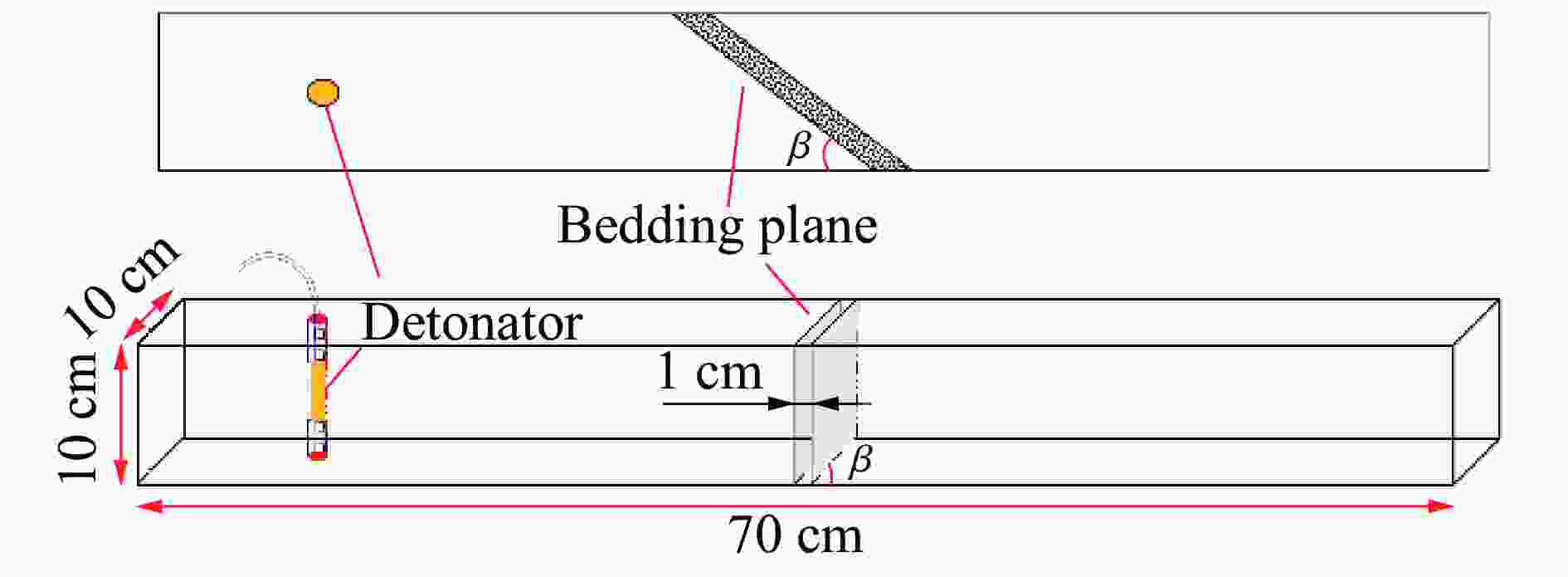
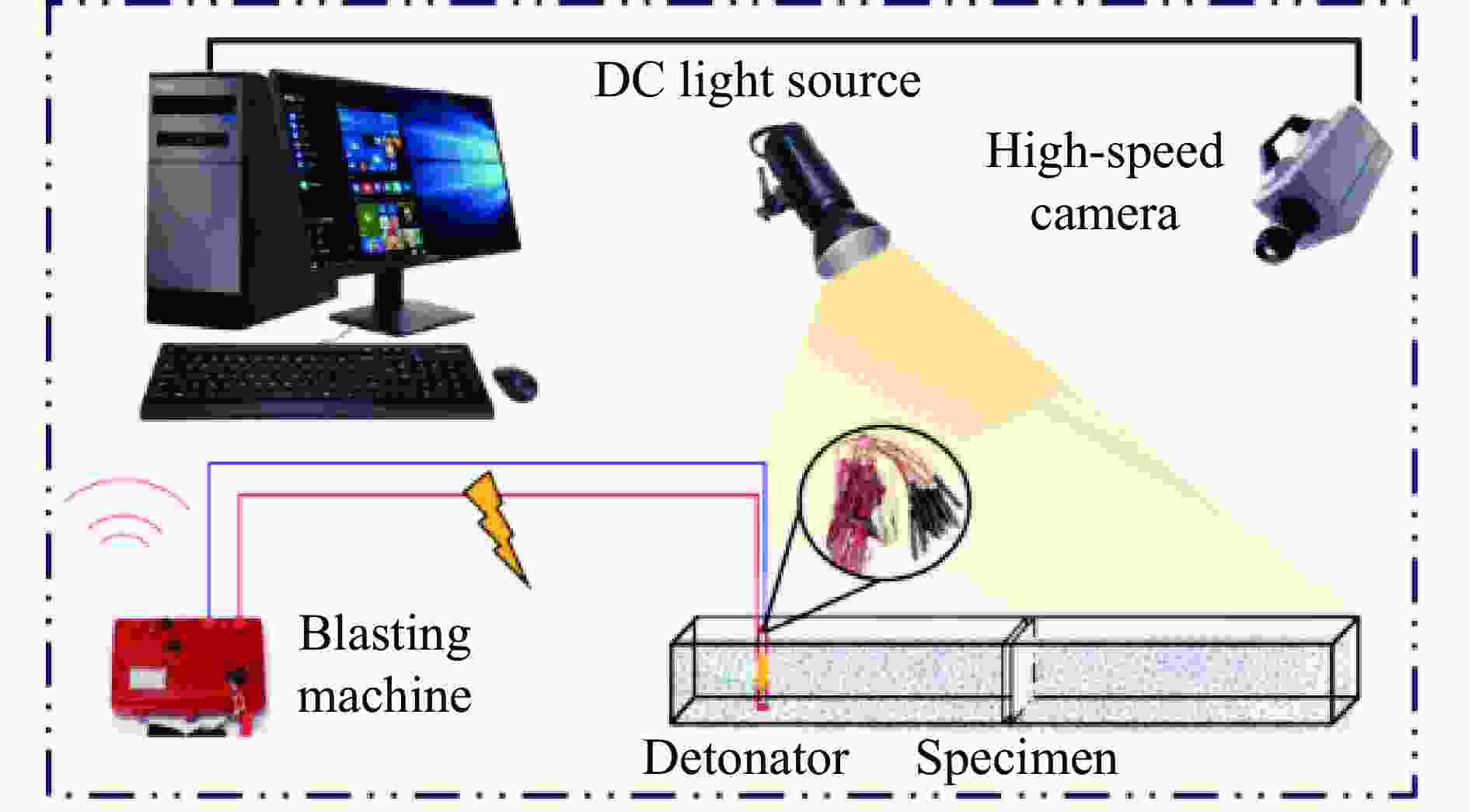
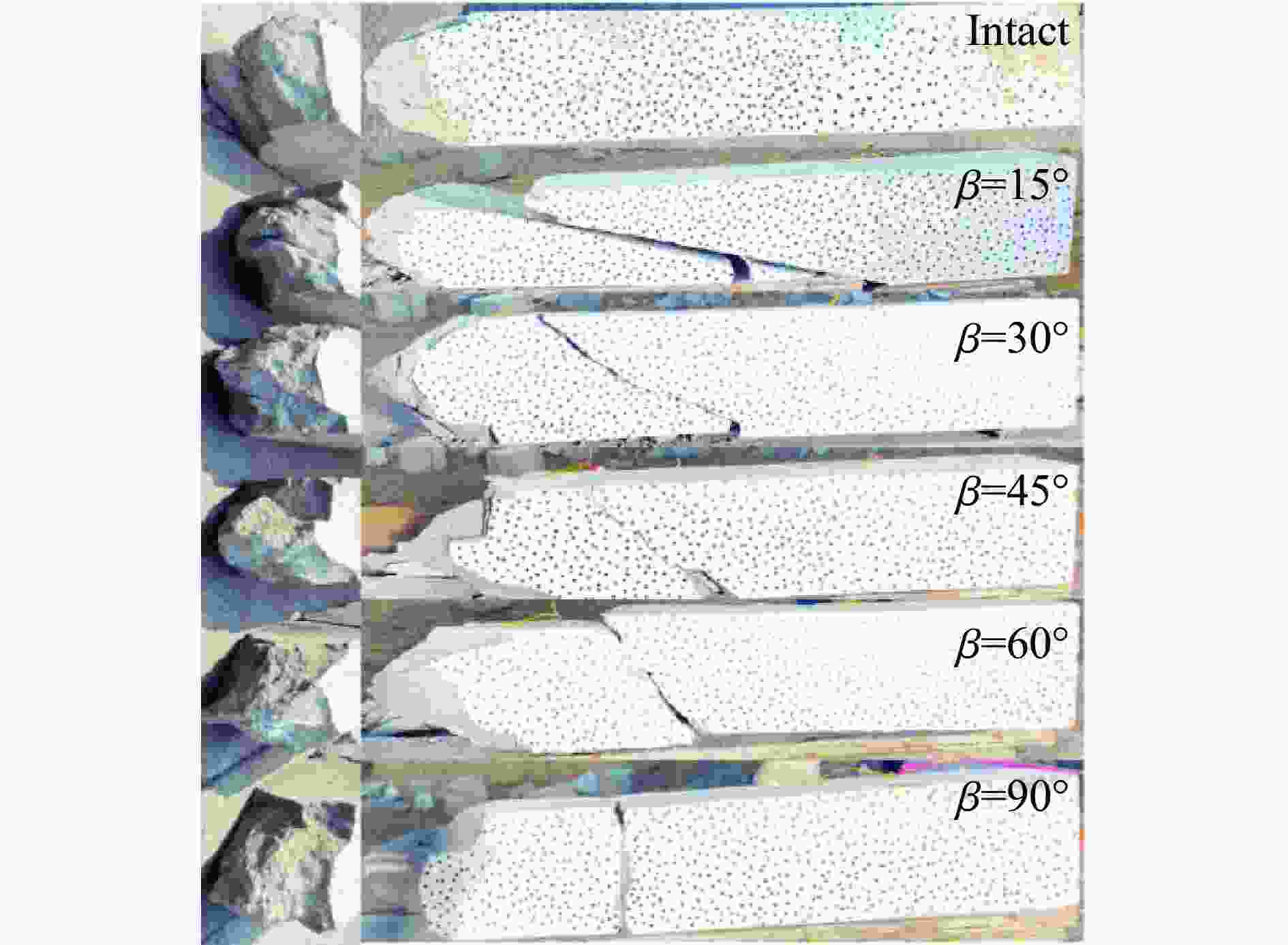
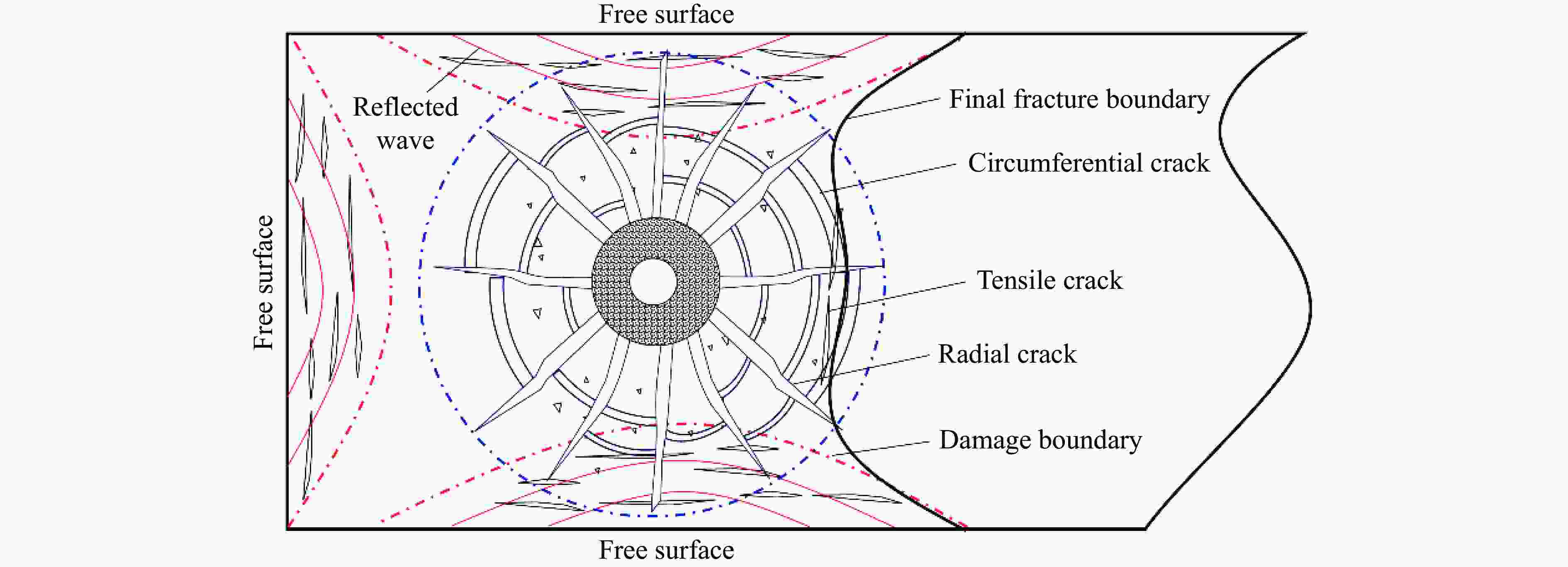
Influence of filled joints with different inclination angles on rock blasting fragmentation
-
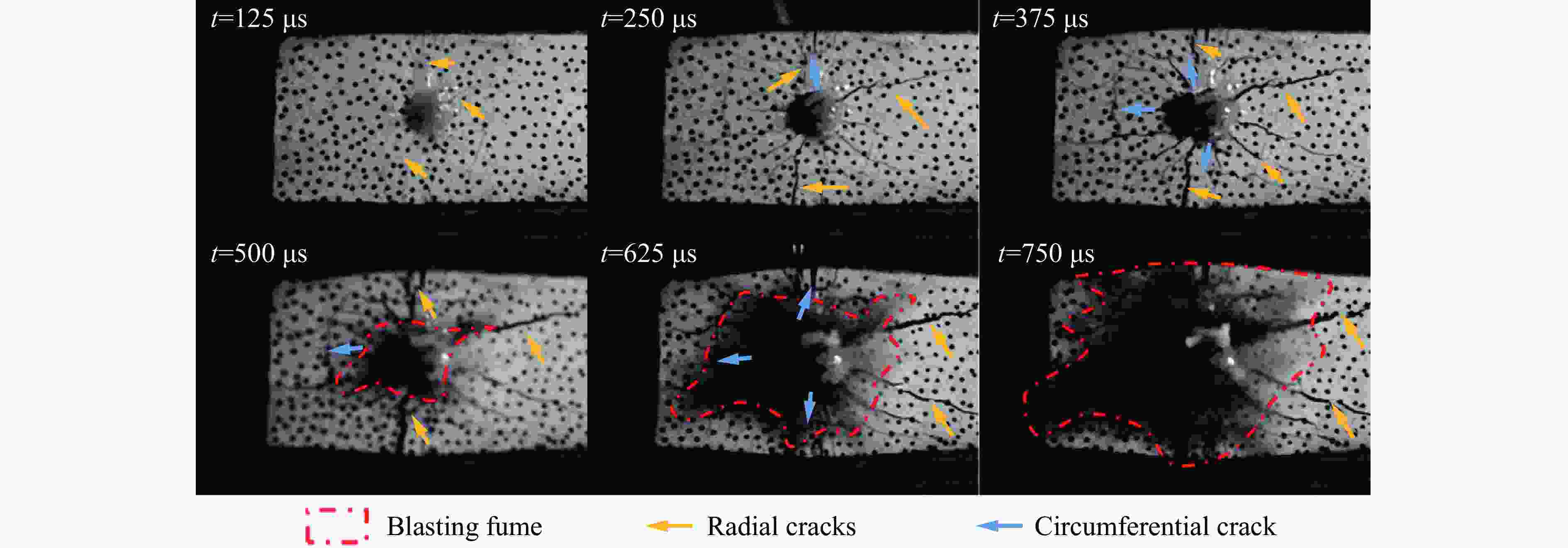
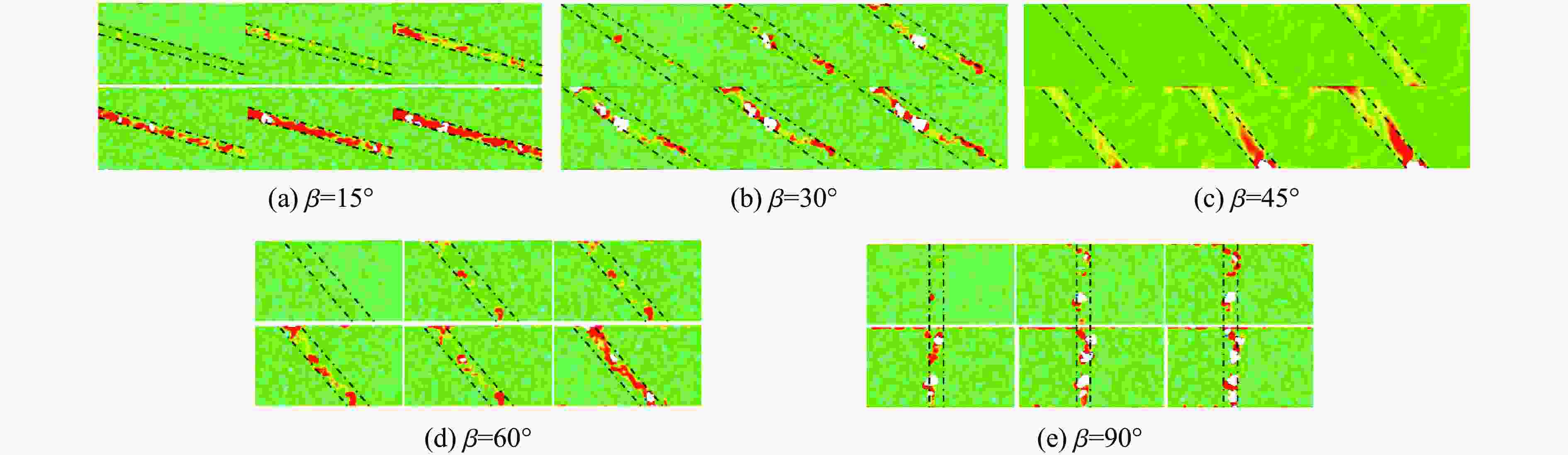
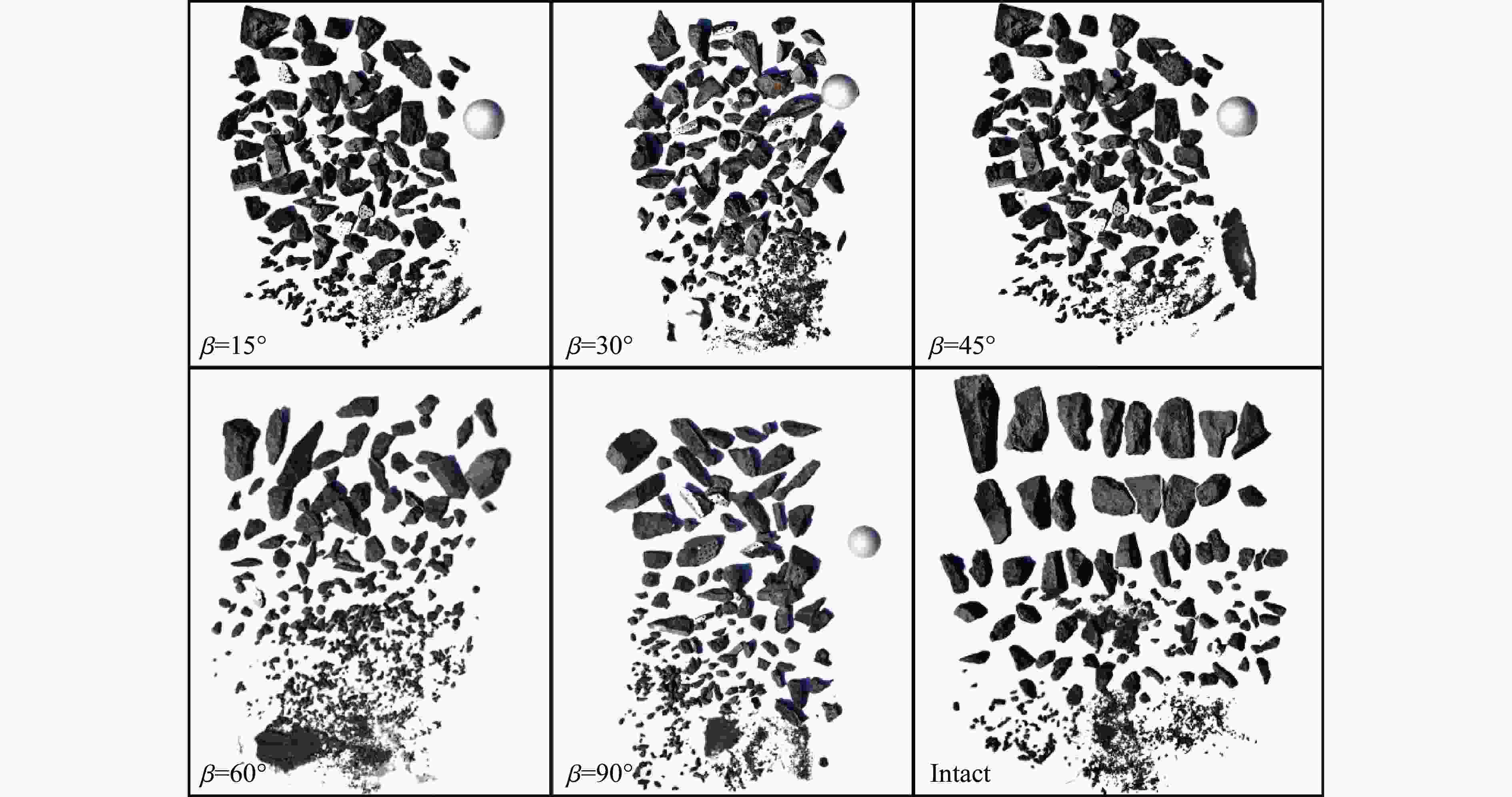
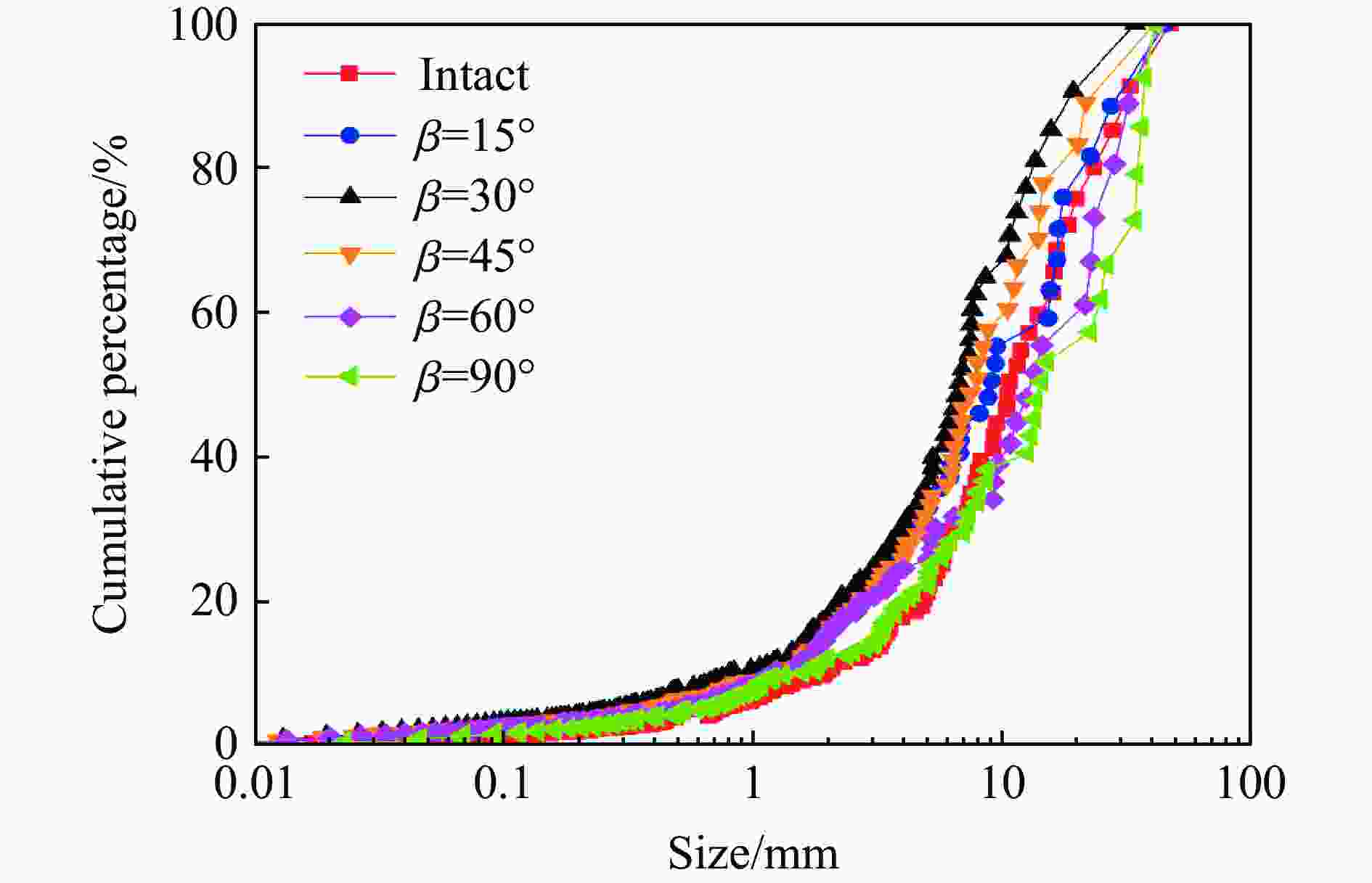
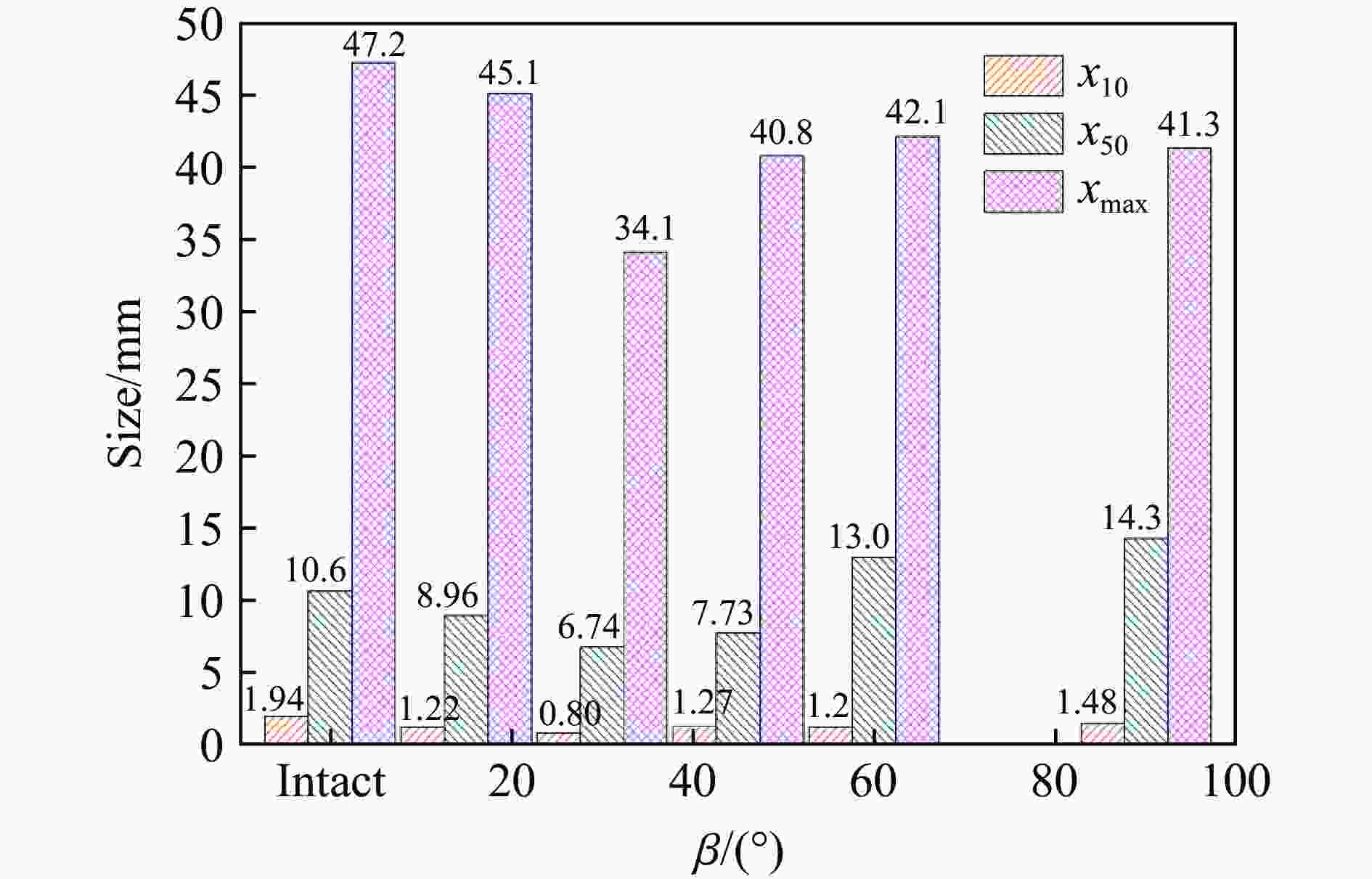
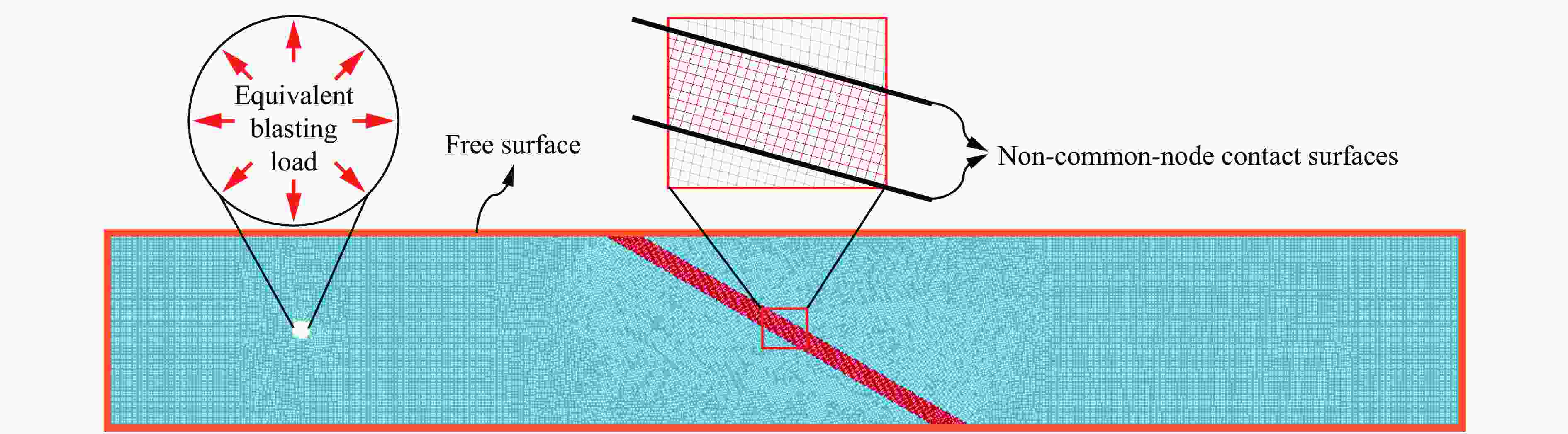
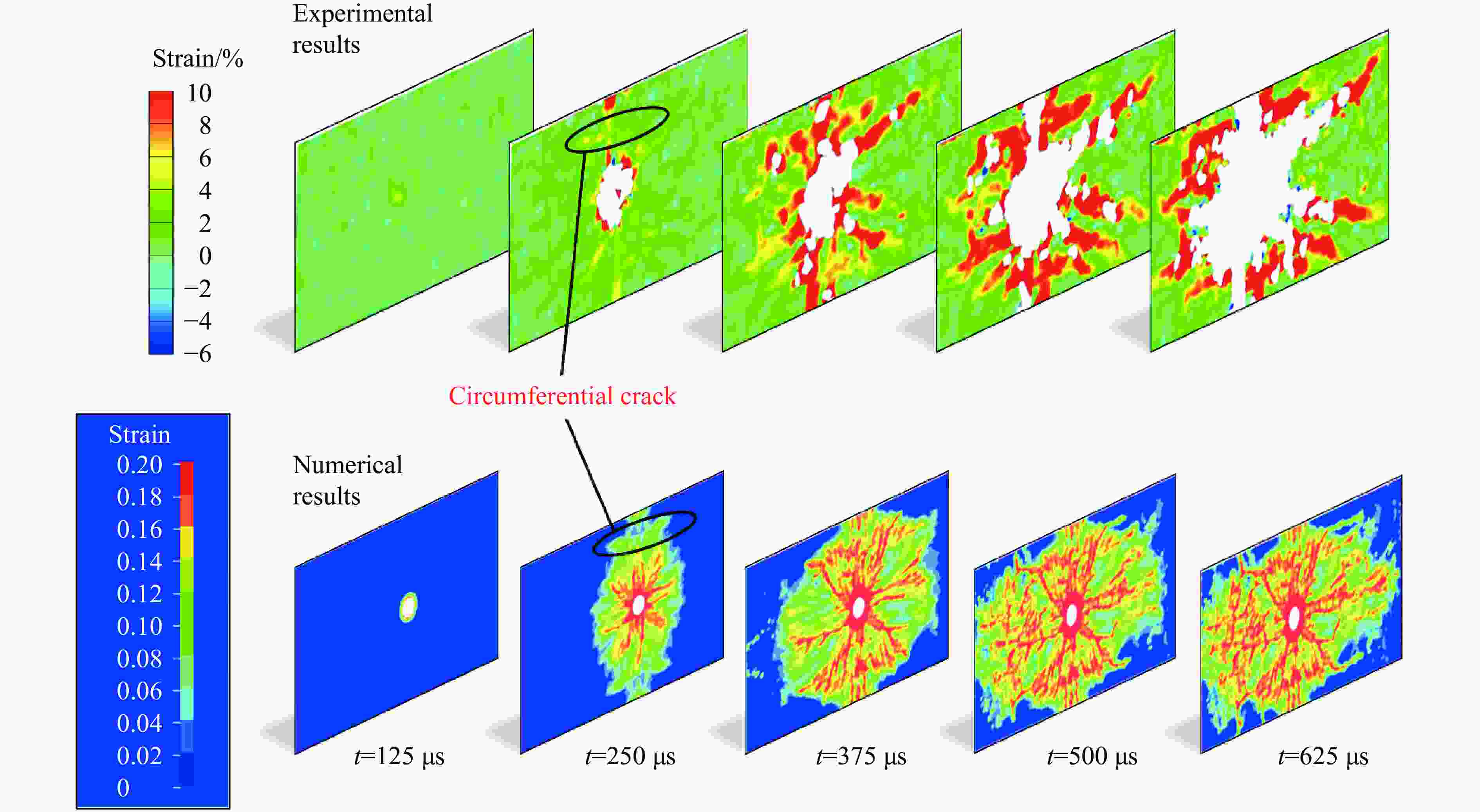
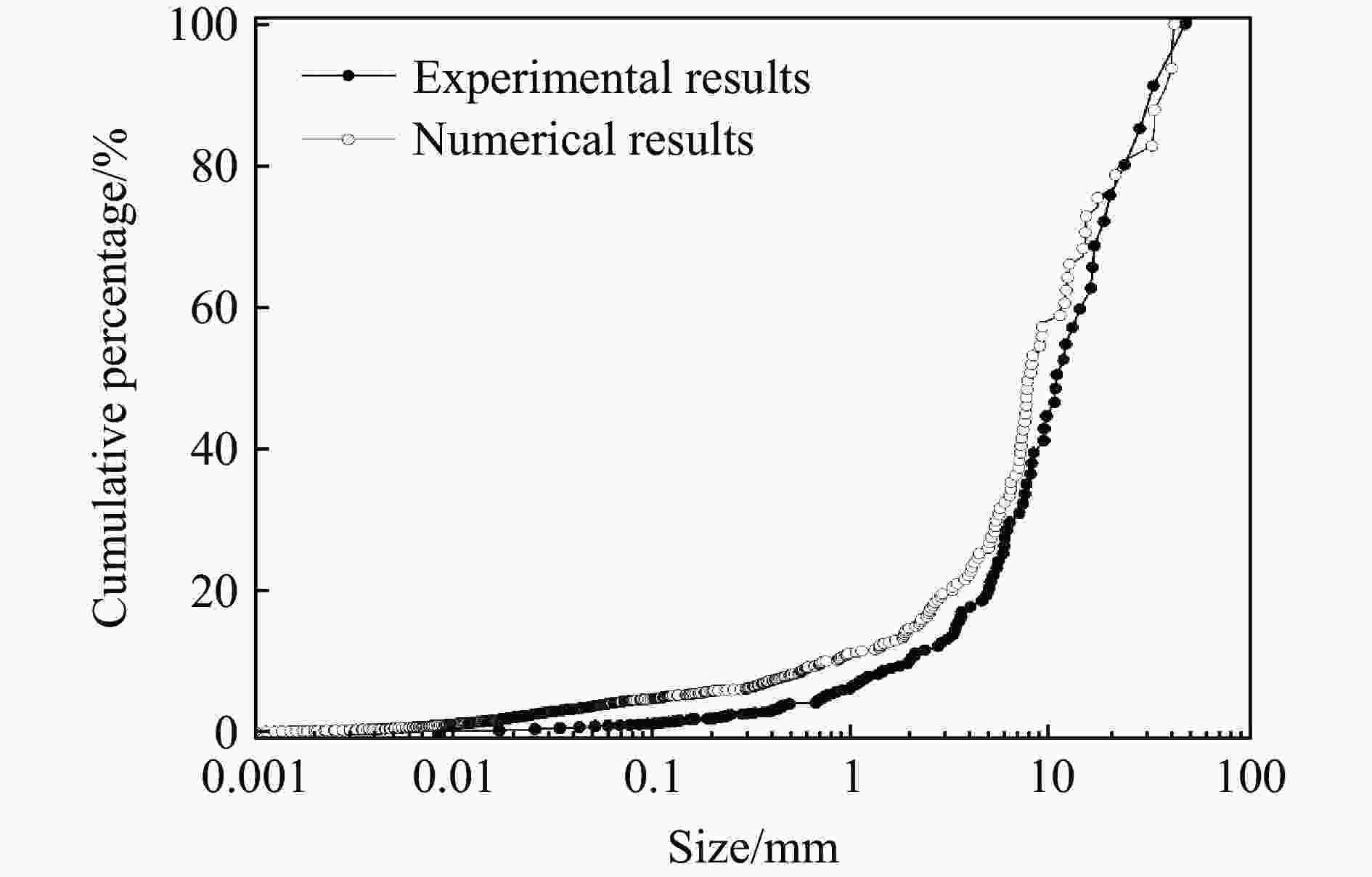
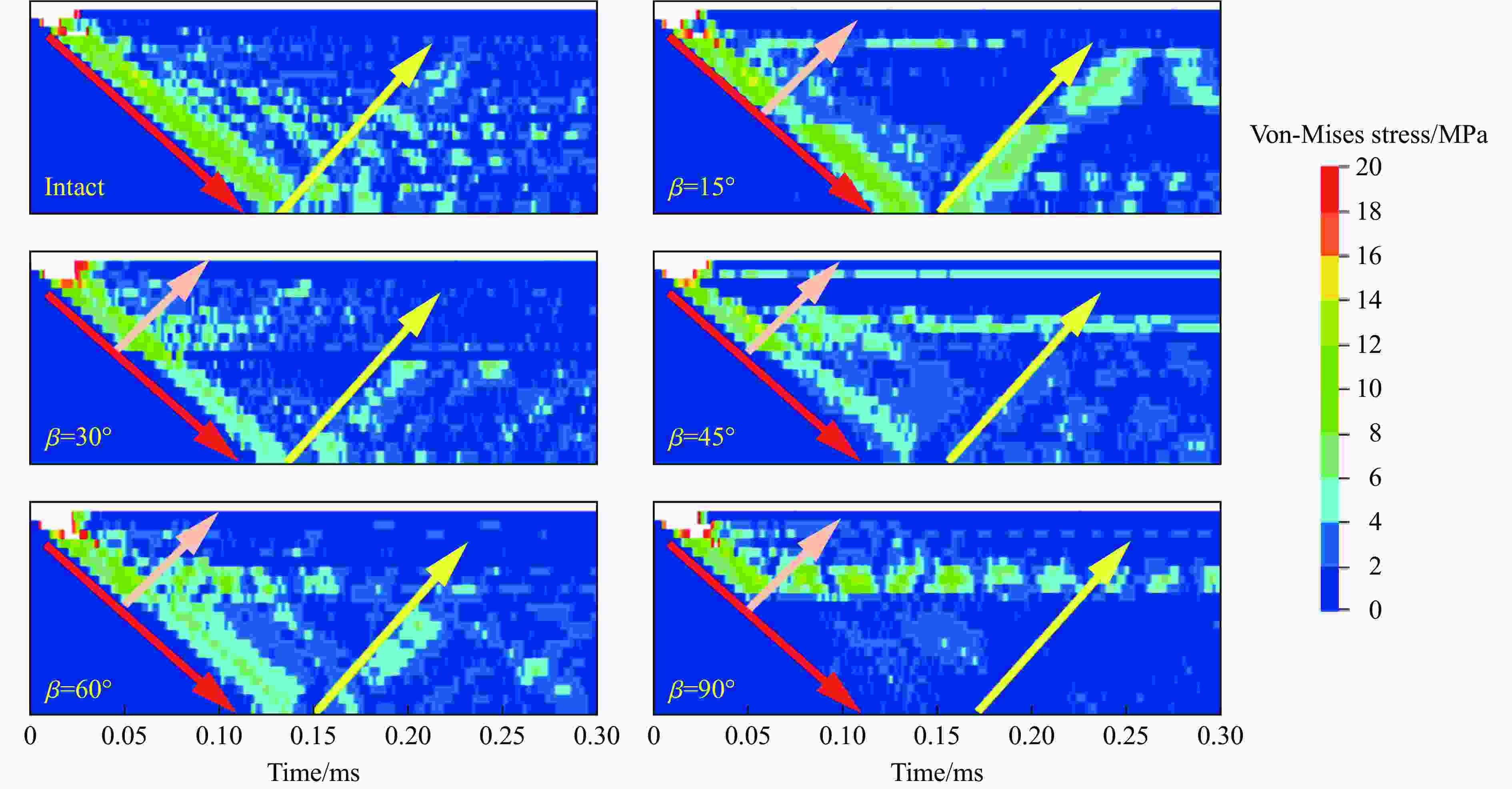
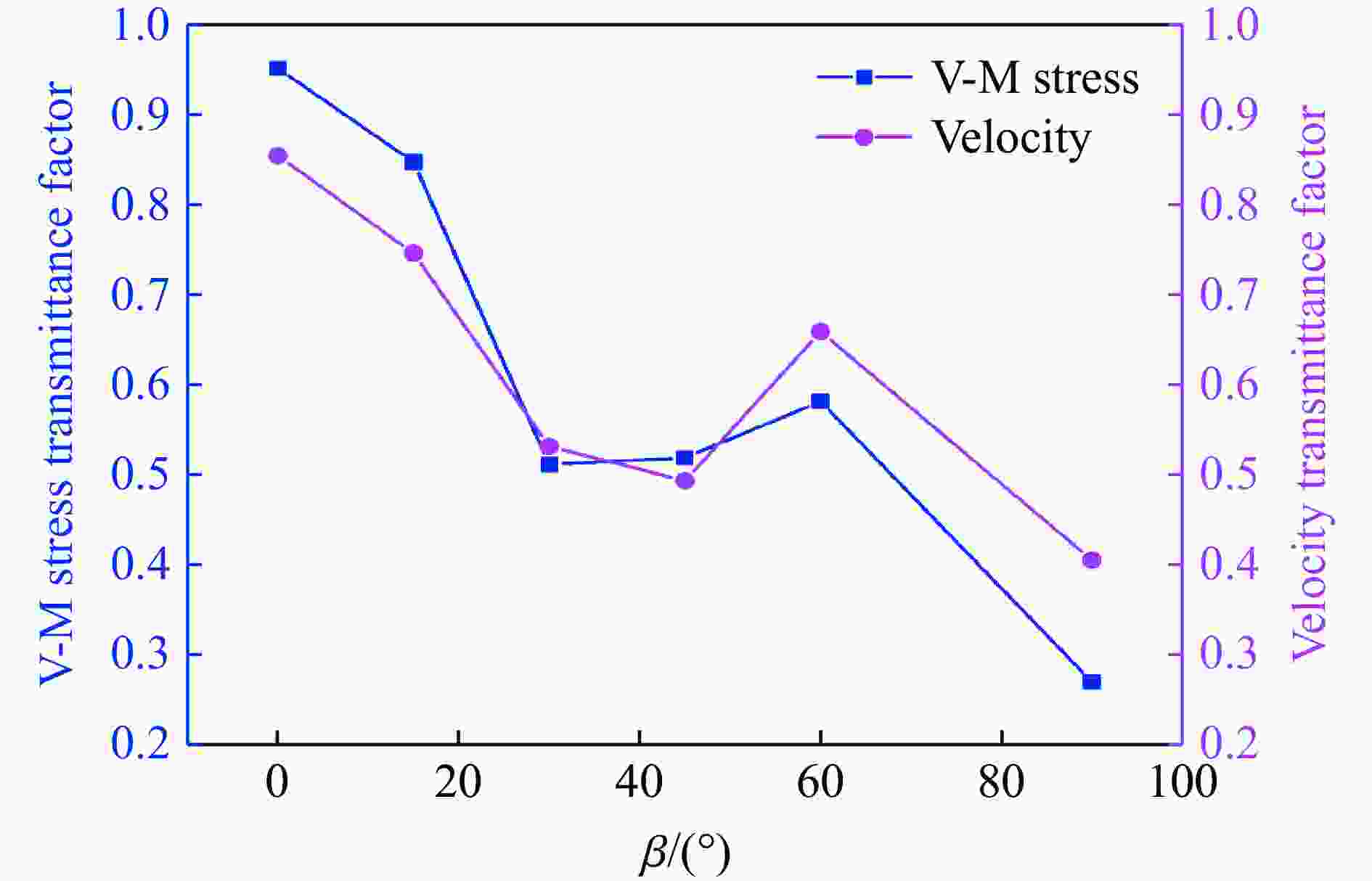
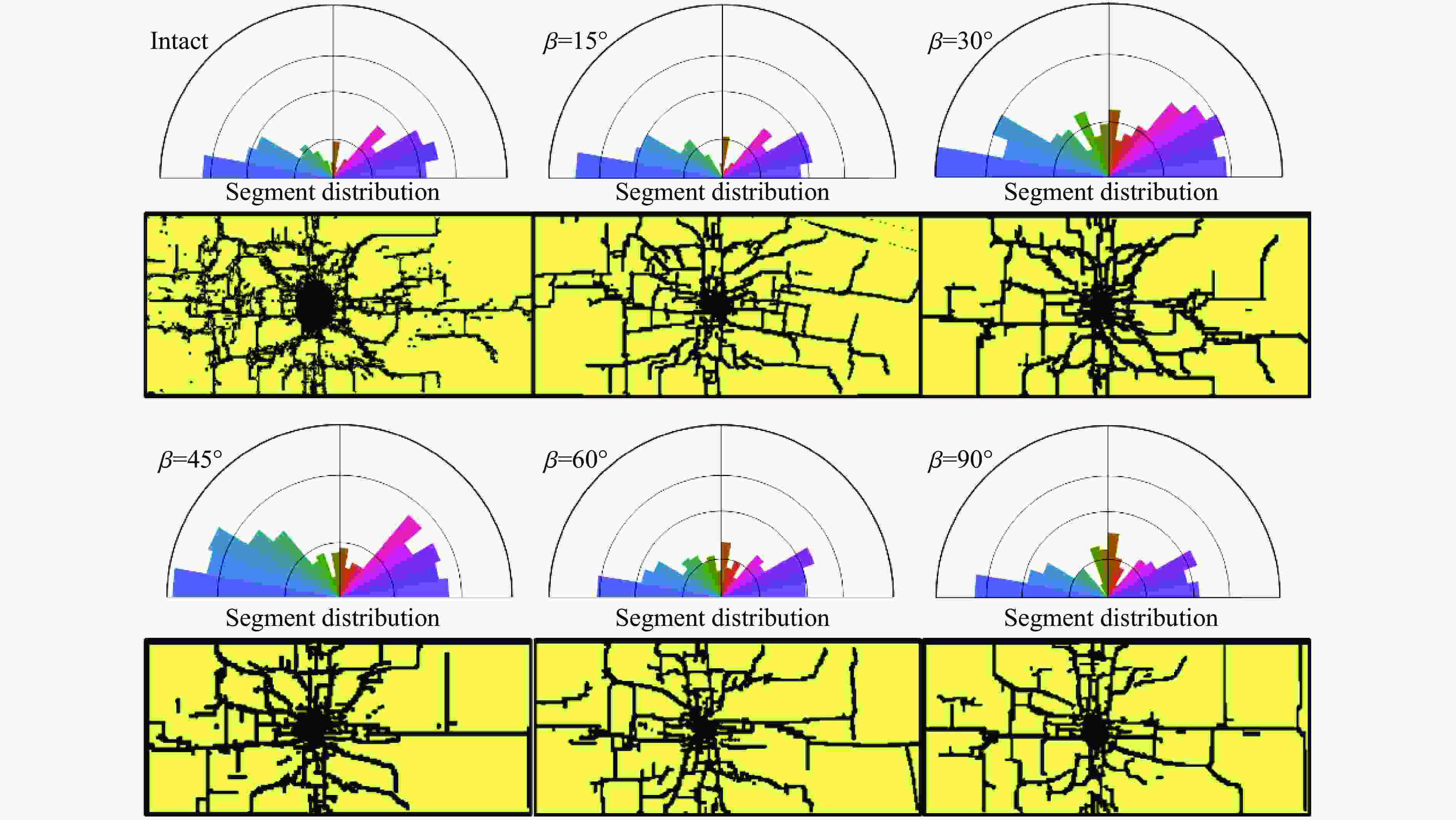
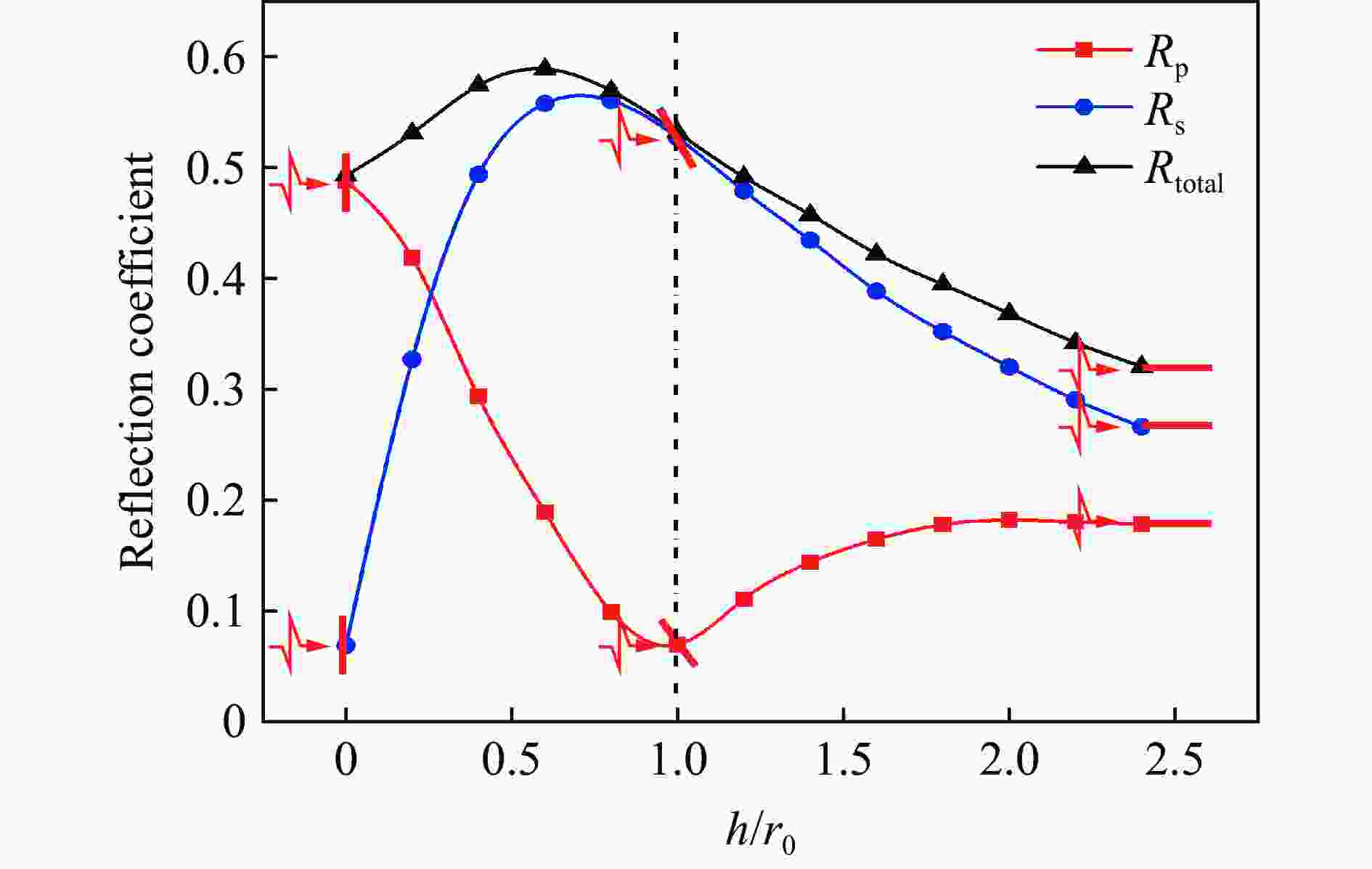
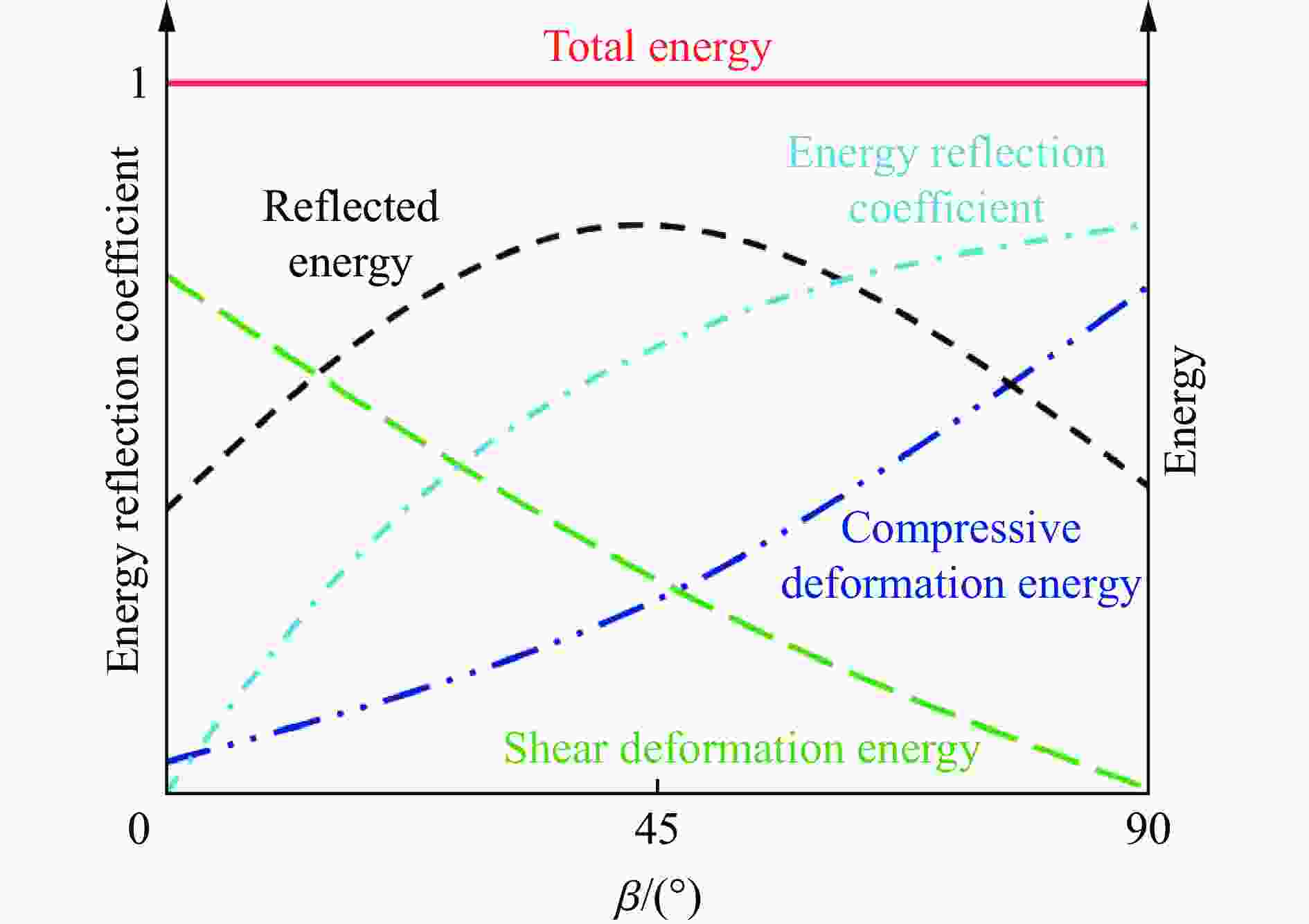
摘要: 为了理解节理与爆炸应力波之间的相互作用,并优化节理岩体的爆破参数,通过试验与数值模拟相结合的方式研究不同节理倾角对爆破块度的影响:采用一组含有不同角度节理的混凝土模型试样开展爆破试验,在试样竖直孔中装填雷管并爆破,使用高速摄像机记录试样爆破破碎过程,观测起爆后不同时刻节理面的动态响应;利用图像处理方法进行爆破块度提取,分析节理倾角对爆破块度的影响;采用LS-DYNA有限元数值模拟获得应力波的传播过程以及应变场的演变过程。试验与数值计算结果表明:节理对爆破块度分布及应力波传播有显著影响,该影响主要源于爆炸应力波在节理处的反射,这与节理的变形特性有关;随着节理倾角增大,爆破块度先减小后增大,节理中的有效应力和峰值质点振动速度透射总体呈下降趋势,但在45°至60°之间回升,其中45°左右为爆破最有利条件。数值裂纹网络重建和图像处理结果表明,随着节理倾角的增加,试样中产生的垂直裂纹增加,水平裂纹有所减少。Abstract: To understand the interaction between joints and blasting stresses and optimizing blasting parameters in jointed rock, the impact of different joint inclinations on blasting fragmentation was studied through a combination of tests and numerical simulations. In this study, a group of concrete model specimens containing joints with different angles was used in the blasting tests to investigate the effect of joint inclination on blast fragmentation. During tests, detonators were placed in vertical boreholes in the specimens and detonated, while high-speed camera was used to capture the fragmentation process. The dynamic responses of joint surfaces at different time intervals after detonation was observed, and blasting fragmentation distribution was extracted using image processing techniques. The effect of joint inclination on blasting fragmentation was analyzed. The propagation of stress waves and the evolution of strain fields within the specimens was obtained in finite element numerical simulations by using LS-DYNA. Experimental and numerical results indicated that the joints have a significant influence on the distribution of blasting fragmentation and the propagation of stress waves. The impact of the joints on the blasting performance was mainly attributed to the reflection of blasting waves from the joints, which was related to the deformation characteristics of the joints. With the increase of joint inclination, the blasting fragmentation initially decreased followed by an increase. The effective stress and peak particle velocity transmission in the joints decreased overall with the increase of joint inclination, but showed a rebound between 45° and 60°. This suggests approximately 45° is the most favorable condition for rock fragmentation under blasting. Moreover, the results obtained from numerical crack network reconstruction and image processing revealed that there was an upsurge in the occurrence of vertical cracks in the specimen as the joint inclination increased, while a decline was observed in the presence of horizontal cracks.
-
表 1 材料基本力学参数
Table 1. Basic mechanical parameters of materials
材料类型 ρ/(kg·m−3) fc/MPa ft/MPa E/GPa ν 混凝土 2162 43.85 2.19 20.7 0.23 石膏砂浆 1905 7.4 1.45 1.56 0.32 注:ρ为密度,fc为抗压强度,ft为抗拉强度,E为弹性模量,ν为泊松比. -
[1] LIU T T, DING L Y, ZHENG Y, et al. Calculating the attenuation of stress waves passing through an in situ stressed joint using a double nonlinear model [J]. Waves in Random and Complex Media, 2024, 34(6): 5056–5076. DOI: 10.1080/17455030.2021.2003477. [2] HUANG X L, QI S W, XIA K W, et al. Particle crushing of a filled fracture during compression and its effect on stress wave propagation [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2018, 123(7): 5559–5587. DOI: 10.1029/2018JB016001. [3] WANG Z L, KONIETZKY H, SHEN R F. Coupled finite element and discrete element method for underground blast in faulted rock masses [J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2009, 29(6): 939–945. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2008.11.002. [4] DENG X F, ZHU J B, CHEN S G, et al. Numerical study on tunnel damage subject to blast-induced shock wave in jointed rock masses [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2014, 43: 88–100. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2014.04.004. [5] DU J H, HUANG X L, YANG G X, et al. UDEC modelling on dynamic response of rock masses with joint stiffness weakening attributed to particle crushing of granular fillings [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2023, 56(3): 1823–1841. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-022-03181-3. [6] LI X F, LI H B, LI J C, et al. Research on transient wave propagation across nonlinear joints filled with granular materials [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2018, 51(8): 2373–2393. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-018-1471-8. [7] HAN Z Y, LI D Y, ZHOU T, et al. Experimental study of stress wave propagation and energy characteristics across rock specimens containing cemented mortar joint with various thicknesses [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 131: 104352. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104352. [8] CHAI L Z, CHAI S B, LI P, et al. Analysis of P-wave propagation in filled jointed rock mass with viscoelastic properties [J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2023, 9(1): 102. DOI: 10.1007/s40948-023-00642-z. [9] LI J C, MA G W. Analysis of blast wave interaction with a rock joint [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2010, 43(6): 777–787. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-009-0062-0. [10] LI J C, RONG L F, LI H B, et al. An SHPB test study on stress wave energy attenuation in jointed rock masses [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(2): 403–420. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-018-1586-y. [11] LI J C, LI N N, LI H B, et al. An SHPB test study on wave propagation across rock masses with different contact area ratios of joint [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 105: 109–116. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.12.011. [12] WANG W, HAO H, LI X, et al. Effects of a single open joint on energy transmission coefficients of stress waves with different waveforms [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2015, 48(5): 2157–2166.WANG W, HAO H, LI X, et al. Effects of a single open joint on energy transmission coefficients of stress waves with different waveforms [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2015, 48(5): 2157–2166. [13] JIANG X D, XUE Y G, KONG F M, et al. Dynamic responses and damage mechanism of rock with discontinuity subjected to confining stresses and blasting loads [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 172: 104404. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104404. [14] YANG R S, DING C X, YANG L Y, et al. Model experiment on dynamic behavior of jointed rock mass under blasting at high-stress conditions [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2018, 74: 145–152. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2018.01.017. [15] YU R G, ZHANG Z H, GAO W L, et al. Numerical simulation of rock mass blasting vibration using particle flow code and particle expansion loading algorithm [J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2023, 122: 102686. DOI: 10.1016/j.simpat.2022.102686. [16] ZHU F, ZHAO J D. Peridynamic modelling of blasting induced rock fractures [J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2021, 153: 104469. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmps.2021.104469. [17] KARMAKAR S, SHAW A. Response of R. C. plates under blast loading using FEM-SPH coupled method [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2021, 125: 105409. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105409. [18] GHAREHDASH S, BARZEGAR M, PALYMSKIY I B, et al. Blast induced fracture modelling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 135: 103235. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.02.001. [19] HAO H, WU Y K, MA G W, et al. Characteristics of surface ground motions induced by blasts in jointed rock mass [J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2001, 21(2): 85–98. DOI: 10.1016/S0267-7261(00)00104-4. [20] JHANWAR J C, JETHWA J L, REDDY A H. Influence of air-deck blasting on fragmentation in jointed rocks in an open-pit manganese mine [J]. Engineering Geology, 2000, 57(1/2): 13–29. DOI: 10.1016/S0013-7952(99)00125-8. [21] XIE X K, LI J C, ZHENG Y L. Experimental study on dynamic mechanical and failure behavior of a jointed rock mass [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2023, 168: 105415. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2023.105415. [22] WANG Z L, KONIETZKY H. Modelling of blast-induced fractures in jointed rock masses [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2009, 76(12): 1945–1955. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2009.05.004. [23] ZHU J B. Theoretical and numerical analyses of wave propagation in jointed rock masses [D]. 2011. DOI: 10.5075/epfl-thesis-5130. [24] 郭文章, 王树任, 陈寿峰. 岩体中的节理对爆破作用的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1999, 19(2): 188–192. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1999)02-0188-5.GUO W Z, WANG S R, CHEN S F. Effect of joint on rock mass under blasting [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1999, 19(2): 188–192. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1999)02-0188-5. [25] 宋彦琦, 李向上, 刘济琛, 等. 节理充填物厚度对运动裂纹扩展的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(8): 083102. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0358.SONG Y Q, LI X S, LIU J C, et al. Effects of joint filling thickness on crack propagation behaviors [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(8): 083102. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0358. [26] 金李, 卢文波, 陈明, 等. 节理岩体的爆破松动机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2009, 29(5): 474–480. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)05-0474-07.JIN L, LU W B, CHEN M, et al. Mechanism of jointed rock loosing under blasting load [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2009, 29(5): 474–480. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2009)05-0474-07. [27] ZHOU H X, GAO Q D, FAN Y, et al. Analysis of causes of vibration differences induced by different kinds of blastholes based on the interpretation of blasting parameters: a case study in dam foundation excavation [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2023, 56(10): 7237–7254. DOI: 10.1007/S00603-023-03457-2. [28] ZUO J J, YANG R S, GONG M, et al. Effect of different filling media between explosive and blast-hole wall on rock blasting [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2023, 56(8): 5705–5717. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-023-03366-4. [29] HAJIBAGHERPOUR A R, MANSOURI H, BAHAADDINI M. Numerical modeling of the fractured zones around a blasthole [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2020, 123: 103535. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103535. [30] YI C P, JOHANSSON D, GREBERG J. Effects of in-situ stresses on the fracturing of rock by blasting [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 104: 321–330. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.12.004. [31] YI C P, JOHANSSON D, NYBERG U, et al. Stress wave interaction between two adjacent blast holes [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2016, 49(5): 1803–1812. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-015-0876-x. [32] LI X B, LI C J, CAO W Z, et al. Dynamic stress concentration and energy evolution of deep-buried tunnels under blasting loads [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 104: 131–146. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.02.018. [33] 陶明, 向恭梁, 赵瑞. 深埋引水隧洞对应力波的散射与动应力集中 [J]. 应用力学学报, 2022, 39(5): 859–868. DOI: 10.11776/j.issn.1000-4939.2022.05.006.TAO M, XIANG G L, ZHAO R. Scattering of stress wave and dynamic stress concentration for deep diversion tunnel [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2022, 39(5): 859–868. DOI: 10.11776/j.issn.1000-4939.2022.05.006. [34] YAHYAOUI S, HAFSAOUI A, AISSI A, et al. Relationship of the discontinuities and the rock blasting results [J]. Journal of Geology, Geography and Geoecology, 2018, 26(1): 208–218. DOI: 10.15421/111821. [35] 陶明, 姚靖, 李夕兵. 平面P波入射具有不完美界面圆形夹塞的动态响应特性 [J]. 爆破, 2022, 39(3): 25–32, 63. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2022.03.004.TAO M, YAO J, LI X B. Dynamic response characteristics of circular inclusion with imperfect interface under plane P-wave incident [J]. Blasting, 2022, 39(3): 25–32,63. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2022.03.004. [36] 丁三毛. 考虑地应力影响的深埋圆形管道在爆破P波作用下的动力响应 [J]. 爆破, 2023, 40(3): 177–183, 198. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.024.DING S M. Dynamic response of deep buried circular pipeline subjected to blasting p-wave considering influence of in-situ stress [J]. Blasting, 2023, 40(3): 177–183, 198. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.024. [37] LI X D, LIU K W, SHA Y Y, et al. Numerical investigation on rock fragmentation under decoupled charge blasting [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2023, 157: 105312. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.105312. [38] HONG Z X, TAO M, LI X D, et al. Experimental study on the influences of charging structure with various filling mediums on rock blasting performances [J]. Powder Technology, 2023, 429: 118925. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2023.118925. [39] YANG J C, LIU Z X, LIU K W, et al. Study on the blasting damage of prestressed rock-like specimens with different coupling mediums [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 181: 104758. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104758. [40] TAO M, LI Z W, CAO W Z, et al. Stress redistribution of dynamic loading incident with arbitrary waveform through a circular cavity [J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2019, 43(6): 1279–1299. DOI: 10.1002/nag.2897. [41] SCHWER L E, JAVIER MALVAR L. Simplified concrete modeling with *mat_concrete_damage_rel3 [R]. Nagoya: JRI LS-Dyna User Week, 2005: 49−60. [42] KRISTOFFERSEN M, PETTERSEN J E, AUNE V, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on the structural response of normal strength concrete slabs subjected to blast loading [J]. Engineering Structures, 2018, 174: 242–255. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.07.022. [43] REN L, YU X M, ZHENG M X, et al. Evaluation of typical dynamic damage models used for UHPC based on SHPB technology [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2022, 269: 108562. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2022.108562. [44] MENG Q F, WU C Q, SU Y, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of blast resistant capacity of high performance geopolymer concrete panels [J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 171: 9–19. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.04.010. [45] LIU K W, LI X D, HAO H, et al. Study on the raising technique using one blast based on the combination of long-hole presplitting and vertical crater retreat multiple-deck shots [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 113: 41–58. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.11.012. [46] ZHAO R, TAO M, WU C Q, et al. Study on size and load rate effect of dynamic fragmentation and mechanical properties of marble sphere [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 142: 106814. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106814. [47] AZIZABADI H R M, MANSOURI H, FOUCHÉ O. Coupling of two methods, waveform superposition and numerical, to model blast vibration effect on slope stability in jointed rock masses [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2014, 61: 42–49. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.04.008. [48] HEALY D, RIZZO R E, CORNWELL D G, et al. FracPaQ: a MATLAB™ toolbox for the quantification of fracture patterns [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2017, 95: 1–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsg.2016.12.003. [49] ZHAO H T, TAO M, LI X B, et al. Estimation of spalling strength of sandstone under different pre-confining pressure by experiment and numerical simulation [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 133: 103359. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.103359. [50] FAN L F, JIA L, WANG M. Evaluation of the displacement discontinuity method on wave propagation through a thickly jointed rock mass [J/OL]. Waves in Random and Complex Media, 2023: 1–14. DOI: 10.1080/17455030.2023.2169388. [51] YANG H, DUAN H F, ZHU J B. Experimental study on the role of clay mineral and water saturation in ultrasonic P-wave behaviours across individual filled rock joints [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2023, 168: 105393. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2023.105393. [52] WANG R, HU Z P, ZHANG D, et al. Propagation of the stress wave through the filled joint with linear viscoelastic deformation behavior using time-domain recursive method [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2017, 50(12): 3197–3207. DOI: 10.1007/s00603-017-1301-4. [53] BANDIS S C, LUMSDEN A C, BARTON N R. Fundamentals of rock joint deformation [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1983, 20(6): 249–268. DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(83)90595-8. -






 下载:
下载: