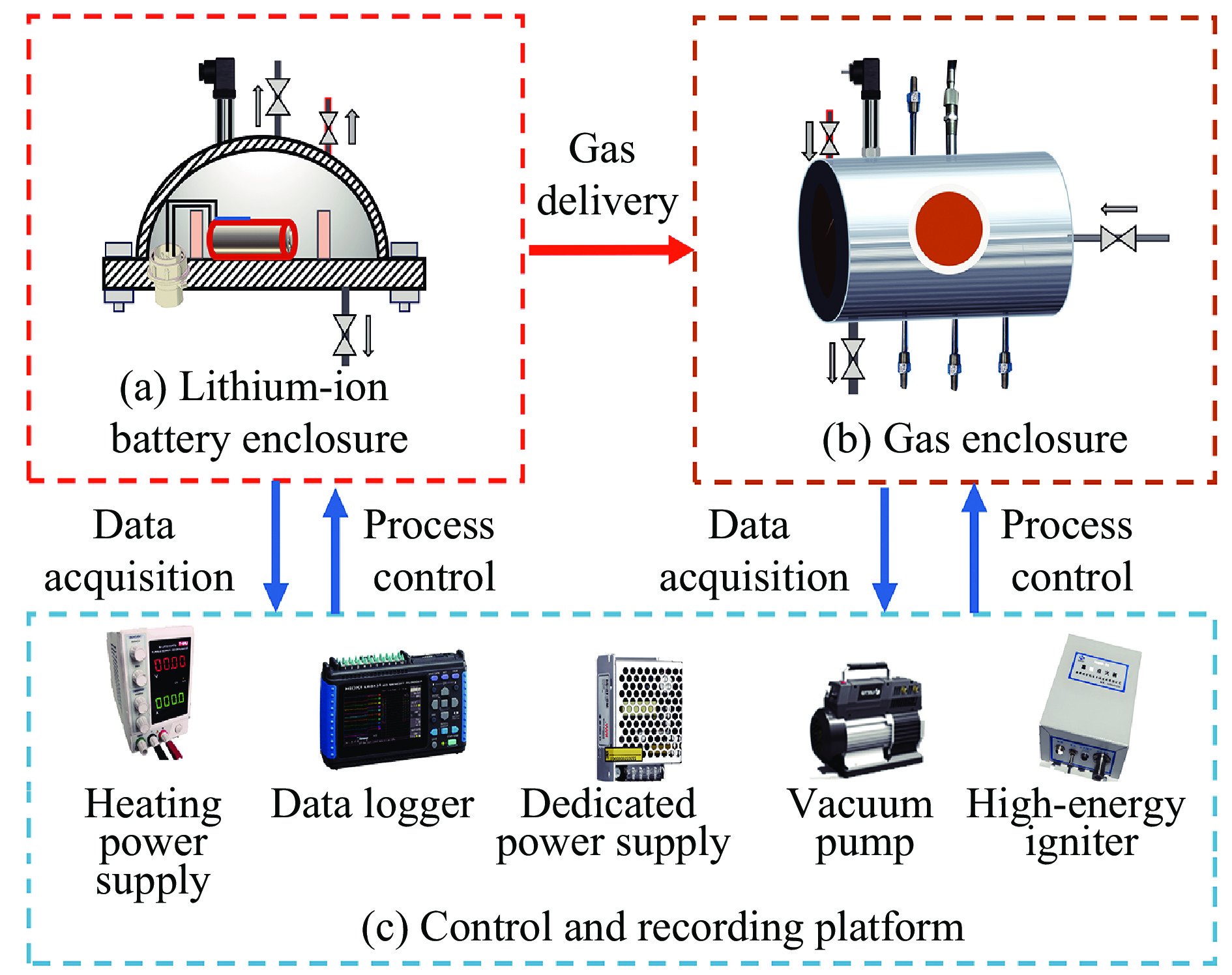
Explosion hazard of thermal runaway in aviation lithium-ion batteries under low-temperature cycling aging conditions
-
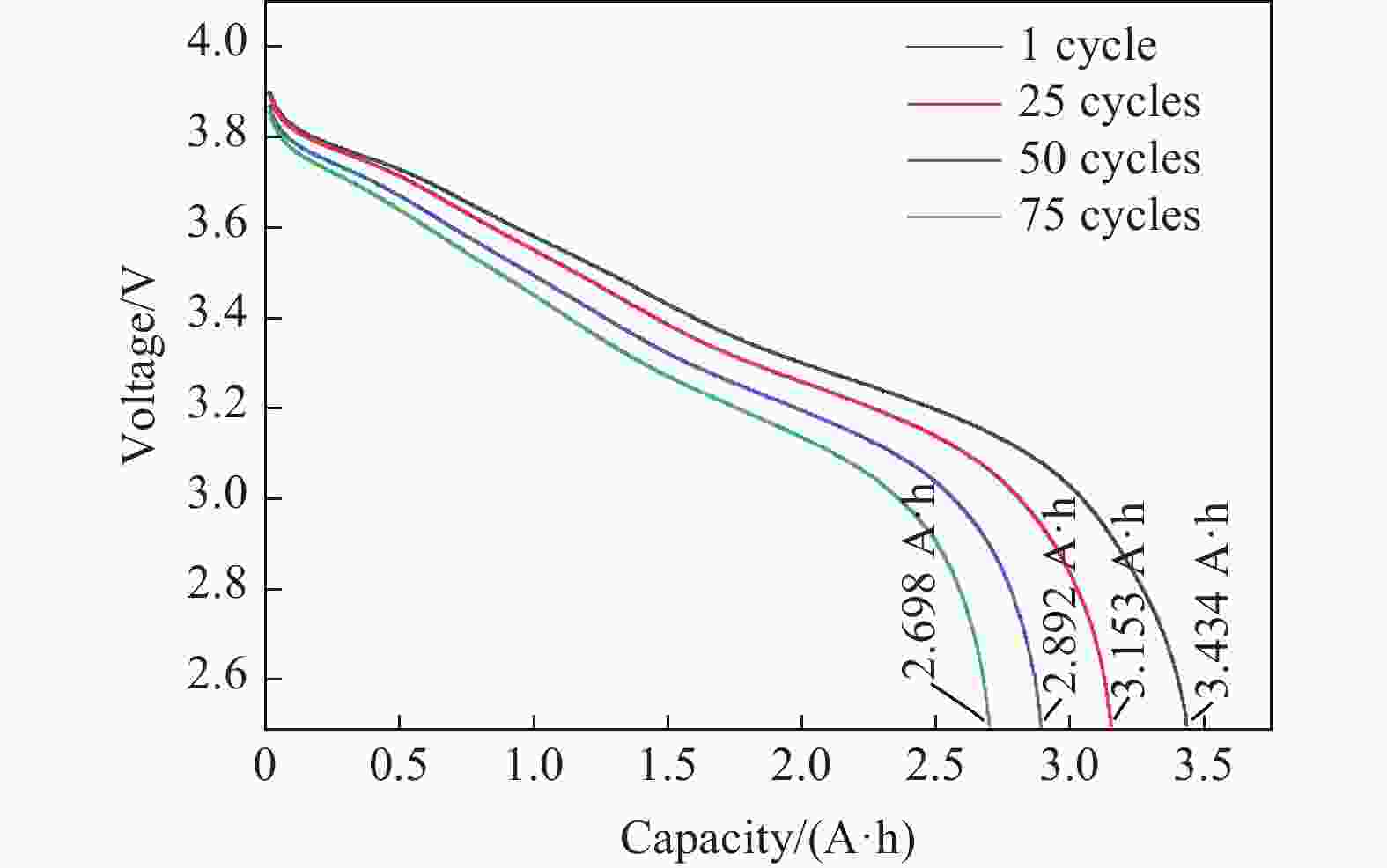
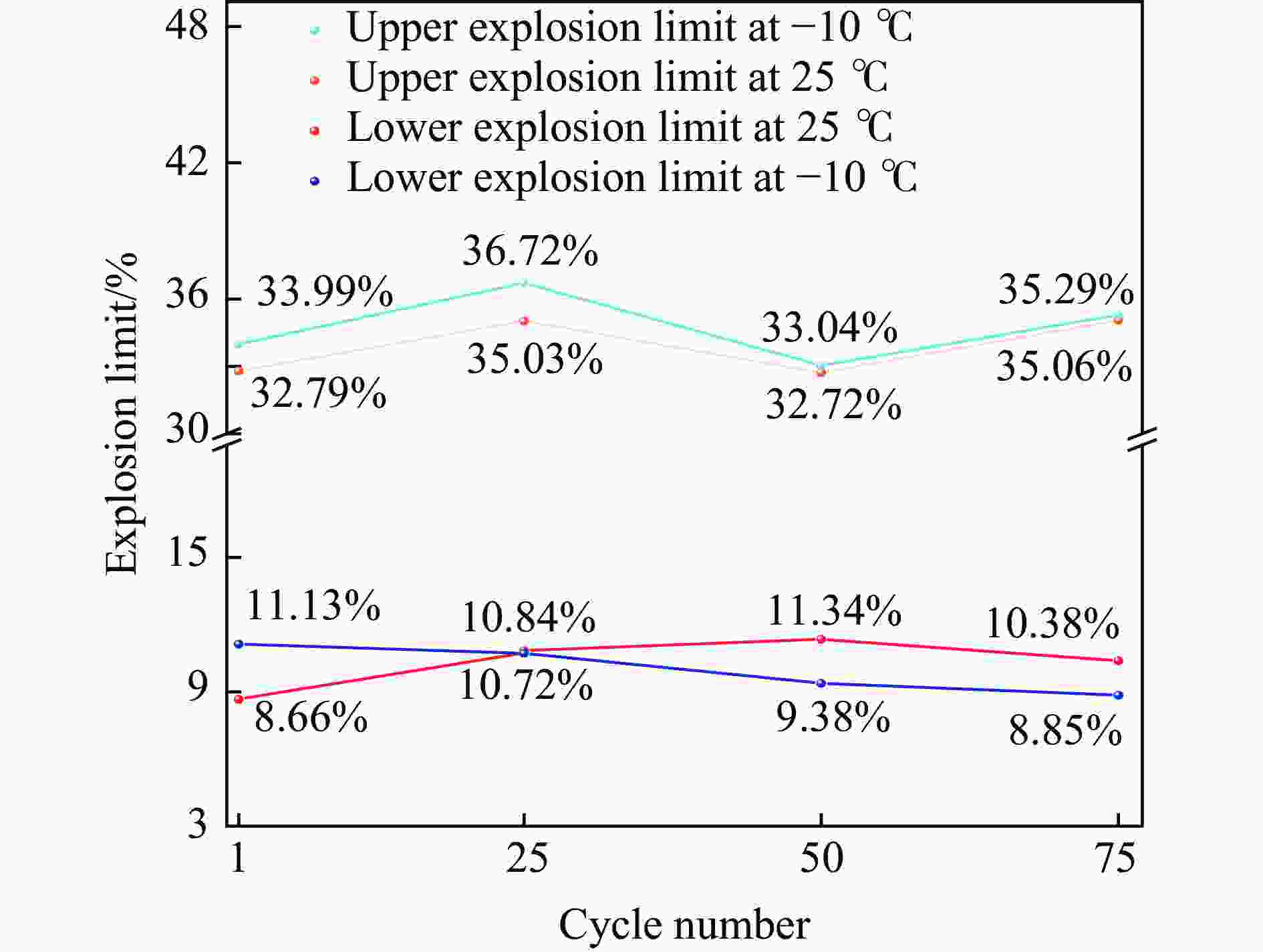
摘要: 鉴于全寿命周期内循环老化后航空锂离子电池热失控反应较新电池有显著差异,且低温环境对锂离子电池系统重大失效危险性影响更加贴近低空实际飞行场景,自主搭建了锂离子电池热失控及气体爆炸测试平台,采用锂离子电池的热失控时间、表面峰值温度和热失控超压及热失控气体的爆炸极限、压力及温度为关键参数,探讨低温(−10 ℃)循环老化对锂离子电池热失控爆炸危险性的影响。实验结果显示,常温循环老化锂离子电池较新电池热失控时间明显提前和电池安全阀开启到完全热失控的时间间隔明显增长,分别为559.86和122.56 s,且热失控气体爆炸下限升高30.95%,气体爆炸压力降低至258.6 kPa;低温环境因素则会使老化锂离子电池热失控的爆炸危险性发生显著变化,导致热失控时间提前至412.38 s,安全阀打开到完全热失控的时间间隔缩短至56.66 s,并使热失控气体爆炸下限降低20.49%,爆炸压力高达319.5 kPa。Abstract: The thermal runaway reactions of lithium-ion batteries exhibit significant deviations following full life-cycle cycling aging when compared to their fresh-state counterparts, particularly under low-temperature conditions. These conditions more closely simulate the operational scenarios encountered in low-altitude aviation, where the risk of catastrophic failure in battery systems is heightened. This study, utilizing a custom-built platform designed for testing thermal runaway and gas explosion phenomena, systematically investigates the impact of low-temperature (−10 °C) cycling aging on the associated explosion hazards. Key parameters analyzed in this research include the initiation time of thermal runaway, the peak surface temperature of the battery, the overpressure generated during thermal runaway, the lower explosion limit (LEL) of the gases produced, and the explosion pressure and temperature, serving as crucial indicators of the system’s safety performance. Experimental results demonstrate that, under ambient temperature conditions, aged batteries exhibit a marked increase in the thermal runaway initiation time, as well as a notable extension in the interval between the activation of the safety valve and the onset of complete thermal runaway (Δt), when compared to fresh batteries. Specifically, thermal runaway occurs at 559.86 s, while Δt increases to 122.56 s. Moreover, the LEL of hazardous gases rises by 30.95%, and the resulting explosion pressure diminishes to 258.6 kPa, suggesting a reduced likelihood of catastrophic failure. However, when subjected to low-temperature cycling aging, the explosion risk profile shifts dramatically. In this case, the thermal runaway initiation time is significantly reduced to 412.38 s, with Δt contracting sharply to 56.66 s. Furthermore, the LEL of the gases decreases by 20.49%, while the explosion pressure surges to 319.5 kPa, indicating an elevated risk of severe explosion. The multifaceted analysis of these hazard indicators reveals a complex interplay between aging processes and environmental conditions, profoundly influencing the explosion risks and thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries. These findings emphasize the critical necessity of developing advanced battery management systems that incorporate predictive early-warning mechanisms, strategic battery layout designs, and improved containment strategies, specifically tailored to the demands of electric aviation. By incorporating the effects of both cycling aging and low-temperature environments into risk assessments, this study provides vital insights for mitigating the elevated hazards associated with thermal runaway and the explosion of emitted gases in aviation applications. Ultimately, these findings contribute to the enhancement of safety protocols and risk mitigation strategies for the reliable and secure operation of lithium-ion battery systems throughout their entire operational lifecycle.
-
表 1 实验工况
Table 1. Experimental operating conditions
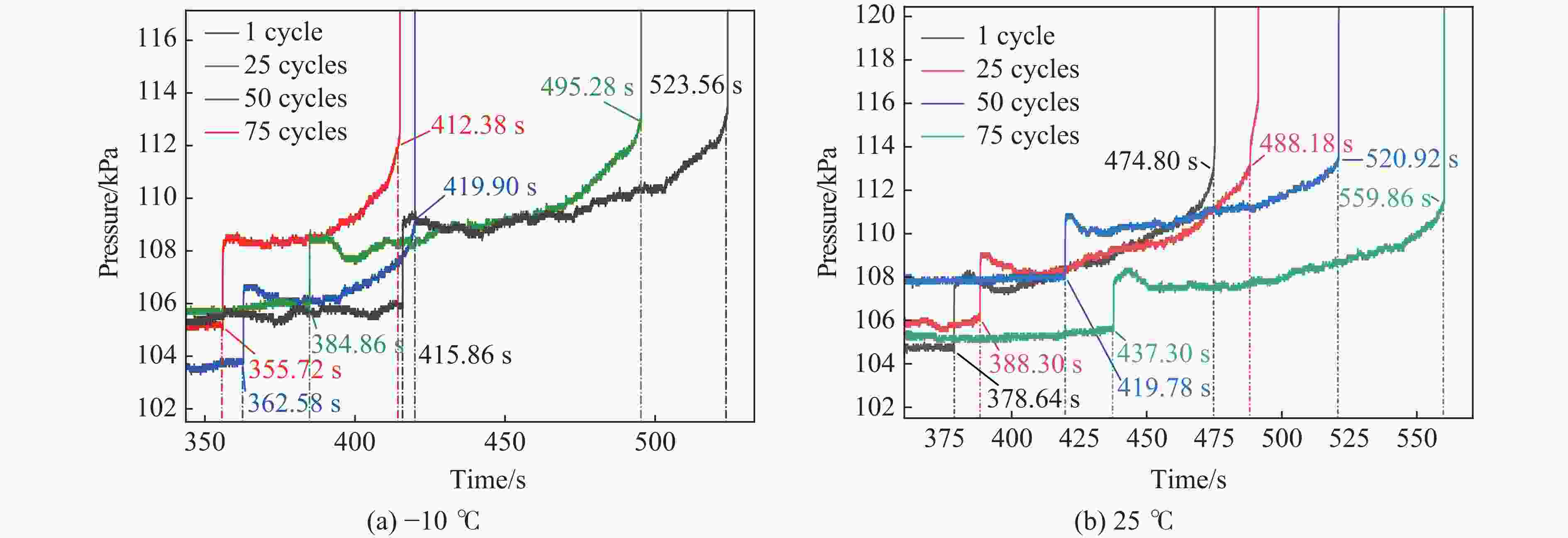
充放电环境温度/℃ 充放电循环/圈 −10 1, 25, 50, 75 25 1, 25, 50, 75 表 2 不同工况下电池发生热失控的关键时间参数
Table 2. Key temporal parameters for thermal runaway of batteries under different operating conditions
工况 tTR/s Δt/s 工况 tTR/s Δt/s 充放电环境温度/℃ 充放电循环/圈 充放电环境温度/℃ 充放电循环/圈 25 1 474.80 96.16 −10 1 523.56 107.70 25 488.18 99.88 25 495.28 110.42 50 520.92 101.14 50 419.90 57.32 75 559.86 122.56 75 412.38 56.66 表 3 不同实验工况下电池舱内气体峰值压力
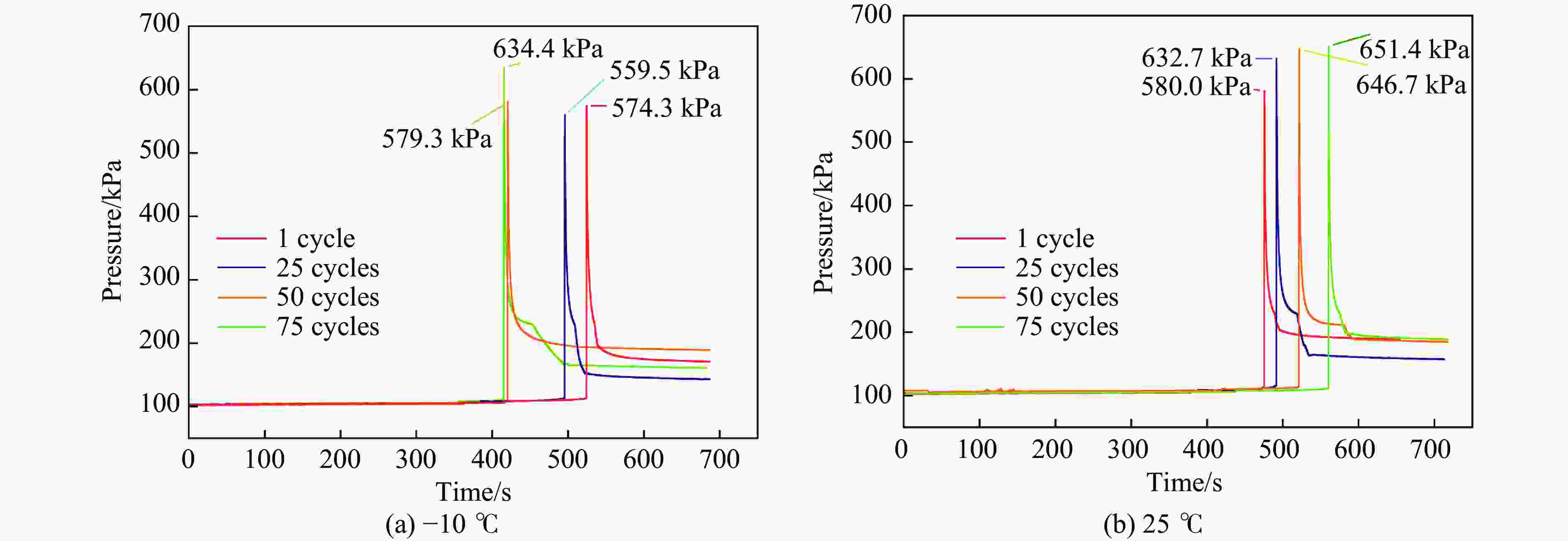
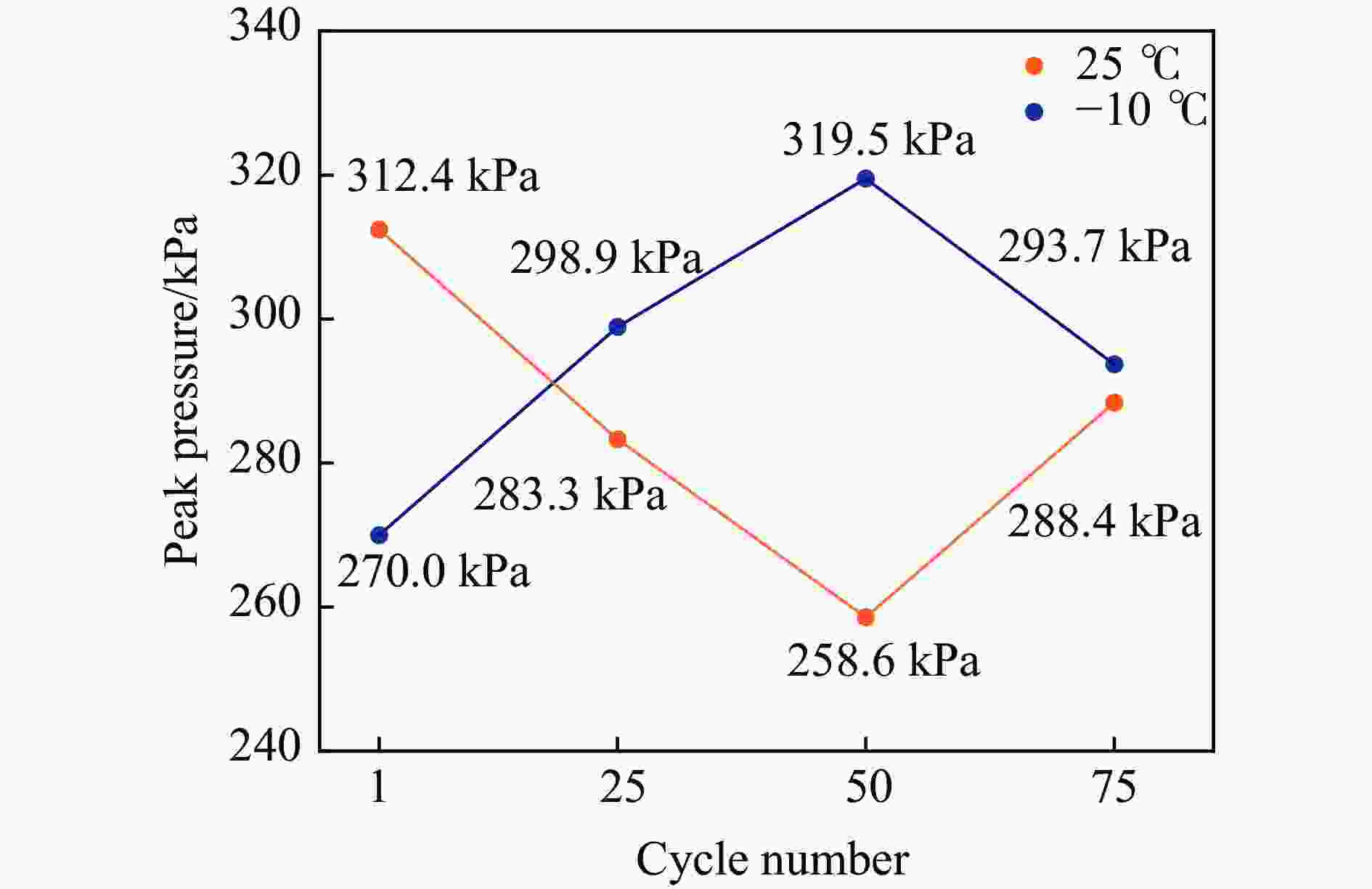
Table 3. Peak gas pressure inside the battery compartment under different experimental conditions
环境温度/℃ 电池舱内峰值压力/kPa 循环1圈 循环25圈 循环50圈 循环75圈 25 580.0 632.7 646.7 651.4 −10 574.3 559.5 579.3 634.4 表 4 不同工况下爆炸火焰不同位置的温度
Table 4. Temperatures at different positions of explosion flame under different conditions
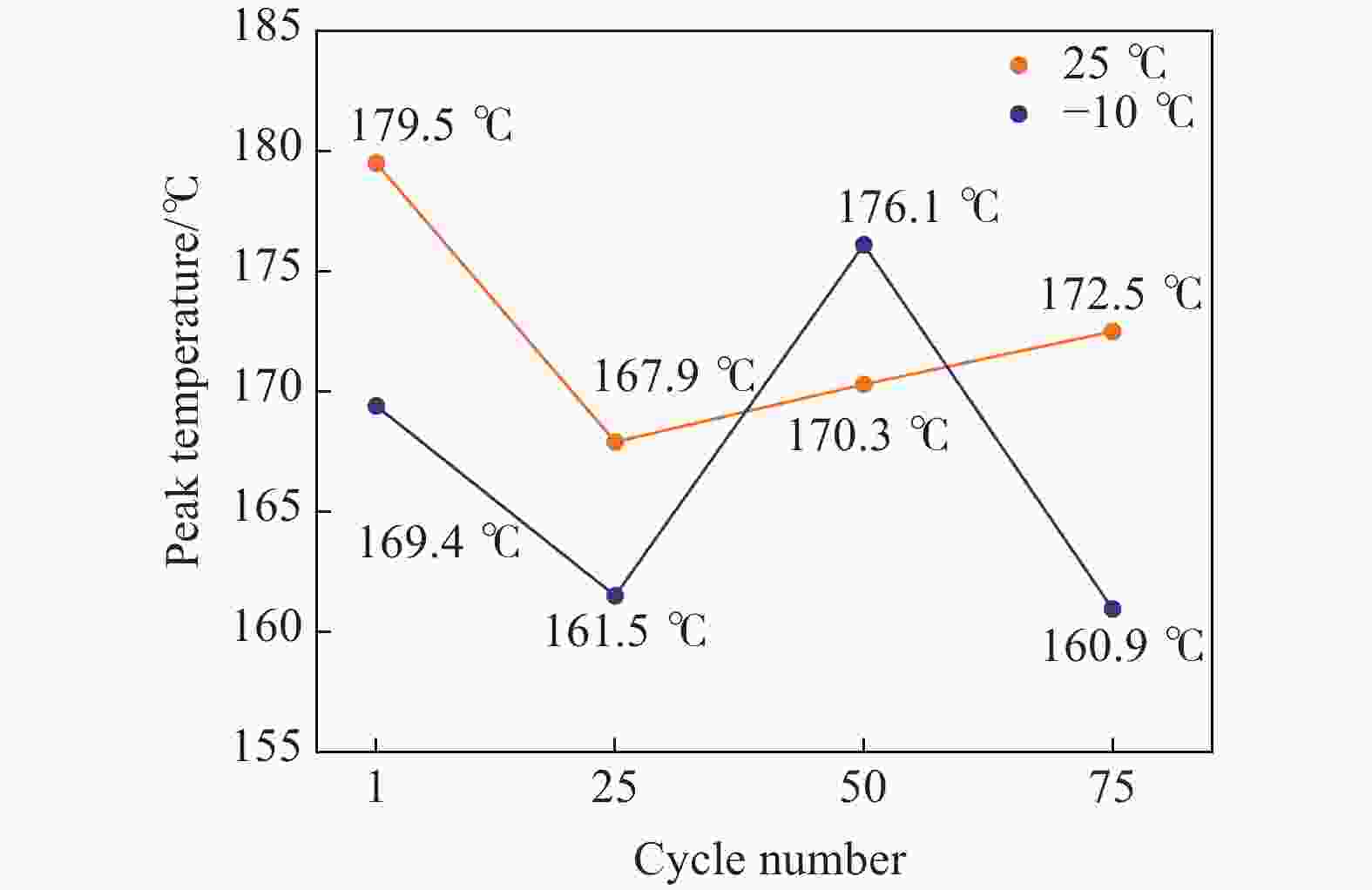
工况 爆炸火焰温度/℃ 充放电环境温度/℃ 充放电循环/圈 中心 左侧 后部 右侧 25 1 181.2 165.1 198.8 172.9 25 184.4 151.9 177.7 157.5 50 186.5 158.9 184.3 151.4 75 180.8 157.4 183.8 168.0 −10 1 188.1 154.4 179.9 155.1 25 174.6 152.3 173.7 145.4 50 189.7 163.4 182.2 169.1 75 175.4 146.4 169.8 152.2 -
[1] EATON J, NARAGHI M, BOYD J G. Regional pathways for all-electric aircraft to reduce aviation sector greenhouse gas emissions [J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 373: 123831. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123831. [2] 杨凤田, 范振伟, 项松, 等. 中国电动飞机技术创新与实践观点 [J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(3): 624619. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24619.YANG F T, FAN Z W, XlANG S, et al. Technical innovation and practice of electric aircraft in China [J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 624619. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2020.24619. [3] SISMANIDOU A, TARRADELLAS J, SUAU-SANCHEZ P, et al. Breaking barriers: an assessment of the feasibility of long-haul electric flights [J]. Journal of Transport Geography, 2024, 115: 103797. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2024.103797. [4] WEI H L, LOU B C, ZHANG Z Z, et al. Autonomous navigation for eVTOL: review and future perspectives [J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(2): 4145–4171. DOI: 10.1109/TIV.2024.3352613. [5] 邓景辉. 电动垂直起降飞行器的技术现状与发展 [J]. 航空学报, 2024, 45(5): 529937. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.29937.DENG J H. Technical status and development of electric vertical take-off and landing aircraft [J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(5): 529937. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.29937. [6] RAJENDRAN S, SRINIVAS S. Air taxi service for urban mobility: a critical review of recent developments, future challenges, and opportunities [J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2020, 143: 102090. DOI: 10.1016/j.tre.2020.102090. [7] BARRERA T P, BOND J R, BRADLEY M, et al. Next-generation aviation Li-ion battery technologies: enabling electrified aircraft [J]. The Electrochemical Society Interface, 2022, 31(3): 69–74. DOI: 10.1149/2.F10223IF. [8] BUTICCHI G, WHEELER P, BOROYEVICH D. The more-electric aircraft and beyond [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2023, 111(4): 356–370. DOI: 10.1109/JPROC.2022.3152995. [9] LI H G, ZHOU D, ZHANG M H, et al. Multi-field interpretation of internal short circuit and thermal runaway behavior for lithium-ion batteries under mechanical abuse [J]. Energy, 2023, 263: 126027. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.126027. [10] XIAO Y, YANG F Q, GAO Z H, et al. Review of mechanical abuse related thermal runaway models of lithium-ion batteries at different scales [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 64: 107145. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2023.107145. [11] 李谦, 于金山, 刘盛终, 等. 不同因素影响下锂离子电池热失控演变特征及危害性综述 [J]. 消防科学与技术, 2023, 42(11): 1482–1487. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2023.11.006.LI Q, YU J S, LIU S Z, et al. Review on the characteristics and hazards of lithium-ion battery thermal runaway under various conditions [J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2023, 42(11): 1482–1487. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2023.11.006. [12] WORKU B E, ZHENG S M, WANG B. Review of low-temperature lithium-ion battery progress: new battery system design imperative [J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022, 46(11): 14609–14626. DOI: 10.1002/er.8194. [13] NG B, COMAN P T, FAEGH E, et al. Low-temperature lithium plating/corrosion hazard in lithium-ion batteries: electrode rippling, variable states of charge, and thermal and nonthermal runaway [J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(4): 3653–3664. DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.0c00130. [14] FU Y Y, LU S, SHI L, et al. Ignition and combustion characteristics of lithium ion batteries under low atmospheric pressure [J]. Energy, 2018, 161: 38–45. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.129. [15] ZHANG Q S, NIU J H, YANG J, et al. In-situ explosion limit analysis and hazards research of vent gas from lithium-ion battery thermal runaway [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 56: 106146. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2022.106146. [16] DENG J, CHEN B H, LU J Z, et al. Thermal runaway and combustion characteristics, risk and hazard evaluation of lithium-iron phosphate battery under different thermal runaway triggering modes [J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 368: 123451. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123451. [17] BAIRD A R, ARCHIBALD E J, MARR K C, et al. Explosion hazards from lithium-ion battery vent gas [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 446: 227257. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227257. [18] 杨娟, 牛江昊, 张青松. 循环老化锂离子电池热失控气体原位爆炸极限实验分析 [J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(23): 428529. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28529.YANG J, NIU J H, ZHANG Q S, et al. In-situ explosion limit of thermal runaway gas explosion in cyclic aging lithium-ion batteries: experimental analysis [J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(23): 428529. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2023.28529. [19] ZHANG Q S, YANG K B, NIU J H, et al. Research on the lower explosion limit of thermal runaway gas in lithium batteries under high-temperature and slight overcharge conditions [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 79: 109976. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2023.109976. [20] YANG J, LIU W H, ZHAO H Y, et al. Experimental investigation of lithium-ion batteries thermal runaway propagation consequences under different triggering modes [J]. Aerospace, 2024, 11(6): 438. DOI: 10.3390/aerospace11060438. [21] 杨娟, 胡佳宁, 佟佳成, 等. 航空锂电池热失控高温喷射冲击实验研究 [J]. 航空学报, 2025, 46(14): 430965. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2024.30965.YANG J, HU J N, TONG J C, et al. Experimental study on high-temperature jet impact induced by thermal runaway in aviation lithium-ion batteries [J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2025, 46(14): 430965. DOI: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2024.30965. [22] German Institute for Standardization. Determination of explosion limits of gases and vapours at elevated pressures, elevated temperatures or with oxidizers other than air: DIN EN 17624: 2022 [S]. German: German Institute for Standardization, 2022-03-01. [23] XIAO Y, ZHAO J R, YIN L, et al. Staged thermal runaway behaviours of three typical lithium-ion batteries for hazard prevention [J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2024, 149(18): 10321–10333. DOI: 10.1007/s10973-024-13080-0. [24] 韩鑫. 低温环境下锂离子电池析锂特性及其影响研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2021. DOI: 10.26944/d.cnki.gbfju.2021.002428.HAN X. Research on the characteristics and influence of lithium plating in lithium-ion batteries at low temperature[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021. DOI: 10.26944/d.cnki.gbfju.2021.002428. [25] 张青松, 包防卫, 牛江昊. 环境压力对锂电池热失控产气及爆炸风险的影响 [J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(7): 2263–2270. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0192.ZHANG Q S, BAO F W, NIU J H. Risk analysis method of thermal runaway gas explosion in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(7): 2263–2270. DOI: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2023.0192. -






 下载:
下载: