An intermediate strain rate LSHPB system for soft materials and its application
-
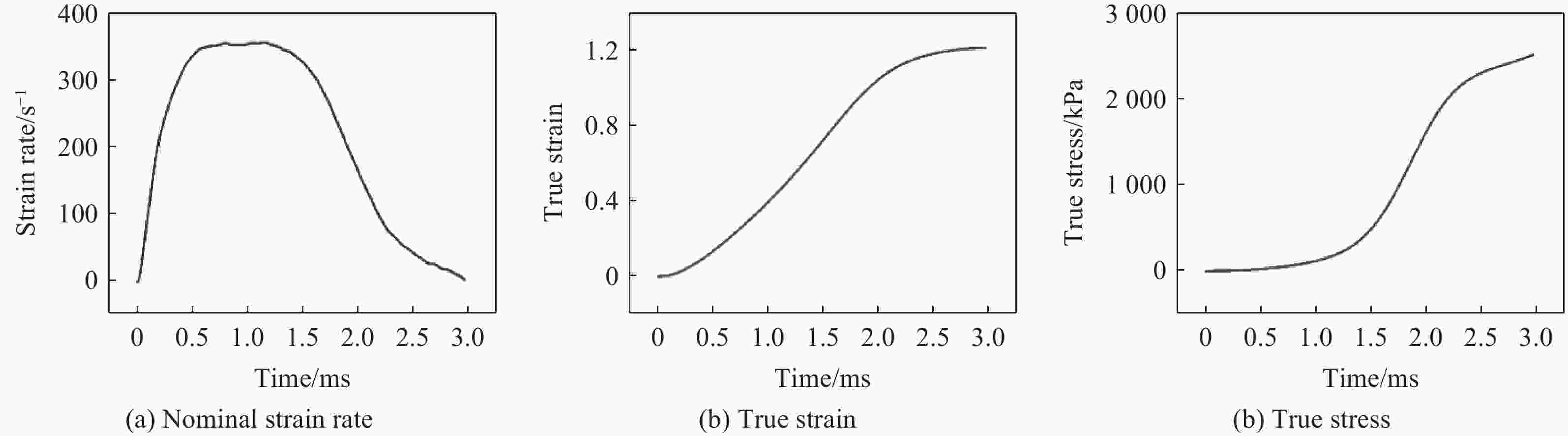
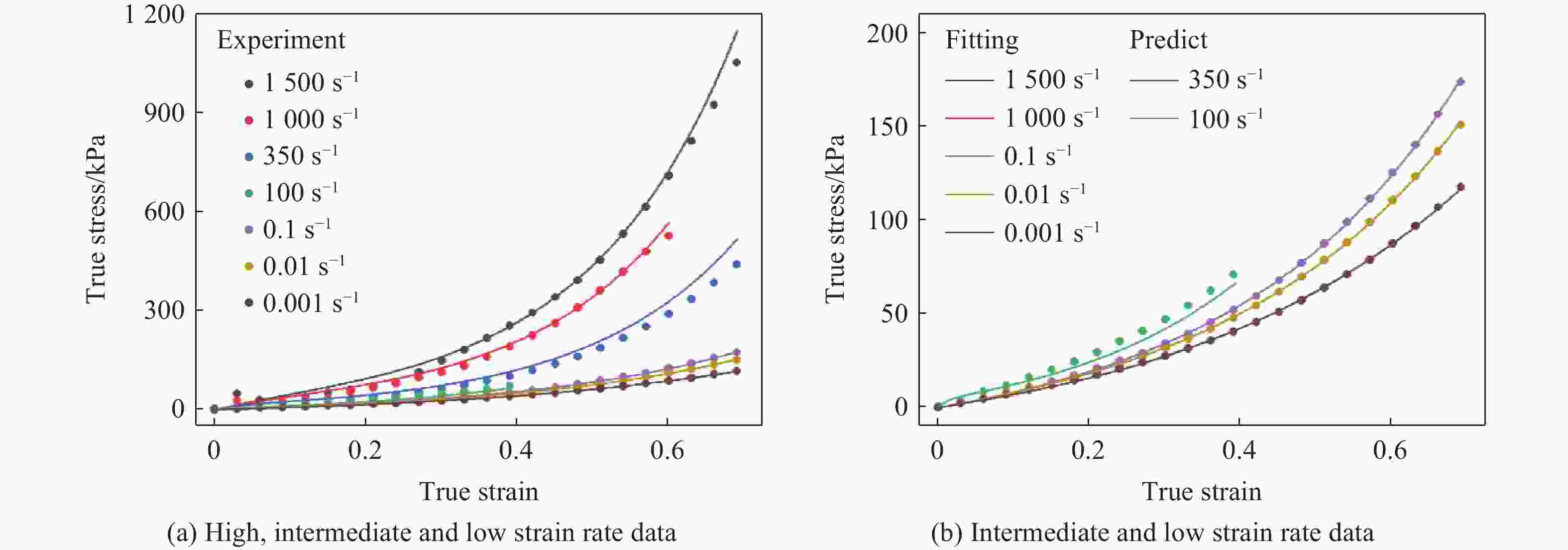
摘要: 生物软材料大多是高含水率的超软材料,其力学性能在宽应变率范围内随着应变率的提高而非线性增强。然而由于实验条件的限制,在中应变率下对超软材料进行大变形测试显得比较困难。设计并建造了长15 m的双子弹电磁驱动长分离式霍普金森压杆(long split Hopkinson pressure bar, LSHPB)系统,可用于超软材料的大变形中应变率测试。使用该LSHPB系统和高速SHPB系统分别对硅橡胶进行了测试,比较两者的实验结果,验证了系统的可靠性。应用LSHPB系统测量了聚乙烯醇(polyvinyl alcohols, PVA)水凝胶在中应变率下的力学性能,并且结合已有的低和高应变率的数据分析,说明了中应变率动态性能测试的必要性。Abstract: Biological soft materials, often with high water content and ultra-softness, display mechanical properties that non-linearly enhance over a broad range of strain rates. However, existing experimental constraints make it challenging to perform large deformation tests on these materials at intermediate strain rates. This study introduces a 15-meter-long long split Hopkinson pressure bar (LSHPB) system, driven by a dual-bullet electromagnetic mechanism, designed for large deformation intermediate strain rate testing of ultra-soft materials. Comparative tests conducted using both the LSHPB and a high-speed SHPB system validated the reliability of the newly developed system. The LSHPB system was then applied to measure the dynamic mechanical performance of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel at intermediate strain rates. The results, combined with existing data from low and high strain rate analyses, underscore the necessity for intermediate strain rate dynamic performance testing. This work not only broadens our understanding of the mechanical behavior of ultra-soft materials like PVA hydrogel across various strain rates but also introduces an innovative experimental technique for studying materials under intermediate strain conditions, thereby advancing the field of soft material dynamics.
-
表 1 材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters
所用数据应变率/s−1 κυT/kPa k α β G11/kPa G21/kPa θ1/s G12/kPa G22/kPa θ2/μs 0.001~0.1, 1000 ~1500 16.7 6.12 0.079 0.58 17.7 0 77.6 338 228 98.9 0.001~100, 1000 16.7 6.12 0.079 0.58 17.7 0 77.6 510 261 50.4 -
[1] ZHANG Y T, ZHANG Y R, TANG L Q, et al. Uniaxial compression constitutive equations for saturated hydrogel combined water-expelled behavior with environmental factors and the size effect [J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2022, 29(28): 7491–7502. DOI: 10.1080/15376494.2021.2000682. [2] ZHANG Y R, XU K J, BAI Y L, et al. Features of the volume change and a new constitutive equation of hydrogels under uniaxial compression [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2018, 85: 181–187. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.06.004. [3] WANG J Y, ZHANG Y R, JIANG Z Y, et al. Mechanical behavior and constitutive equations of porcine brain tissue considering both solution environment effect and strain rate effect [J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2024, 31(10): 2115–2129. DOI: 10.1080/15376494.2022.2150917. [4] WANG J Y, ZHANG Y R, LEI Z Y, et al. Hydrogels with brain tissue-like mechanical properties in complex environments [J]. Materials & Design, 2023, 234: 112338. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.112338. [5] XIE B X, XU P D, TANG L Q, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels measured by double-striker electromagnetic driving SHPB system [J]. International Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2019, 11(2): 1950018. DOI: 10.1142/S1758825119500182. [6] BHUJANGRAO T, FROUSTEY C, IRIONDO E, et al. Review of intermediate strain rate testing devices [J]. Metals, 2020, 10(7): 894. DOI: 10.3390/met10070894. [7] SONG B, CHEN W, LU W Y. Compressive mechanical response of a low-density epoxy foam at various strain rates [J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(17): 7502–7507. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-007-1612-z. [8] 惠旭龙, 白春玉, 刘小川, 等. 宽应变率范围下2A16-T4铝合金动态力学性能 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(5): 871–878. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)05-0871-08.XI X L, BAI C Y, LIU X C, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of 2A16-T4 aluminum alloy at wide-ranging strain rates [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(5): 871–878. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)05-0871-08. [9] SONG B, SYN C J, GRUPIDO C L, et al. A long split Hopkinson pressure bar (LSHPB) for intermediate-rate characterization of soft materials [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2008, 48(6): 809–815. DOI: 10.1007/s11340-007-9095-z. [10] SHIM J, MOHR D. Using split Hopkinson pressure bars to perform large strain compression tests on polyurea at low, intermediate and high strain rates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(9): 1116–1127. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.12.010. [11] 钟东海, 郭鑫, 熊雪梅, 等. 直撞式霍普金森压杆二次加载技术 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(4): 044101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0210.ZHONG D H, GUO X, XIONG X M, et al. Direct-impact double-loading Hopkinson bar technique [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(4): 044101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0210. [12] KIM J M, PARK J S, LEEM D H, et al. Determination of strain rate dependence at intermediate strain rates using acceleration information [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 173: 104482. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104482. [13] JIA B, CHEN P W, RUSINEK A, et al. Thermo-viscoplastic behavior of DP800 steel at quasi-static, intermediate, high and ultra-high strain rates [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2022, 226: 107408. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107408. [14] QIN Z H, ZHU J N, LI W, et al. System ringing in impact test triggered by upper-and-lower yield points of materials [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 108: 295–302. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.04.020. [15] 高光发. 夹心杆系统中一维弹塑性波演化精细分析(Ⅱ): 弹塑性交界面与平台段反射衰减 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(8): 081442. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0392.GAO G F. Meticulous analysis of one-dimensional elasto-plastic wave evolution in sandwich rod systems (part Ⅱ): reflection attenuation at the elasto-plastic interface and platform section [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(8): 081442. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0392. [16] 舒旗, 董新龙, 俞鑫炉. 基于Hopkinson压杆的M型试样动态拉伸实验方法研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(8): 084101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0433.SHU Q, DONG X L, YU X L. A dynamic tensile method for M-shaped specimen loaded by Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(8): 084101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0433. [17] ZHAO H, GARY G, KLEPACZKO J R. On the use of a viscoelastic split Hopkinson pressure bar [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(4): 319–330. DOI: 10.1016/s0734-743x(96)00038-3. [18] XU P D, TANG L Q, ZHANG Y R, et al. SHPB experimental method for ultra-soft materials in solution environment [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 159: 104051. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.104051. [19] LIU Z W, CHEN X M, LV X T, et al. A mini desktop impact test system using multistage electromagnetic launch [J]. Measurement, 2014, 49: 68–76. DOI: 10.1016/j.measurement.2013.11.029. [20] 王维斌, 索涛, 郭亚洲, 等. 电磁霍普金森杆实验技术及研究进展 [J]. 力学进展, 2021, 51(4): 729–754. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-20-024.WANG W B, SUO T, GUO Y Z, et al. Experimental technique and research progress of electromagnetic Hopkinson bar [J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2021, 51(4): 729–754. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-20-024. [21] 杜冰, 郭亚洲, 李玉龙. 一种基于电磁霍普金森杆的材料动态包辛格效应测试装置及方法 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(8): 081101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0050.DU B, GUO Y Z, LI Y L. A novel technique for determining the dynamic Bauschinger effect by electromagnetic Hopkinson bar [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(8): 081101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0050. [22] 胡时胜, 王礼立, 宋力, 等. Hopkinson压杆技术在中国的发展回顾 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(6): 641–657. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)06-0641-17.HU S S, WANG L L, SONG L, et al. Review of the development of Hopkinson pressure bar technique in China [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(6): 641–657. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2014)06-0641-17. [23] 谢倍欣, 汤立群, 姜锡权, 等. 用于软材料的双子弹电磁驱动SHPB系统 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(5): 054101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0394.XIE B X, TANG L Q, JIANG X Q, et al. A double-striker electromagnetic driving SHPB system for soft materials [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(5): 054101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0394. [24] WANG L L, LABIBES K, AZARI Z, et al. Generalization of split Hopkinson bar technique to use viscoelastic bars [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1994, 15(5): 669–686. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743x(94)90166-i. [25] XU P D, TANG L Q, WANG J Y, et al. Mechanical behavior of PVA hydrogels over a wide strain rate range and a new two-phase visco-hyperelastic constitutive model [J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2024: 1–14. DOI: 10.1080/15376494.2024.2386398. [26] BACON C. An experimental method for considering dispersion and attenuation in a viscoelastic Hopkinson bar [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1998, 38(4): 242–249. DOI: 10.1007/bf02410385. [27] LUNDBERG B, HENCHOZ A. Analysis of elastic waves from two-point strain measurement [J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1977, 17(6): 213–218. DOI: 10.1007/BF02324491. [28] 巫绪涛, 胡时胜, 张芳荣. 两点应变测量法在SHPB测量技术上的运用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(4): 309–312. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2003)04-0309-4.WU X T, HU S S, ZHANG F R. Application of two-point strain measurement to the SHPB technique [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(4): 309–312. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2003)04-0309-4. [29] 宋力, 胡时胜. SHPB数据处理中的二波法与三波法 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2005, 25(4): 368–373. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2005)04-0368-06.SONG L, HU S S. Two-wave and three-wave method in SHPB data processing [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2005, 25(4): 368–373. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2005)04-0368-06. [30] GORHAM D A. The effect of specimen dimensions on high strain rate compression measurements of copper [J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1991, 24(8): 1489–1492. DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/24/8/041. -







 下载:
下载: