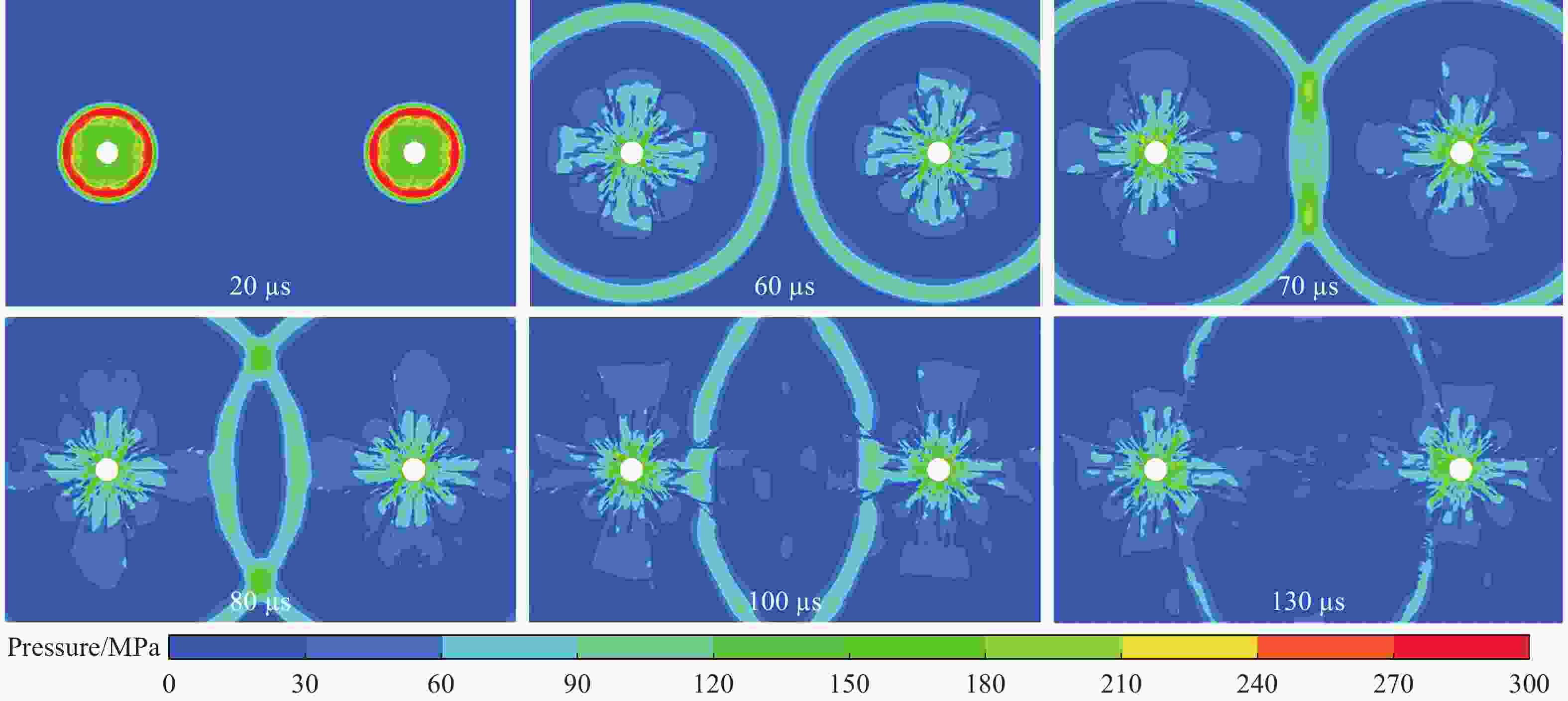
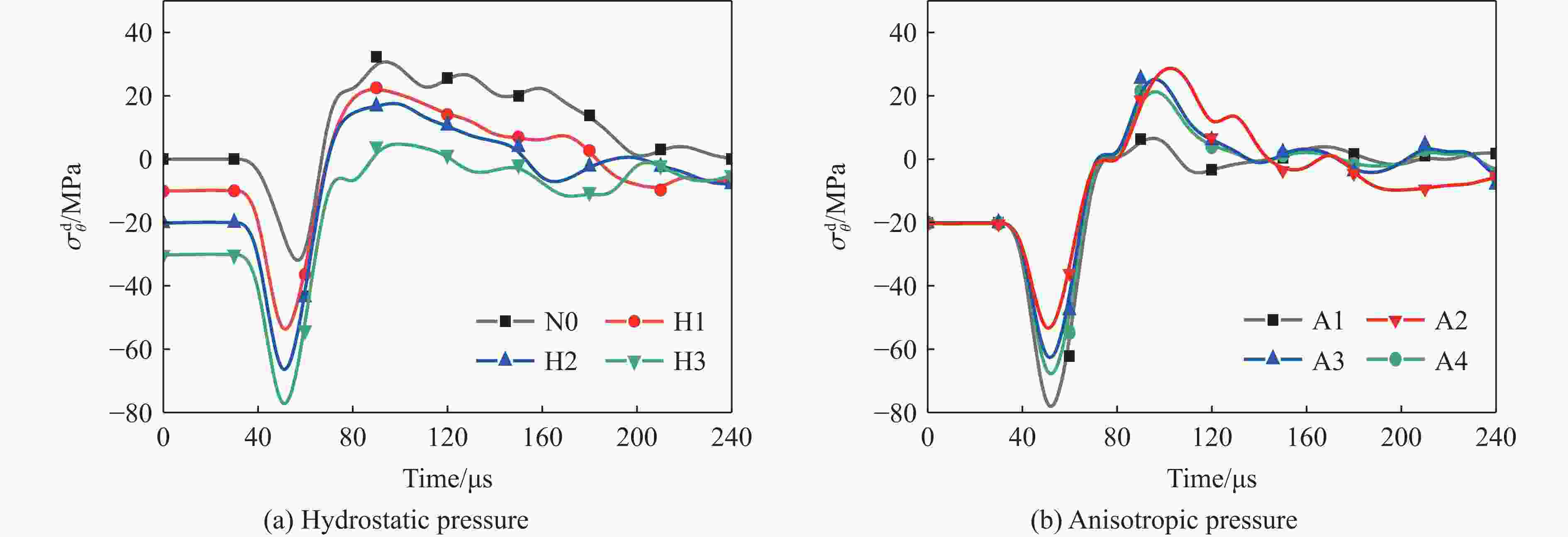
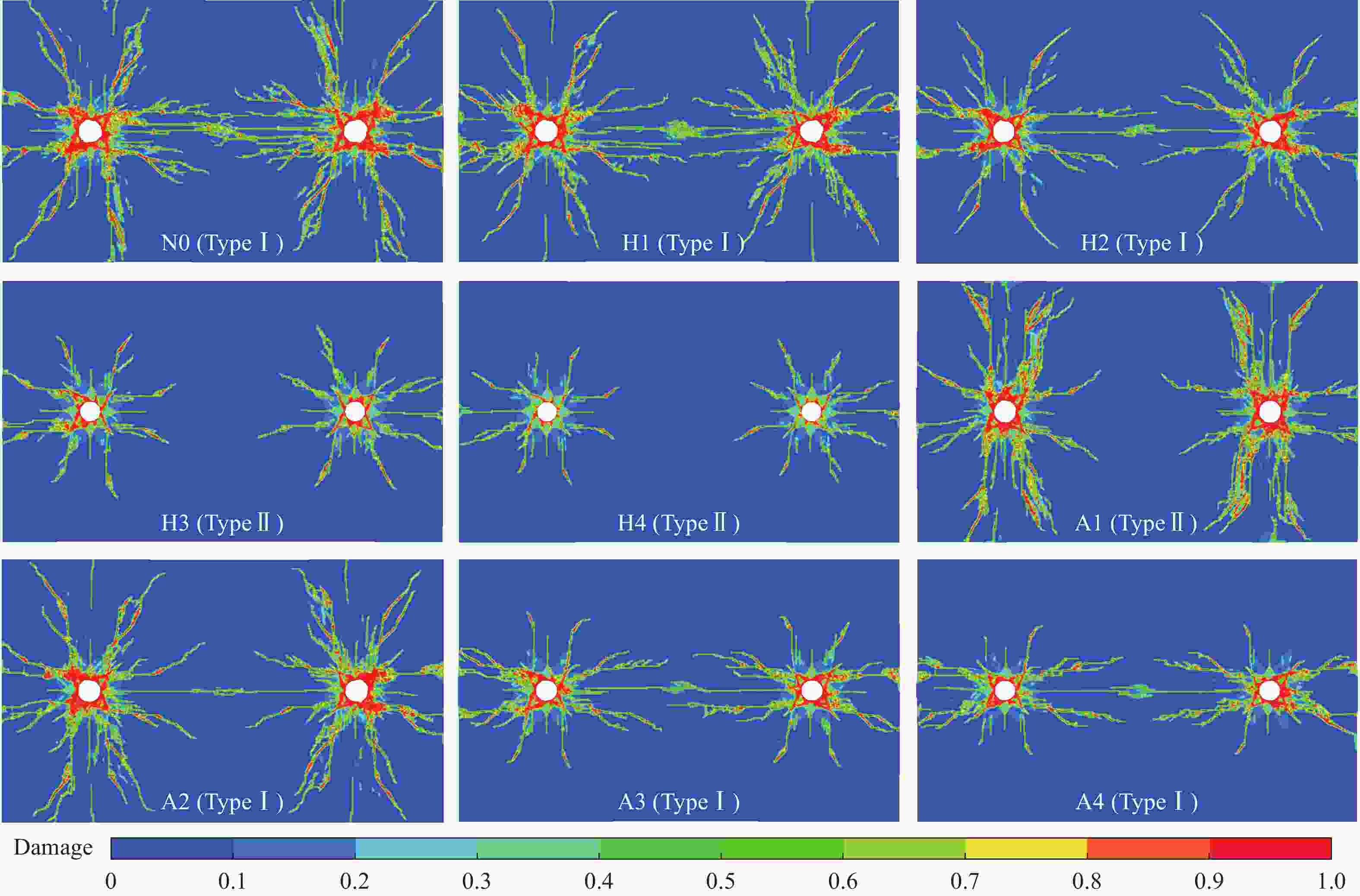
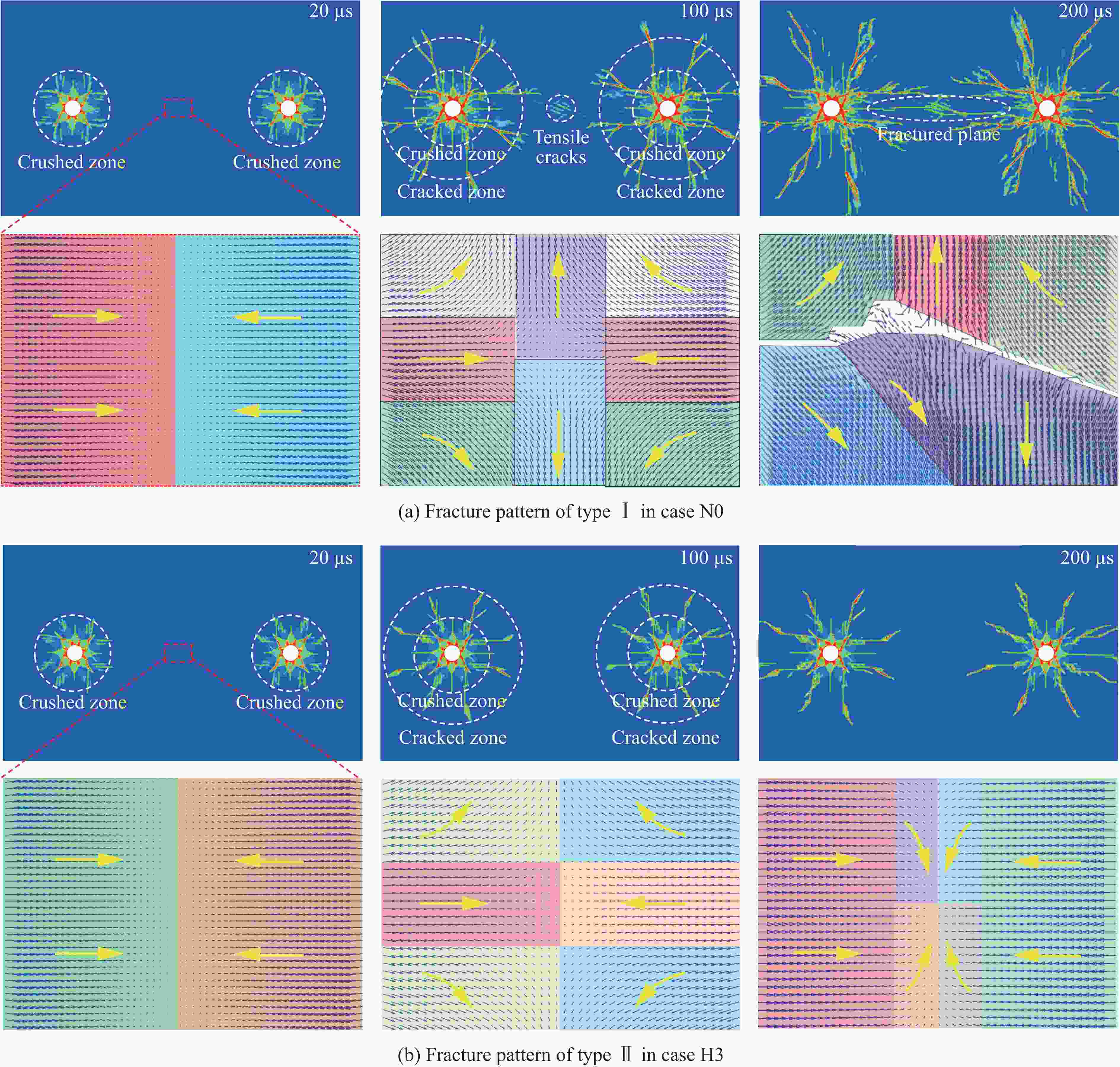
Effect of in-situ stress on fracture formation process of rock mass in presplit blasting
-
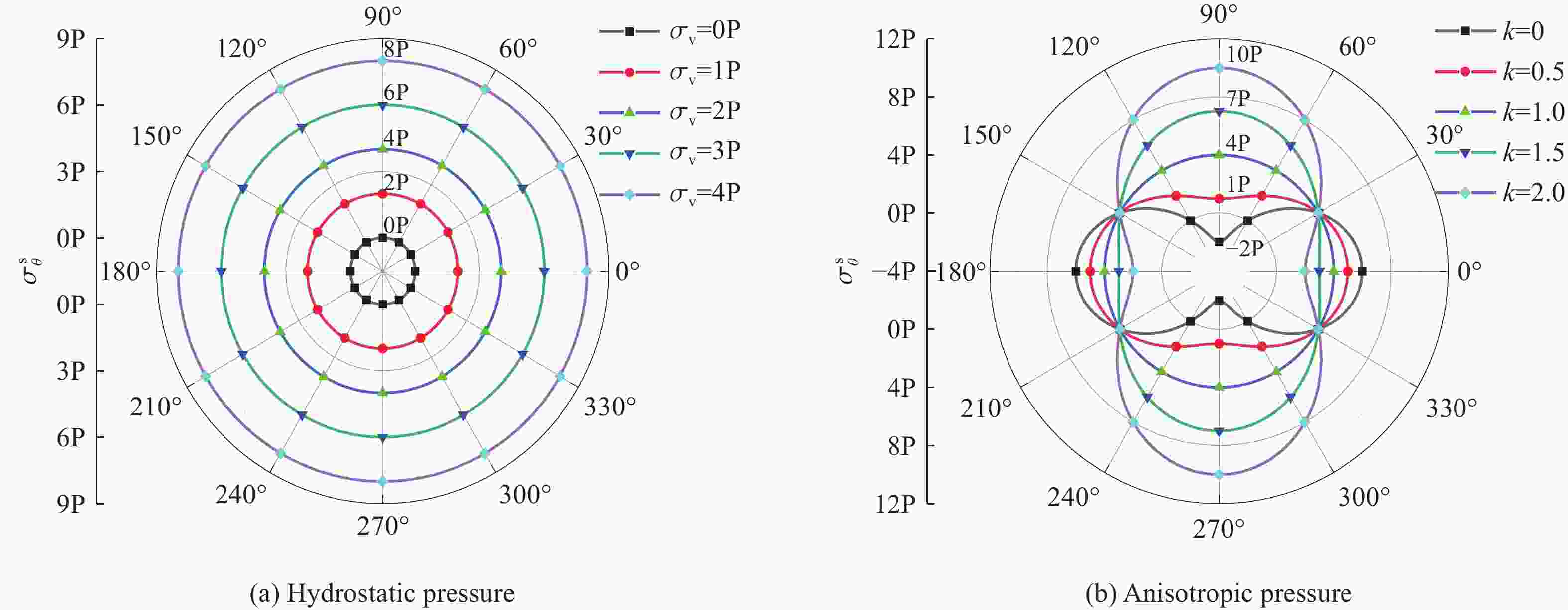
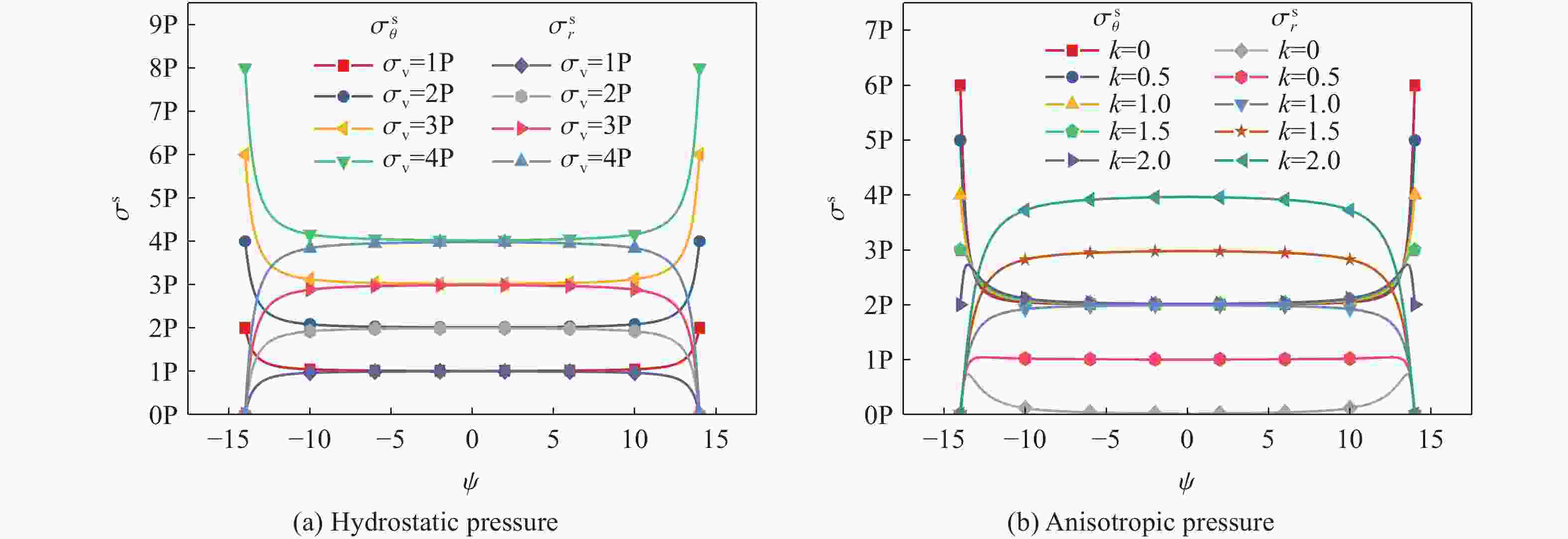
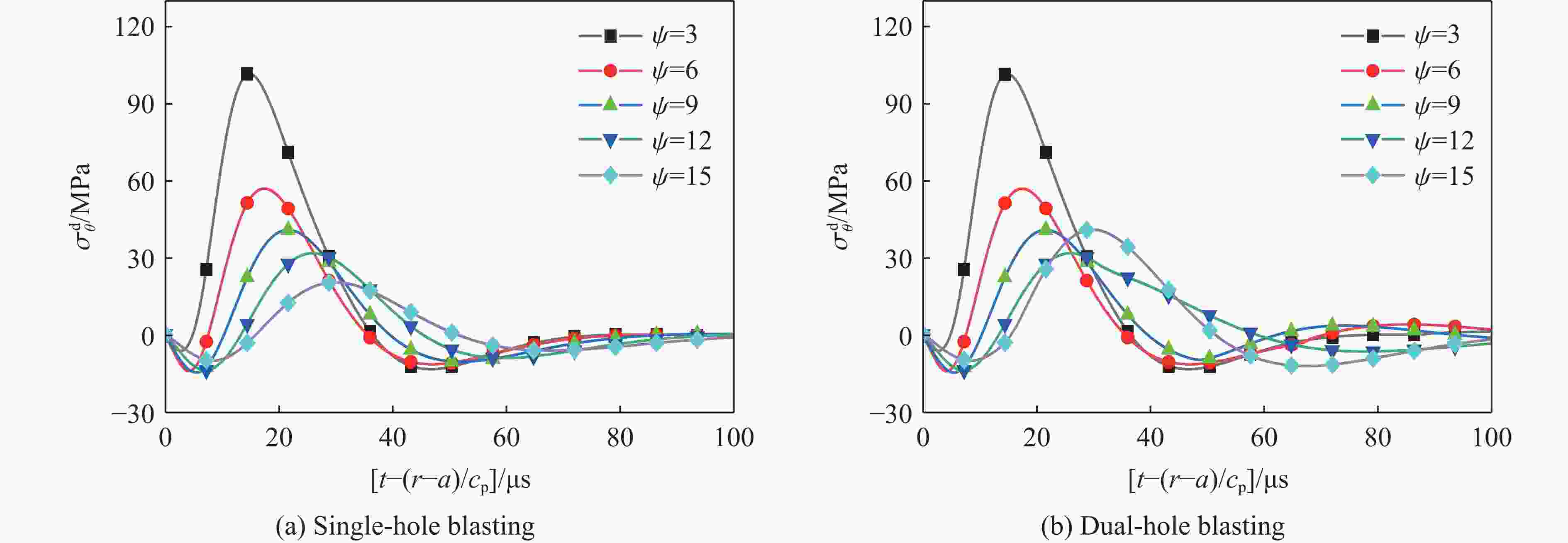
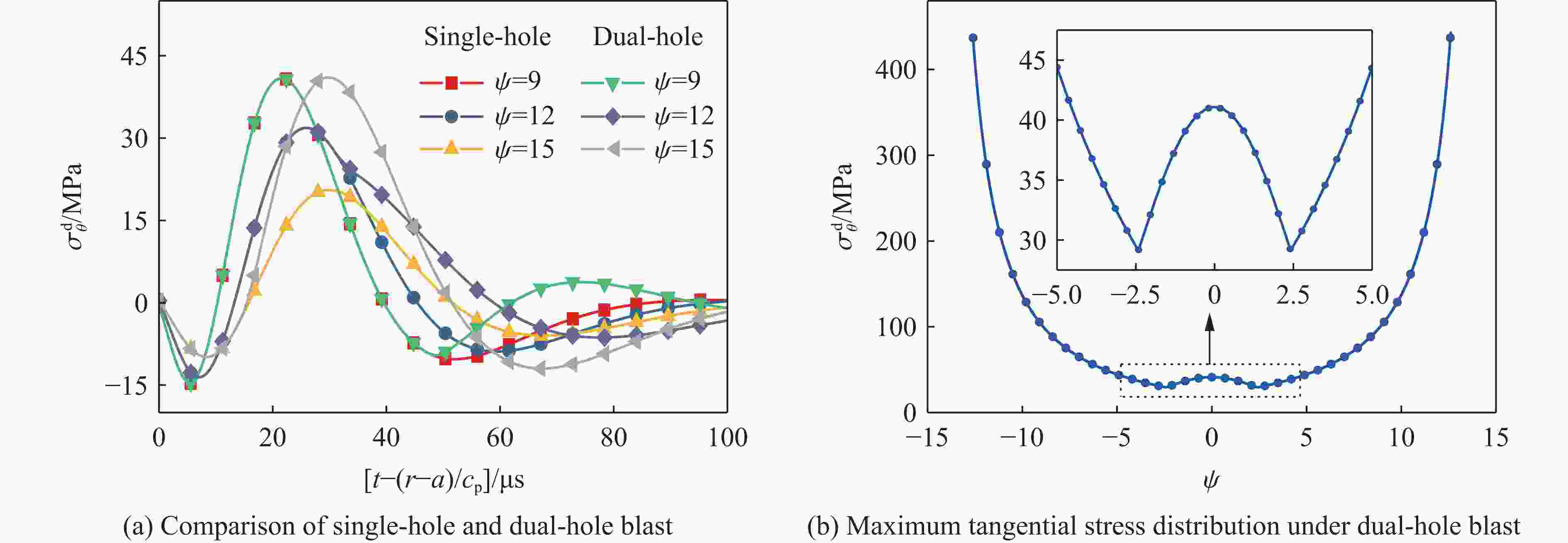
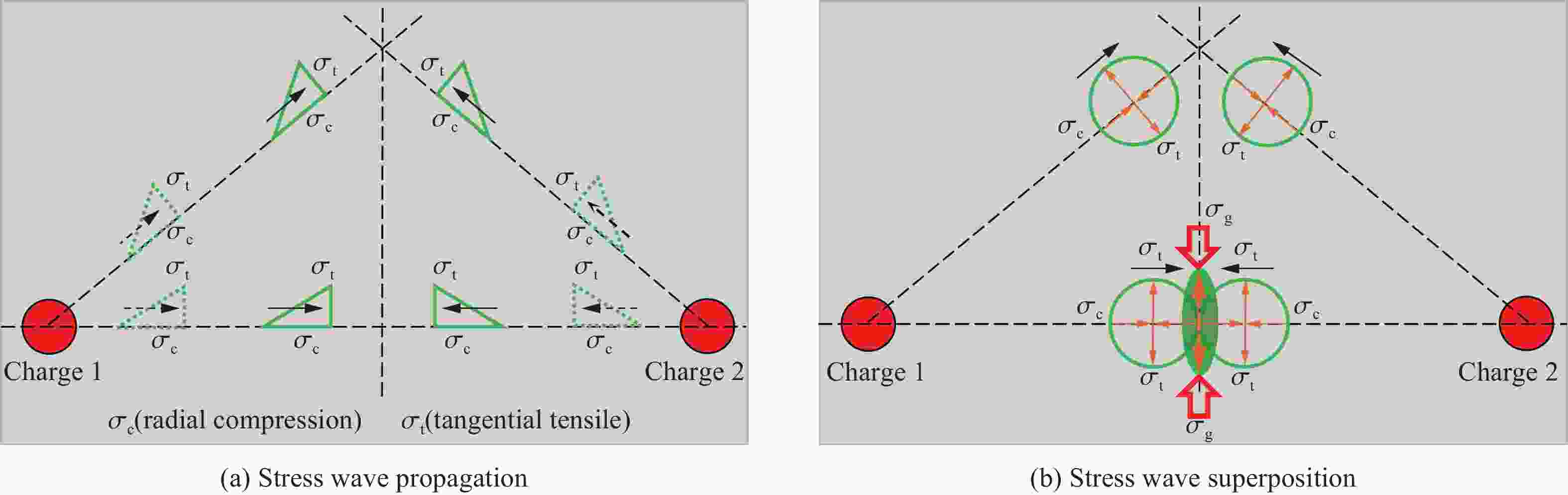
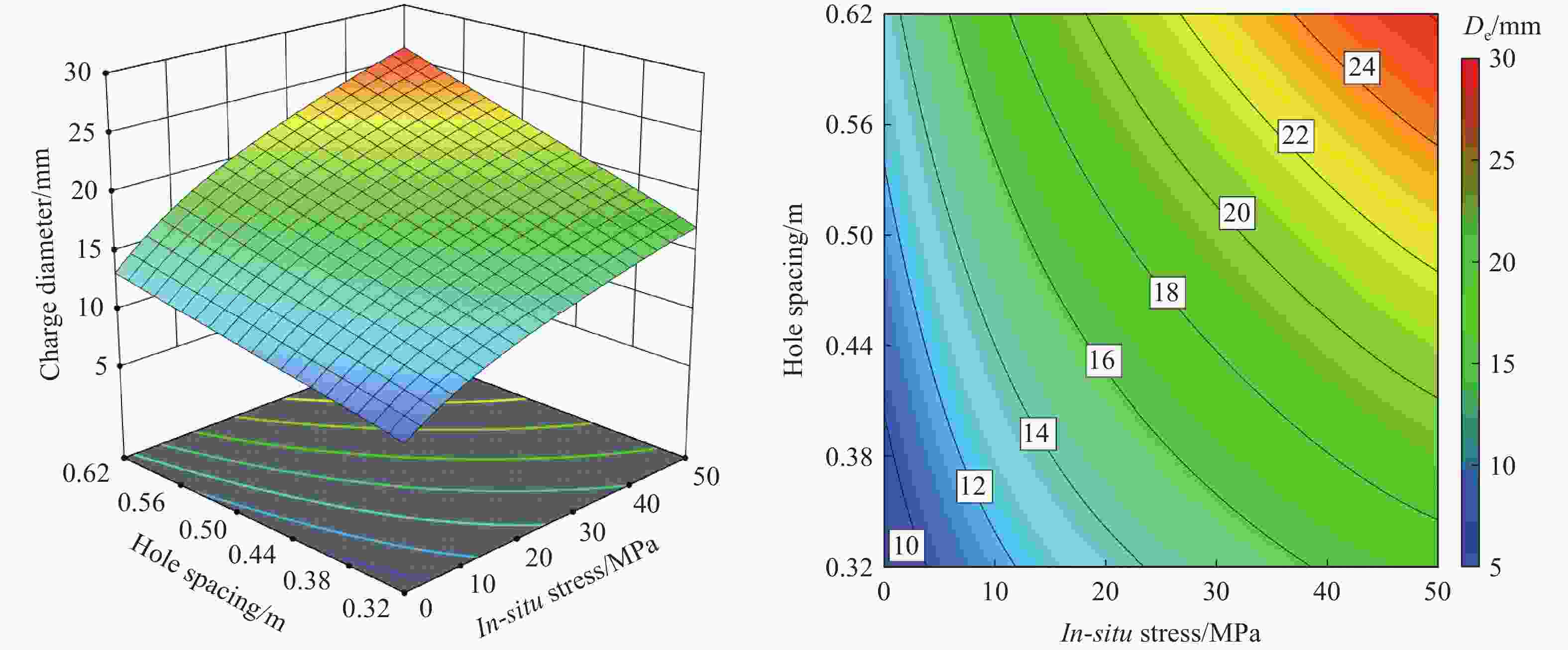
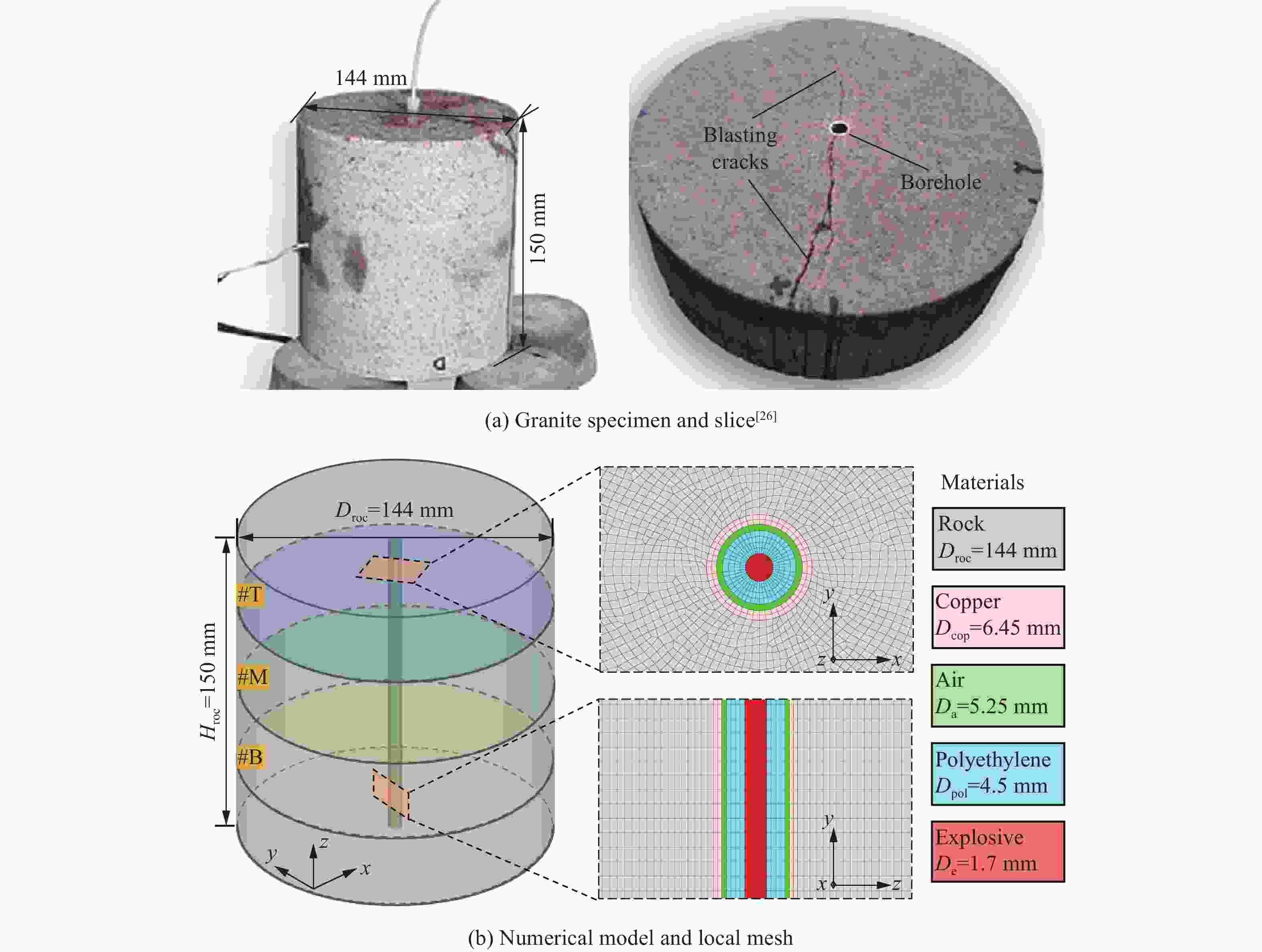
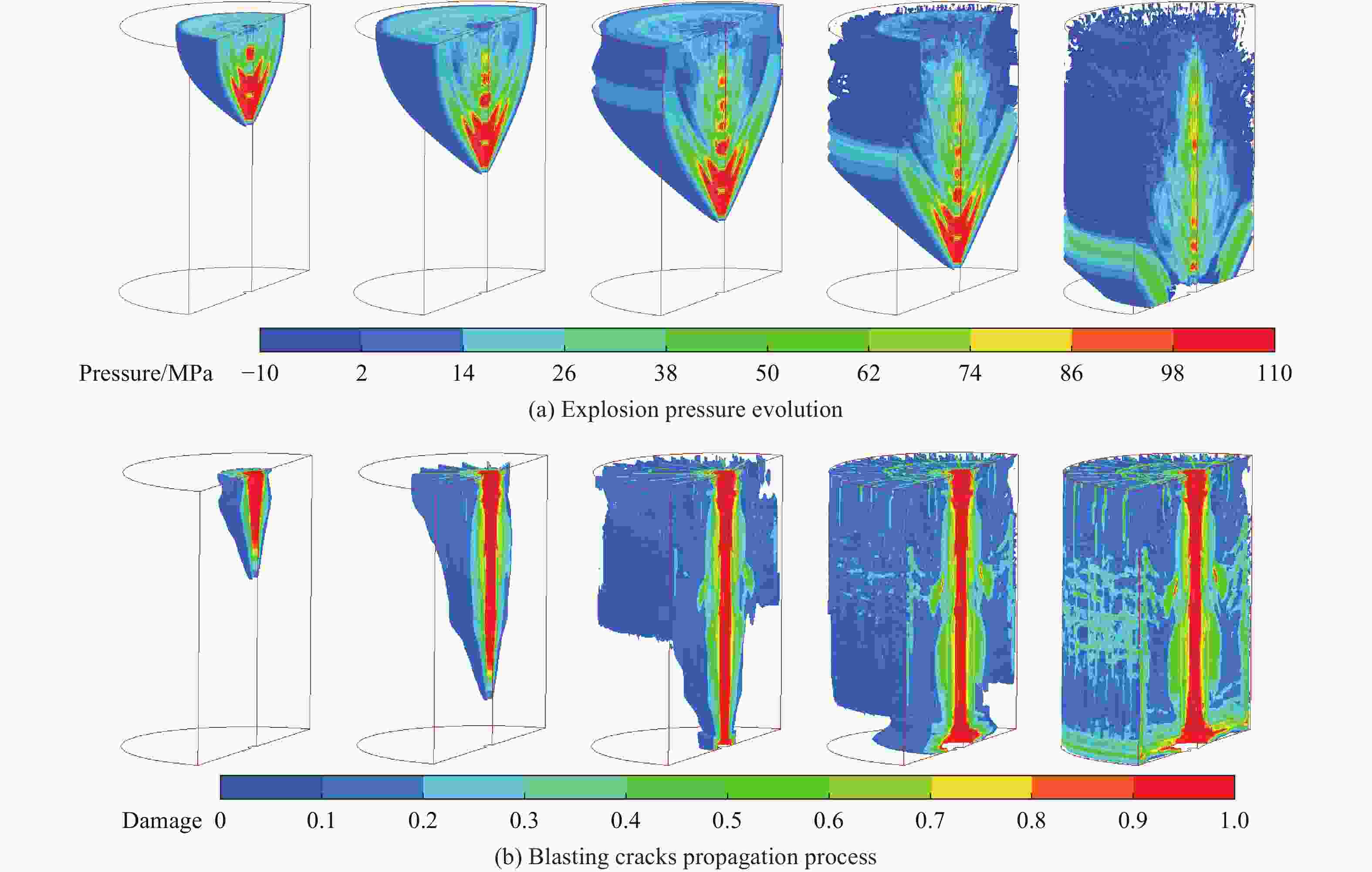
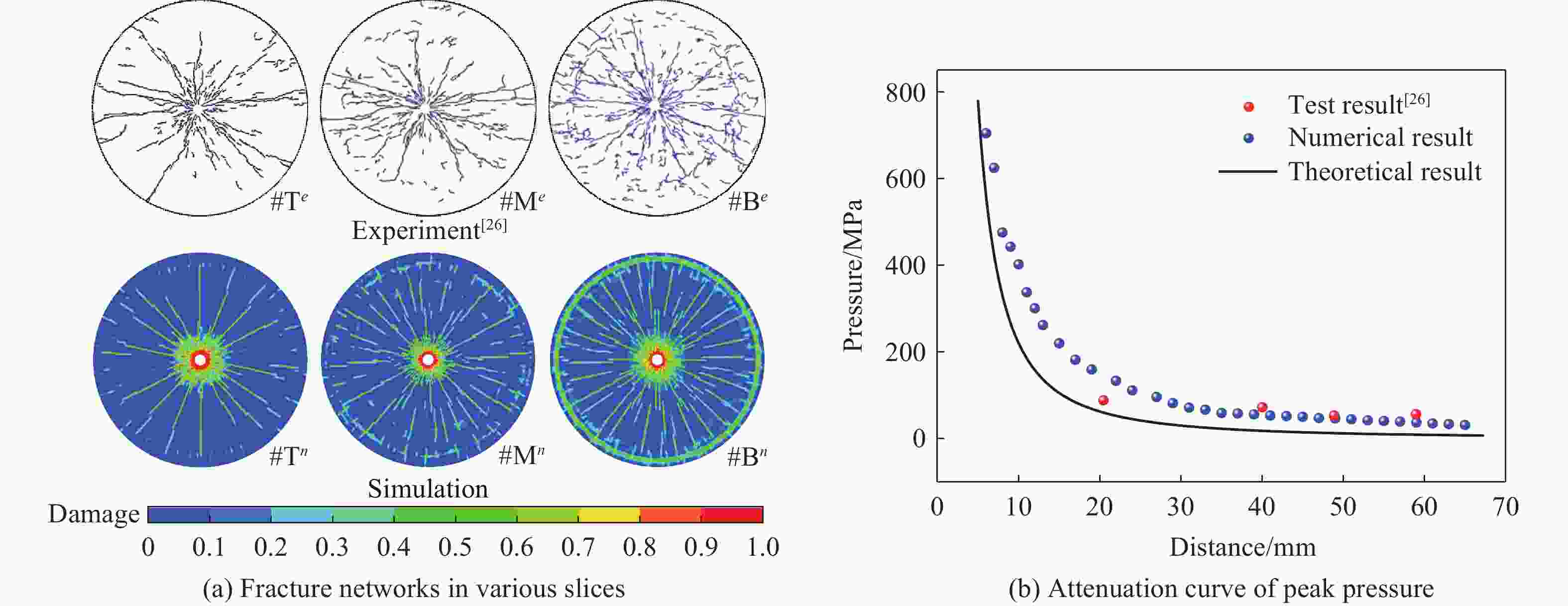
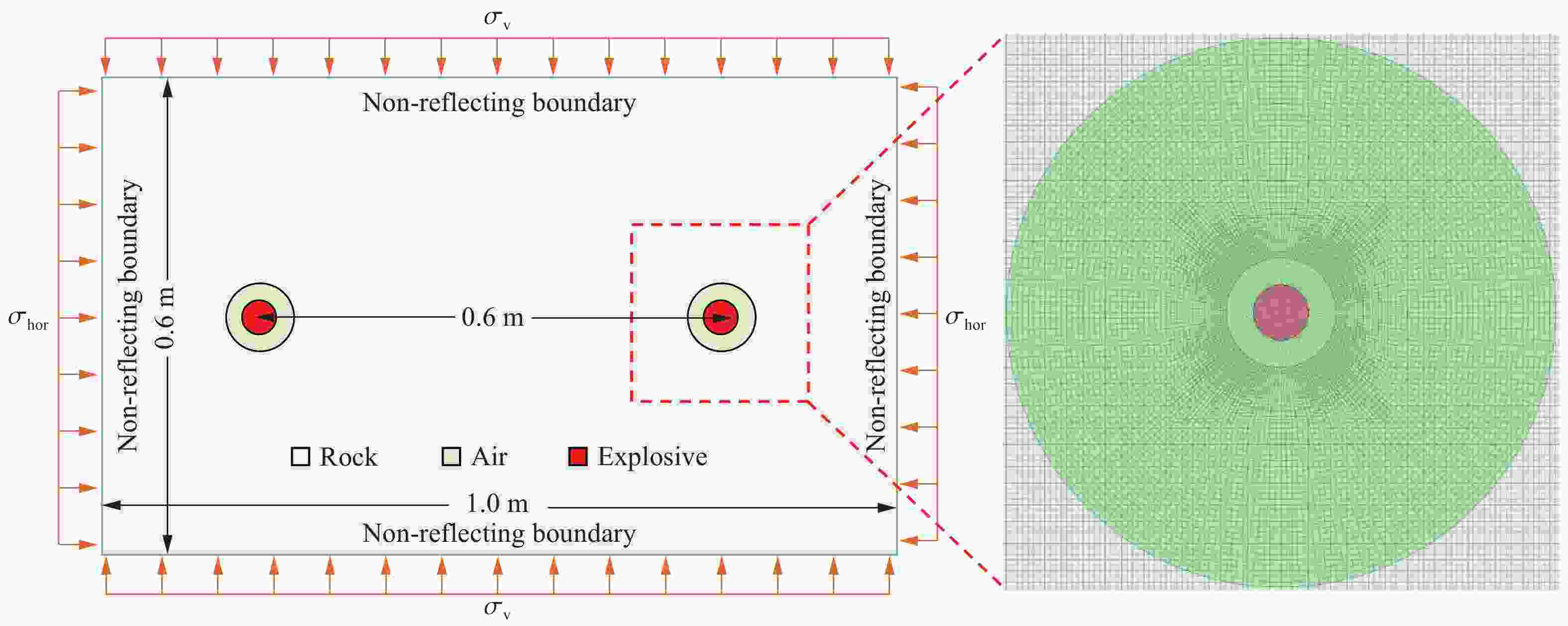
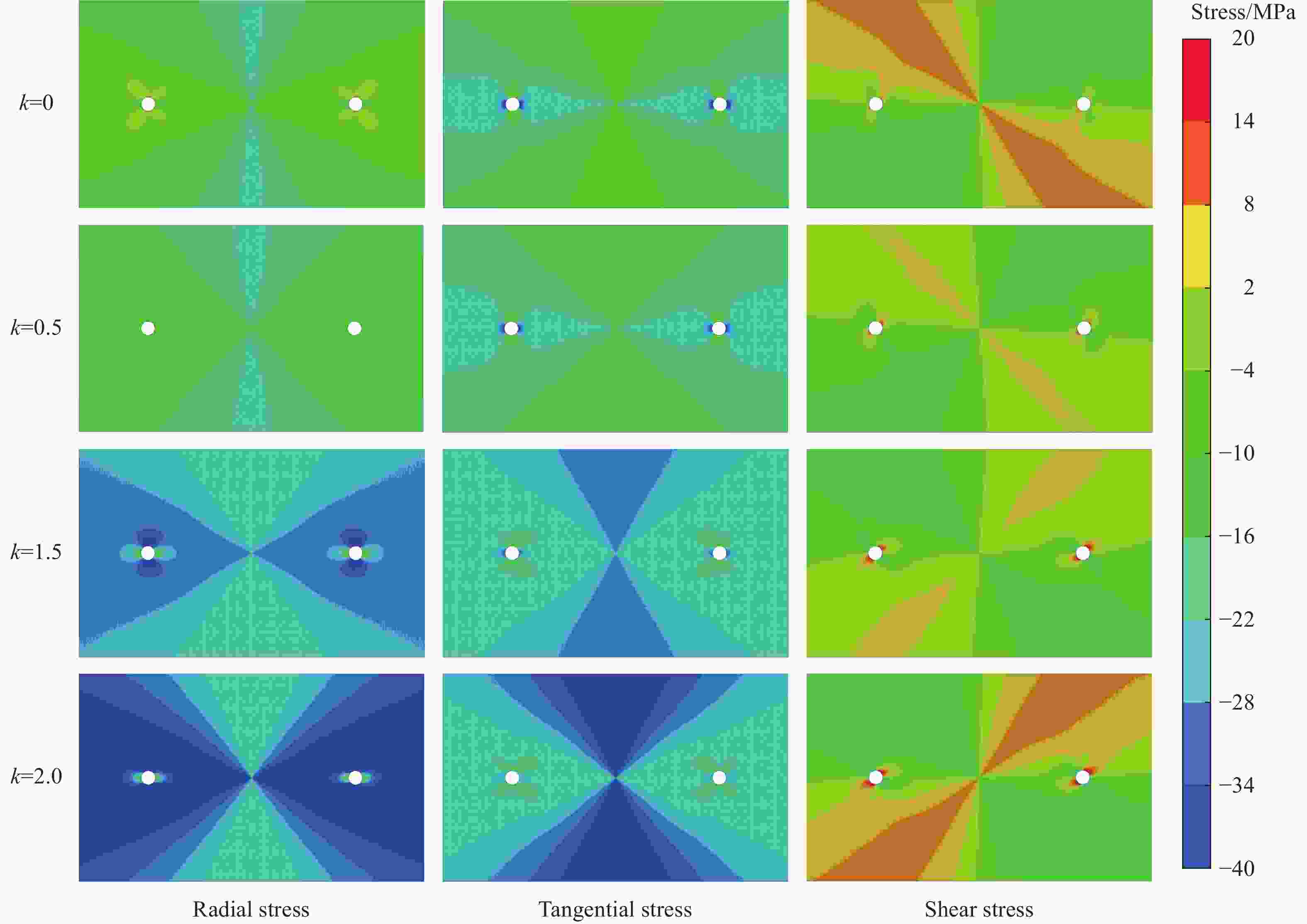
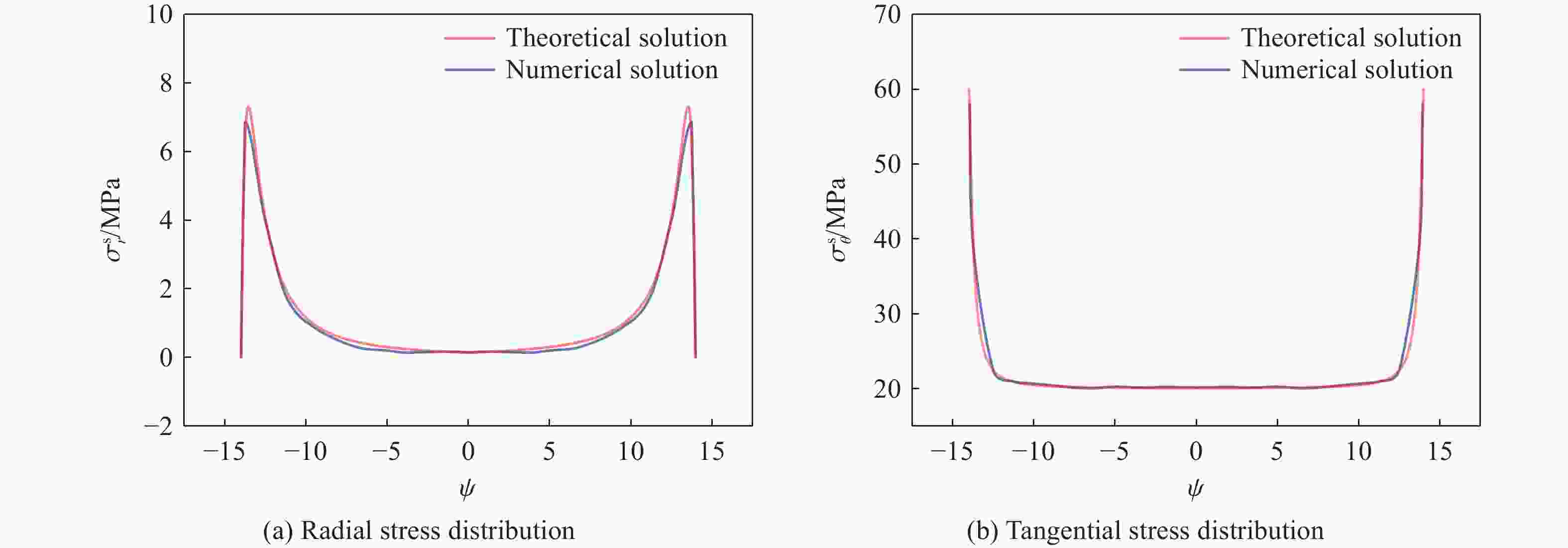
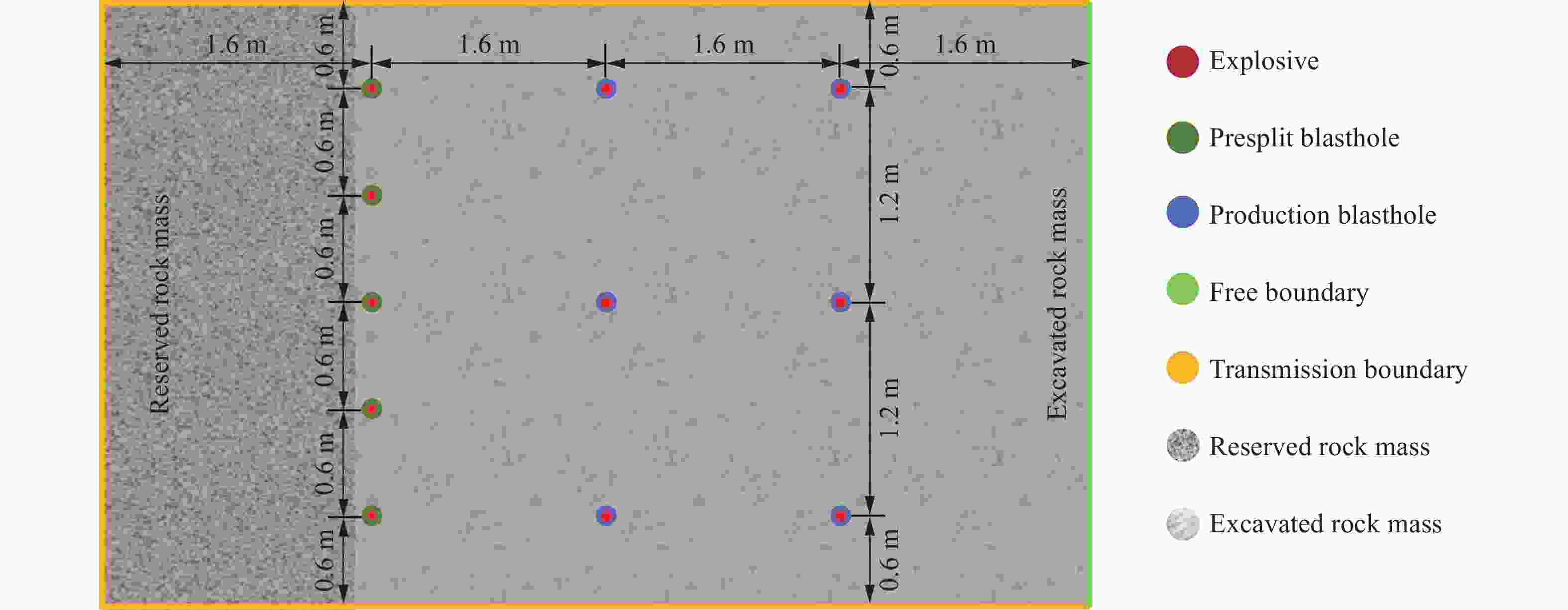
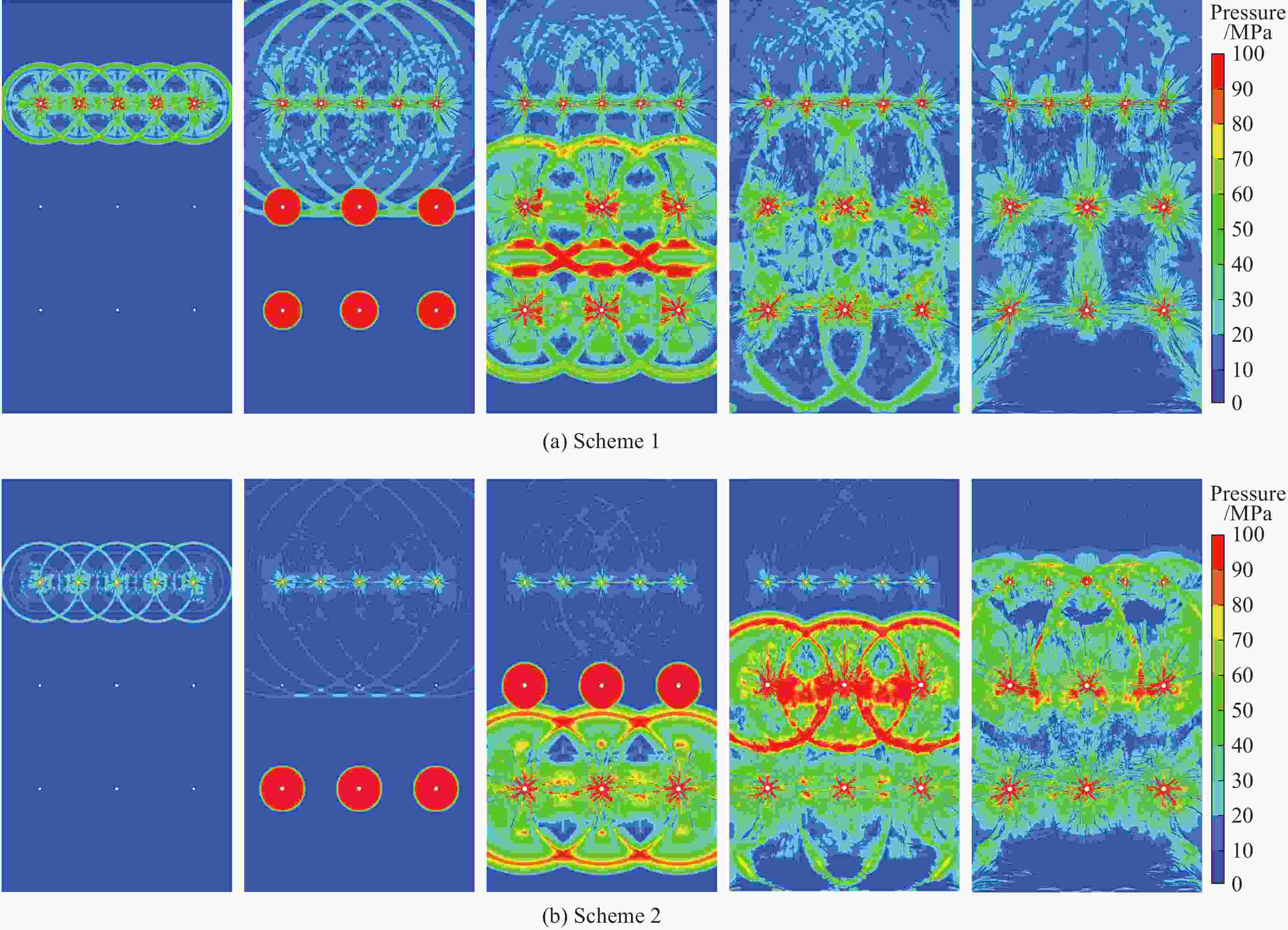
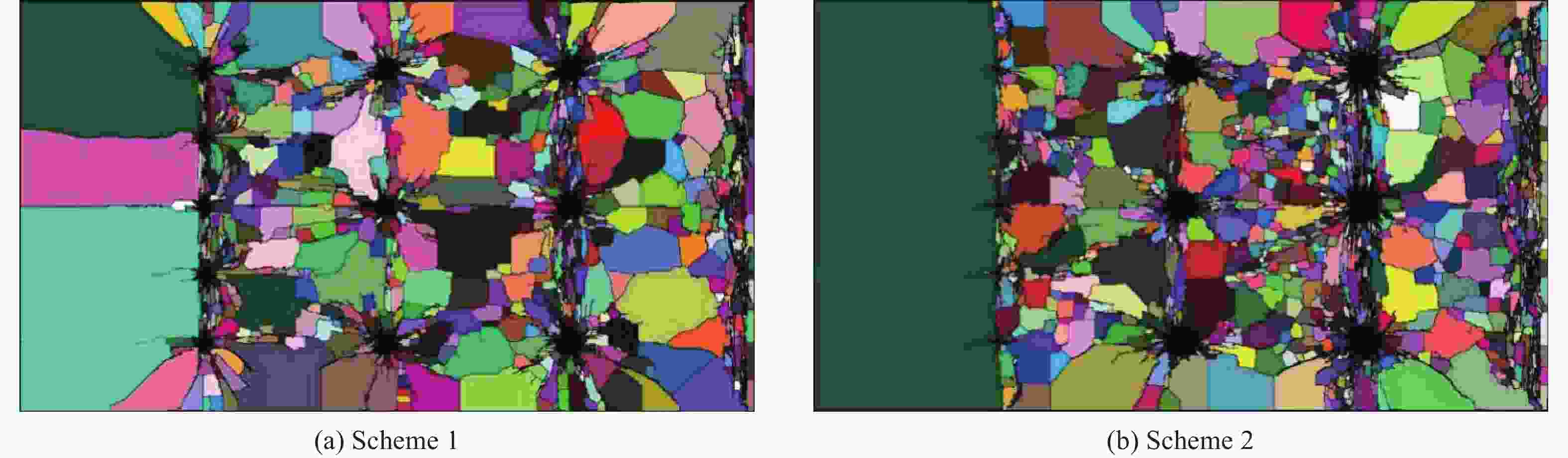
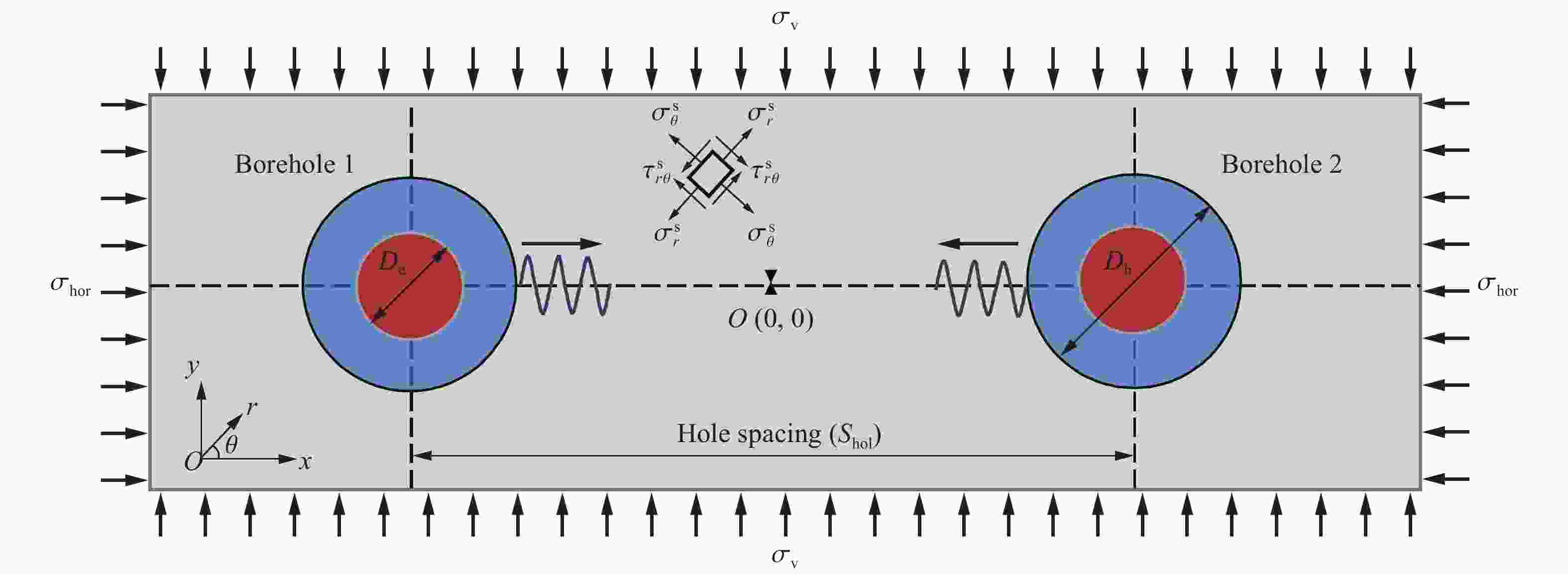
摘要: 基于弹性力学平面应变问题假设,建立了地应力下岩体预裂爆破理论模型。通过Laplace变换和数值反演的方法分析了爆炸应力波的衰减规律,讨论了地应力对岩体预裂爆破应力场分布的影响。此外,采用显式动力学有限元方法,模拟了静水压力和非静水压力条件下岩体预裂爆破的压力演化过程和裂纹扩展行为,并通过Hough变换的方法定量表征了爆炸裂纹的分布特征。研究结果表明:深部岩体预裂爆破成缝困难主要是由于地应力削弱了爆炸引起的切向拉应力作用,孔间岩体质点因切向位移受限而无法形成拉伸破裂面,拉伸破裂成缝机制通过切向拉应力演化和质点位移矢量变化得以验证。基于应力波叠加破坏理论提出的预裂爆破孔间成缝准则可以预测岩体孔间裂纹是否贯穿,得到的不同地应力条件下装药直径和孔距的关系可用于指导预裂孔布置方式,从而为深部岩体预裂爆破提供理论指导。Abstract: The evolution and distribution characteristics of cracks in presplit blasting can be significantly affected by the in-situ stress, often leading to issues such as over or under excavation in deep rock masses. In this paper, a theoretical model for presplit blasting under in-situ stress in rock engineering was developed based on the assumption of plane-strain problem of elastic mechanics. The propagation and attenuation of explosion stress waves were analyzed using a combination of Laplace transforms and numerical inversion. Furthermore, the impact of initial static stress on the blasting-induced dynamic stress field distribution in presplitting was examined and discussed. The Riedel-Hiermaier-Thoma (RHT) model in LS-DYNA code was employed to investigate the dynamic mechanical behavior of rock mass, and its material parameters were calibrated by comparing blasting crack patterns and the explosion pressure attenuation curves. Then, the validated model was used to simulate the damage features of rock presplit blasting under both hydrostatic and anisotropy pressure conditions, thereby analyzing the effects of the static stress and the dynamic pressure on the crack extension behavior. In addition, the distribution characteristics of blasting cracks are quantitatively characterized by the Hough transform method. The results indicate that the difficulty in crack coalescence for deep rock presplit blasting is primarily attributed to the reduction of tangential tensile stress caused by the in-situ stress. This prevents the formation of tensile fracture planes between boreholes due to restricted tangential displacements, which was demonstrated by the evolution of circumferential tensile stress and particle displacement vectors. Moreover, a crack coalescence criterion in presplit blasting was proposed to predict whether inter-borehole cracks penetrate based on the damage theory of stress wave superposition, and the relationship between charge diameter and hole spacing under various in-situ stress can guide the arrangement of boreholes, thus improving the presplit blasting effectiveness for deep rock.
-
Key words:
- presplit blasting /
- in-situ stress /
- crack coalescence mechanism /
- theoretical model /
- deep rock
-
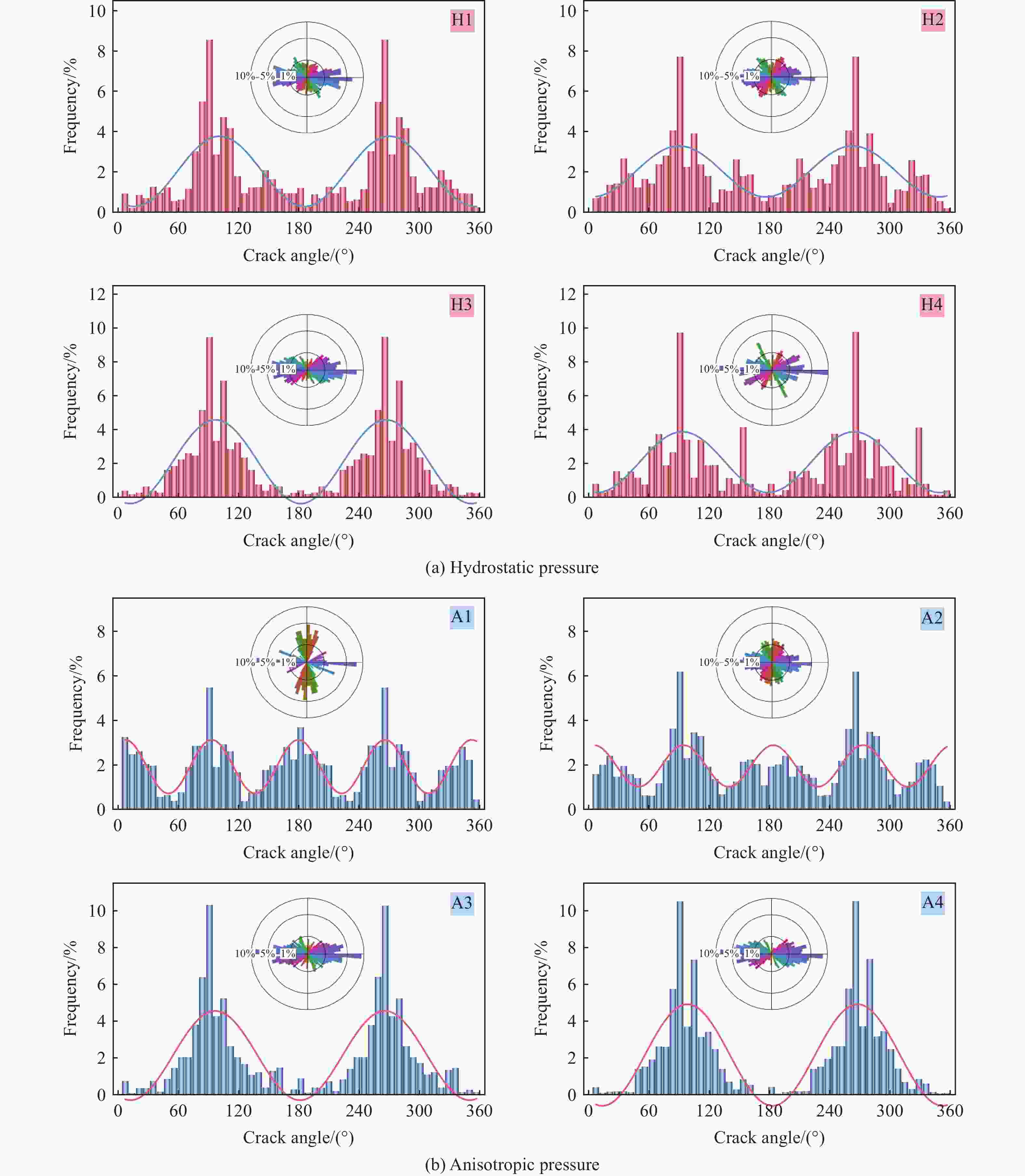
参数 取值 参数 取值 参数 取值 密度ρroc/(kg·m−3) 2620 状态方程参数B0 1.22 剪切模量减小因子ξ 0.50 抗压强度fc/MPa 162 状态方程参数B1 1.22 参考压缩应变率$ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0}^{\mathrm{c}} $/s−1 3.0×10−5 初始孔隙度φ0 1.00 侵蚀塑性应变$ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{s}}^{\mathrm{f}} $ 2.00 参考拉伸应变率$ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0}^{\mathrm{t}} $/s−1 3.0×10−6 损伤因子D1 0.04 压缩屈服面参数$ {G}_{\mathrm{c}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.50 破坏压缩应变率$ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{\mathrm{c}} $/s−1 3.0×1025 损伤因子D2 1.00 拉伸屈服面参数$ {G}_{\mathrm{t}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.70 破坏拉伸应变率$ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{\mathrm{t}} $/s−1 3.0×1025 破坏面参数A 2.48 洛德角相关因子B 0.05 最小损伤残余应变$ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{p}}^{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}} $ 0.012 破坏面参数N 0.79 洛德角相关因子Q0 0.68 孔隙坍塌压力pcrush/MPa 108 残余面参数Af 1.62 压缩应变率指数βc 0.008 孔隙压实压力pcomp/GPa 6.00 残余面参数Nf 0.62 拉伸应变率指数βt 0.011 拉伸体积塑性应变分数$ {f}_{\mathrm{t}}^{\mathrm{p}} $ 0.001 相对抗剪强度$ {F}_{\mathrm{s}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.18 弹性剪切模量G/GPa 21.9 Hugoniot多项式系数A1/GPa 33.95 相对抗拉强度$ {F}_{\mathrm{t}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.06 状态方程参数T1/GPa 33.95 Hugoniot多项式系数A2/GPa 41.42 孔隙度指数Npor 3.0 状态方程参数T2/GPa 0.00 Hugoniot多项式系数A3/GPa 8.71 ρpol/(kg·m−3) cpol/(m·s−1) S1 S2 S3 γpol αpol V0 915 2901 1.481 0.0 0.0 1.64 0.0 1.0 参数 值 参数 值 参数 值 密度ρcop/(kg·m−3) 8330 材料常数ncop 0.31 EOS常数S1 1.49 杨氏模量Ecop/GPa 110 材料常数mcop 1.09 EOS常数S2 0.0 泊松比μcop 0.35 材料常数wcop 0.025 EOS常数S3 0.0 熔化温度T/K 1357 材料常数Acop/GPa 0.089 EOS常数αcop 0.47 初始内能E0/(m·s−1) 0.0 材料常数Bcop/GPa 0.292 EOS常数Ccop 4430 表 4 地应力加载条件
Table 4. In-situ stress conditions used in the numerical study
应力
状态工况 σhor/MPa σv/MPa 应力
状态工况 σhor/MPa σv/MPa 静水
压力H1 10 10 非静水
压力A1 0 20 H2 20 20 A2 10 20 H3 30 30 A3 30 20 H4 40 40 A4 40 20 -
[1] LIU K W, LI X D, HAO H, et al. Study on the raising technique using one blast based on the combination of long-hole presplitting and vertical crater retreat multiple-deck shots [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 113: 41–58. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.11.012. [2] 叶海旺, 唐可, 万涛, 等. 时序控制预裂爆破参数优化及应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2017, 37(3): 502–509. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0502-08.YE H W, TANG K, WAN T, et al. Optimization of time sequence controlled pre-splitting blasting parameters and its application [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2017, 37(3): 502–509. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2017)03-0502-08. [3] LI X D, LIU K W, QIU T, et al. Study of presplit blasting under high in-situ stress [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2023, 288: 109360. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2023.109360. [4] YANG L Y, YANG A Y, CHEN S Y, et al. Model experimental study on the effects of in situ stresses on pre-splitting blasting damage and strain development [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2021, 138: 104587. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104587. [5] LANGEFORS U, KIHLSTRÖM B. The modern technique of rock blasting [M]. 2nd ed. Stockholm: John Wiley and Sons Incorporation, 1963. [6] 许传华, 张西良, 仪海豹, 等. 预裂爆破技术 [M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2024: 7–11.XU C H, ZHANG X L, YI H B, et al. Pre-splitting blasting technology [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2024: 7–11. [7] NICHOLLS H R, DUVALL W I. Presplitting rock in the presence of a static stress field [R]. Washington: U. S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines, 1966. [8] YANG L Y, CHEN S Y, YANG A Y, et al. Numerical and experimental study of the presplit blasting failure characteristics under compressive stress [J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2021, 149: 106873. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.106873. [9] LU W B, Chen M, GENG X, et al. A study of excavation sequence and contour blasting method for underground powerhouses of hydropower stations [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2012, 29: 31–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2011.12.008. [10] HU Y G, LU W B, WU X X, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation of blasting damage control of a high rock slope in a deep valley [J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 237: 12–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.01.003. [11] 杨帅, 刘泽功, 常帅, 等. 地应力作用下聚能爆破煤体损伤特征试验研究 [J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2024, 41(5): 1078–1090. DOI: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2023.0499.YANG S, LIU Z G, CHANG S, et al. Experimental study on damage characteristics of coal body in concentrated shaped charge blasting under in-situ stress [J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2024, 41(5): 1078–1090. DOI: 10.13545/j.cnki.jmse.2023.0499. [12] YANG R S, DING C X, LI Y L, et al. Crack propagation behavior in slit charge blasting under high static stress conditions [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 119: 117–123. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.05.002. [13] 马泗洲, 刘科伟, 杨家彩, 等. 不耦合装药下岩石爆破块体尺寸的分布特征 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(4): 045201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0358.MA S Z, LIU K W, YANG J C, et al. Size distribution characteristics of blast-induced rock fragmentation under decoupled charge structures [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(4): 045201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0358. [14] 白羽. 地应力影响下岩石爆破损伤模型及其数值试验 [D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2014.BAI Y. Blasting damage model and numerical test of rock under effect of in situ stress [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014. [15] 杨建华, 孙文彬, 姚池, 等. 高地应力岩体多孔爆破破岩机制 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(7): 075202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0427.YANG J H, SUN W B, YAO C, et al. Mechanism of rock fragmentation by multi-hole blasting in highly-stressed rock masses [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(7): 075202. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0427. [16] LI X D, LIU K W, SHA Y Y, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on rock fracturing in tunnel contour blasting under initial stress [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 185: 104844. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104844. [17] LU A, YAN P, LU W B, et al. Crack propagation mechanism of smooth blasting holes for tunnel excavation under high in-situ stress [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2024, 304: 110144. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2024.110144. [18] KIRSCH G. Die theorie der elasitzität und die bedurfnisse der festigkeitslehre [J]. Zantralblatt Verlin Deutscher Ingenieure, 1898, 42: 797–807. [19] 谢和平, 高峰, 鞠杨. 深部岩体力学研究与探索 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(11): 2161–2178. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.1369.XIE H P, GAO F, JU Y. Research and development of rock mechanics in deep ground engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(11): 2161–2178. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.1369. [20] YANG J H, JIANG Q H, ZHANG Q B, et al. Dynamic stress adjustment and rock damage during blasting excavation in a deep-buried circular tunnel [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 71: 591–604. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.10.010. [21] 严鹏, 卢文波, 陈明, 等. 隧洞开挖过程初始地应力动态卸载效应研究 [J]. 岩土工程学报, 2009, 31(12): 1888–1894. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.12.013.YAN P, LU W B, CHEN M, et al. Effect of initial geo-stress dynamic unloading during tunnel excavation [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(12): 1888–1894. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.12.013. [22] LI X D, LIU K W, QIU T, et al. Numerical study on fracture control blasting using air-water coupling [J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2023, 9(1): 29. DOI: 10.1007/s40948-023-00546-y. [23] MIKLOWITZ J. Plane-stress unloading waves emanating from a suddenly punched hole in a stretched elastic plate [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1960, 27(1): 165–171. DOI: 10.1115/1.3643892. [24] LI X H, ZHU Z M, WANG M, et al. Numerical study on the behavior of blasting in deep rock masses [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 113: 103968. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.103968. [25] 李夕兵. 凿岩爆破工程 [M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2011. [26] BANADAKI M M D. Stress-wave induced fracture in rock due to explosive action [D]. Toronto: University of Toronto, 2010. [27] 马泗洲, 刘科伟, 杨家彩, 等. 初始应力下岩体爆破损伤特性及破裂机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(10): 105201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0151.MA S Z, LIU K W, YANG J C, et al. Blast-induced damage characteristics and fracture mechanism of rock mass under initial stress [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(10): 105201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0151. [28] BANADAKI M M D, MOHANTY B. Numerical simulation of stress wave induced fractures in rock [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 40/41: 16–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.08.010. [29] LSTC. LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual [Z]. California: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2003. [30] MA S Z, LIU K W, GUO T F, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on the mechanical characteristics and failure mechanism of cracked coal & rock-like combined sample under uniaxial compression [J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2022, 122: 103583. DOI: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2022.103583. [31] HOUGH P V C. Method and means for recognizing complex patterns: US3069654A [P]. 1962-12-18. -






 下载:
下载: