Study on blast load distribution of building surface under surface burst
-
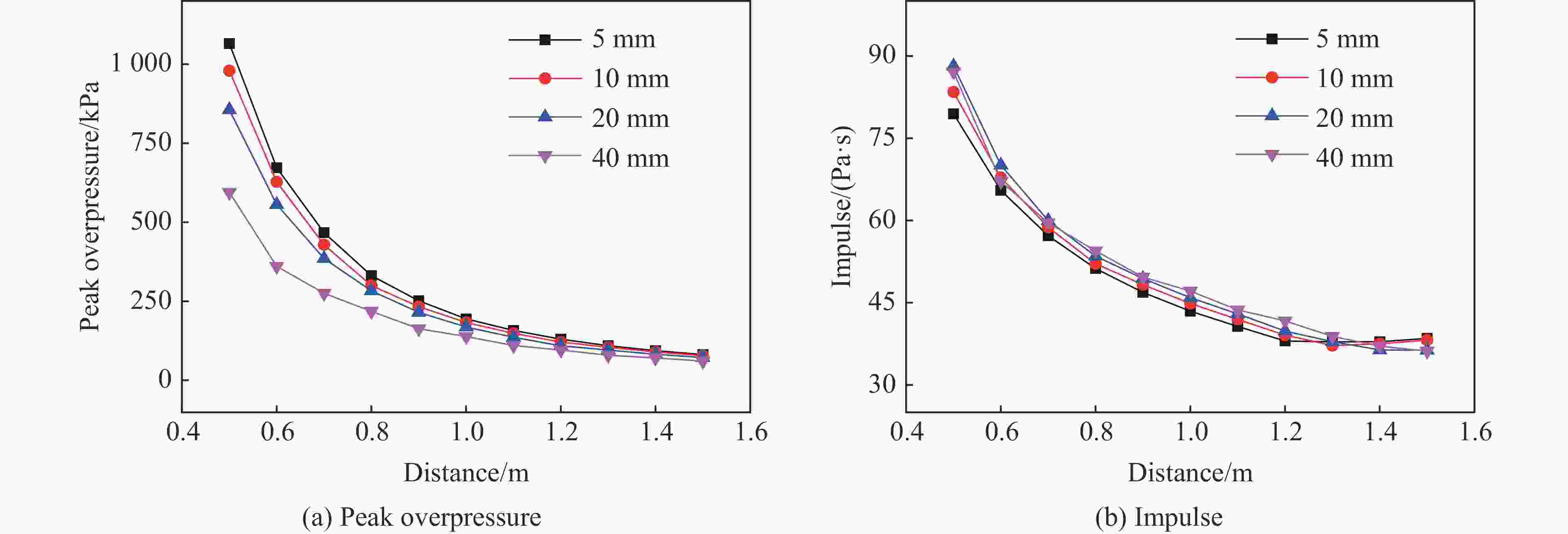
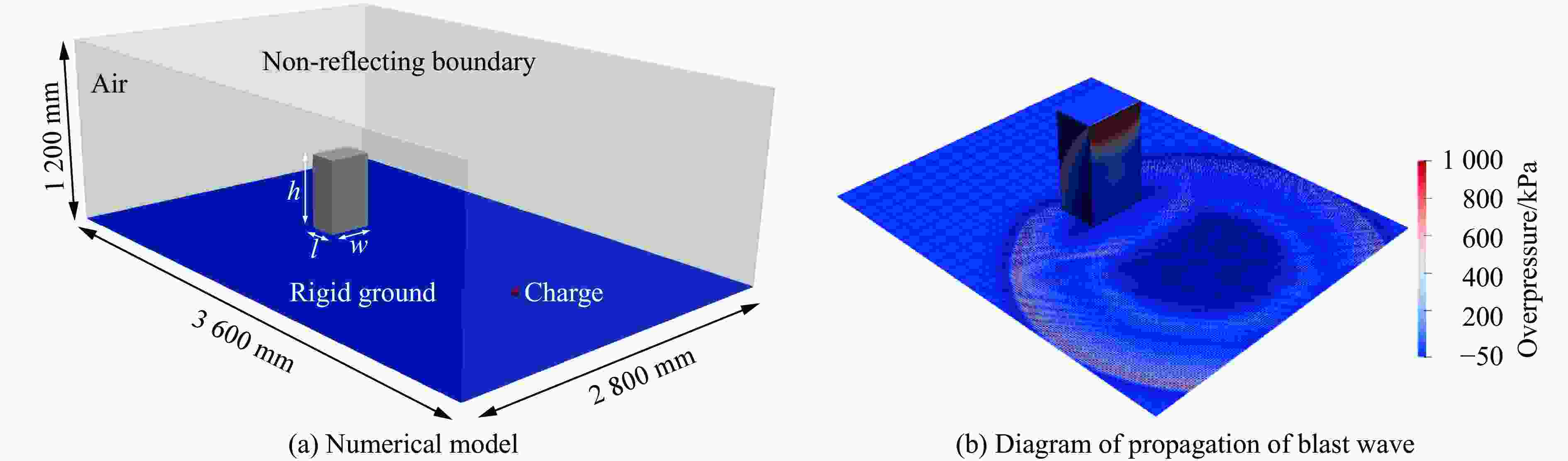
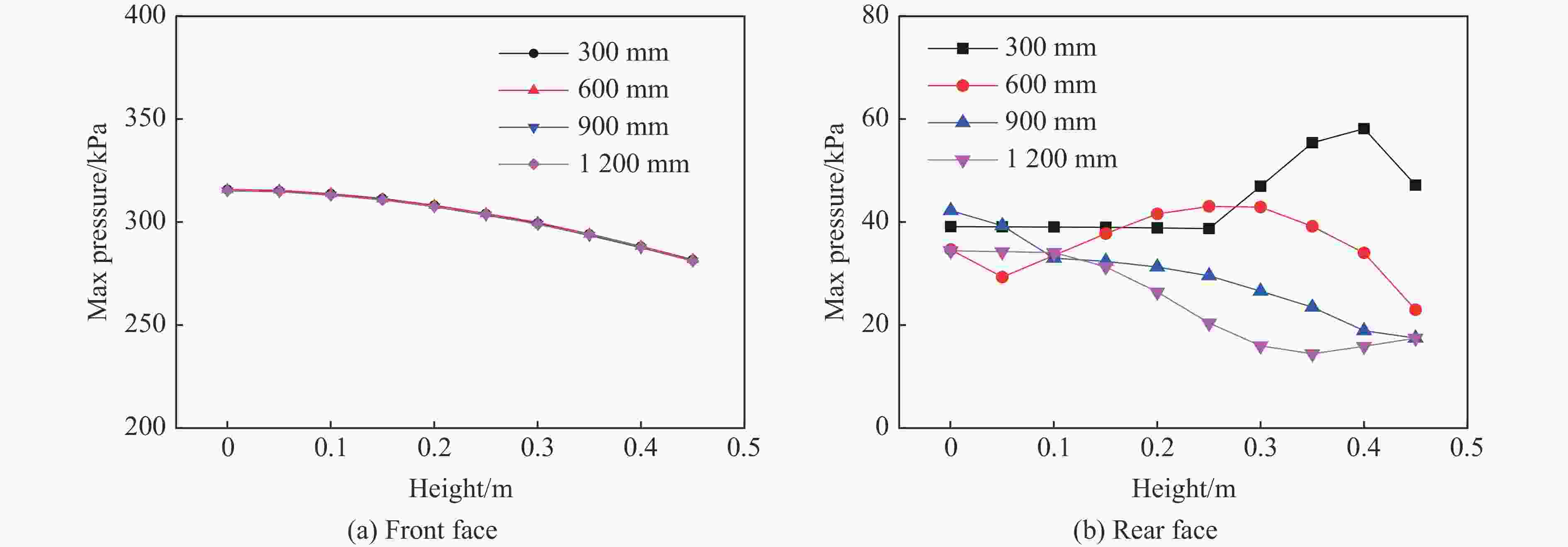
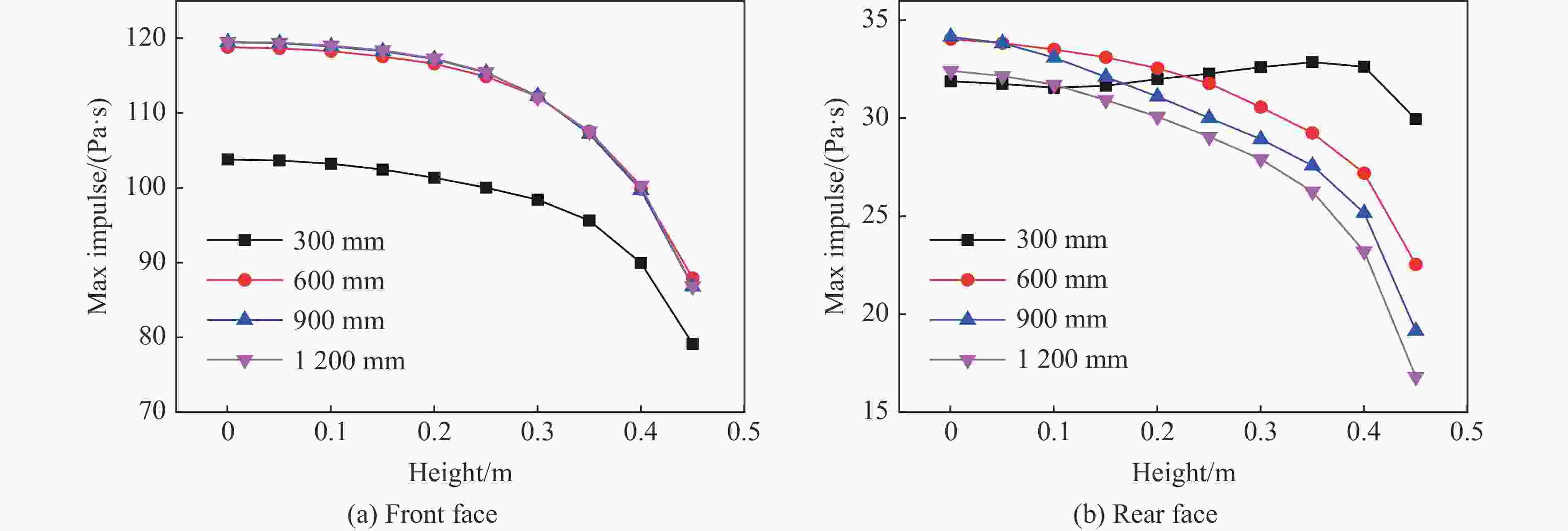
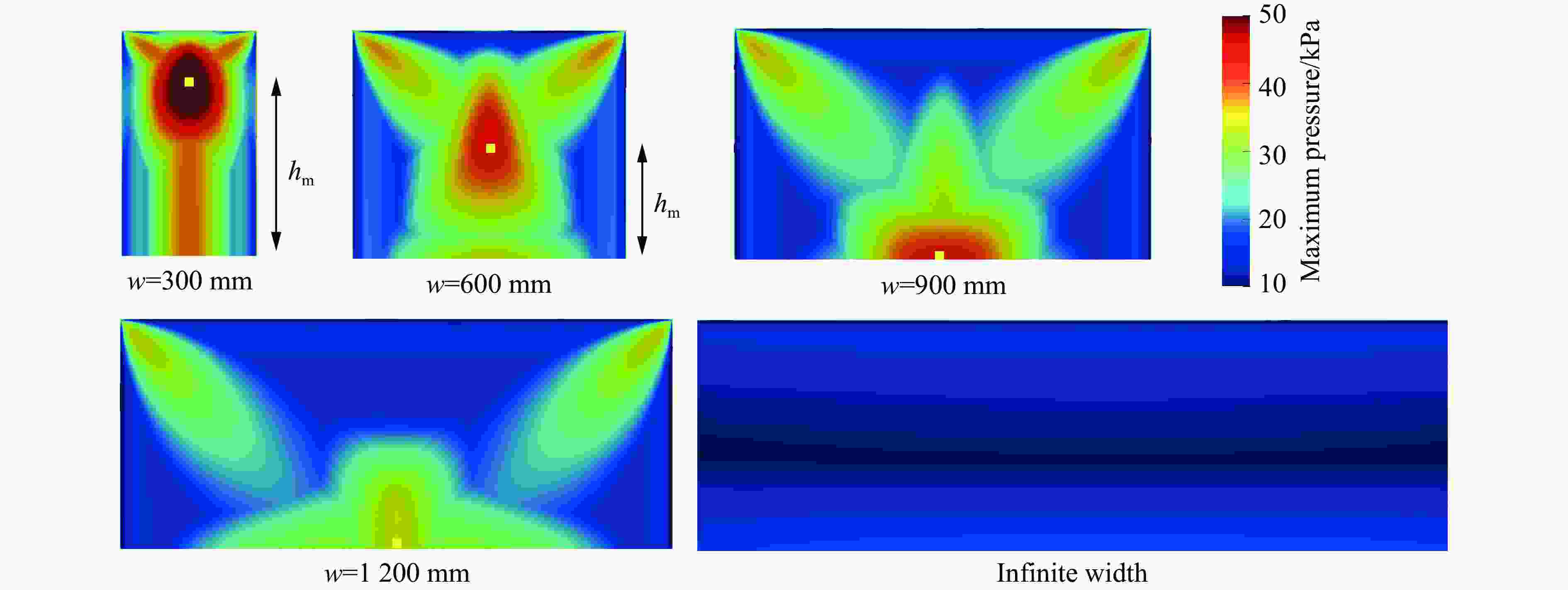
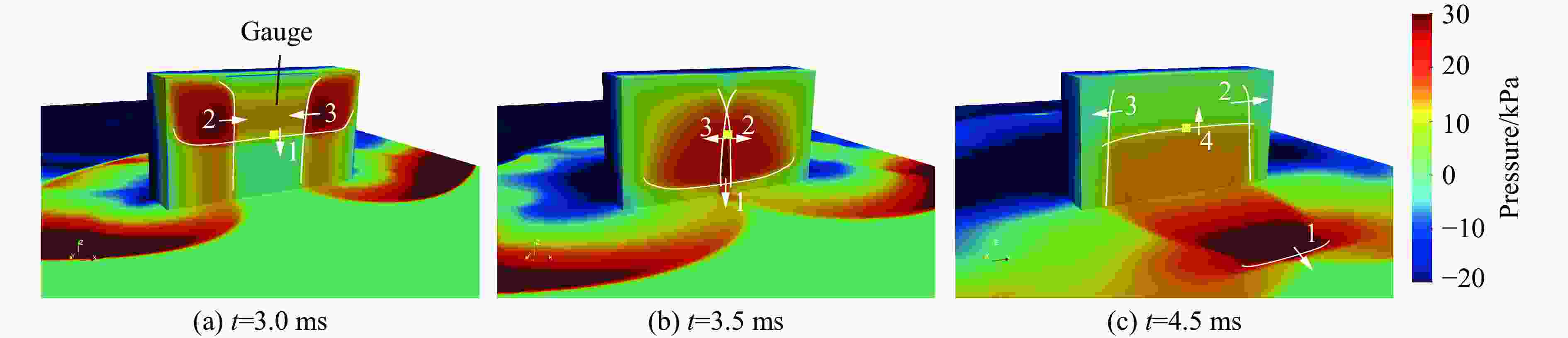
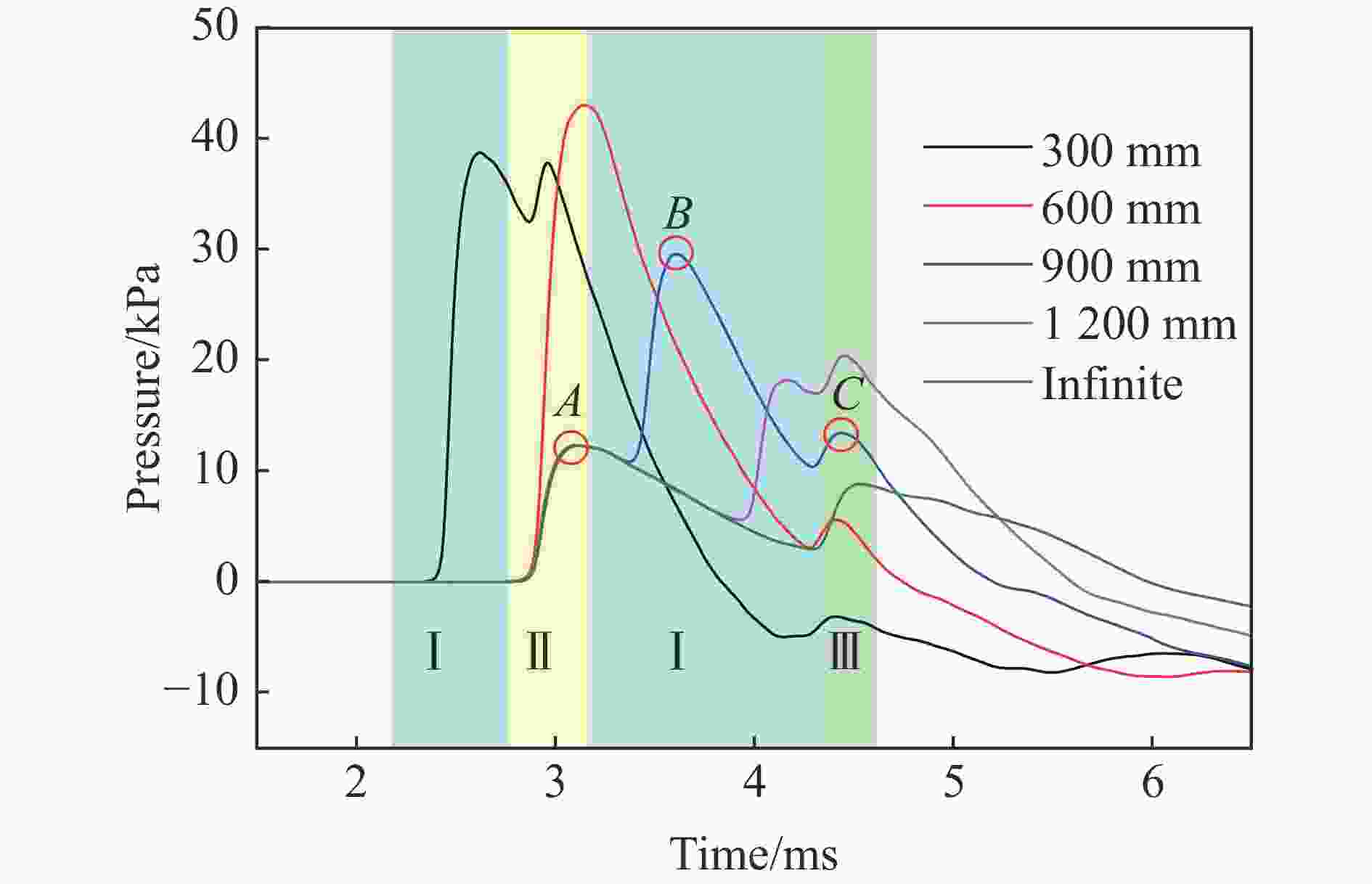
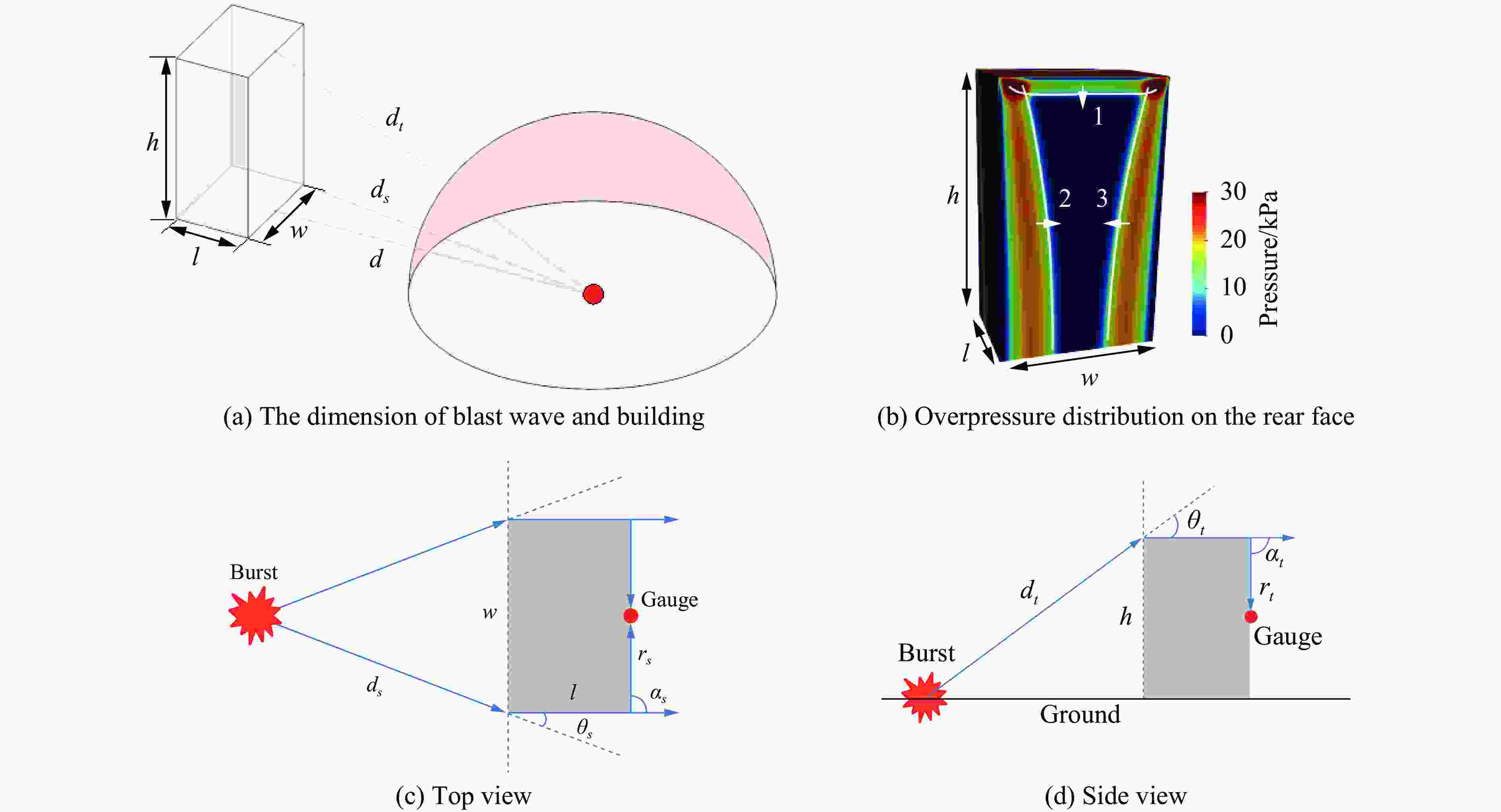
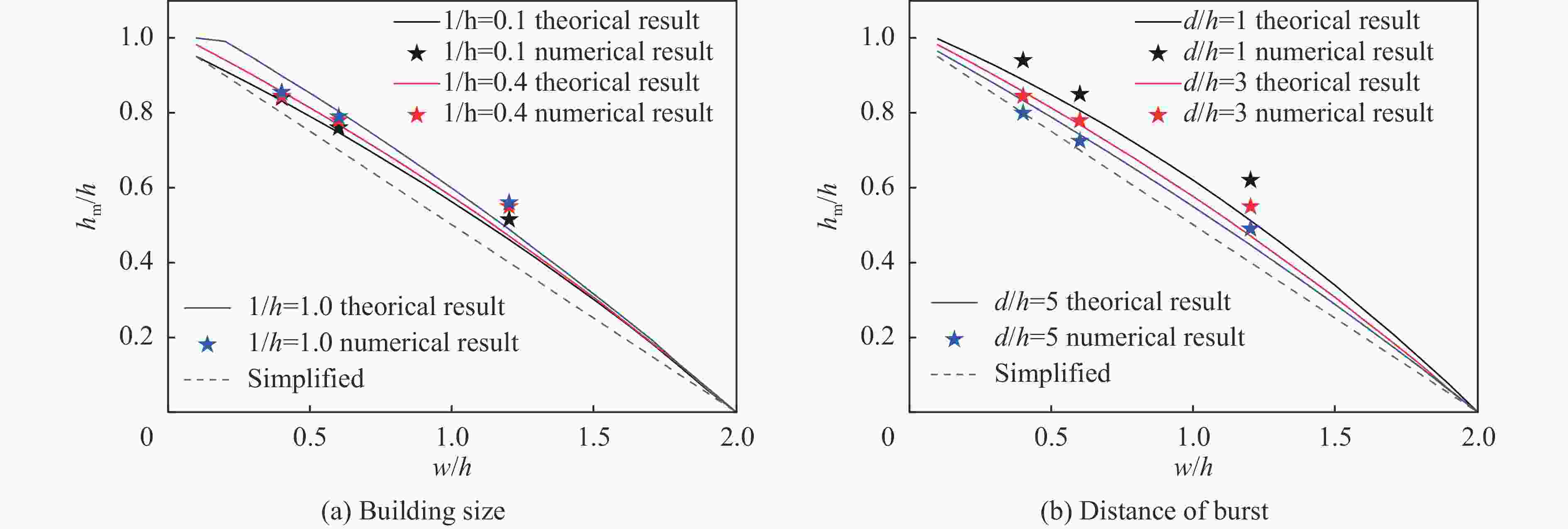
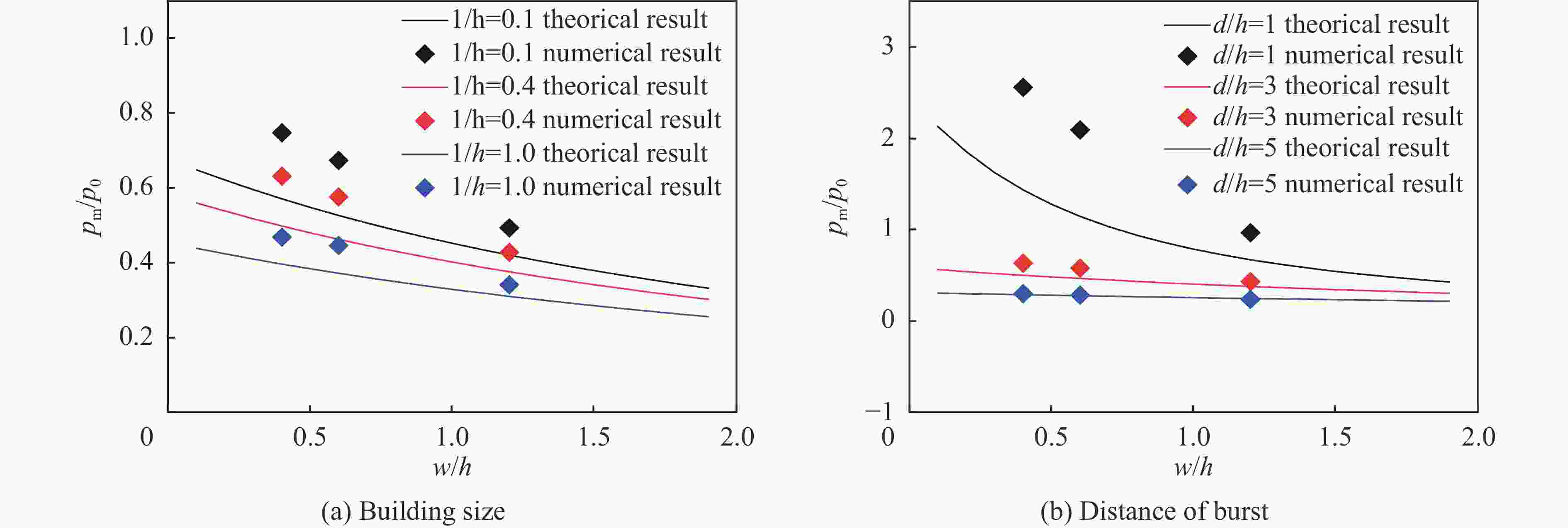
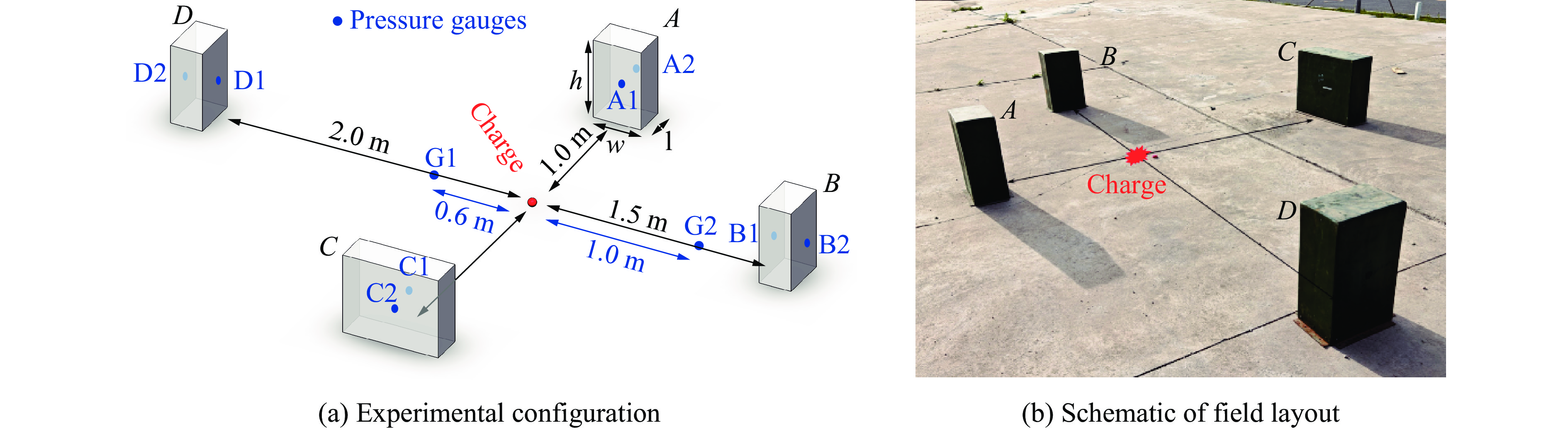
摘要: 为深入研究触地爆下建筑表面冲击波载荷分布规律,首先开展了实验室环境下精细缩比实验,获取了球形炸药触地爆下缩比建筑模型表面测点冲击波压力时间曲线,得到了不同工况下冲击波特征参数分布规律;随后发展了冲击波传播数值模拟方法,并使用缩比实验数据对模拟方法进行校核,通过数值方法重点对建筑背爆面载荷分布及冲击波历程进行分析;最后发展了基于冲击波时程分析和叠加法则的理论分析方法,得到了建筑背爆面载荷分布的量化分析模型,并利用模拟结果进行验证。研究结果表明触地爆下建筑迎爆面最大冲击波载荷位于建筑底部,整体载荷分布较均匀;建筑背爆面载荷主要集中在顶角两侧及中轴线区域,由顶边和侧边绕射冲击波叠加形成,最大超压出现在不同绕射冲击波交汇位置,其位置和大小受建筑尺寸和爆心距影响。Abstract: In order to study the distribution of blast wave load of building surface under surface burst, firstly, the fine scaled experiments under laboratory environment were conducted. The blast wave pressure-time curves on the surface of building model under the situation of surface burst of spherical charge as well as the distribution law of blast wave characteristic parameters were obtained. Subsequently, the numerical simulation method of blast wave propagation was developed and verified by the experimental data. Through simulation, the blast load distribution and time-histories of blast pressure on the rear face of building were analyzed. Finally, the theoretical method based on blast wave time-history analysis and superposition rule was proposed, and the quantitative analysis model of the blast load distribution on the rear face of building which was verified by numerical results was obtained. The results show that the maximum blast load on the front face of building located at the bottom of the building, which the overall distribution was relatively uniform. The blast load on the rear face of building was mainly concentrated on the two sides of the top angle and the central axis, which was formed by the superposition of the diffraction waves from top and side edges, and the maximum overpressure occurred at the intersection position of different diffraction shock waves, which is affected by the building size and explosion distance.
-
Key words:
- surface burst /
- blast load /
- scaled experiment /
- numerical simulation
-
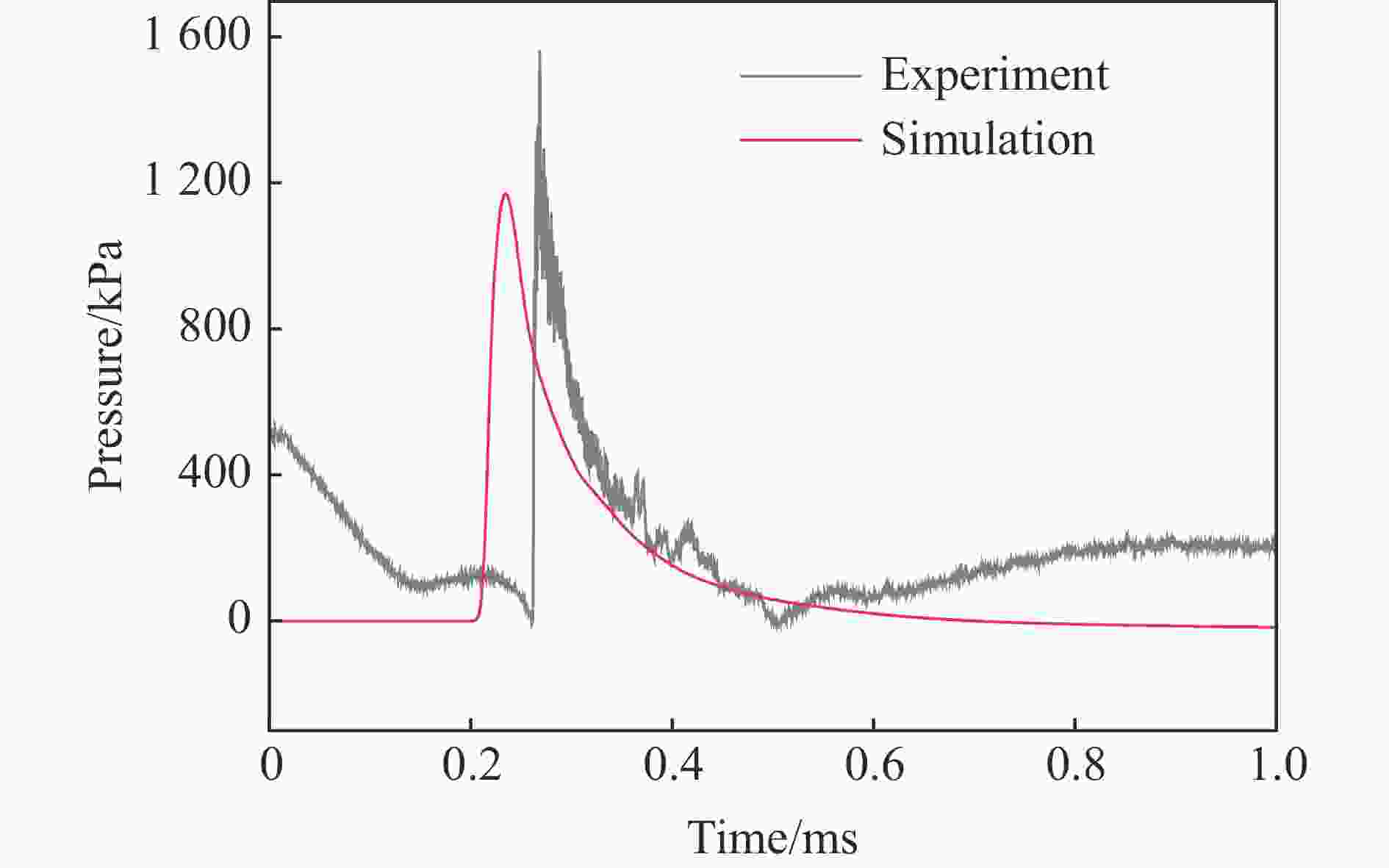
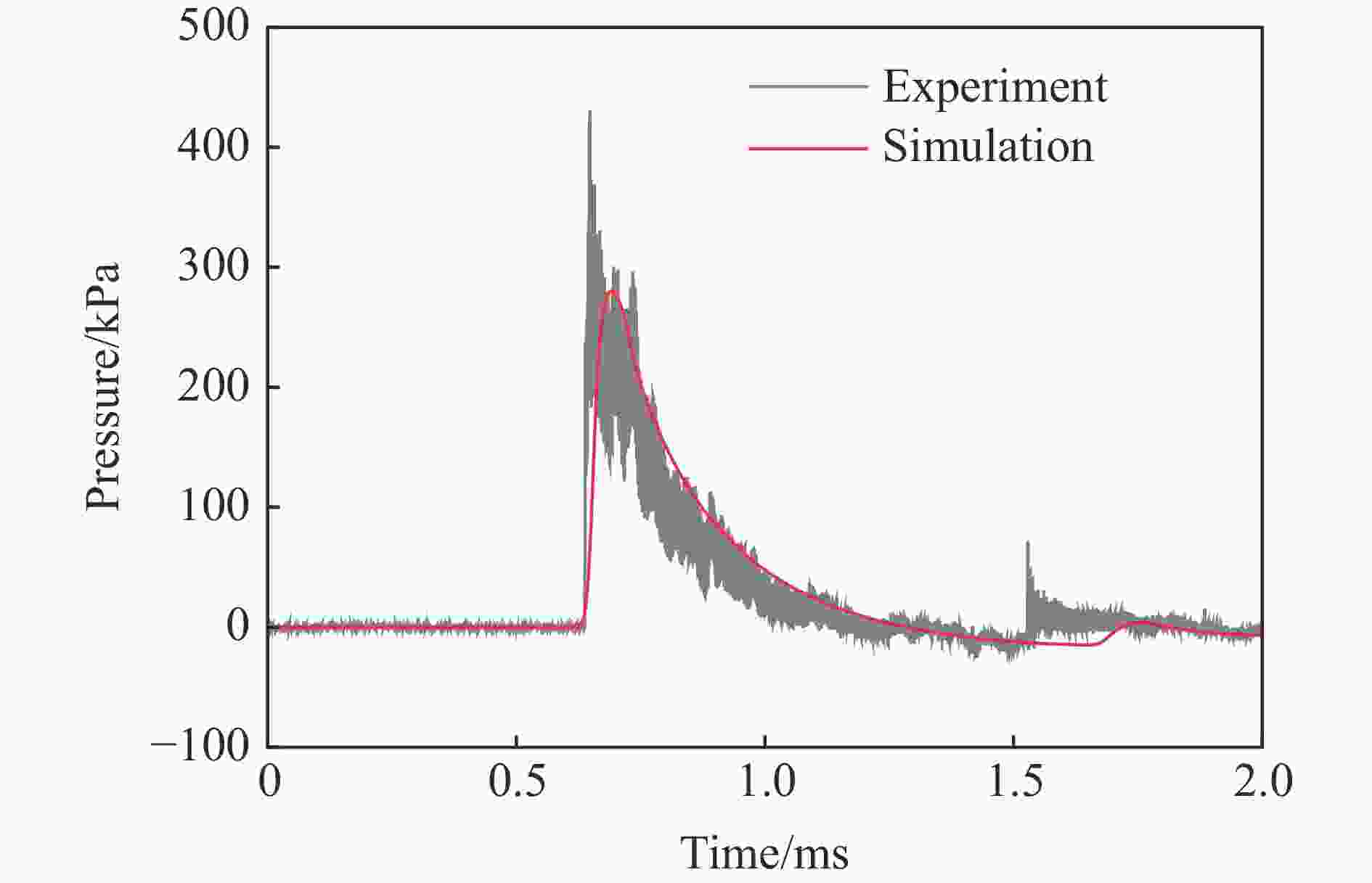
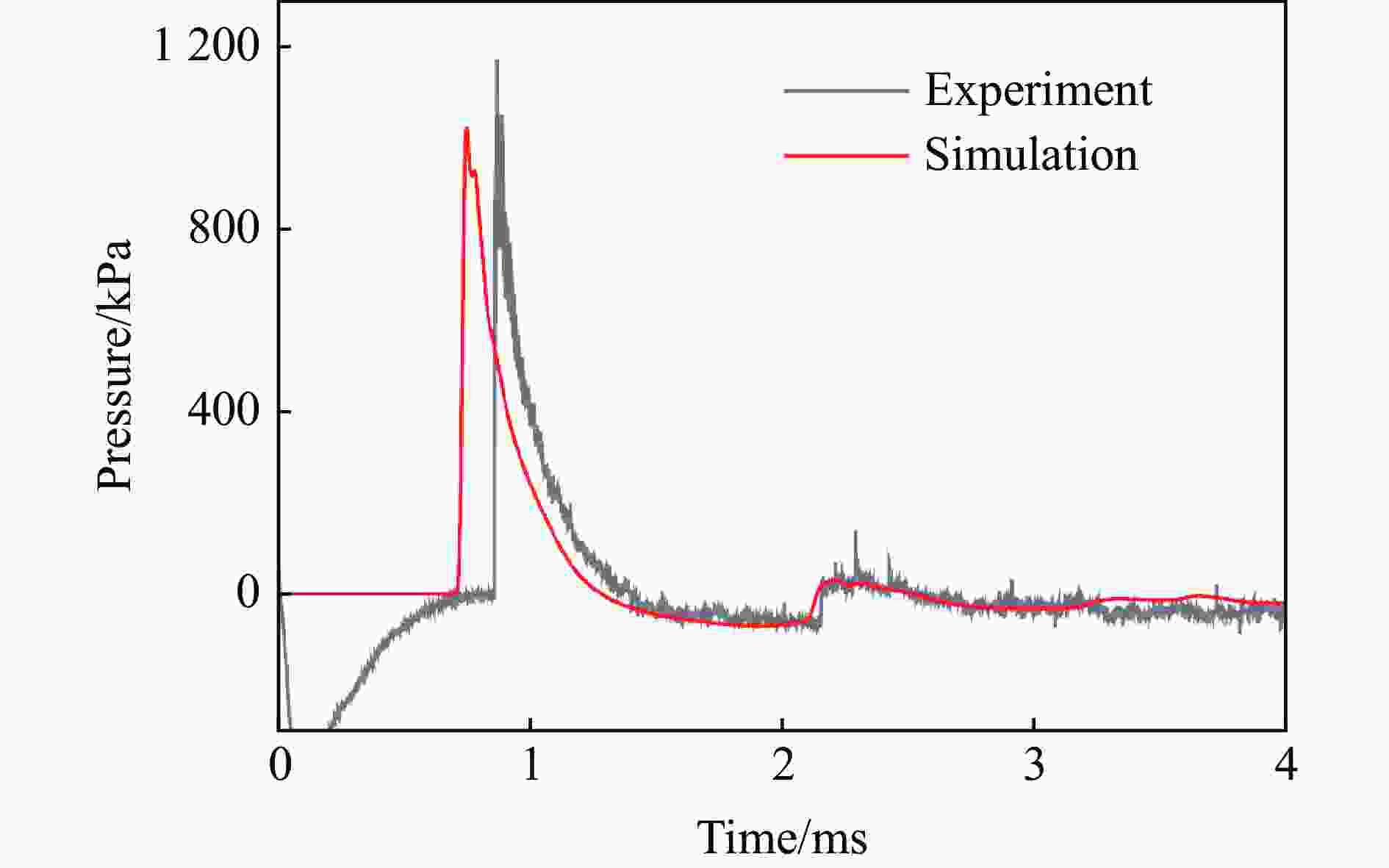
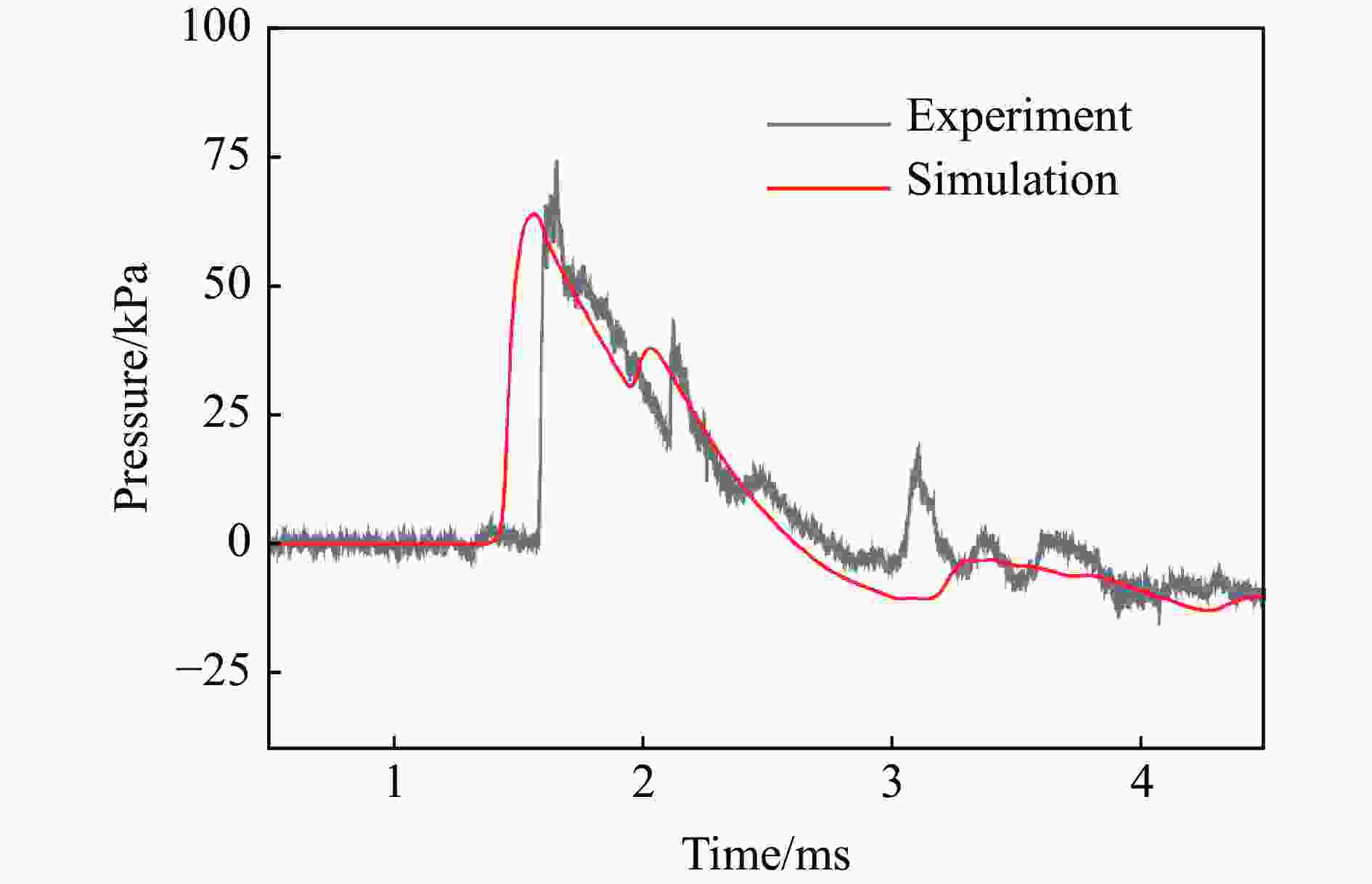
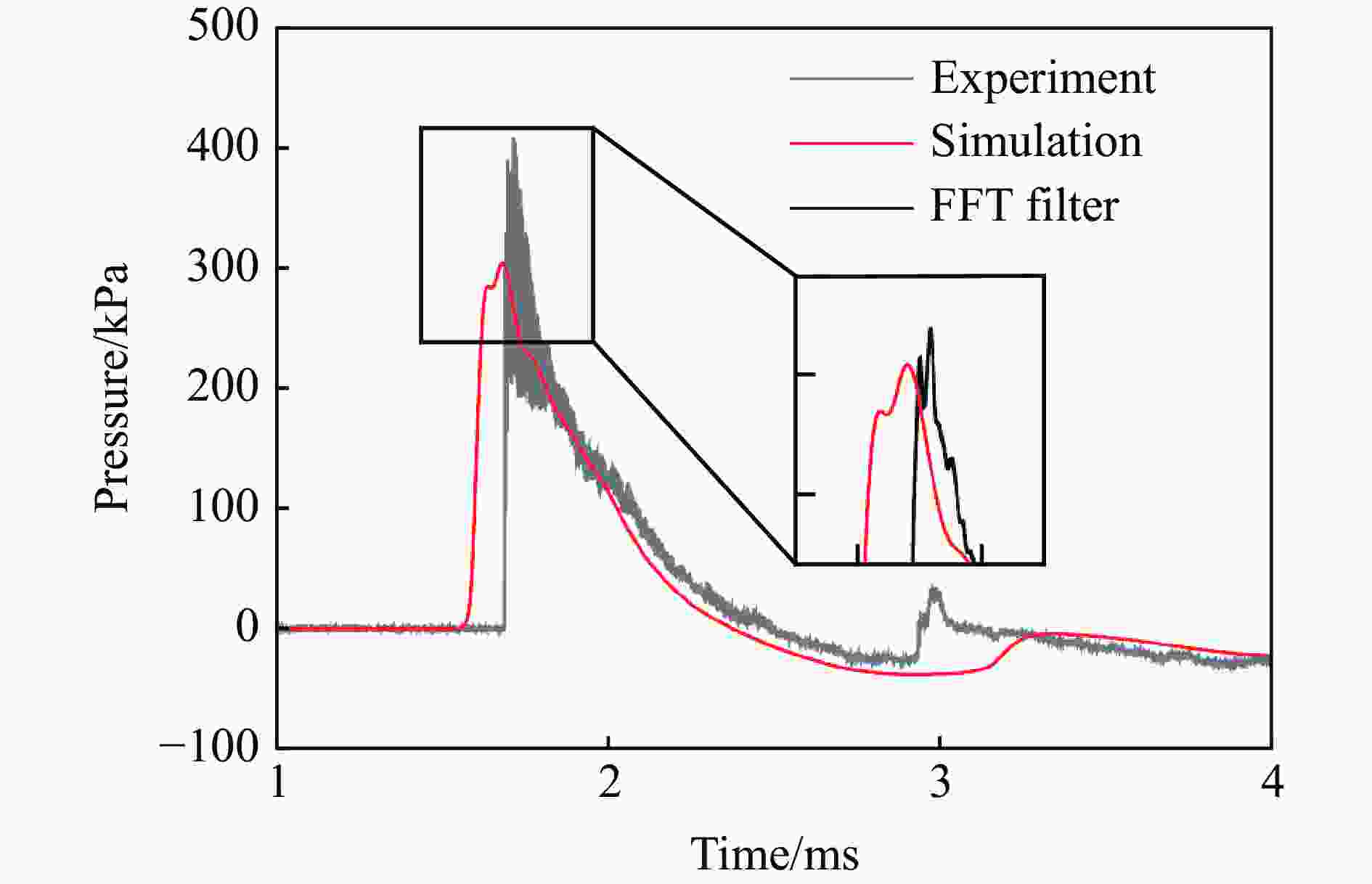
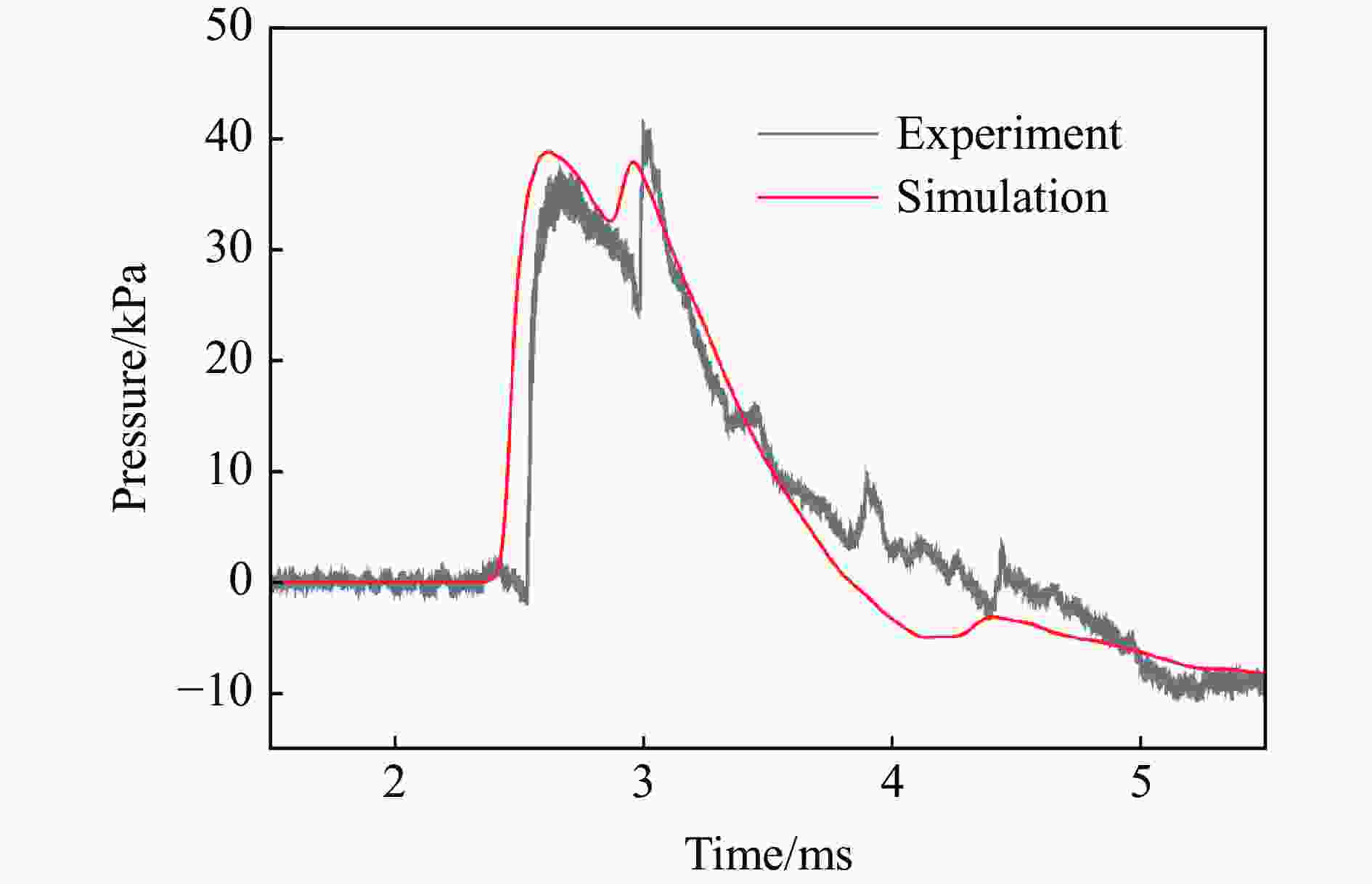
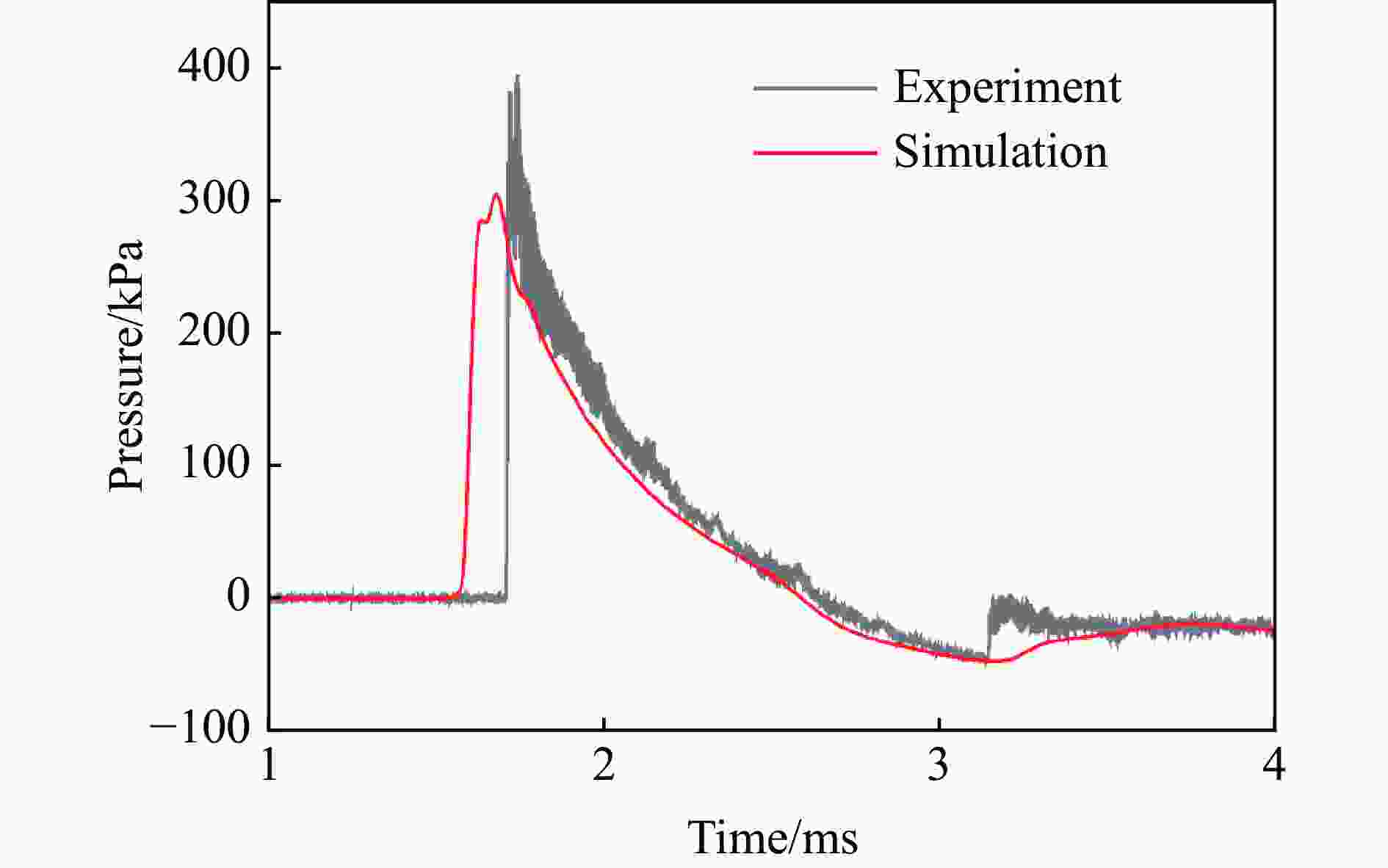
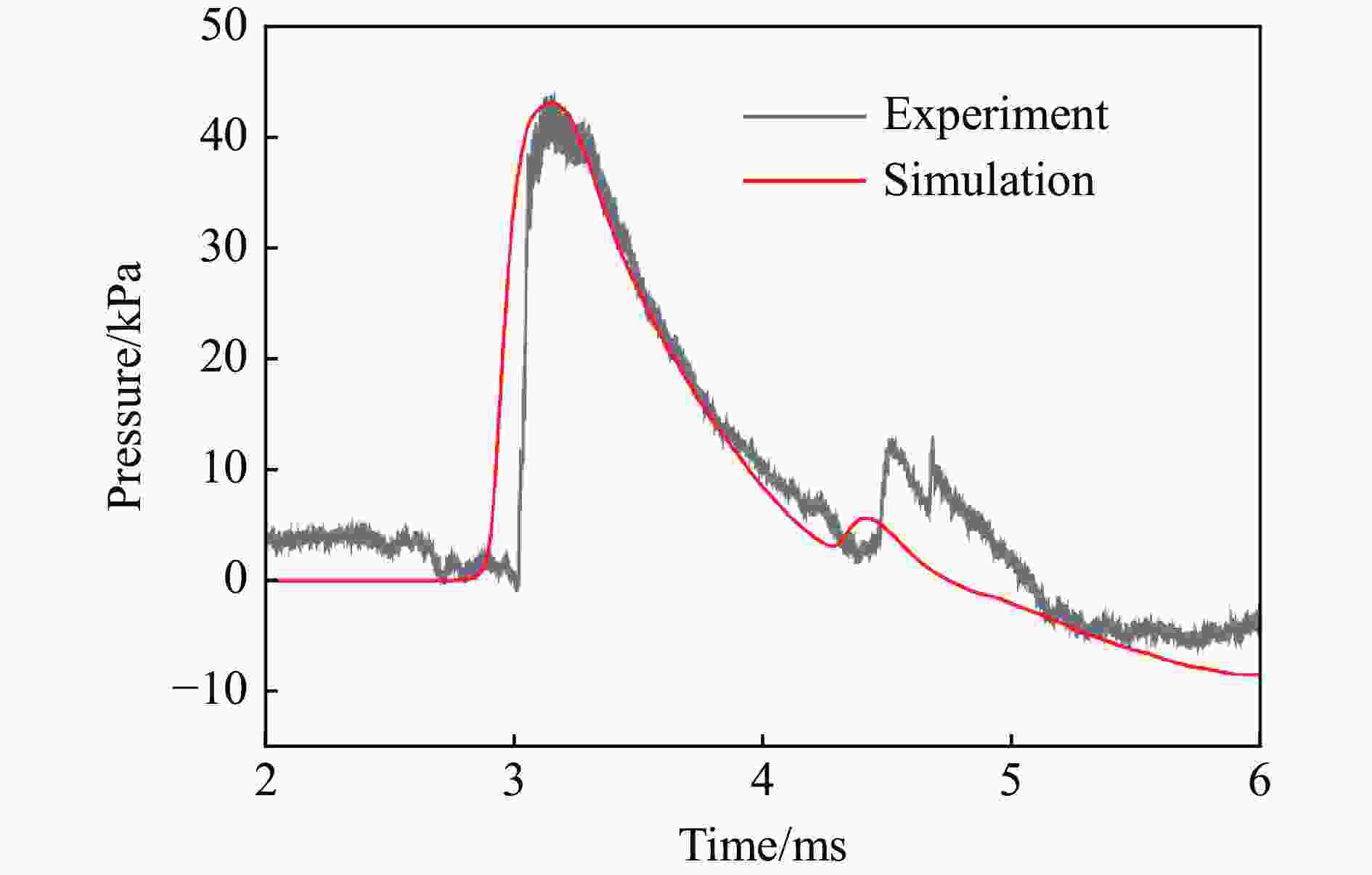
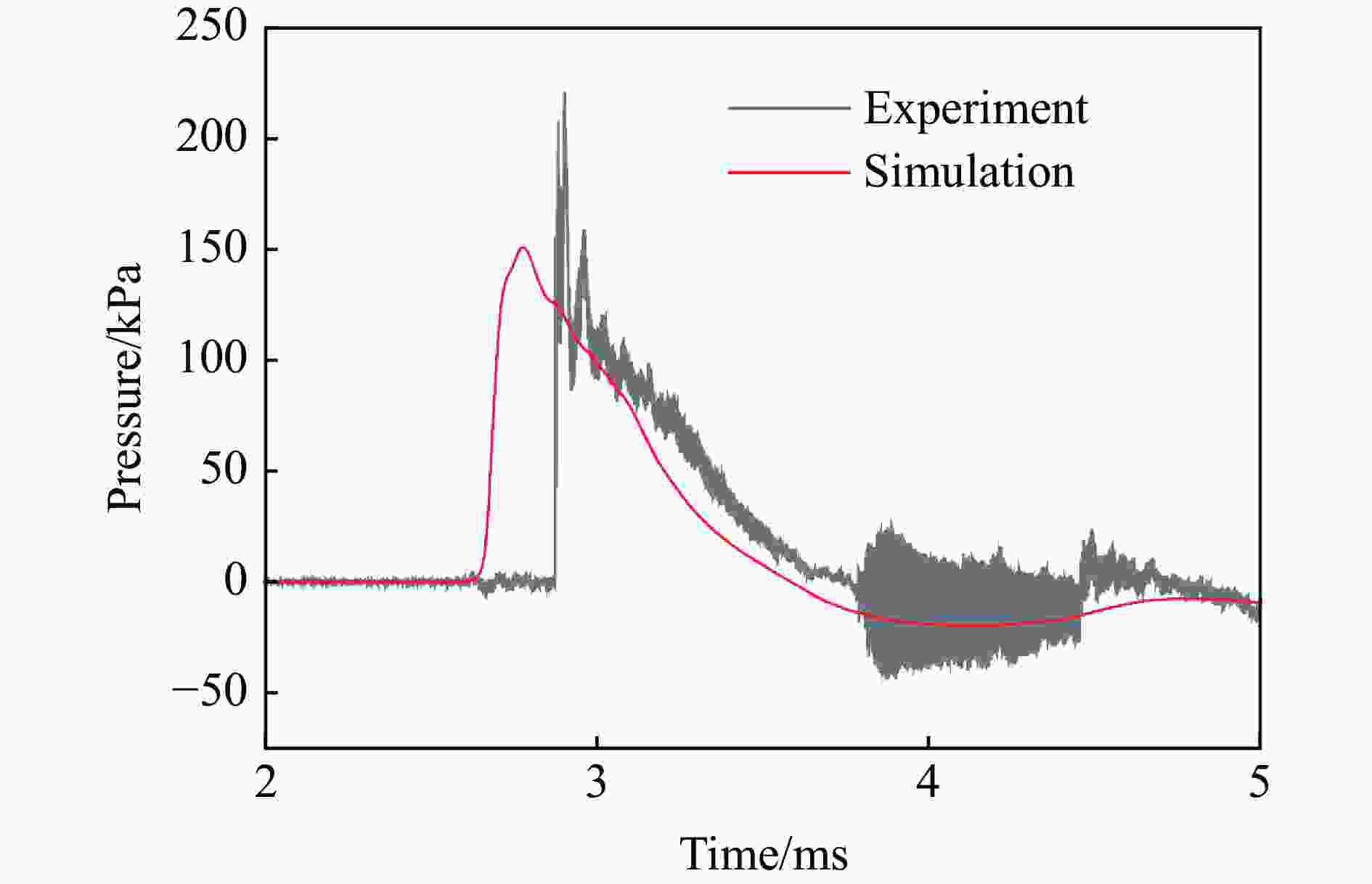
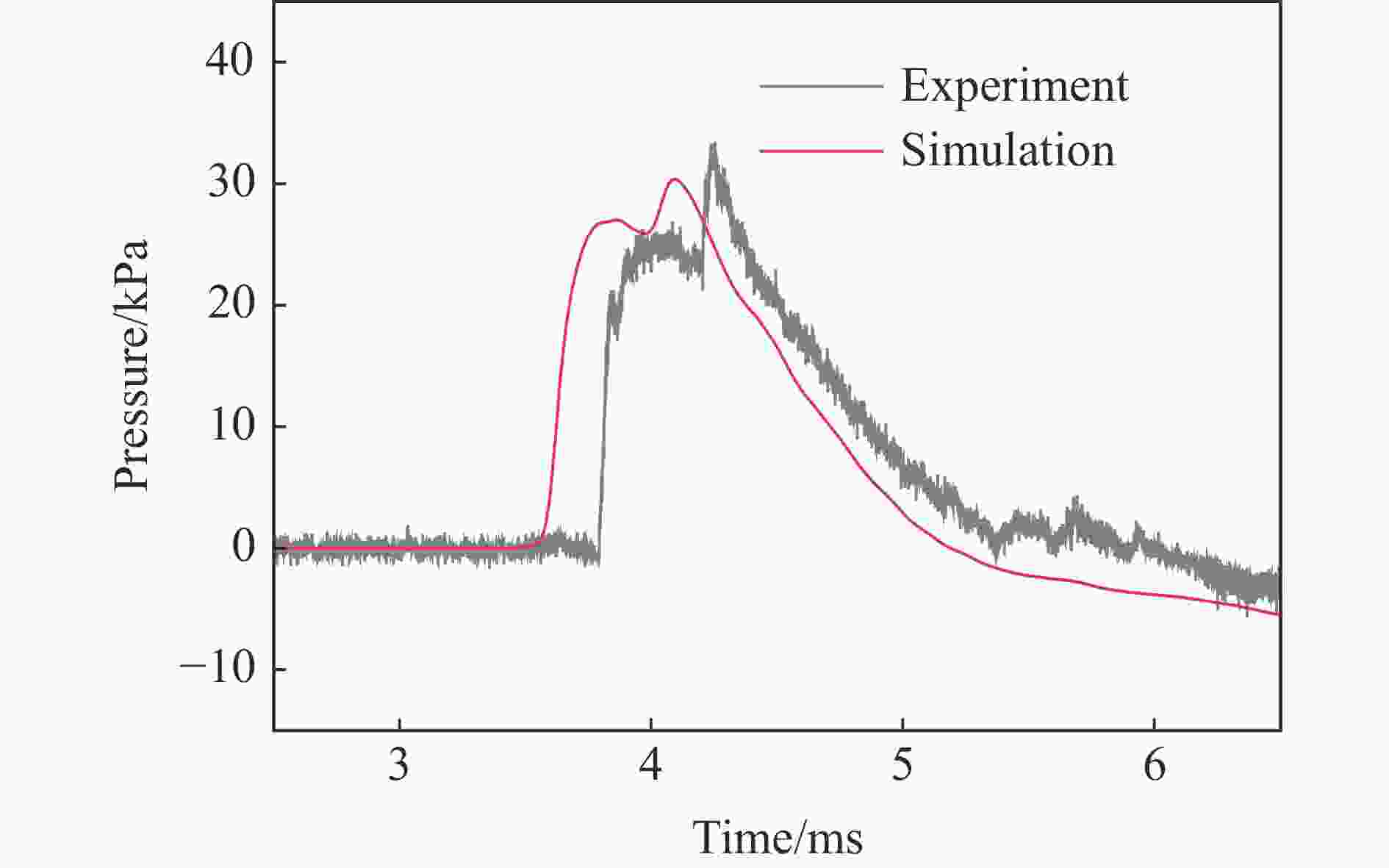
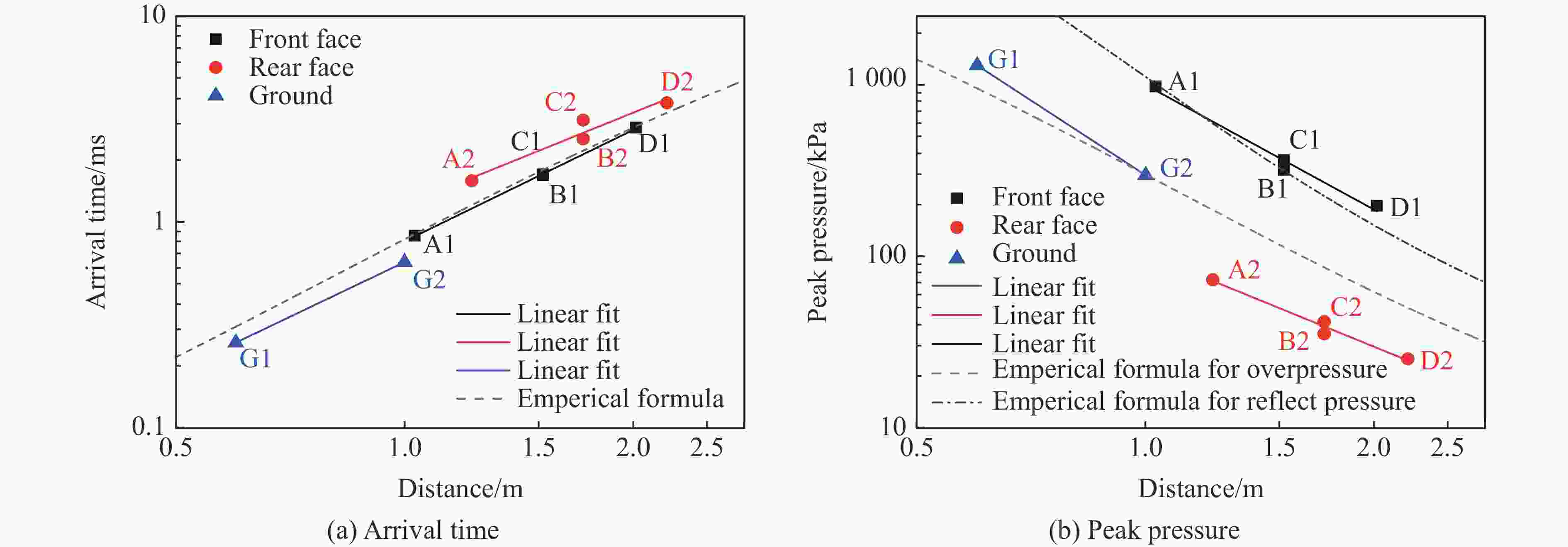
表 1 各测点冲击波参数实验与模拟结果定量对比
Table 1. Quantitative comparison of blast wave parameters at pressure gauges
测点 ta/ms 误差/% td/ms 误差/% pm/kPa 误差/% I/(Pa∙s) 误差/% 实验 模拟 实验 模拟 实验 模拟 实验 模拟 A1 0.86 0.72 −16.3 0.54 0.57 5.56 978.1 1021 4.39 146.5 183.6 25.3 A2 1.59 1.44 −9.43 1.14 1.18 3.51 72.97 63.92 −12.4 30.65 37.00 20.7 B1 1.69 1.59 −5.92 0.80 0.78 −2.50 319.1 304.1 −4.70 86.24 100.0 16.0 B2 2.54 2.44 −3.94 1.78 1.40 −21.3 35.38 32.24 −8.88 29.54 32.28 9.28 C1 1.71 1.59 −7.02 0.93 1.00 7.53 363.2 304.1 −16.3 102.7 114.9 11.9 C2 3.13 2.91 −7.03 2.03 1.84 −9.36 41.56 43.06 3.61 32.17 31.78 −1.21 D1 2.88 2.66 −7.64 0.88 0.92 4.55 197.5 150.9 −23.6 50.88 63.48 24.8 D2 3.80 3.59 −5.53 1.57 1.60 1.91 24.66 27.00 9.49 25.37 26.42 4.14 G1 0.26 0.21 −19.2 0.24 0.49 104 1299 1172 −9.78 84.05 109.4 30.2 G2 0.64 0.64 0.00 0.59 0.64 8.47 297.4 280.2 −5.78 47.53 56.74 19.4 -
[1] TAYLOR G I. The formation of a blast wave by a very intense explosion I. Theoretical discussion [J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1950, 201(1065): 159–174. DOI: 10.1098/rspa.1950.0049. [2] SEDOV L I. Propagation of strong shock waves [J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1946, 10: 241–250. [3] BRODE H L. Numerical solutions of spherical blast waves [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1955, 26(6): 766–775. DOI: 10.1063/1.1722085. [4] HENRYCH J. The dynamics of explosion and its use [M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1979. [5] KINNEY G F, GRAHAM K J. Explosive shocks in air [M]. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 1985. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-86682-1. [6] SADOVSKIY M A. Mechanical action of air shock waves of explosion, based on experimental data [M]. Moscow: Nauka Press, 1952: 6–10. [7] UFC. UFC 3-340-02 Structures to resist the effects of accidental explosions [S]. Washington: The U. S. Department of Defense, 2008. [8] FEMA. Reference manual to mitigate potential terrorist attacks against buildings: FEMA 426 [R]. Federal Emergency Management Agency, 2003. [9] HAO H, HAO Y F, LI J, et al. Review of the current practices in blast-resistant analysis and design of concrete structures [J]. Advances in Structural Engineering, 2016, 19(8): 1193–1223. DOI: 10.1177/1369433216656430. [10] ULLAH A, AHMAD F, JANG H W, et al. Review of analytical and empirical estimations for incident blast pressure [J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2017, 21(6): 2211–2225. DOI: 10.1007/s12205-016-1386-4. [11] ISAAC O S, ALSHAMMARI O G, PICKERING E G, et al. Blast wave interaction with structures-An overview [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2023, 14(4): 584–630. DOI: 10.1177/20414196221118595. [12] REMENNIKOV A M, MENDIS P A. Prediction of airblast loads in complex environments using artificial neural networks [J]. WIT Transactions on the Built Environment, 2006, 87: 269–278. DOI: 10.2495/su060271. [13] BENSELAMA A M, WILLIAM-LOUIS M J P, MONNOYER F. Prediction of blast wave effects on a developed site [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2010, 37(4): 385–396. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2009.08.003. [14] CODINA R H, AMBROSINI R D, DE BORBÓN F M. Numerical study of confined explosions in urban environments [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2013, 4(4): 591–618. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.4.4.591. [15] 都浩, 李忠献, 郝洪. 建筑物外部爆炸超压荷载的数值模拟 [J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 8(5): 413–418. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2007.05.002.DU H, LI Z X, HAO H. Numerical simulation on blast overpressure loading outside buildings [J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology, 2007, 8(5): 413–418. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2007.05.002. [16] 李鑫, 吴桂英, 贾昊凯. 挡墙对爆炸冲击波传播影响的数值模拟 [J]. 工程力学, 2012, 29(2): 245–250.LI X, WU G Y, JIA H K. The numerical simulation of explosion shock wave propagation subject to the retaining wall [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(2): 245–250. [17] 穆朝民, 任辉启, 李永池, 等. 爆炸冲击波作用于墙体及对墙体绕射的实验研究 [J]. 实验力学, 2008, 23(2): 169–174.MU C M, REN H Q, LI Y C, et al. Experimental study of blast wave reflection and diffraction on a shelter wall [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2008, 23(2): 169–174. [18] 王仲琦, 宁建国, 赵衡阳, 等. 挡墙对远场爆炸效应影响的数值模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2000, 20(1): 87–91. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2000.01.016.WANG Z Q, NING J G, ZHAO H Y, et al. Numerical simulation on 2D explosion field with the protective wall [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2000, 20(1): 87–91. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1455.2000.01.016. [19] SOCHET I, EVEILLARD S, VINÇONT J Y, et al. Influence of the geometry of protective barriers on the propagation of shock waves [J]. Shock Waves, 2017, 27(2): 209–219. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-016-0625-4. [20] ZHOU X Q, HAO H. Prediction of airblast loads on structures behind a protective barrier [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(5): 363–375. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.03.003. [21] SUNG S H, CHONG J W. A fast-running method for blast load prediction shielding by a protective barrier [J]. Defence Technology, 2020, 16(2): 308–315. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2019.07.011. [22] HÁJEK R, FOGLAR M. The reduction of peak overpressure using concrete blast barriers [J]. WIT Transactions on the Built Environment, 2014, 141: 265–275. DOI: 10.2495/SUSI140231. [23] TRÉLAT S, SOCHET I, AUTRUSSON B, et al. Strong explosion near a parallelepipedic structure [J]. Shock Waves, 2007, 16(4/5): 349–357. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-006-0069-3. [24] GEBBEKEN N, DÖGE T. Explosion protection-Architectural design, urban planning and landscape planning [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2010, 1(1): 1–21. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.1.1.1. [25] GAJEWSKI T, SIELICKI P W. Experimental study of blast loading behind a building corner [J]. Shock Waves, 2020, 30(4): 385–394. DOI: 10.1007/s00193-020-00936-1. [26] 汪维, 刘光昆, 赵强, 等. 近爆作用下方形板表面爆炸载荷分布函数研究 [J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2020, 50(2): 024615. DOI: 10.1360/SSPMA-2019-0188.WANG W, LIU G K, ZHAO Q, et al. Study on load distributing function of square slab surface under close-in blast loading [J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2020, 50(2): 024615. DOI: 10.1360/SSPMA-2019-0188. [27] 喻君, 刘福余, 方秦. 近场近地爆炸下建筑柱爆炸荷载分布规律及简化模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(1): 015201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0366.YU J, LIU F Y, FANG Q. Distribution pattern and simplified model of blast load for building columns under near-field near-ground explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(1): 015201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0366. [28] REMENNIKOV A M, ROSE T A. Modelling blast loads on buildings in complex city geometries [J]. Computers & Structures, 2005, 83(27): 2197–2205. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruc.2005.04.003. [29] HANSEN O R, HINZE P, ENGEL D, et al. Using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) for blast wave predictions [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2010, 23(6): 885–906. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2010.07.005. [30] ZHENG H W, SHU C, CHEW Y T, et al. A solution adaptive simulation of compressible multi-fluid flows with general equation of state [J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2011, 67(5): 616–637. DOI: 10.1002/fld.2380. [31] SHYUE K M. A fluid-mixture type algorithm for compressible multicomponent flow with Mie-Grüneisen equation of state [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2001, 171(2): 678–707. DOI: 10.1006/jcph.2001.6801. [32] HOUIM R W, ORAN E S. A multiphase model for compressible granular–gaseous flows: formulation and initial tests [J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 789: 166–220. DOI: 10.1017/jfm.2015.728. [33] 赵亚梅. 某微型压力传感器瞬态光效应的实验与数据处理方法研究 [D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2007.ZHAO Y M. Research on experiment and data processing meathod of certain minisize pressure sensor instantaneous light effect [D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2007. [34] 杜红棉, 祖静, 张志杰. 压阻传感器8530B闪光响应规律研究 [J]. 测试技术学报, 2011, 25(1): 78–81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7449.1011.01.014.DU H M, ZU J, ZHANG Z J. Research on photoflash response of piezoresistive transducers 8503B [J]. Journal of Test and Measurement Technology, 2011, 25(1): 78–81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7449.1011.01.014. [35] 张健中, 杜红棉, 韩青林, 等. 压阻式压力传感器光干扰消除实验及测试 [J]. 仪表技术与传感器, 2014(1): 14–15,18. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2014.01.005.ZHANG J Z, DU H M, HAN Q L, et al. Experiment and test of photoflash response elimination for piezoresistive pressure sensor [J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2014(1): 14–15,18. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2014.01.005. [36] NEEDHAM C E. Blast waves [M]. 2nd ed. Cham: Springer, 2018. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-65382-2. -






 下载:
下载: