Numerical study of shock wave generated by hydrogen-oxygen detonation in a large shock tube
-
摘要: 大型激波管作为爆炸冲击毁伤与防护实验平台时,能规避小尺度缩尺实验中由于尺寸效应造成的实验结果不准确,但由于设备的稀缺性,目前仍然缺乏利用大型激波管直接模拟炸药爆炸冲击波形的研究。因此,进行大型激波管内氢氧爆轰驱动方式下冲击波生成与传播过程的数值模拟。根据现存大型激波设备的结构特点,建立具有驱动管、激波整形段和变截面出口特征的大型激波管二维模型。冲击波的生成和传播过程使用含有七步氢氧反应模型的二维非定常黏性可压缩流体控制方程表达,湍流模型选取重整化群k-ε模型,并选用二维瞬态耦合式求解器进行数值模拟计算。根据数值模拟结果,研究在大型激波管中采用氢氧爆轰驱动方式时,驱动初始物理条件、低反应活性气体掺混、激波管几何构型等因素对爆轰形成冲击波波形的影响,并总结多种因素下产生冲击波特征参数的变化规律。最后,选取黑火药爆炸冲击波实验数据作为目标,依据冲击波变化规律,模拟了大型激波管中冲击波波形调控过程。结果表明,在多因素耦合作用调控下,能够实现在大型激波管中利用氢氧爆轰驱动方式对特定爆炸冲击波的模拟复现。
-
关键词:
- 大型激波管 /
- 重整化群 k-ε模型 /
- 激波物理 /
- 波形复现
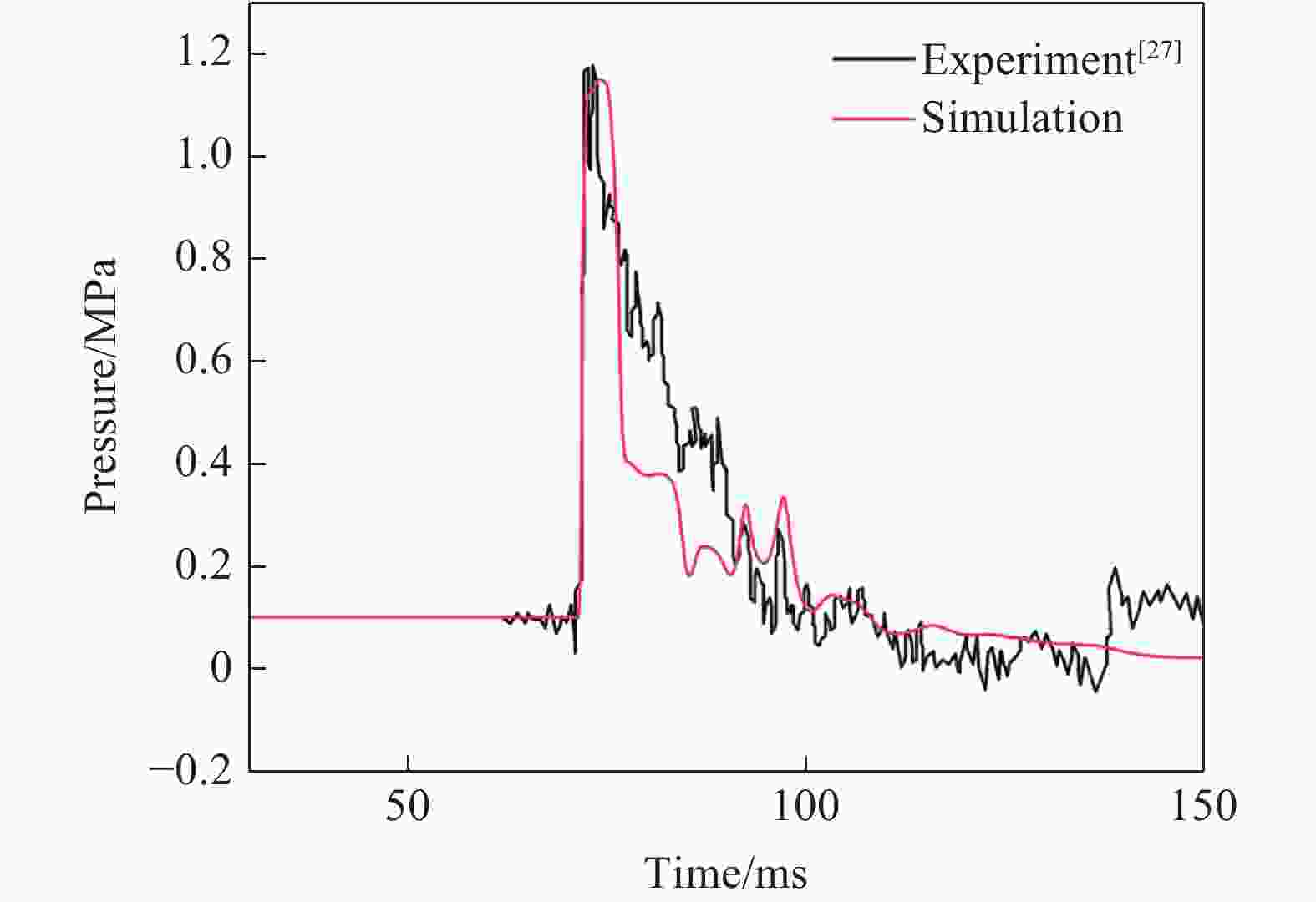
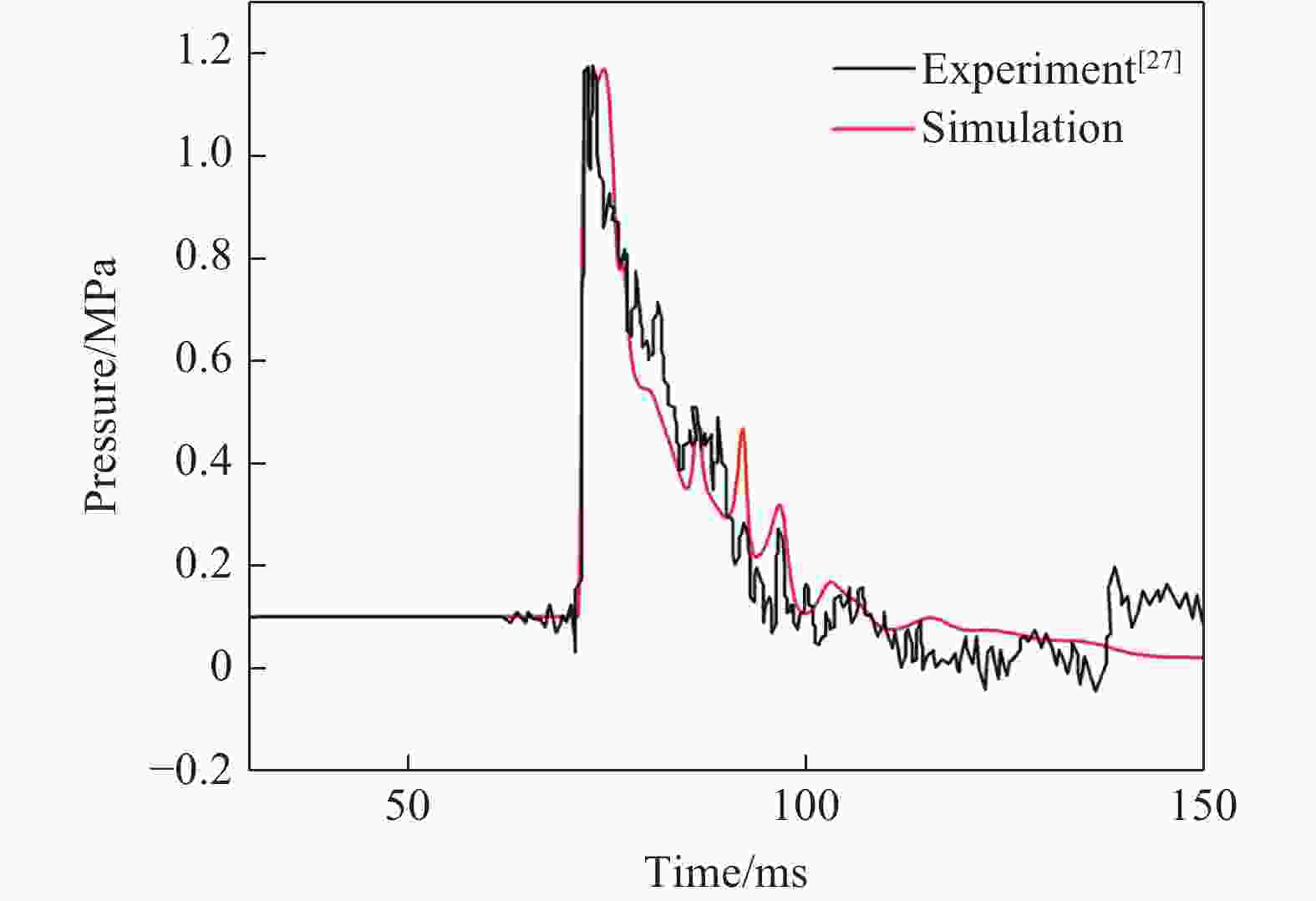
Abstract: Blast wave damage and protection experiments conducted in large-scale shock tubes can avoid the inaccurate experimental results caused by the size effect in small-scale model experiments. However, due to the scarcity of equipment, there is still a lack of research on directly simulating the shock waveforms of explosive explosions using large-scale shock tubes at present. Therefore, a numerical simulation study of the generation and propagation process of shock wave generated by hydrogen-oxygen detonation in a large shock tube were conducted, and the reproduction of blast wave in a large shock tube was realized based on numerical simulation. Based on the designs of existing large shock tubes, a two-dimensional axisymmetric model of a large shock tube with driving tube, shock shaping section and variable angle outlet was established. The governing equation of a two-dimensional unsteady viscous compressible flow together with the seven-step reaction of the hydrogen-oxygen detonation mechanism was used to simulate the generation and propagation process of the shock wave. The renormalization group k-ε model was selected as the turbulence model, and the two-dimensional transient coupling solver was used for numerical simulation. Due to the large scale of the model, turbulence has little effect on the far-field shock wave. Therefore, the finite rate component transport model was selected to couple the interaction between turbulence and chemical reaction, and a two-dimensional transient coupled solver was used. Based on the numerical results, the influence of initial physical conditions of the driving gas, inert gas mixing, and the shock tube configurations on the formation of shock wave waveforms by detonation was studied. The variation laws of shock wave characteristic parameters under various factors were summarized. Finally, using the experimental data of black powder explosion shock waves as the target, the process of shock wave waveform regulation in the large shock tube was simulated according to the shock wave variation laws. The results show that under the combined effect of multiple factors, it is possible to simulate and reproduce the specific explosion shock wave using the hydrogen-oxygen detonation driving method in the large shock tube. -
表 1 不同工况初始条件设置
Table 1. Initial settings of different working conditions
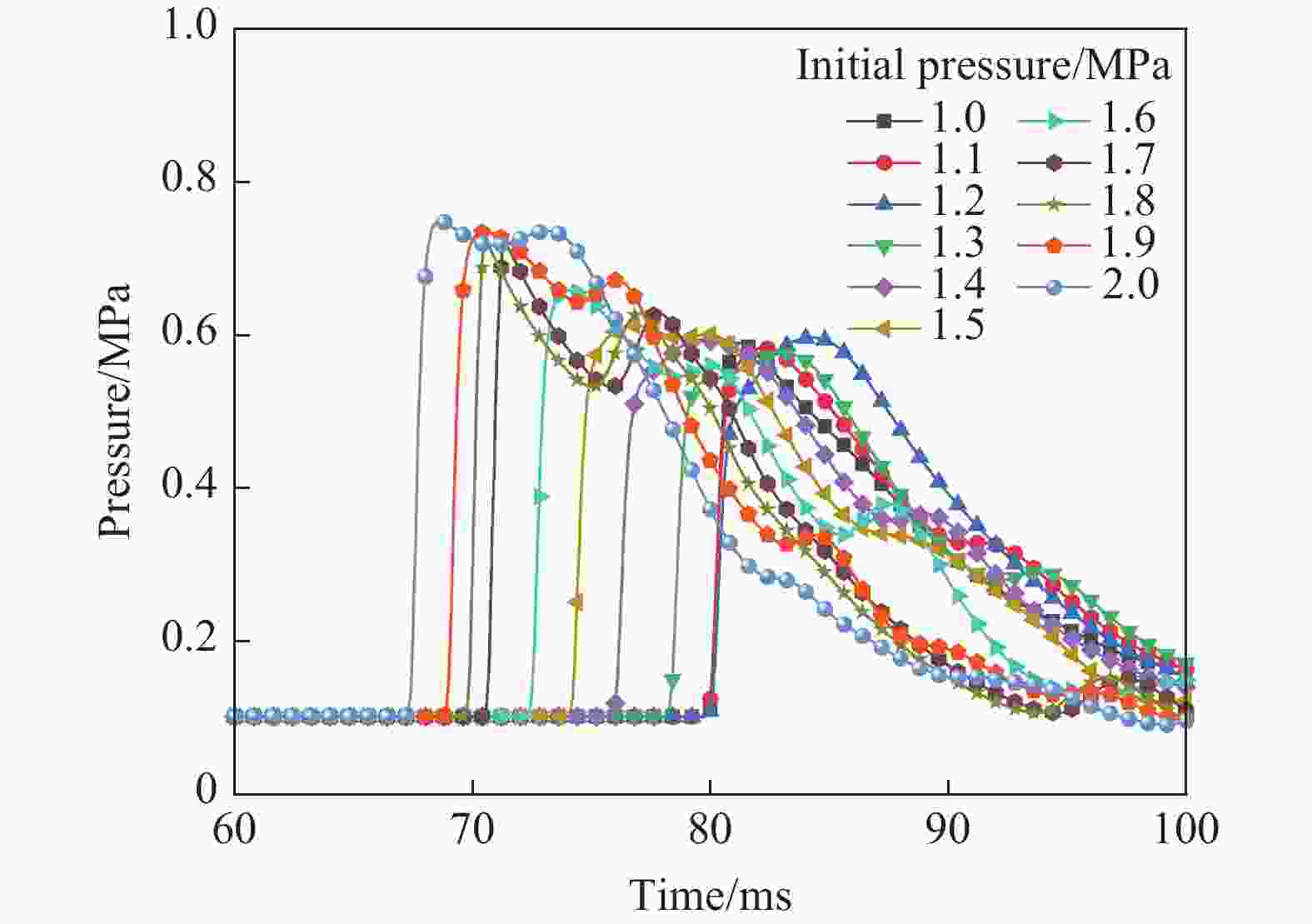
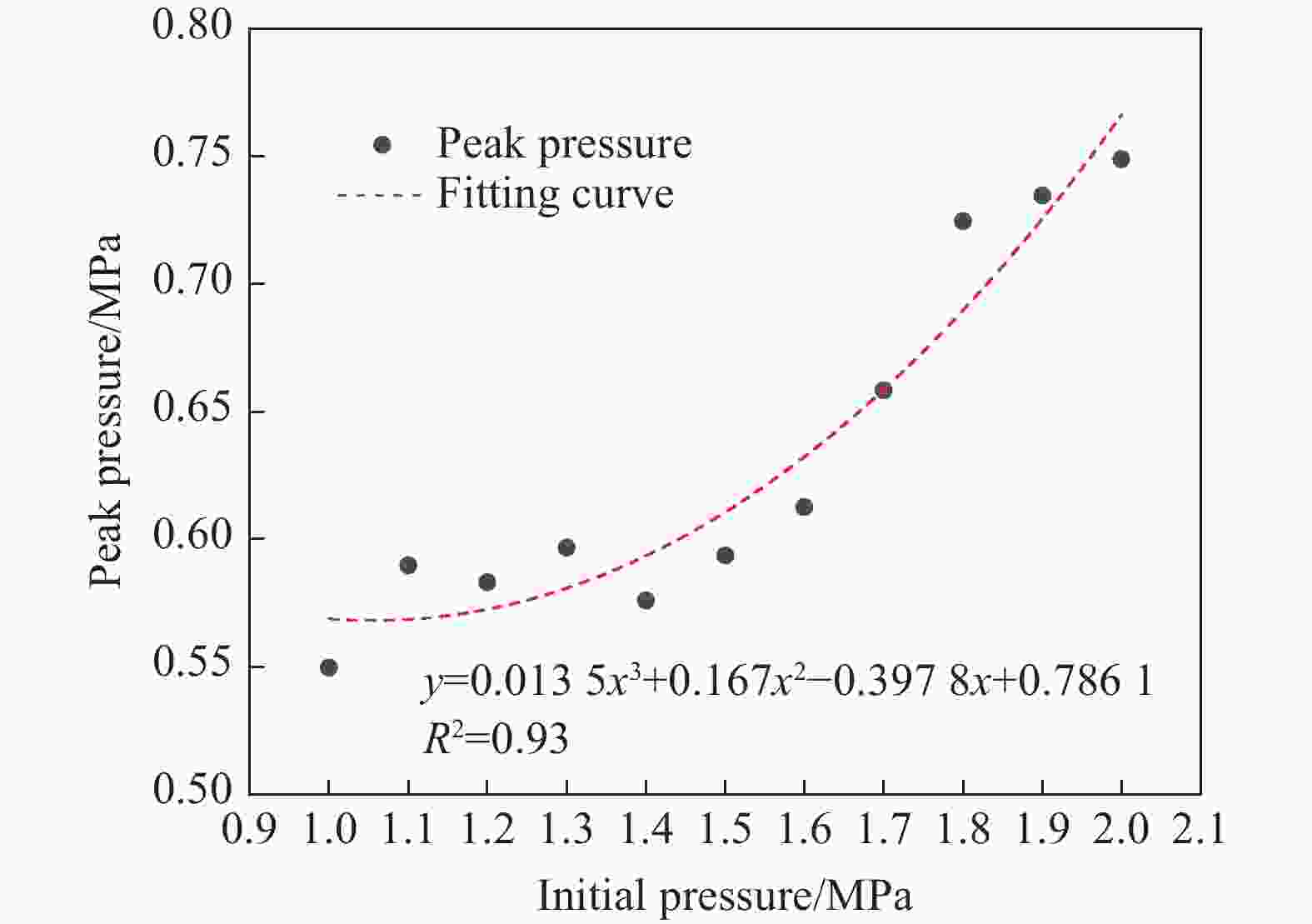
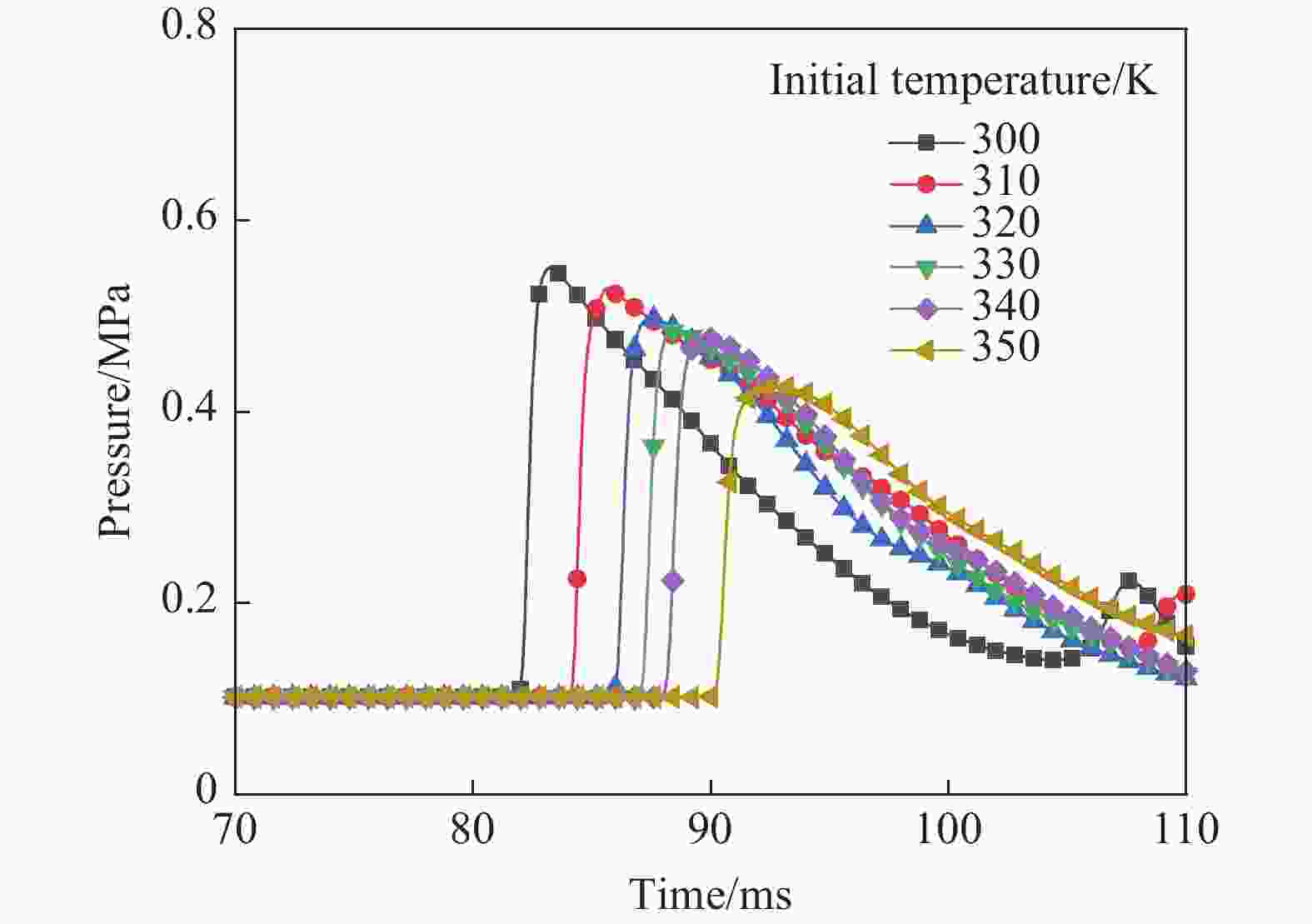
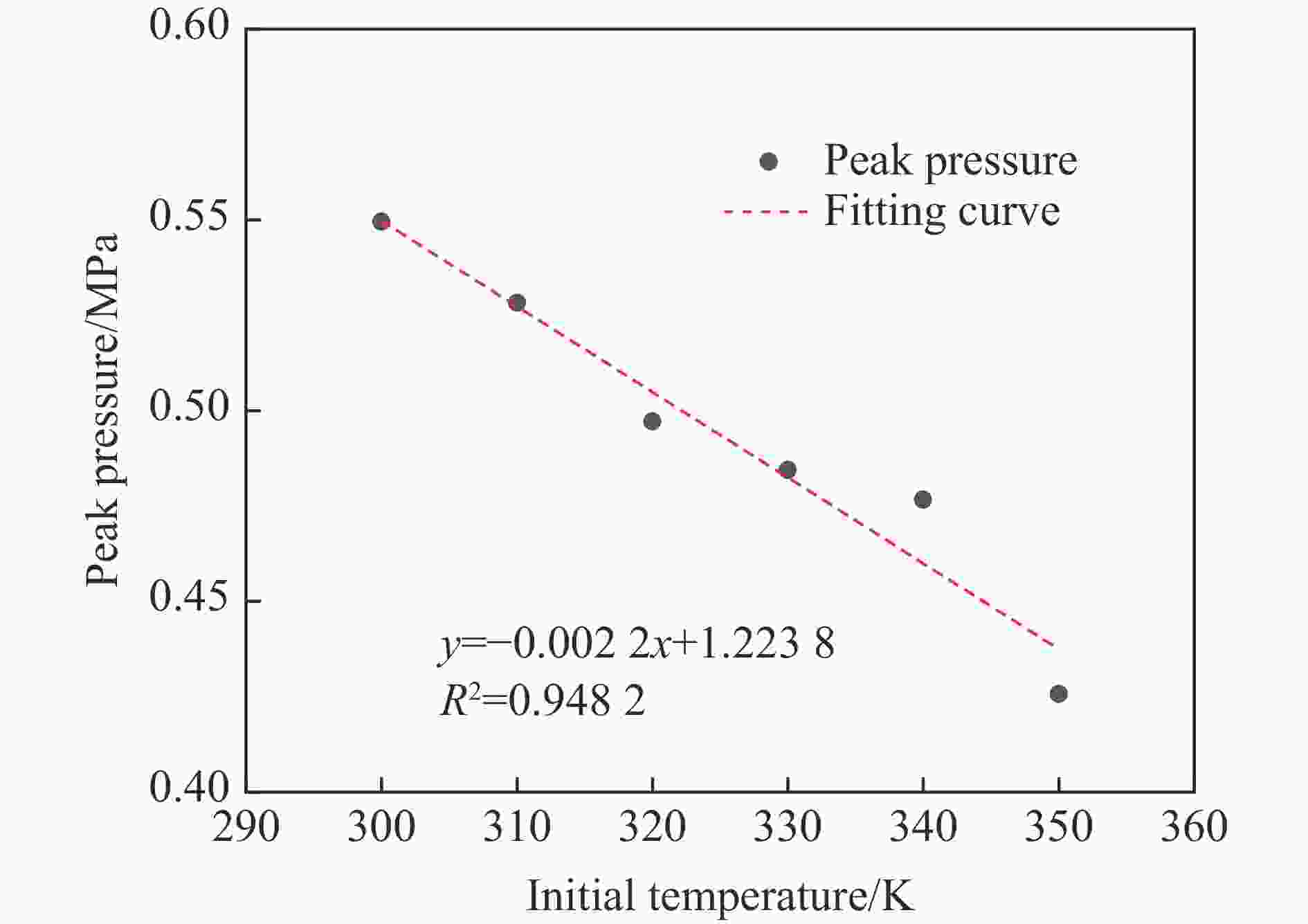
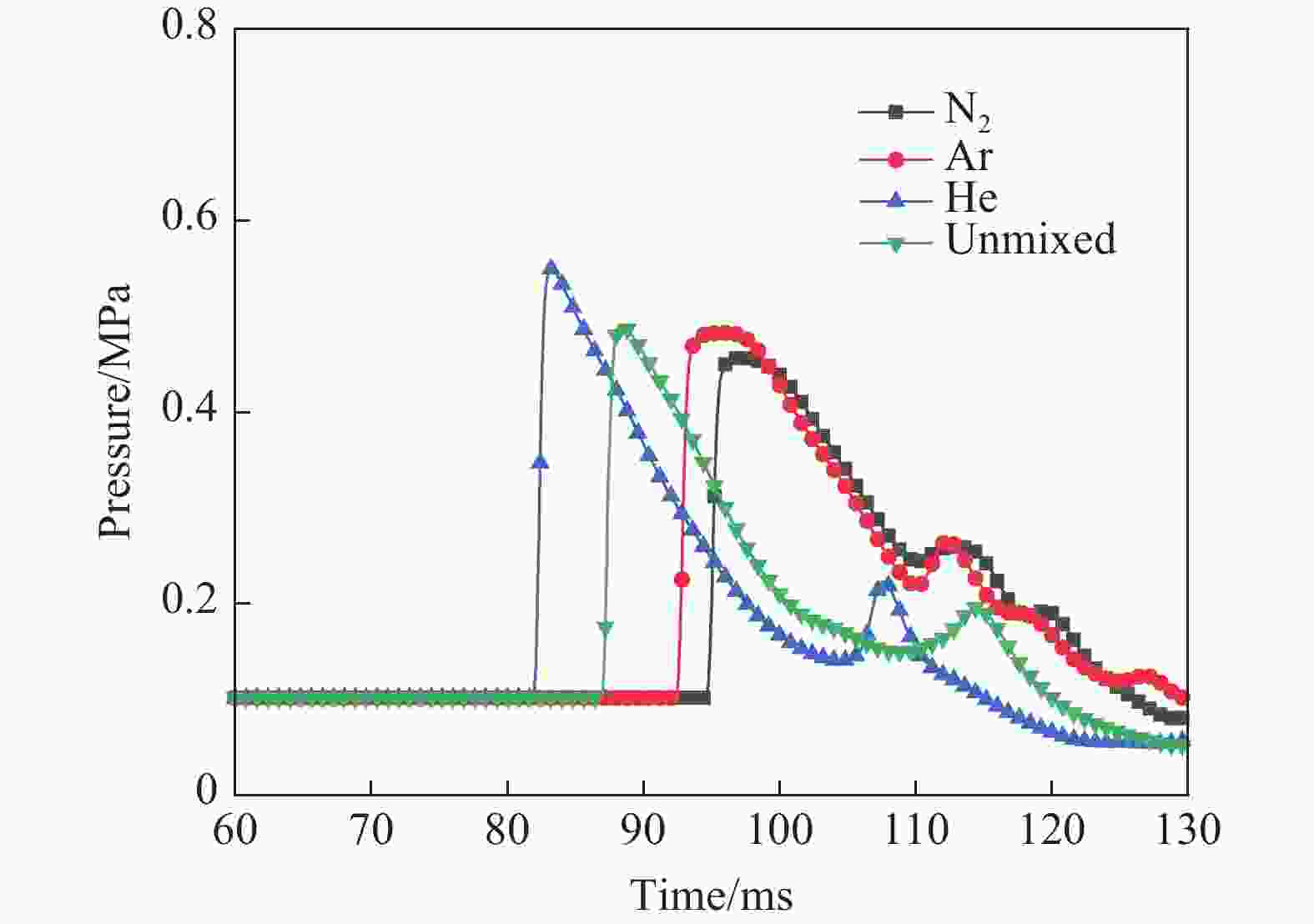
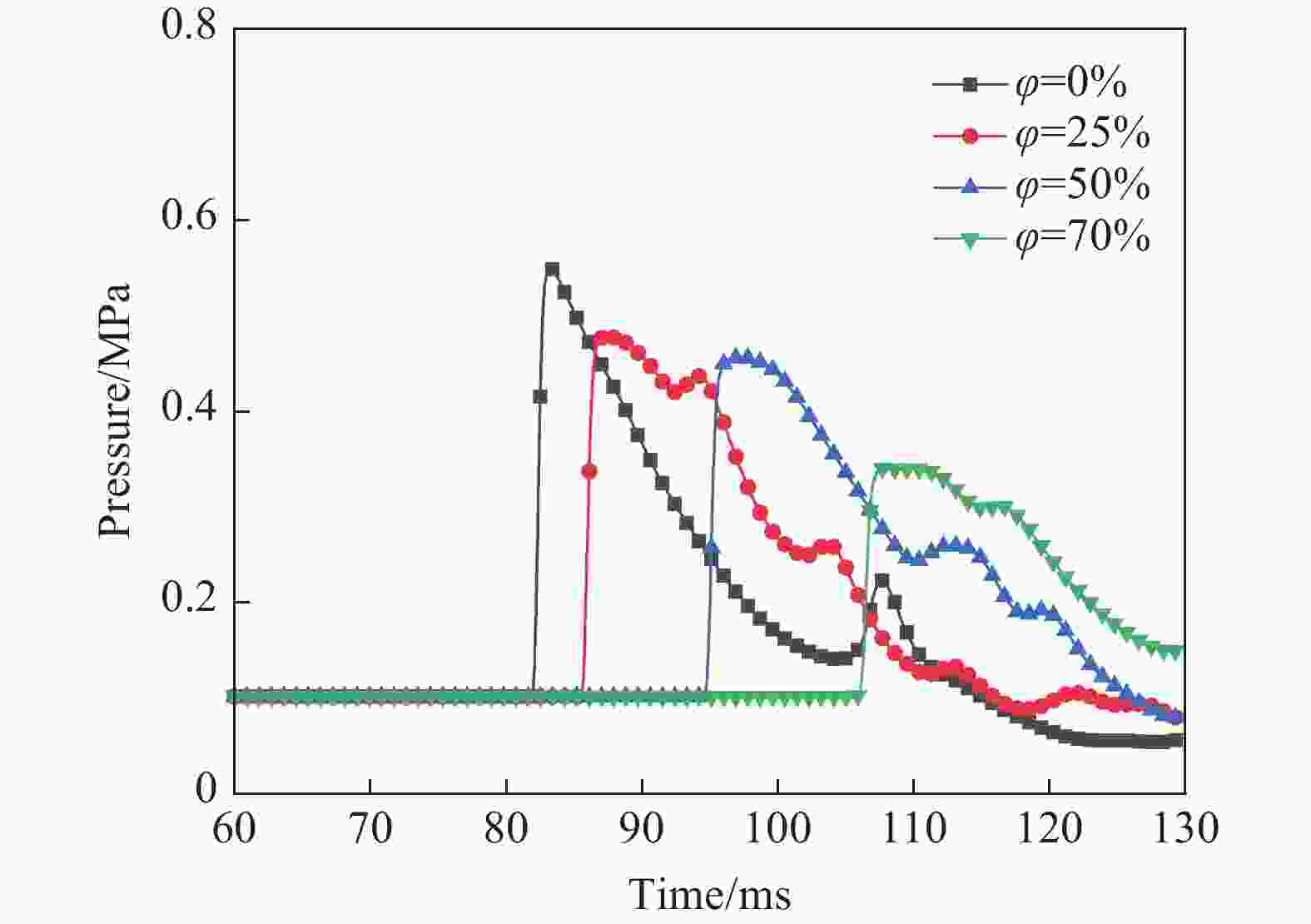
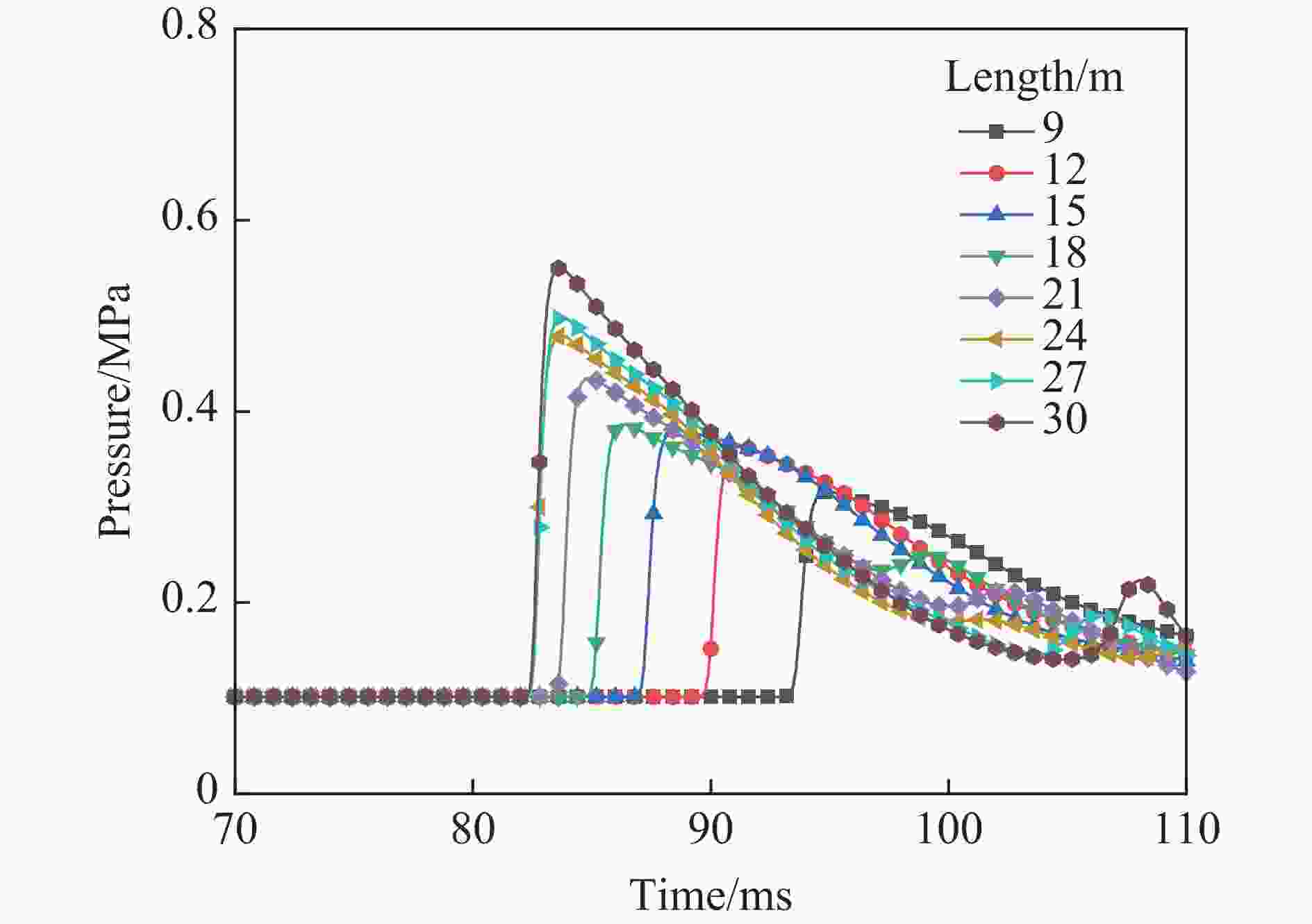
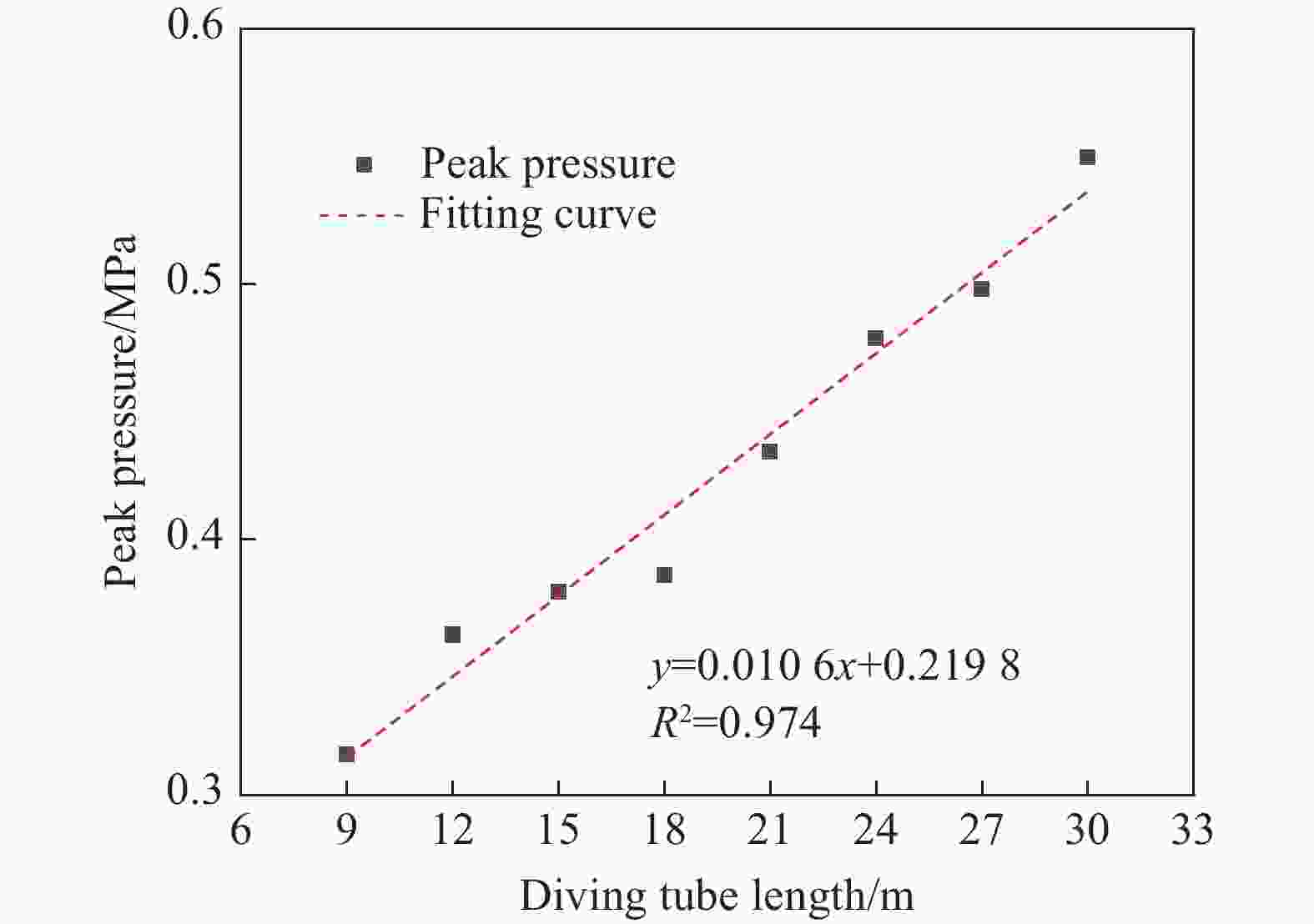
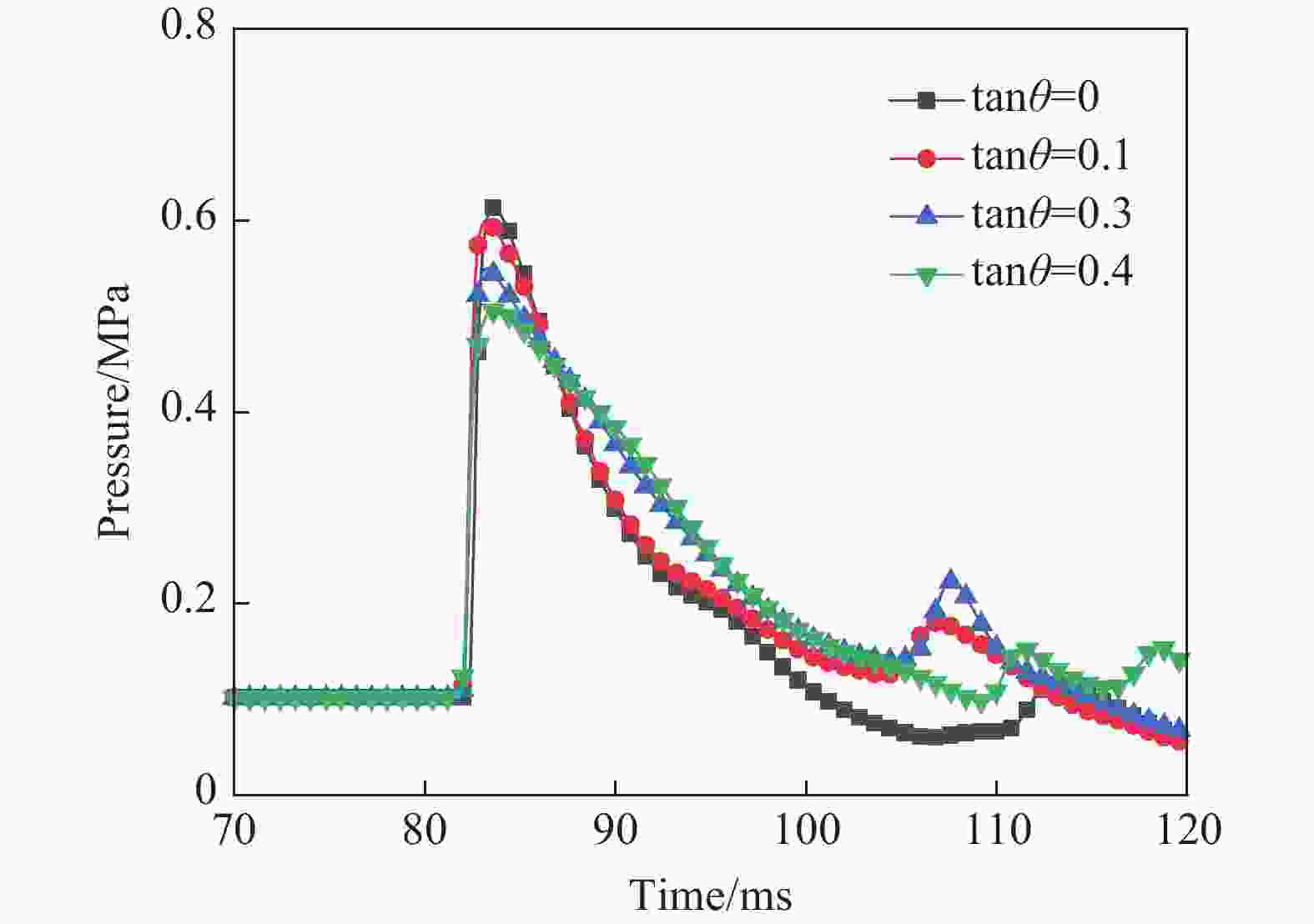
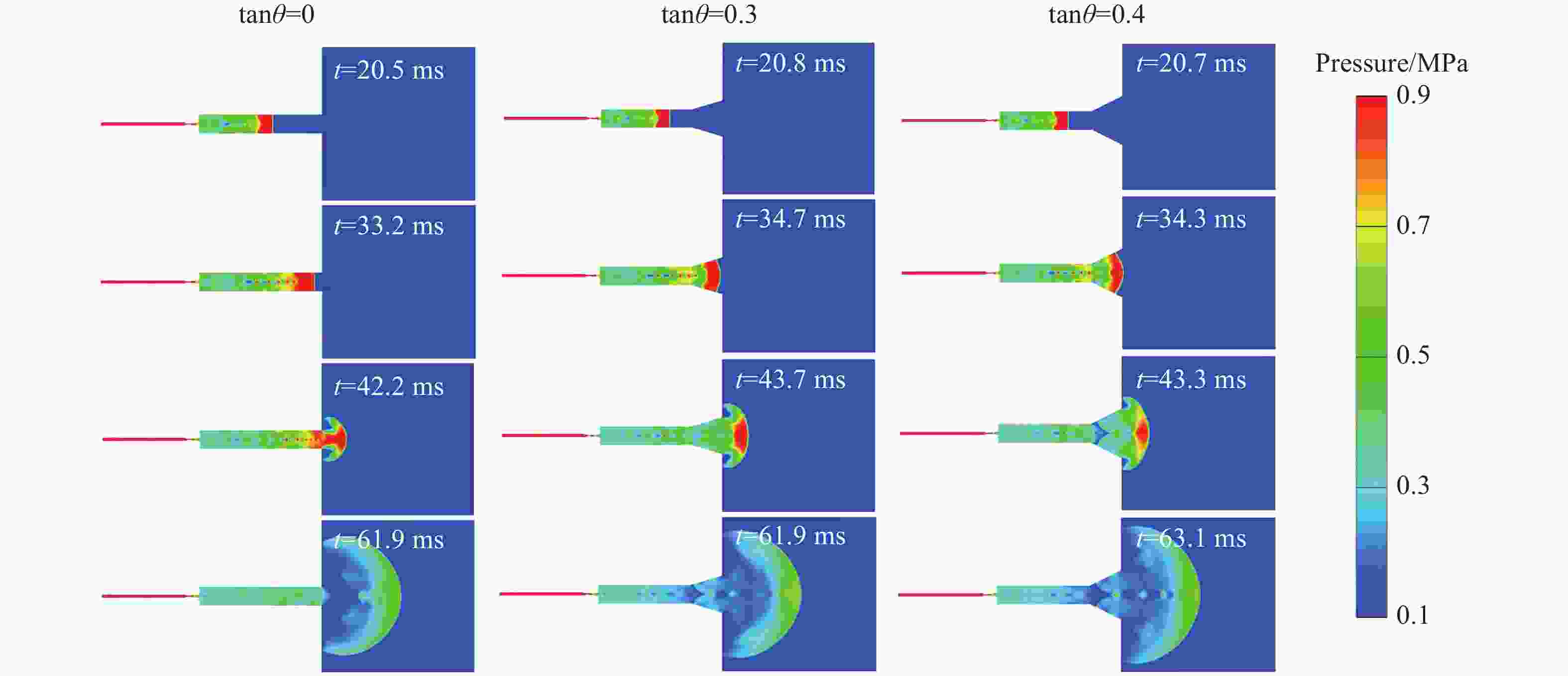
工况 驱动气体组分 低反应活性气体掺混 φ/% T0/K p0/MPa L/m ϕ tan θ 1 H2/O2 无 0 300 1.0~2.0 30 1 0.3 2 H2/O2 无 0 300~350 2.0 30 1 0.3 3 H2/O2 N2/He/Ar 50 300 1.0 30 1 0.3 4 H2/O2 N2 25~50 300 1.0 30 1 0.3 5 H2/O2 无 0 300 3.0 9~30 1 0.3 6 H2/O2 无 0 300 1.0 30 1 0.1~0.4 7 H2/O2 无 0 300 2.685 30 1 0.3 8 H2/O2 N2 25 300 2.69 30 1 0.3 表 2 七步氢氧化学反应简化机理模型参数
Table 2. Parameters for seven-step hydrogen-oxygen chemical reaction mechanism model
反应步 基元反应 A n Ea/(kJ∙mol−1) 1 H2+O2 = OH+OH 1.70×1013 0.00 101.07 2 H+O2 = O+OH 1.20×1017 −0.91 34.77 3 H2+OH = H2O+H 2.20×1013 0.00 10.84 4 H2+O = OH+H 5.06×104 2.67 13.24 5 OH+OH = H2O+O 6.30×1012 0.00 2.30 6 OH+H+M = H2O+M 2.12×1022 −2.00 0.0 7 H+H+M = H2+M 7.30×1017 −1.00 0.0 注:(1)第6步第三体(碰撞系数)分别为H2(2.5)、H2O(12.0)、N2(1.0)、Ar(0.4)、He(0.4);(2)第7步第三体(碰撞系数)分别为H2(2.5)、H2O(12.0)、N2(1.0)、Ar(0.5)、He(0.5)。 -
[1] 杨鑫, 石少卿, 程鹏飞, 等. 爆炸冲击波在空气中传播规律的经验公式对比及数值模拟 [J]. 四川建筑, 2007, 27(5): 71–73. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8983.2007.05.033. [2] 陈宏, 赵伟, 林建民, 等. 用双爆轰驱动的激波管技术 [C]//第十届全国激波与激波管学术讨论会论文集. 黄山: 中国力学学会直属激波与激波管专业组, 2002. [3] 张玉磊, 王胜强, 袁建飞, 等. 不同量级TNT爆炸冲击波参数相似律实验研究 [J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2016, 36(6): 53–56. DOI: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2016.06.014.ZHANG Y L, WANG S Q, YUAN J F, et al. Experimental research on similarity law of explosive shock wave parameters with different orders of magnitude TNT [J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2016, 36(6): 53–56. DOI: 10.15892/j.cnki.djzdxb.2016.06.014. [4] SADOVSKII M A. Mechanical action of air shock waves of explosion, based on experimental data [M]. Moscow, USA: Nauka Press, 1952. [5] BRODE H L. Numerical solutions of spherical blast waves [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1955, 26(6): 766–775. DOI: 10.1063/1.1722085. [6] BRODE H L. Blast wave from a spherical charge [J]. The Physics of Fluids, 1959, 2(2): 217–229. DOI: 10.1063/1.1705911. [7] HENRYCH J. The dynamics of explosion and its use [M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1979. [8] MILLS C. The design of concrete structure to resist explosions and weapon effects [C]//Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Concrete for Hazard Protections. Edinburgh, 1987: 61–73. [9] 周丰峻, 郑磊, 孙云厚, 等. 真实空气中TNT装药爆炸近区冲击波传播特性研究 [J]. 中国工程科学, 2017, 19(6): 18–26. DOI: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2017.06.004.ZHOU F J, ZHENG L, SUN Y H, et al. Research on propagation characteristic in close-in field of shock wave of TNT charge explosion [J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2017, 19(6): 18–26. DOI: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2017.06.004. [10] 刘科种. 爆炸能量输出结构与高威力炸药研究 [D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2009.LIU K Z. Study on explosive energy output structure and high explosive charge [D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2009. [11] 康越, 张仕忠, 张远平, 等. 基于激波管评价的单兵头面部装备冲击波防护性能研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(8): 085901. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0395.KANG Y, ZHANG S Z, ZHANG Y P, et al. Research on anti-shockwave performance of the protective equipment for the head of a soldier based on shock tube evaluation [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(8): 085901. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0395. [12] WU C Q, HAO H. Modeling of simultaneous ground shock and airblast pressure on nearby structures from surface explosions [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(6): 699–717. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2004.03.002. [13] 仲倩, 王伯良, 黄菊, 等. TNT空中爆炸超压的相似律 [J]. 火炸药学报, 2010, 33(4): 32–35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2010.04.008.ZHONG Q, WANG B L, HUANG J, et al. Study on the similarity law of TNT explosion overpressure in air [J]. Chinese Journal of Explosives and Propellants, 2010, 33(4): 32–35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7812.2010.04.008. [14] 张军, 黄含军, 王军评, 等. 炸药驱动式爆炸管的载荷计算 [J]. 装备环境工程, 2021, 18(5): 21–27. DOI: 10.7643/issn.1672-9242.2021.05.004.ZHANG J, HUANG H J, WANG J P, et al. Simulation on the blast load inside the explosively drived shock tube [J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering, 2021, 18(5): 21–27. DOI: 10.7643/issn.1672-9242.2021.05.004. [15] 白旭. 激波管波形控制技术研究 [J]. 仪表技术, 2023(1): 69–74. DOI: 10.19432/j.cnki.issn1006-2394.2023.01.012.BAI X. Research on shock tube waveform control technology [J]. Instrumentation Technology, 2023(1): 69–74. DOI: 10.19432/j.cnki.issn1006-2394.2023.01.012. [16] 杨军, 薛斌. 激波管管长对阶跃压力波形的影响分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(3): 252–257. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.03.035.YANG J, XUE B. Effects of shock tube length on step pressure waveform [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(3): 252–257. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2019.03.035. [17] 杨基明, 李祝飞, 朱雨建, 等. 激波的传播与干扰 [J]. 力学进展, 2016, 46(1): 201613. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-16-009.YANG J M, LI Z F, ZHU Y J, et al. Shock wave propagation and interactions [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2016, 46(1): 201613. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-16-009. [18] 任辉启, 王世合, 周松柏, 等. 大型爆炸波模拟装置研制及其应用 [C]//第十六届全国激波与激波管学术会议论文集. 洛阳: 中国力学学会激波与激波管专业委员会, 2014: 10–22. [19] 谷笳华, 李仲发, 方治家. 用氢氧爆轰驱动气体直接模拟爆炸波 [C]//第十届全国激波与激波管学术讨论会. 黄山: 中国力学学会直属激波与激波管专业组, 2002. [20] 俞鸿儒, 赵伟, 袁生学. 氢氧爆轰驱动激波风洞的性能 [J]. 气动实验与测量控制, 1993, 7(3): 38–42.YU H R, ZHAO W, YUAN S X. Performance of shock tunnel with H2-O2 detonation driver [J]. Amrodynamic Experiment and Measurement & Control, 1993, 7(3): 38–42. [21] 俞鸿儒. 氢氧燃烧及爆轰驱动激波管 [J]. 力学学报, 1999, 31(4): 389–397. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.1999.04.002.YU H R. Oxy-hydrogen combustion and detonation driven shock tube [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 1999, 31(4): 389–397. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0459-1879.1999.04.002. [22] 俞鸿儒, 李斌, 陈宏. 激波管氢氧爆轰驱动技术的发展进程 [J]. 力学进展, 2005, 35(3): 315–322. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2005.03.002.YU H R, LI B, CHEN H. The development of gaseous detonation driving techniques for a shock tube [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2005, 35(3): 315–322. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2005.03.002. [23] 崔云霄, 王万鹏, 王雷元, 等. 压缩气体驱动大型激波管内部流场的数值模拟 [C]//中国计算力学大会2014暨第三届钱令希计算力学奖颁奖大会论文集. 贵阳: 中国力学学会计算力学专业委员会, 2014. [24] 韩文虎, 张博, 王成. 气相爆轰波起爆与传播机理研究进展 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(12): 121402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0398.HAN W H, ZHANG B, WANG C. Progress in studying mechanisms of initiation and propagation for gaseous detonations [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(12): 121402. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0398. [25] DAVIDENKO D, GÖKALP I, DUFOUR E, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrogen supersonic combustion and validation of computational approach [C]//12th AIAA International Space Planes and Hypersonic Systems and Technologies. Norfolk: 2013. DOI: 10.2514/6.2003-7033. [26] YAMANAKA A, ARIGA Y, OBBARA T, et al. Study on performance of detonation-driven shock tube [J]. JSME International Journal Series B Fluids and Thermal Engineering, 2002, 45(2): 425–431. DOI: 10.1299/jsmeb.45.425. [27] 佐建君. 典型环境中特定炸药爆炸冲击波超压及安全防护 [D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2006. -






 下载:
下载: