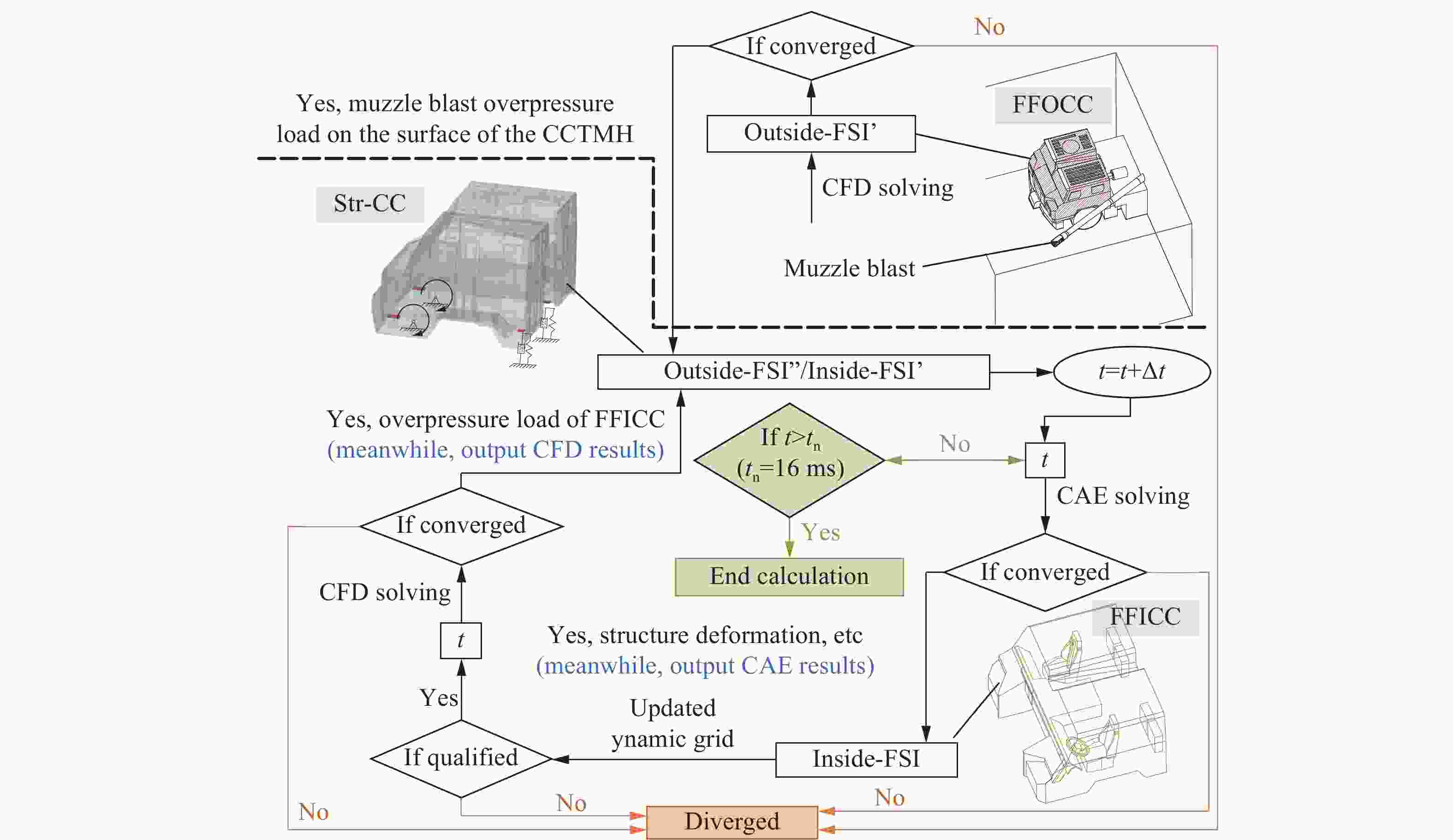
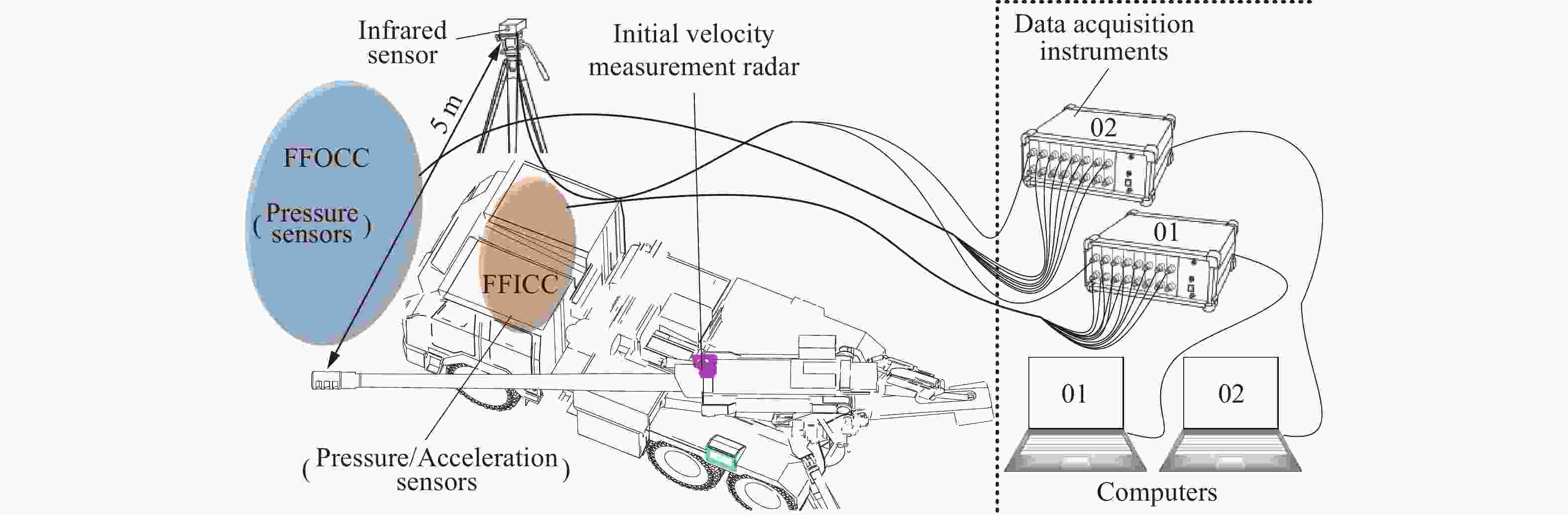
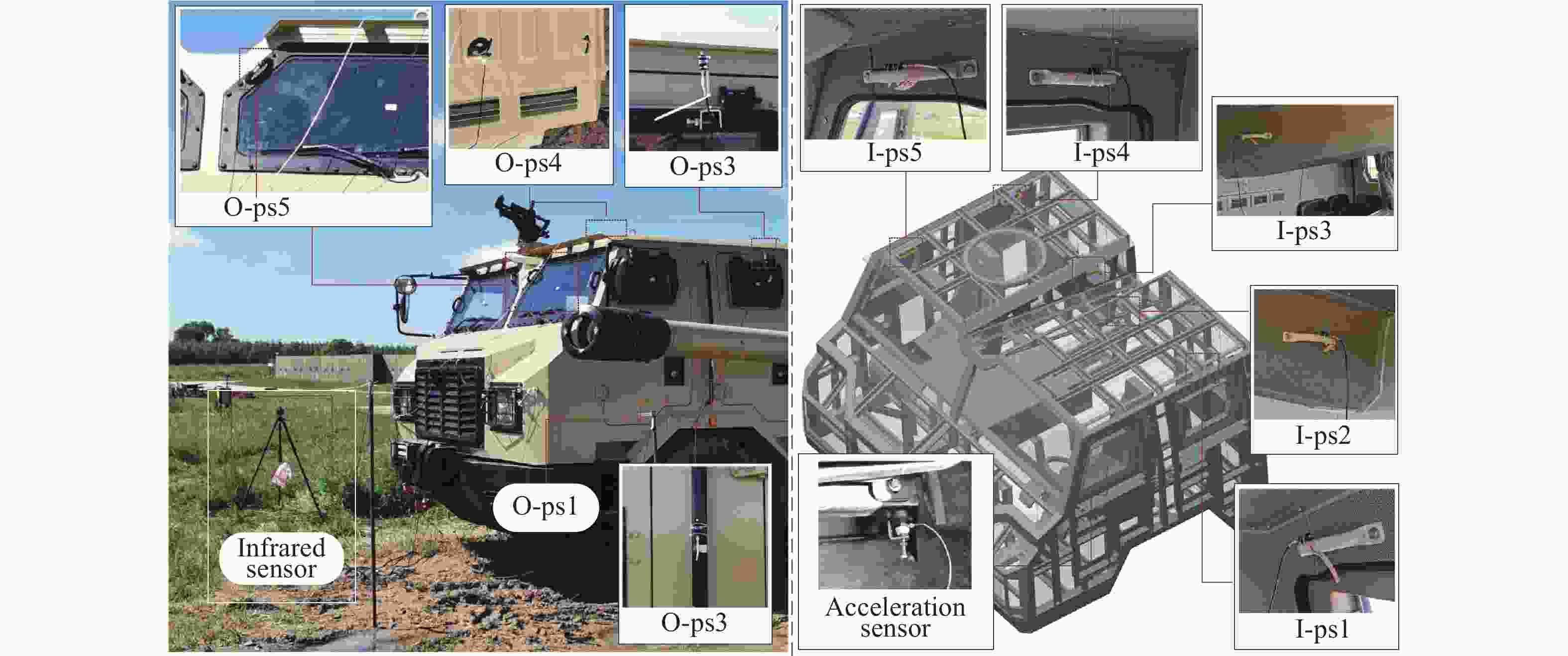
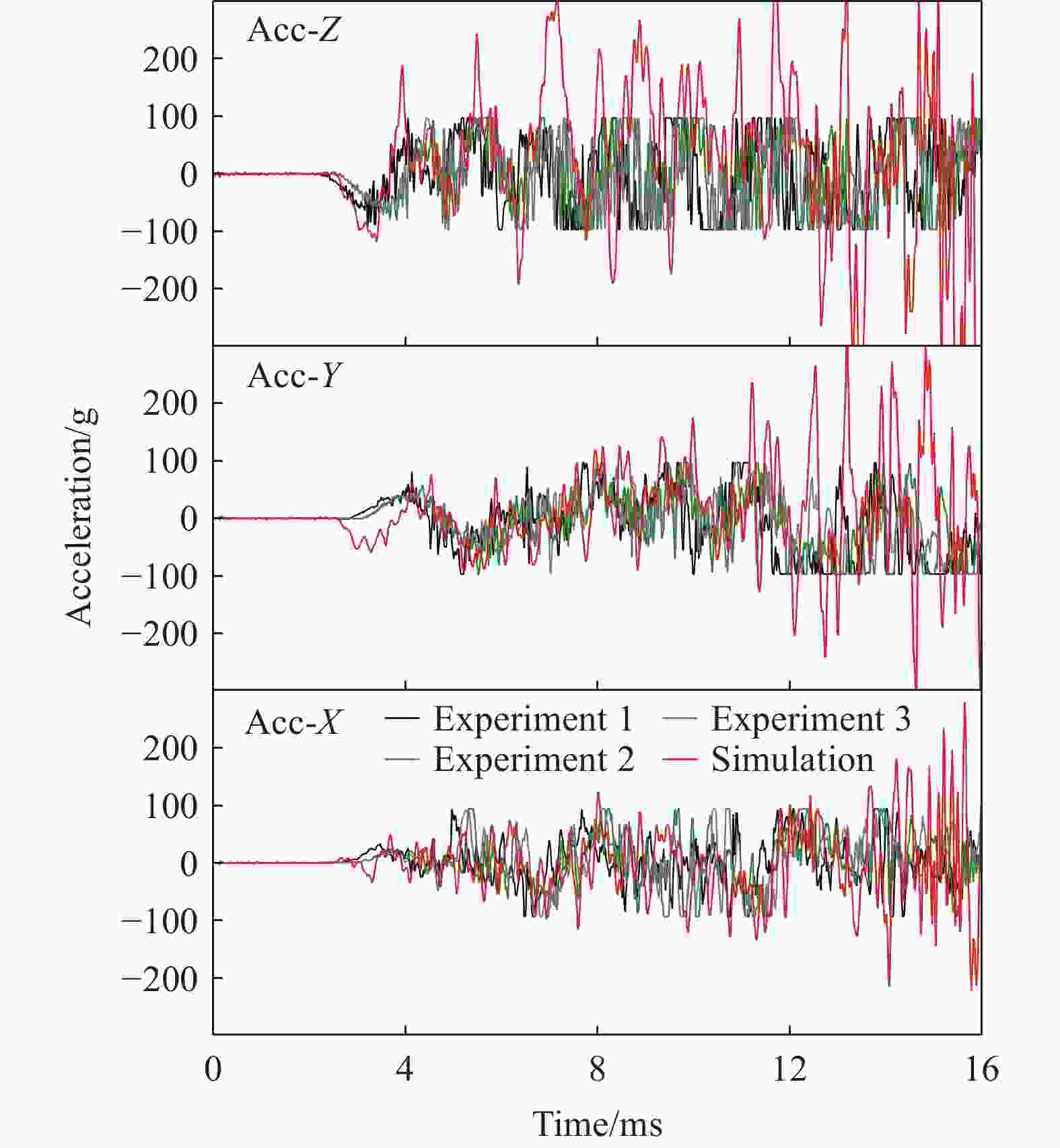
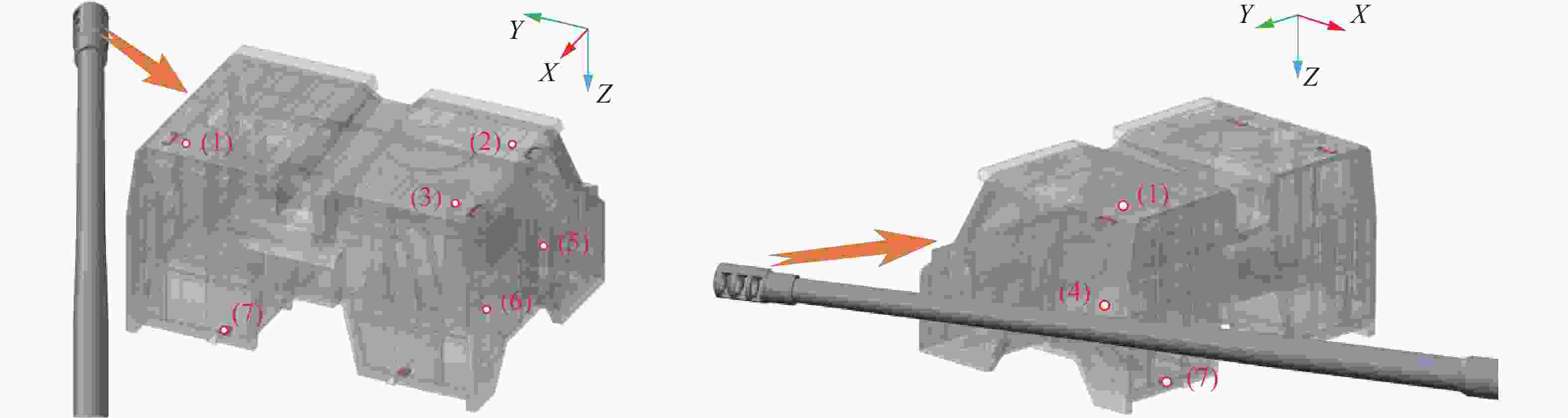
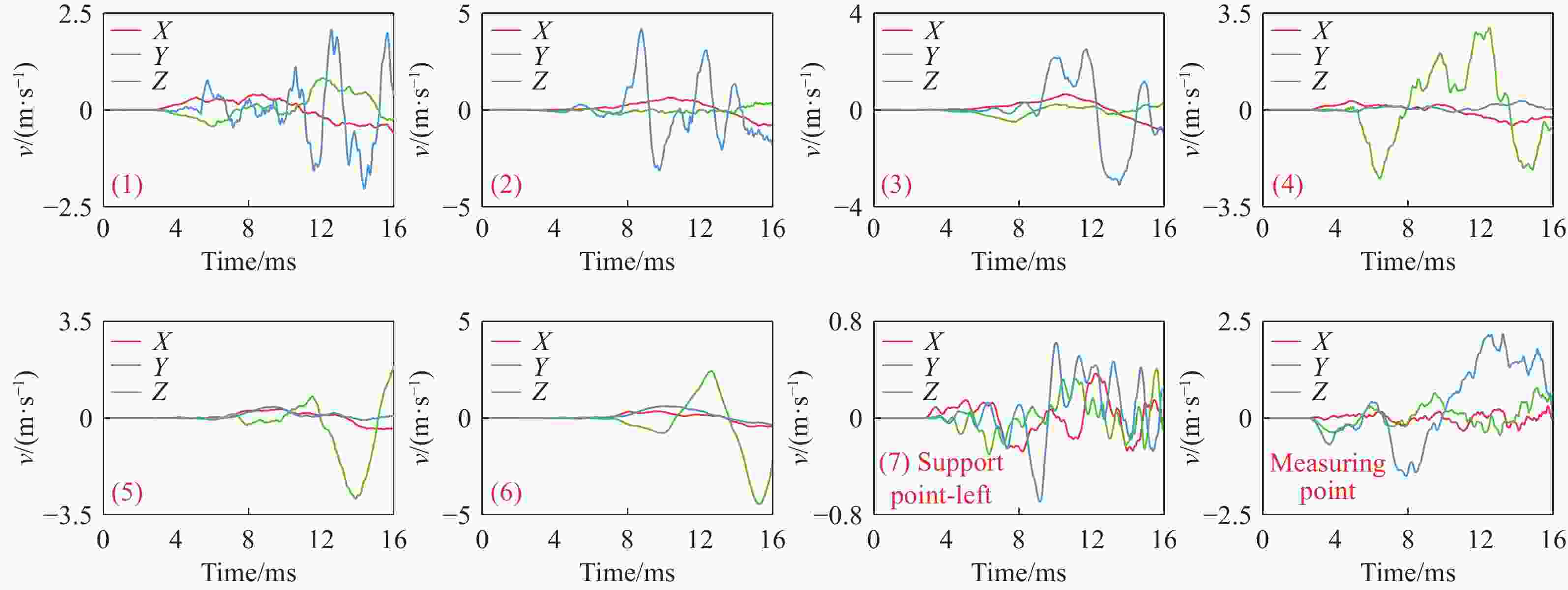
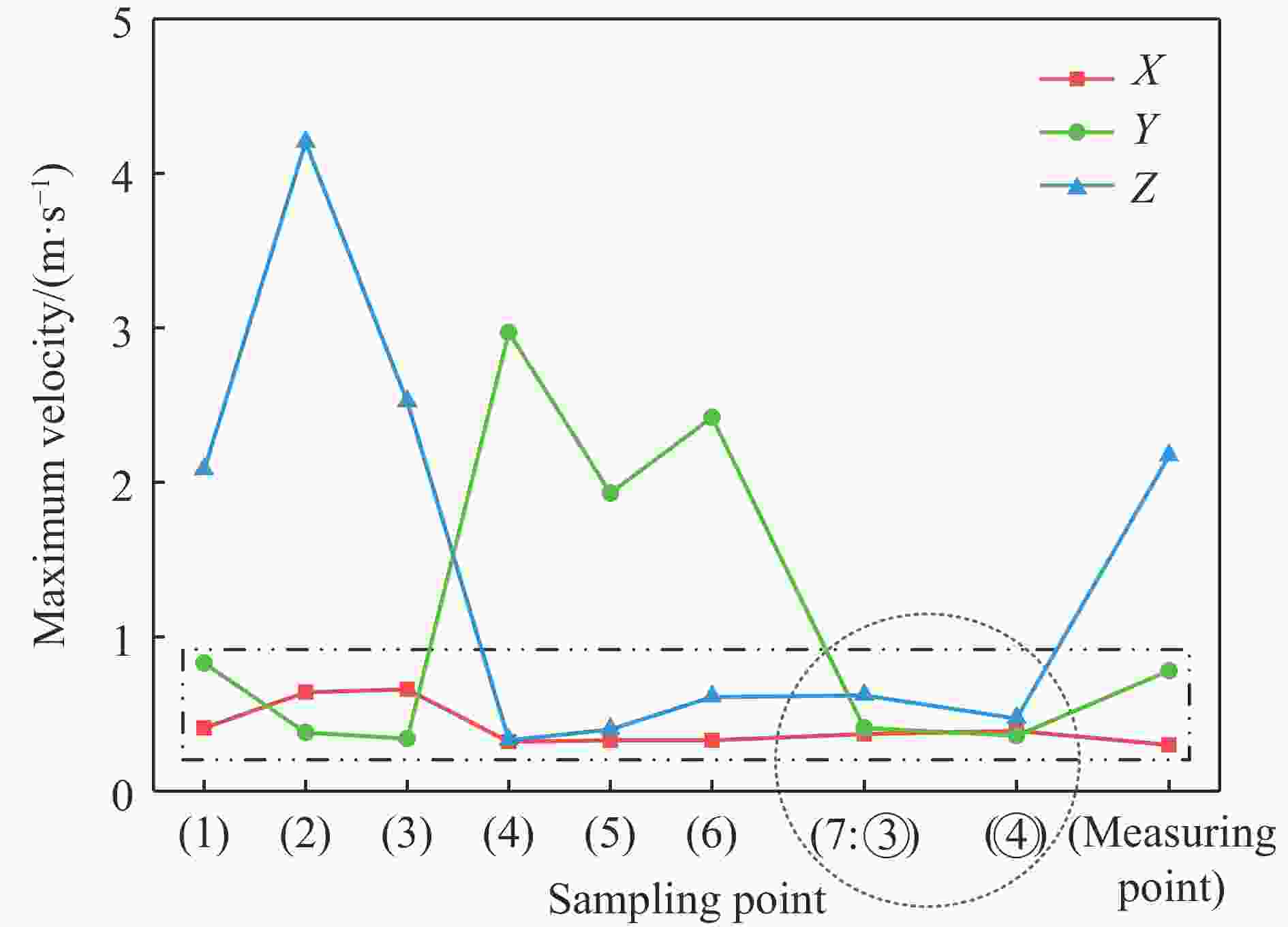
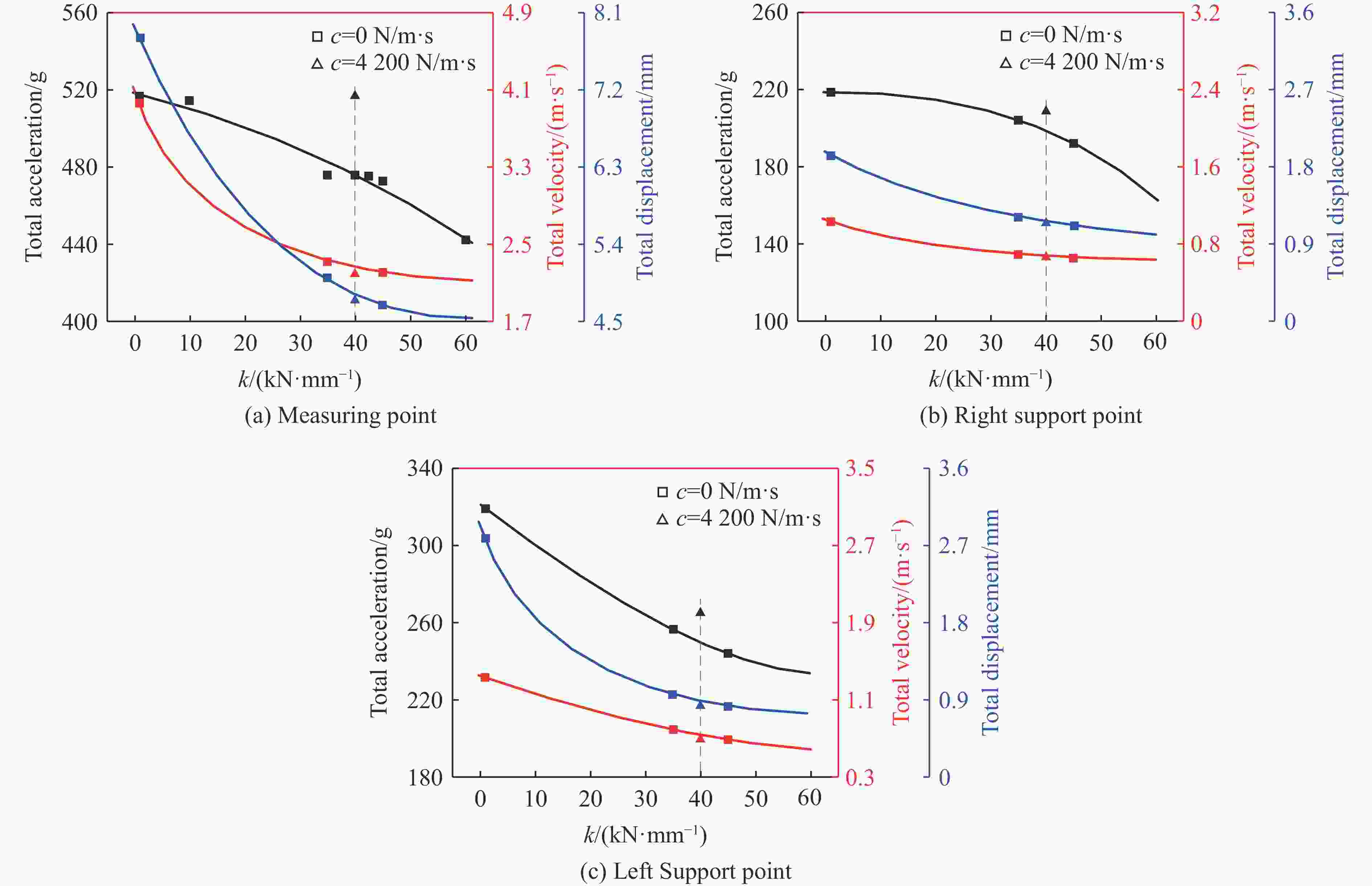
Influence of support conditions on the flow field overpressure inside the crew compartment of a truck-mounted howitzer under muzzle blast
-
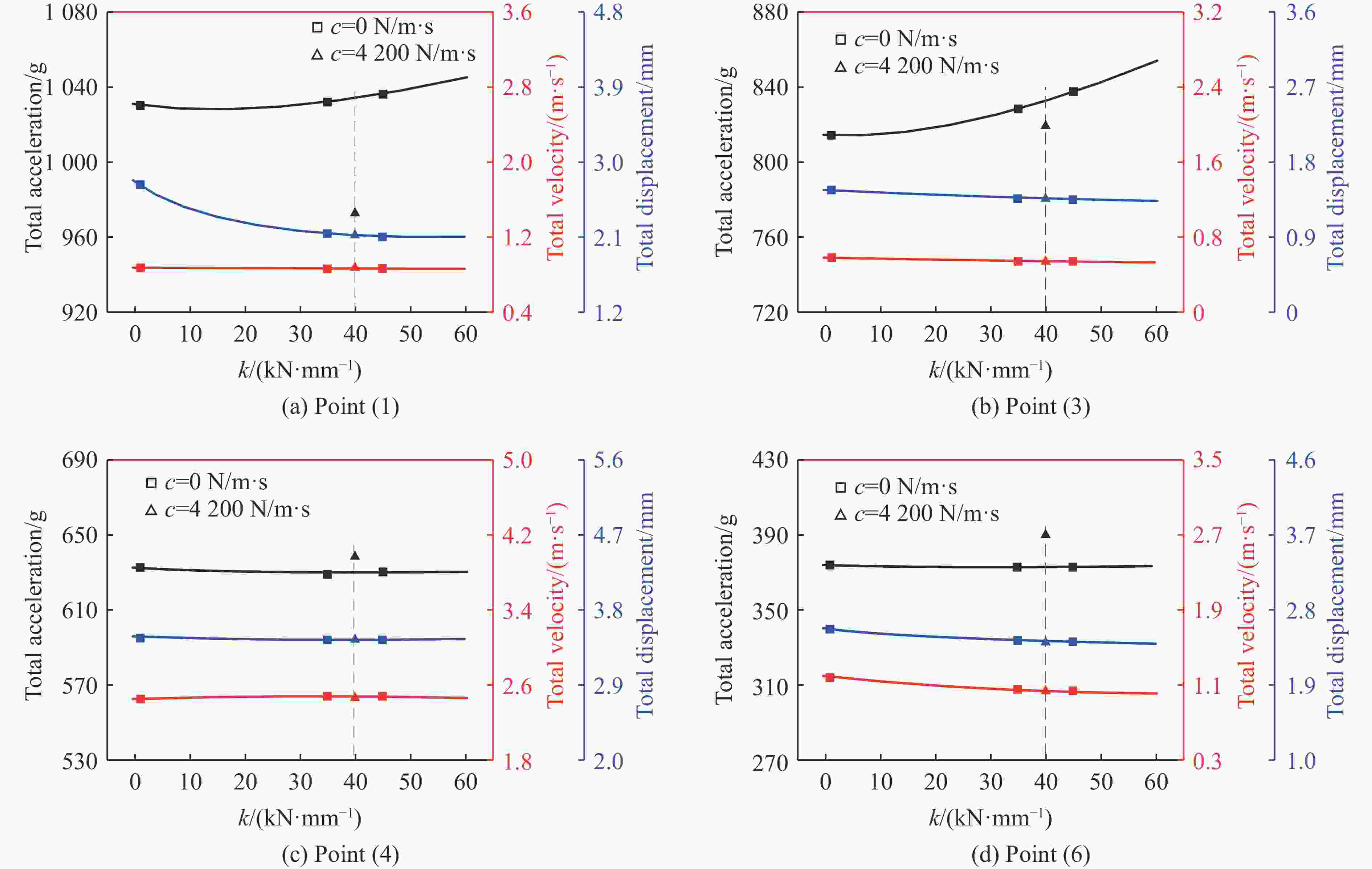
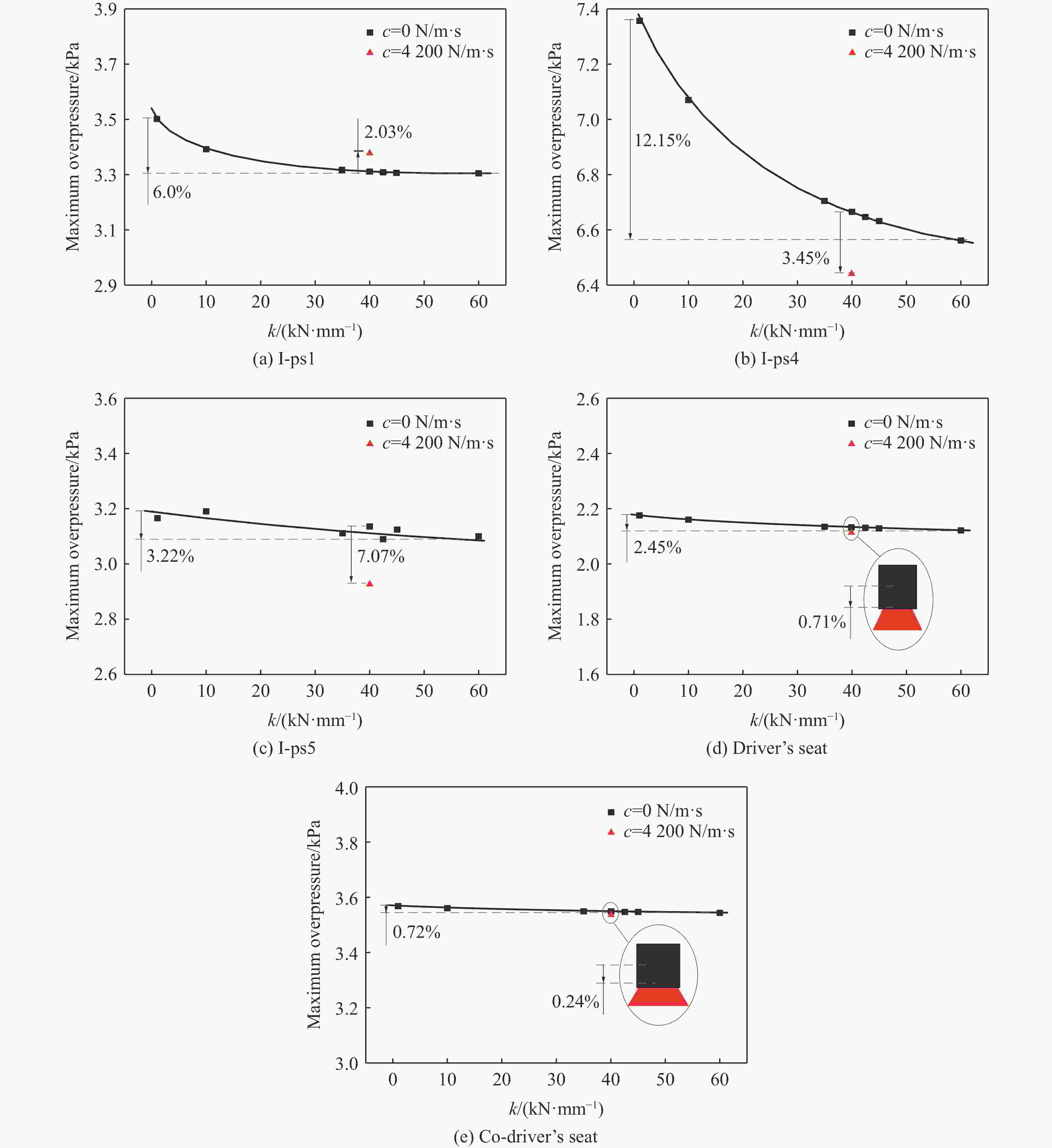
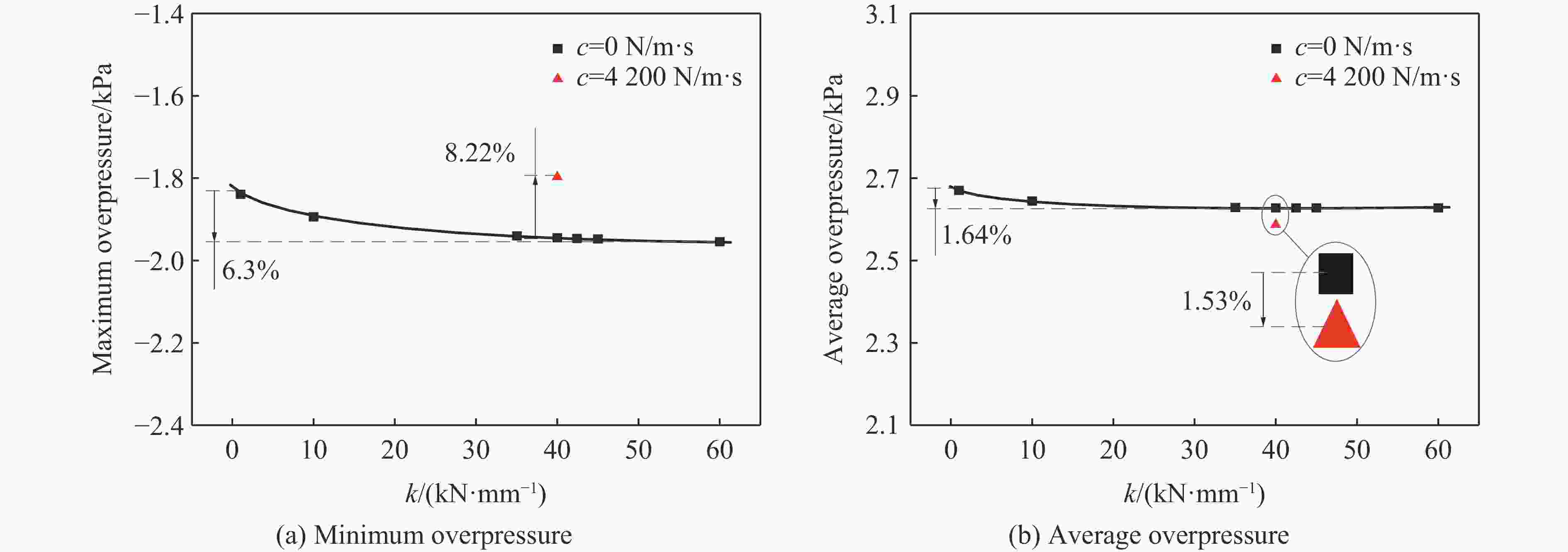
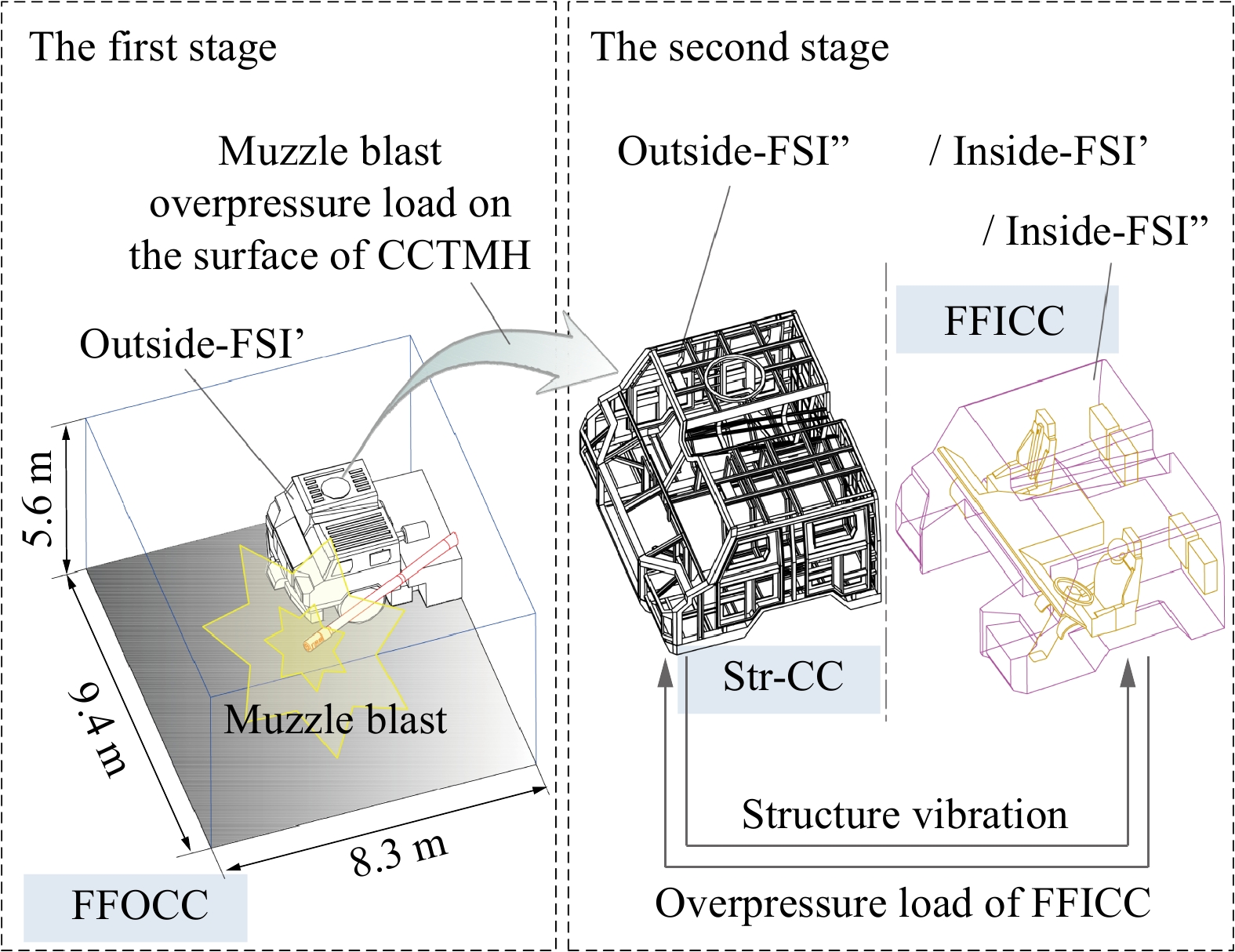
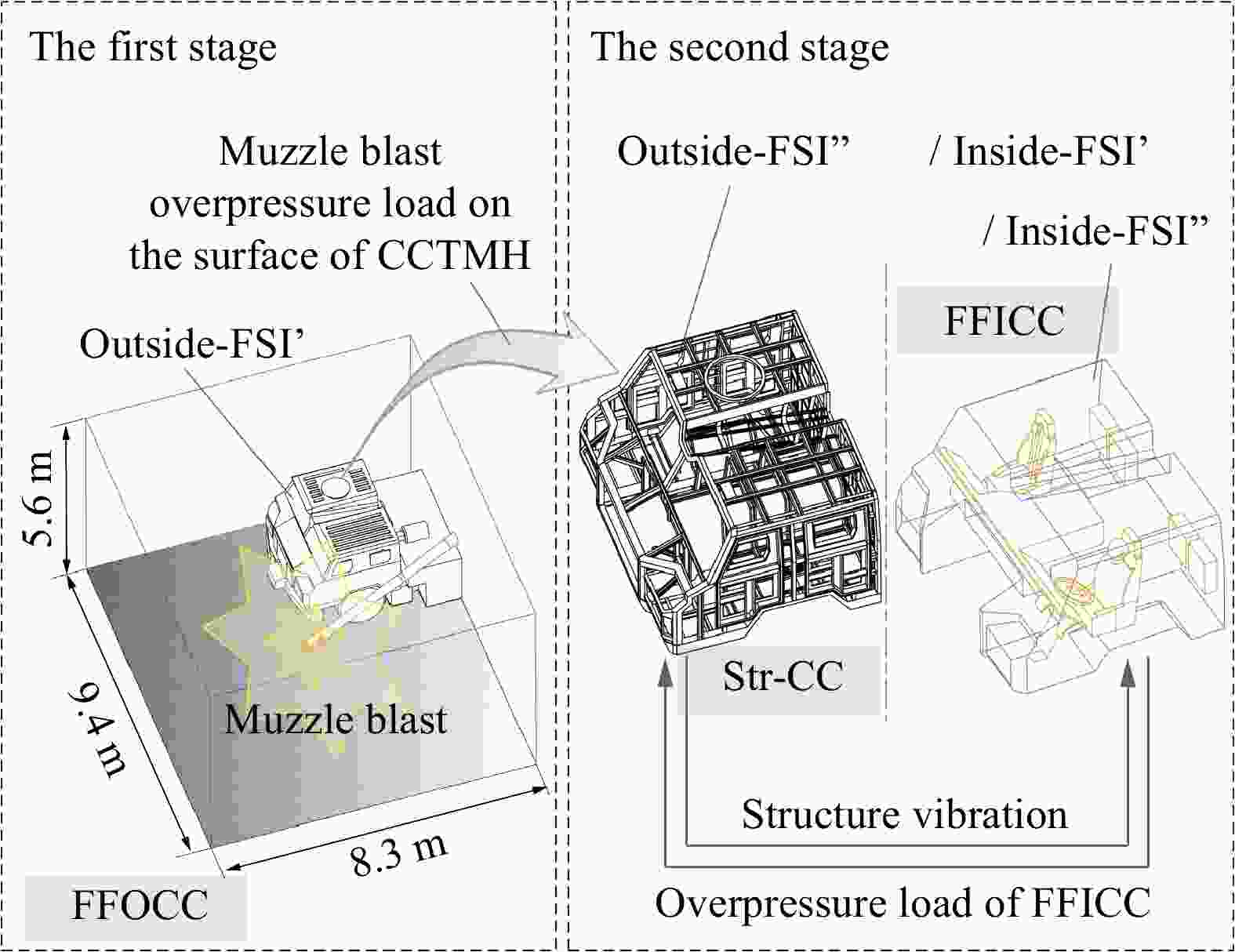
摘要: 为探究支撑条件改变对驾驶室内流场超压的具体影响,以某外贸型号装备为对象:建立了极限射击工况下、从炮口至驾驶室内部的冲击波传播数值模型;开展了涵盖驾驶室外、内流场超压与结构加速度等数据采集的系统性验证试验。基于经验证的数值模型,分别对8种不同支撑条件下的驾驶室内流场超压进行仿真计算。结果表明:虽然驾驶室内不同空间对支撑条件变化的响应敏感度不同,但随着支撑刚度由小到大变化,驾驶室结构的加速度、速度峰值均显著减小,内流场超压峰值减小;支撑阻尼的存在使得驾驶室结构的加速度响应明显增强,但有利于进一步减弱其速度响应、降低内流场的超压峰值。Abstract: During firing of a truck-mounted howitzer, the crew compartment structure deforms elastically due to the muzzle blast load, creating pressure disturbances in the internal flow field of cabin. The resulting overpressure causes a significant threat to personnel and equipment safety. To meet driving requirements, the crew compartment of the truck-mounted howitzer is suspended on the chassis frame via an elastic support structure. At the same time, the stiffness and damping of the support structure are important factors affecting the deformation response of the cabin structure under the impact of the muzzle blast load. Therefore, adjusting the support parameters to optimize the flow field environment inside the crew compartment demonstrates high practical utility. To investigate the effects of different cabin support conditions on the flow field overpressure inside the crew compartment of a truck-mounted howitzer, a foreign trade type of equipment was taken as the object. An entire path numerical model simulating the shock wave propagation from the cannon's muzzle to the interior of the cabin under extreme firing conditions was established. Systematic validation tests were conducted, capturing overpressure data in both the external and internal flow fields of the crew compartment, as well as the acceleration of the cabin structure. Based on the validated numerical model, simulations were performed to calculate the structural responses and internal flow field overpressures under eight different support conditions. The results indicate that while different areas within the cabin exhibit varying sensitivity to changes in support conditions, increasing the support stiffness leads to significant reductions in the peak acceleration and velocity of the cabin structure, as well as a decrease in the peak overpressure within the internal flow field. However, the presence of damping in the support structure significantly enhances the acceleration response of the cabin structure, yet it further diminishes its velocity response and lower the peak overpressure in the internal flow field of the crew compartment.
-
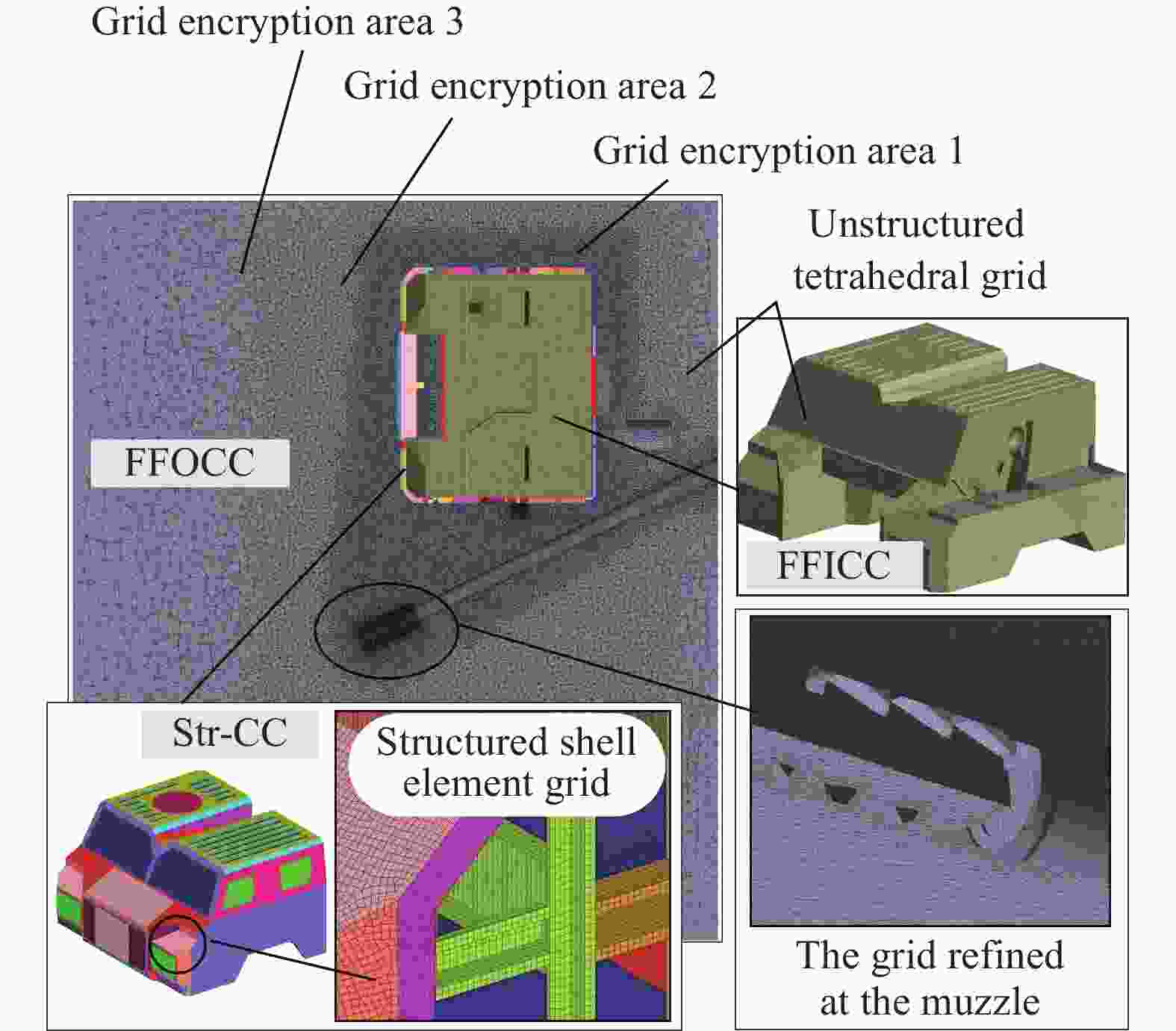
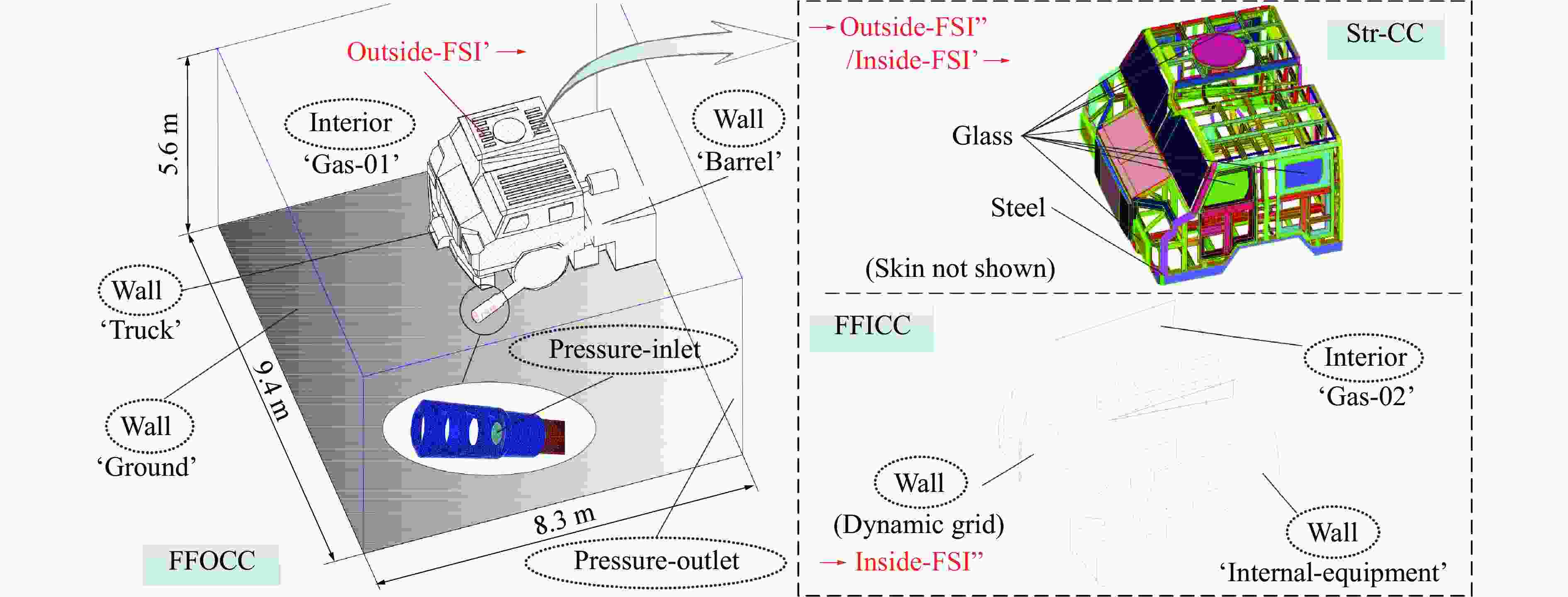
表 1 各计算域网格数量
Table 1. Number of grids in each computing domain
计算域 网格类型 网格数量 驾驶室外流场 四面体非结构网格 14 221 352 驾驶室内流场 四面体非结构网格(动网格) 5 023 750 驾驶室结构场 壳单元结构网格 700 647 表 2 材料参数
Table 2. Parameters of materials
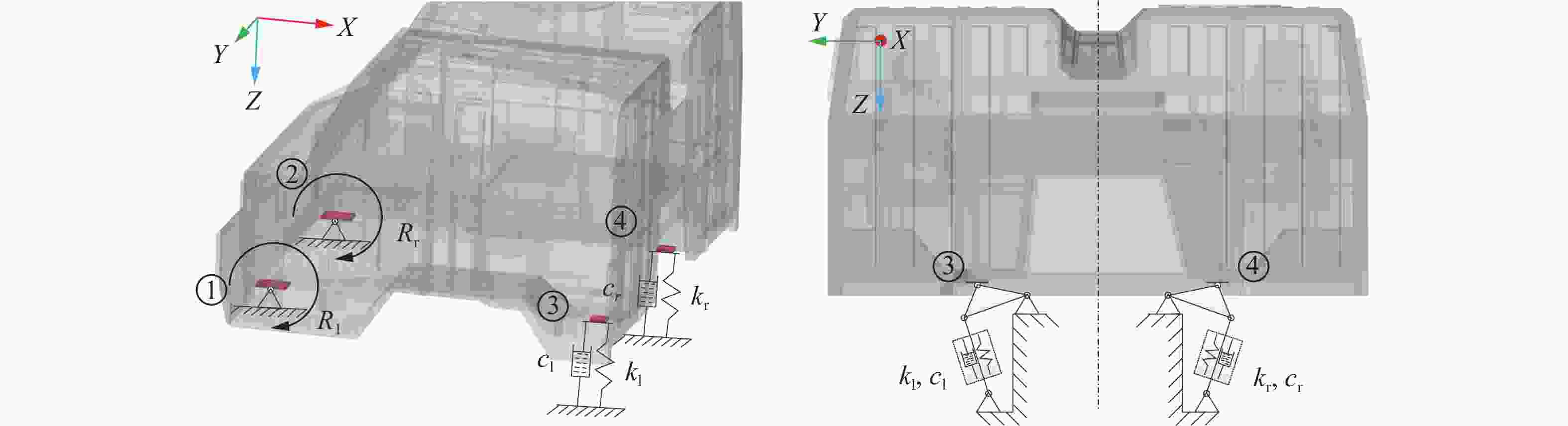
材料 密度/(kg·m−3) 弹性模量/GPa 剪切模量/GPa 泊松比 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 抗弯强度/MPa 防弹钢板 7850 210 79.4 0.3 800 900 普通钢板 7850 210 79.4 0.3 245 390 防弹玻璃 2500 70 30 0.24 80 表 3 不同工况下的支撑刚度和阻尼
Table 3. Support stiffness and damping under different conditions
工况 kl(=kr)/(kN·mm−1) cl(=cr)/(N·m−1·s) kl(=kr)/(kN·mm−1) cl(=cr)/(N·m−1·s) kl(=kr)/(kN·mm−1) 1 1 0 5 40 4200 2 10 0 6 42.5 0 3 35 0 7 45 0 4 40 0 8 60 0 表 4 传感器参数
Table 4. Parameters of sensors
设备名称 型号 灵敏度 量程 压力传感器(外流场) KISTLER 211B4 3.626 mV/kPa 1400 kPa压力传感器(内流场) KISTLER 211B6 14.50 mV/kPa 340 kPa 加速度传感器 KISTLER 8763B100BB 57.46 mV/g ±100g 表 5 超压峰值的仿真结果与试验结果的对比
Table 5. Comparison between simulated and experimental peak overpressures
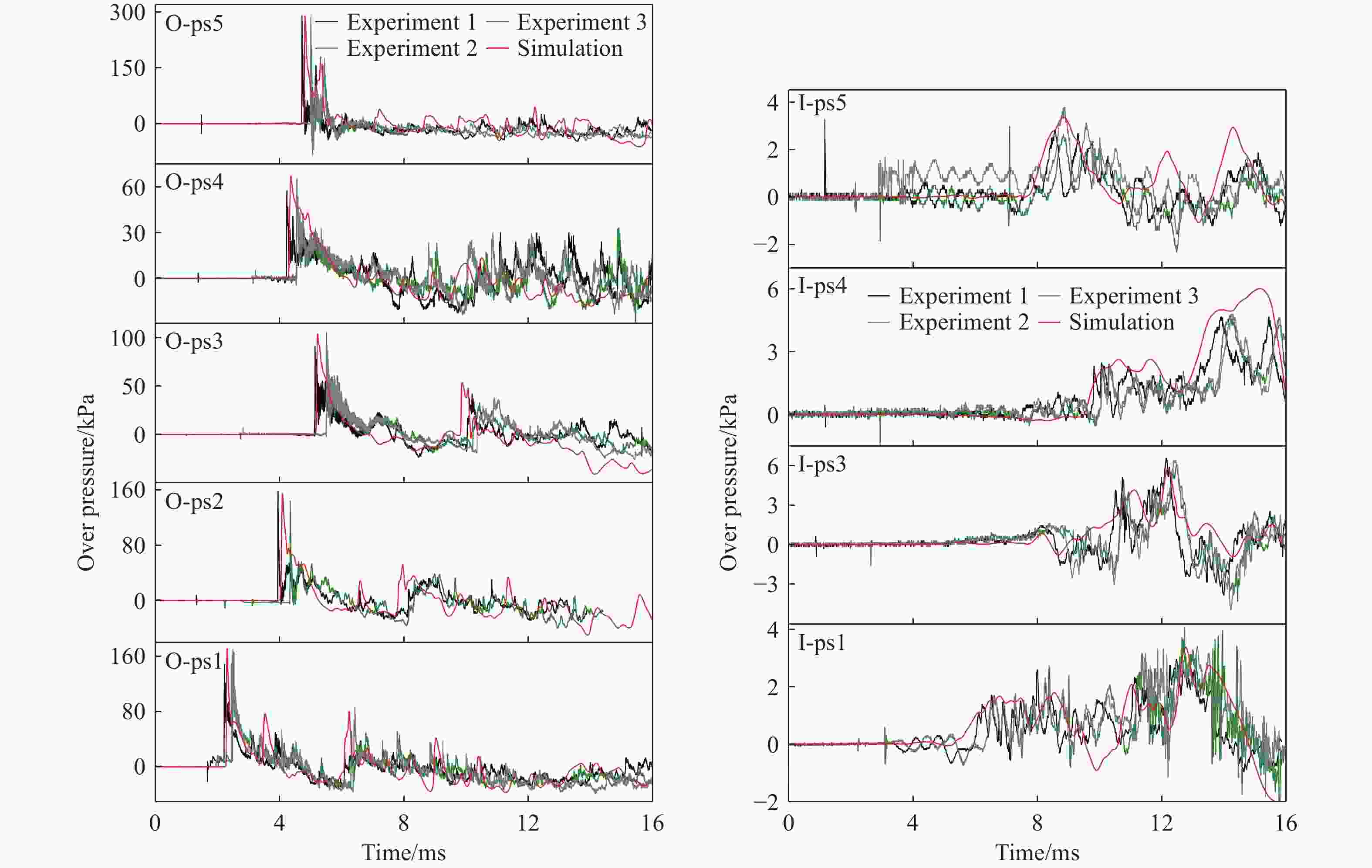
压力传感器 冲击波超压峰值/kPa 仿真值与试验平均值的
相对误差/%仿真 试验1 试验2 试验3 试验平均值 O-ps1 170.93 147.81 165.94 170.27 161.34 5.94 O-ps2 154.73 158.21 153.09 −− 155.65 0.59 O-ps3 104.83 92.18 101.93 106.24 100.12 4.70 O-ps4 67.45 58.24 65.00 66.12 63.12 6.86 O-ps5 290.52 291.95 294.55 260.83 282.44 2.86 I-ps1 3.38 2.96 4.08 3.45 3.50 3.43 I-ps2 4.29 − − − − − I-ps3 5.78 6.57 6.09 6.41 6.35 8.98 I-ps4 6.01 5.15 5.31 5.30 5.25 14.41 I-ps5 3.36 2.82 2.67 3.76 3.08 9.09 注:−表示未获得相关有效数据。 -
[1] 钱林方, 徐亚栋, 陈龙淼. 车载炮设计理论和方法 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022: 1–2. [2] 魏胜程, 钱林方, 徐亚栋, 等. 车载炮驾驶室表面炮口冲击波超压特性 [J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(11): 3792–3805. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0687.WEI S C, QIAN L F, XU Y D, et al. Characteristics of muzzle shock wave overpressure on the surface of vehicle-mounted howitzer’s crew compartment [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(11): 3792–3805. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0687. [3] WEI S C, QIAN L F, XU Y D, et al. Flow field distribution and overpressure characteristics inside the crew compartment of a truck-mounted howitzer under the effect of muzzle blast [J]. Defence Technology, 2025, 44: 190–205. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2024.09.008. [4] LI Z J, WANG H, CHEN C S, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation into the evolution of the shock wave when a muzzle jet impacts a constrained moving body [J]. Defence Technology, 2024, 33: 317–326. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2023.09.012. [5] 缪伟, 尹强, 钱林方. 火炮后效期火药气体流空过程的近似计算方法 [J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(7): 1381–1391. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.07.005.MIAO W, YIN Q, QIAN L F. An approximate calculation method for ejection of propellant gas during after-effect period of artillery [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(7): 1381–1391. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.07.005. [6] 王丹宇, 南风强, 廖昕, 等. 考虑化学反应的大口径火炮炮口流场特性 [J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(8): 1624–1630. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.08.006.WANG D Y, NAN F Q, LIAO X, et al. Characteristics of muzzle flow field of large caliber gun considering chemical reaction [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(8): 1624–1630. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.08.006. [7] BAI W B, YU Y G, ZHANG X W. Numerical simulation of the underwater gun using gas-curtain launch [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2024, 36(3): 036128. DOI: 10.1063/5.0196584. [8] 孙全兆, 范社卫, 王殿荣, 等. 某突击炮炮口流场数值模拟研究 [J]. 弹道学报, 2019, 31(4): 63–67. DOI: 10.12115/j.issn.1004-499X(2019)04-011.SUN Q Z, FAN S W, WANG D R, et al. Numerical study of muzzle flow field of assault gun [J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2019, 31(4): 63–67. DOI: 10.12115/j.issn.1004-499X(2019)04-011. [9] LI P F, ZHANG X B. Numerical research on adverse effect of muzzle flow formed by muzzle brake considering secondary combustion [J]. Defence Technology, 2021, 17(4): 1178–1189. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2020.06.019. [10] LI P F, ZHANG X B. Numerical research on the impinging effect of sequential muzzle blast waves formed by successive shooting at high frequency [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2020, 45(9): 1416–1427. DOI: 10.1002/prep.202000043. [11] SUN Z Q, LI Q, QU P, et al. Numerical investigation of the flame suppression mechanism of porous muzzle brake [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(7): 075120. DOI: 10.1063/5.0156175. [12] 康越, 马天, 王俊龙, 等. 不同海拔高度炮口冲击波动态演化特性数值模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(12): 121421. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0108.KANG Y, MA T, WANG J L, et al. Numerical simulation study on the dynamic evolution characteristics of muzzle shock waves at different altitudes [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(12): 121421. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0108. [13] 余海伟, 袁军堂, 汪振华, 等. 新型结构炮口制退器的膛口冲击波数值研究与性能分析 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2020, 34(6): 101–111. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200568.YU H W, YUAN J T, WANG Z H, et al. Muzzle blast wave investigation and performance analysis of new-structure muzzle brake based on numerical simulation [J]. Chinese Journal of high Pressure Physics, 2020, 34(6): 101–111. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200568. [14] 李鸿志, 姜孝海, 王杨, 等. 中间弹道学 [M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014: 35–41.LI H Z, JIANG X H, WANG Y, et al. Intermediate ballistics [M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 35–41. [15] ZHUO C F, FENG F, WU X S, et al. Numerical simulation of the muzzle flows with base bleed projectile based on dynamic overlapped grids [J]. Computers and Fluids, 2014, 105: 307–320. DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2014.08.006. [16] LUO Y, XU D, LI H. Analysis of the dynamic characteristics of the muzzle flow field and investigation of the influence of projectile nose shape [J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(4): 1468. DOI: 10.3390/app10041468. [17] LEI H X, ZHAO J L, WANG Z J. Numerical simulation and experiments on muzzle blast overpressure in large-caliber weapons [J]. Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Review, 2016, 9(5): 111–116. DOI: 10.25103/jestr.095.17. [18] CHEN Q K, LI P F, ZHOU Q, et al. Research on the measurement of muzzle shock wave pressure field for a naval gun [J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 791(1): 012096. DOI: 10.1088/1755-1315/791/1/012096. [19] MOUMEN A, STIRBU B, GROSSEN J, et al. Particle image velocimetry for velocity measurement of muzzle flow: detailed experimental study [J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 405: 117509. DOI: 10.1016/J.POWTEC.2022.117509. [20] 赖富文, 孔凡胜, 高赫, 等. 基于LXI总线的炮口冲击波分布式测试系统设计 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2021, 42(9): 183–188. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.09.029.LAI F W, KONG F S, GAO H, et al. Design of distributed system for measuring muzzle blast wave based on LXI bus [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2021, 42(9): 183–188. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2021.09.029. [21] SEKAR V, JIANG Q H, SHU C, et al. Fast flow field prediction over airfoils using deep learning approach [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2019, 31(5): 057103. DOI: 10.1063/1.5094943. [22] DURU C, ALEMDAR H, BARAN O U. A deep learning approach for the transonic flow field predictions around airfoils [J]. Computers and Fluids, 2022, 236: 105312. DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2022.105312. [23] NGUYEN N T T, MASKALY G R, LIAO A S, et al. Predicting shockwaves in radiograph images using different deep learning models [C]//SPIE Optical Engineering+Applications. San Diego: SPIE, 2021: 112–123. DOI: 10.1117/12.2594621. [24] HUI X Y, BAI J Q, WANG H, et al. Fast pressure distribution prediction of airfoils using deep learning [J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 105: 105949. DOI: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105949. [25] JIN S Y, CHEN S S, FENG C, et al. Deep learning for airfoil aerodynamic-electromagnetic coupling optimization with random forest [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2024, 36(1): 017110. DOI: 10.1063/5.0182455. [26] ZHOU M D, QIAN L F, CAO C Y, et al. Research on simulation of gun muzzle flow field empowered by artificial intelligence [J]. Defence Technology, 2024, 32: 196–208. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2023.02.006. [27] 陈钢. 内腔声-结构耦合系统的数值模拟与优化设计 [D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2008: 15–33.CHEN G. Numerical simulation and design optimization for interior acoustic-structural coupled systems [D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2008: 15–33. [28] 王彬星. 重型汽车车内声压级预测与主要噪声源分析 [D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2013: 83–111.WANG B X. Sound pressure level prediction and main source analysis of heavy duty truck interior noise [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2013: 83–111. [29] MA J, WANG J, HAN Y, et al. Towards data-driven modeling for complex contact phenomena via self-optimized artificial neural network methodology [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2023, 182: 105223. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2022.105223. [30] 魏然. 爆炸冲击下车身结构防护机理及多学科优化研究 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2017: 29–52.WEI R. Protection mechanism and multidisciplinary optimization of vehicle body structure under blast shock [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2017: 29–52. [31] MA J, BAI M H, WANG J, et al. A novel variable restitution coefficient model for sphere-substrate elastoplastic contact/impact process [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2024, 202: 105773. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2024.105773. [32] ZHOU S J, CHEN G S, QIAN L F, et al. HLFEMP: a coupled MPM-FEM method under a hybrid updated and total lagrangian framework [J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2024, 136: 115644. DOI: 10.1016/j.apm.2024.115644. [33] ZHUO C F, YAO W J, WU X S, et al. Research on the muzzle blast flow with gas-particle mixtures based on Eulerian-Eulerian approach [J]. Journal of Mechanics, 2016, 32(2): 185–195. DOI: 10.1017/jmech.2015.44. [34] 张小兵. 枪炮内弹道学 [M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014: 142–144.ZHANG X B. Interior ballistics of guns [M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2014: 142–144. [35] 陈南. 汽车振动与噪声控制 [M]. 3版. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2021: 62–76. -






 下载:
下载: