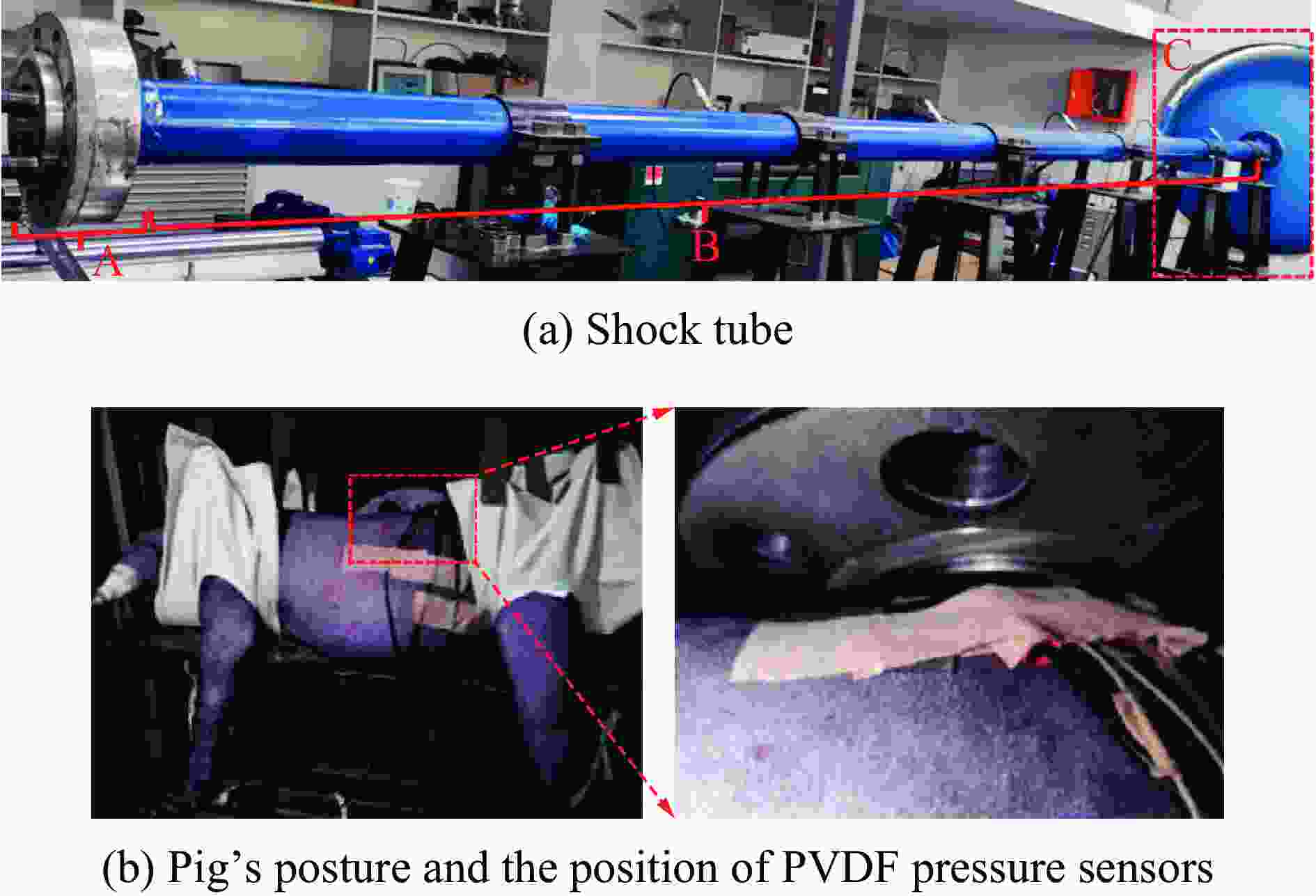
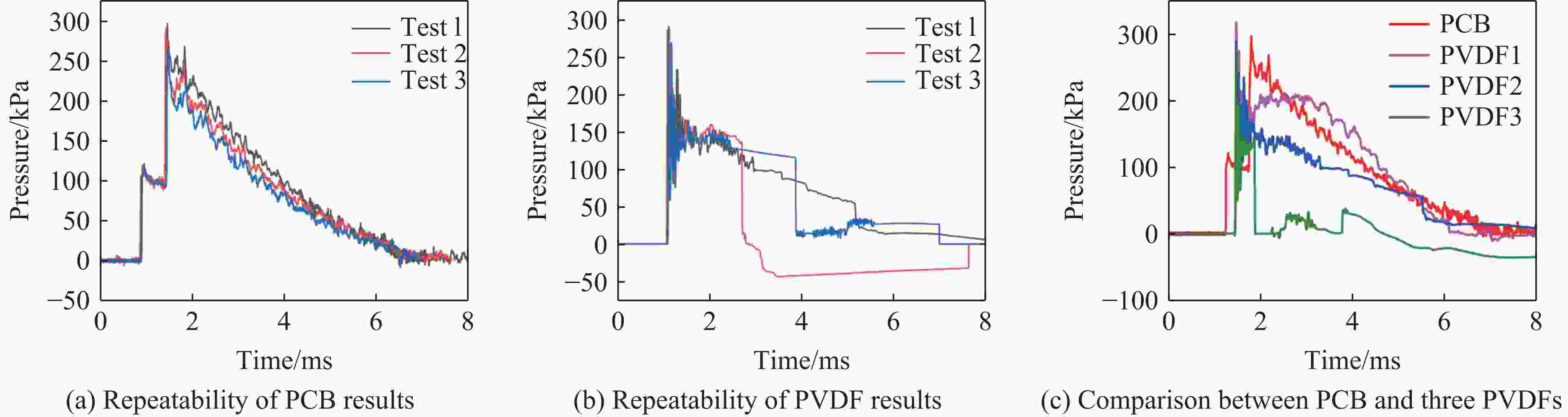
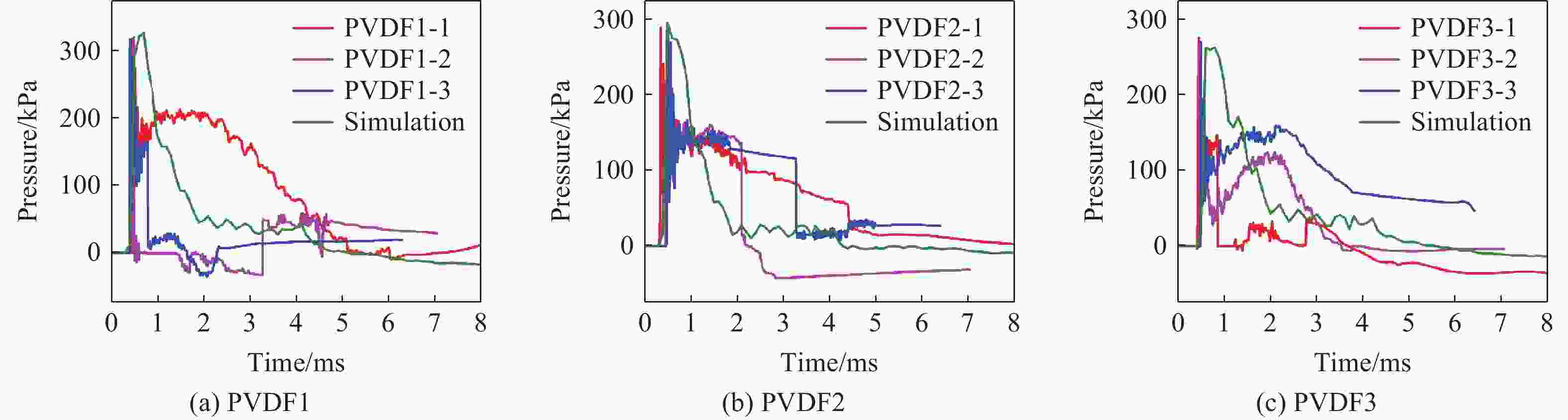
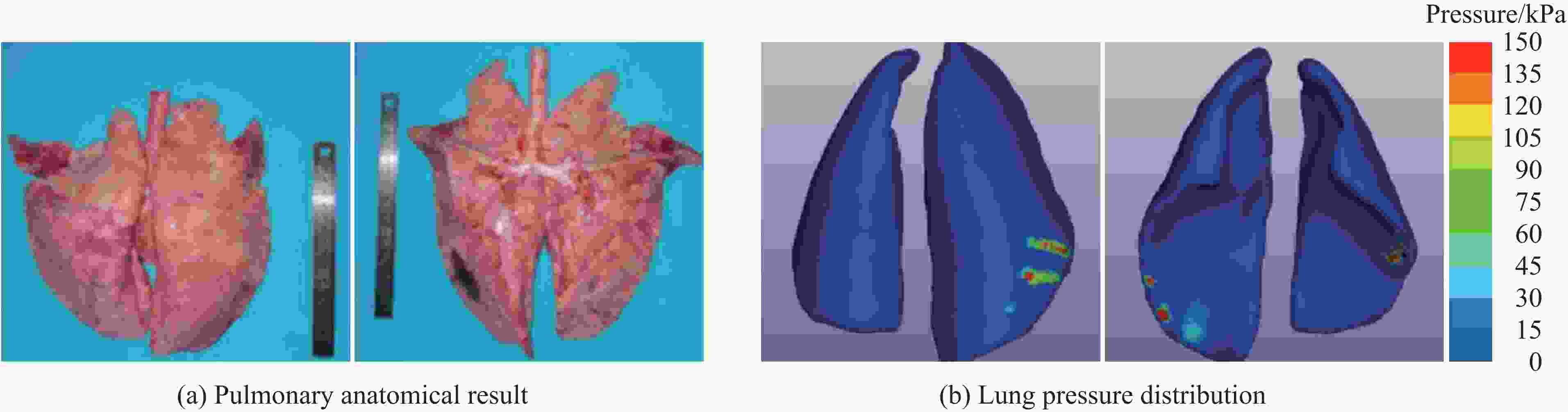
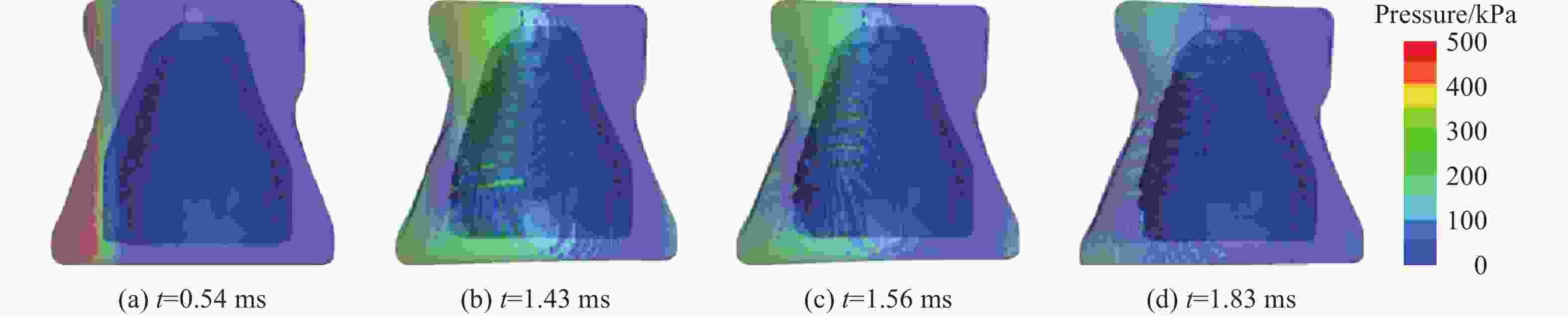
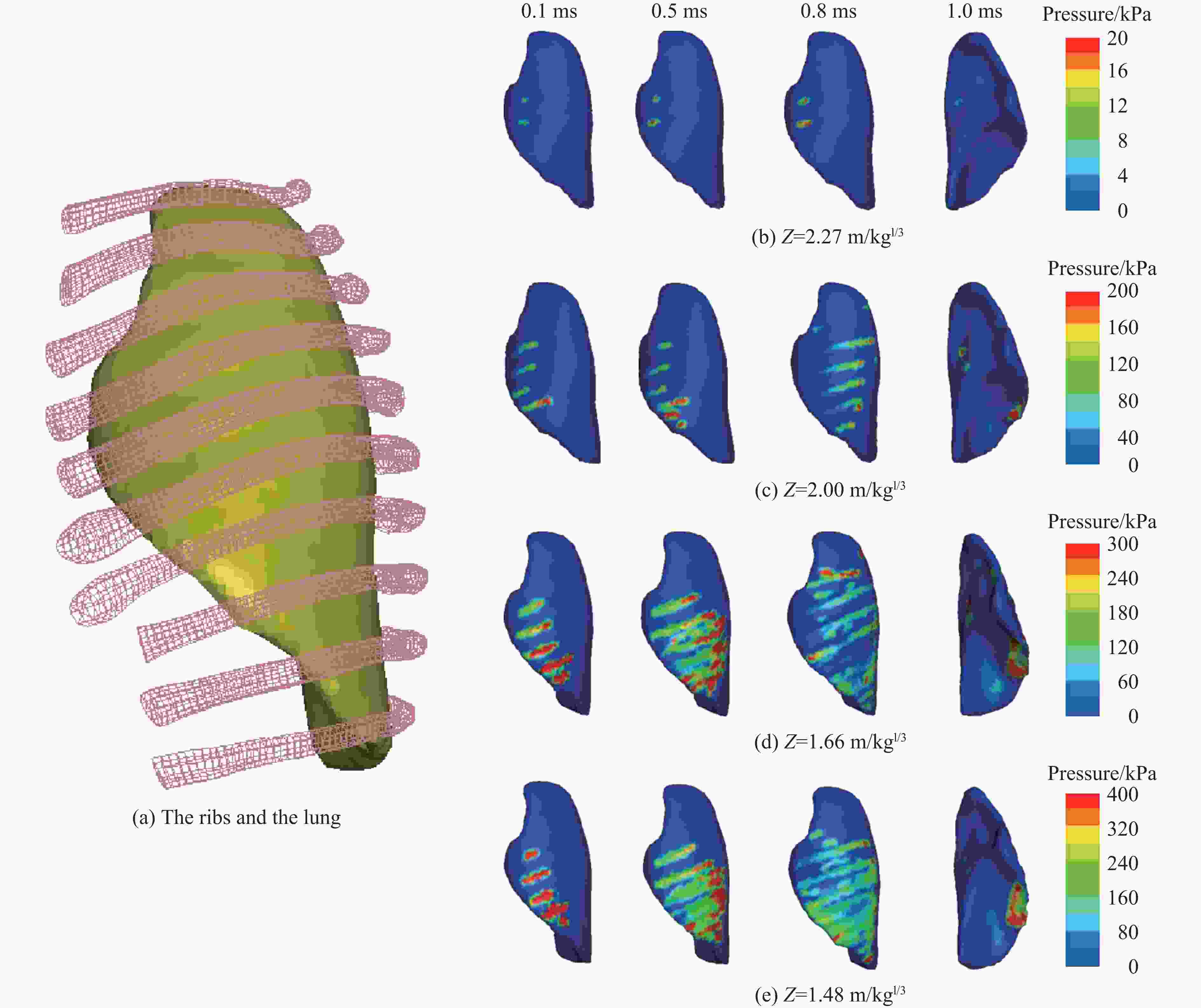
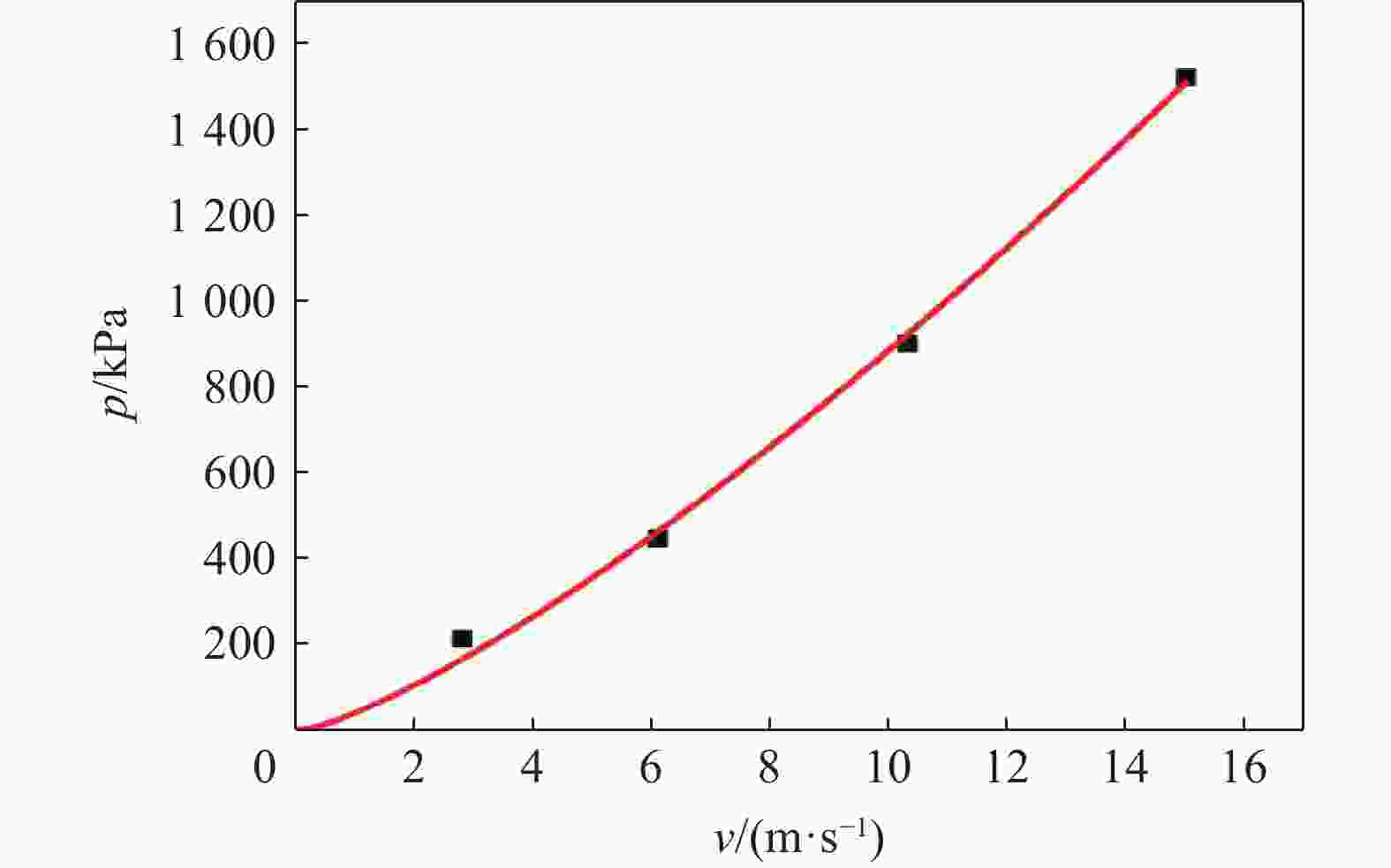
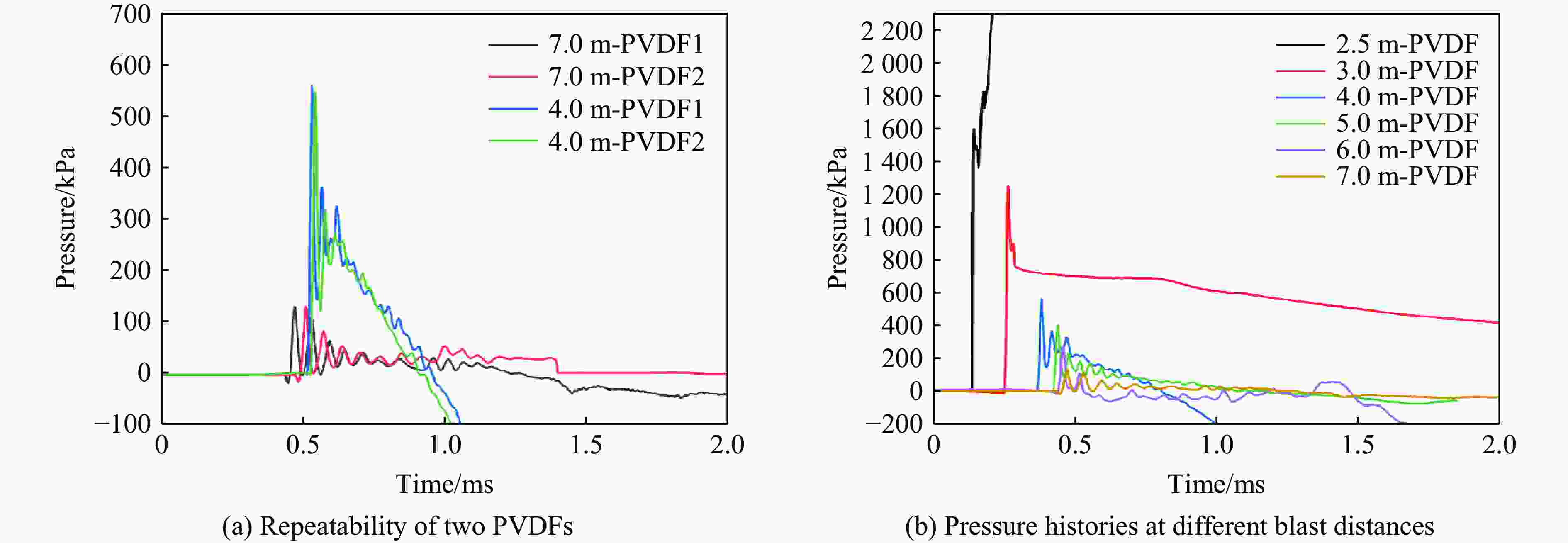
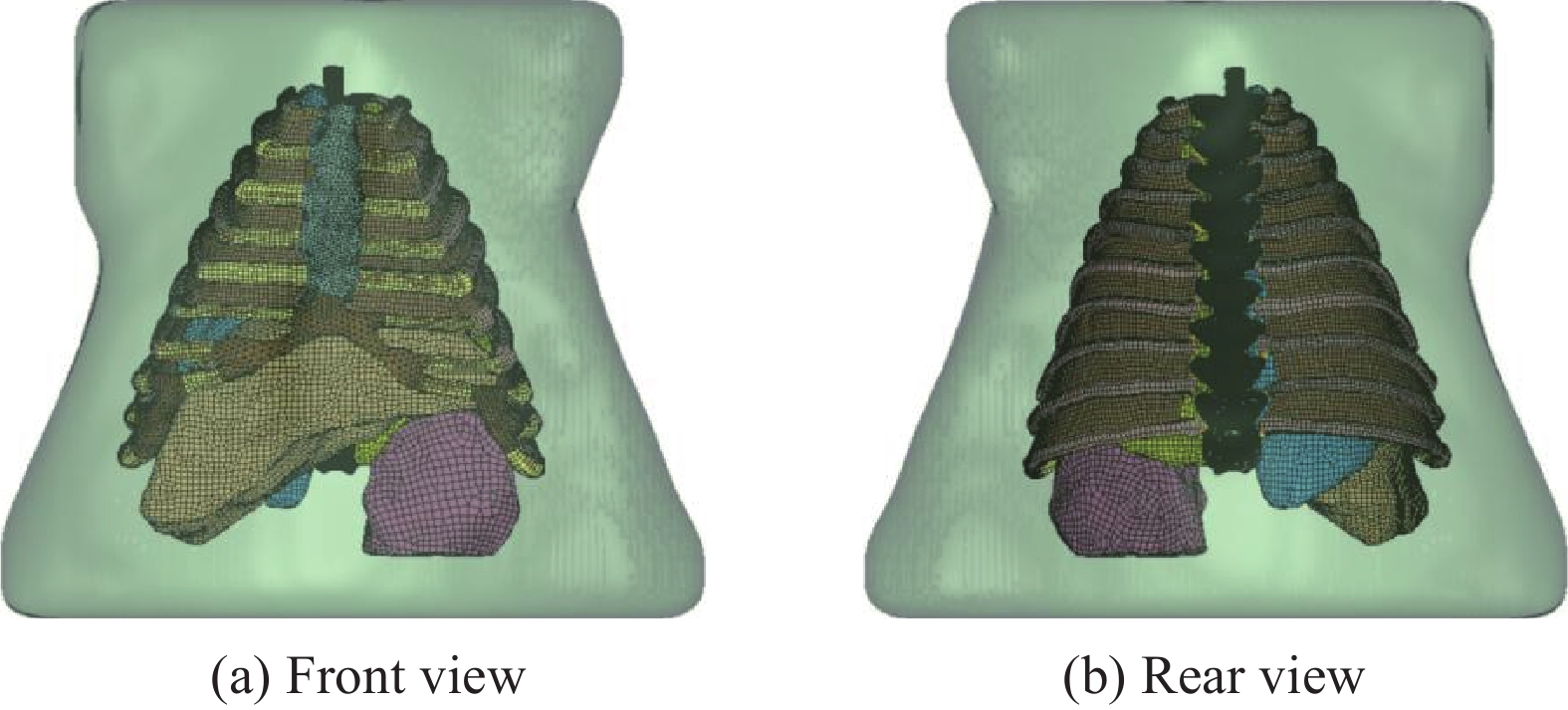
Injury properties of porcine lung under blast load
-
摘要: 为了深入研究爆炸冲击波作用下生物体肺部的力学响应和损伤特性,首先建立了猪胸部有限元模型,借助新研制的PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride)柔性冲击波压力传感器测试了激波管试验中动物的体表压力,验证了有限元模型的准确性。然后,使用已验证的模型开展了不同比例距离下猪肺部损伤特性研究,分析了在不同强度冲击波作用下肺部的损伤程度和损伤区域,并建立了胸肺部表皮压力峰值与肺损伤的关系。最后,通过开展爆炸试验,获得了不同比例距离下猪的肺部损伤情况和胸部表皮压力曲线,验证了所建立的胸肺部表皮压力峰值与肺损伤关系的正确性。Abstract: In order to study the mechanical response and injury characteristics of living lungs under the action of blast shock waves, this study first established a finite element model of the chest of a small pig and used a newly developed PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) flexible pressure sensor to test the surface pressure of animals in shock tube experiments, verifying the accuracy of the finite element model. Secondly, the validated model was used to study the characteristics of lung injury of pigs at different blast distances, analyzing the lung injury location and severity under different intensities of shock waves. Moreover, the relation between the peak pressure on the surface of the chest and the grade of lung injury was established. Finally, blast tests were performed to obtain the lung injury of pigs as well as the chest surface pressure histories at different blast distances, which can be used to verify the correctness of the established relation.
-
Key words:
- animal finite element model /
- blast shock wave /
- lung injury /
- peak pressure
-
表 1 胸部模型骨骼材料参数
Table 1. Bone material parameters of chest model
骨骼结构 密度/(kg∙m−3) 杨氏模量/MPa 泊松比 屈服强度/MPa 胸椎骨 2500 11000 0.40 — 胸椎间盘 1040 300 0.40 — 胸骨皮质骨 2 000 14000 0.30 90 肋间软骨 1500 12.5 0.40 4.9 肋骨松质骨 1000 40 0.45 1.8 肋骨皮质骨 2 000 11500 0.30 90 胸骨松质骨 1000 40 0.45 1.8 表 2 胸部模型软组织材料参数
Table 2. Soft tissue material parameters of chest model
组织 密度/(kg∙m−3) 线性体积模量/MPa 阻尼系数 剪切模量/MPa 心脏 1000 100 0.1 0 肺 288 150 0.4 0.04 胃 1000 4.59 0.1 0 肌肉 1000 2 000 0.4 0.04 表 3 不同比例距离下冲击波的等效参数
Table 3. The equivalent parameters of the shock wave at each proportional distance
序号 WTNT/kg R/m Z/(m∙kg−1/3) Δpm/kPa τ+/ms 1 1.08 2.30 2.27 150 2 2 1.30 2.17 2.00 200 2 3 1.70 2.00 1.66 300 2 4 2.00 1.86 1.48 400 2 表 4 胸廓运动速度、猪胸肺部表皮压力峰值与肺部损伤的对应关系
Table 4. Relations between thoracic motility velocity, the peak pressure on the chest and the lung injury in pigs
v/(m∙s−1) [30] p/kPa 肺损伤 <3.6 <232 无伤 3.6~7.5 232~609 微伤至轻伤 4.3~9.8 294~865 轻伤至中伤 7.5~16.9 609~ 1766 中伤至重伤 >12.8 > 1227 50%死亡 表 5 爆炸试验工况
Table 5. Blast test record
试验编号 猪编号 猪质量/kg TNT质量/kg 爆距/m 比例距离/(m∙kg−1/3) 1 1# 24.0 10 5.0 2.32 2# 25.5 10 6.0 2.78 3# 27.0 10 7.0 3.25 2 4# 27.5 10 3.5 1.62 5# 24.5 10 4.0 1.86 6# 24.0 10 4.0 1.86 3 7# 24.0 10 2.5 1.16 8# 25.5 10 3.0 1.39 9# 26.0 10 4.0 1.86 表 6 各个工况下猪肺部解剖伤情
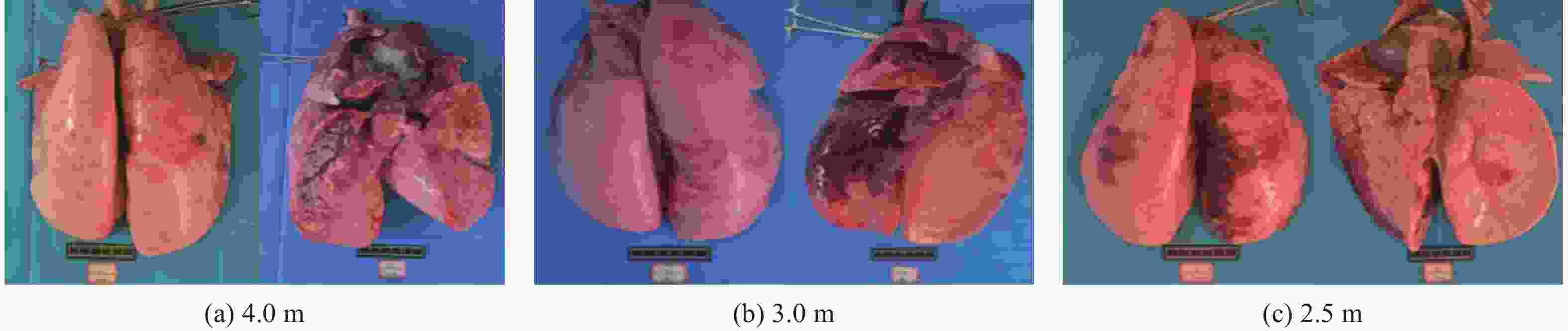
Table 6. Anatomical injuries of pig lungs at various blast distances
爆距/m 肺部解剖伤情 解剖结果(AIS评估) 7.0 没有明显损伤 无伤 6.0 轻微损伤 轻微肺损伤 5.0 轻微损伤 轻微肺损伤 4.0 气管没有异常,左肺出血,右肺出血较严重 轻度肺损伤 3.0 气管没有异常,左肺出血较严重,右肺出血严重 中度到重度肺损伤 2.5 气管中有大量血沫,左肺出血较严重,右肺出血非常严重 重度肺损伤 表 7 猪肺伤情汇总与损伤判据判断伤情
Table 7. Summary of pig lung injury and the injury criterion determines the severity of the injury
爆距/m 体表压力峰值/kPa 解剖结果(AIS评估) 预测结果(本文损伤关系) 7.0 128 无伤 无伤 6.0 270 轻微肺损伤 微伤至轻伤 5.0 403 轻微肺损伤 微伤至轻伤 4.0 559 轻度肺损伤 轻伤至中伤 3.0 1253 中度到重度肺损伤 中伤至重伤 2.5 1600 重度肺损伤 50%死亡 -
[1] HUGHES S M, BORDERS III C W, ADEN J K, et al. Long-term outcomes of thoracic trauma in U. S. service members involved in combat operations [J]. Military Medicine, 2020, 185(11/12): 131–136. DOI: 10.1093/milmed/usaa165. [2] SALEM M H, BUX G M K, HUDEEL A. War thoracic wounds among civilians casualties in Aden during the 2015 [J]. Electronic Journal of University of Aden for Basic and Applied Sciences, 2020, 1(3): 159–166. DOI: 10.47372/ejua-ba.2020.3.39. [3] ZHANG B. Blast lung injury [M]//WANG Z G, JIANG J X. Explosive Blast Injuries: Principles and Practices. Singapore: Springer, 2023: 295–300. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-19-2856-7_19. [4] CERNAK I, SAVIC J, IGNJATOVIC D, et al. Blast injury from explosive munitions [J]. The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care, 1999, 47(1): 96–103. DOI: 10.1097/00005373-199907000-00021. [5] SCOTT T E, KIRKMAN E, HAQUE M, et al. Primary blast lung injury: a review [J]. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 2017, 118(3): 311–316. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aew385. [6] SMITH J E. The epidemiology of blast lung injury during recent military conflicts: a retrospective database review of cases presenting to deployed military hospitals, 2003–2009 [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2011, 366(1562): 291–294. DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0251. [7] TELAND J A. Review of blast injury prediction models: FFI-rapport 2012/00539 [R]. Norway: Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (FFI), 2012. [8] COOPER G J, TOWNEND D J, CATER S R, et al. The role of stress waves in thoracic visceral injury from blast loading: modification of stress transmission by foams and high-density materials [J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 1991, 24(5): 273–285. DOI: 10.1016/0021-9290(91)90346-O. [9] 唐献述, 王树民, 龙源, 等. 爆炸空气冲击波对动物伤害效应试验研究 [J]. 工程爆破, 2012, 18(2): 104–106, 96. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2012.02.028.TANG X S, WANG S M, LONG Y, et al. Experimental study on the effect of explosion air shockwave on the animal injury [J]. Engineering Blasting, 2012, 18(2): 104–106, 96. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7051.2012.02.028. [10] 王海宾, 赵英虎, 高莉, 等. 甲烷爆炸冲击波作用下密闭管道内动物损伤效应试验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2018, 39(8): 1639–1647. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.08.022.WANG H B, ZHAO Y H, GAO L, et al. Experimental investigation into the damage effect of methane explosion shock wave on animals in enclosed pipeline [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2018, 39(8): 1639–1647. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2018.08.022. [11] VASSOUT P, FRANKE R, PARMENTIER G, et al. Mesures de pression et d’accélérations intracorporelles chez le porc exposé à des ondes de choc fortes en champ libre [R]. France: French-German Research Institute of Saint Louis, 1986: 86. [12] 陈海斌, 王正国, 杨志焕, 等. 冲击波传播的三个时段模拟实验中动物肺的损伤 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2000, 20(3): 264–269. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2000)03-0264-6.CHEN H B, WANG Z G, YANG Z H, et al. Injury of animal lungs in the experiments to simulate the three phases of shock wave propagation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2000, 20(3): 264–269. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2000)03-0264-6. [13] 陈海斌, 王正国. 爆炸性减压对兔肺的损伤作用 [J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2000, 16(2): 109–111. DOI: 10.3760/j:issn:1001-8050.2000.02.016.CHEN H B, WANG Z G. Injury action on rabbit lung by explosive decompression [J]. Chinese Journal of Trauma, 2000, 16(2): 109–111. DOI: 10.3760/j:issn:1001-8050.2000.02.016. [14] 段维勋. 胸部爆炸伤动物模型的建立及伤情特点分析的实验研究 [D]. 西安: 第四军医大学, 2002: 1–64.DUAN W X. Experimental researches on establishment of animal model of thoracic explosive injury and analysis of wound characteristics [D]. Xi’an: Air Force Medical University, 2002: 1–64. [15] 王峰, 杨志焕, 朱佩芳, 等. 高原冲击伤伤情特点的实验研究 [J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2008, 10(6): 549–551. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4237.2008.06.026.WANG F, YANG Z H, ZHU P F, et al. Experimental study on characteristics of blast injury at high altitude [J]. Journal of Traumatic Surgery, 2008, 10(6): 549–551. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4237.2008.06.026. [16] 袁丹凤, 杨傲, 麻超, 等. 冲击波强度与幼年大鼠肺冲击伤程度的量效关系 [J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2021, 38(6): 780–784. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2021.06.022.YUAN D F, YANG A, MA C, et al. Dose-effect relationship between shock wave intensity and blast lung injury in juvenile rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Physics, 2021, 38(6): 780–784. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2021.06.022. [17] 张良. 准静态撞击下猪胸腔内应力分布及其三维重现与肺损伤 [D]. 重庆: 中国人民解放军陆军军医大学, 2005: 1–56.ZHANG L. Distribution and 3-D reconstruction of intrathoracic stress in the swine chest subjected to impact [D]. Chongqing: Army Medical University, 2005: 1–56. [18] 杨春霞. 羊肺脏有限元模型的建立及其在冲击波作用下的仿真分析 [D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2010: 1–60.YANG C X. Establishmen of finite element model of sheep lung and finite-element simulation of blast wave [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2010: 1–60. [19] MORDAKA J, MEIJER R, VAN ROOIJ L, et al. Validation of a finite element human model for prediction of rib fractures: SAE technical paper 2007-01-1161 [R]. TNO Science and Industry: SAE, 2007. [20] KIMPARA H, LEE J B, YANG K H, et al. Development of a three-dimensional finite element chest model for the 5th percentile female [R]. Wayne State University, Toyota Central R & D Labs., Inc.: SAE, 2005. [21] SHIN J, UNTAROIU C, LESSLEY D, et al. Thoracic response to shoulder belt loading: investigation of chest stiffness and longitudinal strain pattern of ribs: SAE technical paper 2009-01-0384 [R]. Center for Applied Biomechanics, University of Virginia: SAE, 2009. DOI: 10.4271/2009-01-0384. [22] IWAMOTO M, NAKAHIRA Y, TAMURA A, et al. Development of advanced human models in THUMS [C]//Proceedings of the 6th European LS-DYNA Users’ Conference. Nagakute City: Toyota Central R&D Labs., Inc., 2007. [23] YANG K H, HU J W, WHITE N A, et al. Development of numerical models for injury biomechanics research: a review of 50 years of publications in the Stapp car crash conference [C]//Proceedings of the 50th Stapp Car Crash Conference. Dearborn, Michigan: SAE, 2006: 429–490. [24] RUAN J, EL-JAWAHRI R, CHAI L, et al. Prediction and analysis of human thoracic impact responses and injuries in cadaver impacts using a full human body finite element model [C]//Proceedings of the 47th Stapp Car Crash Conference. San Diego: SAE, 2003. [25] ROBIN S. HUMOS: human model for safety: a joint effort towards the development of refined human-like car occupant models [C]//Proceedings of the 17th International Technical Conference on the Enhanced Safety of Vehicles. Amsterdam: SAE, 2001. [26] RUAN J S, EL-JAWAHRI R, BARBAT S, et al. Biomechanical analysis of human abdominal impact responses and injuries through finite element simulations of a full human body model [C]//Proceedings of the 49th Stapp Car Crash Conference. National Library of Medicine: SAE, 2005. [27] 范志强, 常瀚林, 何天明, 等. 基于PVDF复合压电效应的低强度冲击波柔性测量 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(1): 013102. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0152.FAN Z Q, CHANG H L, HE T M, et al. Flexible measurement of low-intensity shock wave based on coupling piezoelectric effect of PVDF [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(1): 013102. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0152. [28] GREER A. Numerical modeling for the prediction of primary blast injury to the lung [D]. Waterloo: University of Waterloo, 2007: 117–141. [29] 卢芳云, 蒋邦海, 李翔宇, 等. 武器战斗部投射与毁伤 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 1–316. [30] AXELSSON H, YELVERTON J T. Chest wall velocity as a predictor of nonauditory blast injury in a complex wave environment [J]. The Journal of Trauma: Injury, Infection, and Critical Care, 1996, 40(3S): 31S–37S. DOI: 10.1097/00005373-199603001-00006. -







 下载:
下载: