Investigation on cracking behavior and influencing factors of jointed rock masses under the coupling effect of confining pressure and blasting
-
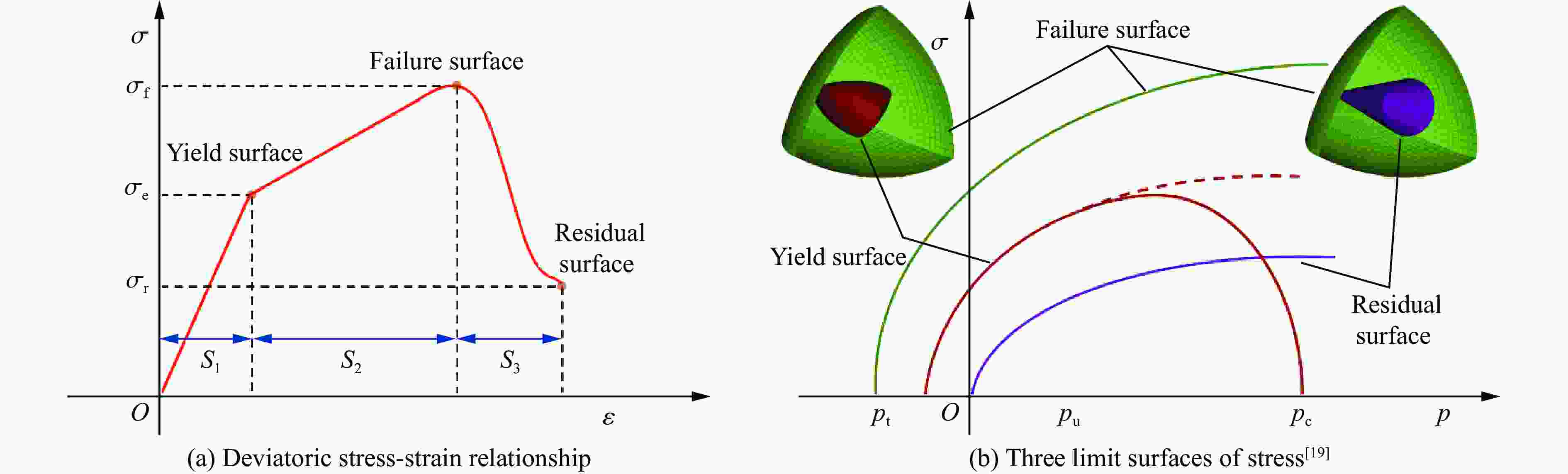
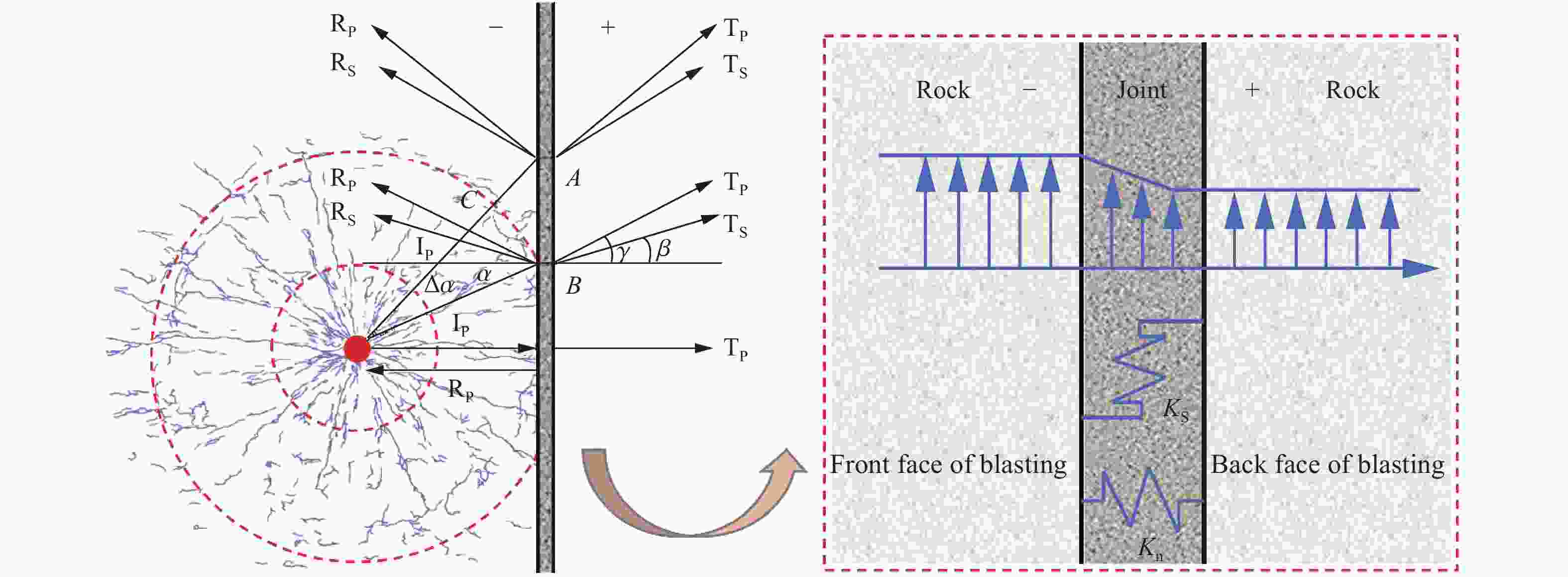
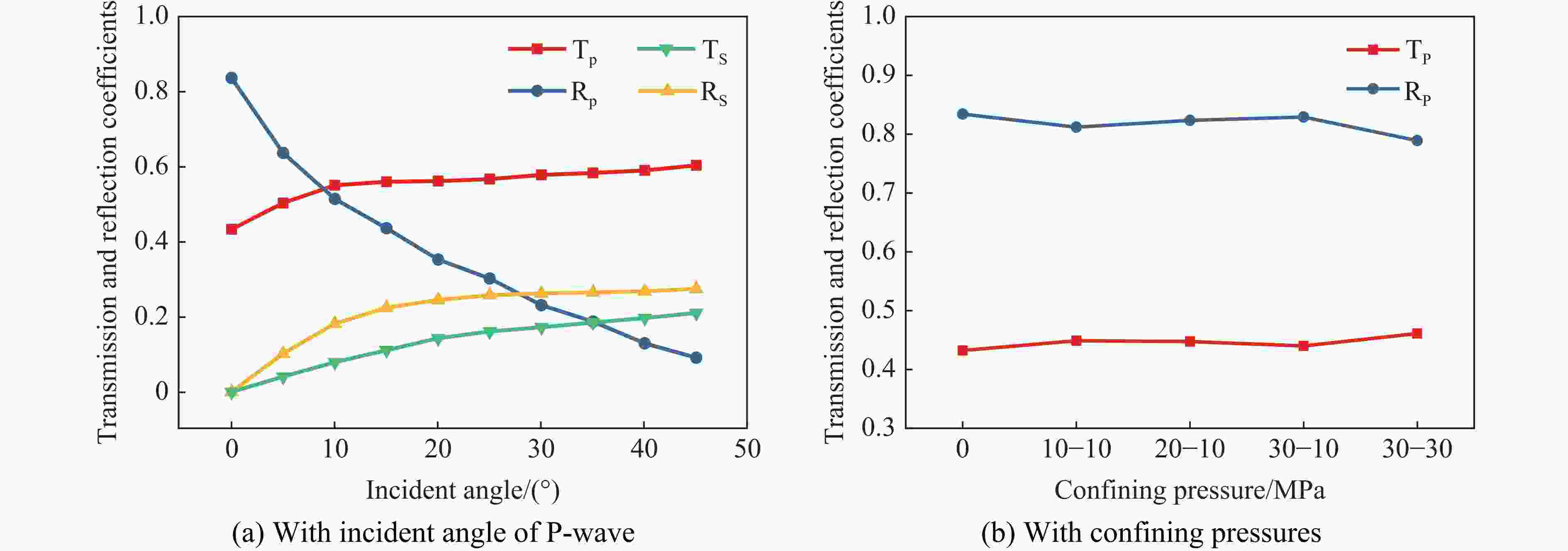
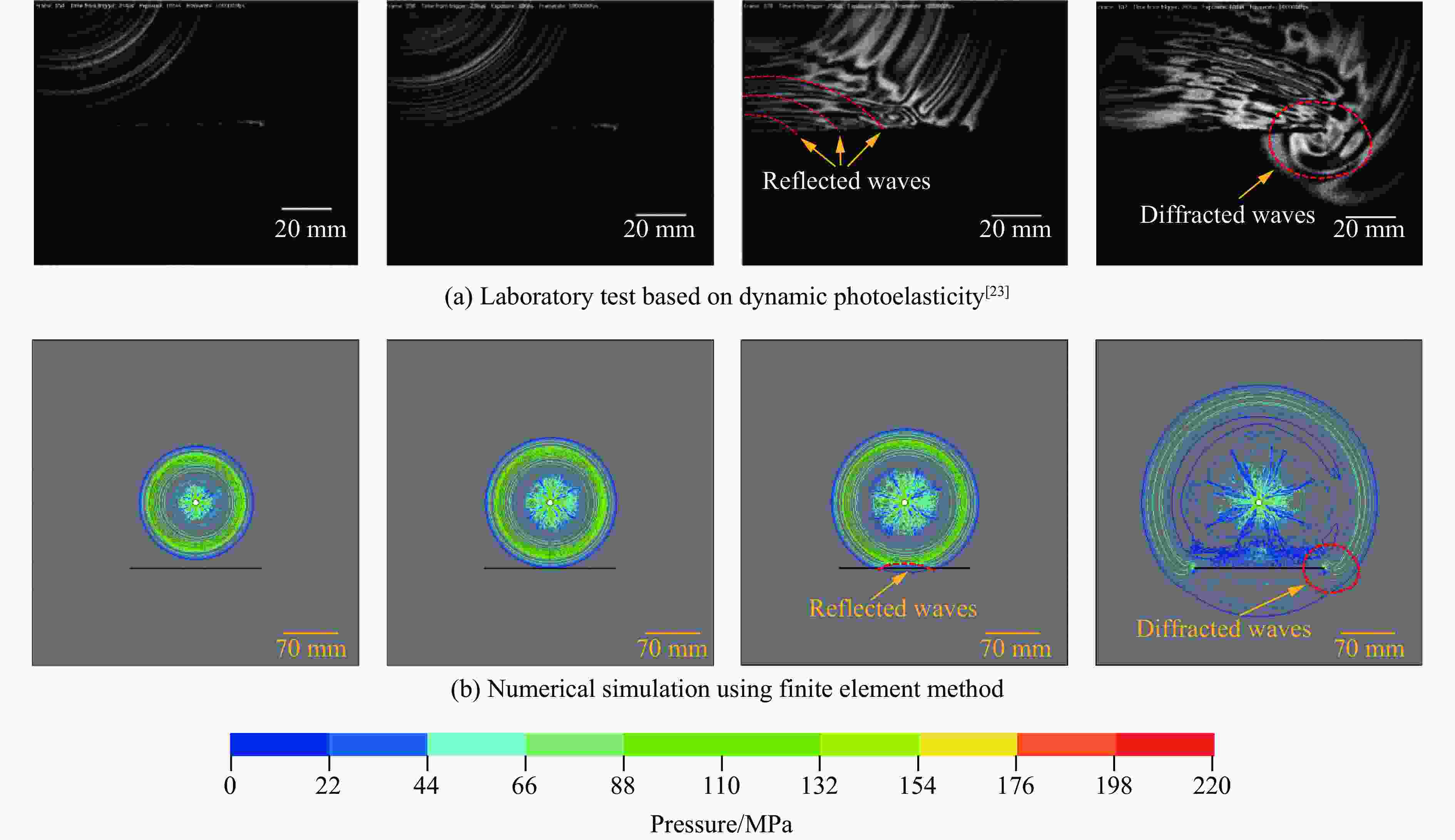
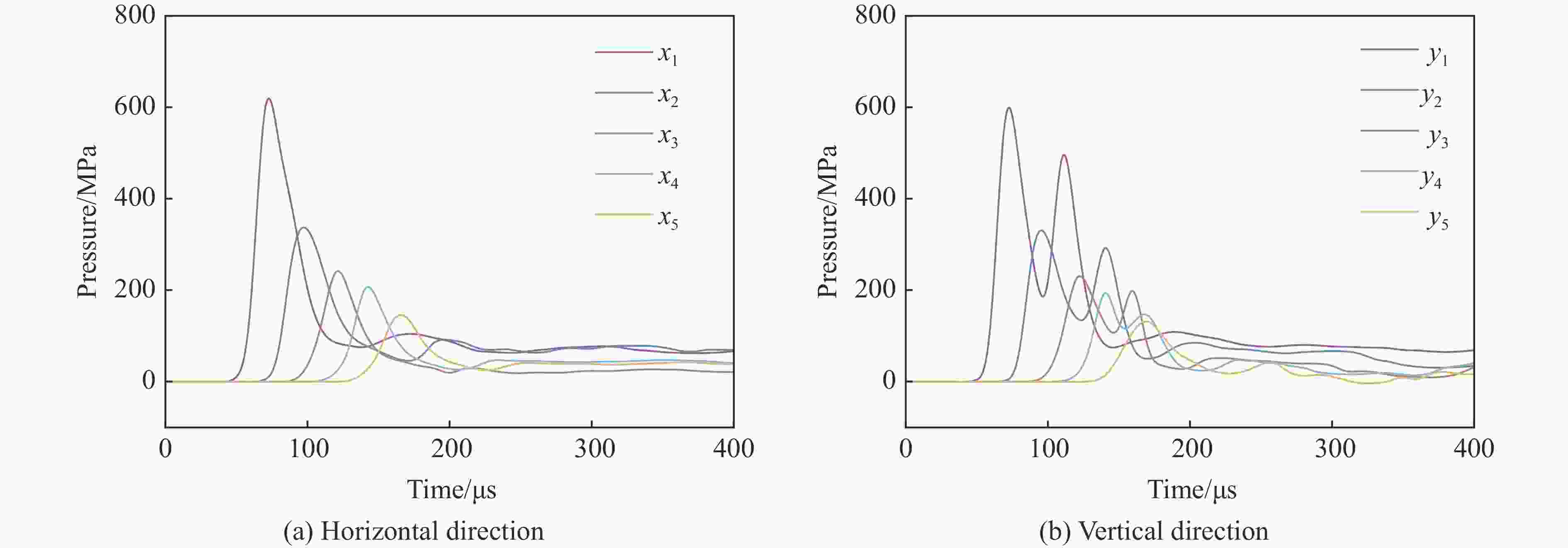
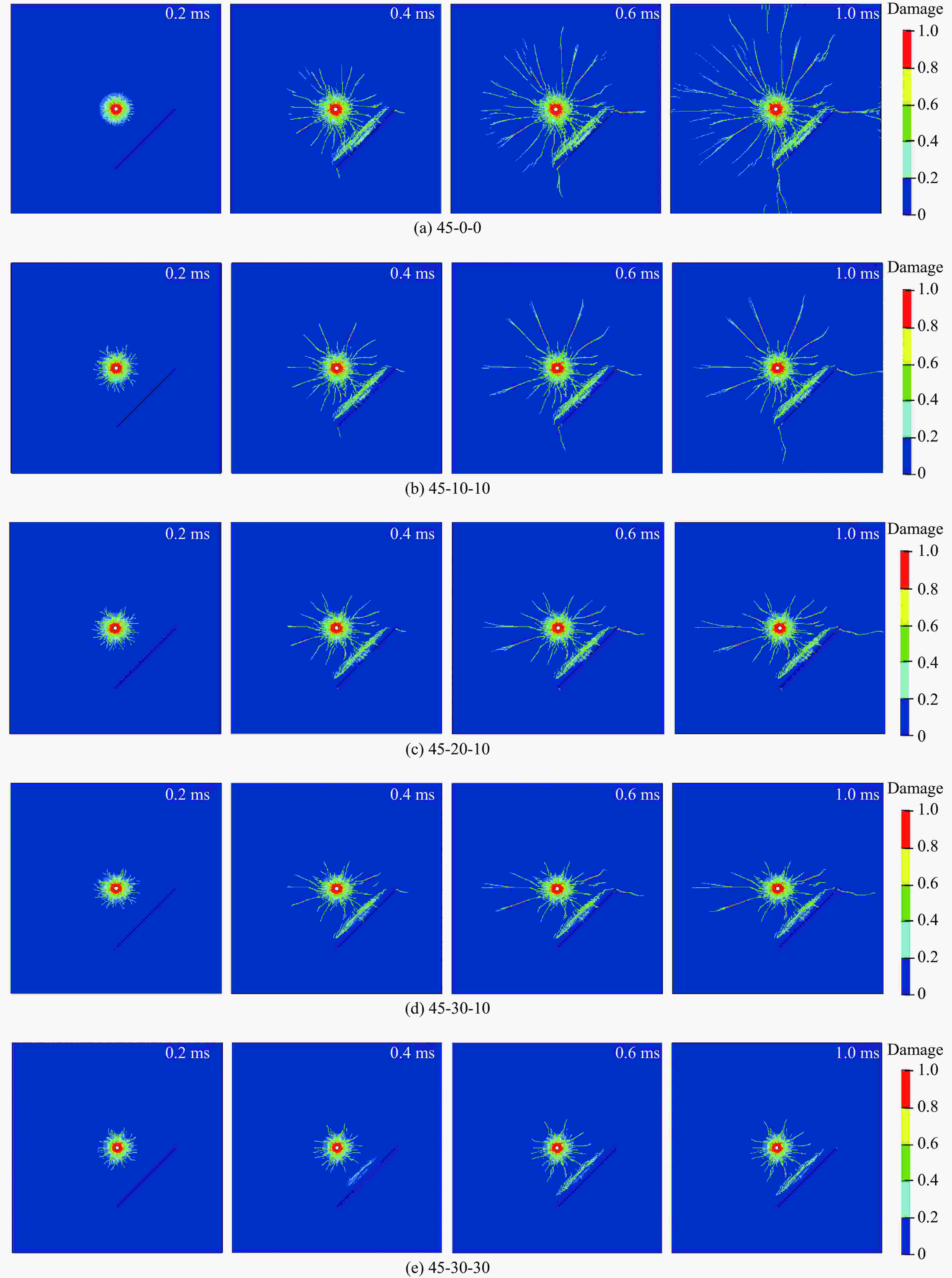
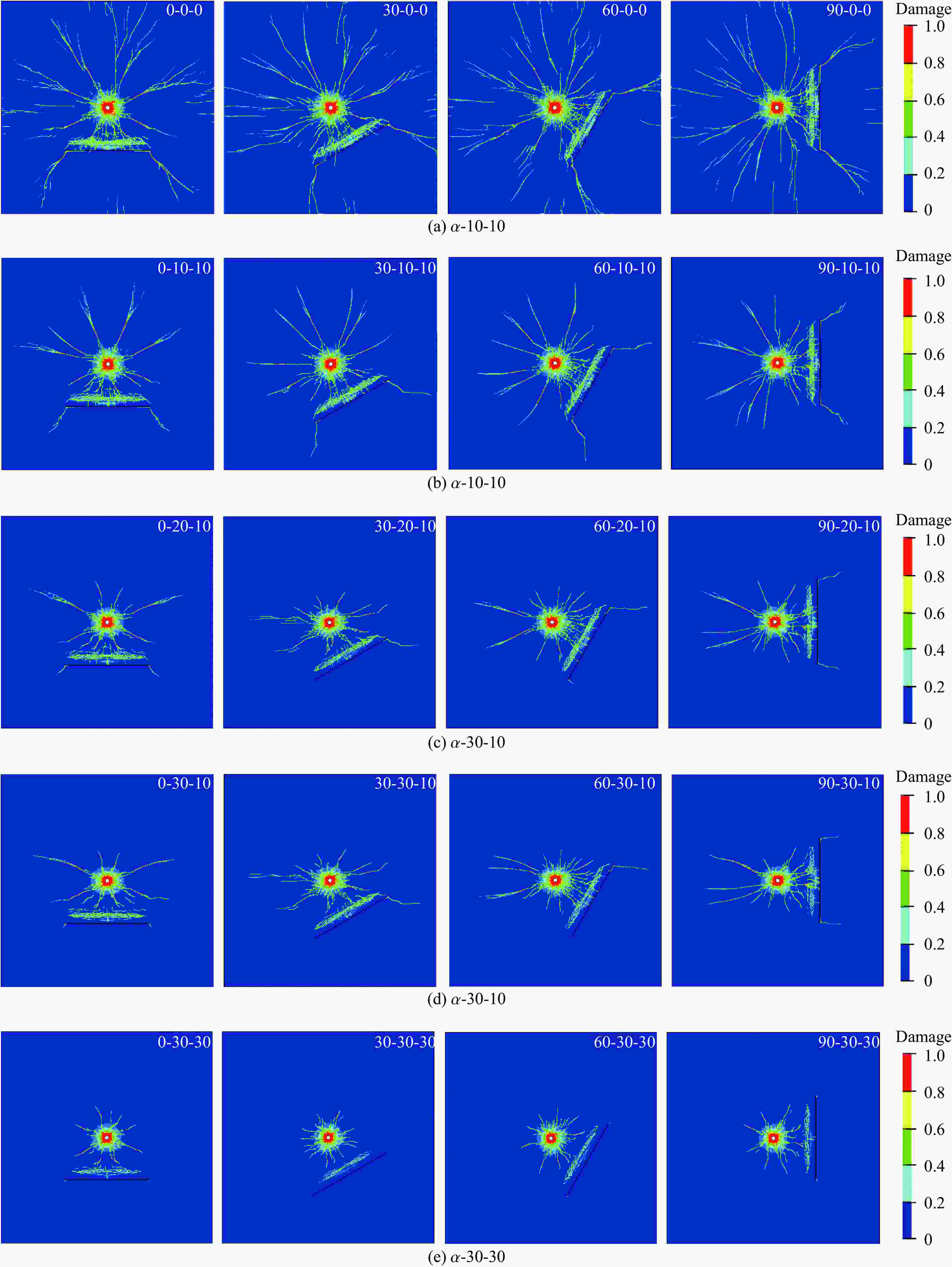
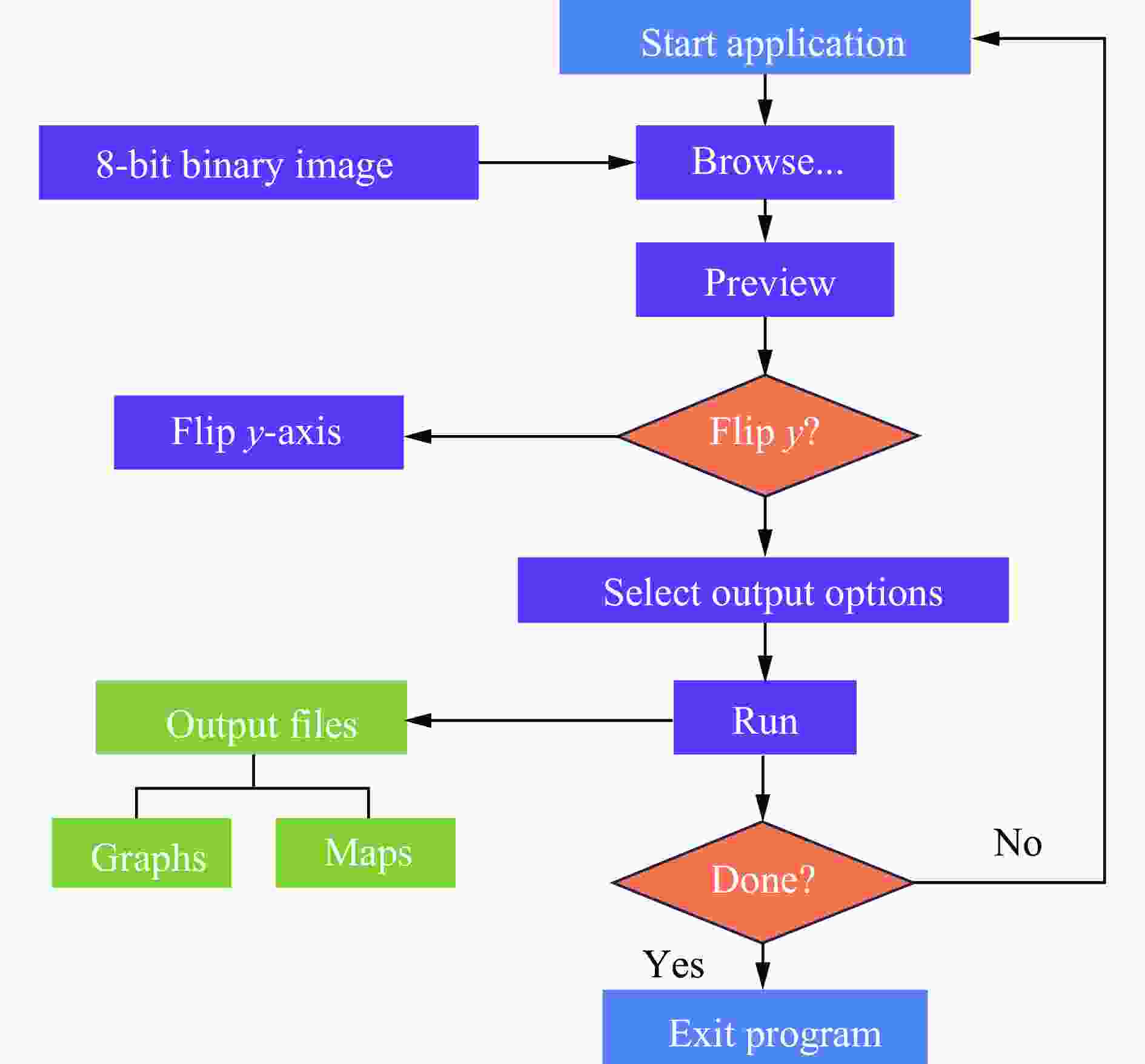
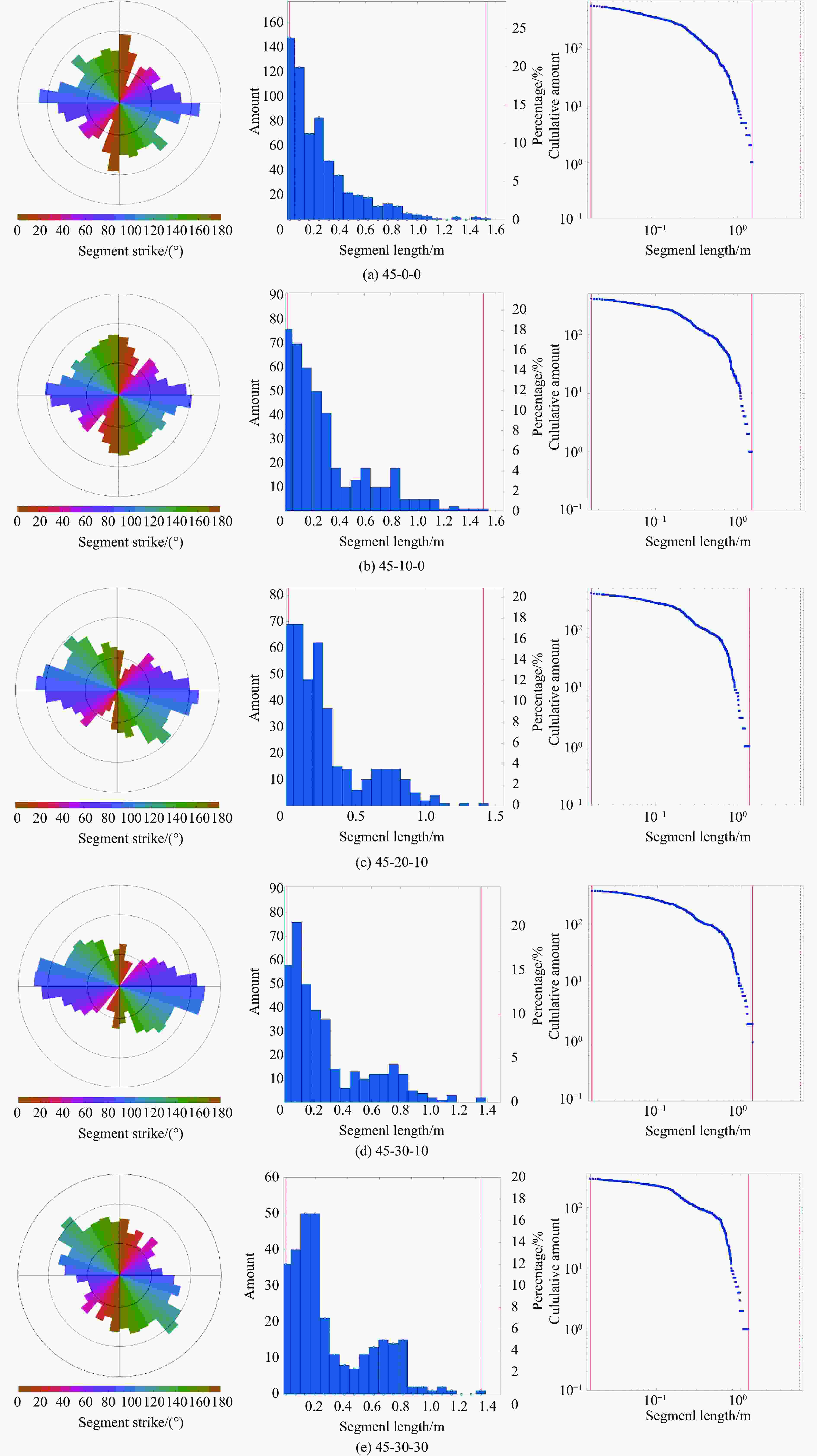
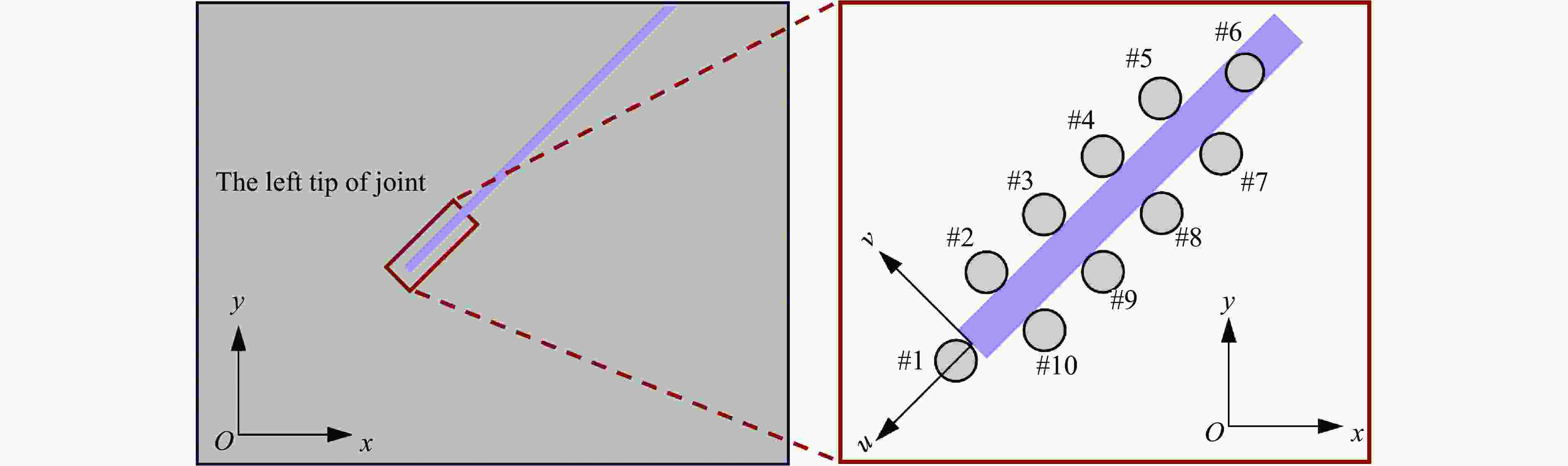
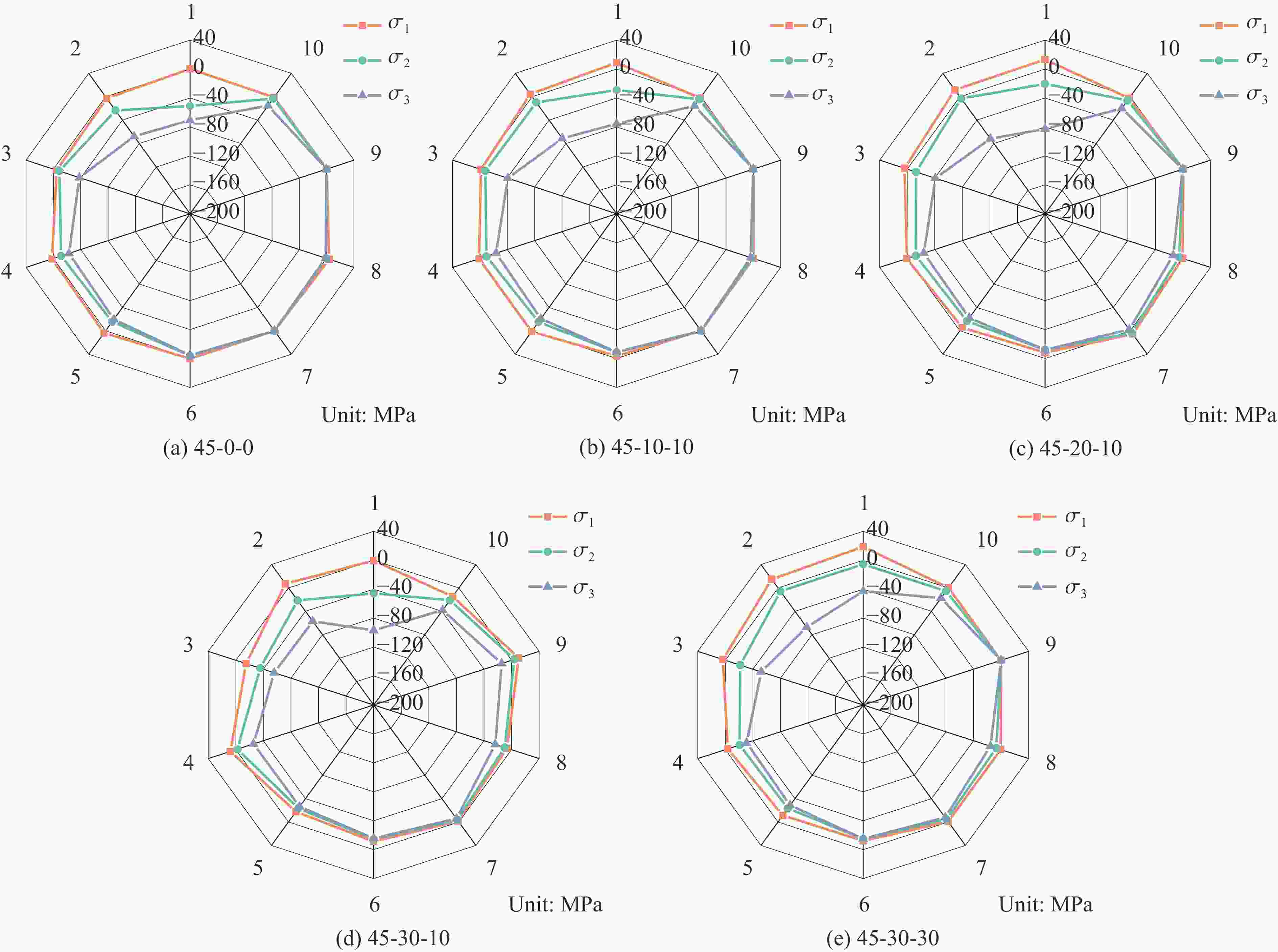
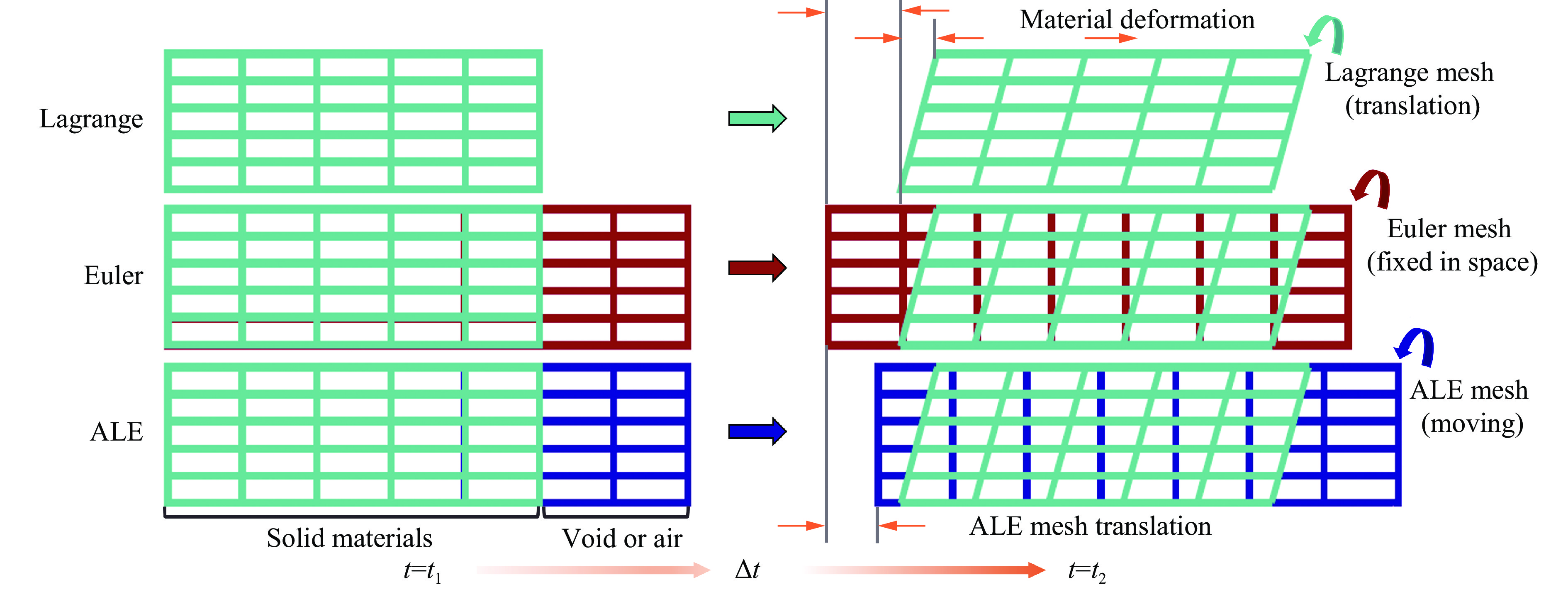
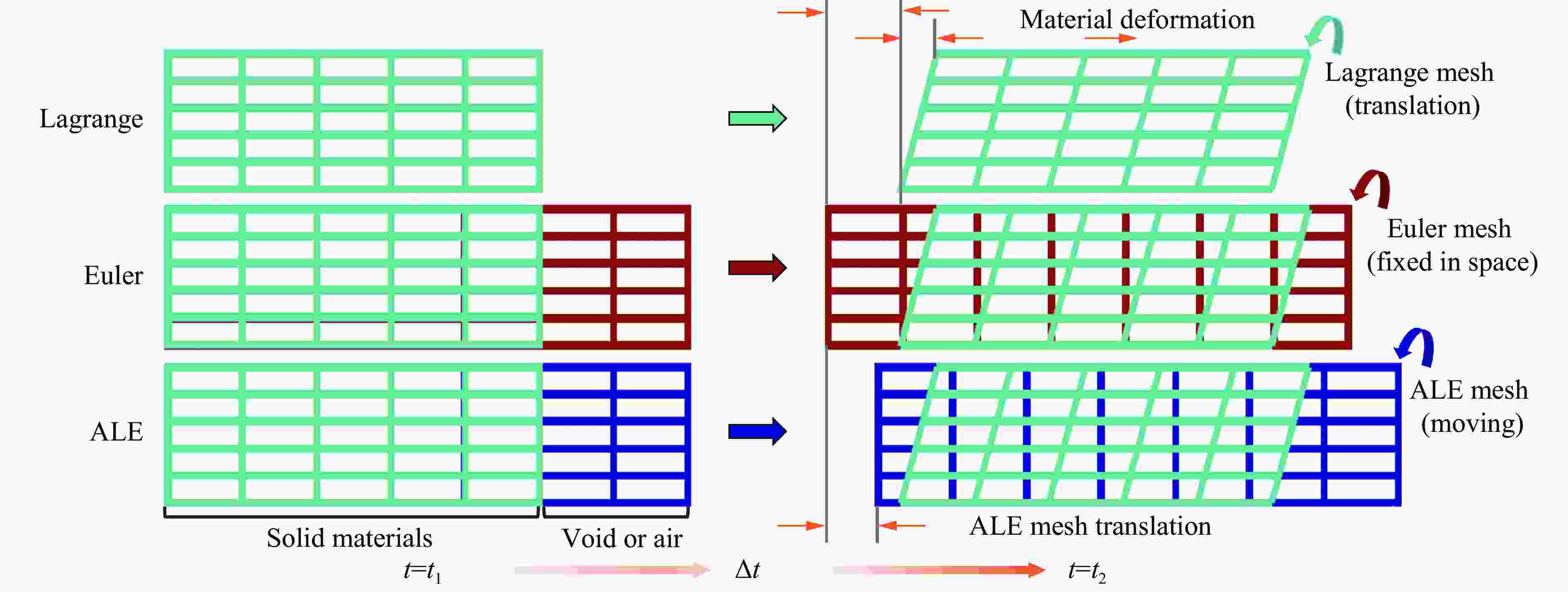
摘要: 为了深入研究围压与爆破耦合作用下节理岩体的动力响应及损伤机制,采用显式动力学数值模拟方法,并结合任意拉格朗日-欧拉算法和流固耦合技术,对节理岩体的破裂过程进行模拟。基于时域递归理论,分别计算了爆炸应力波穿过节理面时的透射与反射系数。通过爆炸光弹性试验,分析了爆炸应力波在节理岩体中的传播过程与特征。此外,利用Riedel-Hiermaier-Thoma (RHT) 损伤模型,讨论了不同节理角度及不同围压对爆破裂纹扩展行为的影响,并结合FracPaQ程序定量描述了爆破裂纹的分布规律。最后,通过分析节理尖端的主应力分布及动态应力强度因子变化规律,揭示了节理岩体的爆破损伤机制。结果表明:节理面与非静水压力对爆破裂纹扩展均有导向作用,且非静水压力的导向效应会因节理面的存在而减弱;非静水压力下,应力波透、反射系数随着水平方向压力的增加分别呈减小和增大的趋势。由节理面两侧法向与切向位移的变化规律,发现剪切应力是尖端翼裂纹扩展的主要原因。根据动态应力强度因子判断,拉伸裂纹在爆破初期主导节理尖端的损伤,而剪切裂纹在后期占主导地位。Abstract: Propagation features of blast-induced stress waves undergo substantial alterations as they traverse heterogeneous interfaces. In rock engineering, the prevalence of discontinuous structural planes, such as joints and fissures, becomes increasingly pronounced with increasing burial depth. To gain a comprehensive insight into the dynamic response and damage mechanism, an explicit dynamics numerical method incorporating the ALE algorithm and fluid-solid coupling technology was adopted, which allows for precise simulation of the fracture process within jointed rock mass under the combined effects of confining pressure and blasting load. Based on the time-domain recurrence theory, the transmission and reflection coefficients of the stress wave were calculated, and the propagation process and features of the stress wave were then analyzed by the explosion photoelasticity test using an epoxy resin plate. Additionally, the Riedel-Hiermaier-Thoma (RHT) damage model was used to investigate the influence of different joint angles and confining pressures on cracking behavior. Furthermore, the cracks were quantitatively assessed using the FracPaQ program. Finally, the damage mechanism of the jointed rock mass was revealed by analyzing the principal stress distribution and displacement change as well as the dynamic stress intensity factors (DSIFs) of the joint tip. The results show that both the joint and the anisotropic pressure have a guiding effect on crack extension, and the effect of the anisotropic pressure will be weakened by the presence of the joint. For the anisotropic pressure condition, the stress wave transmission and reflection coefficients tended to decrease and increase, respectively, with increasing pressure in the horizontal direction. From the change rule of normal and tangential displacement on both sides of the joint surface, it is found that shear stress is the main cause of tip-wing crack expansion. An analysis of the DSIFs reveals that tensile cracks predominantly contribute to damage at the joint tip during the initial phase of blasting, with shear cracks becoming the dominant form of damage in the later stages.
-
Key words:
- in-situ stress /
- jointed rock mass /
- explosion stress wave /
- crack extension /
- damage mechanism
-
表 1 花岗岩的RHT模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of RHT model for granite
参数名称 符号 取值 参数名称 符号 取值 参数名称 符号 取值 损伤因子 D1 0.04 密度 ρr 2620 kg/m3剪切模量减小因子 ξ 0.50 损伤因子 D2 1.00 侵蚀塑性应变 $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{s}}^{\mathrm{f}} $ 2.00 参考压缩应变率 $ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0}^{\mathrm{c}} $ 3.0×10−5 s−1 初始孔隙度 α0 1.00 抗压强度 fc 162 MPa 参考拉伸应变率 $ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{0}^{\mathrm{t}} $ 3.0×10−6 s−1 失效面参数 A 2.48 压缩屈服面参数 $ {G}_{\mathrm{c}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.50 破坏压缩应变率 $ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 3.0×1025 s−1 失效面参数 N 0.79 拉伸屈服面参数 $ {G}_{\mathrm{t}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.70 破坏拉伸应变率 $ {\dot{\varepsilon }}_{t} $ 3.0×1025 s−1 残余面参数 Af 1.62 洛德角相关因子 B 0.05 最小损伤残余应变 $ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{p}}^{\mathrm{m}} $ 0.012 残余面参数 Nf 0.62 洛德角相关因子 Q0 0.68 孔隙坍塌压力 pcrush 108 MPa 孔隙度指数 NP 3.00 压缩应变率指数 βc 0.008 孔隙压实压力 pcomp 6.00 GPa 状态方程参数 B0 1.22 拉伸应变率指数 βt 0.011 拉伸体积塑性应变分数 $ P_{\mathrm{t}}^{\mathrm{f}} $ 0.001 状态方程参数 B1 1.22 弹性剪切模量 G 21.9 GPa Hugoniot多项式系数 A1 33.95 GPa 相对抗剪强度 $ {F}_{\mathrm{s}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.18 状态方程参数 T1 33.95 GPa Hugoniot多项式系数 A2 41.42 GPa 相对抗拉强度 $ {F}_{\mathrm{t}}^{\mathrm{*}} $ 0.06 状态方程参数 T2 0.00 GPa Hugoniot多项式系数 A3 8.71 GPa ρe/(kg·m−3) DJ/(m·s−1) PCJ/GPa $ {E}_{0}^{\mathrm{J}} $/(kJ·m−3) AJ/GPa BJ/GPa R1 R2 ωJ 1320 6690 16.0 7.38×106 586 21.6 5.81 1.77 0.282 表 3 空气模型材料参数
Table 3. Parameters for the air material
ρa/(kg·m−3) C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 $ {E}_{0}^{\mathrm{a}} $/(kJ·m−3) V0 1.29 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.4 0.4 0.0 250 1.0 表 4 节理模型材料参数
Table 4. Parameters for the joint material
ρj/(kg·m−3) Ej/GPa μj Et/MPa σ0/MPa βj VP 2200 28 0.24 25 250 0.5 0.0 表 5 围压加载条件
Table 5. Confining pressure conditions in numerical simulation
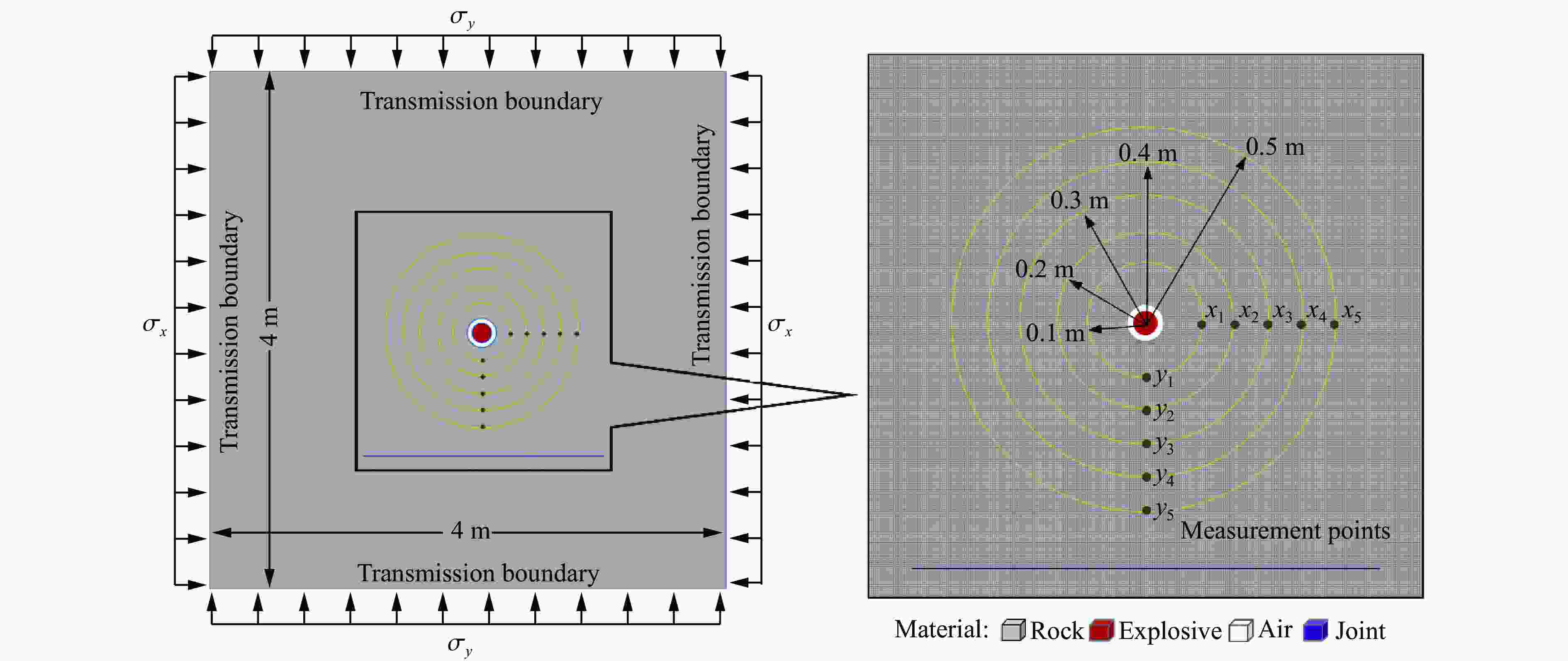
应力状态 工况 σx/MPa σy/MPa 应力状态 工况 σx/MPa σy/MPa 静水压力 α-10-10 10 10 非静水压力 α-20-10 20 10 α-30-30 30 30 α-30-10 30 10 -
[1] 单仁亮, 赵岩, 王海龙, 等. 下穿铁路隧道爆破振动衰减规律研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(8): 085201. DOI: 11883/bzycj-2021-0324. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0324.SHAN R L, ZHAO Y, WANG H L, et al. Attenuation of blasting vibration in a railway tunnel [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(8): 085201. DOI: 11883/bzycj-2021-0324. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0324. [2] LU W B, CHEN M, GENG X, et al. A study of excavation sequence and contour blasting method for underground powerhouses of hydropower stations [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2012, 29: 31–39. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2011.12.008. [3] 李夕兵, 姚金蕊, 宫凤强. 硬岩金属矿山深部开采中的动力学问题 [J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(10): 2551–2563. DOI: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2011.10.022.LI X B, YAO J R, GONG F Q. Dynamic problems in deep exploitation of hard rock metal mines [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2011, 21(10): 2551–2563. DOI: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2011.10.022. [4] 董千. 不同地应力下节理岩体中爆炸应力波传播与衰减规律研究 [D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2018.DONG Q. Study on propagation and attenuation law of blasting stress wave in jointed rock mass under different in-situ stresses [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2018. [5] 王明洋, 钱七虎. 爆炸应力波通过节理裂隙带的衰减规律 [J]. 岩土工程学报, 1995, 17(2): 42–46.WANG M Y, QIAN Q H. Attenuation law of explosive wave propagation in cracks [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1995, 17(2): 42–46. [6] MINDLIN R D. Waves and vibrations in isotropic elastic plates [M]//GOODIER J N, HOFF N J. Structural Mechanics. New York: Pergamon, 1960. [7] SCHOENBERG M. Elastic wave behavior across linear slip interfaces [J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1980, 68(5): 1516–1521. DOI: 10.1121/1.385077. [8] ZHAO J, CAI J G. Transmission of elastic P-waves across single fractures with a nonlinear normal deformational behavior [J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2001, 34(1): 3–22. DOI: 10.1007/s006030170023. [9] 李建春, 范立峰, 李郑梁. 岩体中应力波传播规律研究方法进展 [J]. 应用力学学报, 2022, 39(5): 845–858. DOI: 10.11776/j.issn.1000-4939.2022.05.005.LI J C, FAN L F, LI Z L. Progress of methods for wave propagation across rock masses [J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2022, 39(5): 845–858. DOI: 10.11776/j.issn.1000-4939.2022.05.005. [10] 杨仁树, 丁晨曦, 杨立云, 等. 节理对爆生裂纹扩展影响的试验研究 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(10): 26–30, 44. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.10.005.YANG R S, DING C X, YANG L Y, et al. Experimental study on the effects of joints on the blasting induced cracks propagation [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(10): 26–30, 44. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.10.005. [11] NICHOLLS H R, DUVALL W I. Presplitting rock in the presence of a static stress field [R]. Washington DC: U. S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines, 1966. [12] KUTTER H K, FAIRHURST C. On the fracture process in blasting [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1971, 8(3): 181–202. DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(71)90018-0. [13] ZHU Z M, XIE H P, MOHANTY B. Numerical investigation of blasting-induced damage in cylindrical rocks [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2008, 45(2): 111–121. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.04.012. [14] YI C P, JOHANSSON D, GREBERG J. Effects of in-situ stresses on the fracturing of rock by blasting [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 104: 321–330. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.12.004. [15] XIE L X, LU W B, ZHANG Q B, et al. Analysis of damage mechanisms and optimization of cut blasting design under high in-situ stresses [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2017, 66: 19–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2017.03.009. [16] MOBARAKI B, VAGHEFI M. Numerical study of the depth and cross-sectional shape of tunnel under surface explosion [J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2015, 47: 114–122. DOI: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.01.003. [17] 马泗洲, 刘科伟, 杨家彩, 等. 初始应力下岩体爆破损伤特性及破裂机理 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(10): 105201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0151.MA S Z, LIU K W, YANG J C, et al. Blast-induced damage characteristics and fracture mechanism of rock mass under initial stress [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(10): 105201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0151. [18] YANG J C, LIU K W, LI X D, et al. Stress initialization methods for dynamic numerical simulation of rock mass with high in-situ stress [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(10): 3149–3162. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-020-4535-3. [19] 马泗洲, 刘科伟, 杨家彩, 等. 不耦合装药下岩石爆破块体尺寸的分布特征 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(4): 045201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0358.MA S Z, LIU K W, YANG J C, et al. Size distribution characteristics of blast-induced rock fragmentation under decoupled charge structures [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(4): 045201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0358. [20] ZHAO J, ZHAO X B, CAI J G. A further study of P-wave attenuation across parallel fractures with linear deformational behaviour [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2006, 43(5): 776–788. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2005.12.007. [21] LI J C. Wave propagation across non-linear rock joints based on time-domain recursive method [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2013, 193(2): 970–985. DOI: 10.1093/gji/ggt020. [22] 周文海, 胡才智, 包娟, 等. 含节理岩体爆破过程中应力波传播与裂纹扩展的数值研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2022, 54(9): 2501–2512. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-237.ZHOU W H, HU C Z, BAO J, et al. Numerical study on crack propagation and stress wave propagation during blasting of jointed rock mass [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2022, 54(9): 2501–2512. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-237. [23] CHEN C, YANG R S, XU P, et al. Experimental study on the interaction between oblique incident blast stress wave and static crack by dynamic photoelasticity [J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2022, 148: 106764. DOI: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2021.106764. [24] JAYASINGHE L B, SHANG J L, ZHAO Z Y, et al. Numerical investigation into the blasting-induced damage characteristics of rocks considering the role of in-situ stresses and discontinuity persistence [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2019, 116: 103207. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103207. [25] HEALY D, RIZZO R E, CORNWELL D G, et al. FracPaQ: a MATLAB™ toolbox for the quantification of fracture patterns [J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2017, 95: 1–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsg.2016.12.003. [26] XIE Q M, SHI D D, CHEN X D, et al. Investigation on dynamic splitting mechanical properties of weakly cemented siltstone based on digital image correlation method and FracPaQ algorithm [J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2024, 243: 213310. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoen.2024.213310. [27] 高维廷, 朱哲明, 朱伟, 等. 动荷载下岩石裂纹动态扩展行为实验研究综述 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(8): 081101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0526.GAO W T, ZHU Z M, ZHU W, et al. Experimental studies on crack propagation behaviors of rock materials under dynamic loads: a review [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(8): 081101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0526. -






 下载:
下载: