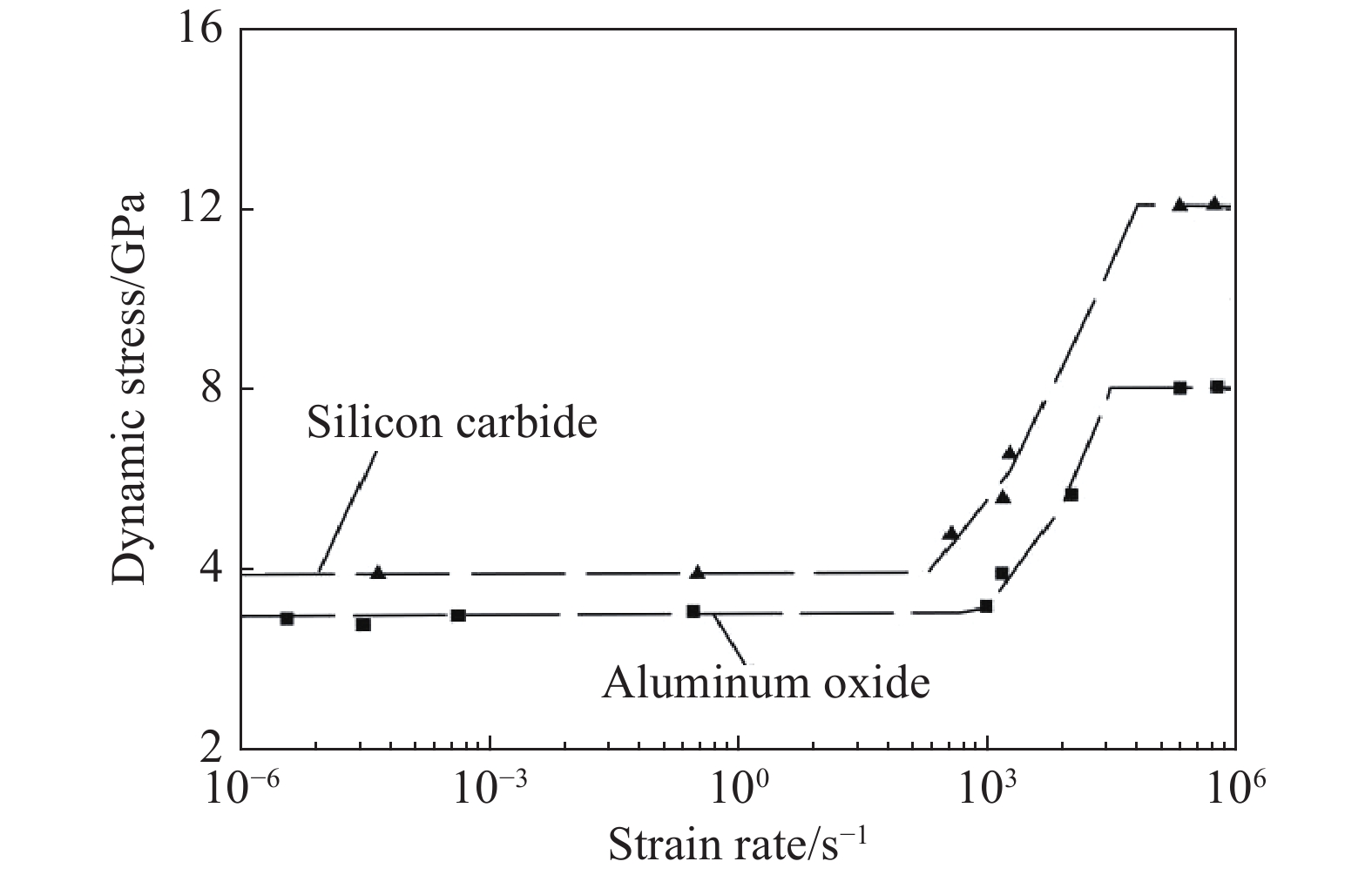
| [1] |
SADOVSKY M A, BOLKHOVITINOV L G, PISARENKO V F. Deformation of geophysical medium and seismic process[M]. Nauka, Moscow, 1987.
|
| [2] |
BRACE W F, BYERLEE J D. Stick-slip as a mechanism for earthquake [J]. Science, 1966, 153(3739): 990–992. DOI: 10.1126/science.153.3739.990.
|
| [3] |
KOSTROV B V. Mechanics of sources of tectonic earthquakes[M]. Nauka, Moscow, 1975.
|
| [4] |
KANAMORI H, STEWART G S. Mode of strain release along Gibbs fracture zone, mid-atlantic ridge [J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1976, 11(4): 312–332. DOI: 10.1016/0031-9201(76)90018-2.
|
| [5] |
AKI K, BOUCHON M, CHOUET B, et al. Quantitative prediction of strong motion for a potential earthquake fault [J]. Annals of Geophysics, 2010, 53(1): 81–91. DOI: 10.4401/ag-4665.
|
| [6] |
MYACHKIN V I. Preparation processes of earthquakes[M]. Nauka, Moscow, 1978.
|
| [7] |
DIETRICH J H. Modeling of rock friction: 1. experimental results and constitutive equations [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1979, 84(B5): 2161–2168. DOI: 10.1029/JB084iB05p02161.
|
| [8] |
RICE J R, RUINA A L. Stability of steady frictional slipping [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1983, 50(2): 343–349. DOI: 10.1115/1.3167042.
|
| [9] |
SCHOLZ C H. The Mechanics of Earthquakes and Faulting[M]. Cambridge University Press, 1990.
|
| [10] |
DOBROVOLSKY I P. Theory of preparation of tectonic earthquakes[M]. Nauka, Moscow, 1991.
|
| [11] |
DOBROVOLSKY I P. The mathematical theory of earthquake preparation and prediction[M]. Fizmatlit, Moscow, 2009.
|
| [12] |
SOBOLEV G A, PONOMOREV A V. The Physics of Earthquakes and Precursors[M]. Nauka, Moscow, 2003.
|
| [13] |
KOCHARYAN G G. Geomechanics of faults[M]. Geos, Moscow, 2016.
|
| [14] |
SCHOLZ C H, CAMPOS J. The seismic coupling of subduction zones revisited [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012, 117(B5): 1–22. DOI: 10.1029/2011JB009003.
|
| [15] |
CARPENTER B M, IKARI M J, MARONE C. Laboratory observations of time-dependent frictional strengthening and stress relaxation in natural and synthetic fault gouges [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2016, 121(2): 1183–1201. DOI: 10.1002/2015JB012136.
|
| [16] |
IKARI M J, MARONE C, SAFFER D M. On the relation between fault strength and frictional stability [J]. Geology, 2011, 39(1): 83–86. DOI: 10.1130/G31416.1.
|
| [17] |
BOATWRIGHT J, COCCO M. Frictional constraints on crustal faulting [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1996, 101(B6): 13895–13909. DOI: 10.1029/96jb00405.
|
| [18] |
PERSSON B N J. Sliding friction: physical principles and applications[M]. Nano Science and Technology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin and Heidelberg, 1998.
|
| [19] |
MUSER M H, URBAKH M, ROBBINS M O. Statistical mechanics of static and low-velocity kinetic friction [J]. Advances in Chemical Physics, 2003, 126: 187–272.
|
| [20] |
BAUBERGER T, CAROLI C. Solid friction from stick-slip down to pinning and aging [J]. Advances in Physics., 2006, 55(3/4): 279–348. DOI: 10.1080/00018730600732186.
|
| [21] |
ZHENG G, RICE J R. Conditions under which velocity-weakening friction allows a self-healing versus a cracklike mode of rupture [J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1998, 88(6): 1466–1483. DOI: 10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00192-9.
|
| [22] |
RICE J R, LAPUSTA N, RANJITH K. Rate and state dependent friction and the stability of sliding between elastically deformable solids [J]. Journal of Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2001, 49(9): 1865–1898. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-5096(01)00042-4.
|
| [23] |
DI TORO G, HIROSE T, NIELSEN S, et al. Natural and experimental evidence of melt lubrication of faults during earthquakes [J]. Science, 2006, 311(5761): 647–649. DOI: 10.1126/science.1121012.
|
| [24] |
DI TORO G, HAN R, HIROSE T, et al. Fault lubrication during earthquakes [J]. Nature, 2011, 471(7339): 494–8. DOI: 10.1038/nature09838.
|
| [25] |
GOLDSBY D L, TULLIS T E. Flash heating leads to low frictional strength of crustal rocks at earthquake slip rates [J]. Science, 2011, 334(6053): 216–218. DOI: 10.1126/science.1207902.
|
| [26] |
AHARONOV E, SCHOLZ C H. A physics-based rock friction constitutive law: Steady state friction [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123(2): 1591–1614. DOI: 10.1002/2016JB013829.
|
| [27] |
SPAGNUOLO E, NIELSEN S, VIOLAY M, et al. An empirically based steady state friction law and implications for fault stability [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43(7): 3263–71. DOI: 10.1002/2016GL067881.
|
| [28] |
CHEN J Y, NIEMEIJER A R, SOIERS C J. Microphysical modeling of carbonate fault friction at slip rates spanning the full seismic cycle [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2021, 126(3): 021024. DOI: 10.1029/2020JB021024.
|
| [29] |
SELVADURAI P, GLASER S. Asperity generation and its relationship to seismicity on a planar fault: A laboratory simulation [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2017, 208(2): 1009–1025. DOI: 10.1093/gji/ggw439.
|
| [30] |
RECHES Z, ZU X, CARPENTWER B M. Energy-flux control of the steady-state, creep, and dynamic slip modes of faults [J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 10627. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46922-1.
|
| [31] |
IKARI M J, MARONE C, SAFFER D M, et al. Slip weakening as a mechanism for slow earthquakes [J]. Nature Geosciences, 2013, 6(6): 468–472. DOI: 10.1038/NGEO18198.
|
| [32] |
CHEN X, MADDEN A S, BICKMORE B R, et al. Dynamic weakening by nanoscale smoothing during high-velocity fault slip [J]. Geology, 2013, 41(7): 739–7428. DOI: 10.1130/G34169.1.
|
| [33] |
BYERLEE J D. Friction of rocks [J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1978, 116(4/5): 615–626. DOI: 10.1007/BF00876528.
|
| [34] |
CHESTER J S, CHESTER F M, KRONENBERG A K. Fracture surface energy of the Punchbowl fault, San Andreas system [J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7055): 133–136. DOI: 10.1038/nature03942.
|
| [35] |
SIBSON R H. Thickness of the seismic slip zone[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 2003, 93 (3): 1169–1178. DOI: 10.1785/0120020061.
|
| [36] |
MAJMUDAR T S, BEHINGGER R P. Contact force measurements and stress induced anisotropy in granular materials [J]. Nature, 2005, 435(7045): 1079–1082. DOI: 10.1038/nature03805.
|
| [37] |
ANTONY S J. Link between single-particle properties and macroscopic properties in particulate assemblies: role of structures within structures [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2007, 365(1861): 2879–2891. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2007.0004.
|
| [38] |
RICHEFEU V, El YOUSSOUFI MS, AZEMA E, et al. Force transmission in dry and wet granular media [J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 190(1/2): 258–263. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2008.04.069.
|
| [39] |
KOCHARYAN G G, NOVIKOV V A, OSTAPCHUK A A, et al. A study of different fault slip modes governed by the gouge material composition in laboratory experiments [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2017, 208(1): 521–528. DOI: 10.1093/gji/ggw409.
|
| [40] |
BUDKOV A M, KOCHARYAN G G. Experimental study of different modes of block sliding along interface: part 3: numerical modeling [J]. Physical Mesomechanics, 2017, 20(2): 203–208. DOI: 10.1134/S1029959917020102.
|
| [41] |
OSTAPCHUK A A, MOROZOVA K G. On the mechanism of laboratory earthquake nucleation highlighted by acoustic emission [J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 7245. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-64272-1.
|
| [42] |
OSTAPCHUK A A, MOROZOVA K G, MARKOV V, et al. Acoustic emission reveals multiple slip modes on a frictional fault [J]. Frontiers of Earth Science, 2021, 9: 657487. DOI: 10.3389/feart.2021.657487.
|
| [43] |
LU K, BRODSY E E, KAVEHPOUR H P. Shear-weakening of the transitional regime for granular flow: the role of compressibility [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 587: 347–372. DOI: 10.1017/S0022112007007331.
|
| [44] |
HAYWARD K S, HAWKINS R, COX S F, et al. Rheological controls on asperity weakening during earthquake slip [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2019, 124(12): 12736–12762. DOI: 10.1029/2019JB018231.
|
| [45] |
POZZI G, PAOLA N, NIELSEN S, et al. Coseismic fault lubrication by viscous deformation [J]. Nature Geoscience, 2021, 14(6): 437–442. DOI: 10.1038/s41561-021-00747-8.
|
| [46] |
FAGERENG A, BEALL A. Is complex fault zone behaviour a reflection of rheological heterogeneity? [J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 2021, 379(2193): 20190421. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2019.0421.
|
| [47] |
RADIONOV V N, SIZOV I A, TSVETKOV V M. Fundamental of geomechanics[M], Nedra, Moscow, 1986.
|
| [48] |
TURUNTAEV S B, KULIJKIN A M, GERASOMOVZ T I, et al. Dynamics of localization shear deformation in sand [J]. Doklady Akademii Nauk (Reports of Russian Academy of Science), 1997, 354(1): 105–108.
|
| [49] |
LANDAU L D, LIFSHITZ E M. Theory of elasticity[M]. Pergamon, New York, 1959.
|
| [50] |
ALONSO-MARROQUIN F, VARDOULAKIS I. Micromechanics of shear bands in granular media[C]//Powders and Grains 2005-Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Micromechanics of Granular Media (2005), The Netherlands: A. A. Balkema, Leiden, 2005: 701–704.
|
| [51] |
ABEDI S, RECHENMACHER A L, ORLANDO A D. Vortex formation and dissolution in sheared sand [J]. Granular Matter, 2012, 14(6): 695–705. DOI: 10.1007/s10035-012-0369-5.
|
| [52] |
KIM V A, KARIMOV S A. Manifestation of physical mesomechanics at contact interaction [J]. Journal of state technical university of komsomolsky at Amur, Science on nature and technique, 2014, 1(18): 79–85.
|
| [53] |
BIRD R B, ARMSTRONG R C, HASSAGER O. Dynamics of polymeric liquid[M]. 2nd ed. Wiley, New York, 1987.
|
| [54] |
CHOW T S. Mesoscopic physics of complex materials[M]. Springer, New York, 2000.
|
| [55] |
SIMMONS J H, Mohr R K, MONTROSE C J. Non-newtonian viscous flow in glass[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1982, 53(6): 4075–4080. DOI: 10.1063/1.331272.
|
| [56] |
SIMMONS J H, OCHOA R, SIMMONS K D, et al. Non-Newtonian viscous flow in soda-lime-silica glass at forming and annealing temperatures[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 105(3), 1988: 313–322. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3093(88)90325-0.
|
| [57] |
SIMMONS J H. What is so exciting about non-linear viscous flow in glass, molecular dynamics simulations of brittle fracture and semiconductor-glass quantum composites[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1988, 239: 1–15. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3093(98)00741-8.
|
| [58] |
GRADY D E. Shock wave properties of brittle solids: 950846 [R]. Sandia National Laboratory, 1995: 9–20.
|






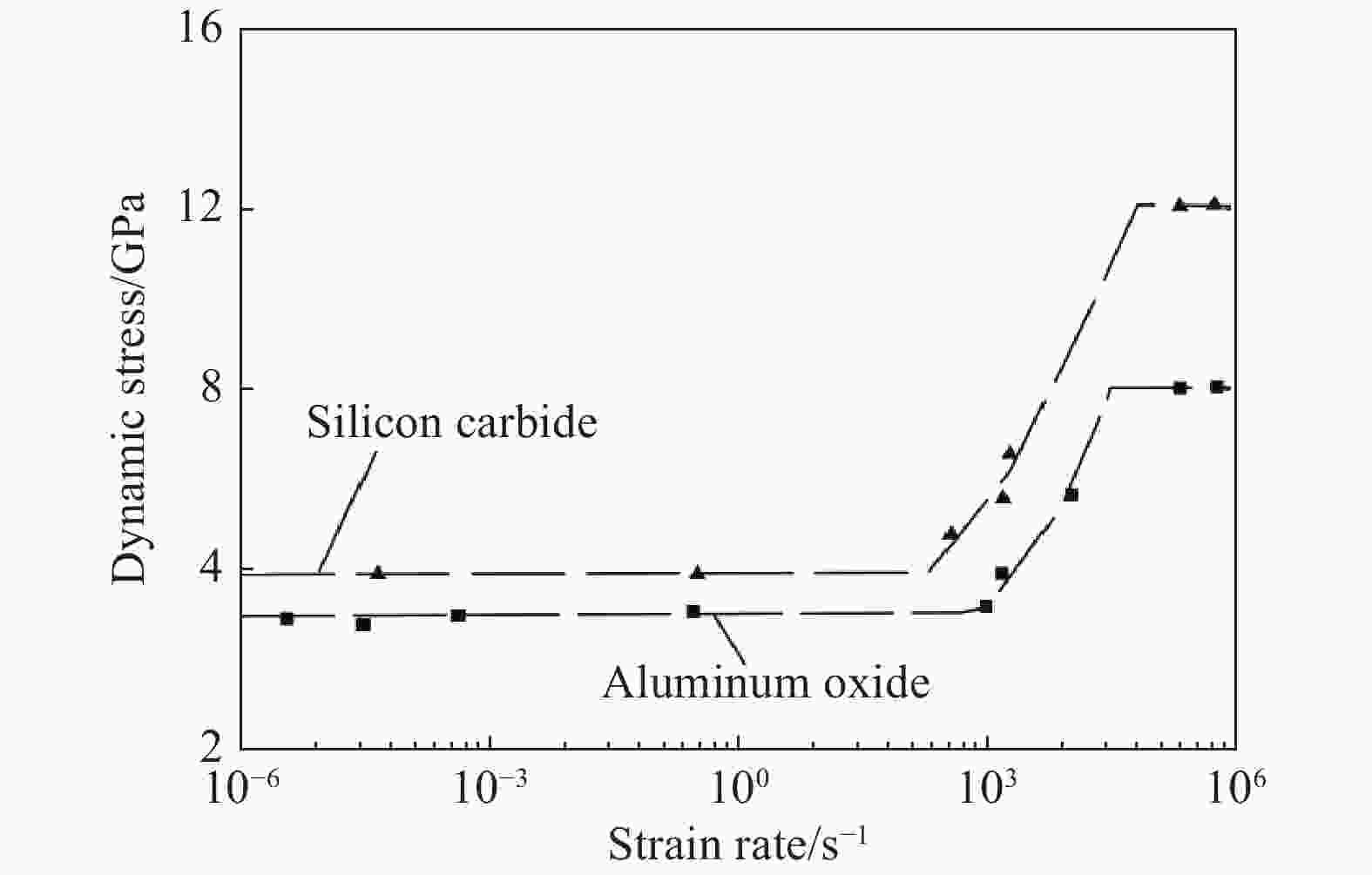
 下载:
下载: