Study on failure zones and attenuation law of stress waves in concrete induced by cylindrical charge explosion
-
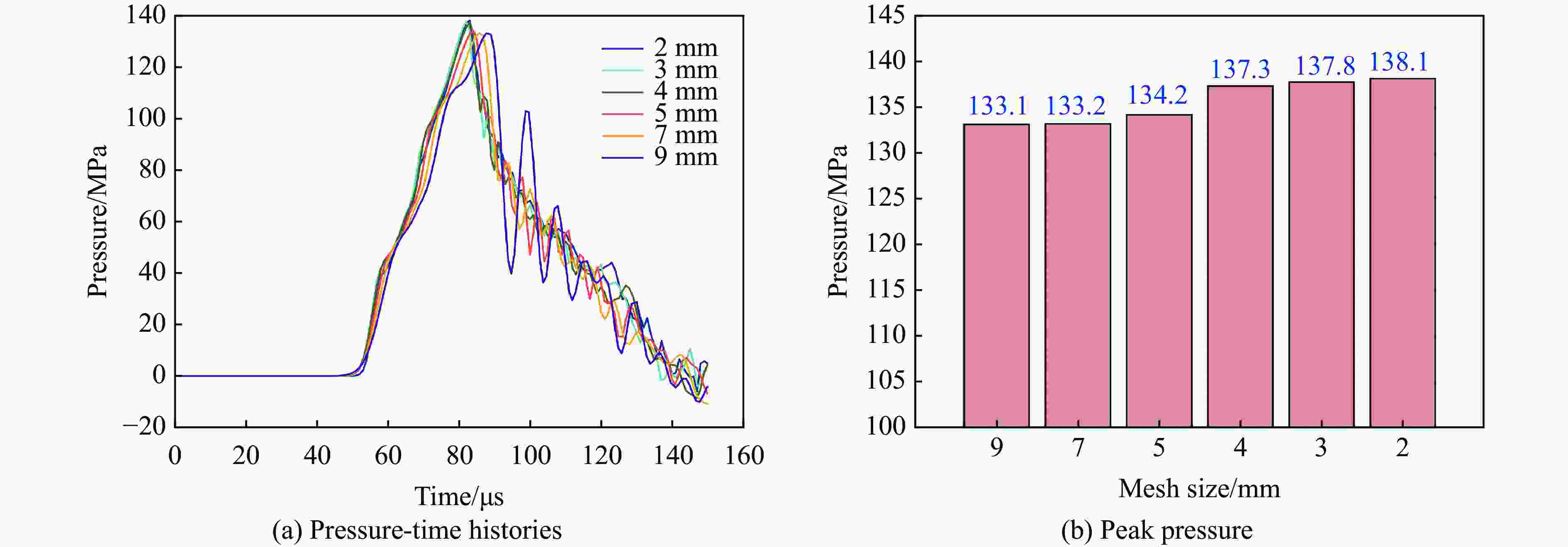
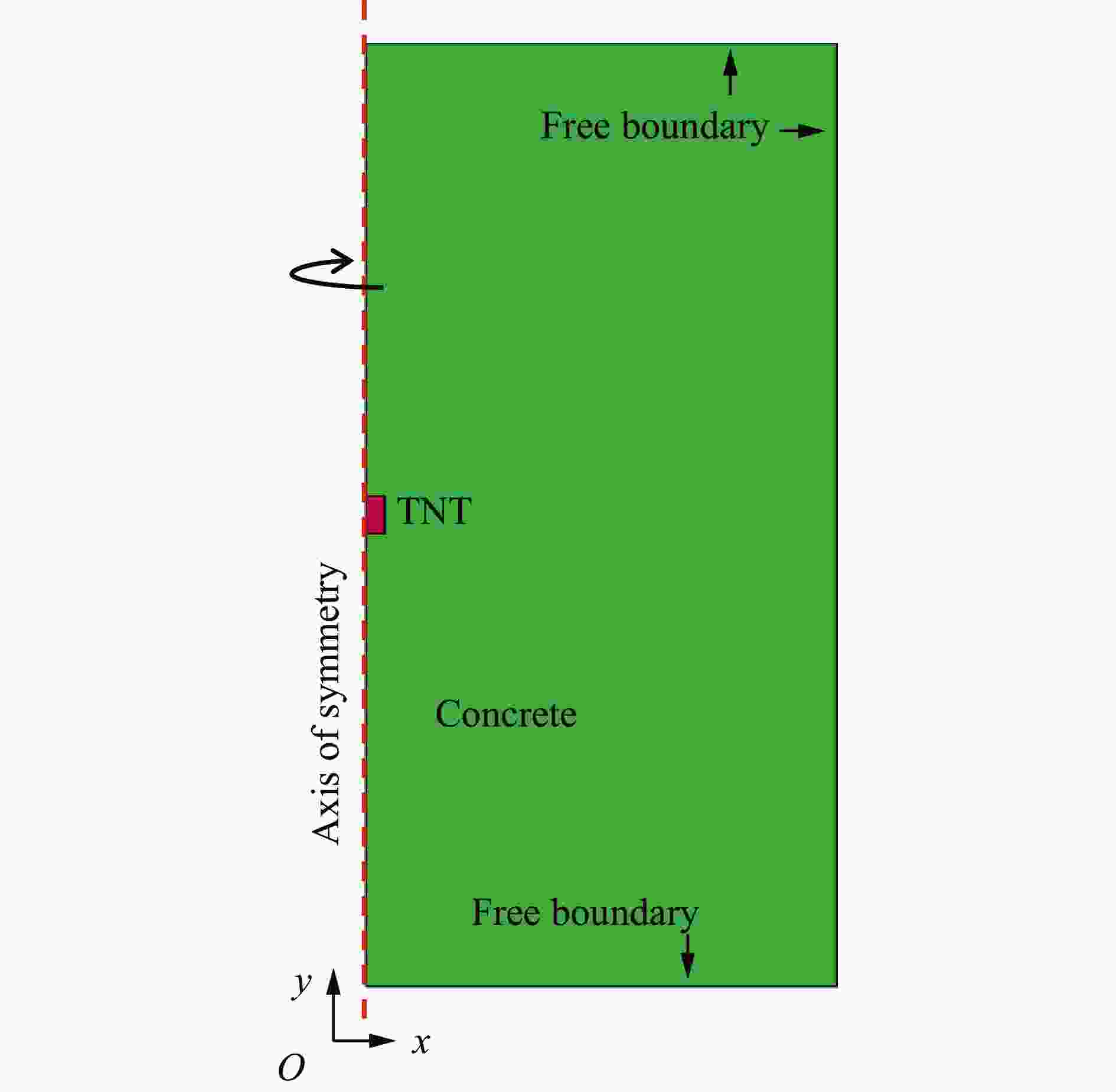
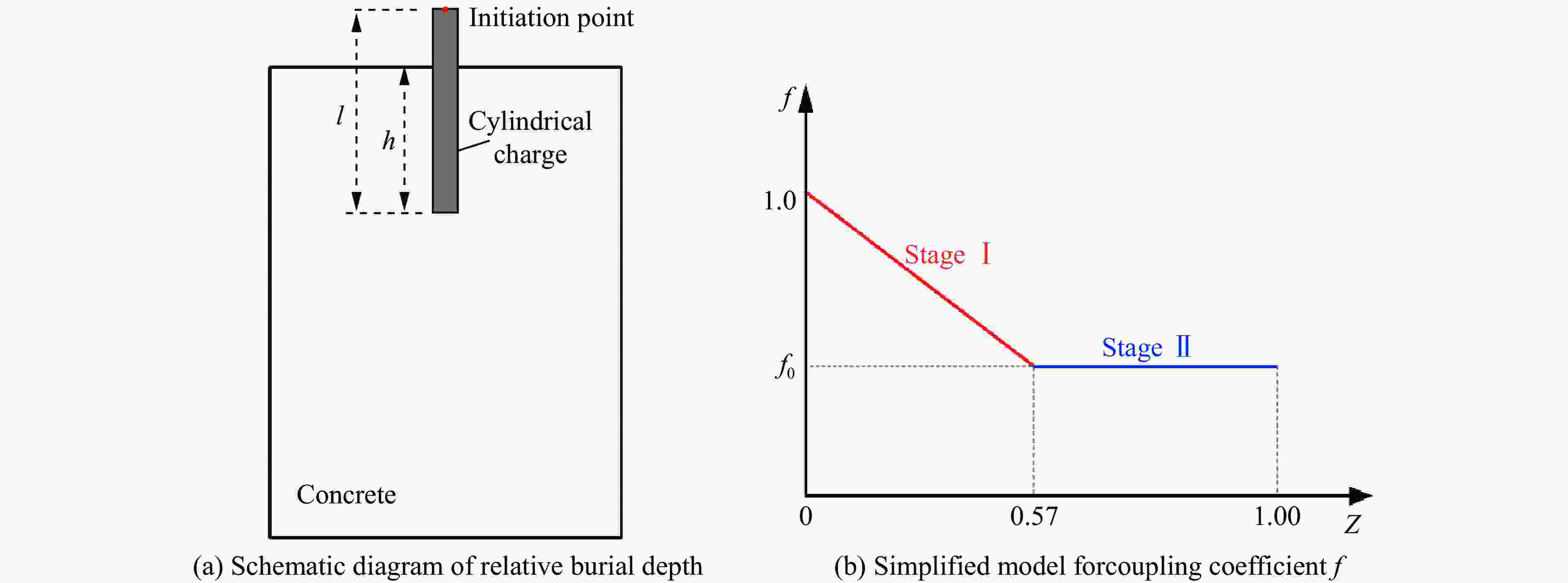
摘要: 为了探究柱形装药爆炸应力波在混凝土介质中的传播规律,基于Karagozian and Case concrete (KCC)本构模型和多物质ALE算法(multi-material ALE,MMALE)开展数值模拟研究。首先,通过与已有的试验数据进行对比,验证了本构模型参数和数值算法的适用性;在此基础上以峰值应力为准则,对装药周围混凝土介质的爆炸破坏分区进行划分,并讨论了各破坏分区中爆炸应力波的衰减规律;之后,分析了装药长径比对爆炸破坏分区和爆炸应力波传播规律的影响;最后,进一步考虑装药埋深的影响,并建立柱形装药爆炸应力波峰值应力计算公式。研究结果表明:各爆炸破坏分区中爆炸应力波衰减规律存在显著差异,与中远区(过渡区和破裂区)相比,装药近区(拟流体区和压碎区)衰减更快,另外,柱形装药长径比增加会加快法向峰值应力的衰减;并且建立的爆炸应力波峰值应力计算公式可以较为准确快速地计算出不同形状、不同埋深下柱形装药爆炸应力波的法向峰值应力。Abstract: In blast-resistant structural design for conventional weapons, previous studies on blast-induced stress waves in solid media have predominantly focused on soil and rock media (i.e., ground shock issues), whereas research on the propagation and attenuation laws of stress waves in concrete remains relatively limited. Based on the Karagozian and Case concrete (KCC) constitutive model in conjunction with the multi-material ALE (MMALE) algorithm, the propagation laws of stress waves in concrete induced by cylindrical charge explosion were numerically investigated. Firstly, the applicability of the constitutive model parameters and numerical algorithm were validated by comparing the results with the existing experiments. Subsequently, the peak stress was employed as a criterion to delineate the explosive damage zones in the concrete surrounding the charge. Additionally, the attenuation laws of explosion stress waves in each damage zone were discussed. Finally, the effect of burial depth was taken into further considered, and a formula for calculating the peak stress in concrete induced by cylindrical charge explosion was established. It was found that the attenuation patterns of blast-induced stress waves differ significantly in each explosion failure zone. The stress waves in the near-field zone (quasi-fluid and crushing zones) demonstrates a more rapid attenuation rate compared to that in the mid-field zone (transition and fracture zones). Furthermore, an increase in the aspect ratio of the cylindrical charge leads to an acceleration in the attenuation of the normal peak stress. Moreover, the established formula for calculating the peak stress of blast-induced stress waves enables accurate and rapid determination of the normal peak stress generated by cylindrical charges with varying geometries and burial depths, which can be served as a valuable reference for blast-resistant design of concrete structures.
-
Key words:
- concrete /
- cylindrical charges /
- failure zones /
- explosion stress waves /
- peak stress
-
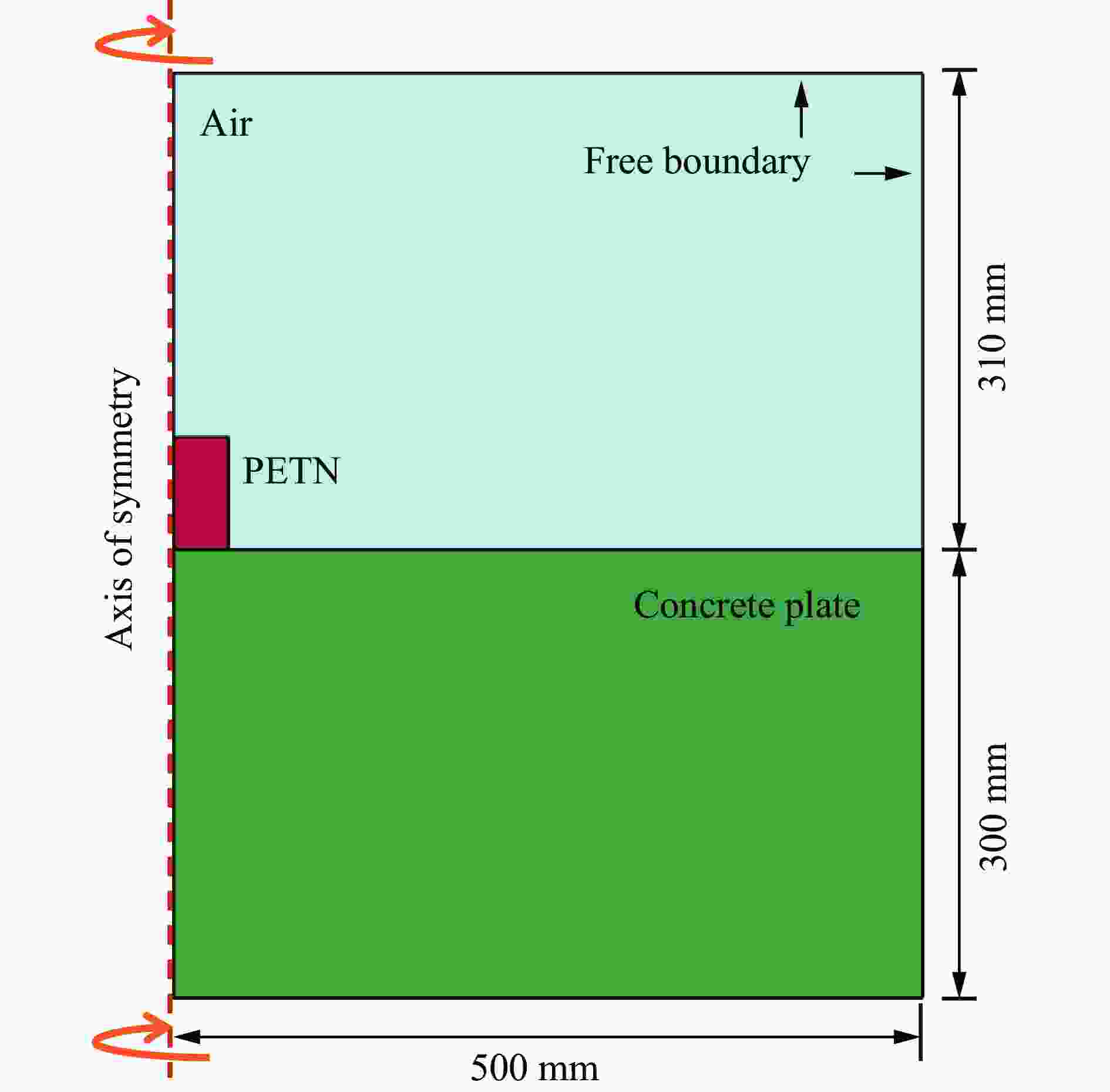
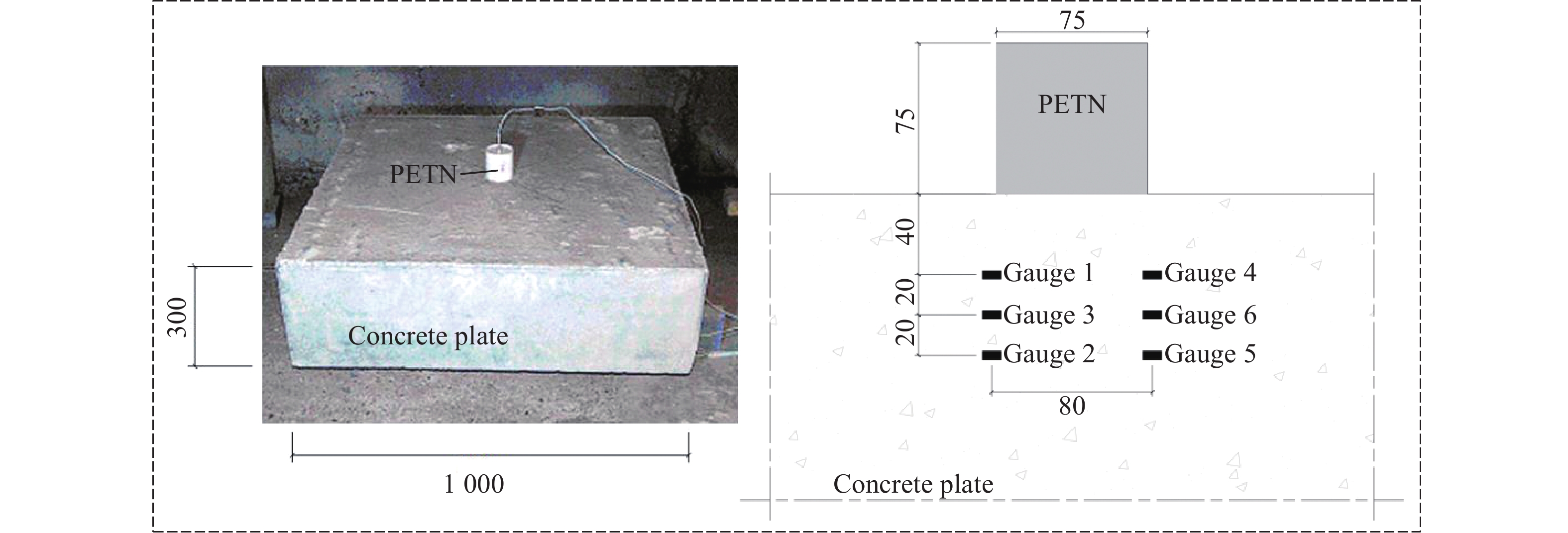
ρ/(kg·m−3) D/(m·s−1) pCJ/GPa A/GPa B/GPa ω R1 R2 E/ (GJ·m−3) 1500 7450 22 625.3 23.29 0.28 5.25 1.60 8.56 ρ/(kg·m−3) C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 E/(MJ·m−3) 1.2929 0 0 0 0 0 0.4 0 0.25 表 3 第1组试验中各测点峰值应力的试验结果与数值模拟结果的对比
Table 3. Comparison of stress peak of tests with that of numerical simulation in the first group
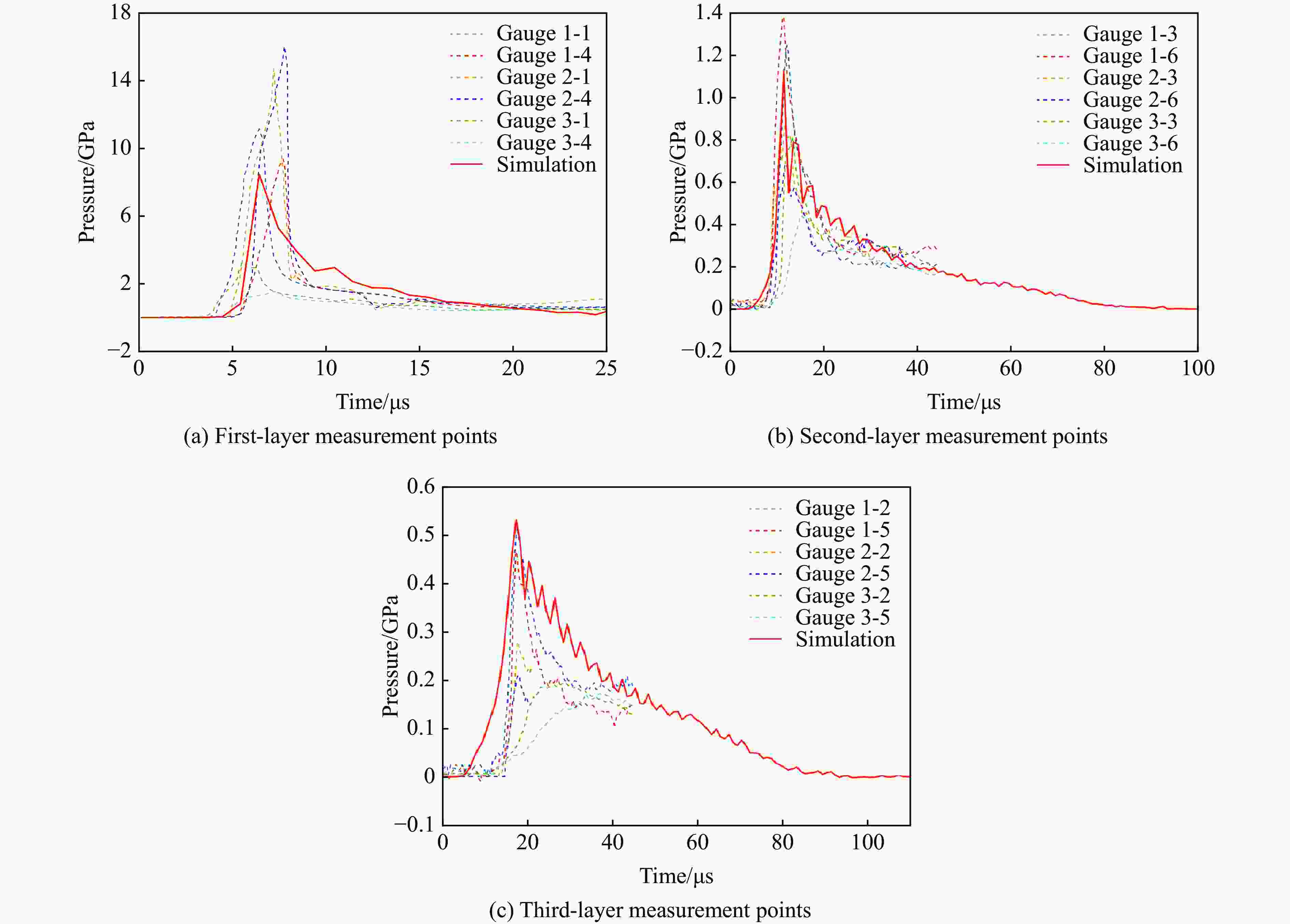
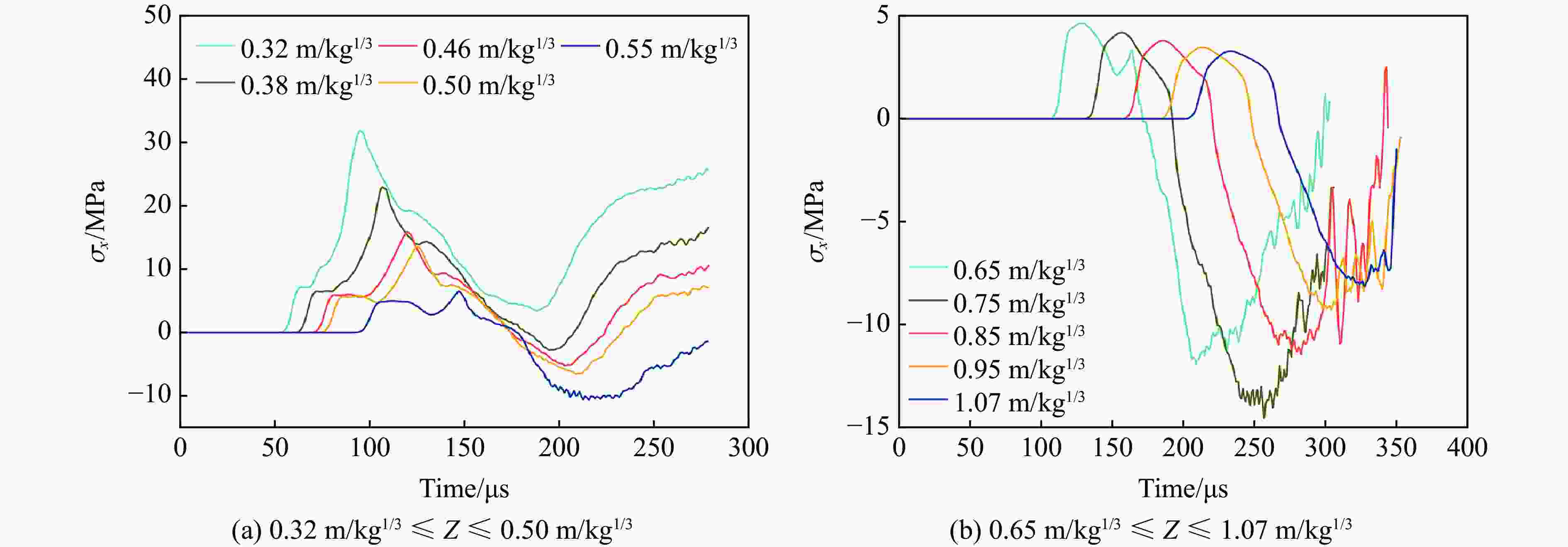
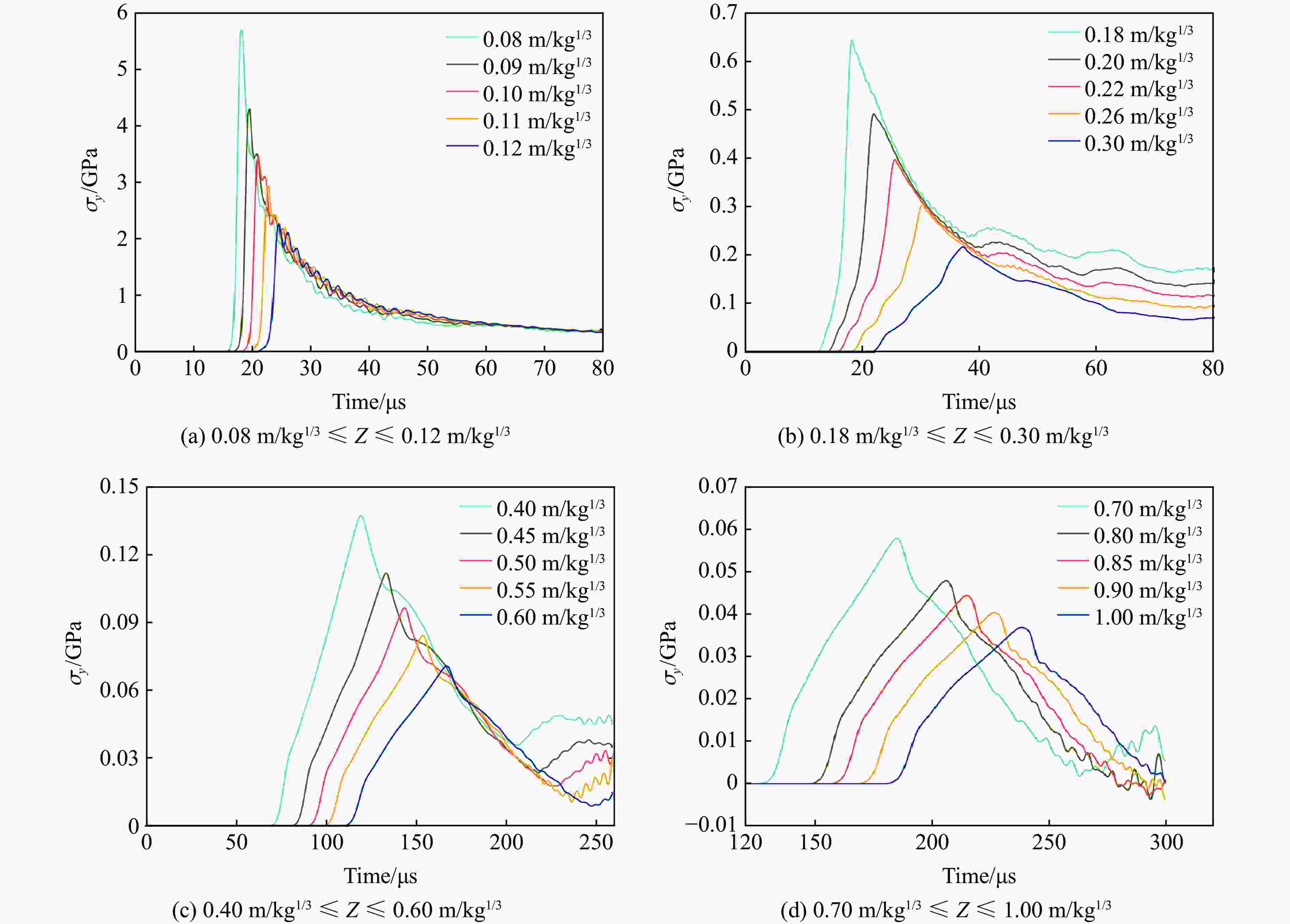
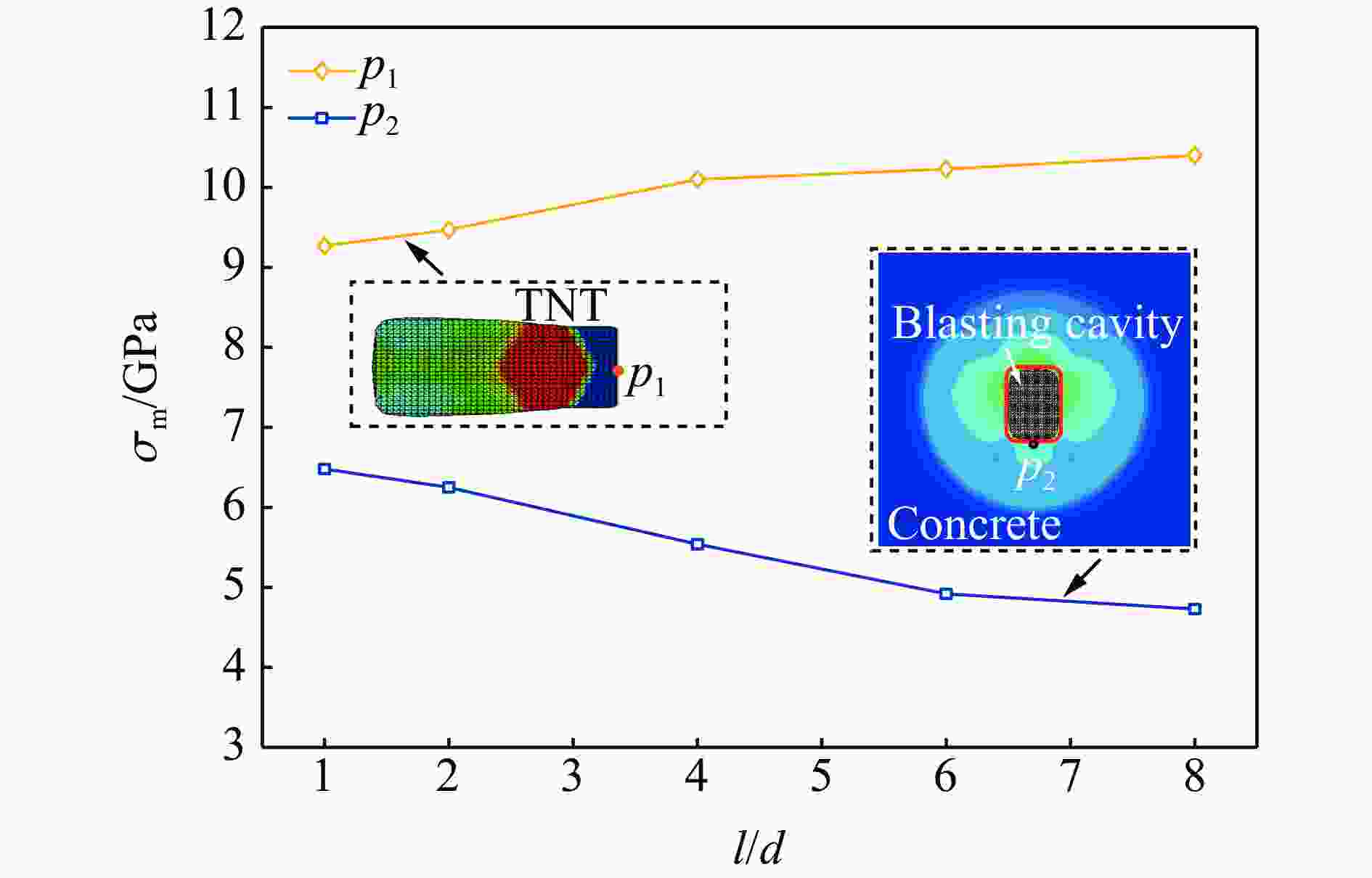
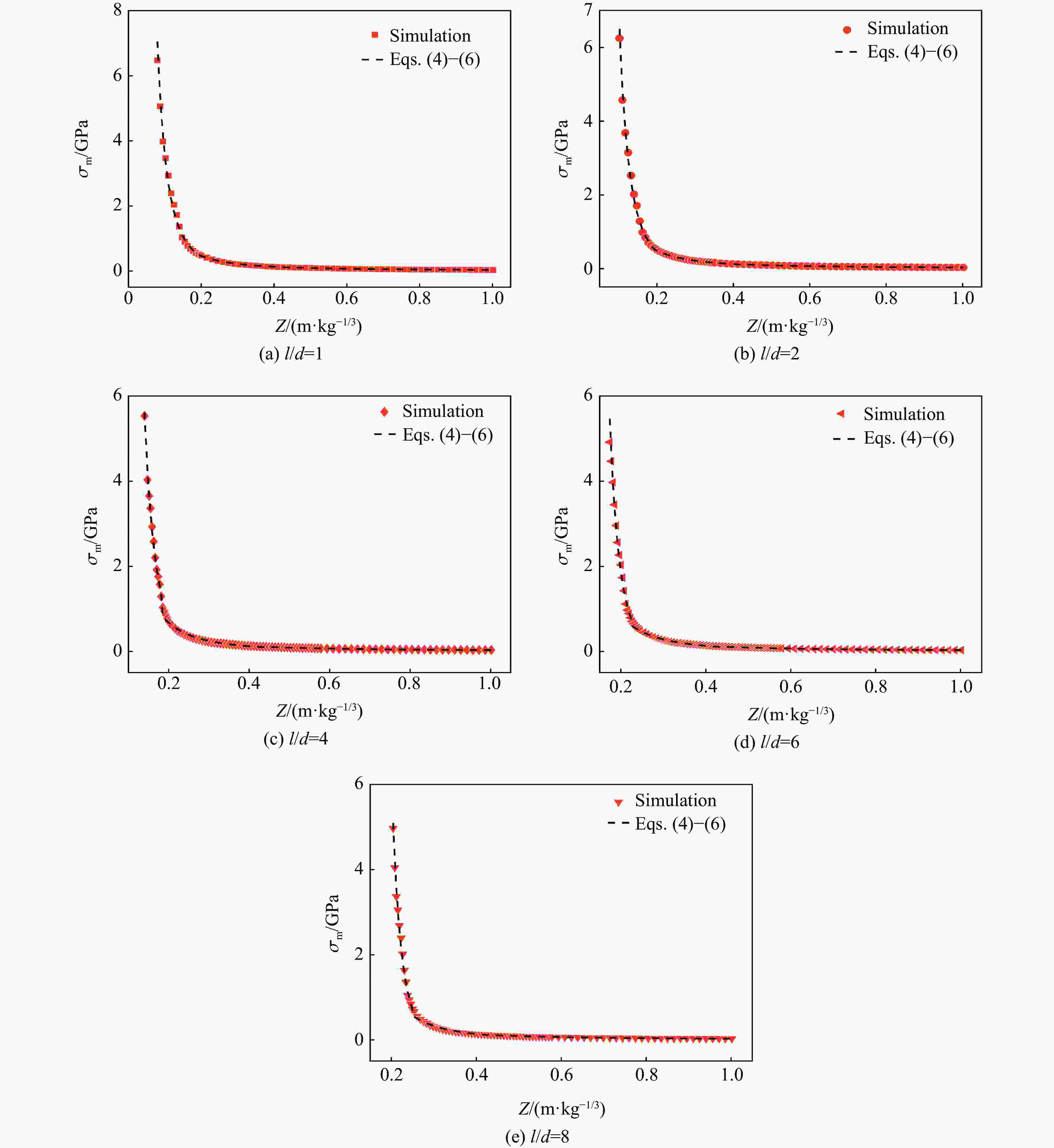
测点试验值/GPa 试验平均值/GPa 数值模拟值/GPa 平均误差/% 11.156 9.366 10.261 8.476 17.40 (gauge 1-1) (gauge 1-4) 1.248 1.384 1.316 1.134 13.83 (gauge 1-3) (gauge 1-6) 0.518 0.466 0.492 0.531 7.93 (gauge 1-2) (gauge 1-5) 注:平均误差=(试验平均值−数值模拟值)/平均值×100%。 表 4 混凝土自由场破坏分区边界尺寸及介质受力特征
Table 4. Concrete failure zone boundaries in a free field and stressed medium properties
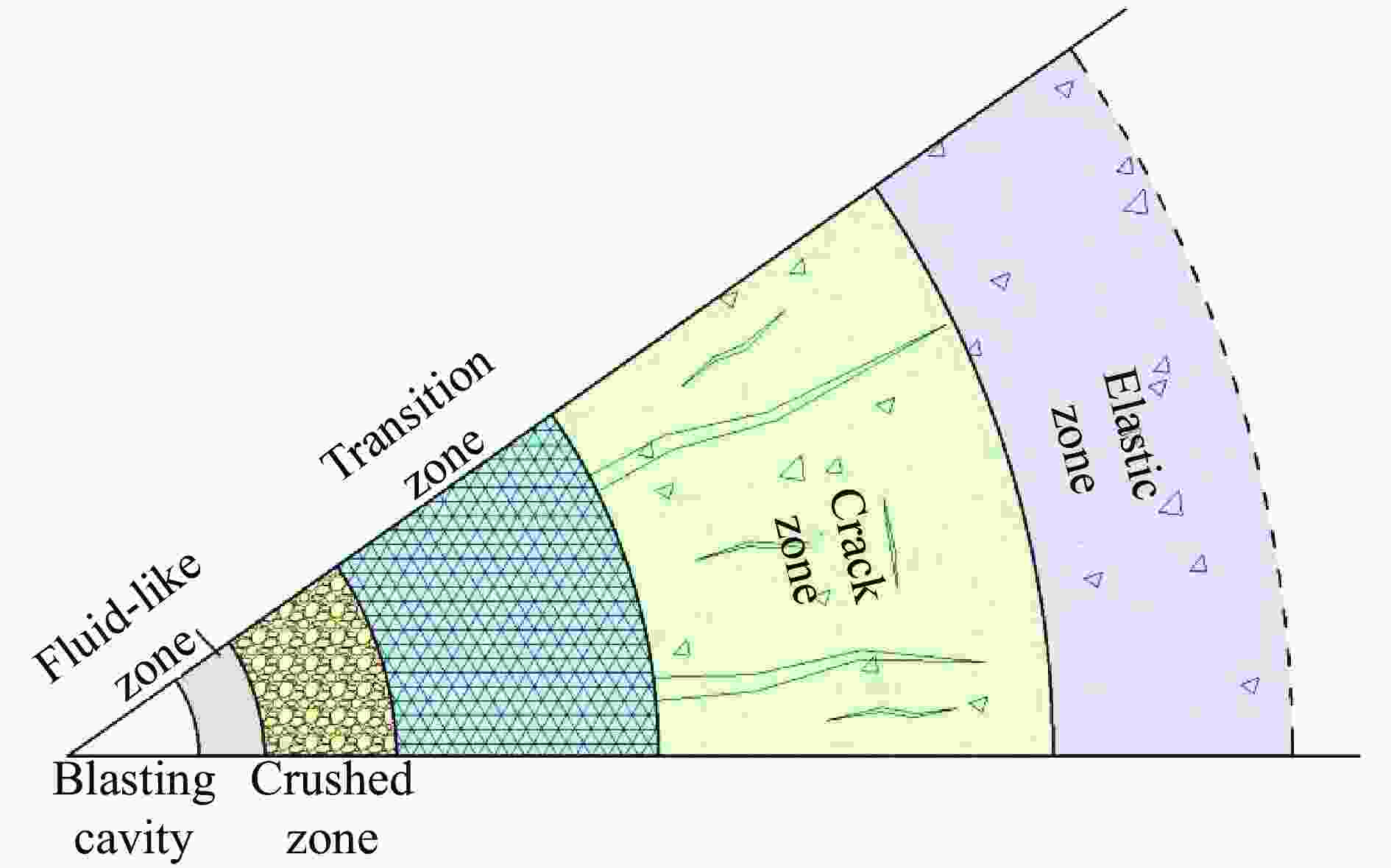
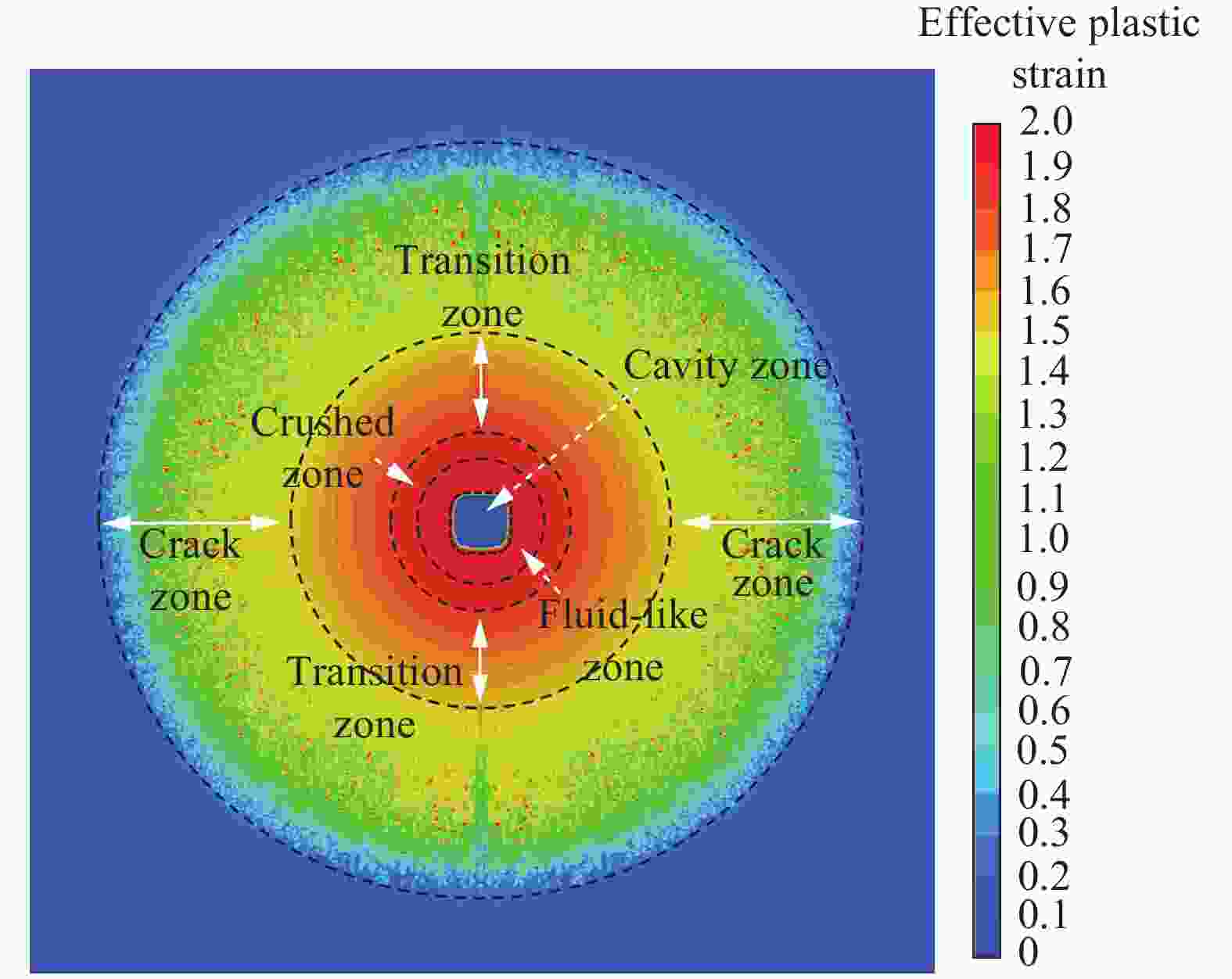
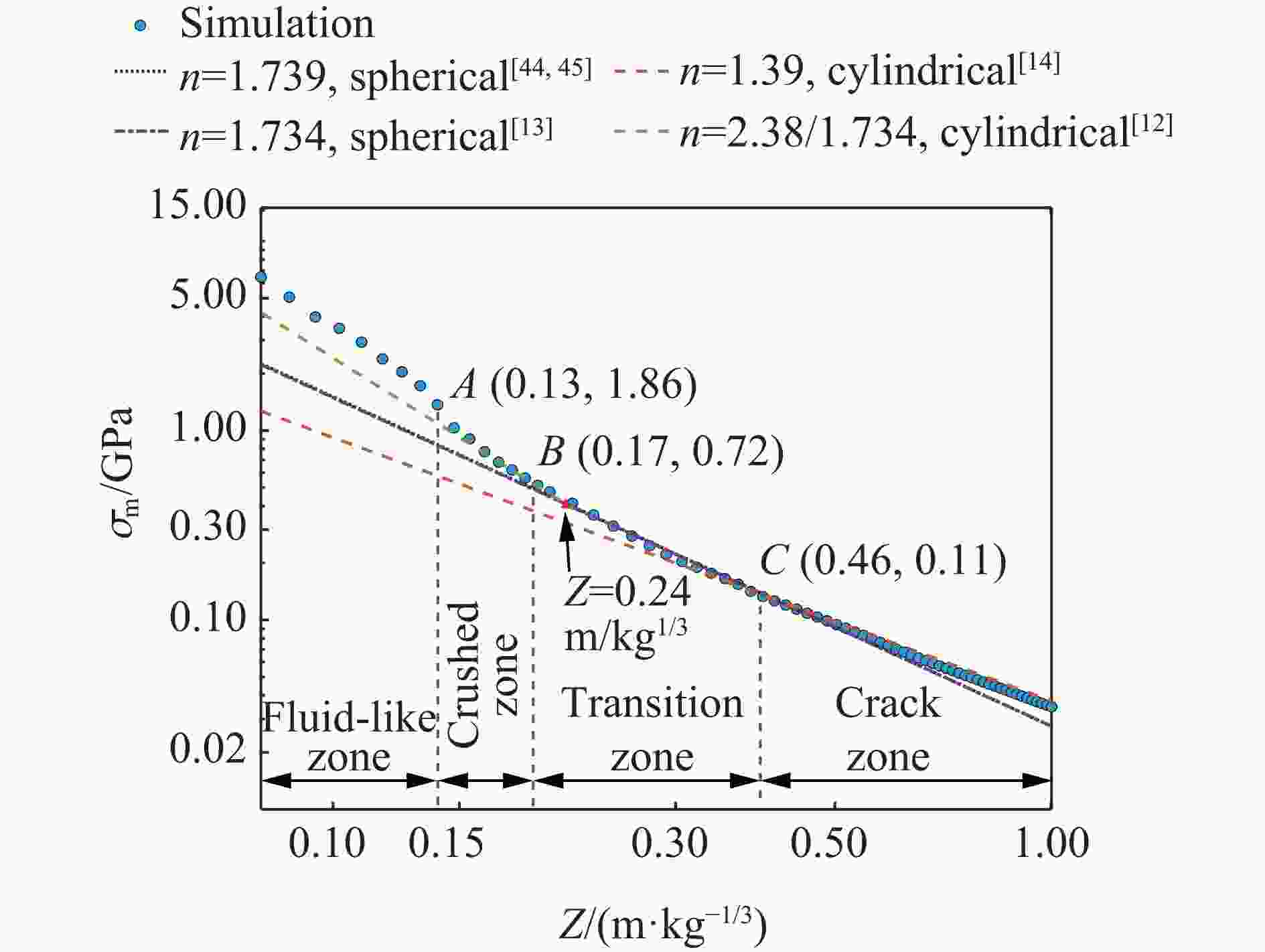
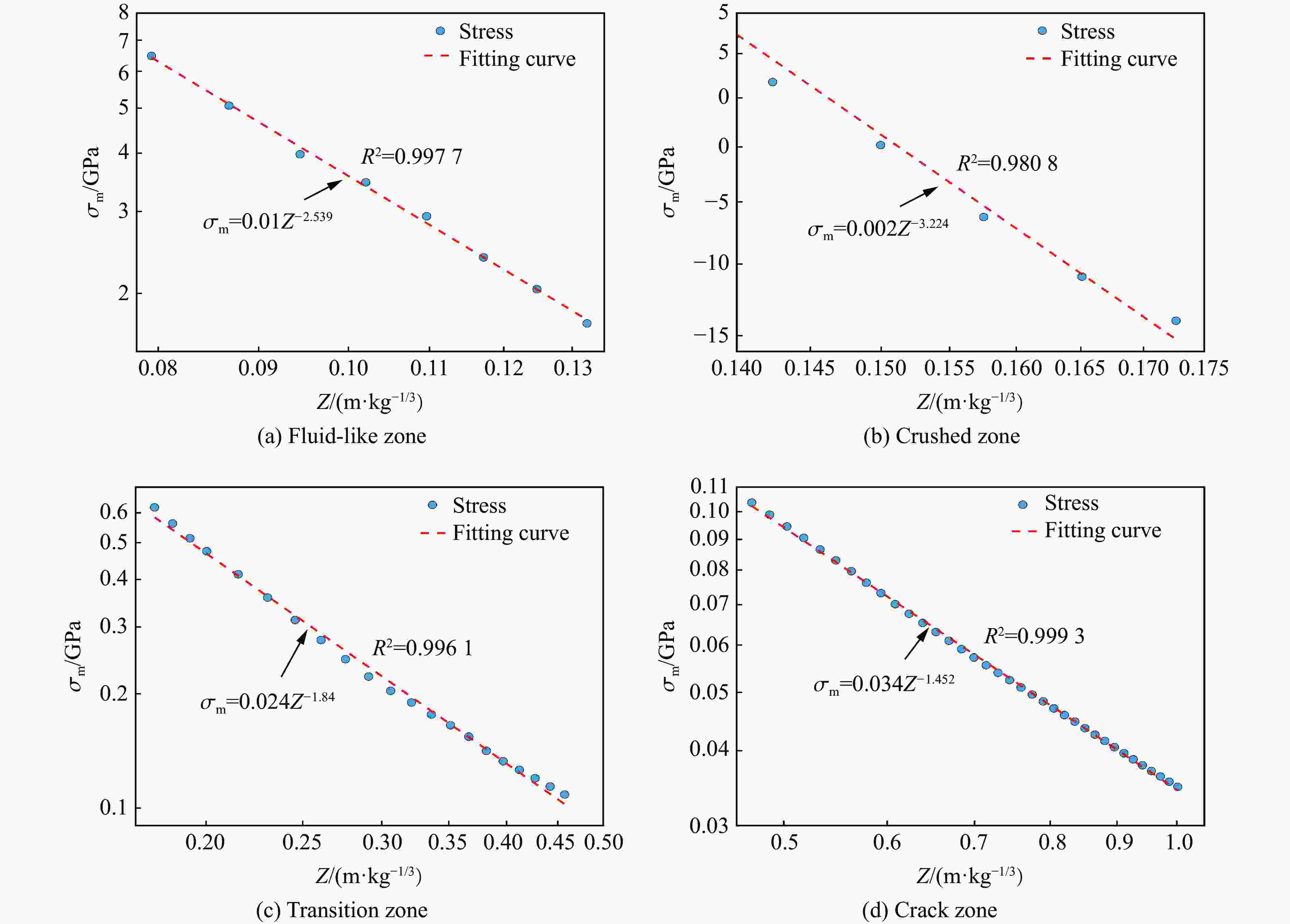
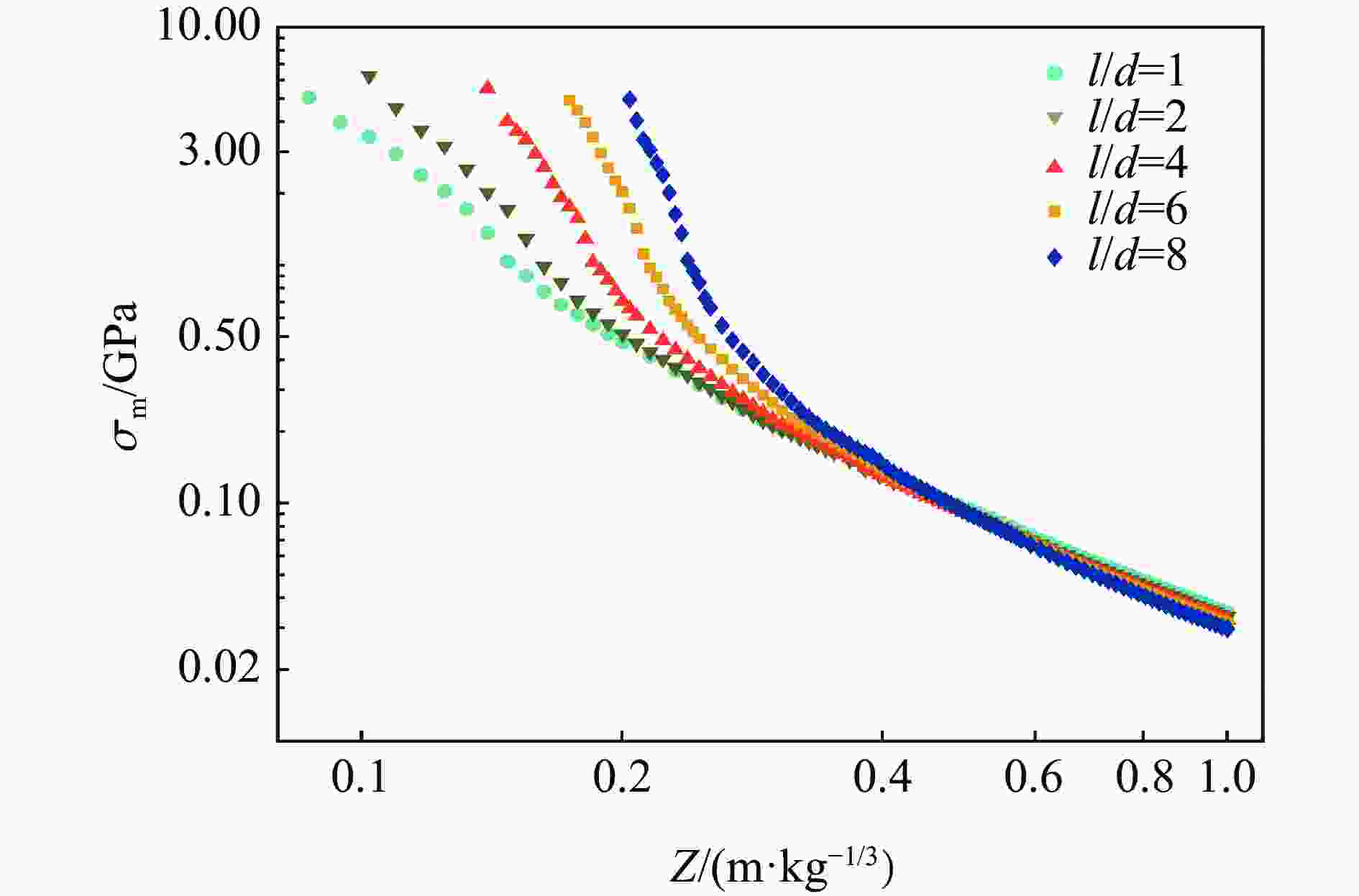
破坏分区类型 边界尺寸/(m·kg−1/3) 混凝土介质受力特征 近流体区 0.08~0.13 混凝土受强间断冲击波作用,其峰值应力远大于混凝土剪切强度,介质呈塑性流动状态 压碎区 0.13~0.17 爆炸应力值远大于混凝土抗压强度,介质被完全压碎 过渡区 0.17~0.46 混凝土介质受环向和径向压力共同作用,发生压剪破坏,裂隙呈网状分布 破裂区 0.46~1.0 混凝土介质主要受环向拉应力作用,发生拉伸破坏,形成径向裂隙 弹性区 ≥ 1.0 介质未发生塑性变形,处于弹性状态 表 5 不同长径比的柱形装药各破坏分区参数
Table 5. Parameters for different length-to-diameter ratios of cylindrical charges in each failure zone
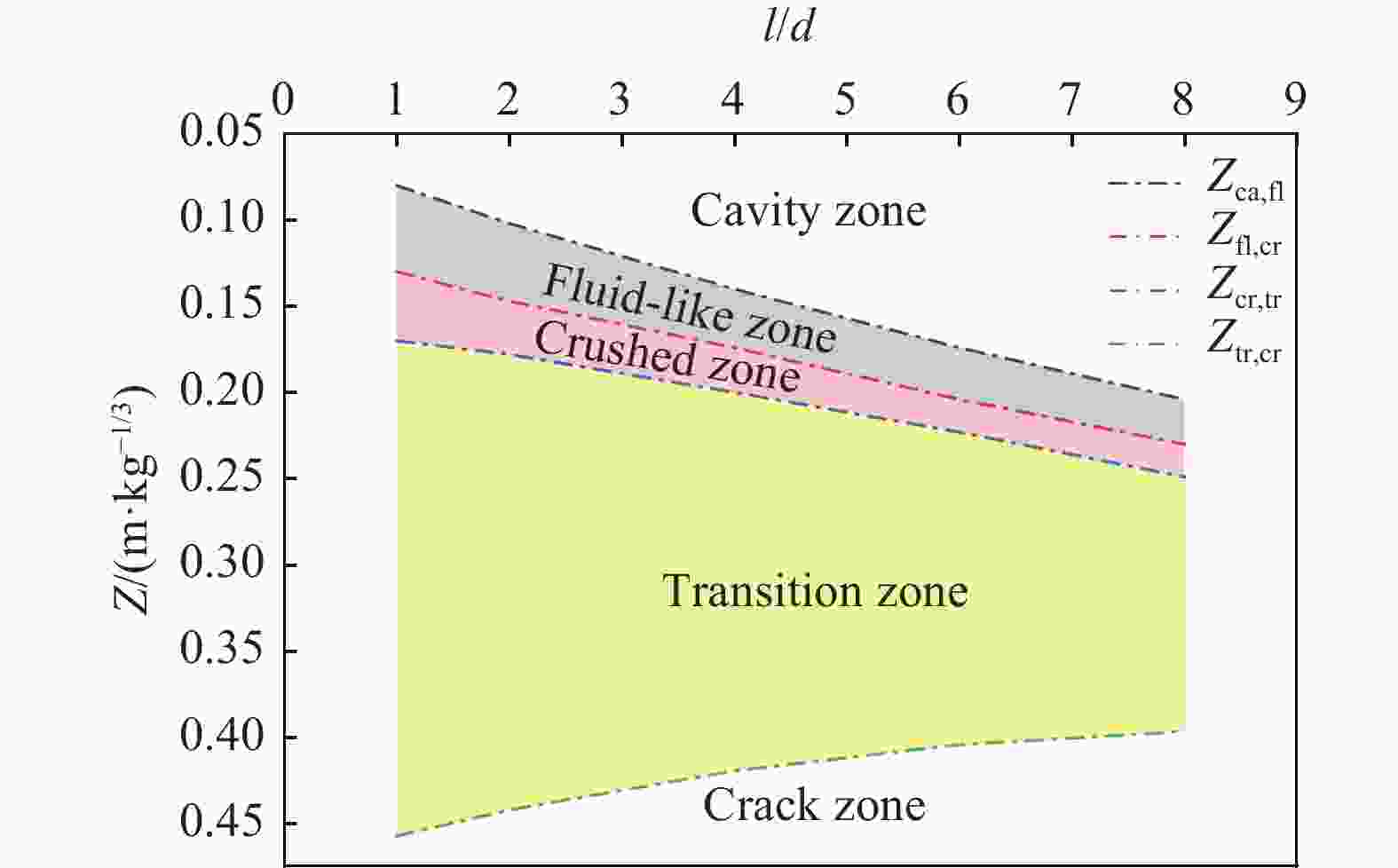
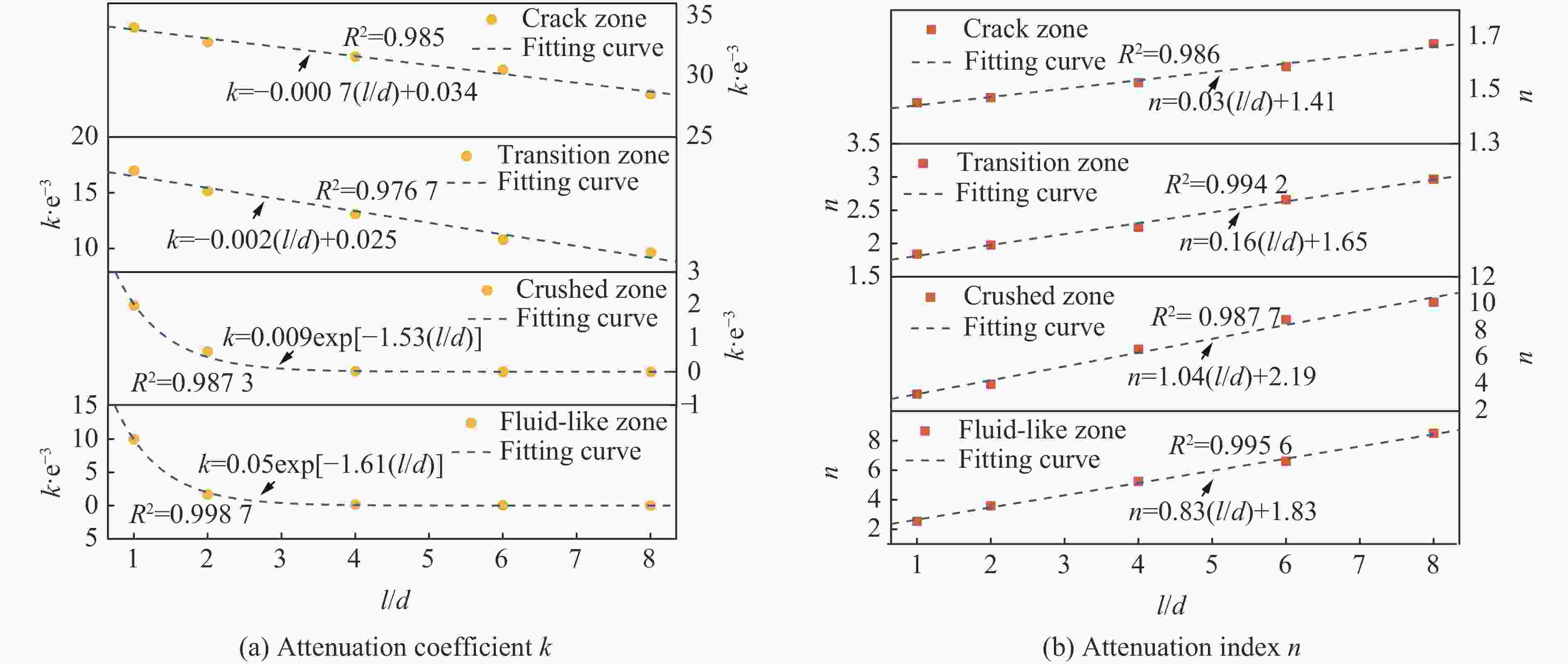
l/d 分区 Z/(m·kg−1/3) k n R2 2 近流体区 0.10~0.15 1.70×10−3 3.59 0.9937 压碎区 0.15~0.18 6.05×10−4 3.96 0.9862 过渡区 0.18~0.44 2.03×10−2 1.98 0.9943 破裂区 0.44~1.00 3.28×10−2 1.47 0.9991 4 近流体区 0.14~0.17 1.82×10−4 5.25 0.9945 压碎区 0.17~0.20 1.69×10−5 6.59 0.9780 过渡区 0.20~0.42 1.62×10−2 2.24 0.9891 破裂区 0.42~1.00 3.16×10−2 1.52 0.9991 6 近流体区 0.17~0.20 4.88×10−5 6.61 0.9964 压碎区 0.20~0.22 1.34×10−6 8.83 0.9705 过渡区 0.22~0.40 1.16×10−2 2.66 0.9826 破裂区 0.40~1.00 3.05×10−2 1.59 0.9985 8 近流体区 0.20~0.23 6.66×10−6 8.49 0.9897 压碎区 0.23~0.25 5.39×10−7 10.15 0.9773 过渡区 0.25~0.40 9.30×10−3 2.97 0.9783 破裂区 0.40~1.00 2.85×10−2 1.67 0.9975 -
[1] KRAUTHAMMER T. Modern protective structures [M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2008. DOI: 10.1201/9781420015423. [2] PLOOSTER M N. Blast effects from cylindrical explosive charges: experimental measurements [M]. Fort Belvoir: Defense Technical Information Center, 1982: 11–18. [3] ISMAIL M M, MURRAY S G. Study of the blast waves from the explosion of nonspherical charges [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 1993, 18(3): 132–138. DOI: 10.1002/prep.19930180304. [4] WU C Q, FATTORI G, WHITTAKER A, et al. Investigation of air-blast effects from spherical-and cylindrical-shaped charges [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2010, 1(3): 345–362. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.1.3.345. [5] SHI Y C, WANG N, CUI J, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of charge shape effect on blast load induced by near-field explosions [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 165: 266–277. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.07.018. [6] 黄家蓉, 刘光昆, 吴飚, 等. 爆炸冲击作用下混凝土中动态应力波测试与模拟 [J]. 防护工程, 2020, 42(4): 23–28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2020.04.003.HUANG J R, LIU G K, WU B, et al. Testing and simulation of dynamic stress wave in concrete under explosion and impact [J]. Protective Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 23–28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1854.2020.04.003. [7] GEBBEKEN N, GREULICH S, PIETZSCH A. Hugoniot properties for concrete determined by full-scale detonation experiments and flyer-plate-impact tests [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 32(12): 2017–2031. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.08.003. [8] SHERKAR P, SHIN J, WHITTAKER A, et al. Influence of charge shape and point of detonation on blast-resistant design [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2016, 142(2): 04015109. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001371. [9] XIAO W F, ANDRAE M, GEBBEKEN N. Effect of charge shape and initiation configuration of explosive cylinders detonating in free air on blast-resistant design [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2020, 146(8): 04020146. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0002694. [10] GAO C, KONG X Z, FANG Q, et al. Numerical investigation on free air blast loads generated from center-initiated cylindrical charges with varied aspect ratio in arbitrary orientation [J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18(9): 1662–1678. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.07.013. [11] 王明涛, 程月华, 吴昊. 柱形装药空中爆炸冲击波荷载研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(4): 043201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0197.WANG M T, CHENG Y H, WU H. Study on blast loadings of cylindrical charges air explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(4): 043201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0197. [12] GAO C, KONG X Z, FANG Q. Experimental and numerical investigation on the attenuation of blast waves in concrete induced by cylindrical charge explosion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 174: 104491. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104491. [13] 高矗, 孔祥振, 方秦, 等. 混凝土中爆炸应力波衰减规律的数值模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(12): 123202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0041.GAO C, KONG X Z, FANG Q, et al. Numerical study on attenuation of stress wave in concrete subjected to explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(12): 123202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0041. [14] 杨耀宗, 孔祥振, 方秦, 等. 混凝土中带壳柱形装药爆炸应力波衰减规律的数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(11): 112202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0342.YANG Y Z, KONG X Z, FANG Q, et al. Numerical investigation on attenuation of stress waves in concrete induced by cylindrical cased charge explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(11): 112202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0342. [15] 吴祥云, 曲建波, 张光明, 等. 岩石中不同埋深爆炸自由场直接地冲击参数的预计方法 [C]//崔京浩. 第20届全国结构工程学术会议论文集(第Ⅰ册). 《工程力学》杂志社, 2011: 262–267.WU X Y, QU J B, ZHANG G M, et al. Prediction method of the direct ground shock parameters of explosion at different buried depths in free field of rock [C]//CUI J H. Proceedings of the Twentieth National Conference on Structural Engineering (No. I). Engineering Mechanics Magazine, 2011: 262–267. [16] LIU Z Y, ZHAI J Z, SU S. Numerical simulation on conical shaped charge with copper liner in several typical shapes [J]. Materials Research Proceedings, 2019, 13(3): 7–12. DOI: 10.21741/9781644900338-2. [17] ABIR M, ARUMUGAM D, DHANA B, et al. Numerical simulation of blast wave propagation in layered soil featuring soil-structure interaction [C]// COMPDYN. Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering. Rhodes Island, 2017: 4752–4765. DOI: 10.7712/120117.5759.16936. [18] KULAK R F, BOJANOWSKI C. Modeling of cone penetration test using SPH and MM-ALE approaches [C]// Ansys Company. Proceedings of the 8th European LS-DYNA® Users Conference. Strasbourg, 2011: 1–10. [19] VAN DORSSELAER N, LAPOUJADE V. A contribution to new ALE 2D method validation [C]// Ansys Company. Proceedings of the 11th International LS-DYNA® Users Conference. Dearborn, 2010: 39–50. [20] MALVAR L J, CRAWFORD J E, WESEVICH J W, et al. A plasticity concrete material model for DYNA3D [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(9/10): 847–873. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(97)00023-7. [21] TU Z G, LU Y. Evaluation of typical concrete material models used in hydrocodes for high dynamic response simulations [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(1): 132–146. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.12.010. [22] 匡志平, 陈少群. 混凝土K&C模型材料参数分析与模拟 [J]. 力学季刊, 2015, 36(3): 517–526. DOI: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2015.03.019.KUANG Z P, CHEN S Q. Analysis and simulation for the material parameters of K&C concrete model [J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2015, 36(3): 517–526. DOI: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2015.03.019. [23] SU Q, WU H, FANG Q. Calibration of KCC model for UHPC under impact and blast loadings [J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2022, 127: 104401. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2021.104401. [24] KONG X Z, FANG Q, LI Q M, et al. Modified K&C model for cratering and scabbing of concrete slabs under projectile impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 108: 217–228. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.02.016. [25] XIAO W F, ANDRAE M, GEBBEKEN N. Air blast TNT equivalence factors of high explosive material PETN for bare charges [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 377: 152–162. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.05.078. [26] 甘露, 陈力, 宗周红, 等. 近距离爆炸比例爆距的界定标准及荷载模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(6): 064902. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0194.GAN L, CHEN L, ZONG Z H, et al. Definition of scaled distance of close-in explosion and blast load calculation model [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(6): 064902. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0194. [27] HOPKINSON B. British ordnance board minutes [J]. Journal of the Society for Army Historical Research, 1915, 230(57): 88–107. [28] TU H, FUNG T C, TAN K H, et al. An analytical model to predict the compressive damage of concrete plates under contact detonation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 134: 103344. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103344. [29] 刘琦, 翟超辰, 张跃飞, 等. 地面和埋置爆炸土中地冲击作用分区数值模拟及试验研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(8): 082201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0326.LIU Q, ZHAI C C, ZHANG Y F, et al. Numerical simulation and test study on ground shock subzones in soil produced by ground and buried explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(8): 082201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0326. [30] FORBES J W. Shock wave compression of condensed matter: a primer [M]. Berlin: Springer, 2012. [31] DOBRATZ B M. LLNL explosives handbook: properties of chemical explosives and explosives and explosive simulants: UCRL-52997 [R]. Lawrence: Livermore National Laboratory, 1981. [32] 郑哲敏, 解伯民, 刘育魁, 等. 地下核爆炸流体弹塑性计算方案和若干结果 [M]//郑哲敏. 郑哲敏文集. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. [33] 郑哲敏. 爆炸成形模型律 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004.ZHENG Z M. Explosion forming model law [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004. [34] 李守巨, 何庆志, 费鸿禄. 岩石爆破破坏分区的研究 [J]. 爆破, 1991(1): 16–19.LI S J, HE Q Z, FEI H L. Research on the division of rock blasting damage zones [J]. Blasting, 1991(1): 16–19. [35] 钱七虎, 王明洋. 岩土中的冲击爆炸效应 [M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2010.QIAN Q H, WANG M Y. Impact and explosion effects in rock and soil [M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2010. [36] 王明洋, 邓宏见, 钱七虎. 岩石中侵彻与爆炸作用的近区问题研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(16): 2859–2863. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.008.WANG M Y, DENG H J, QIAN Q H. Study on problems of near cavity of penetration and explosion in rock [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(16): 2859–2863. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.16.008. [37] 张志呈. 定向断裂控制爆破机理综述 [J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2000, 20(5): 40–42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2763.2000.05.015.ZHANG Z C. Summary of the mechanism of directional fracture controlled blasting [J]. Mining Research and Development, 2000, 20(5): 40–42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2763.2000.05.015. [38] 冷振东. 岩石爆破中爆炸能量的释放与传输机制 [D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017.LENG Z D. Explosion energy release and transmission mechanism in rock blasting [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2017. [39] MANDAL J, GOEL M D, AGARWAL A K. Surface and buried explosions: an explorative review with recent advances [J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2021, 28(7): 4815–4835. DOI: 10.1007/s11831-021-09553-2. [40] AMELSFORT R, WEERHEIJM J T. The failure mode of concrete slabs due to contact charges [R]. John Wiley & Sons, 1994. [41] SALAMI M R. Analytical expressions for uniaxial tensile strength of concrete in terms of uniaxial compressive strength [J]. Transportation Research Record, 1992(1335): 52–54. [42] 宋守志. 条形药包爆炸时的高速冲击效应 [C]//第四届全国岩石破碎学术讨论会论文集. 成都: 中国岩石力学与工程学会, 中国金属学会采矿学会, 中国土木工程学会隧道及地下工程学会, 1989: 4.SONG S Z. High-speed impact effects of linear charge explosion [C]// Proceedings of the 4th National Symposium on Rock Fragmentation. Chengdu: Chinese Society for Rock Mechanics and Engineering, Chinese Society of Metals Mining Society, Chinese Society of Civil Engineering Tunnel and Underground Engineering Society, 1989: 4. [43] 王明洋, 李杰, 邓国强. 超高速动能武器钻地毁伤效应与工程防护 [M]. 北京 : 科学出版社, 2021.WANG M Y, LI J, DENG G Q. Penetration and destruction effects of hypervelocity kinetic energy weapons and engineering protection [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. [44] 李重情, 穆朝民, 石必明. 变埋深条件下混凝土中爆炸应力传播规律的研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(6): 140–145. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.07.021.LI Z Q, MU C M, SHI B M. Investigate on shock stress propagation in concrete at different depths under blasting [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(6): 140–145. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.07.021. [45] MU C M, ZHOU H, MA H F. Prediction method for ground shock parameters of explosion in concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 291: 123372. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123372. [46] LEONG E C, ANAND S, CHEONG H K, et al. Re-examination of peak stress and scaled distance due to ground shock [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2007, 34(9): 1487–1499. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.10.009. [47] YANKELEVSKY D Z, KARINSKI Y S, FELDGUN V R. Re-examination of the shock wave’s peak pressure attenuation in soils [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2011, 38(11): 864–881. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.05.011. [48] FAN Y, CHEN L, LI Z, et al. Modeling the blast load induced by a close-in explosion considering cylindrical charge parameters [J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 24: 83–108. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.02.005. [49] US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station. Fundamentals of protective design for conventional weapons [M]. Washington: US Department of the Army, 1986. -






 下载:
下载: