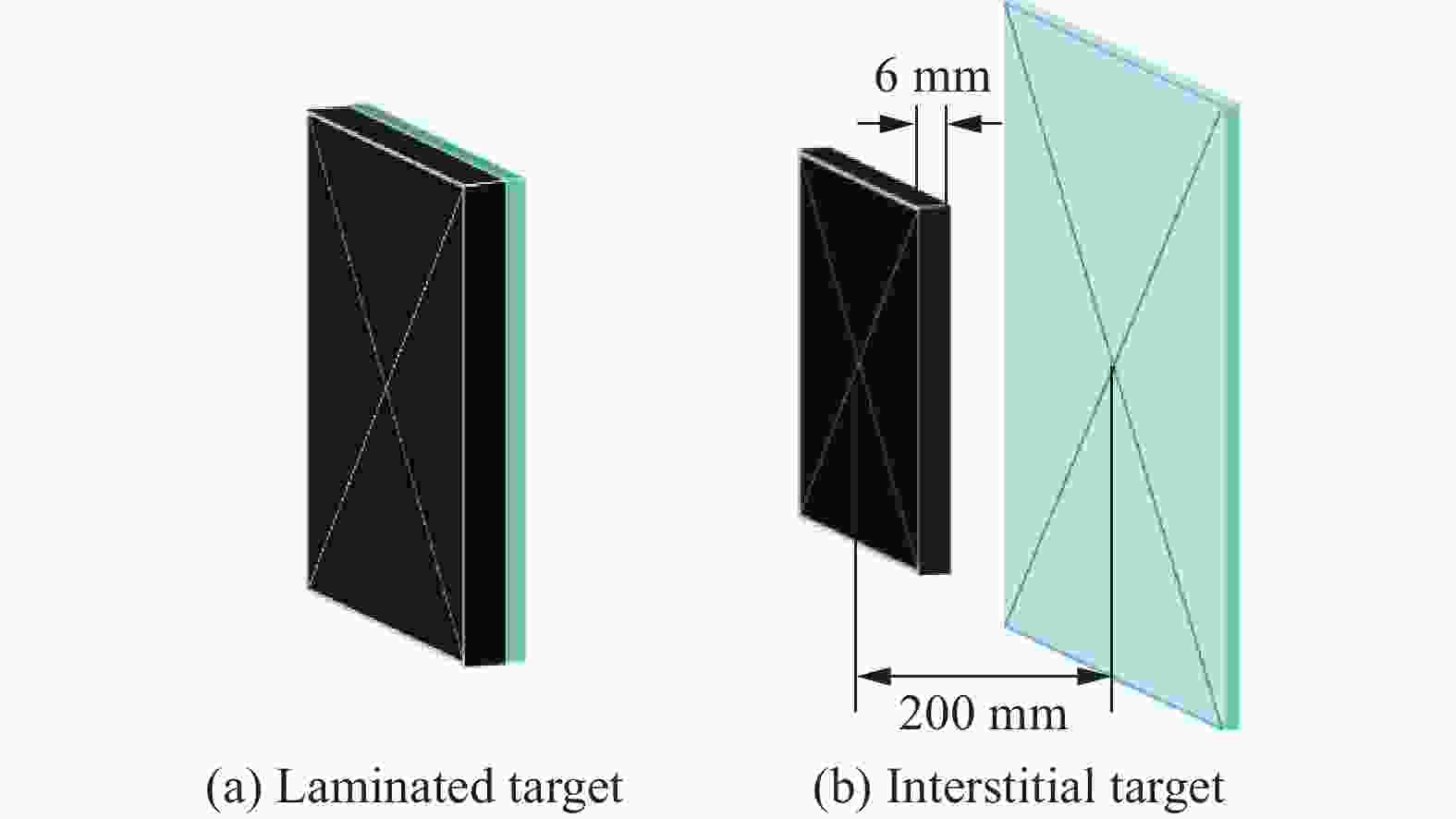
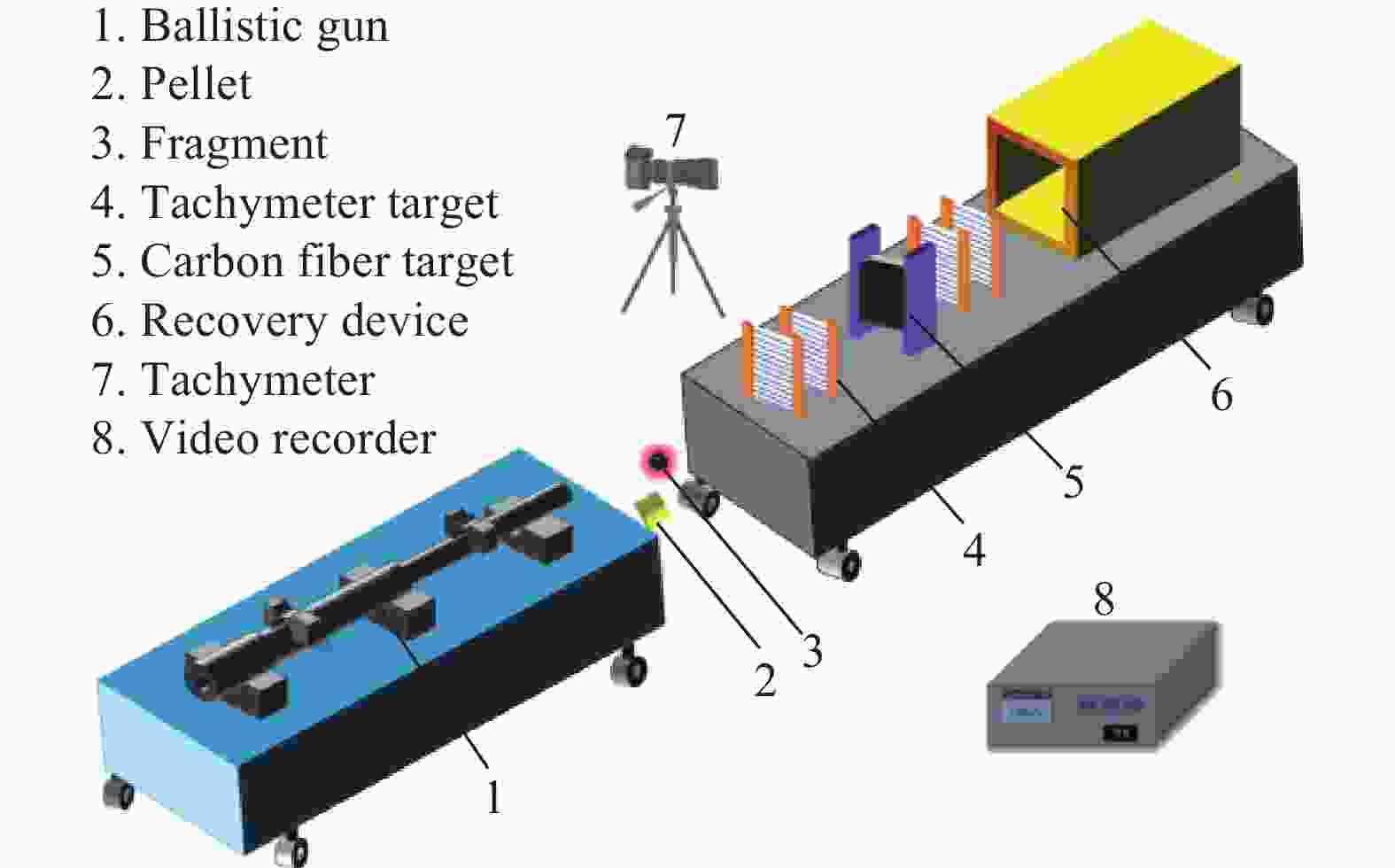
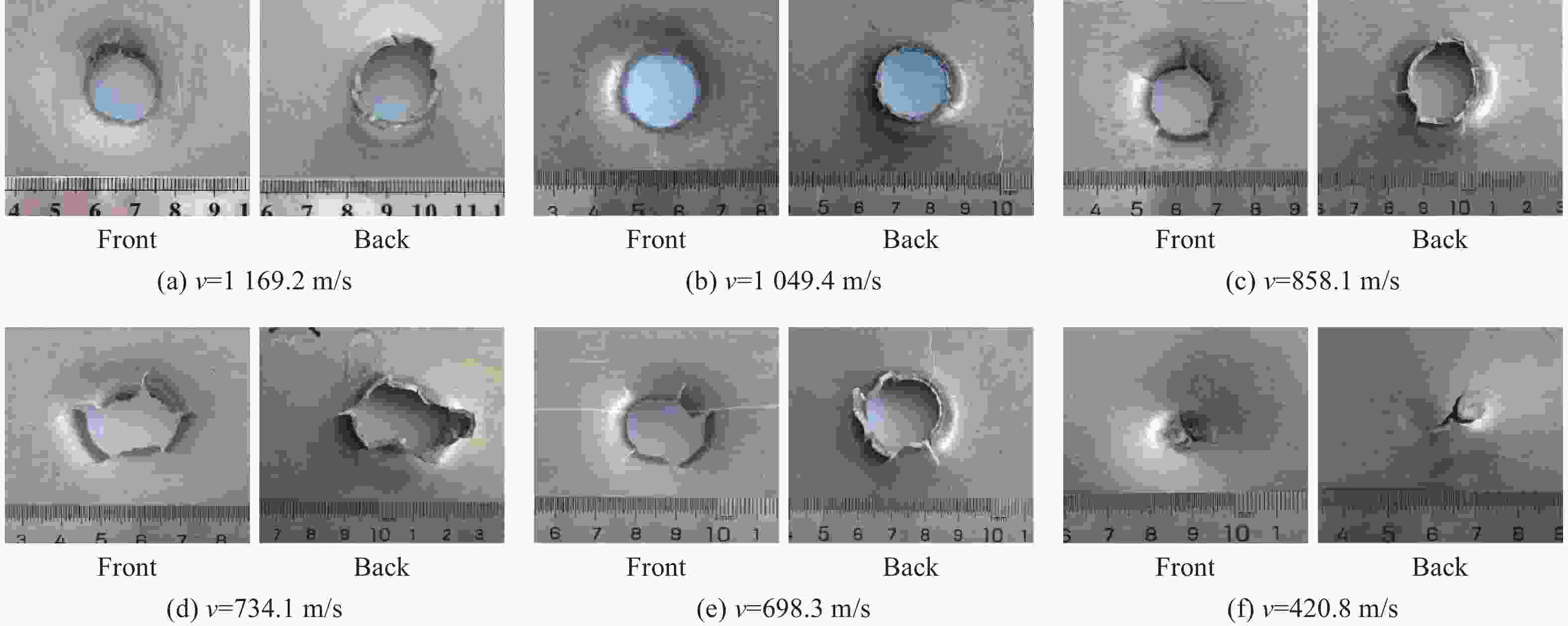
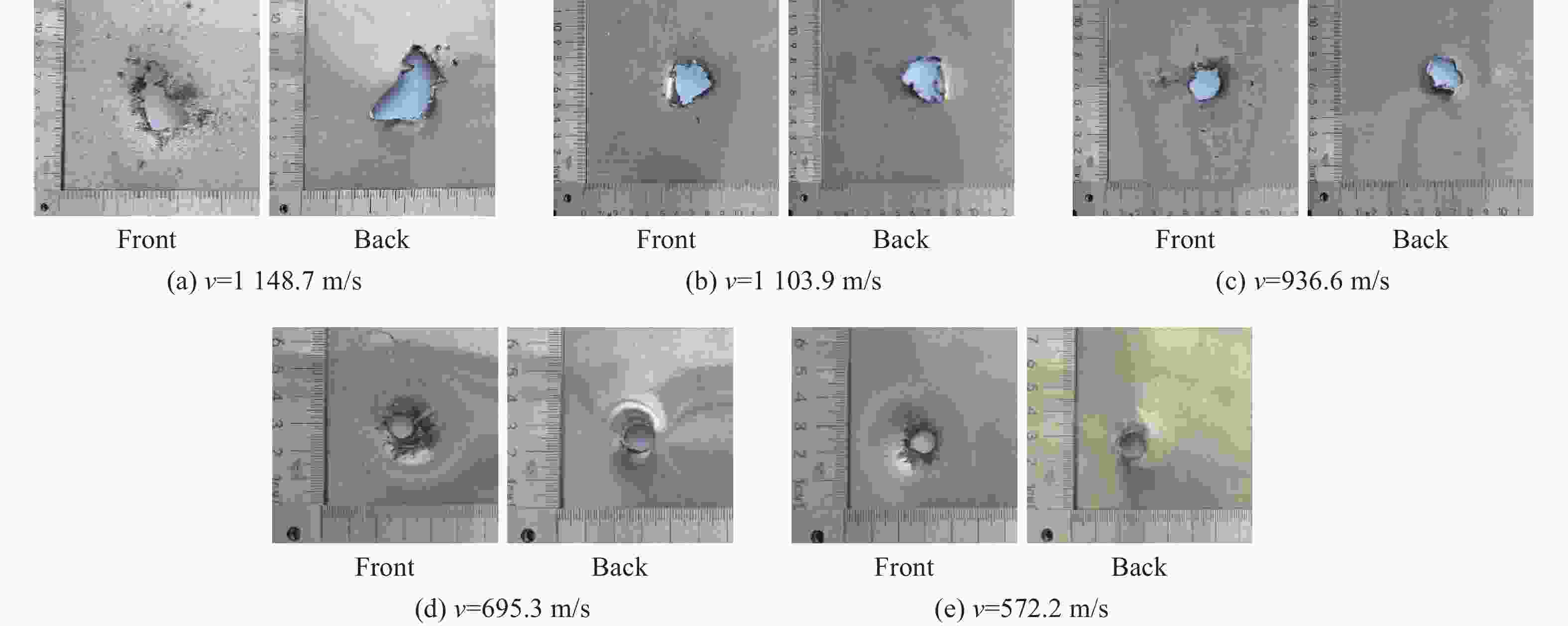
Experimental study of Zr-based amorphous alloy fragmentation penetration through CFRP and post-effective LY12 targets
-
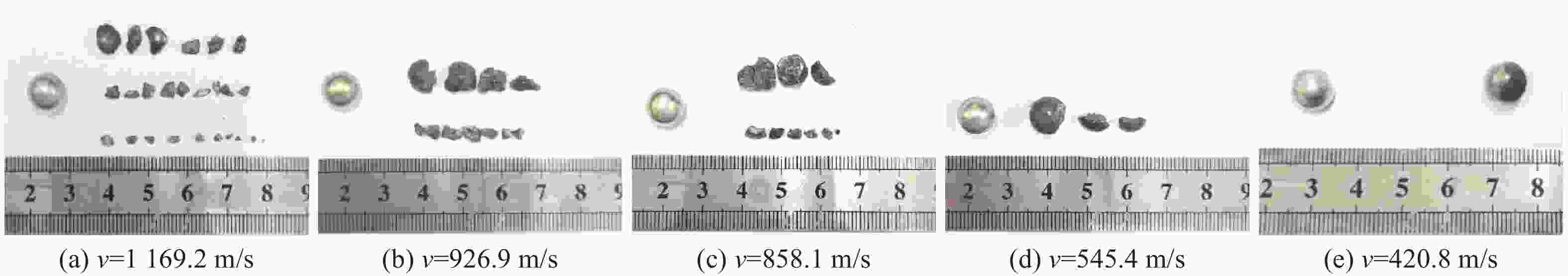
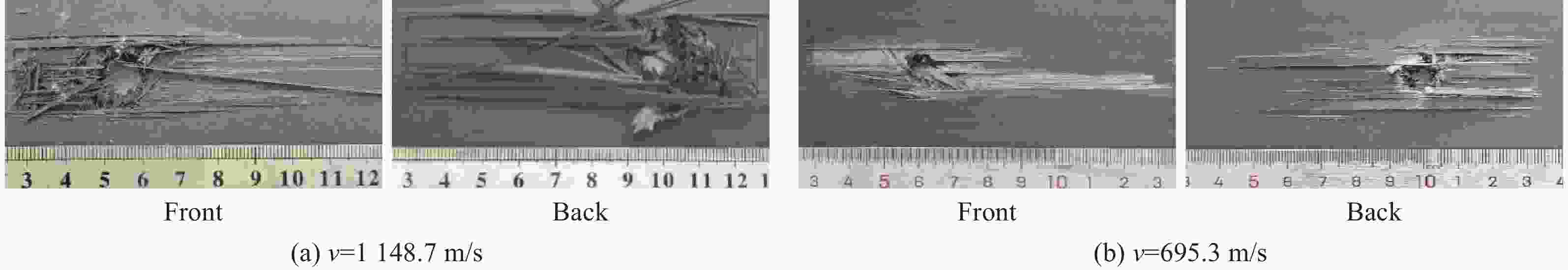
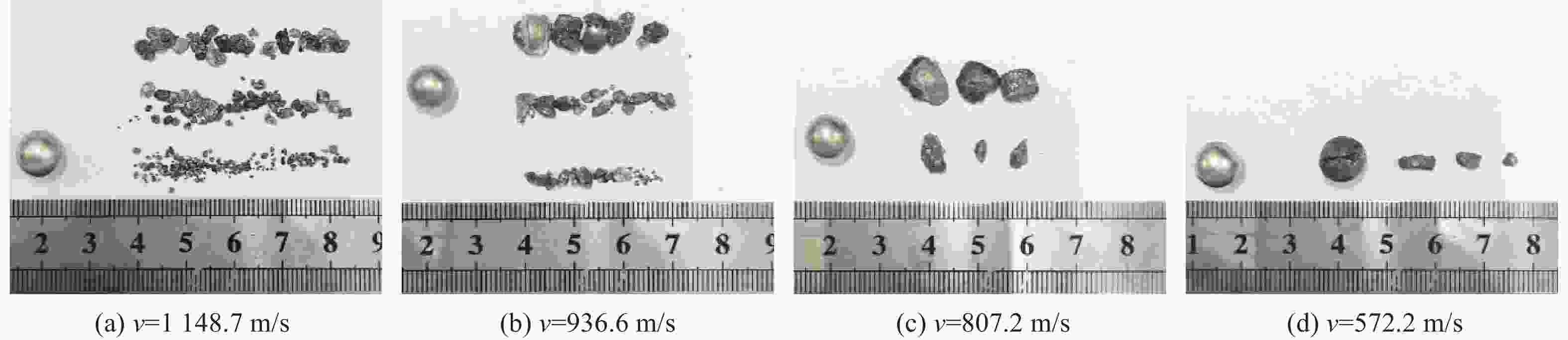
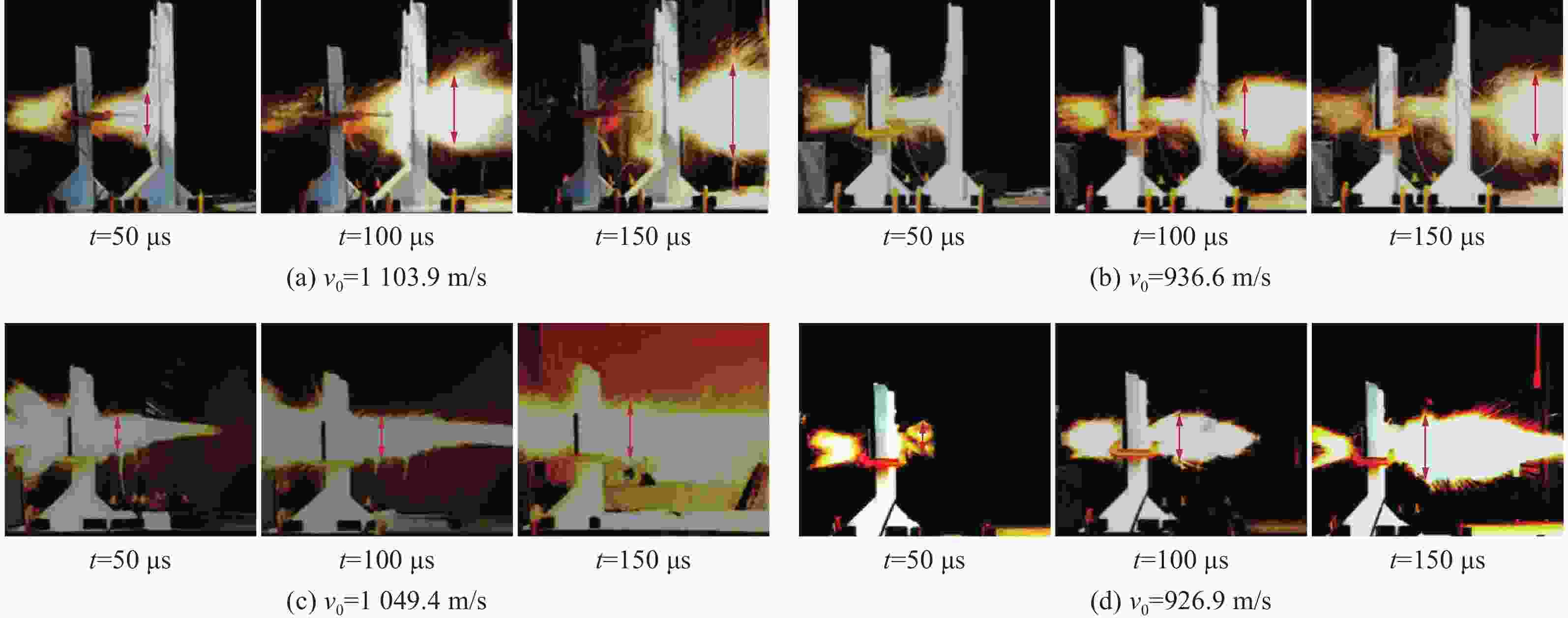
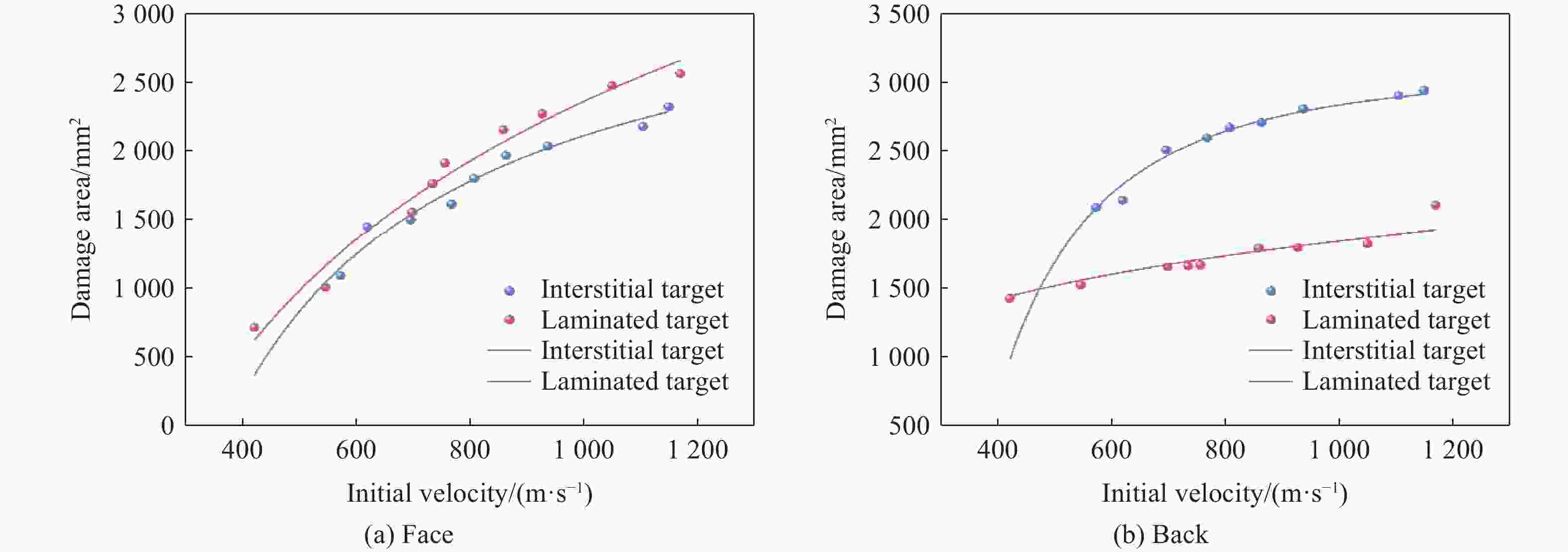
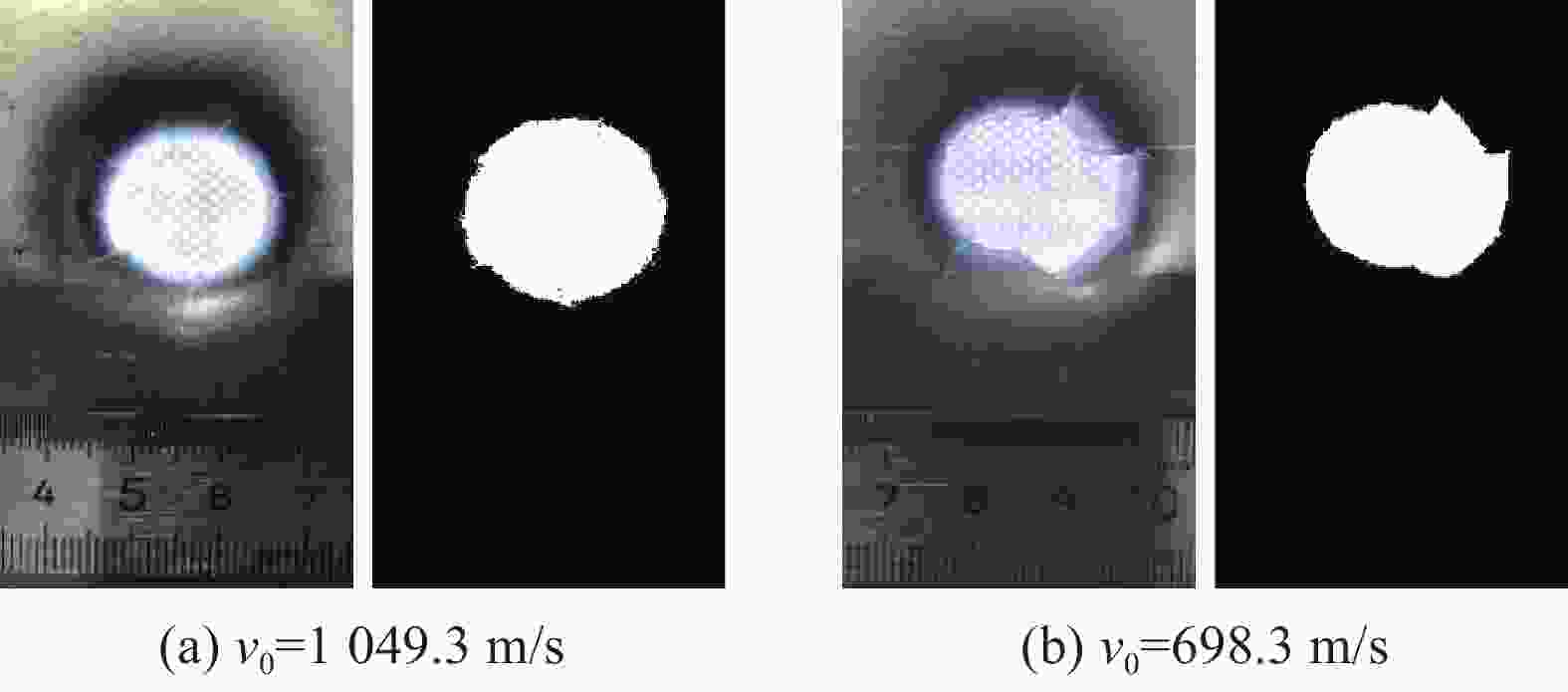
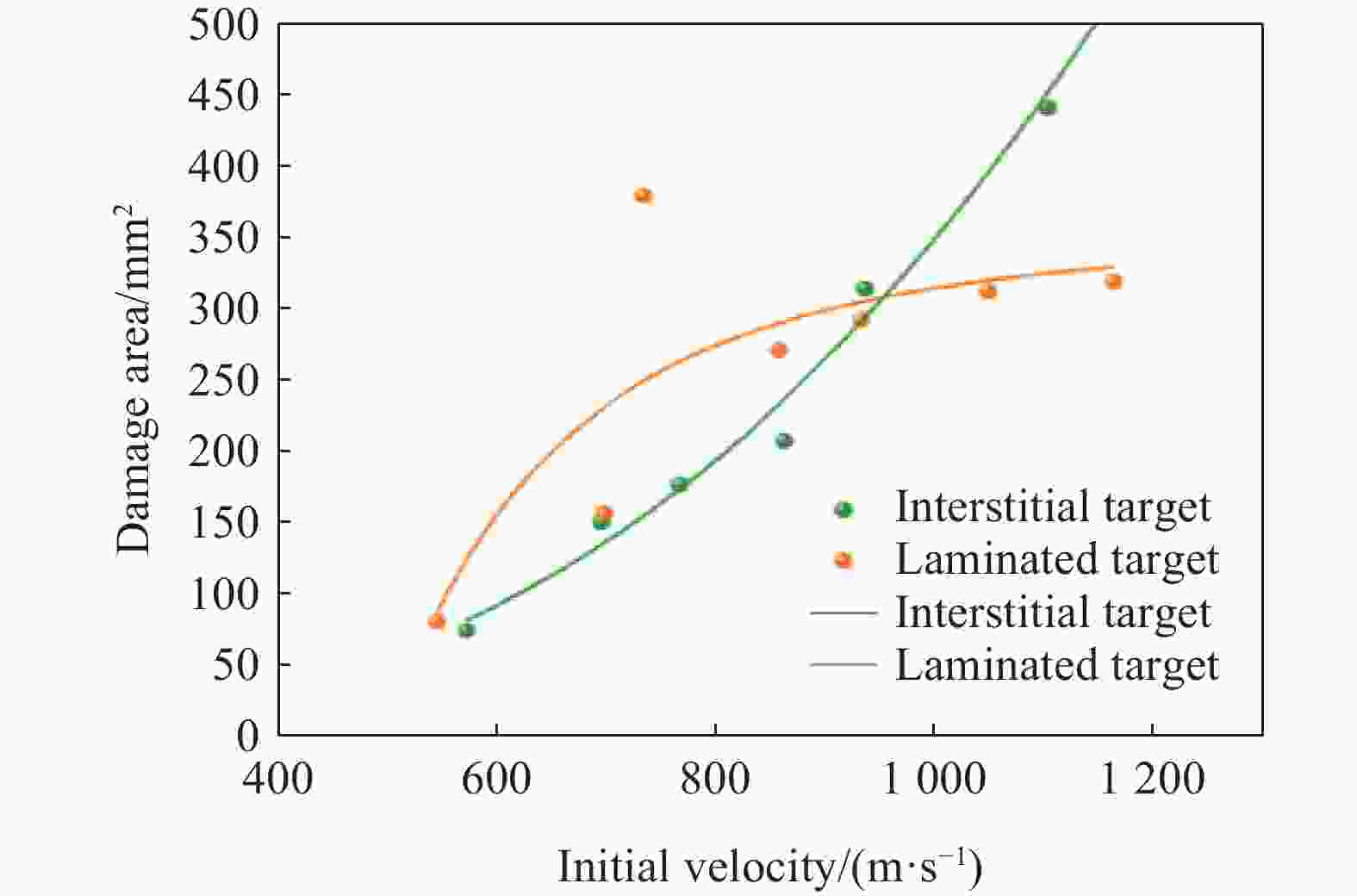
摘要: 为研究锆基非晶合金破片侵彻碳纤维损伤机理和后效靶毁伤能力,采用12.7 mm弹道枪开展了球形锆基非晶合金破片侵彻6 mm厚碳纤维靶和后效2 mm厚LY12靶组成的叠合靶和间隔靶的弹道枪试验研究,采用图像识别技术分析了后效LY12靶毁伤的面积。研究结果表明:碳纤维靶的毁伤面积与破片速度正相关,且无明显扩孔反应,迎弹面主要为纤维剪切破坏和压缩变形毁伤,背弹面则主要为拉伸撕裂破坏以及层间失效。破片冲击相同设置靶板时,LY12靶的毁伤面积随冲击速度增加而增大,速度低于954.7 m/s时,间隔靶后效LY12靶的毁伤面积小于叠合靶后效LY12靶毁伤面积,随着速度提高,间隔靶后效LY12靶的毁伤面积快速提高,而叠合靶后效LY12靶毁伤面积的增长趋于平缓,且前者远大于后者。因此,高速撞击时,设置间隔靶对于后效毁伤更有利。Abstract: In order to investigate the damage mechanisms of zirconium-based amorphous alloy fragments penetrating carbon fiber targets and their subsequent effects on target failure, ballistic experiments were conducted using a 12.7 mm ballistic gun. The experiments involved spherical zirconium-based amorphous alloy fragments impacting a composite target system consisting of a 6-mm thick carbon fiber laminate and a 2-mm thick LY12 alloy plate. These targets were arranged in both stacked and spaced configurations to evaluate the effects of target configuration on the damage caused by fragment impact. To quantitatively assess the subsequent damage, image recognition technology was employed to analyze the damage area of the LY12 target after impact.The results indicated that the damage area of the carbon fiber target was positively correlated with the velocity of the impacting fragment, with no significant hole expansion observed. On the front side, damage primarily resulted from fiber shear failure and compressive deformation, while the back face of the carbon fiber laminate exhibited tensile tearing and interlaminar delamination. These findings suggest that the carbon fiber target experienced a combination of mechanical damage modes, including shear and compressive deformation on the impact side, and tensile and delamination failures on the rear face, as a result of the high-velocity impact.In the case of the LY12 aluminum alloy target, the damage area increased with fragment velocity. When the velocity was below 954.7 m/s, the damage area on the LY12 target in the spaced configuration was smaller than that of the stacked configuration. However, as the fragment velocity increased, the damage area of the LY12 target in the spaced configuration grew rapidly, while the damage area in the stacked configuration increased more gradually. At higher velocities, the damage area in the spaced configuration was significantly larger than that in the stacked configuration. This trend suggests that for high-velocity impacts, the spaced configuration of the targets was more effective in promoting greater damage to the LY12 target.
-
Key words:
- Zr-based amorphous alloys /
- intrusion /
- carbon fibers /
- destructive capacity
-
表 1 试验结果
Table 1. Experimental results
类型 v0/(m·s−1) 穿透碳纤维靶 穿透LY12 靶 类型 v0/(m·s−1) 穿透碳纤维靶 穿透LY12 靶 叠合靶 1169.2 是 是 间隔靶 1148.7 是 是 1049.4 是 是 1103.9 是 是 926.9 是 是 936.6 是 是 858.1 是 是 862.9 是 是 755.6 是 是 807.2 是 是 734.1 是 是 767.5 是 是 698.3 是 是 695.3 是 是 545.4 是 是 619.3 是 是 420.8 否 否 572.2 是 是 表 2 不同设置靶板中LY12靶毁伤面积
Table 2. Destruction area of LY12 targets at different set
类型 初始速度/(m·s−1) LY12毁伤面积/mm2 类型 初始速度/(m·s−1) LY12毁伤面积/mm2 叠合靶 1169.2 317.4 间隔靶 1148.7 508.2 1049.4 310.6 1103.9 439.2 933.6 290.9 936.9 312.4 858.1 269.3 862.9 206.9 734.1 377.5 767.5 176.6 698.3 156.6 695.3 150.0 545.4 75.3 572.2 80.7 420.8 0 -
[1] 张先锋, 赵晓宁. 多功能含能结构材料研究进展 [J]. 含能材料, 2009, 17(6): 731–739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2009.06.021.ZHANG X F, ZHAO X N. Review on multifunctional energetic structural materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2009, 17(6): 731–739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9941.2009.06.021. [2] XU F Y, ZHENG Y F, YU Q B, et al. Experimental study on penetration behavior of reactive material projectile impacting aluminum plate [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 95: 125–132. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.05.007. [3] WALTERS W P, KECSKES L J, PRITCHETT J E. Investigation of a bulk metallic glass as a shaped charge liner material: ARL-TR 3864 [R]. Aberdeen Proving Ground: Army Research Laboratory, 2006. [4] CONNER R D, DANDLIKER R B, SCRUGGS V, et al. Dynamic deformation behavior of tungsten-fiber/metallic-glass matrix composites [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2000, 24(5): 435–444. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(99)00176-1. [5] 张云峰, 罗兴柏, 刘国庆, 等. W/ZrNiAlCu亚稳态合金复合材料破片对RHA靶的侵彻释能特性 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(2): 023301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0065.ZHANG Y F, LUO X B, LIU G Q, et al. Penetration and energy release effect of W/ZrNiAlCu metastable reactive alloy composite rragment against RHA target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(2): 023301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0065. [6] 尚春明, 施冬梅, 张云峰, 等. Zr基非晶合金的燃烧释能特性 [J]. 含能材料, 2020, 28(6): 564–568. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2019219.SHANG C M, SHI D M, ZHANG Y F, et al. Combustion and energy release characteristics of Zr-based amorphous alloys [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2020, 28(6): 564–568. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2019219. [7] 王佳敏, 张先锋, 查旭, 等. ZrTiCuNiBe非晶合金及其钨丝增强复合材料的冲击释能特性研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1036–1046. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2023.084.WANG J M, ZHANG X F, CHA X, et al. Study on impact energy release characteristics of ZrTiCuNiBe amorphous alloy and its tungsten-fiber reinforced composites [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2023, 43(10): 1036–1046. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2023.084. [8] 杨林, 于述贤, 范群波. Zr77.1Cu13Ni9.9非晶合金破片侵彻LY12铝合金及TC4钛合金靶板毁伤后效及机理对比研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 417–428. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.092.YANG L, YU S X, FAN Q B. Damage effect and mechanism of Zr77.1Cu13Ni9.9 bulk metallic glasses fragment penetrating LY12 aluminum alloy and TC4 titanium alloy target plate [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2023, 43(4): 417–428. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2022.092. [9] CHEN X, DU C X, CHENG C, et al. Impact-induced chemical reaction behavior of ZrTiNiCuBe bulk metallic glass fragments impacting on thin plates [J]. Materials and Technology, 2018, 52(6): 737–743. DOI: 10.17222/mit.2018.089. [10] 张玉令, 施冬梅, 张云峰, 等. W骨架/Zr基非晶合金复合材料破片侵彻能力与后效研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(5): 053301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0063.ZHANG Y L, SHI D M, ZHANG Y F, et al. Investigation of penetration ability and aftereffect of Zr-based metallic glass reinforced porous W matrix composite fragments [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(5): 053301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0063. [11] 李建利, 赵帆, 张元, 等. 碳纤维及其复合材料在军工领域的应用 [J]. 合成纤维, 2014, 43(3): 33–35, 40. DOI: 10.16090/j.cnki.hcxw.2014.03.007.LI J L, ZHAO F, ZHANG Y, et al. Application of carbon fiber and its composites in military industry [J]. Synthetic Fiber in China, 2014, 43(3): 33–35, 40. DOI: 10.16090/j.cnki.hcxw.2014.03.007. [12] 黄亿洲, 王志瑾, 刘格菲. 碳纤维增强复合材料在航空航天领域的应用 [J]. 西安航空学院学报, 2021, 39(5): 44–51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9233.2021.05.009.HUANG Y Z, WANG Z J, LIU G F. Application of carbon fiber reinforced composite in aerospace [J]. Journal of Xi’an Aeronautical University, 2021, 39(5): 44–51. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9233.2021.05.009. [13] 李健, 洪术华, 沈金平. 复合材料在海洋船舶中的应用 [J]. 机电设备, 2019, 36(4): 57–59. DOI: 10.16443/j.cnki.31-1420.2019.04.013.LI J, HONG S H, SHEN J P. Applications of composite materials on marine ships [J]. Mechanical and Electrical Equipment, 2019, 36(4): 57–59. DOI: 10.16443/j.cnki.31-1420.2019.04.013. [14] 周杰, 何勇, 何源, 等. Al/PTFE/W反应材料的准静态压缩性能与冲击释能特性 [J]. 含能材料, 2017, 25(11): 903–912. DOI: 10.11943/j.issn.1006-9941.2017.11.004.ZHOU J, HE Y, HE Y, et al. Quasi-static compression properties and impact energy release characteristics of Al/PTFE/W reactive materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2017, 25(11): 903–912. DOI: 10.11943/j.issn.1006-9941.2017.11.004. [15] 罗普光, 毛亮, 魏晨杨, 等. 锆基非晶活性材料动态力学性能及本构关系 [J]. 含能材料, 2021, 29(12): 1176–1181. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2021068.LUO P G, MAO L, WEI C Y, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive relations of Zr-based amorphous reactive material [J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2021, 29(12): 1176–1181. DOI: 10.11943/CJEM2021068. [16] 侯先苇, 张先锋, 熊玮, 等. 活性无序合金冲击的释能特性及在毁伤元中应用研究进展 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(9): 091401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0189.HOU X W, ZHANG X F, XIONG W, et al. Research progress on impact energy release characteristics of reactive disordered alloy and its application in kill elements [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(9): 091401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0189. [17] 杜宁, 张先锋, 熊玮, 等. 爆炸驱动典型活性材料能量释放特性研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(4): 042301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0239.DU N, ZHANG X F, XIONG W, et al. Energy-release characteristics of typical reactive materials under explosive loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(4): 042301. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0239. [18] 王震鸣. 复合材料结构力学 [J]. 力学进展, 2012, 16(2): 202–209. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-1986-2-j1986-024.WANG Z M. The mechanics of composite structures [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2012, 16(2): 202–209. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-1986-2-j1986-024. -







 下载:
下载: