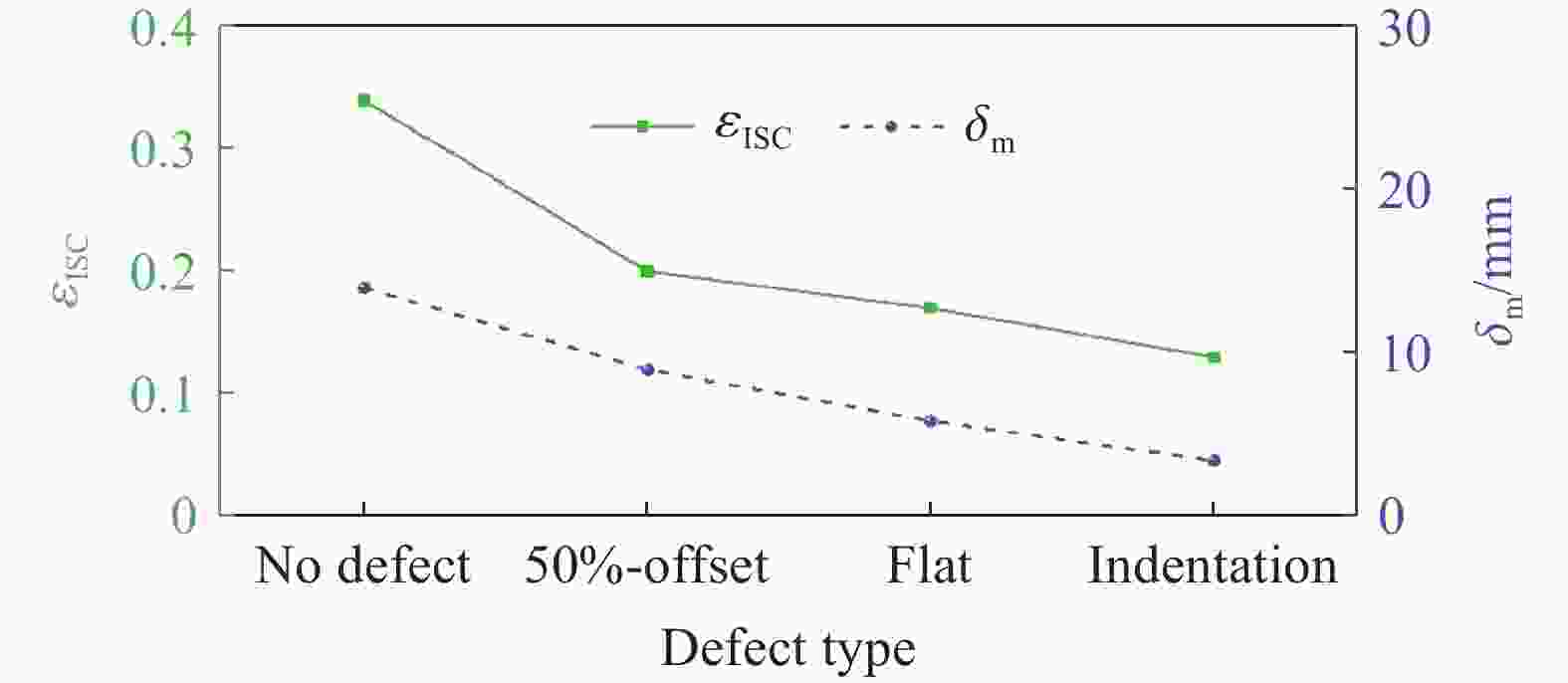
| [1] |
COMELLO S, GLENK G, REICHELSTEIN S. Transitioning to clean energy transportation services: life-cycle cost analysis for vehicle fleets [J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 285: 116408. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.116408.
|
| [2] |
MANIRATHINAM T, NARAYANAMOORTHY S, GEETHA S, et al. Assessing performance and satisfaction of micro-mobility in smart cities for sustainable clean energy transportation using novel APPRESAL method [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 436: 140372. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.140372.
|
| [3] |
CHU S, MAJUMDAR A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future [J]. Nature, 2012, 488(7411): 294–303. DOI: 10.1038/nature11475.
|
| [4] |
CHEN B, XIONG R, LI H L, et al. Pathways for sustainable energy transition [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 228: 1564–1571. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.372.
|
| [5] |
GANDOMAN F H, JAGUEMONT J, GOUTAM S, et al. Concept of reliability and safety assessment of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles: basics, progress, and challenges [J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 251: 113343. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113343.
|
| [6] |
TAO J J, WANG S L, CAO W, et al. A comprehensive review of state-of-charge and state-of-health estimation for lithium-ion battery energy storage systems [J]. Ionics, 2024, 30(10): 5903–5927. DOI: 10.1007/s11581-024-05686-z.
|
| [7] |
ZUBI G, DUFO-LÓPEZ R, CARVALHO M, et al. The lithium-ion battery: state of the art and future perspectives [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 89: 292–308. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.002.
|
| [8] |
DIOUF B, PODE R. Potential of lithium-ion batteries in renewable energy [J]. Renewable Energy, 2015, 76: 375–380. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2014.11.058.
|
| [9] |
LIU B H, JIA Y K, LI J, et al. Safety issues caused by internal short circuits in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(43): 21475–21484. DOI: 10.1039/C8TA08997C.
|
| [10] |
RUIZ V, PFRANG A, KRISTON A, et al. A review of international abuse testing standards and regulations for lithium ion batteries in electric and hybrid electric vehicles [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 81: 1427–1452. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.195.
|
| [11] |
SEVARIN A, FASCHING M, RAFFLER M, et al. Influence of cell selection and orientation within the traction battery on the crash safety of electric-powered two-wheelers [J]. Batteries, 2023, 9(4): 195. DOI: 10.3390/batteries9040195.
|
| [12] |
SUN P Y, BISSCHOP R, NIU H C, et al. A review of battery fires in electric vehicles [J]. Fire Technology, 2020, 56(4): 1361–1410. DOI: 10.1007/s10694-019-00944-3.
|
| [13] |
XING Y Y, LI Q M. Evaluation of the mechanical shock testing standards for electric vehicle batteries [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 194: 105077. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2024.105077.
|
| [14] |
SHUAI W Q, LI E Y, WANG H. An equivalent circuit model of a deformed Li-ion battery with parameter identification [J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(11): 8372–8387. DOI: 10.1002/er.5500.
|
| [15] |
WANG G W, WU J J, ZHENG Z J, et al. Effect of deformation on safety and capacity of Li-ion batteries [J]. Batteries, 2022, 8(11): 235. DOI: 10.3390/batteries8110235.
|
| [16] |
LIU J, MA Z C, GUO Z X, et al. Experimental investigation on mechanical-electrochemical coupling properties of cylindrical lithium-ion batteries [J]. Energy, 2024, 293: 130536. DOI: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.130536.
|
| [17] |
JIA Y K, LIU B H, HONG Z G, et al. Safety issues of defective lithium-ion batteries: identification and risk evaluation [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(25): 12472–12484. DOI: 10.1039/D0TA04171H.
|
| [18] |
CHEN X P, YUAN Q, WANG T, et al. Experimental study on the dynamic behavior of prismatic lithium-ion battery upon repeated impact [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2020, 115: 104667. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104667.
|
| [19] |
朱瑞卿, 胡玲玲, 周名哲. 锂电池多次冲击下的失效模式及损伤机制 [J]. 固体力学学报, 2023, 44(6): 795–804. DOI: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2023.032.ZHU R Q, HU L L, ZHOU M Z. Failure modes and damage mechanisms of lithium-ion batteries under repeated impacts [J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2023, 44(6): 795–804. DOI: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2023.032.
|
| [20] |
魏和光, 周名哲, 朱瑞卿, 等. 受冲击荷载后未失效电池力学性能和电性能的劣化 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2025, 45(2): 021421. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0312.WEI H G, ZHOU M Z, ZHU R Q, et al. Mechanical and electrical degradation of impaired batteries after impact loading [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2025, 45(2): 021421. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0312.
|
| [21] |
ZHOU D, LI H G, LI Z H, et al. Toward the performance evolution of lithium-ion battery upon impact loading [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 432: 141192. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141192.
|
| [22] |
顾丽蓉, 王敬德, 张新春, 等. 挤压/冲击工况下圆柱形锂离子电池失效的影响因素分析 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2024, 38(4): 045301. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240708.GU L R, WANG J D, ZHANG X C, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of failure for cylindrical lithium-ion batteries under compression/impact conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2024, 38(4): 045301. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20240708.
|
| [23] |
LIU B H, JIA Y K, YUAN C H, et al. Safety issues and mechanisms of lithium-ion battery cell upon mechanical abusive loading: a review [J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 24: 85–112. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2019.06.036.
|
| [24] |
LI J N, LI W, SONG J Y, et al. Accurate measurement of the contact resistance during internal short circuit in lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2022, 169(2): 020505. DOI: 10.1149/1945-7111/ac4c79.
|
| [25] |
SANTHANAGOPALAN S, RAMADASS P, ZHANG J. Analysis of internal short-circuit in a lithium ion cell [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 194(1): 550–557. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.05.002.
|
| [26] |
YUAN C H, WANG L B, YIN S, et al. Generalized separator failure criteria for internal short circuit of lithium-ion battery [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 467: 228360. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2020.228360.
|
| [27] |
LIU J L, DUAN Q L, QI K Z, et al. Capacity fading mechanisms and state of health prediction of commercial lithium-ion battery in total lifespan [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 46: 103910. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103910.
|
| [28] |
REDONDO-IGLESIAS E, VENET P, PELISSIER S. Modelling lithium-ion battery ageing in electric vehicle applications: calendar and cycling ageing combination effects [J]. Batteries, 2020, 6(1): 1–14. DOI: 10.3390/batteries6010014.
|
| [29] |
LIU Y J, XIA Y, XING B B, et al. Mechanical-electrical-thermal responses of lithium-ion pouch cells under dynamic loading: a comparative study between fresh cells and aged ones [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 166: 104237. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104237.
|
| [30] |
WANG L B, LI J P, CHEN J Y, et al. Revealing the internal short circuit mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries upon dynamic loading based on multiphysics simulation [J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 351: 121790. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121790.
|






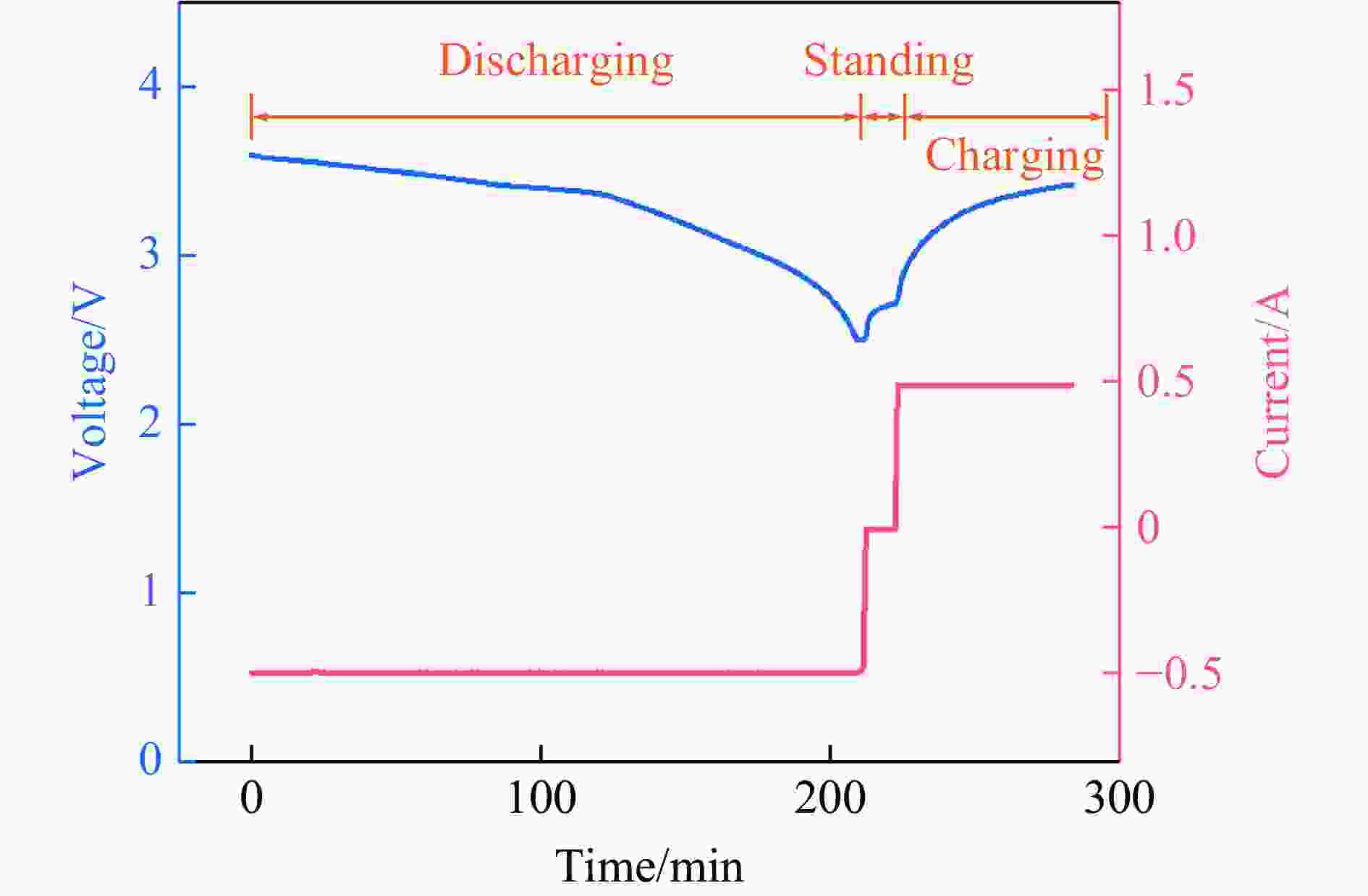
 下载:
下载: