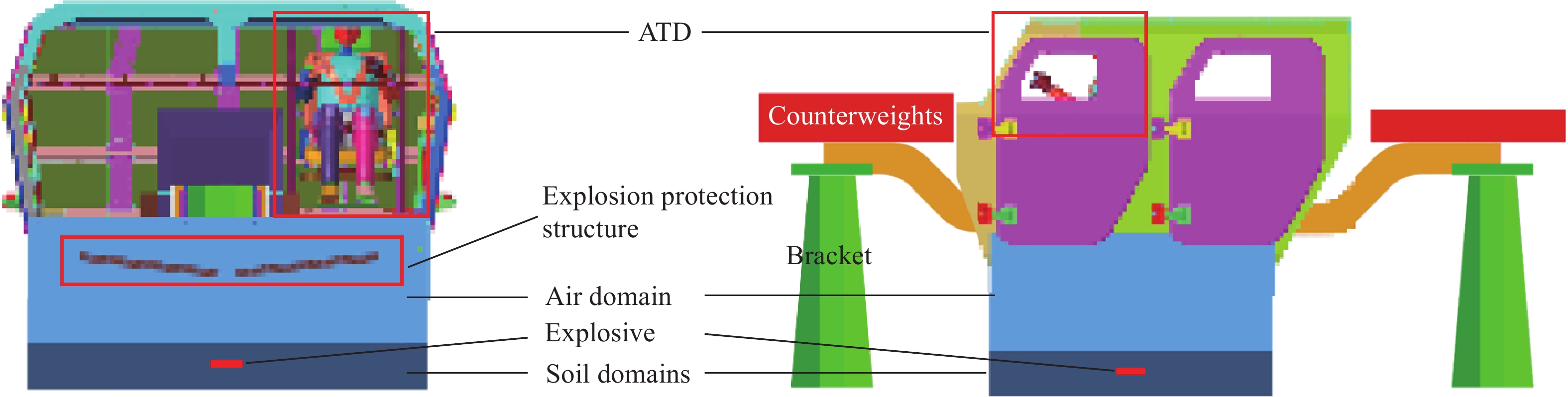
On data-driven optimization design of protective structures for vehicles against explosion
-
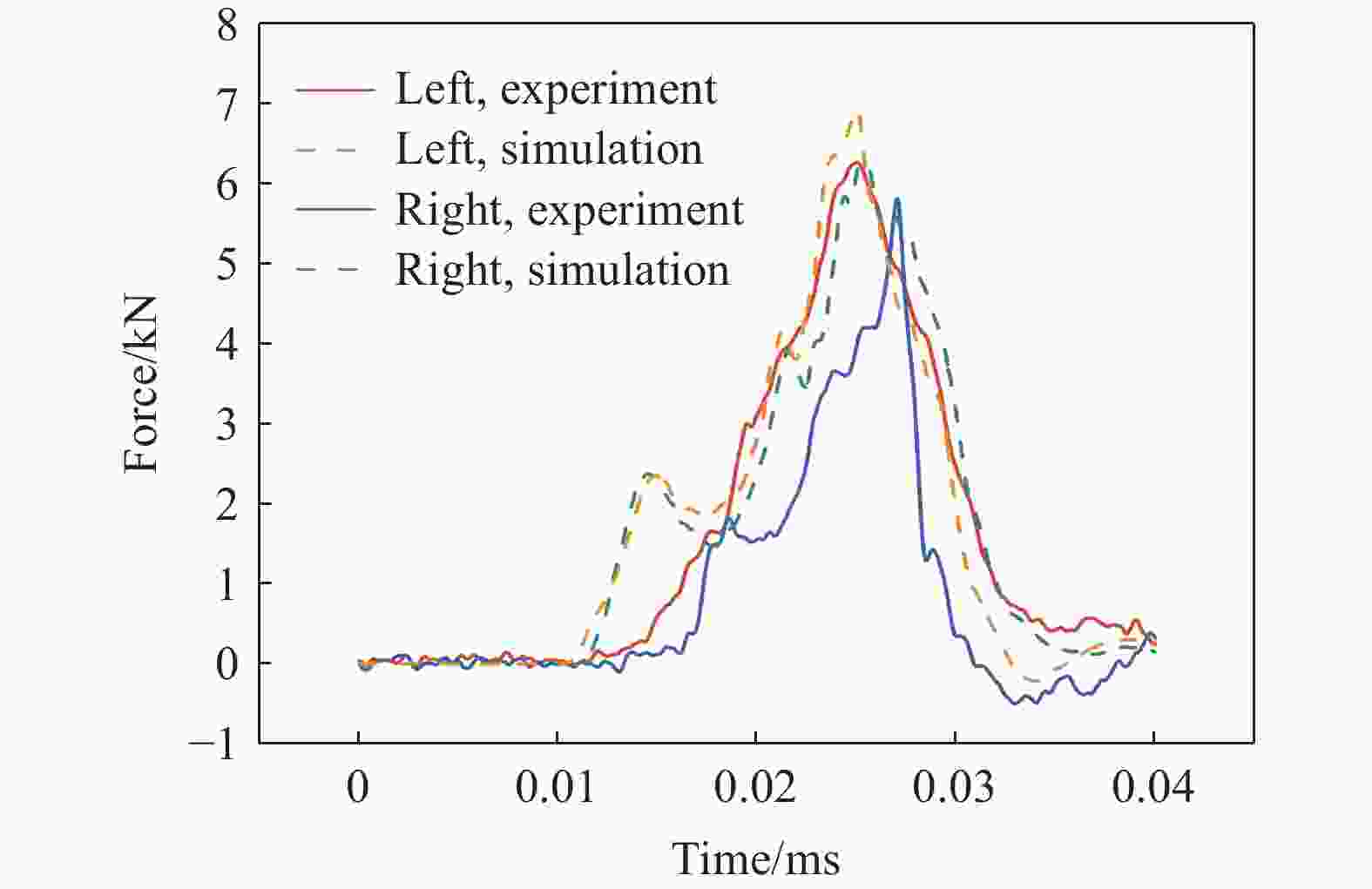
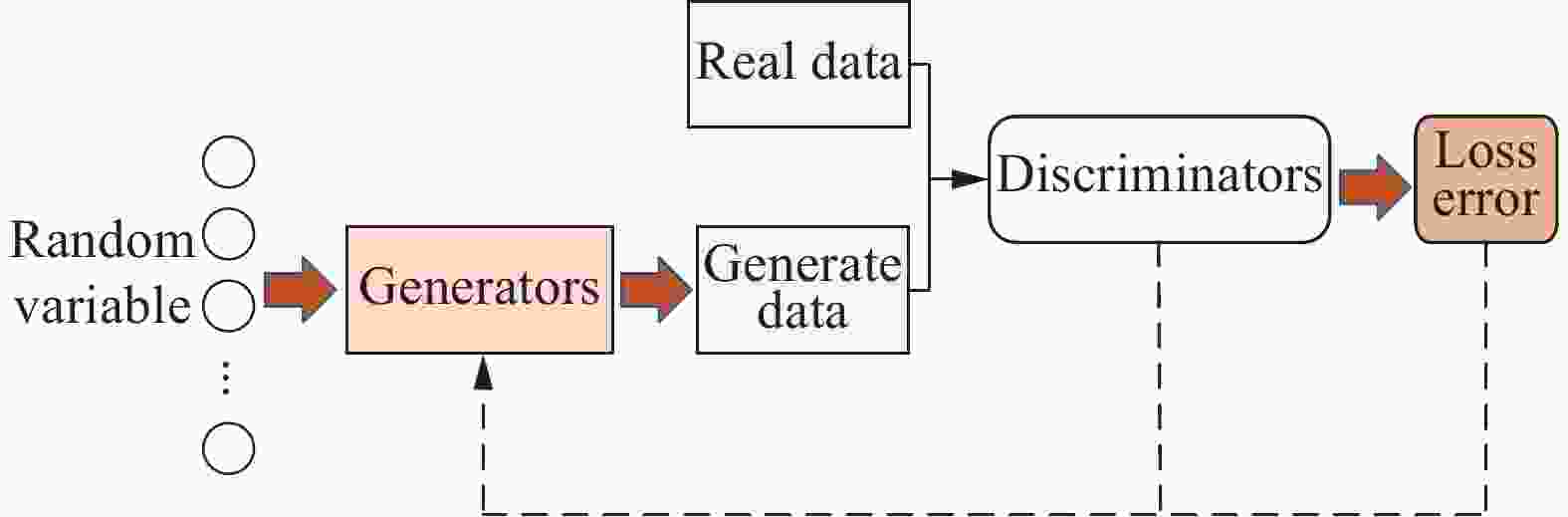
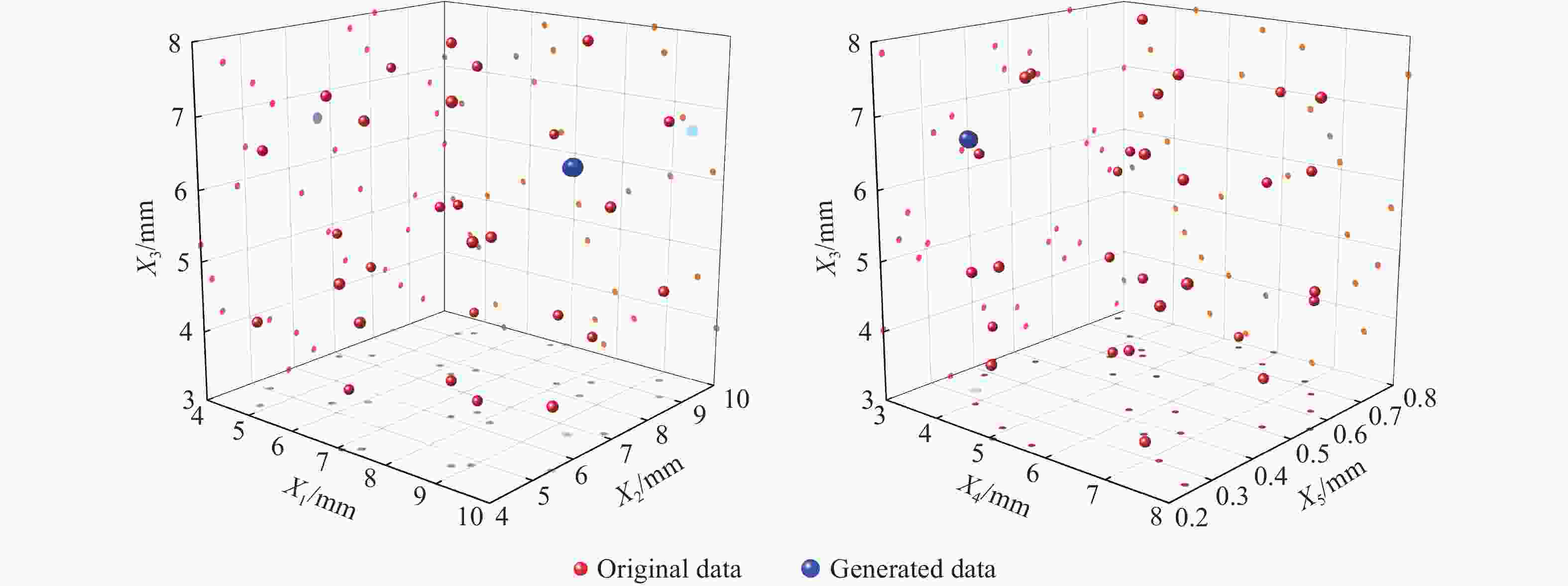
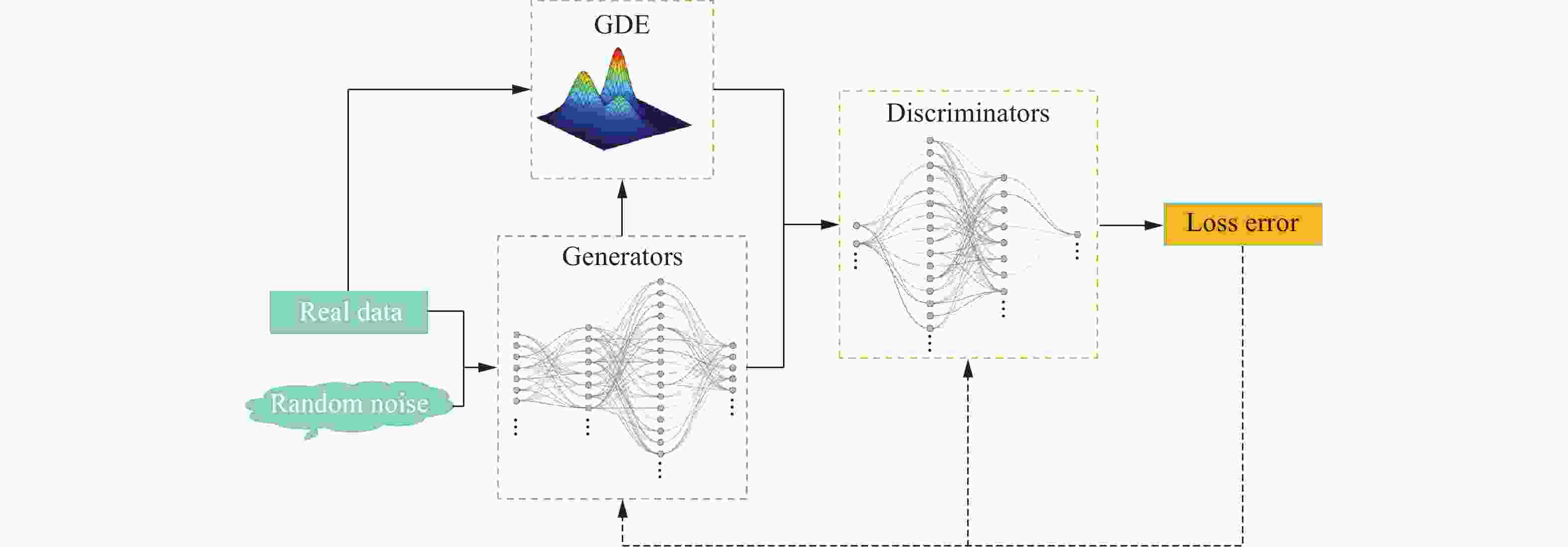
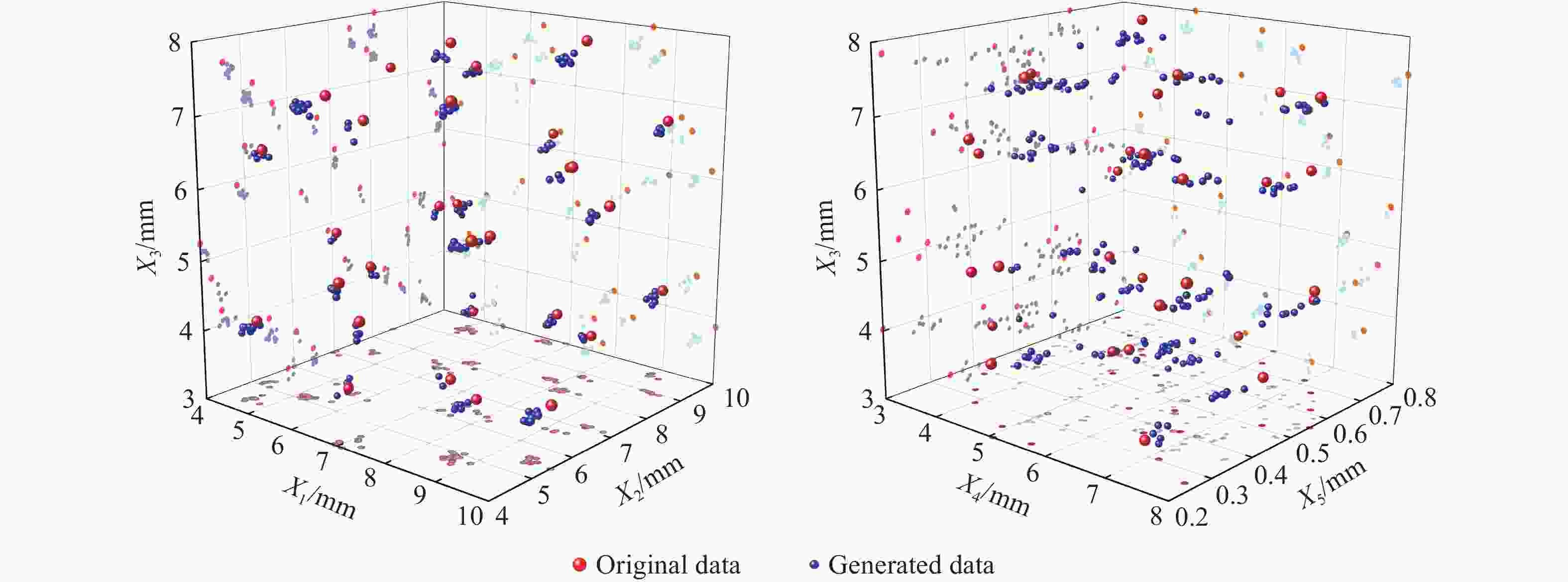
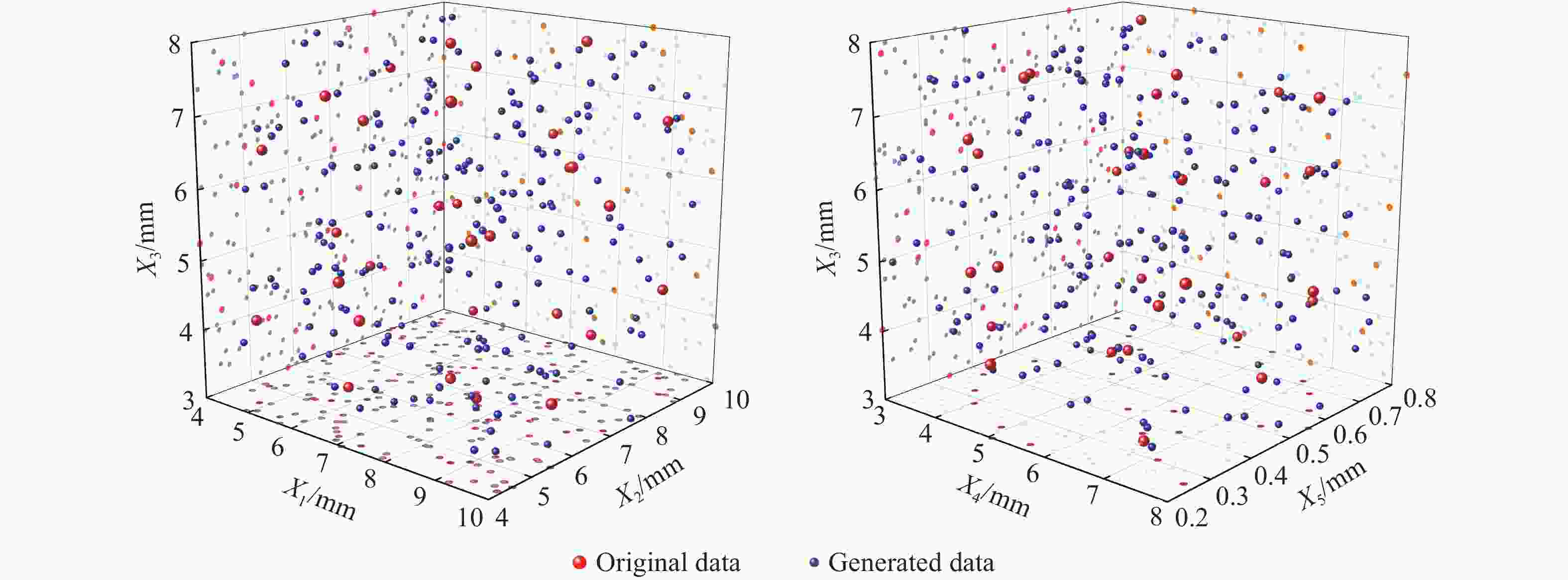
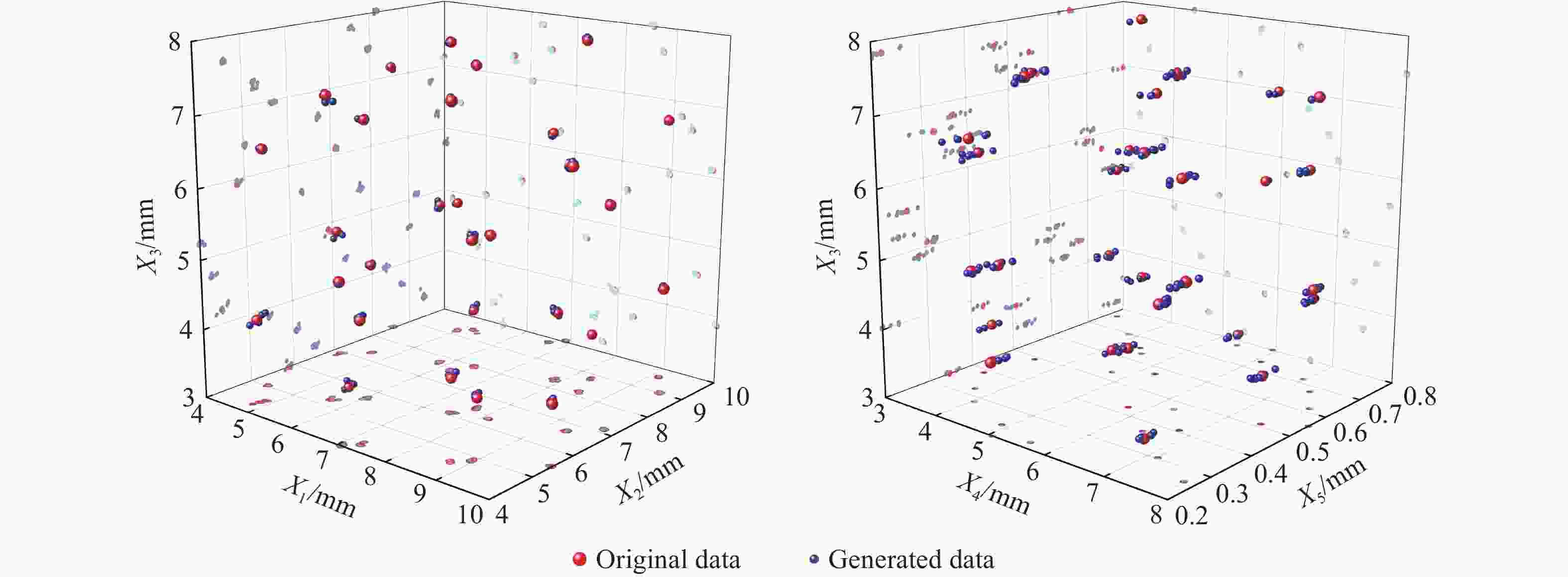
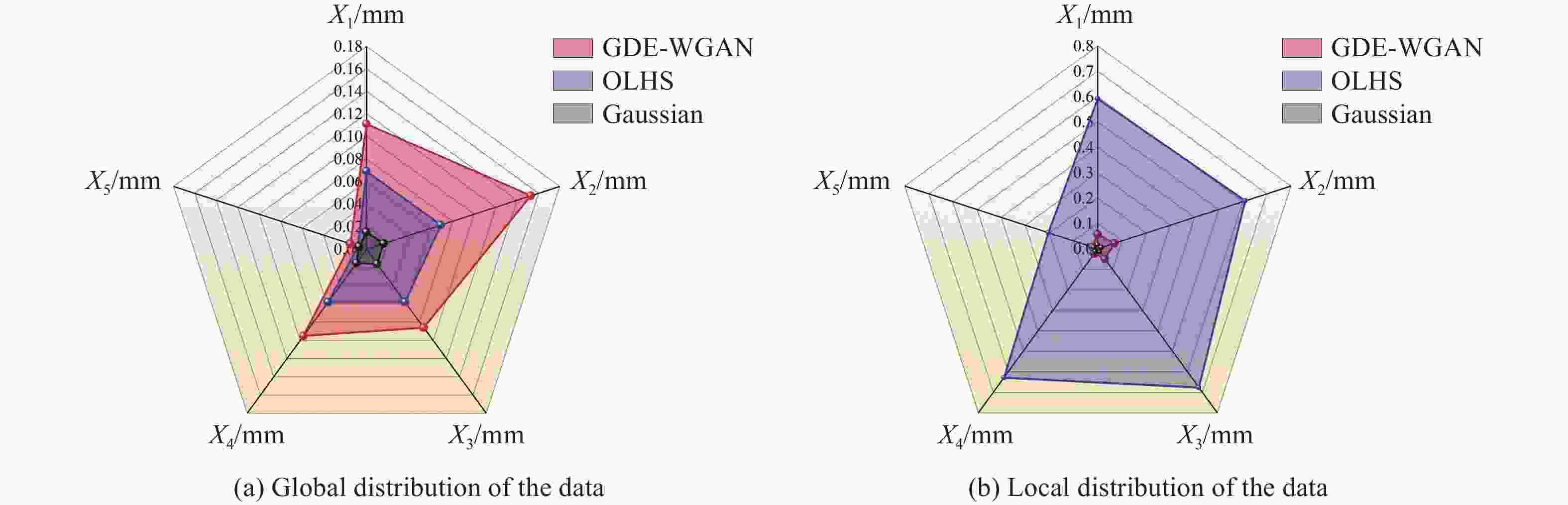
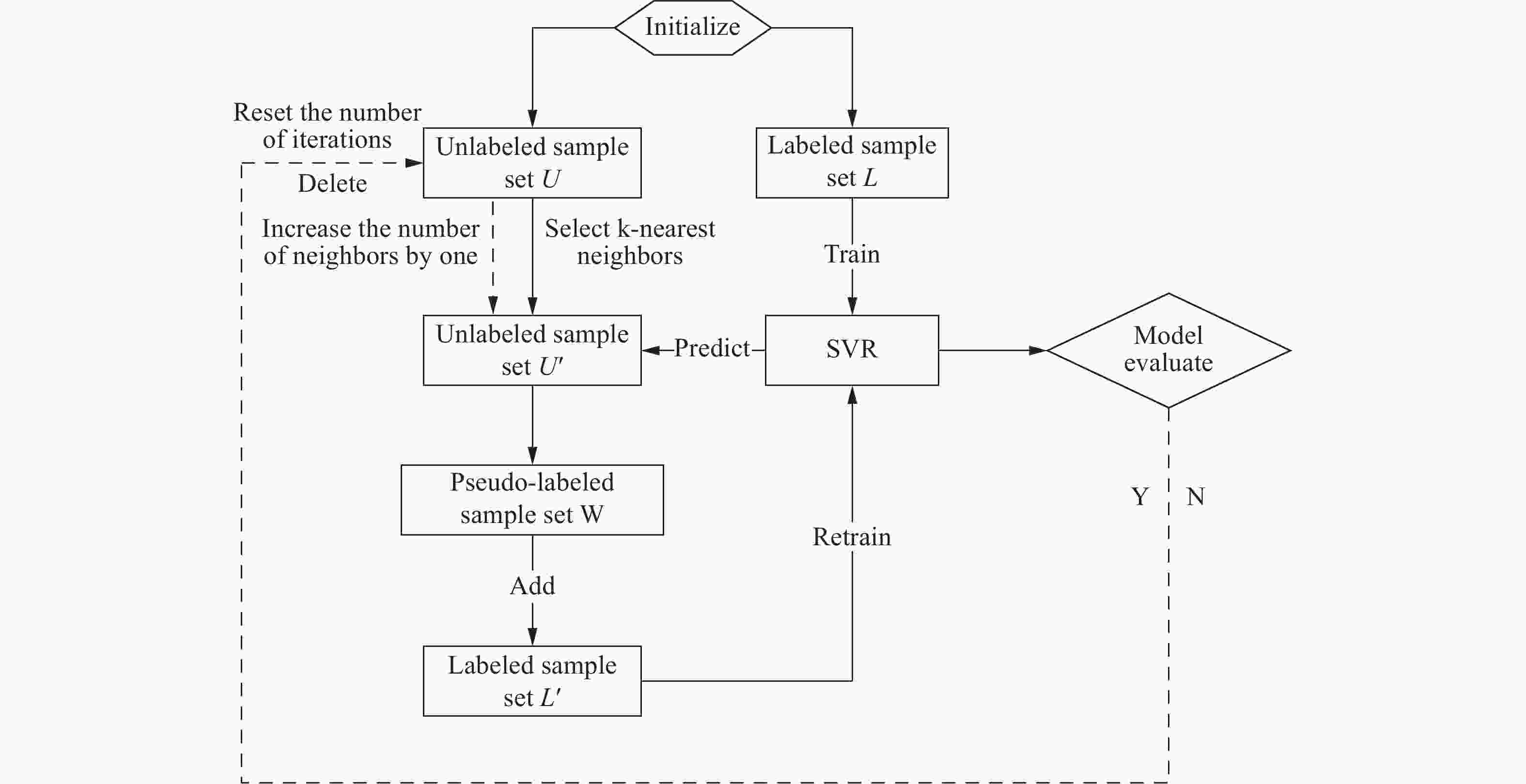
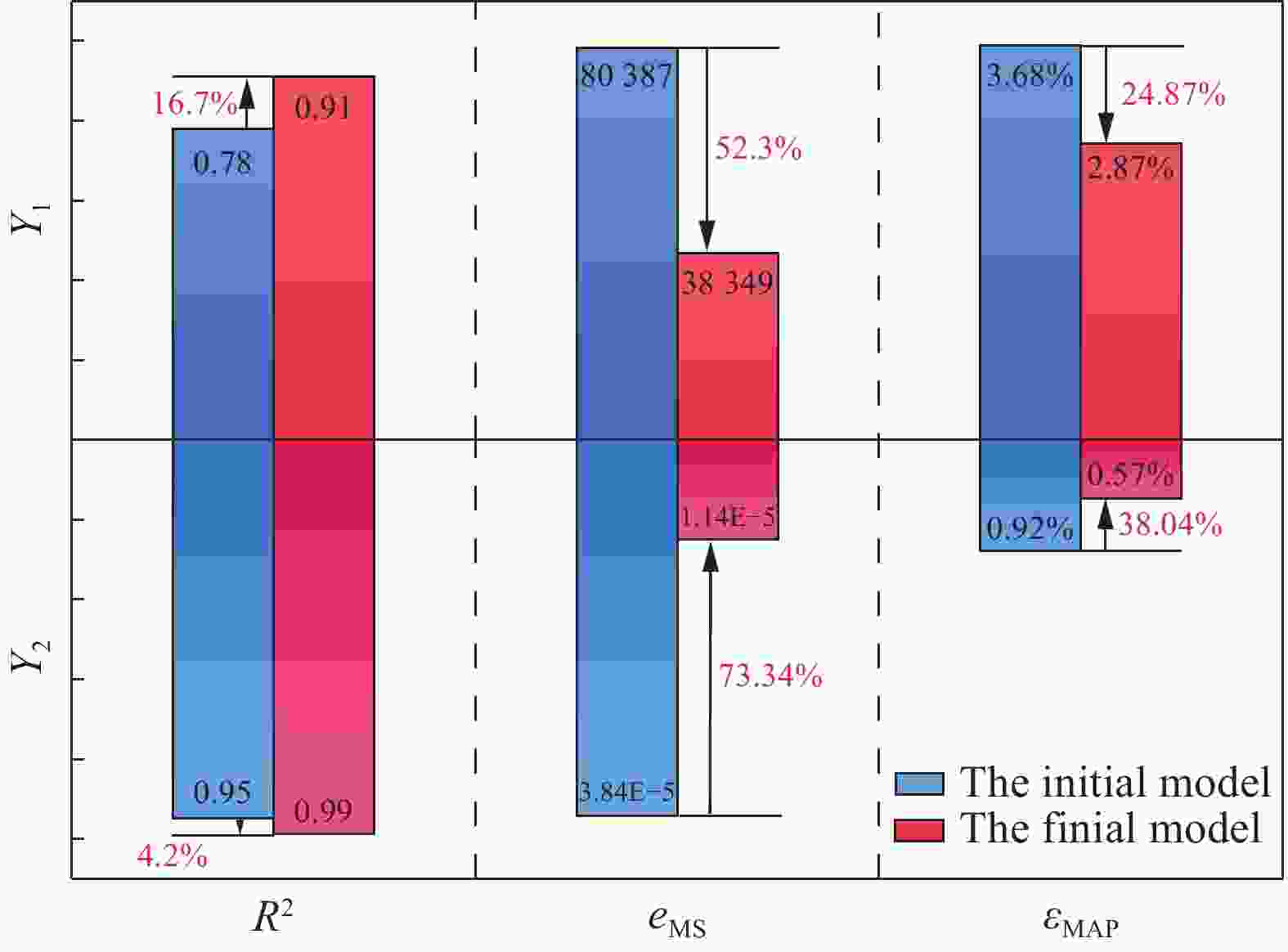
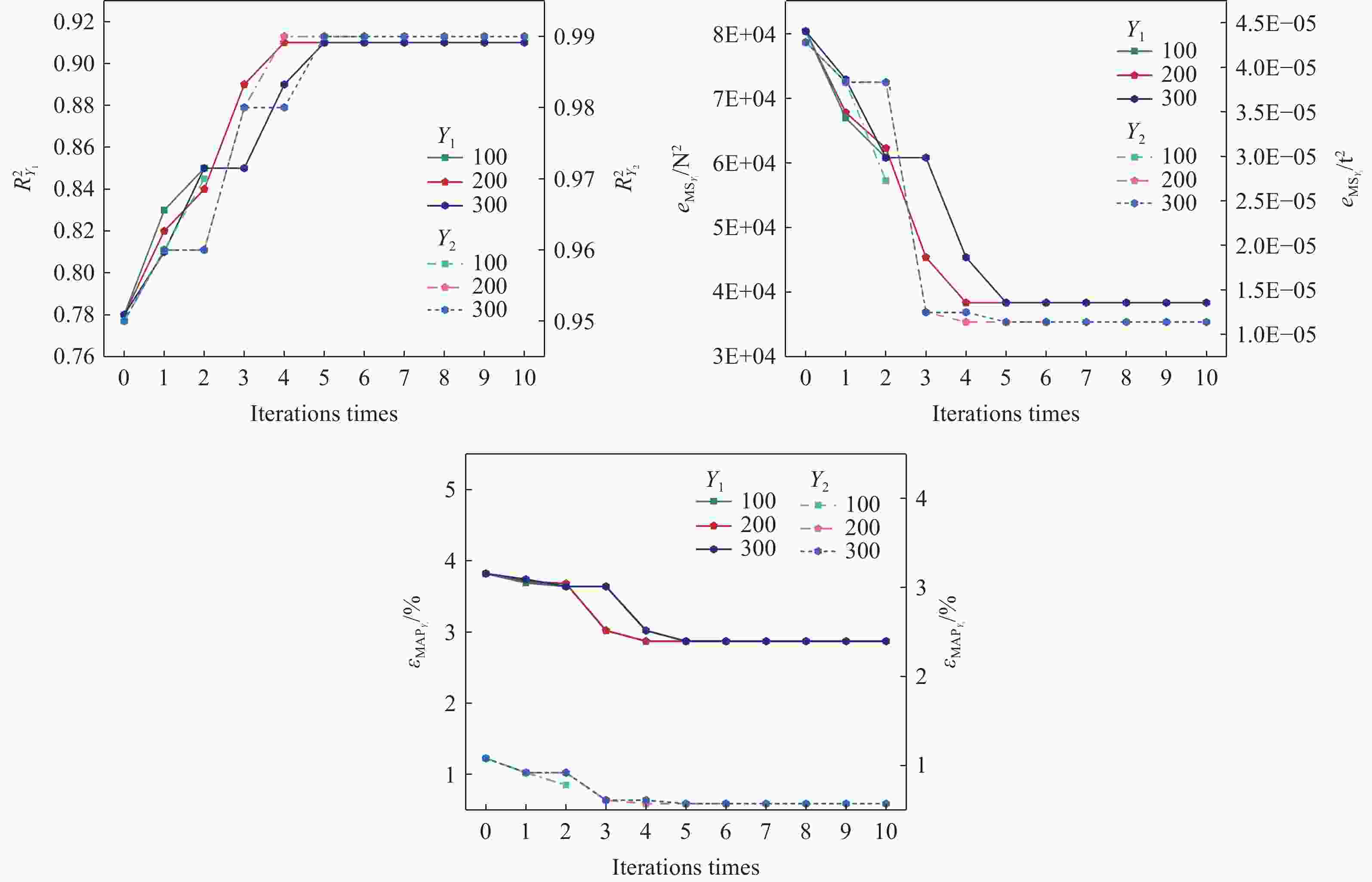
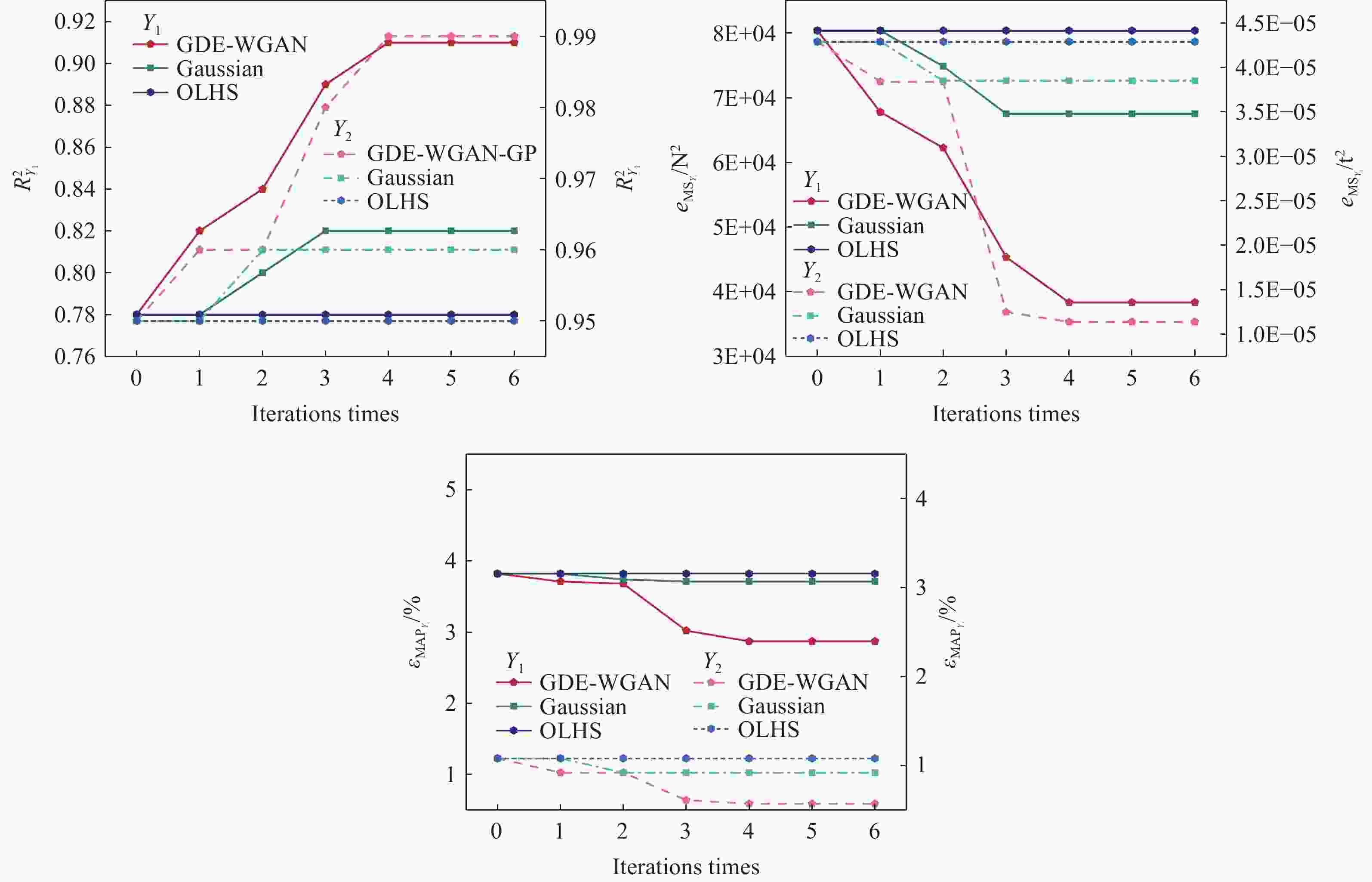
摘要: 针对车辆爆炸防护结构优化中数据来源匮乏、代理模型精度低、优化效率低和可靠性不足的问题,提出了一种数据增广方法结合半监督回归的数据驱动方法。通过改进生成对抗网络(generative adversarial network,GAN),提出了Gaussian密度估算-对抗生成网络(Gaussian density estimation-Wasserstein generative adversarial network,GDE-W-GAN);分别采用GDE-WGAN、Gaussian模型、最优拉丁超立方方法,并结合半监督支持向量回归,对原始数据集进行增广,通过对比不同方法的数据增广效果,验证了GDE-WGAN的可行性和优越性;通过多目标优化分别求解数据增广前后代理模型的最优解,并通过有限元仿真验证比较。结果表明,GDE-WGAN结合半监督回归的方法可以显著提升代理模型的拟合精度,2个输出变量的决定系数R2分别提升了16.7%和4.2%。结合半监督回归的数据增广优化方法在准确性和优化效率方面具有较大提升。Abstract: In order to address the needs of modern combat vehicles for both personnel protection and lightweight design, optimizing their blast-resistant structures is necessary. Due to the high cost of physical experiments, finite element simulation has been commonly used instead. However, simulations of explosion and vehicle responses require extensive computational resources and incur high computational costs, leading to limited data availability for the optimization of explosion-proof structures. Since structural optimization demands sufficient data support, larger amount of valid data can improve the accuracy of the surrogate model and the precision of the optimal solution, yielding better optimization results. To overcome these challenges, a data-driven optimization method for vehicle’s explosion-proof structures was proposed, integrating data augmentation and semi-supervised regression. To address the limitations of generative adversarial networks (GANs) in handling numerical data, an improved model, a Gaussian density estimation-Wasserstein generative adversarial network (GDE-WGAN), was developed by modifying both the generator and discriminator of the WGAN model, a variant of the GANs. The feasibility of the proposed method was demonstrated based on the principle of information gain. The data generated by the GDE-WGAN were incorporated into a self-training framework, where an adaptive confidence assessment mechanism dynamically adjusted the way that the semi-supervised support vector regression model utilizes the generated data. The feasibility and superiority of the method were validated by comparing the enhanced performance of the semi-supervised regression model using different numerical data expansion techniques. Finally, multi-objective optimization was performed to obtain the optimal solutions of the data-augmented semi-supervised regression model and the initial model, followed by verification and comparison with finite element simulation results. It shows that the GDE-WGAN significantly enhances the performance of the semi-supervised regression model, and the generated data exhibit greater randomness and diversity through the network structure of the GANs, which benefits semi-supervised learning. When handling semi-supervised regression for high-dimensional nonlinear numerical data, both global and local data distribution similarities play a crucial role. Furthermore, finite element simulations indicate that the improved model predicts results more accurately than the initial model and achieves superior optimization outcomes.
-
表 1 最优拉丁超立方实验采样样本
Table 1. Optimal Latin hypercube experimental sampling samples
No. X1/mm X2/mm X3/mm X4/mm X5/mm 1 5.240 9.380 3.340 4.720 0.531 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 15 5.450 5.860 3.000 6.620 0.345 16 6.90 10.000 5.760 6.100 0.738 ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· ··· 29 9.590 8.970 4.550 4.210 0.593 30 8.140 6.280 5.590 7.830 0.262 表 2 传统优化流程代理模型性能指标
Table 2. Performance metrics of the surrogate model in the traditional optimization process
预测目标 R2 eMS εMAP 假人左胫骨力 0.61 168365 N20.0557 爆炸防护结构总体质量 0.87 9.74×10−5 t2 0.0199 表 3 生成器和判别器网络的结构参数
Table 3. Structure parameters for generator and discriminator networks
模型类型 层类型 输入维度 输出维度 激活函数 生成器 全连接层 105 128 无 128 256 ReLU 256 128 ReLU 128 5 无 判别器 全连接层 11 512 无 512 256 ReLU 128 64 ReLU 64 1 Sigmoid 表 4 GDE-WGAN超参数设定
Table 4. GDE-WGAN hyperparameter settings
超参数 对应符号 赋值 总训练轮数 nepoches 10000 批大小 B 64 判别器更新次数 ncritic 5 权重剪切限制 λgp 5 Adam优化学习率 c 0.01 Adam优化器指数衰减率 (β1, β2) (0.5, 0.9) 特征标准差 f(G(z)) 特征范围的$ \dfrac{1}{4} $ 表 5 初始模型与最终模型预测帕累托最优解及对应优化结构参数
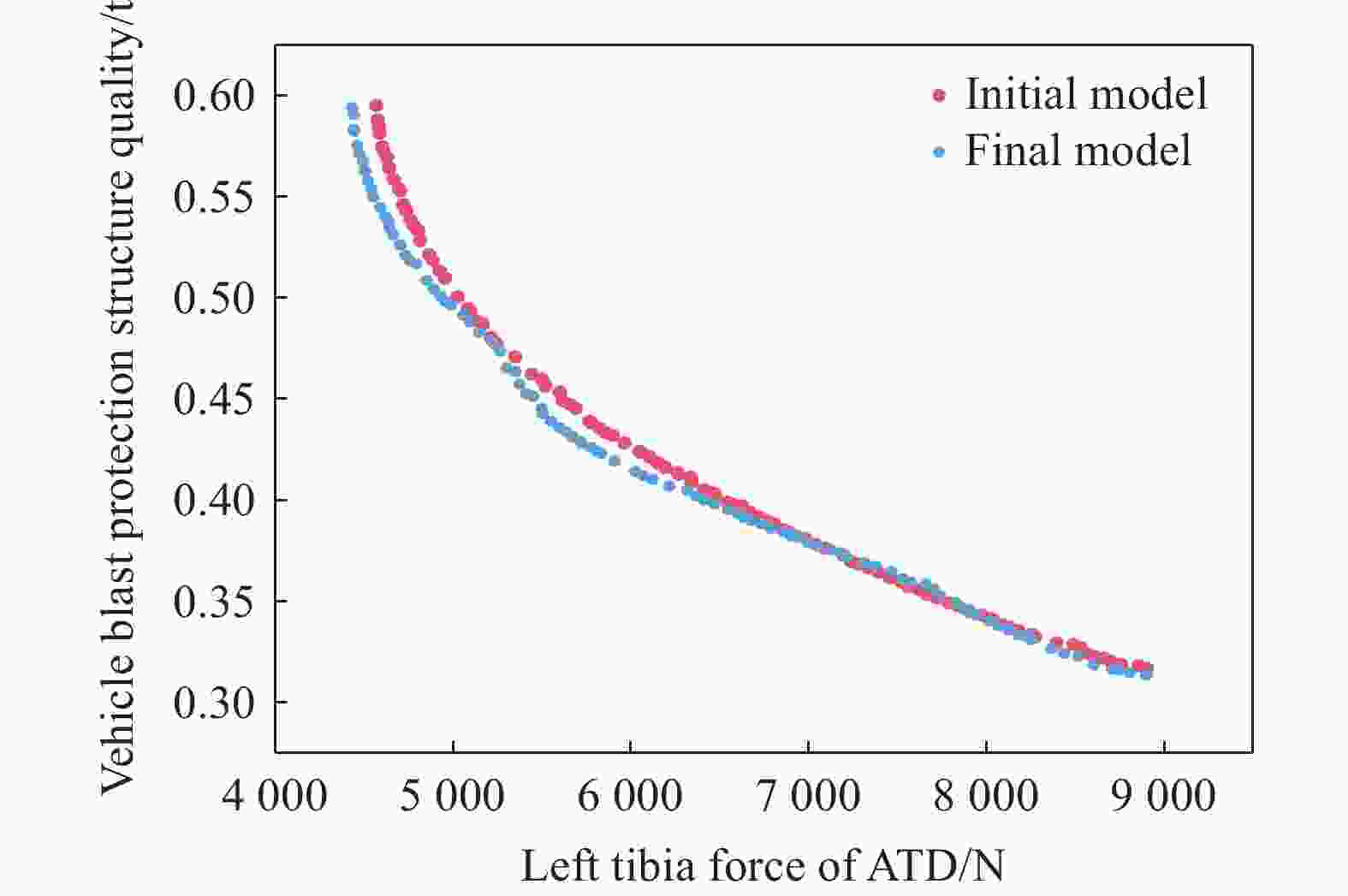
Table 5. Pareto optimal solutions predicted by the initial and final models and corresponding optimized structural parameters
模型 X1/mm X2/mm X3/mm X4/mm X5/mm $ {Y}_{1} $/N $ {Y}_{2} $/t 初始模型 9.7 8 5.7 5.6 0.6 4574.1 0.595 最终模型 9.9 7.7 5.6 5.1 0.57 4438 0.593 表 6 初始模型和最终模型预测结果与仿真计算结果的对比
Table 6. Comparison of errors between predicted results of the initial and final models and simulation results
模型 Y1 Y2 预测
结果/N计算
结果/N误差/% 预测
结果/t计算
结果/t误差/% 初始模型 4574.1 5174 11.6 0.595 0.566 5.12 最终模型 4438 4756 6.7 0.593 0.574 3.31 -
[1] 吴凯. 基于不确定性的车辆底部防护结构优化设计 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2021: 1–14. DOI: 10.27241/d.cnki.gnjgu.2021.001134.WU K, Uncertainty-based design optimization for vehicle bottom protection structures [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2021: 1–14. DOI: 10.27241/d.cnki.gnjgu.2021.001134. [2] 陈学军, 杨学文, 张永珍. 地雷爆炸作用下装甲车辆底部防护结构优化仿真研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2014, 35(S2): 353–357.CHEN X J, YANG X W, ZHANG Y Z. A simulation study of structural optimization of armor vehicle bottom protection under the landmine explosion [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2014, 35(S2): 353–357. [3] ŚWIERCZEWSKI M, SŁAWIŃSKI G. Modelling and numerical analysis of explosion under the wheel of light armoured military vehicle [J]. Engineering Transactions, 2017, 65(4): 587–599. DOI: 10.24423/engtrans.793.2017. [4] YANG Y, LIOU W W, SHENG J, et al. Shock wave impact simulation of a vehicle occupant using fluid/structure/dynamics interactions [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2013, 52: 11–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2012.09.002. [5] 方海涛. 车辆底部波纹抗爆炸防护结构防护机理及优化设计研究 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2019: 3–9. DOI: 10.27241/d.cnki.gnjgu.2019.000745.FANG H T, Research on the protection mechanism and optimized design of corrugated anti-explosion protection structures at the vehicle undercarriage [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2019: 3–9. DOI: 10.27241/d.cnki.gnjgu.2019.000745. [6] CONG M, ZHOU Y B, ZHANG M, et al. Design and optimization of multi-V hulls of light armoured vehicles under blast loads [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 168: 108311. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2021.108311. [7] 李明星, 王显会, 周云波, 等. 基于神经网络的车辆抗冲击防护组件优化 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(2): 024203-1-024203-9. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0055.LI M X, WANG X H, ZHOU Y B, et al. Research on optimization of vehicle anti-shock protection components based on neural network[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(2): 024203-1-024203-9. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0055 [8] 徐克非, 王显会, 周云波, 等. 爆炸环境下车辆底部V型结构多参数优化研究 [J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2020, 41(1): 28–32,37. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2020.01.006.XU K F, WANG X H, ZHOU Y B, et al. Multi-parameter optimization of underbody V-shaped structure under explosion load [J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2020, 41(1): 28–32,37. DOI: 10.11809/bqzbgcxb2020.01.006. [9] XIAO B, ZHANG Y X, CHEN Y, et al. A semi-supervised learning detection method for vision-based monitoring of construction sites by integrating teacher-student networks and data augmentation [J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2021, 50: 101372. DOI: 10.1016/j.aei.2021.101372. [10] ZHOU B, DUAN H R, WU Q W, et al. Short-term prediction of wind power and its ramp events based on semi-supervised generative adversarial network [J]. International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems, 2021, 125: 106411. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijepes.2020.106411. [11] MU G Q, CHEN J. Developing a conditional variational autoencoder to guide spectral data augmentation for calibration modeling [J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 2501008. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3142060. [12] ZHANG X, ZOU Y Y, LI S Y. Semi-supervised generative adversarial network with guaranteed safeness for industrial quality prediction [J]. Computers and Chemical Engineering, 2021, 153: 107418. DOI: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2021.107418. [13] NJIMA W, BAZZI A, CHAFII M. DNN-based indoor localization under limited dataset using GANs and semi-supervised learning [J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 69896–69909. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3187837. [14] 马琳琪, 李校男, 晁涛, 等. 基于高斯数据增广的小样本数据无人机编队类型抗扰识别 [J]. 无人系统技术, 2023, 6(6): 42–50. DOI: 10.19942/j.issn.2096-5915.2023.06.59.MA L Q, LI X N, CHAO T, et al. Anti-disturbance identification of UAV formation types based on Gaussian data augmentation with small sample data [J]. Unmanned Systems Technology, 2023, 6(6): 42–50. DOI: 10.19942/j.issn.2096-5915.2023.06.59. [15] WU B Y, MENG D L, ZHAO H X. Semi-supervised learning for seismic impedance inversion using generative adversarial networks [J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(5): 909. DOI: 10.3390/rs13050909. [16] SHI X M, GU L J, LI X F, et al. Automated spectral transfer learning strategy for semi-supervised regression on Chlorophyll: a retrievals with Sentinel-2 imagery [J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2024, 17(1): 2313856. DOI: 10.1080/17538947.2024.2313856. [17] LI Y L, LIAO Y L, SUN Z Y, et al. Semi-supervised contrastive regression for pharmaceutical processes [J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 238: 121974. DOI: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121974. [18] LI Z, JIN H P, DONG S L, et al. Semi-supervised ensemble support vector regression based soft sensor for key quality variable estimation of nonlinear industrial processes with limited labeled data [J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2022, 179: 510–526. DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2022.01.026. [19] ZHENG J H, LIU Y X, LIU Y, et al. Semi-supervised process data regression and application based on latent factor analysis model [J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 2527511. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2023.3317484. [20] CALDERON-RAMIREZ S, OALA L, TORRENTS-BARRENA J, et al. Dataset similarity to assess semisupervised learning under distribution mismatch between the labeled and unlabeled datasets [J]. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 4(2): 282–291. DOI: 10.1109/TAI.2022.3168804. [21] ZHENG Q C, WU M Y, SUN X W, et al. Combined Bayesian and error assessment-based model calibration method for vehicle under-belly blast with uncertainty [J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2022, 65(5): 136. DOI: 10.1007/s00158-022-03226-9. [22] SHORTEN C, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning [J]. Journal of Big Data, 2019, 6(1): 60. DOI: 10.1186/s40537-019-0197-0. [23] SHORTEN C, KHOSHGOFTAAR T M, FURHT B. Text data augmentation for deep learning [J]. Journal of Big Data, 2021, 8(1): 101. DOI: 10.1186/s40537-021-00492-0. [24] NANNI L, MAGUOLO G, PACI M. Data augmentation approaches for improving animal audio classification [J]. Ecological Informatics, 2020, 57: 101084. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoinf.2020.101084. [25] 王宁. 生成对抗网络地震数据增强方法研究 [D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021: 47–59. DOI: 10.27643/d.cnki.gsybu.2021.000536.WANG N, Research on interpolation method of seismic data based on generative adversarial network [D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2021: 47–59. DOI: 10.27643/d.cnki.gsybu.2021.000536. [26] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks [J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139–144. DOI: 10.1145/3422622. [27] ZHOU Z H, LI M. Semi-supervised regression with co-training [C]//Proceedings of the 19th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Edinburgh: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc. , 2005: 908–913. [28] 秦世强, 杨睿, 苏晟. 基于自训练半监督神经网络的结构损伤识别 [J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2024, 44(2): 38–49. DOI: 10.13197/j.eeed.2024.0205.QIN S Q, YANG R, SU M. Structural damage identification based on self-training semi-supervised neural network [J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 2024, 44(2): 38–49. DOI: 10.13197/j.eeed.2024.0205. [29] 丁世飞, 孙玉婷, 梁志贞, 等. 弱监督场景下的支持向量机算法综述 [J]. 计算机学报, 2024, 47(5): 987–1009. DOI: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.00987.DING S F, SUN Y T, LIANG Z Z, et al. Survey on support vector machine algorithms in weakly supervised scenarios [J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2024, 47(5): 987–1009. DOI: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2024.00987. [30] MEY A, LOOG M. Improved generalization in semi-supervised learning: a survey of theoretical results [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(4): 4747–4767. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3198175. [31] 刘建伟, 刘媛, 罗雄麟. 半监督学习方法 [J]. 计算机学报, 2015, 38(8): 1592–1617. DOI: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01592.LIU J W, LIU Y, LUO X L. Semi-supervised learning methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2015, 38(8): 1592–1617. DOI: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2015.01592. [32] STORN R, PRICE K. Differential evolution: a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces [J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 1997, 11(4): 341–359. DOI: 10.1023/A:1008202821328. [33] SLOWIK A, KWASNICKA H. Evolutionary algorithms and their applications to engineering problems [J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(16): 12363–12379. DOI: 10.1007/s00521-020-04832-8. [34] 魏然, 王显会, 周云波, 等. 帕累托最优在车辆底部防护结构设计中的应用研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2015, 36(6): 1061–1066. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.06.014.WEI R, WANG X, ZHOU Y, et al. Application of pareto optimality in protective structure design of vehicle underbody [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2015, 36(6): 1061–1066. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2015.06.014. [35] 朱孙科, 陈历, 倪颖倩, 等. 基于NSGA-Ⅱ的复合材料防撞梁碰撞损伤多目标优化 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2024, 31(2): 173–181. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2024.02.022.ZHU J K, CHEN L, NI Y Q, et al. Multi-objective optimization of collision damage of reinforced plastic anti-collision beams based on NSGA-Ⅱ [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2024, 31(2): 173–181. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2024.02.022. -






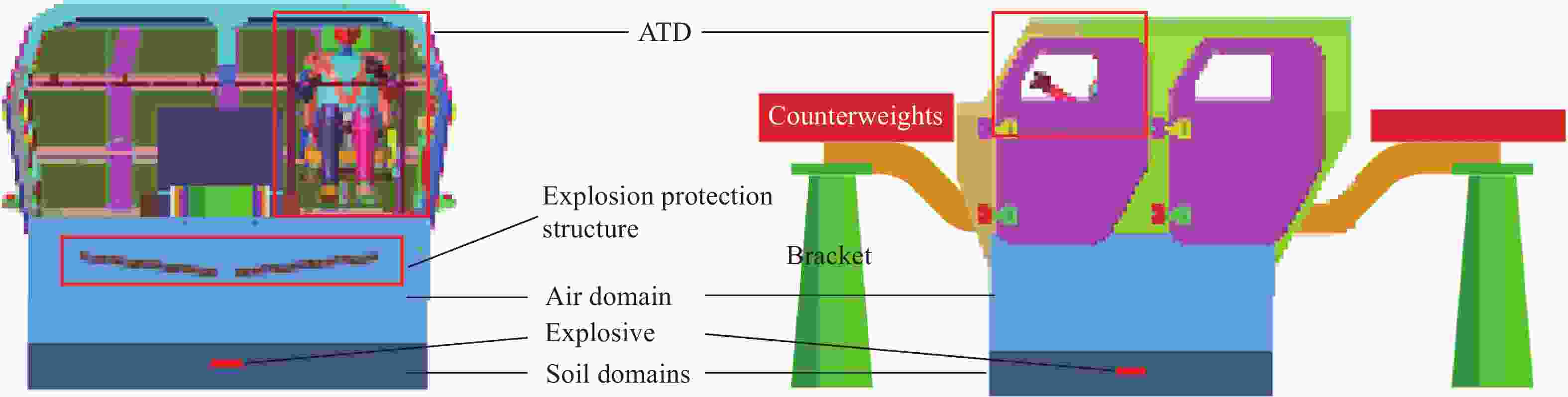
 下载:
下载: