A digital intelligence simulation model for explosion power field and urban building damage effect and its application
-
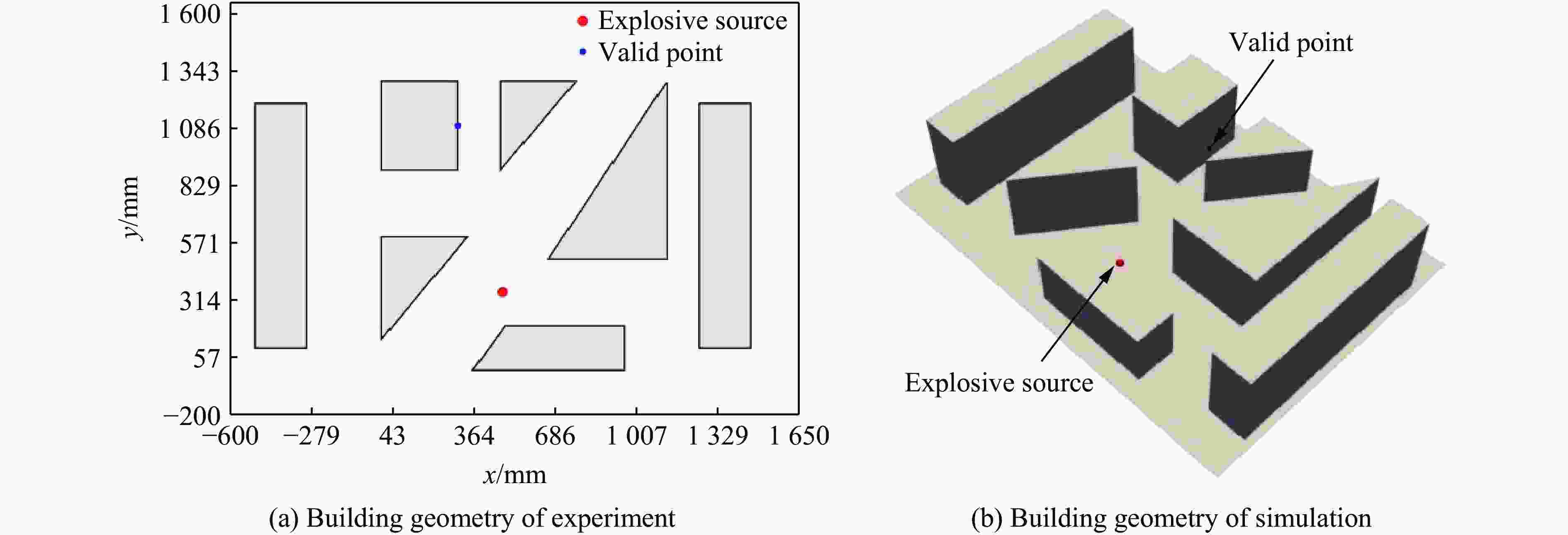
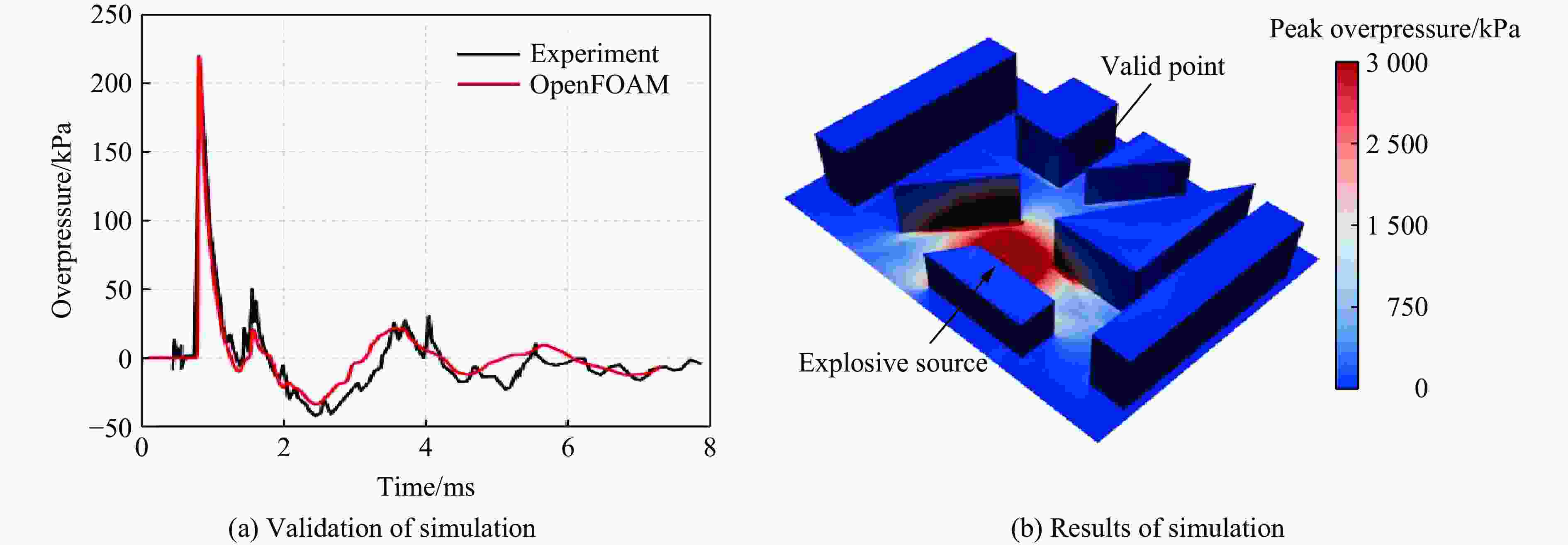
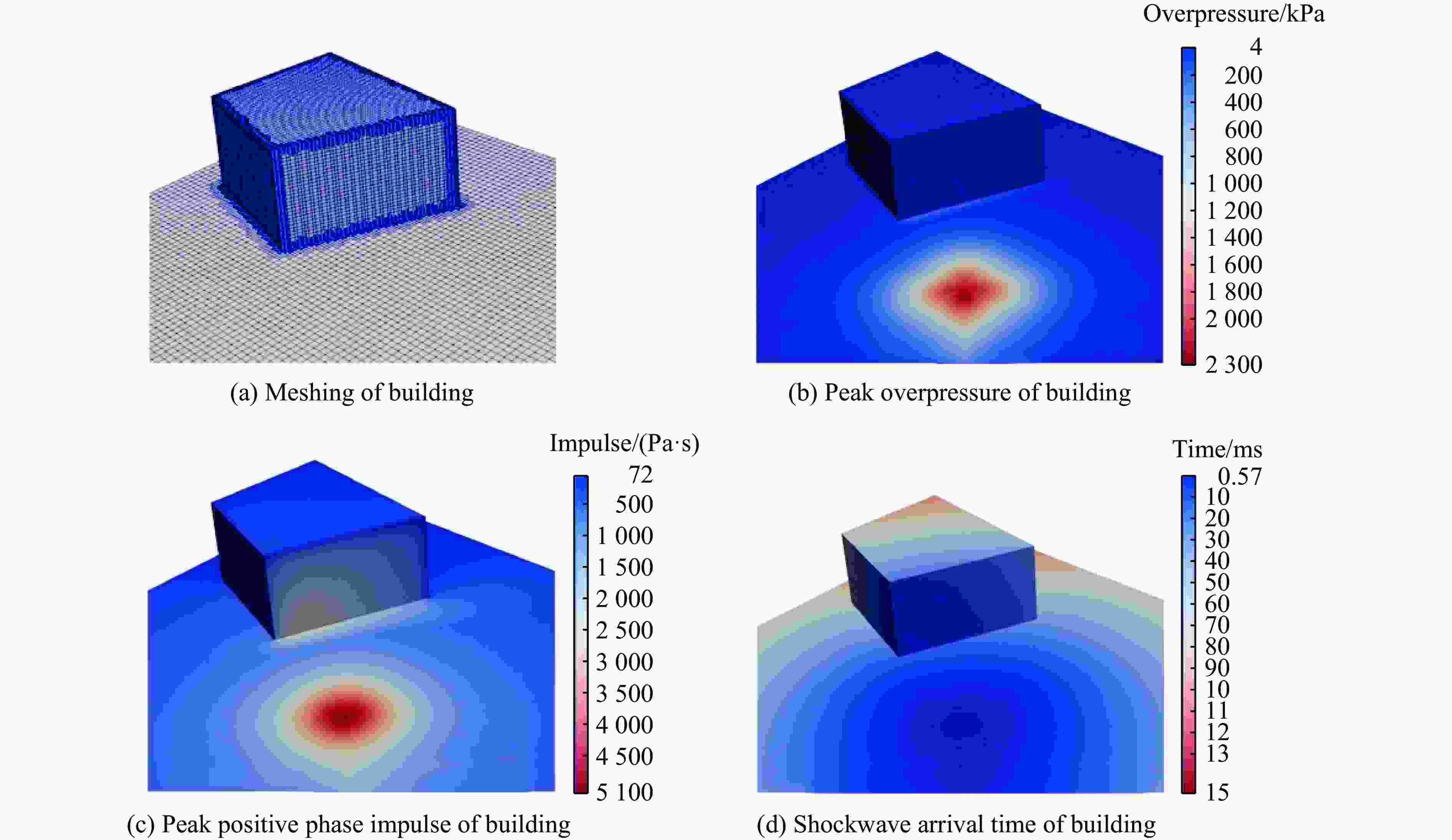
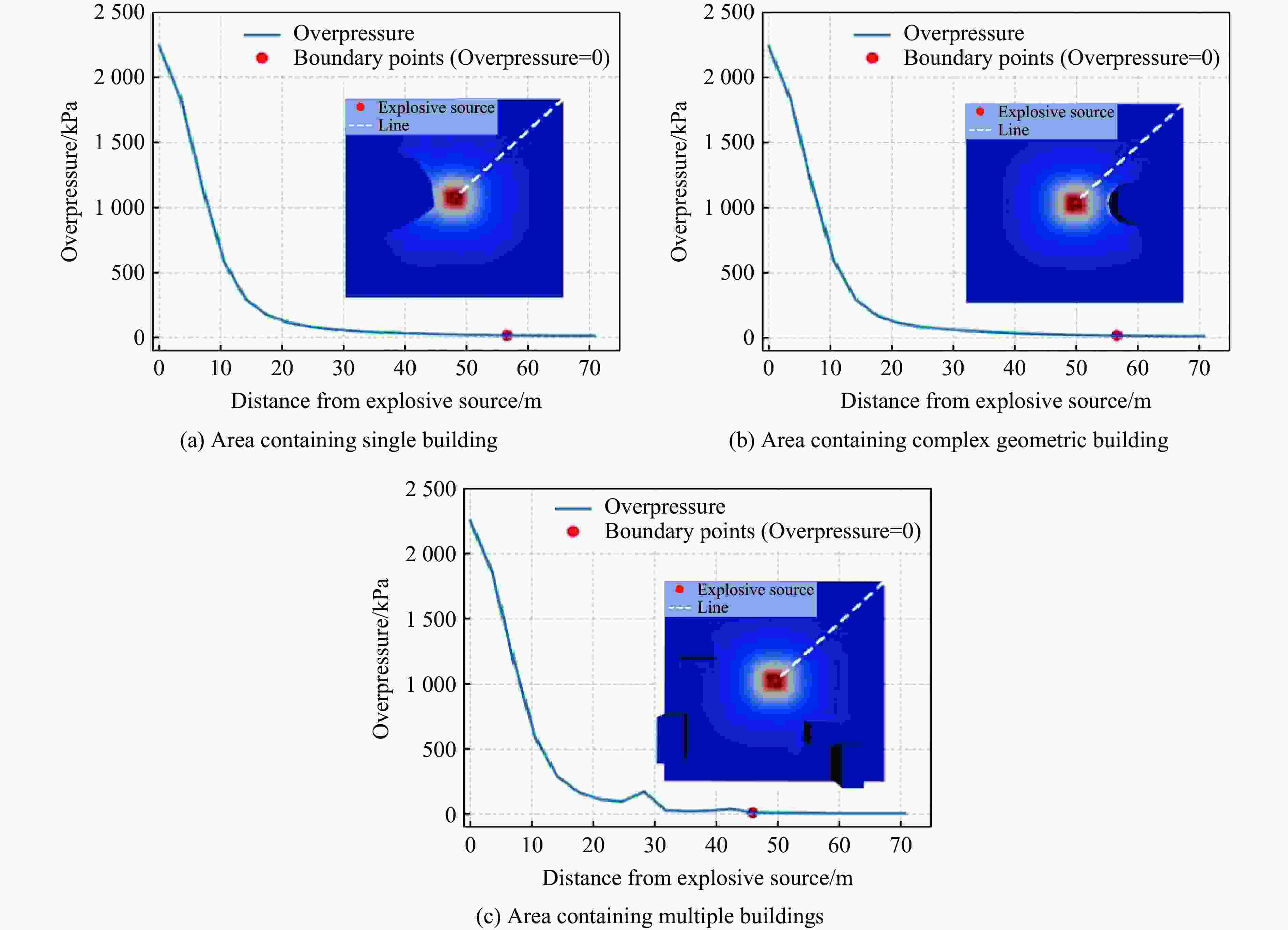
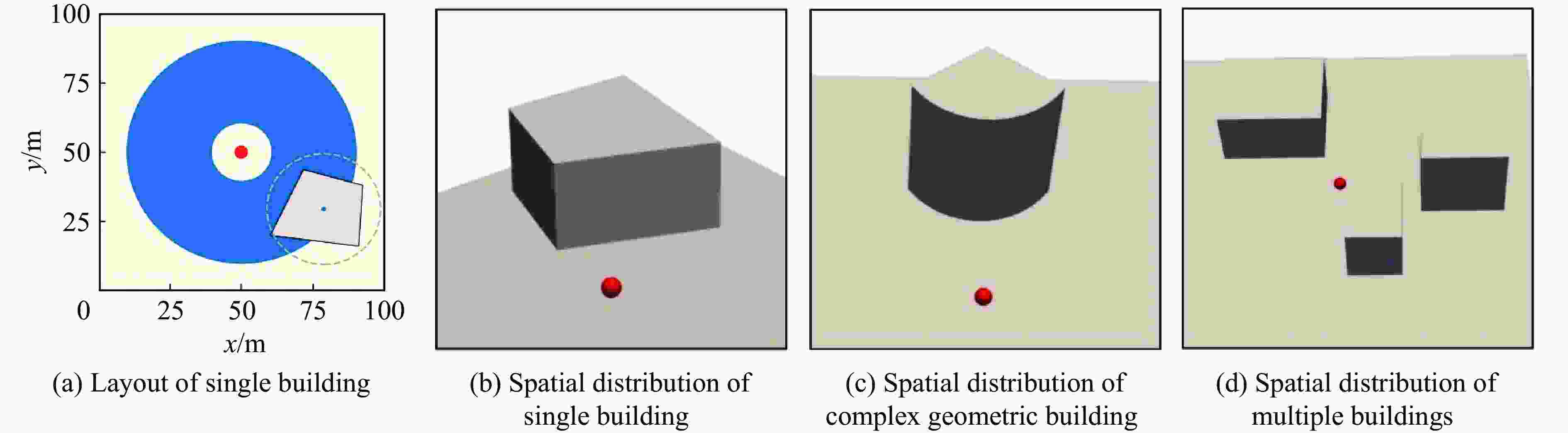
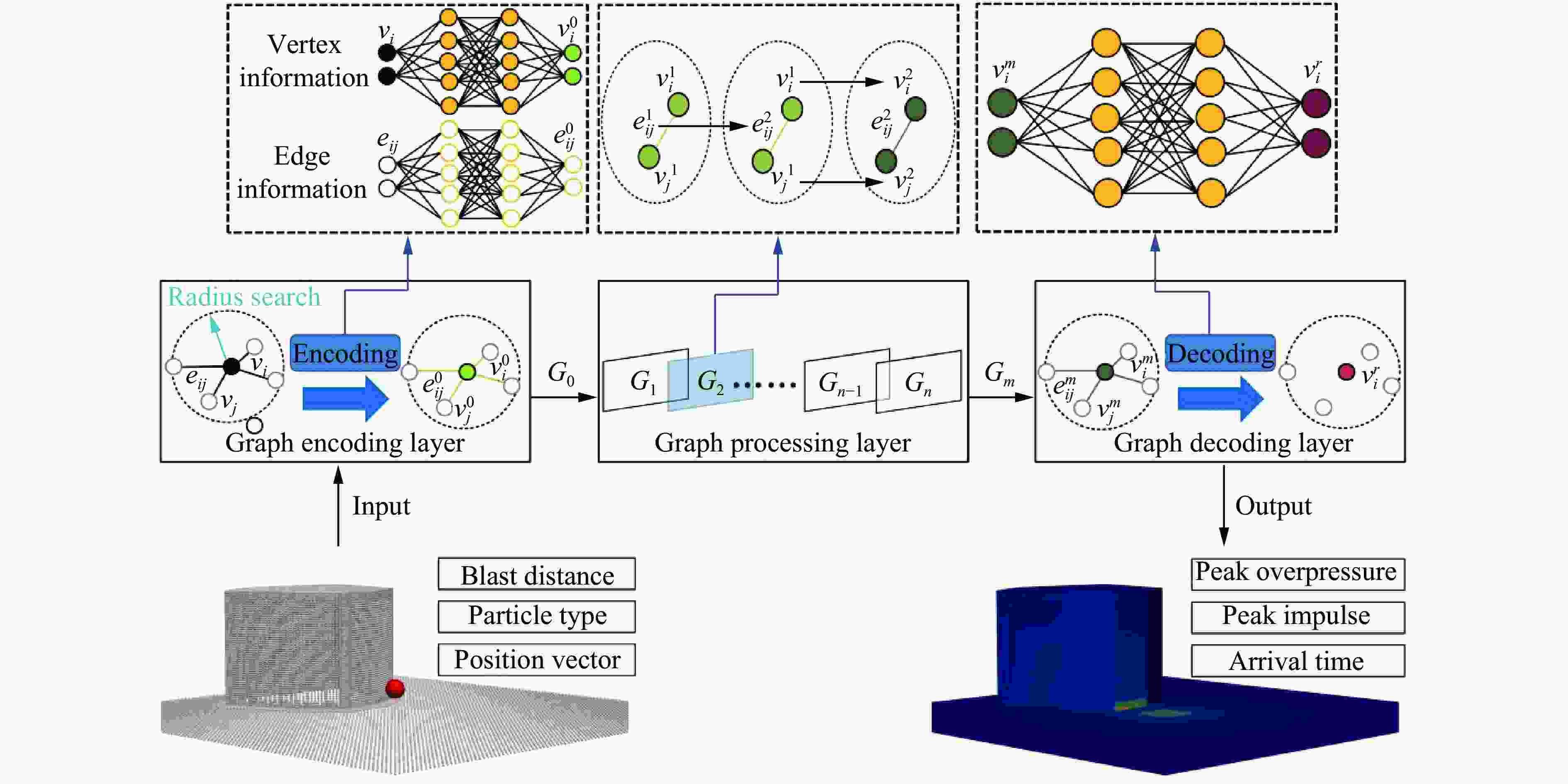
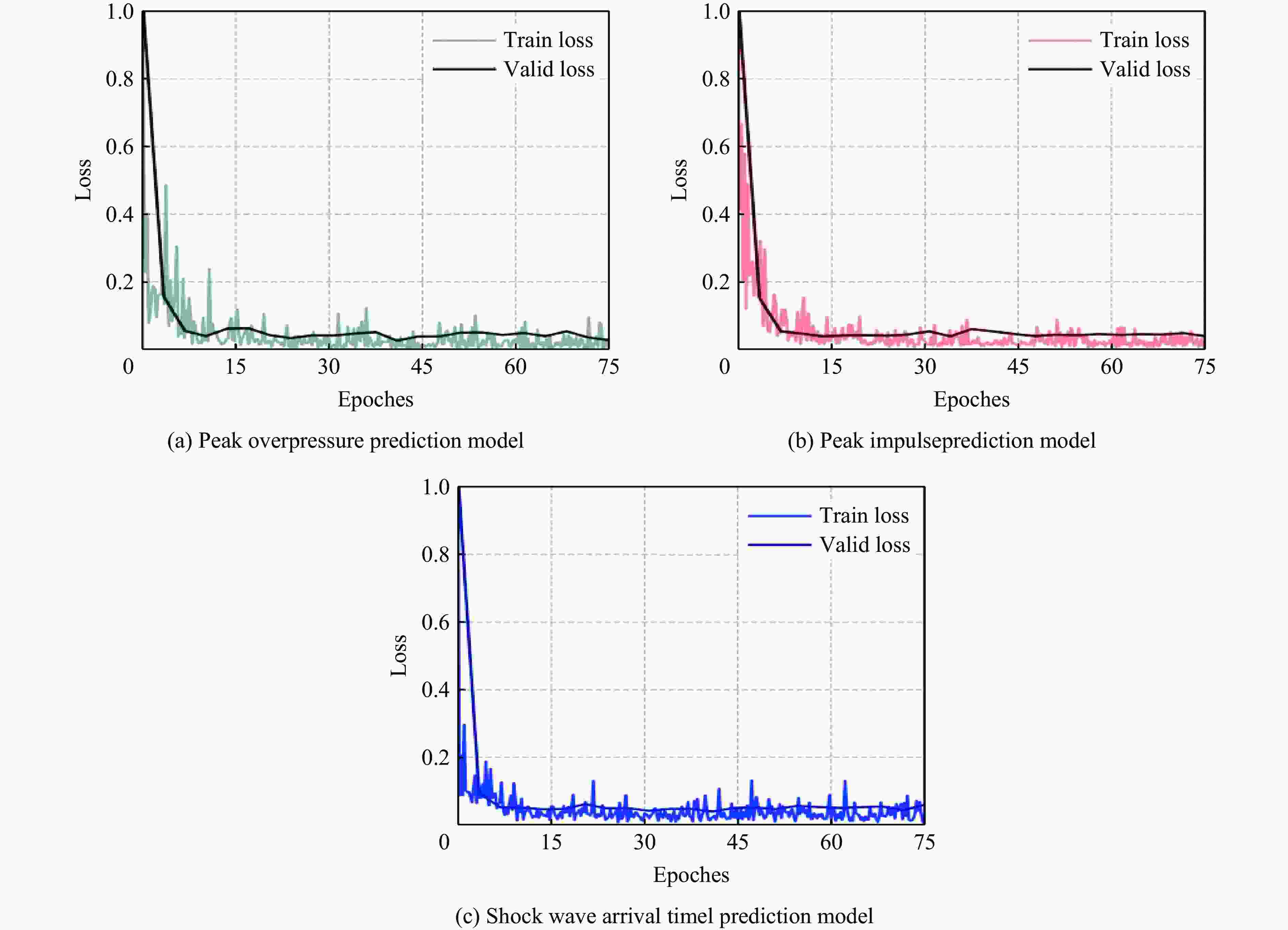
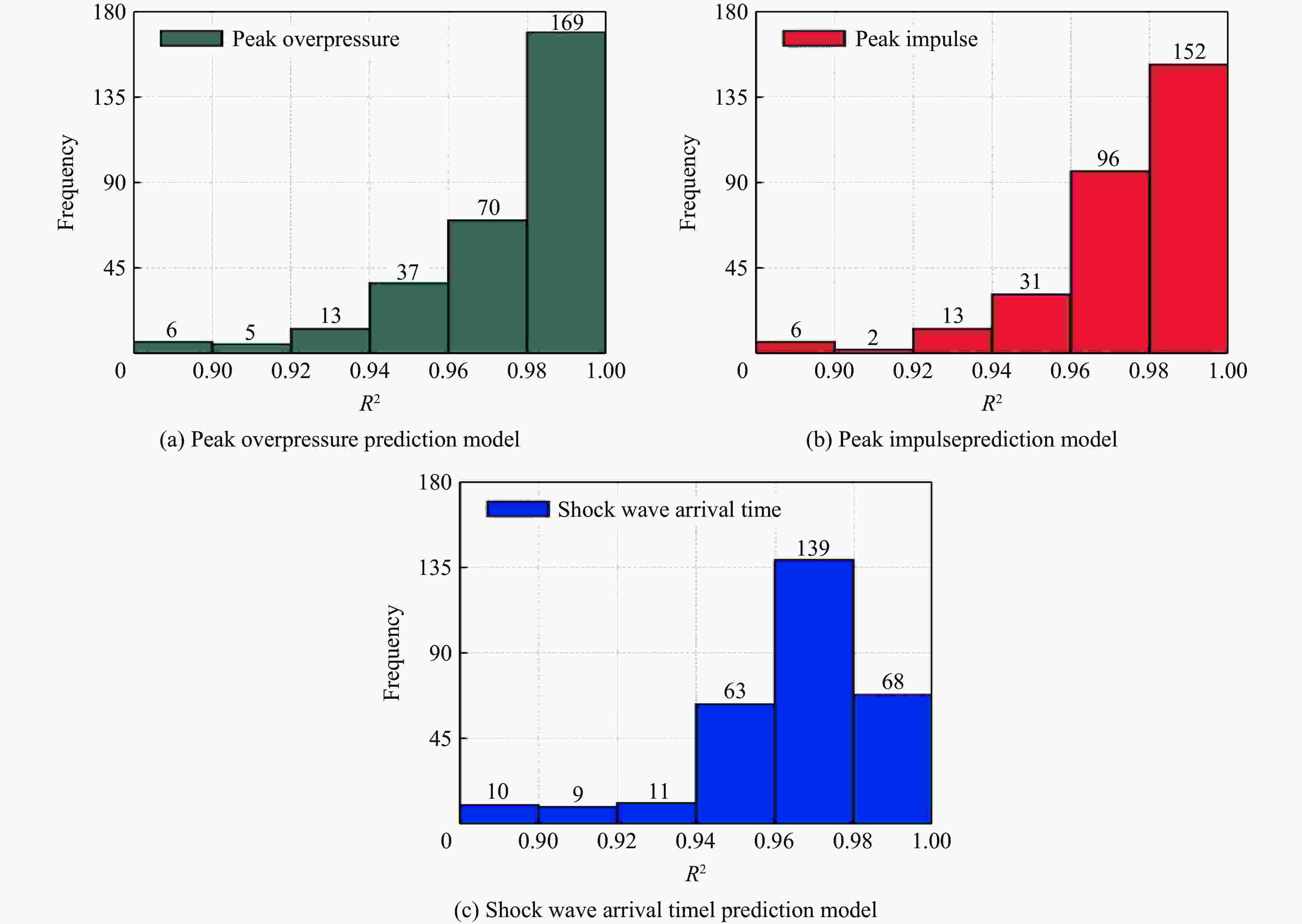
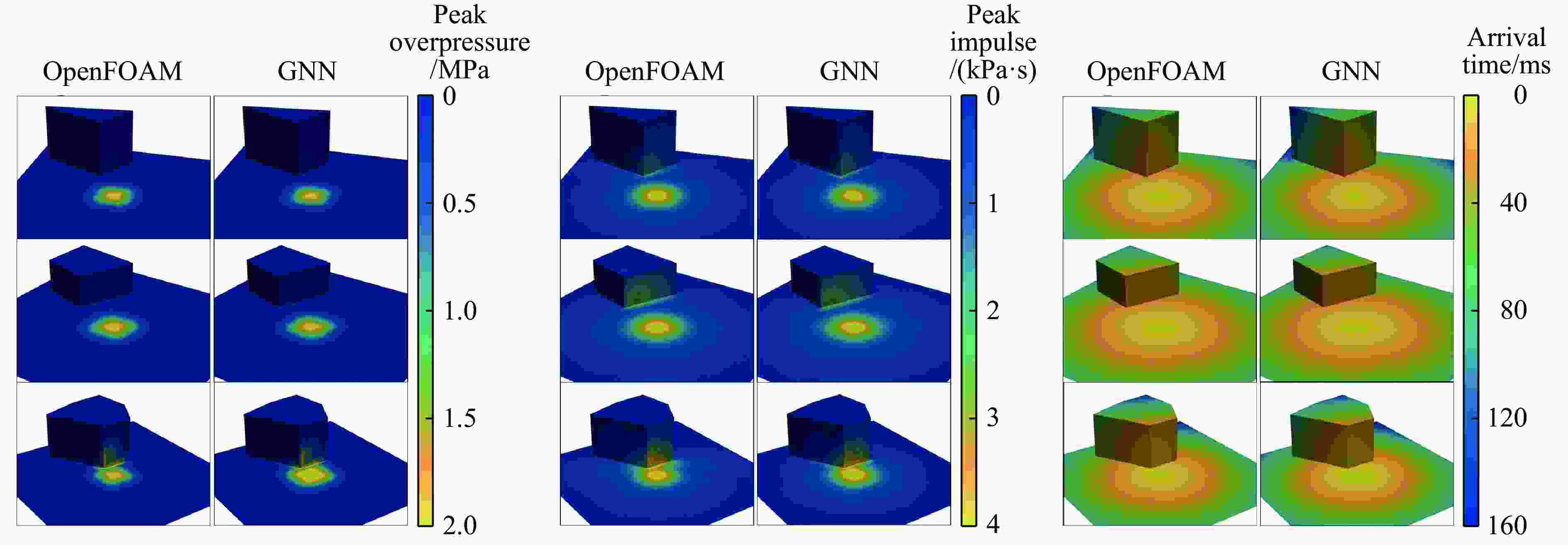
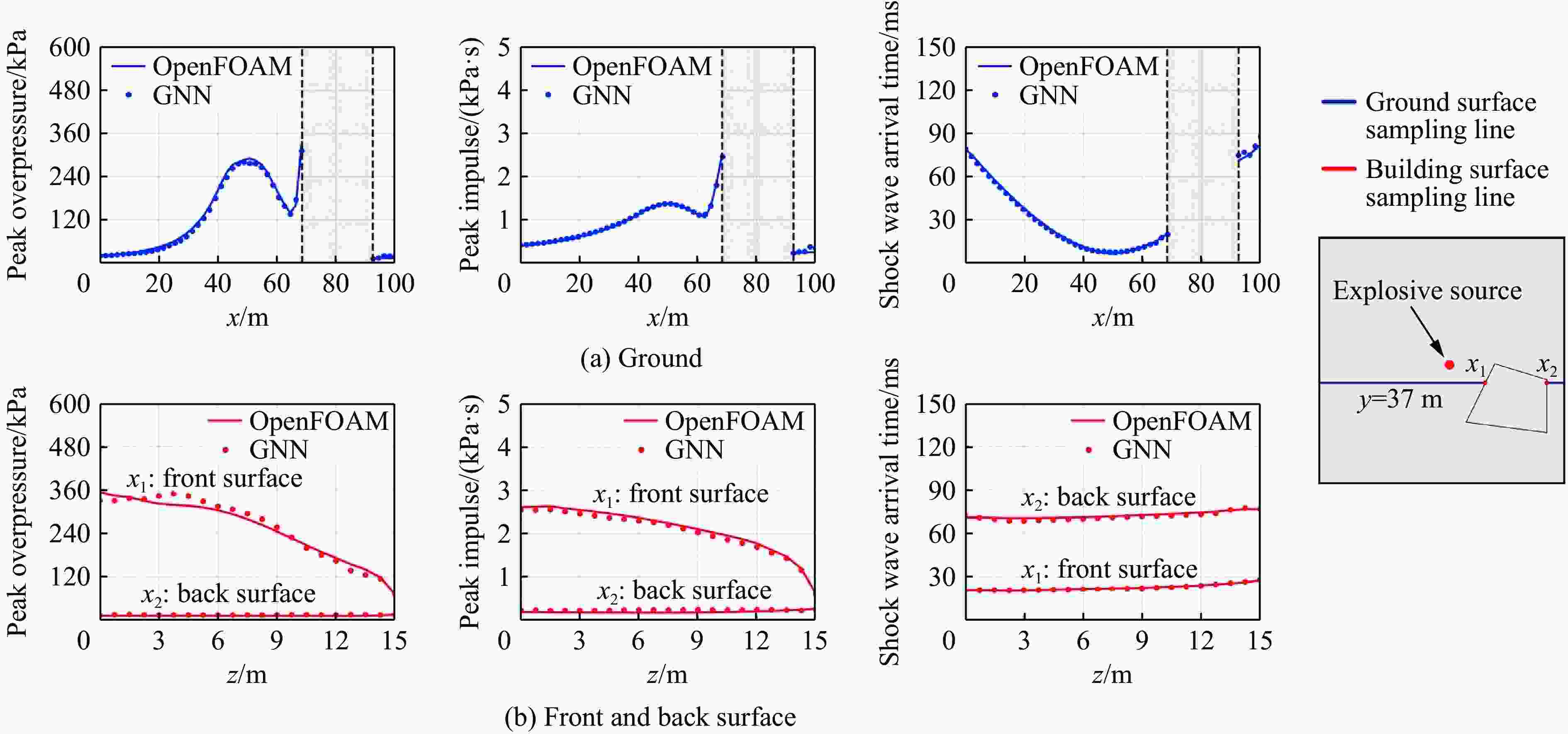
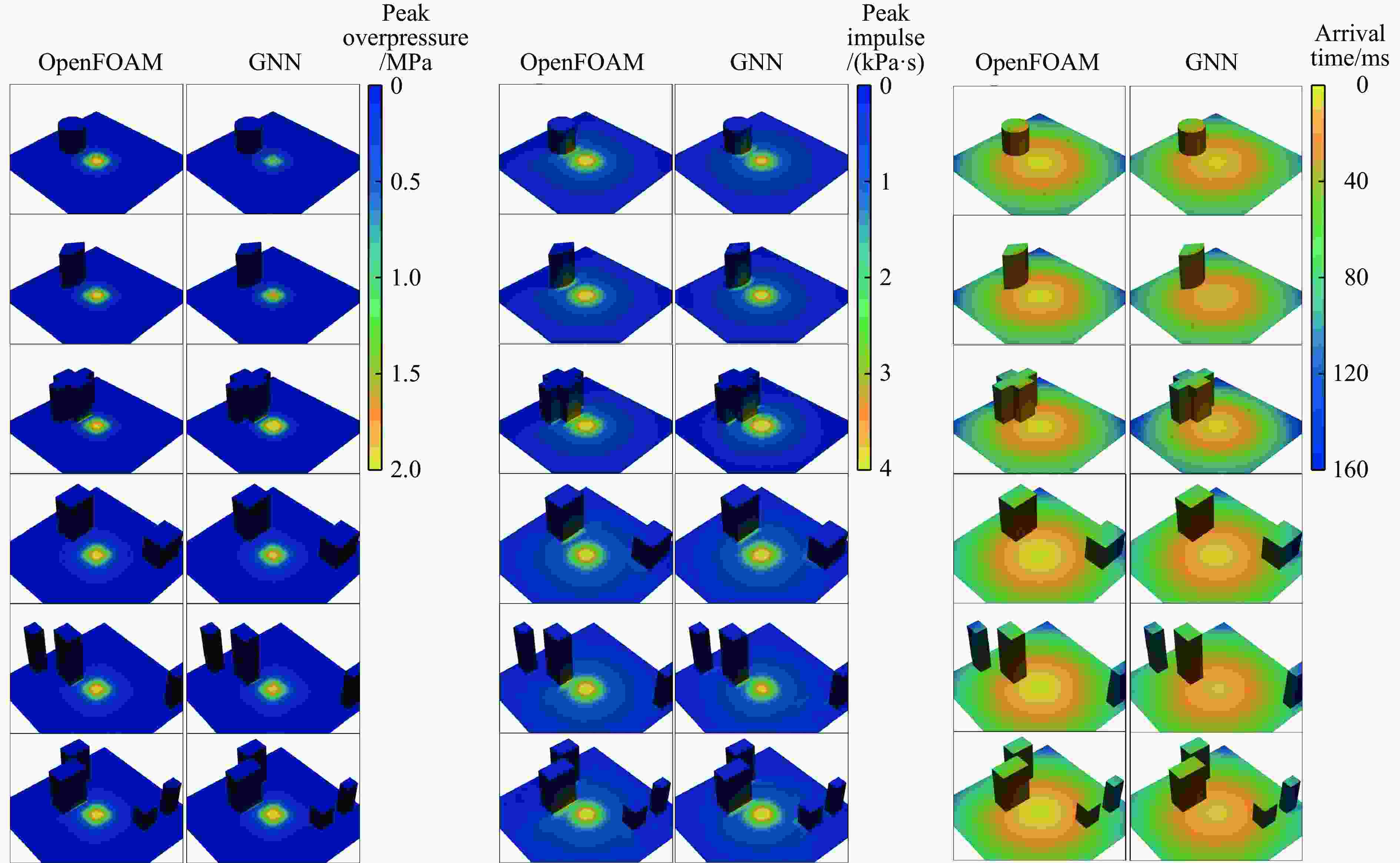
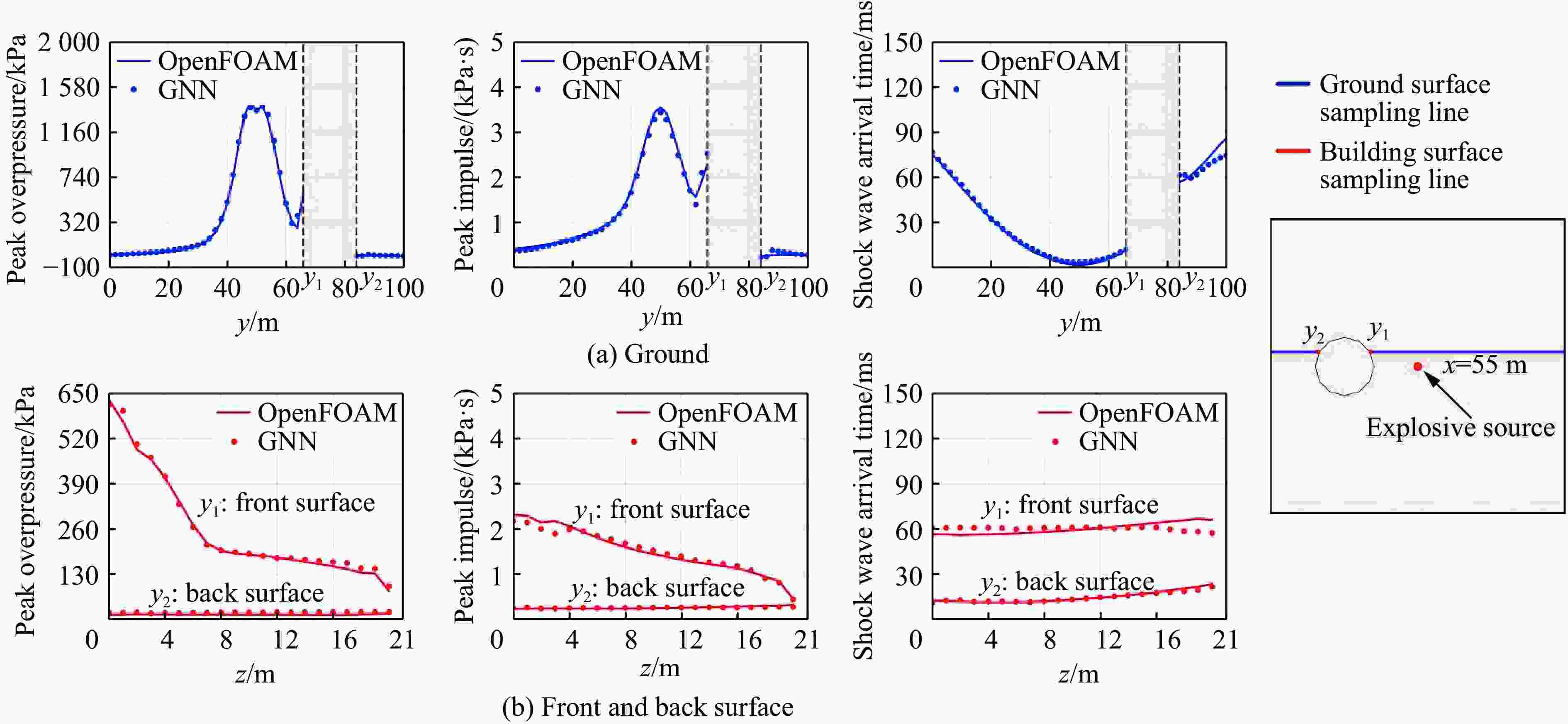
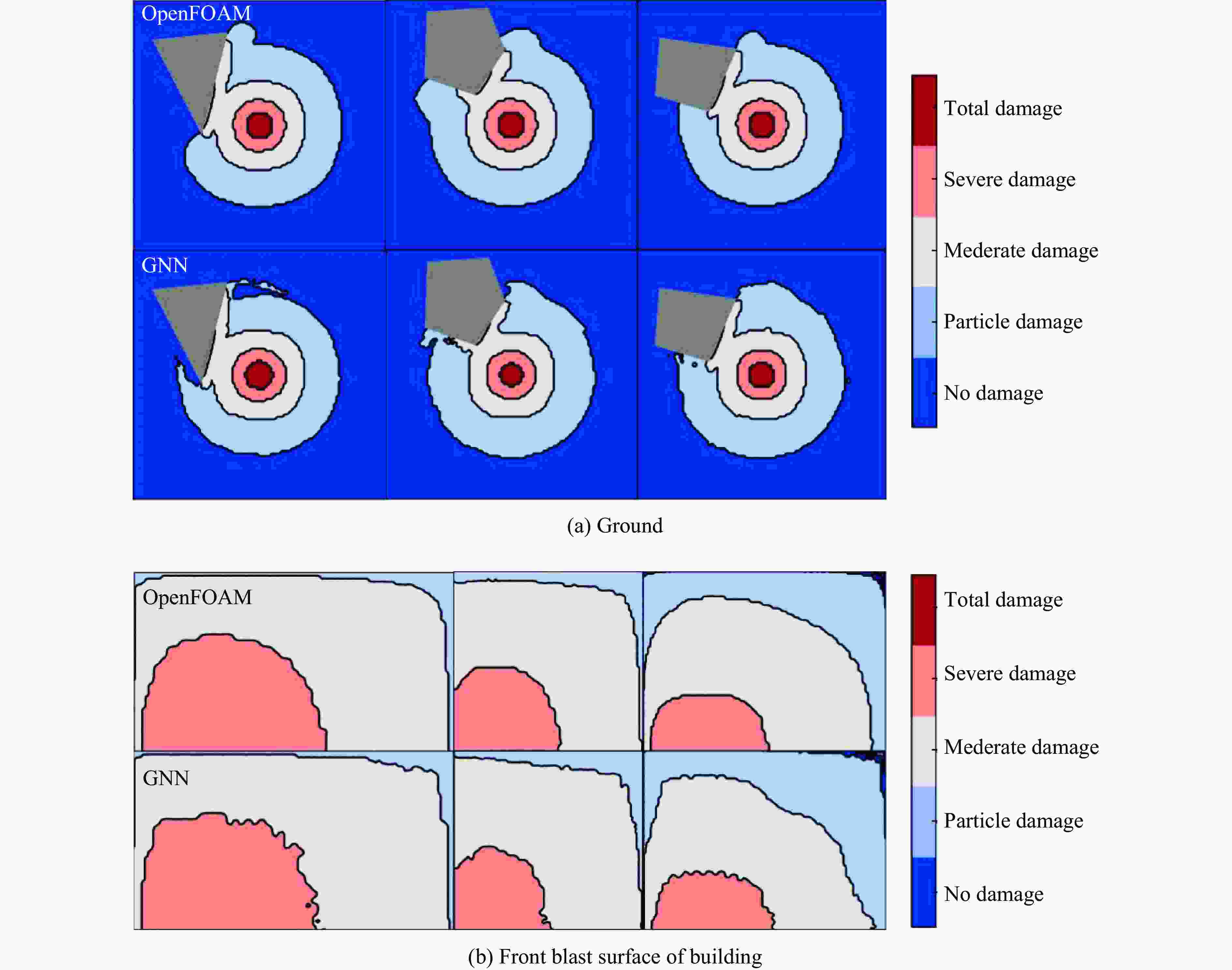
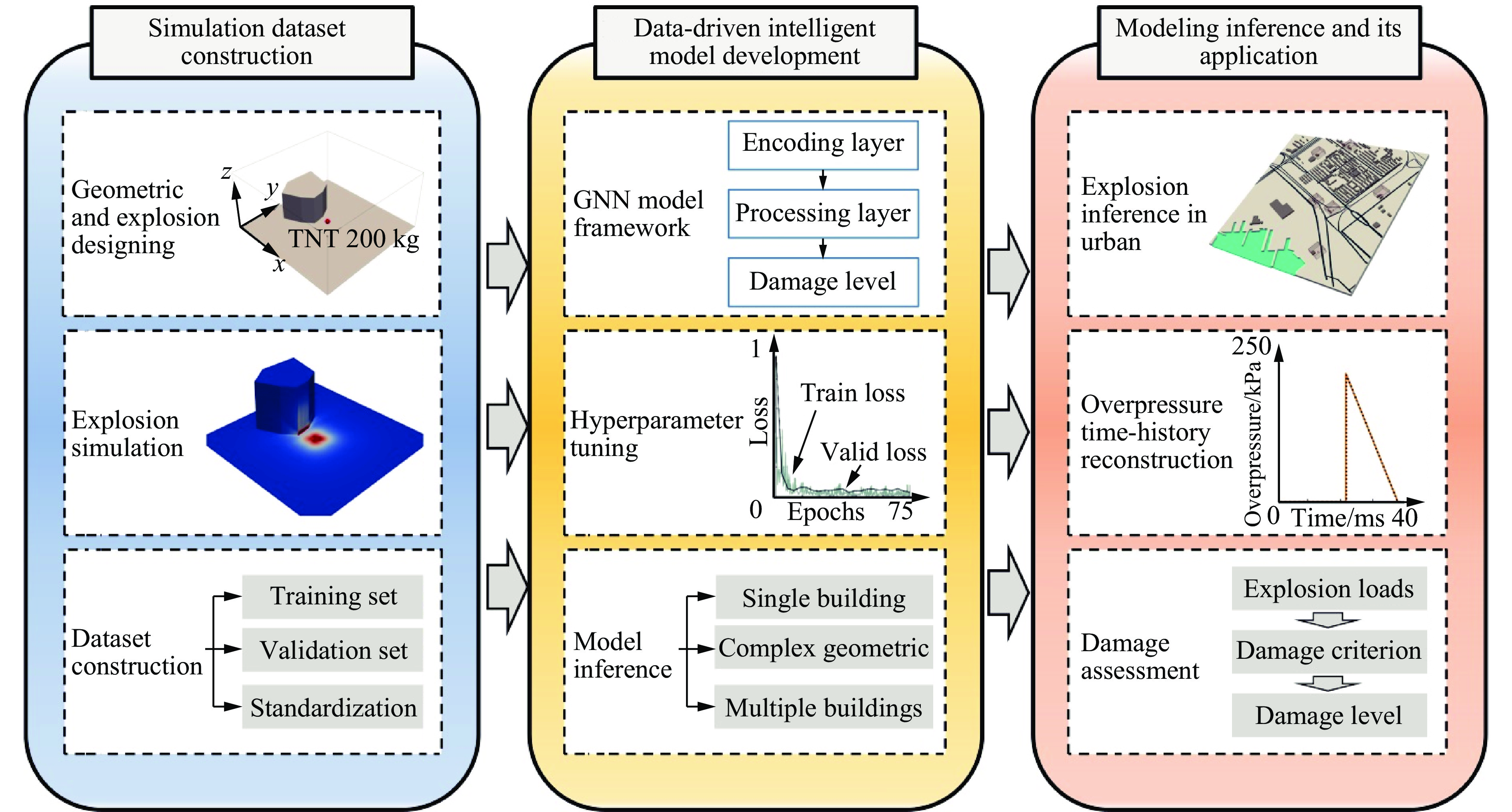
摘要: 为准确预测建筑外爆威力场,解决传统经验公式中未能充分考虑环境因素的复杂性而导致的精度受限、数值仿真在处理大规模城市场景时效率低下的难题,构建了一种基于图神经网络(graph neural network, GNN)的爆炸威力场预测模型,直接利用建筑的几何特征,对其表面的爆炸峰值超压、峰值冲量及冲击波到达时间等三维物理场的进行预测。与数值仿真结果的对比验证表明,本文模型展现出了卓越的预测性能:对不同几何结构的单体建筑表面超压参数的预测均方误差为0.97%;对复杂几何建筑、建筑群落建筑表面超压参数的平均预测误差为3.17%;当应用于实际城市区域时,平均预测误差为1.29%;物理场单次预测耗时不超过0.6 s,与数值仿真相比速度提升3~4个数量级。基于模型的高精度预测,不仅可以重构建筑表面任意位置的超压时程曲线,还能准确评估结构的毁伤程度。Abstract: To accurately predict the explosion power fields in buildings, solving the failure of traditional empirical formulas often failing to account for complex environmental factor due to their inability to account for complex environmental factors, and that of numerical simulations inefficient for large-scale urban scenarios and do not meet the needs of rapid damage assessment. Addressing this challenge, an innovative prediction model for explosion power fields based on Graph Neural Networks (GNN) was constructed using an end-to-end strategy. This model enabled rapid and precise forecasting of three-dimensional physical fields, including peak overpressure, peak impulse, and shock-wave arrival times on building surfaces. Compared to numerical simulations, the proposed GNN model demonstrated excellent predictive performance: it achieved a mean square error of 0.97% for predicting surface overpressure parameters of single buildings with varying geometries, and an average prediction error of 3.17% for complex geometric buildings and building communities. When applied to real-world urban settings, the model maintains an average prediction error of 1.29%, completing individual physical field predictions in under 0.6 seconds—three to four orders of magnitude faster than numerical simulations. Furthermore, the model's high-precision predictions allow for the reconstruction of overpressure time history curves at any building surface location and the accurate assessment of structural damage. The proposed GNN model offers a novel approach for rapidly and accurately predicting explosion power fields in urban buildings during blast events. This advancement significantly enhances the capabilities for explosion damage assessment and anti-explosion design in ultra-large-scale complex engineering scenarios, providing substantial engineering value.
-
表 1 GNN和OpenFOAM计算硬件配置对比表格
Table 1. 1 Computing Hardware Configuration Comparison Table of GNN and OpenFOAM
计算方法 操作系统 开发语言 CPU GPU GNN Ubuntu 20.04 Python Intel Xeon
Gold 5317GeForce RTX
4090keOpenFOAM Ubuntu 20.04 C++ AMD EPYC 7H12 无显卡 表 2 复杂几何建筑与建筑群落测试集模型预测性能
Table 2. Predictive performance of GNN models on the test sets of the complex geometric building and multiple buildings
建筑类型 εRSE/% 计算时间/s 峰值超压 峰值冲量 到时 OpenFOM GNN 复杂建筑—十二边形 1.15 2.34 0.85 991 0.15 复杂建筑—扇形 1.51 3.68 1.33 857 0.14 复杂建筑—十字形 1.16 6.69 2.74 984 0.35 建筑群落—2栋 1.95 8.16 2.04 991 0.27 建筑群落—3栋 1.67 7.57 3.07 1450 0.36 建筑群落—4栋 2.61 6.52 1.99 2045 0.51 表 3 城市区域爆炸事件GNN模型预测性能
Table 3. Predictive performance of the GNN model for the blasts in urban areas
爆炸事件 εRSE/% 计算时间/s 峰值超压 峰值冲量 到时 OpenFOAM GNN 1 2.74 6.06 0.89 1143 0.37 2 0.92 5.10 0.85 875 0.34 3 1.19 4.72 1.22 984 0.20 4 0.74 5.32 1.48 928 0.21 5 0.98 4.24 2.63 961 0.13 6 1.36 3.01 0.80 1105 0.23 -
[1] 殷文骏, 程帅, 刘文祥, 等. 远场爆炸冲击波作用下高层建筑上部结构动态响应试验研究 [J]. 兵工学报, 2024, 45(11): 4039–4051. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0960.YIN W J, CHENG S, LIU W X, et al. Experimental study on dynamic response of upper structure of high-rise building under far-field explosion shock wave loading [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2024, 45(11): 4039–4051. DOI: 10.12382/bgxb.2023.0960. [2] 王明涛, 程月华, 吴昊. 柱形装药空中爆炸冲击波荷载研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2024, 44(4): 043201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0197.WANG M T, CHENG Y H, WU H. Study on blast loadings of cylindrical charges air explosion [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2024, 44(4): 043201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2023-0197. [3] 童晓. 爆炸场冲击波压力测量及数据处理方法研究 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2015.TONG X. Research on shock wave pressure measurement and data processing method in explosion field [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2015. [4] 都浩, 李忠献, 郝洪. 建筑物外部爆炸超压荷载的数值模拟 [J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 8(5): 413–418. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2007.05.002.DU H, LI Z X, HAO H. Numerical simulation on blast overpressure loading outside buildings [J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology, 2007, 8(5): 413–418. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3443.2007.05.002. [5] 李忠献, 师燕超, 周浩璋, 等. 城市复杂环境中爆炸波的传播规律与超压荷载 [J]. 工程力学, 2009, 26(6): 178–183.LI Z X, SHI Y C, ZHOU H Z, et al. Propagation law and overpressure load of blast wave in urban complex environment [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2009, 26(6): 178–183. [6] 王栋. 拱形地下结构抗爆性能试验研究 [D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2022. DOI: 10.27266/d.cnki.gqhau.2022.000098.WANG D. Experimental study on anti-explosion performance of arched underground structure [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2022. DOI: 10.27266/d.cnki.gqhau.2022.000098. [7] ZHOU X S, ZHANG X M, REN T H, et al. Waveform characteristics of tunnel blast waves and a wave-blocking method [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2022, 2022: 3013130. DOI: 10.1155/2022/3013130. [8] KRÁLIK E J, BARAN M. Numerical analysis of the exterior explosion effects on the buildings with barriers [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 390: 230–234. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.390.230. [9] ZHANG M T, PEI Y, YAO X, et al. Damage assessment of aircraft wing subjected to blast wave with finite element method and artificial neural network tool [J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 25: 203–219. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2022.05.010. [10] 严国建, 周明安, 余轮, 等. 空气中爆炸冲击波超压峰值的预测 [J]. 采矿技术, 2011, 11(5): 89–90,112. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2011.05.035.YAN G J, ZHOU M A, YU L, et al. Prediction of peak overpressure of explosion shock wave in air [J]. Mining Technology, 2011, 11(5): 89–90,112. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2900.2011.05.035. [11] ZHANG K, ZHANG K, BAO R. Prediction of gas explosion pressures: a machine learning algorithm based on KPCA and an optimized LSSVM [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2023, 83: 105082. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2023.105082. [12] 潘美霖, 彭卫文, 冷春江, 等. 基于贝叶斯深度学习的复杂结构爆炸载荷的快速估计 [J/OL]. 爆炸与冲击, [2024-12-02]. https://www.bzycj.cn/cn/article/doi/ 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0191. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0191.PAN M L, PENG W W, LENG C J, et al. Fast estimation of blast loading in complex structures based on Bayesian deep learning [J/OL]. Explosion and Shock Waves, [2024-12-02]. https://www.bzycj.cn/cn/article/doi/ 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0191. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2024-0191. [13] 陈皓, 郭明明, 田野, 等. 卷积神经网络在流场重构研究中的进展 [J]. 力学学报, 2022, 54(9): 2343–2360. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-130.CHEN H, GUO M M, TIAN Y, et al. Progress of convolution neural networks in flow field reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2022, 54(9): 2343–2360. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-22-130. [14] WANG Z Q, HUA Y, AUBRY N, et al. Fast optimization of multichip modules using deep learning coupled with Bayesian method [J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 141: 106592. DOI: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2022.106592. [15] HUA Y, WANG Z Q, YUAN X Y, et al. Estimation of steady-state temperature field in Multichip Modules using deep convolutional neural network [J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2023, 40: 101755. DOI: 10.1016/j.tsep.2023.101755. [16] 闫盼盼, 牛青林, 高文强, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的地面尾喷焰流场预测 [J]. 力学学报, 2024, 56(4): 980–990. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-412.YAN P P, NIU Q L, GAO W Q, et al. Prediction of ground rocket exhaust plume flow field based on convolutional neural network [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2024, 56(4): 980–990. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-23-412. [17] 吴昊恺, 陈耀然, 周岱, 等. 基于CNN与GAN深度学习模型近壁面湍流场超分辨率重构的精细化研究 [J]. 力学学报, 2024, 56(8): 2231–2242. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-24-019.WU H K, CHEN Y R, ZHOU D, et al. Refined study of super-resolution reconstruction of near-wall turbulence field based on CNN and GAN deep learning model [J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2024, 56(8): 2231–2242. DOI: 10.6052/0459-1879-24-019. [18] PFAFF T, FORTUNATO M, SANCHEZ-GONZALEZ A, et al. Learning mesh-based simulation with graph networks [C]//International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna: OpenReview. net, 2021. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2010.03409. [19] KANG M A, PARK C H. Prediction of peak pressure by blast wave propagation between buildings using a conditional 3D convolutional neural network [J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 26114–26124. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3257345. [20] PENG J Z, AUBRY N, LI Y B, et al. Physics-informed graph convolutional neural network for modeling geometry-adaptive steady-state natural convection [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 216: 124593. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2023.124593. [21] SHAO X Q, LIU Z J, ZHANG S Q, et al. PIGNN-CFD: a physics-informed graph neural network for rapid predicting urban wind field defined on unstructured mesh [J]. Building and Environment, 2023, 232: 110056. DOI: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2023.110056. [22] 郝祎琛, 谢心喻, 丁家琦, 等. 瞬态多相流场图神经网络时空预测方法研究 [J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2024, 45(9): 1761–1769. DOI: 10.11990/jheu.202207004.HAO Y C, XIE X Y, DING J Q, et al. Spatiotemporal prediction method for the transient multiphase flow field via graph neural network [J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2024, 45(9): 1761–1769. DOI: 10.11990/jheu.202207004. [23] LI Q L, WANG Y, CHEN W S, et al. Machine learning prediction of BLEVE loading with graph neural networks [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 241: 109639. DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2023.109639. [24] CULLIS I G, NIKIFORAKIS N, FRANKL P, et al. Simulating geometrically complex blast scenarios [J]. Defence Technology, 2016, 12(2): 134–146. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2016.01.005. [25] IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift [C]//Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Lille: JMLR. org, 2015: 448–456. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1502.03167. [26] LI T Y, ZOU S F, CHANG X H, et al. Predicting unsteady incompressible fluid dynamics with finite volume informed neural network [J]. Physics of Fluids, 2024, 36(4): 043601. DOI: 10.1063/5.0197425. [27] FEY M, LENSSEN J E. Fast graph representation learning with PyTorch geometric [EB/OL]. arXiv: 1903.02428, 2019. [2024-12-02]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.02428. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1903.02428. [28] CHANG D T. Tiered graph autoencoders with PyTorch geometric for molecular graphs [EB/OL]. arXiv: 1908.08612, 2019. [2024-12-02]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.08612. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1908.08612. [29] LI S, ZHAO Y L, VARMA R, et al. PyTorch distributed: experiences on accelerating data parallel training [J]. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 2020, 13(12): 3005–3018. DOI: 10.14778/3415478.3415530. [30] 姚成宝, 王宏亮, 浦锡锋, 等. 空中强爆炸冲击波地面反射规律数值模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(11): 112201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0287.YAO C B, WANG H L, PU X F, et al. Numerical simulation of intense blast wave reflected on rigid ground [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(11): 112201. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2018-0287. [31] FEJES P, HORKAI A. Creating city models in ArchiCAD software environment [J]. The International Journal of Engineering and Science, 2021, 10(1): 11–17. DOI: 10.9790/1813-1001011117. [32] 阎石, 刘蕾, 齐宝欣, 等. 爆炸荷载作用下方钢管混凝土柱的动力响应及破坏机理 [J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2011, 31(5): 477–482. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2132.2011.05.002.YAN S, LIU L, QI B X, et al. Dynamic response and failure mode analysis of concrete infilled rectangular steel tube columns under blasting loading [J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2011, 31(5): 477–482. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2132.2011.05.002. [33] 焦燏烽, 赵果, 侯延利. 框架柱在爆炸冲击荷载作用下动力系数及破坏模式研究 [J]. 建筑科学, 2015, 31(9): 32–37. DOI: 10.13614/j.cnki.11-1962/tu.2015.09.006.JIAO Y F, ZHAO G, HOU Y L. Dynamic factor and failure modes research of the frame column under blast pressure [J]. Building Science, 2015, 31(9): 32–37. DOI: 10.13614/j.cnki.11-1962/tu.2015.09.006. [34] PRUGH R W. The effects of explosive blast on structures and personnel [J]. Process Safety Progress, 1999, 18(1): 5–16. DOI: 10.1002/prs.680180104. -






 下载:
下载: