Process and mechanism of blasting damage and fracture of calcium conglomerate in Hushan ranium mine
-
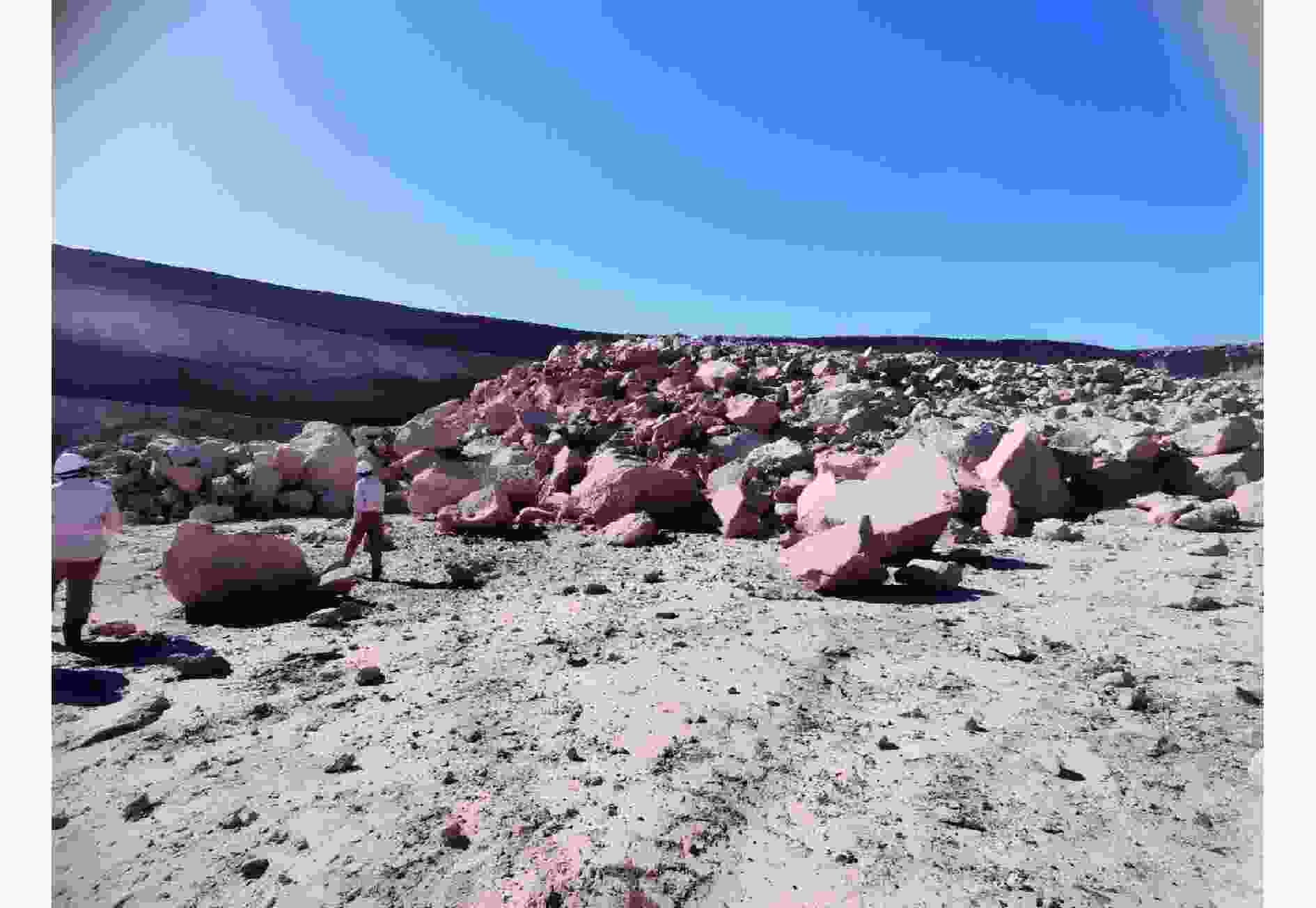
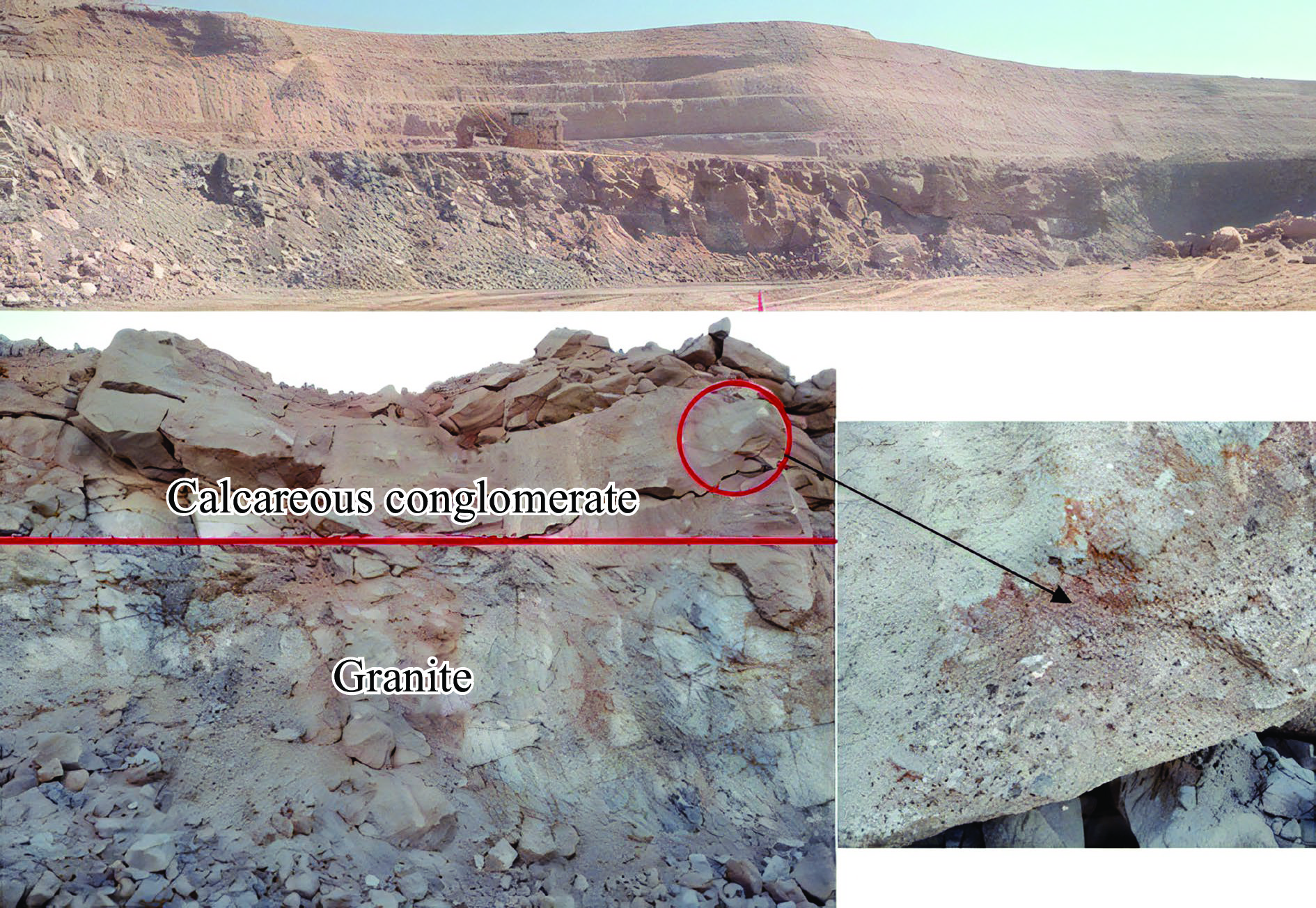
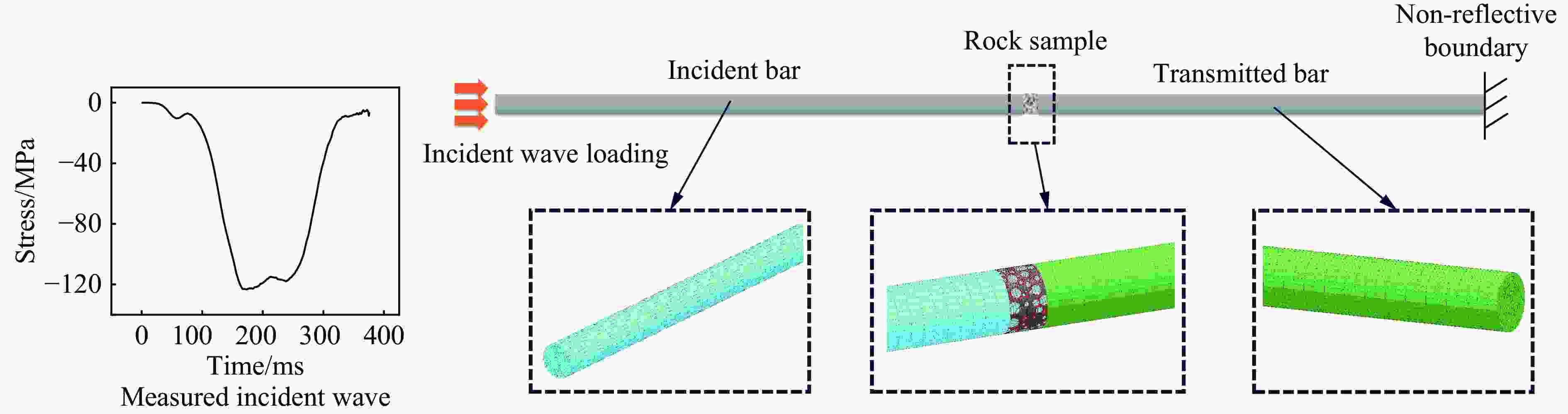
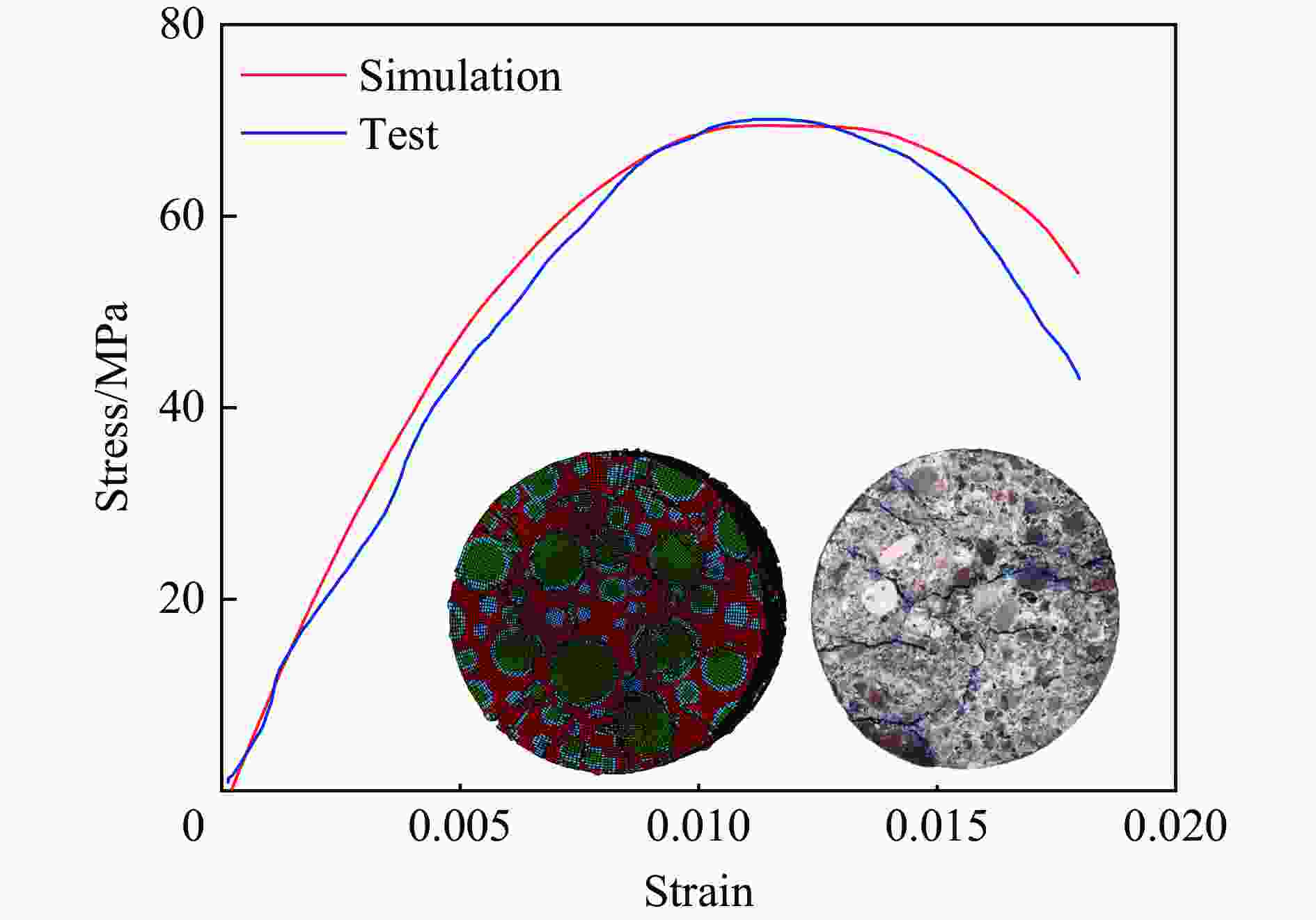
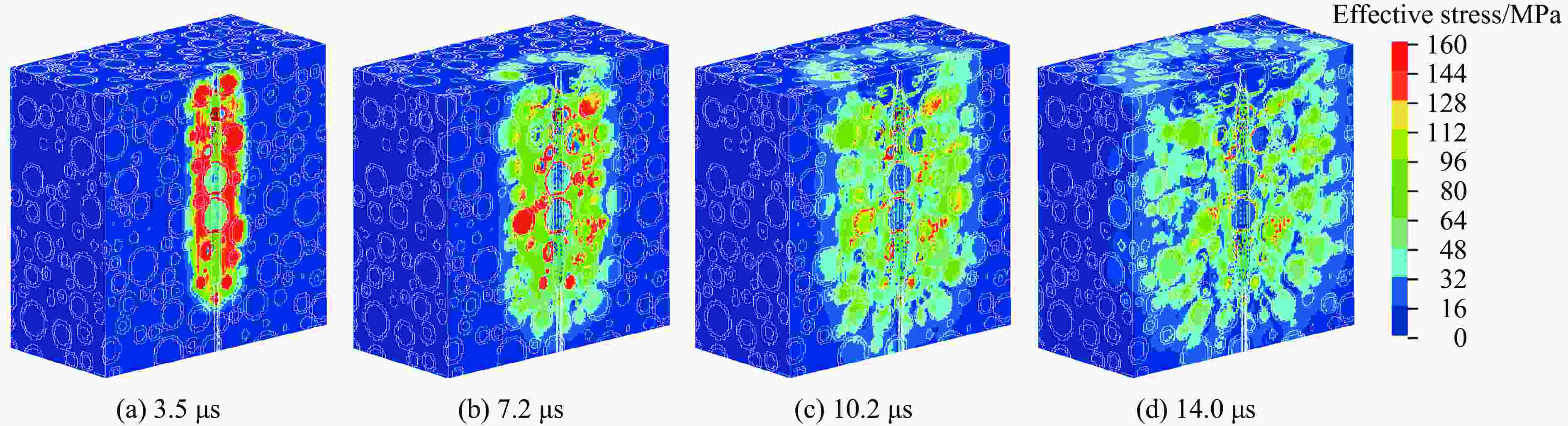
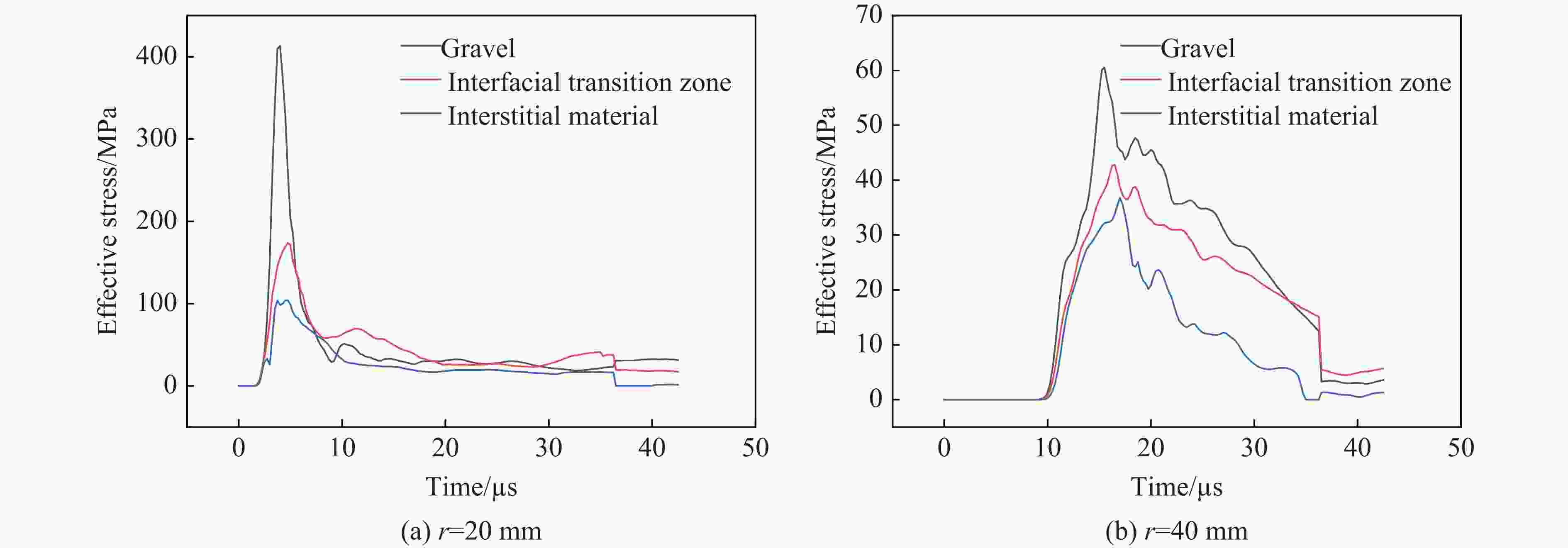
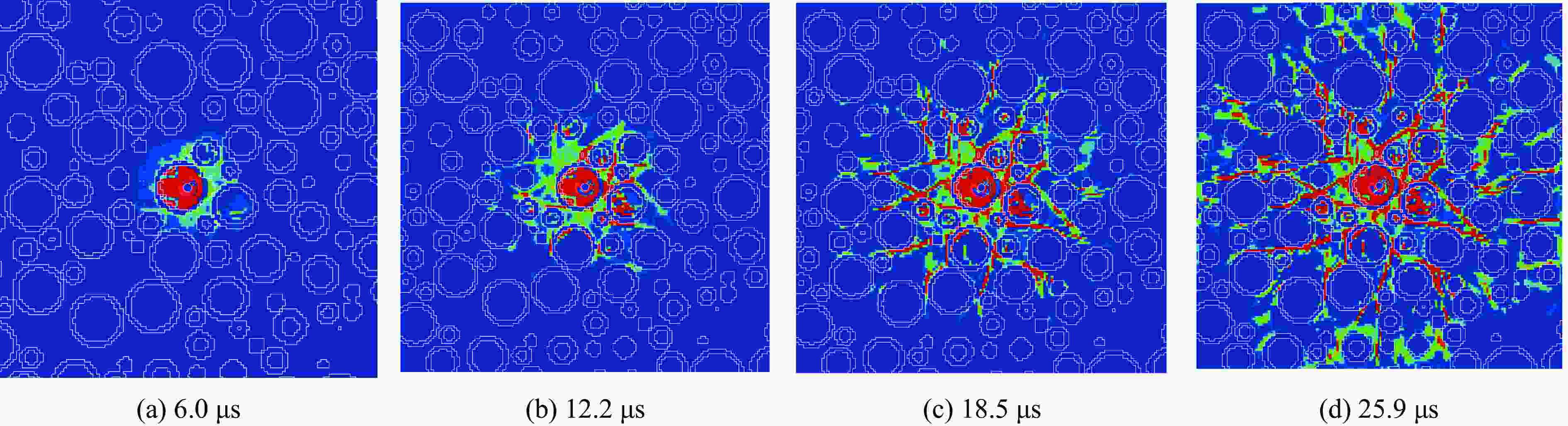
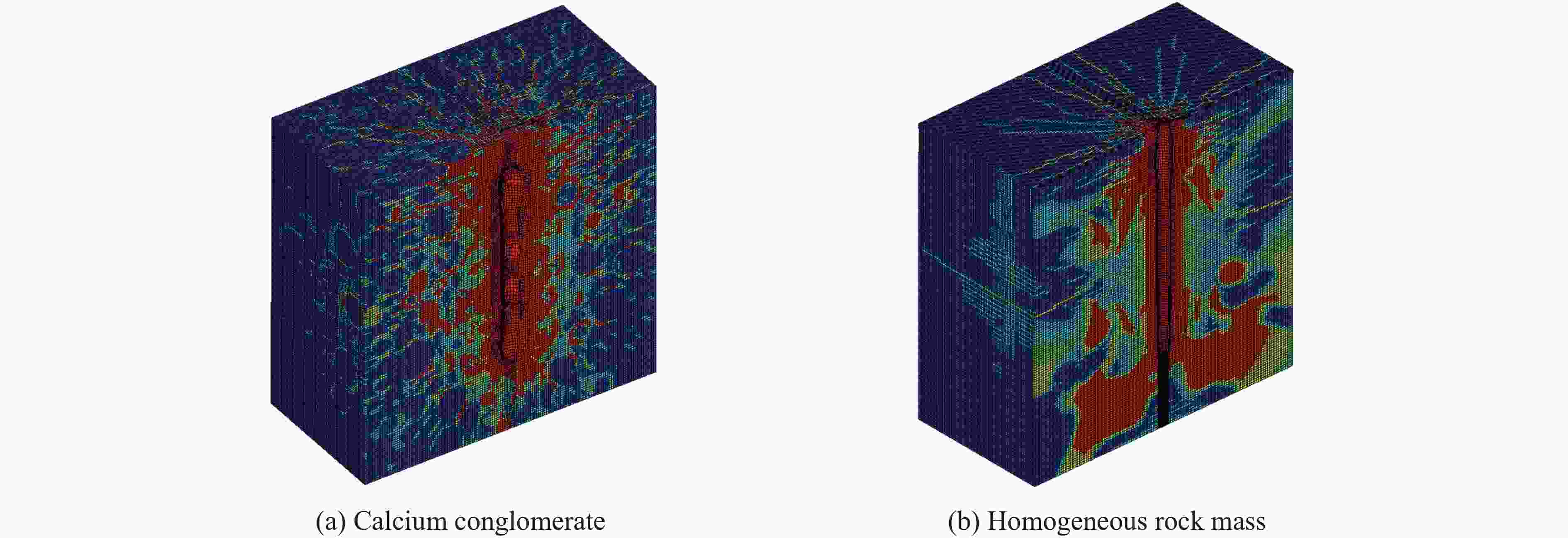
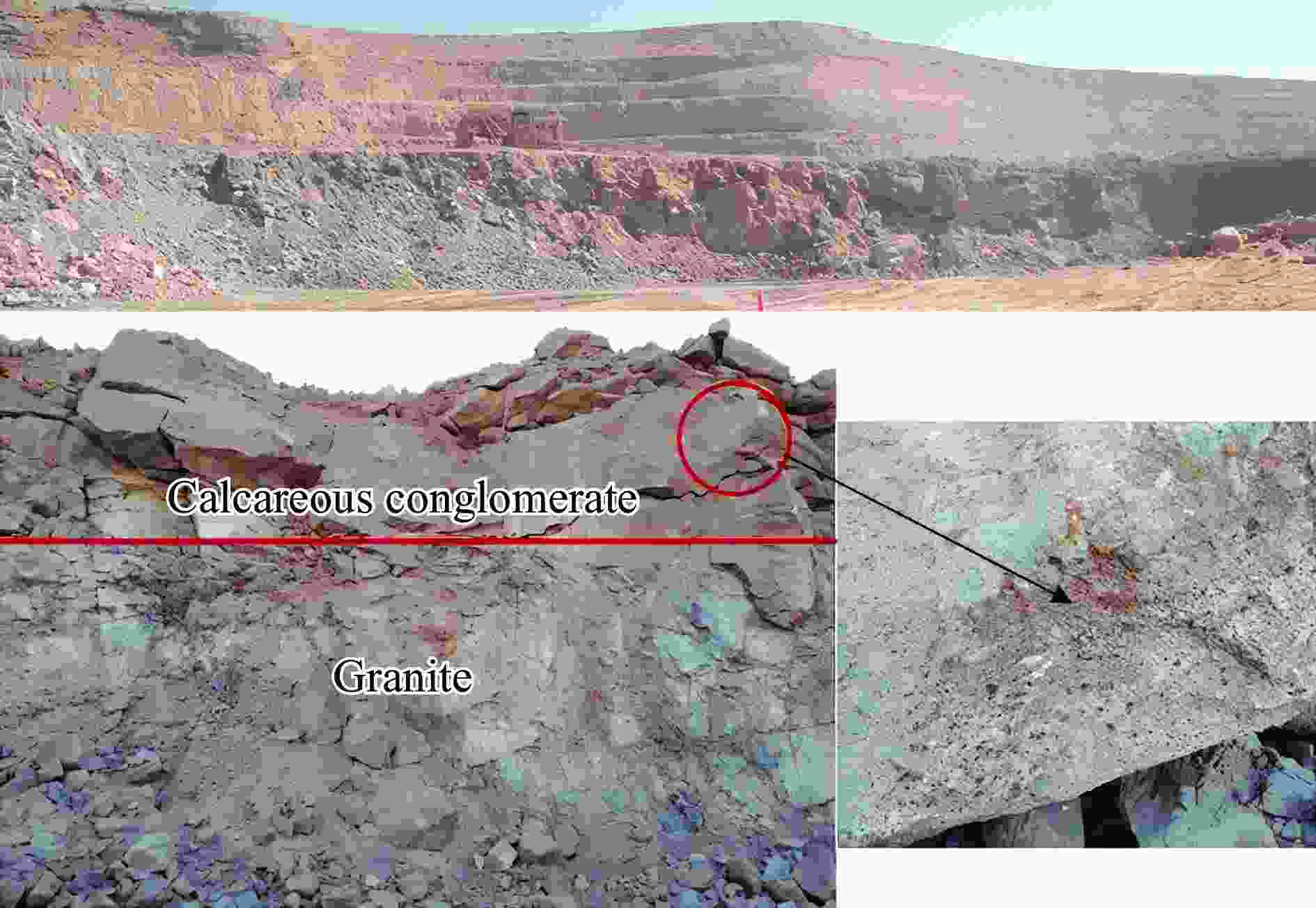
摘要: 为研究爆破作用下钙结砾岩的破坏规律,基于损伤断裂力学理论揭示了钙结砾岩爆破损伤断裂过程与机理,采用LS-DYNA软件和Fortran编程建立了包括填隙物、砾石和界面过渡区(interfacial transition zone,ITZ)的细观数值模型,分析了钙结砾岩爆炸应力波传播规律及损伤特征。钙结砾岩爆破损伤断裂过程可分为4个阶段,即砾石和填隙物均发生压缩破坏;砾石发生拉伸破坏,填隙物发生压缩破坏;砾石和填隙物均发生拉伸破坏;砾石和填隙物交接面发生拉伸破坏。数值模拟结果表明:砾石在爆破荷载作用下表征出更高的等效应力,填隙物等效应力最小,ITZ处出现明显的应力集中现象,随着距离的增大,砾石与填隙物承受的应力差距减小。砾石的损伤较小,存在损伤“绕石”现象,填隙物的损伤较大。钙结砾岩爆破裂纹的扩展形式以沿着应力波的传播方向优先选择物理力学性能较低的填隙物以及交接面进行发育为主,对于砾石的破坏较弱。爆破块度主要表现为填隙物包裹砾石,爆破块度分布受交接面的黏结力、砾石分布的影响。Abstract: To study the damage law of calcareous conglomerate under blasting, firstly, the damage fracture process and mechanism of calcareous conglomerate under blasting load were revealed based on the theory of damage fracture mechanics. A meso-scale model of conglomerate, including filler, conglomerate and interfacial transition zone (ITZ), was established by using LS-DYNA and Fortran programming, and the propagation law of explosive stress wave and its damage characteristics were analyzed. The damage fracture process of calcareous conglomerate under blasting can be divided into four stages, namely: compression damage in both gravel and fill; tensile damage in gravel and compression damage in fill; tensile damage in both gravel and fill; and tensile damage at the intersection of gravel and fill. Numerical results show that under blasting loads, the gravel has higher equivalent stresses, the fill has the lowest, stress concentration is evident at the ITZ, and the stress gap between the gravel and the fill decreases as the distance increases. The conglomerate sustains relatively minor damage, with a notable phenomenon of damage occurring around it. However, the filler experiences significant damage. The expansion of blasting crack in calcareous conglomerate forms mainly along the direction of stress wave propagation. Cracks tend to develop along the filler with lower physical and mechanical properties, as well as along the junction surfaces. The damage to the gravel is comparatively less severe. Blasting blockiness is mainly manifested as the filler wrapping gravel, and the distribution of blasting blockiness is affected by the bonding force at the intersection surface and the distribution of gravel.
-
表 1 砾石和填隙物的基本物理力学参数
Table 1. Basic physical and mechanical parameters of gravel and fillers
材料种类 密度/(g·mm−3) 抗压强度/MPa 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 砾石 2.66 167.8 41.2 0.23 填隙物 2.14 35.0 13.4 0.20 表 2 界面过渡区的K&C本构模型参数
Table 2. K&C constitutive model parameters for interface transition zone
密度/(g·mm−3) 抗压强度/MPa 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 1.5 25.0 9.3 0.25 表 3 炸药材料参数及状态方程参数
Table 3. Material parameters and state equation parameters of explosive
ρ0/(kg·m−3) D/(m·s−1) $ {p_{\mathrm{CJ}}} $/GPa A1/GPa B/GPa R1 R2 1150 4300 3.43 214.4 0.182 4.5 0.9 -
[1] 杨小林. 岩石爆破损伤断裂的细观机理及其力学特性研究 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(5): 665. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.05.031.YANG X L. Meso-mechanism of damage and fracture on rock blasting and its mechanical behaviors [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(5): 665. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.05.031. [2] 褚怀保, 杨小林, 梁为民, 等. 煤体爆破损伤断裂过程与机理研究 [J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2018, 35(2): 410–414. DOI: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2018.02.025.CHU H B, YANG X L, LIANG W M, et al. Study on the damage-fracture process and mechanism of coal blasting [J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2018, 35(2): 410–414. DOI: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2018.02.025. [3] FAN L F, WONG L N Y. Stress wave transmission across a filled joint with different loading/unloading behavior [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2013, 60: 227–234. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.12.046. [4] RAINA A K. Influence of joint conditions and blast design on pre-split blasting using response surface analysis [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(10): 4057–4070. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-019-01822-8. [5] SINGH S P, XAVIER P. Causes, impact and control of overbreak in underground excavations [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2005, 20(1): 6–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2004.05.004. [6] 李守巨, 李德, 武力, 等. 非均质岩石单轴压缩试验破坏过程细观模拟及分形特性 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(5): 849–854. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2013.0673.LI S J, LI D, WU L, et al. Meso-simulation and fractal characteristics for uniaxial compression test of inhomogeneous rock [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(5): 849–854. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2013.0673. [7] YANG R S, DING C X, YANG L Y, et al. Model experiment on dynamic behavior of jointed rock mass under blasting at high-stress conditions [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 74: 145–152. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.01.017. [8] 沈世伟, 廖文旺, 徐燕, 等. 不同节理间距条件下岩体双孔爆破动焦散试验研究 [J]. 煤碳学报, 2018, 43(8): 2180–2186. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.1223.SHEN S W, LIAO W W, XU Y, et al. Dynamic caustics test of rock mass under different joint spacing conditions with two-hole blasting [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(8): 2180–2186. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.1223. [9] 岳中文, 杨仁树, 郭东明, 等. 爆炸应力波作用下缺陷介质裂纹扩展的动态分析 [J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(4): 949–954. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2009.04.004.YUE Z W, YANG R S, GUO D M, et al. Dynamic analysis of crack propagation in media containing flaws under the explosive stress wave [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(4): 949–954. DOI: 10.16285/j.rsm.2009.04.004. [10] 刘钊, 张树辉, 臧小静. 含双垂直缺陷岩体爆生裂纹扩展行为试验研究 [J]. 爆破, 2024, 41(1): 21–26, 66. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.01.004.LIU Z, ZHANG S H, ZANG X J. Experimental study on propagation behavior of blast-induced crack in rock mass with double vertical defects [J]. Blasting, 2024, 41(1): 21–26, 66. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2024.01.004. [11] 陈勇, 王应朋, 杨玉贵, 等. 基于LCEM-GFEM方法爆炸载荷作用下含缺陷岩体损伤机理研究(英文) [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2024, 31(2): 496–510. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-024-5582-y.CHEN Y, WANG Y P, YANG Y G, et al. Damage mechanism and fracture evolution of rock containing defects with LCEM-GFEM method under explosive load [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2024, 31(2): 496–510. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-024-5582-y. [12] 邢灏喆, 王明洋, 范鹏贤, 等. 基于高速3D-DIC技术的砂岩动力特性粒径效应研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(11): 113101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0088.XING H Z, WANG M Y, FAN P X, et al. Grain-size effect on dynamic behavior of sandstone based on high-speed 3D-DIC technique [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(11): 113101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0088. [13] 邱泓杰, 邱贤阳, 张舒, 等. 爆破动载下锯齿状岩-充界面胶结充填体损伤规律研究 [J/OL]. 煤炭学报: 1–14.[2024-05-13]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.1635.QIU H J, QIU X Y, ZHANG S, et al. Study on the damage pattern of the cemented backfill at the jagged rock-fill interface under dynamic loading of blasting [J/OL]. Journal of China Coal Society: 1–14[2024-05-13]. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2023.1635. [14] LI G W, DENG G Z, MA J G. Numerical modelling of the response of cemented paste backfill under the blasting of an adjacent ore stope [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 343: 128051. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128051. [15] SUAZO G, VILLAVICENCIO G. Numerical simulation of the blast response of cemented paste backfilled stopes [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 100: 1–14. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.04.007. [16] EMAD M Z, MITRI H, KELLY C. Dynamic model validation using blast vibration monitoring in mine backfill [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 107: 48–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.04.047. [17] JAYASINGHE L B, SHANG J L, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Numerical investigation into the blasting-induced damage characteristics of rocks considering the role of in-situ stresses and discontinuity persistence [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2019, 116: 103207. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103207. [18] MA G W, AN X M. Numerical simulation of blasting-induced rock fractures [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2008, 45(6): 966–975. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.12.002. [19] LEE J S, AHN S K, SAGONG M. Attenuation of blast vibration in tunneling using a pre-cut discontinuity [J] Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2016, 52: 30-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.11.010. [20] 胡小川, 丁学正, 苏国韶, 等. 基于UDEC-GBM的矿物晶粒解理特征对硬岩石破坏过程的影响 [J]. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(7): 1160–1170. DOI: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.12.10.002.HU X C, DING X Z, SU G S, et al. Effect of cleavage characteristics of mineral grains on the failure process of hard rock based on UDEC-GBM modeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(7): 1160–1170. DOI: 10.13374/j.issn2095-9389.2020.12.10.002. [21] 戴俊. 爆破工程 [M]. 2版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2015: 97–106.DAI J. Blasting engineering [M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2015: 97–106. [22] 杨小林, 王树仁. 岩石爆破损伤断裂的细观机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2000, 20(3): 247–252. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2000)03-0247-6.YANG X L, WANG S R. Meso-Mechanism of damage and fracture on rock blasting [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2000, 20(3): 247–252. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2000)03-0247-6. [23] MURAKAMI Y. Stress intensity factors handbook [M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1987: 97–99. [24] HOUSEHOLDER A S. Monte Carlo method [M]. Washington DC: U. S. Government Printing Office, 1951: 78–84. [25] RAGHAVAN P, GHOSH S. Concurrent multi-scale analysis of elastic composites by a multi-level computational model [J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 193(6/7/8): 497–538. DOI: 10.1016/j.cma.2003.10.007. [26] HE C L, GAO J M, CHEN D Y, et al. Investigation of stress wave interaction and fragmentation in granite during multihole blastings [J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 185187–185197. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3030253. [27] YANG X D, SUN L H, SONG J L, et al. Study on the effect of bond strength on the failure mode of coarse-grained sandstone in weakly cemented stratum [J]. Minerals, 2021, 12(1): 55. DOI: 10.3390/min12010055. [28] 吴彰钰, 张锦华, 余红发, 等. 基于三维随机细观模型的珊瑚混凝土力学性能模拟 [J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2021, 49(11): 2518–2528. DOI: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20210124.WU Z Y, ZHANG J H, YU H F, et al. Numerical analysis on mechanical properties of coral aggregate concrete using 3D random mesoscale model [J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2021, 49(11): 2518–2528. DOI: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20210124. -







 下载:
下载: