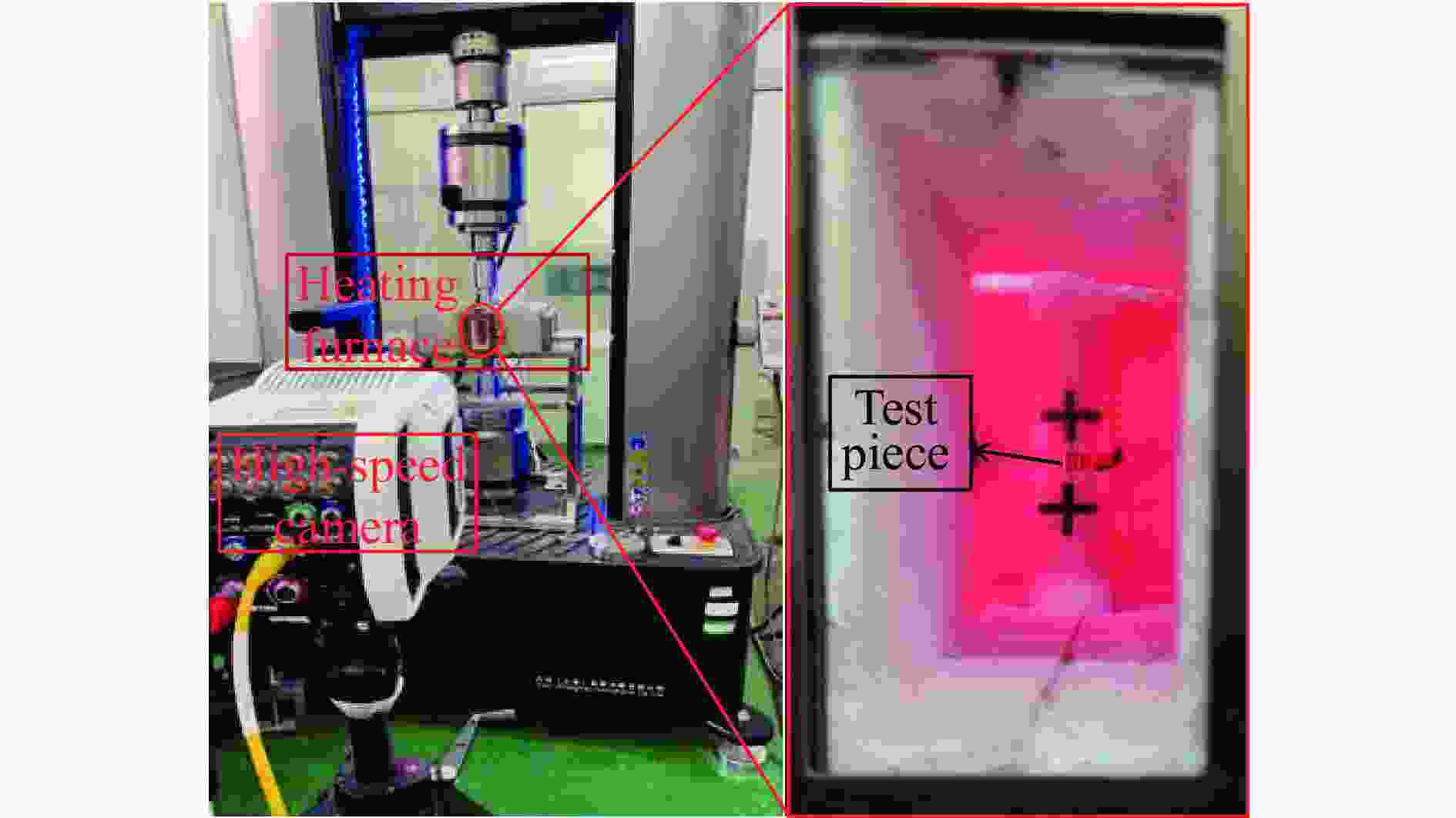
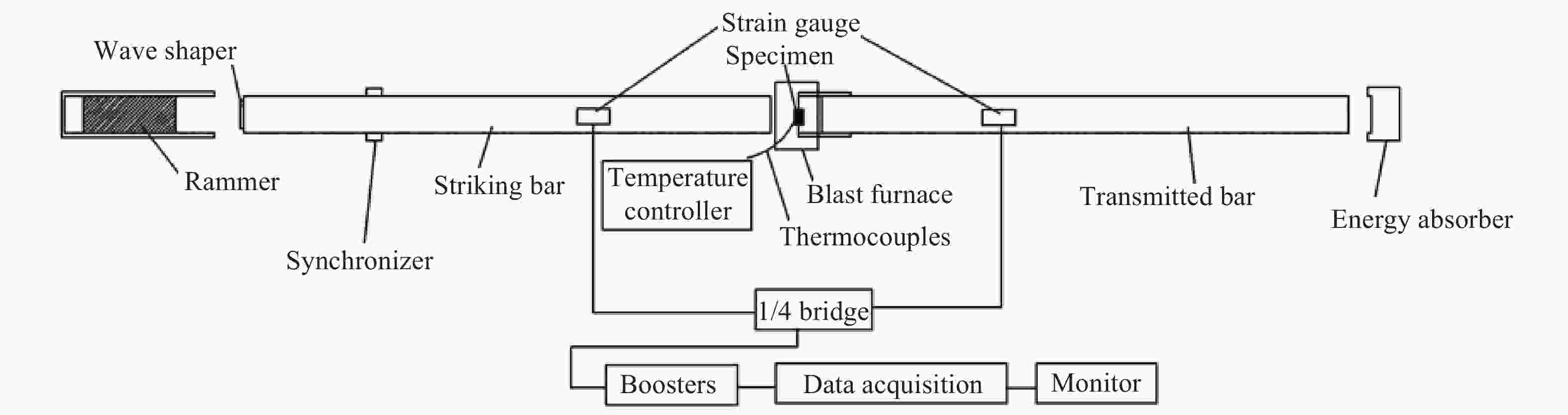
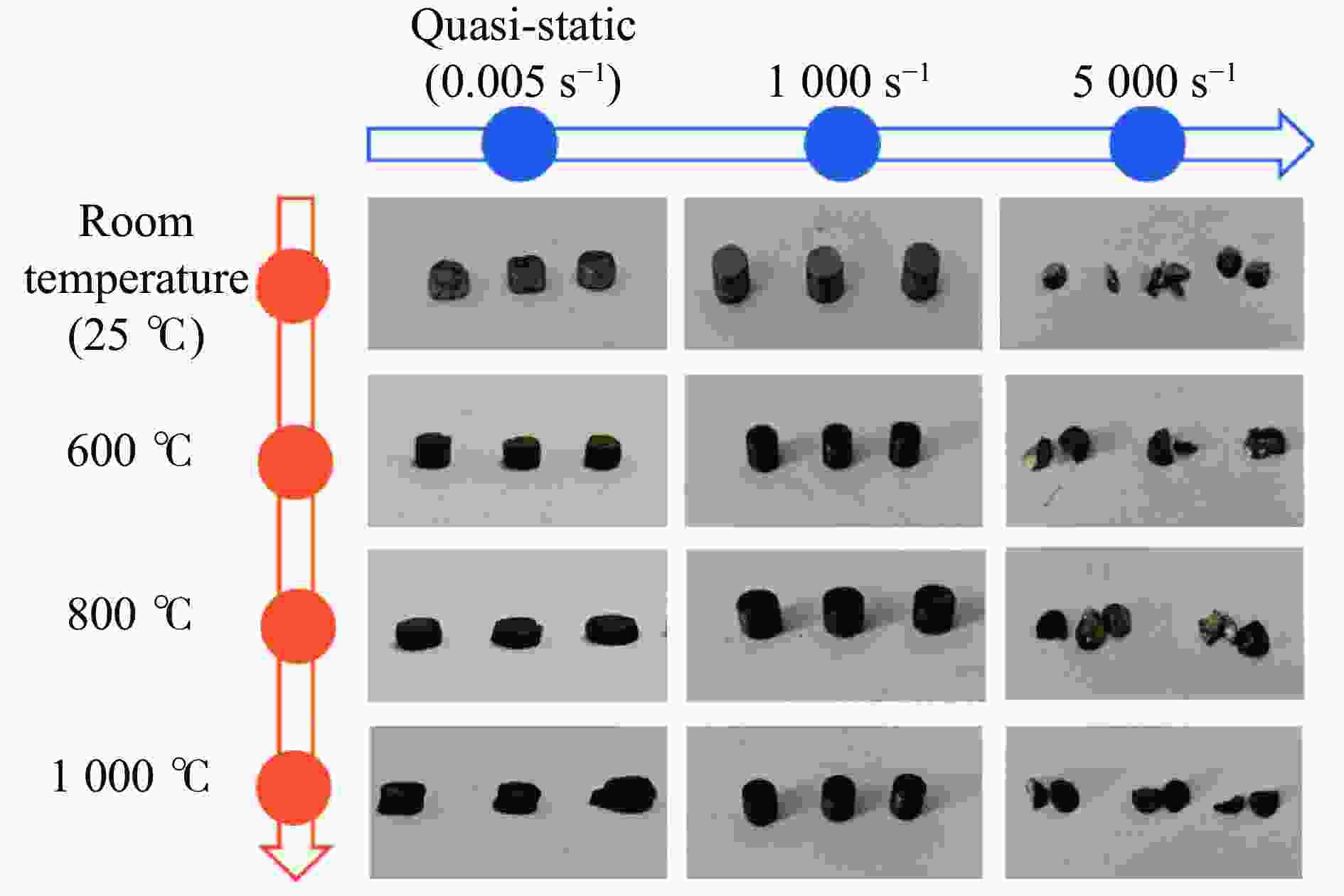
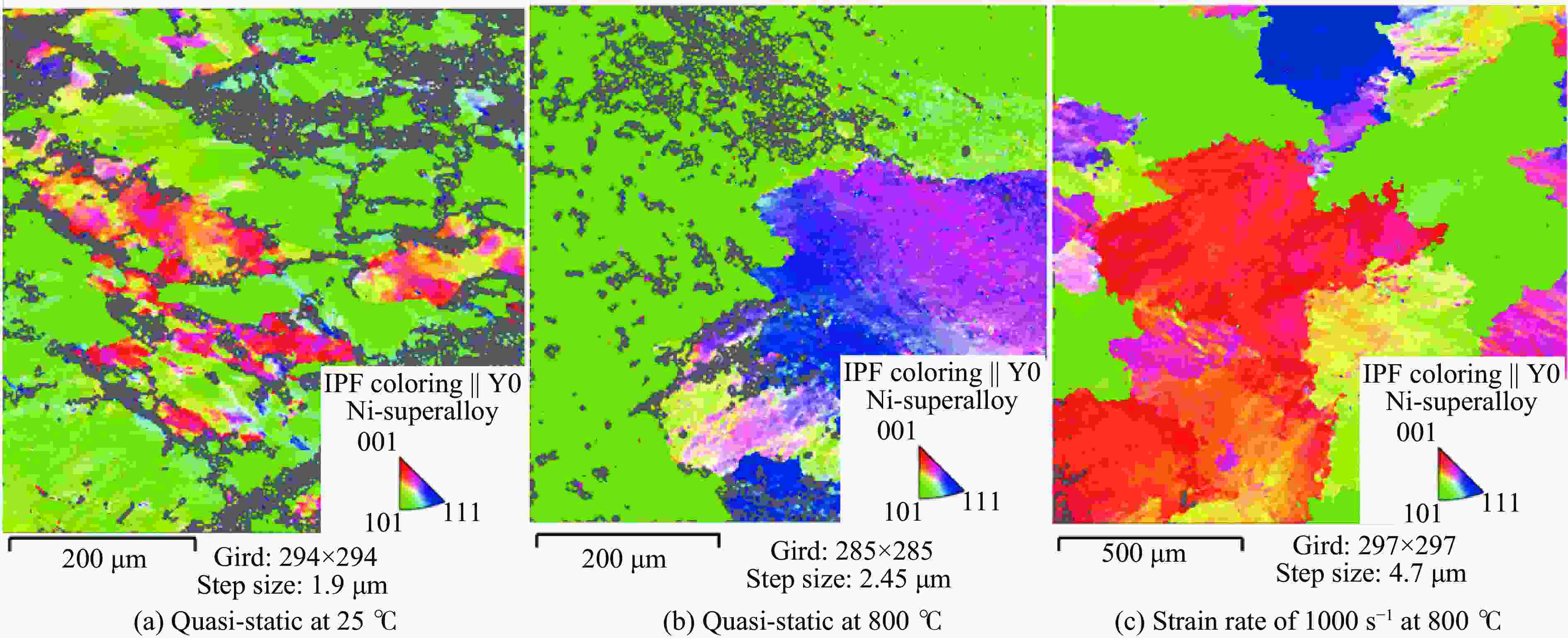
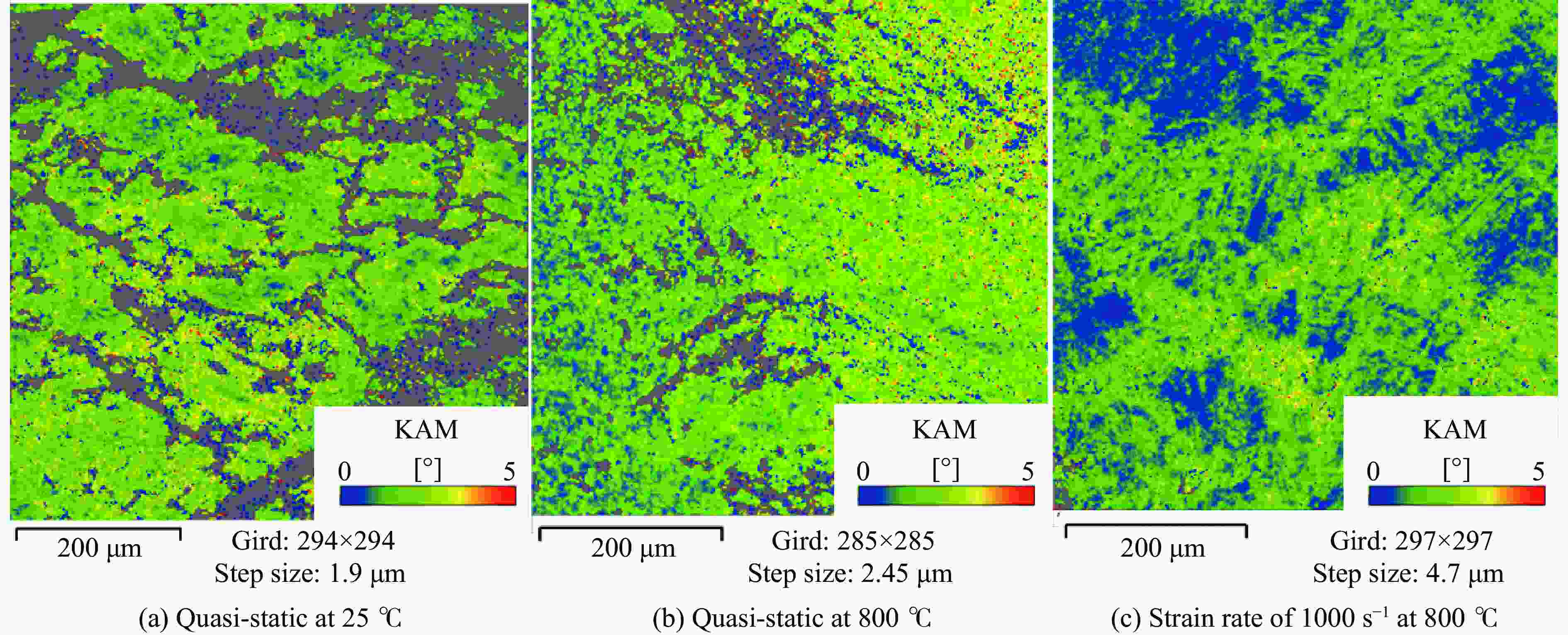
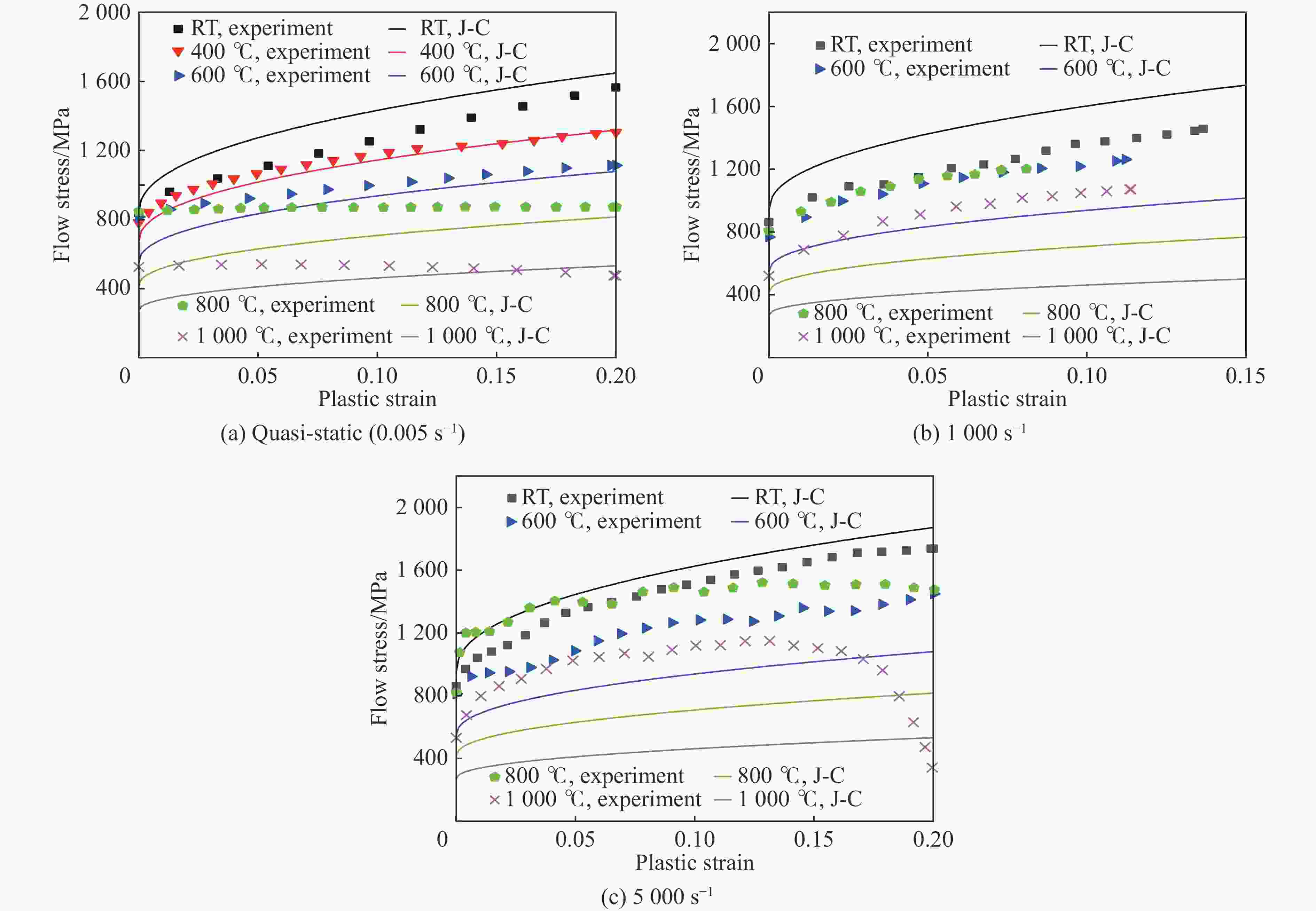
High-temperature dynamic mechanical properties and intrinsic relationships of K447A alloy
-
摘要: K447A是一种广泛用于航空发动机关键热端部件的镍基高温合金,通过在25~
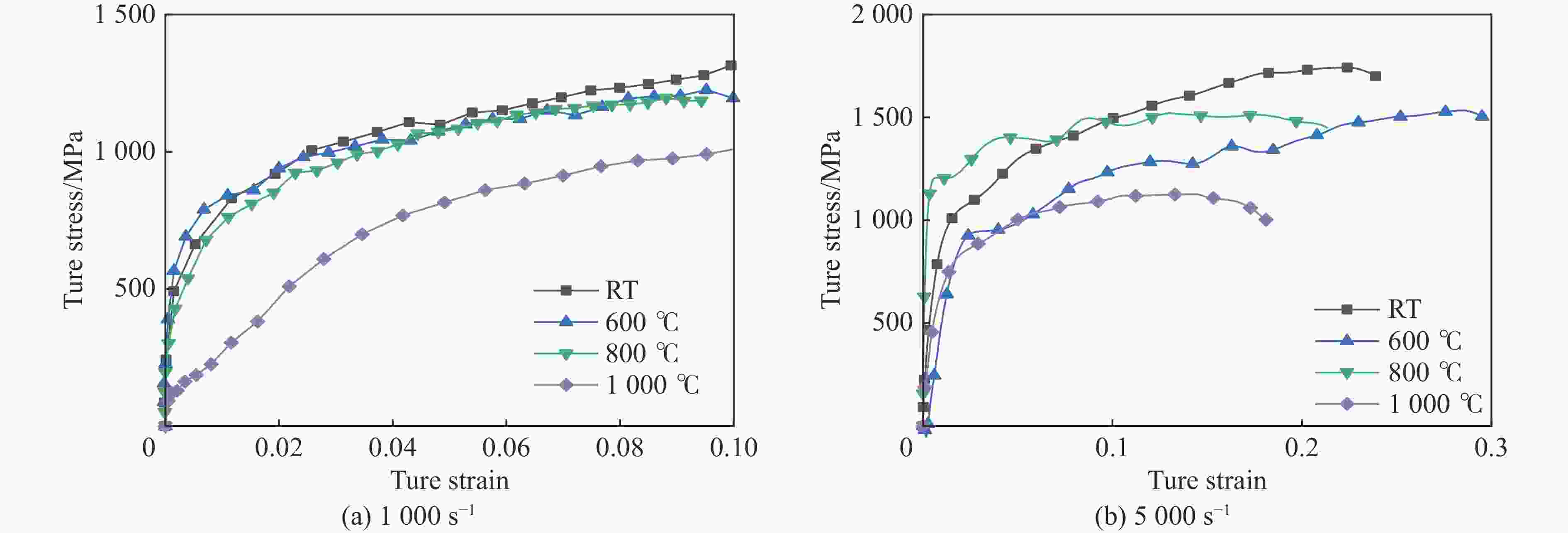
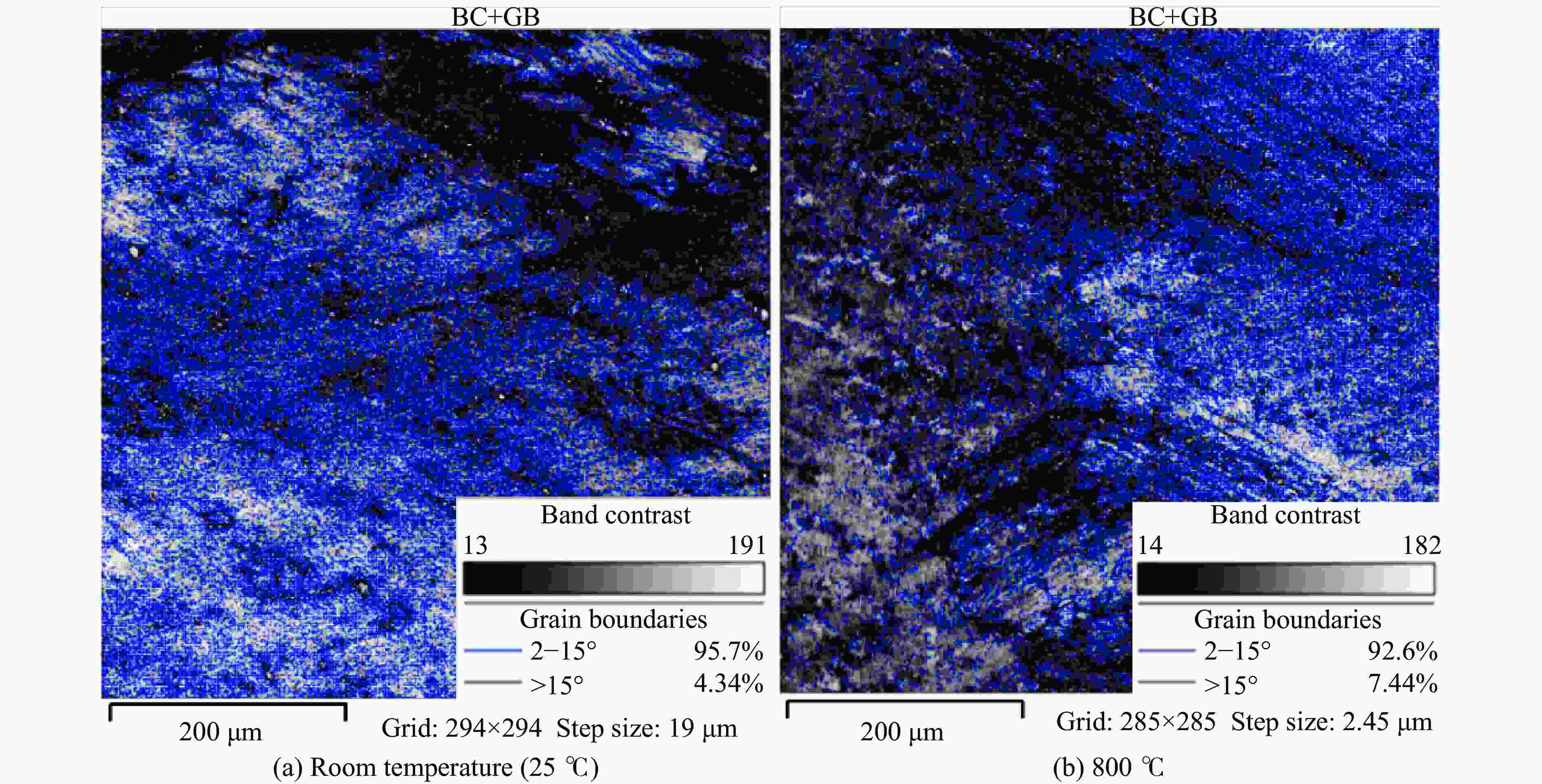
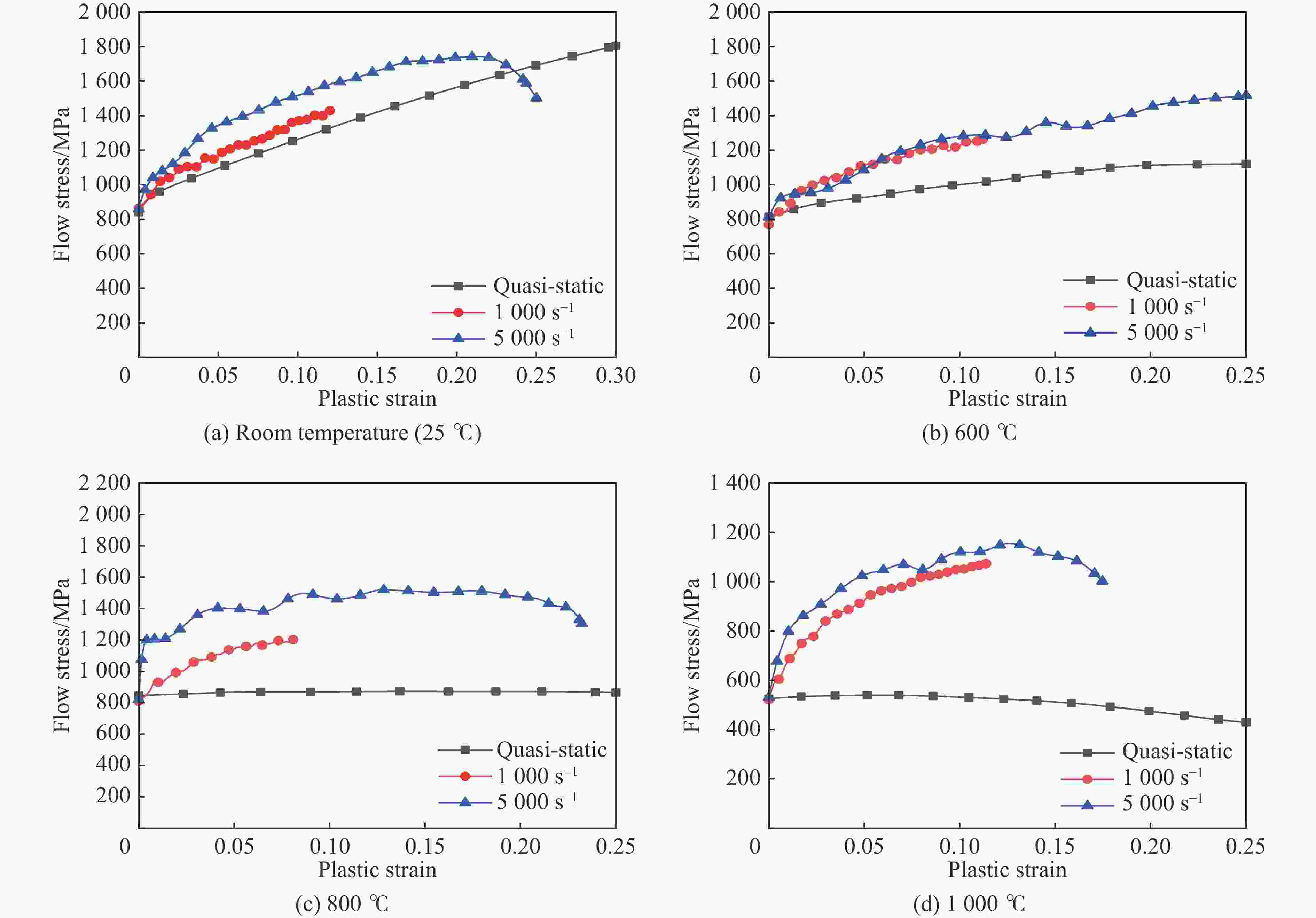
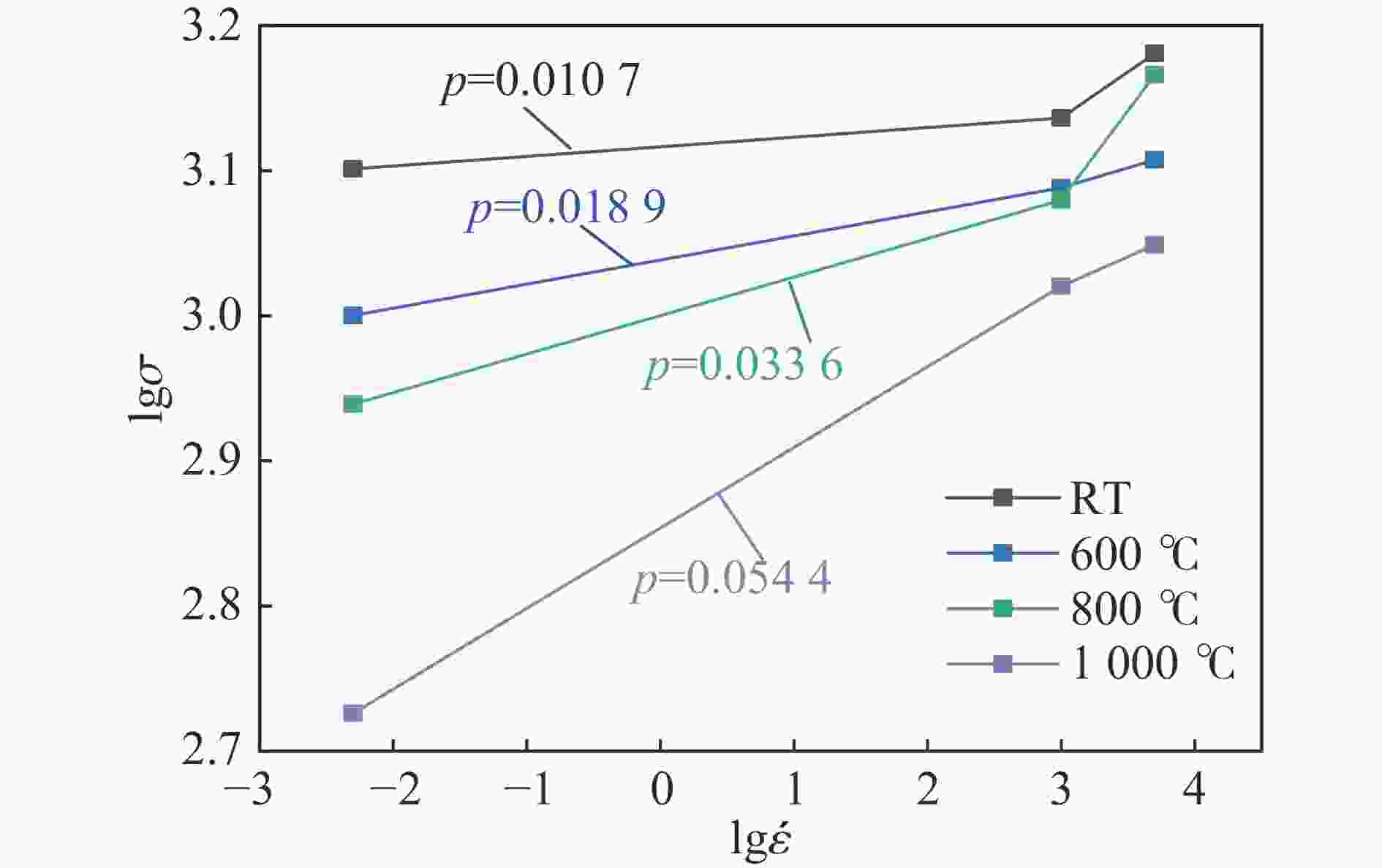
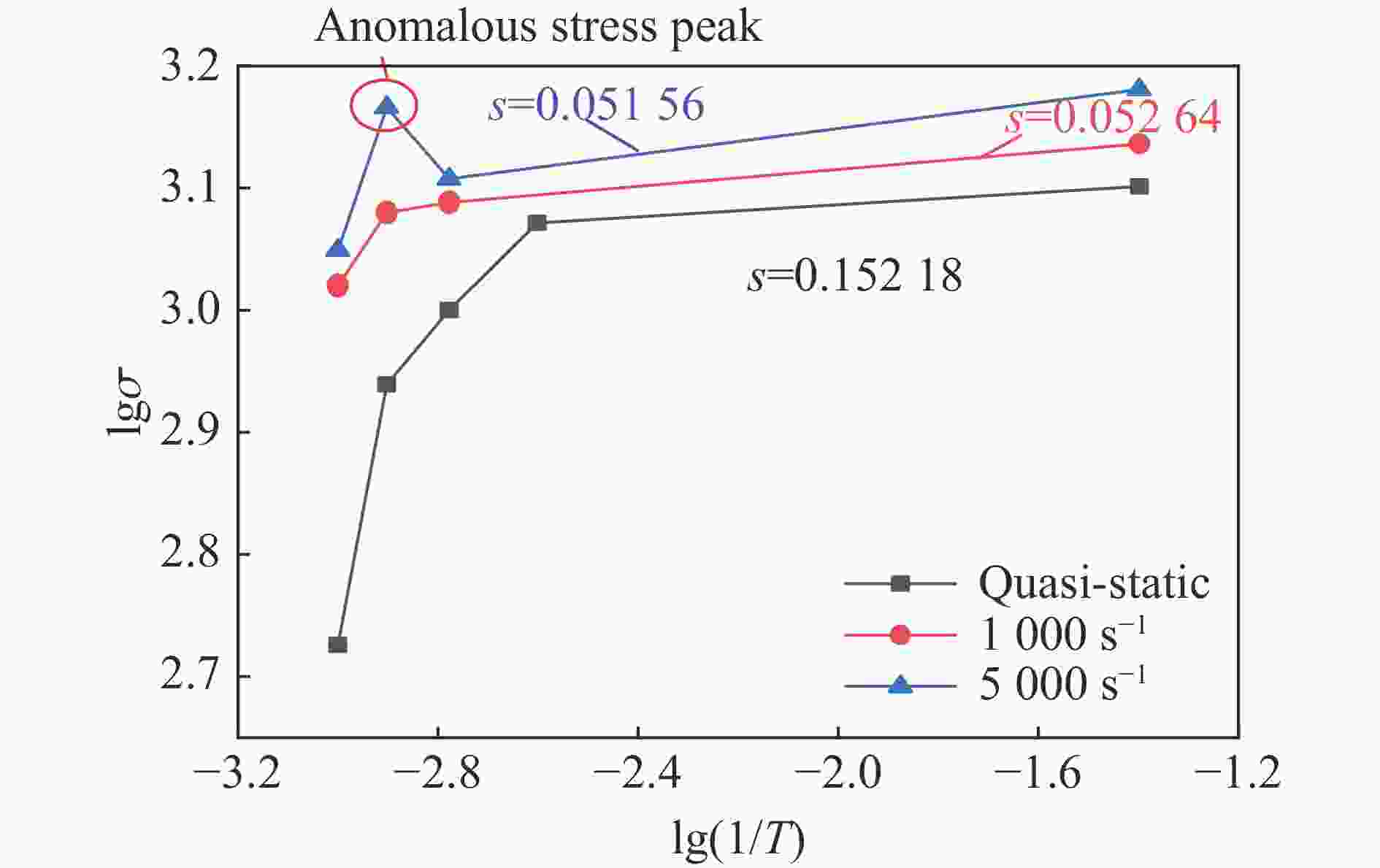
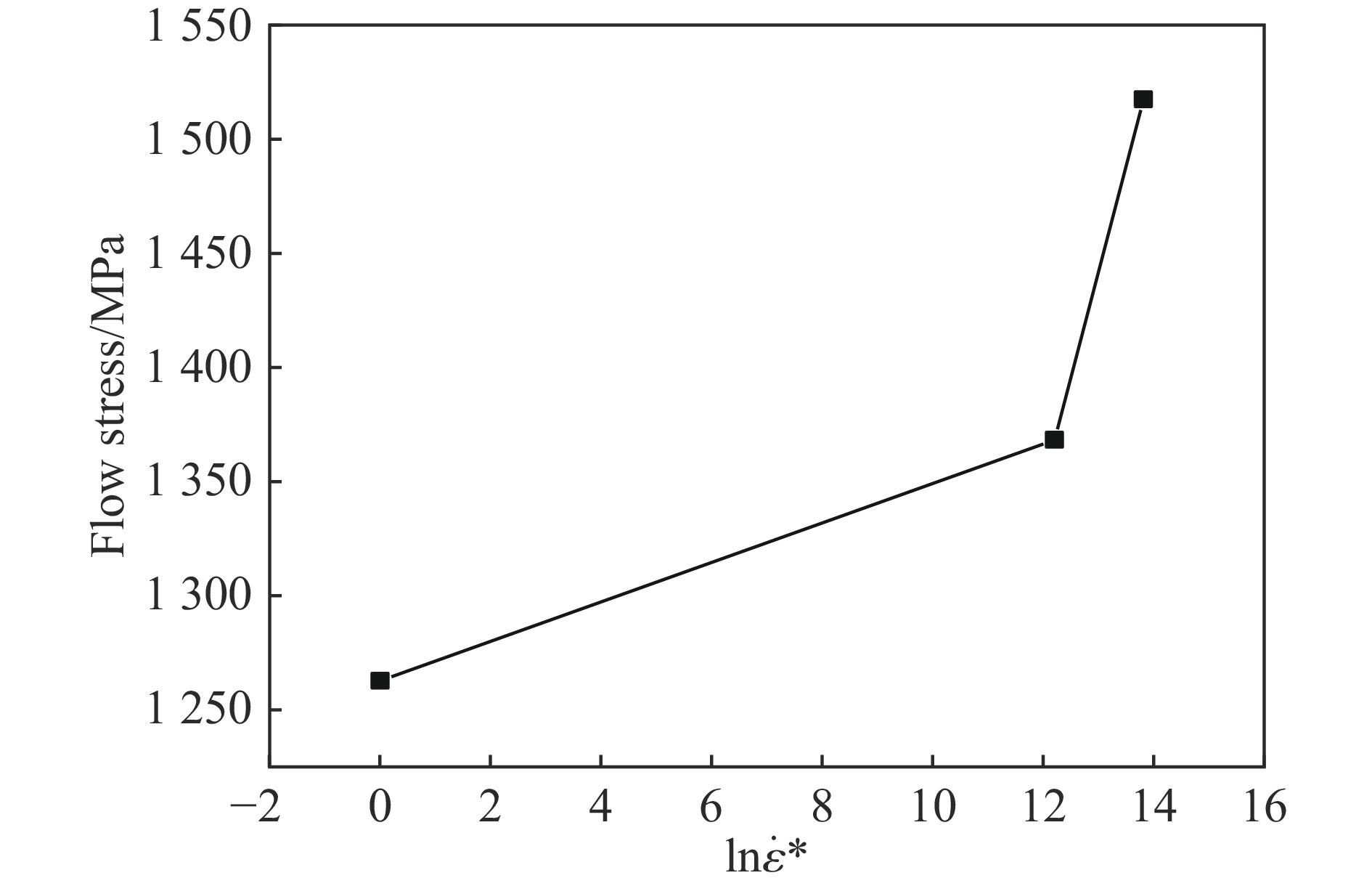
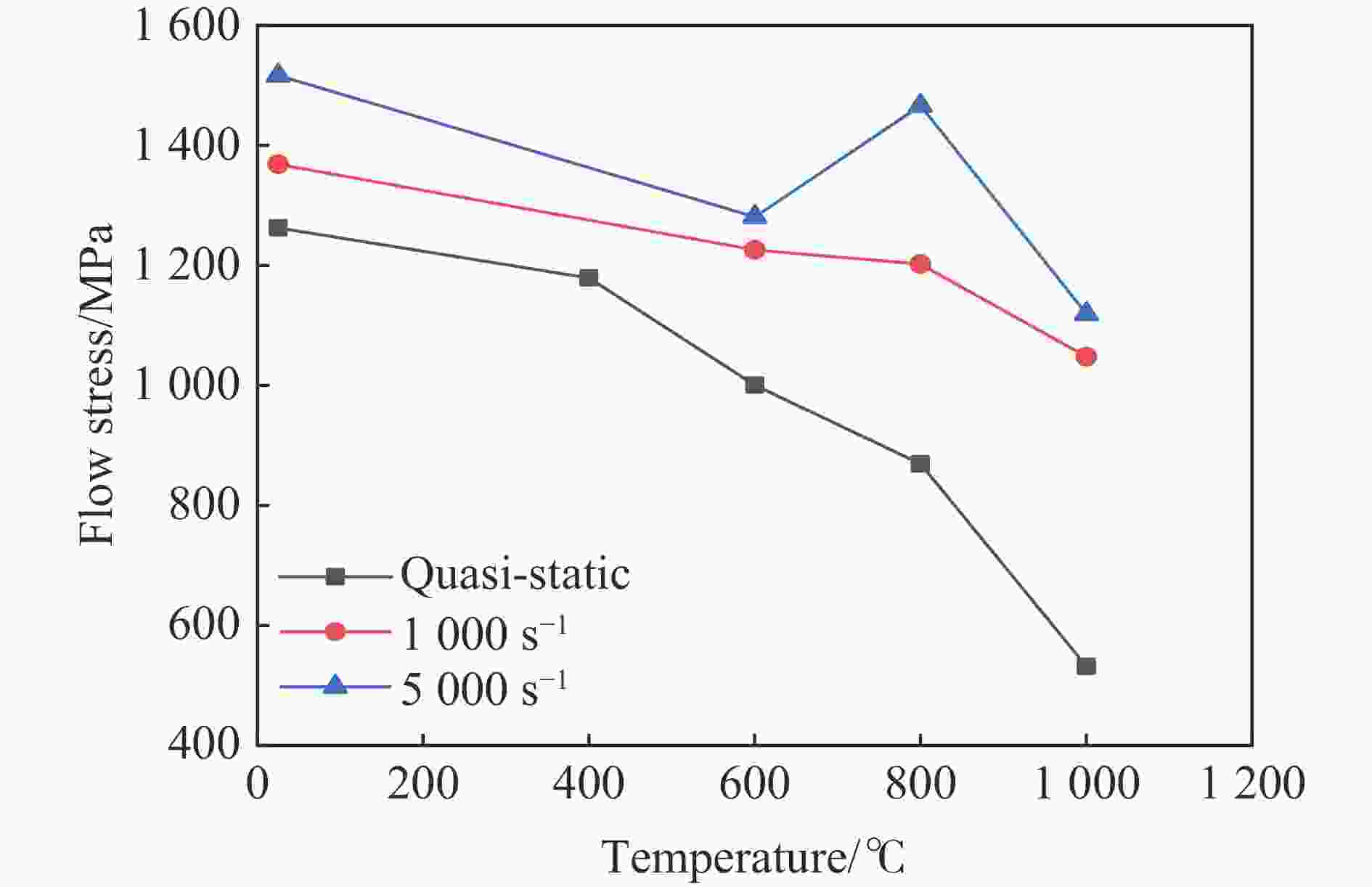
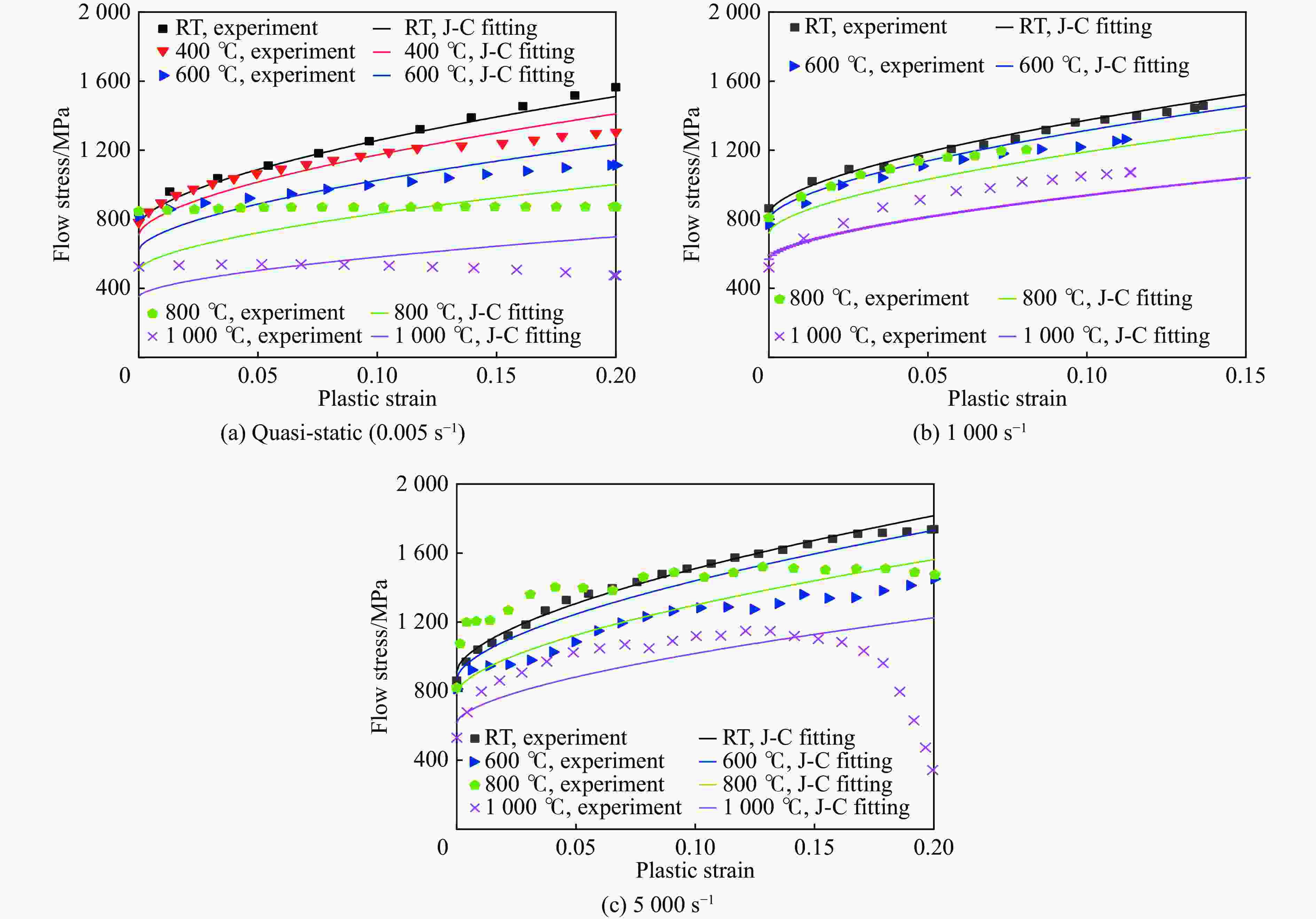
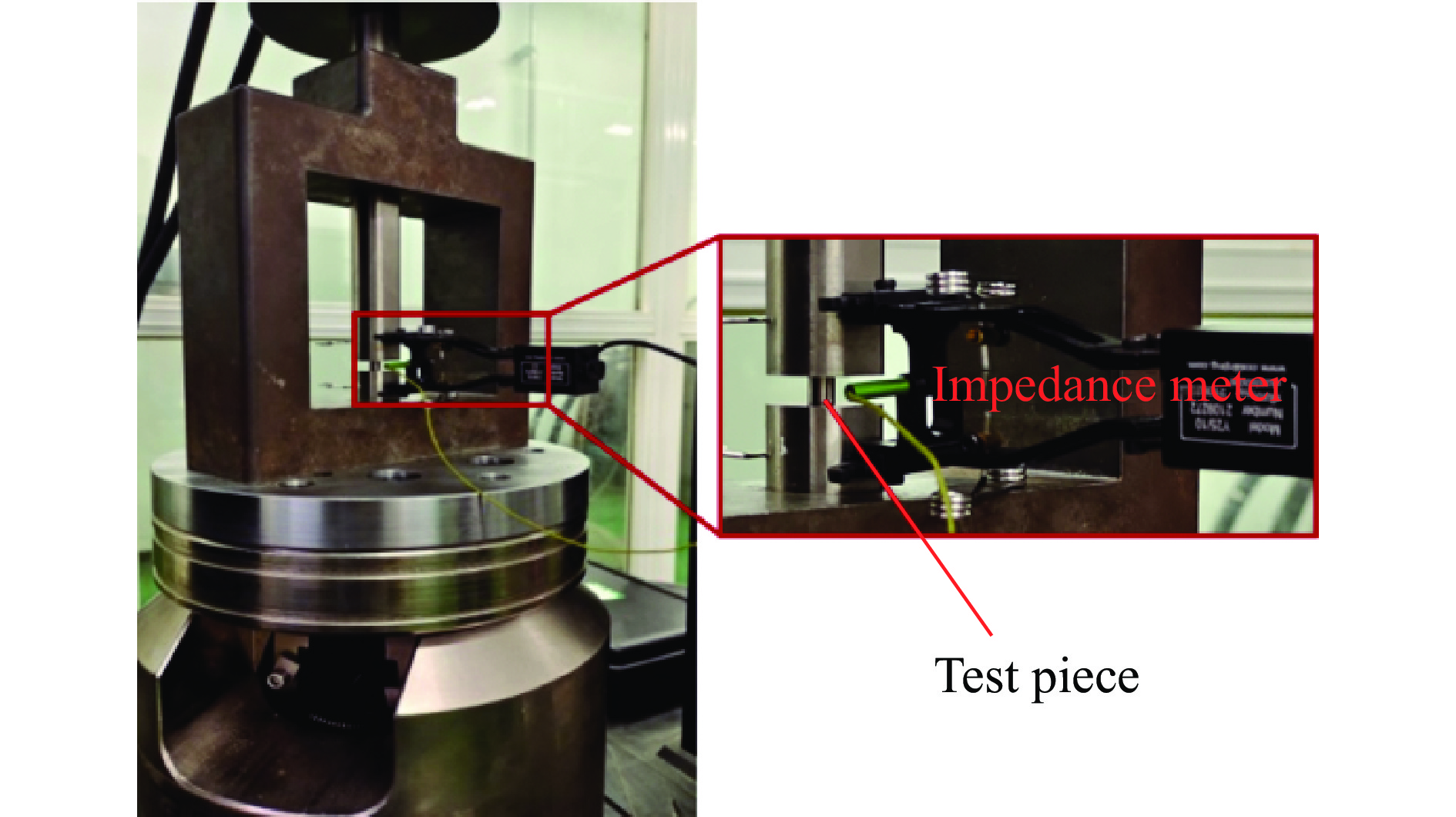
1000 ℃温度范围内进行准静态和高应变率压缩试验,系统研究了K447A高温合金的动态力学性能,并深入剖析了温度和应变率对其塑性流动行为的影响。研究结果表明:K447A合金的塑性变形过程中同时存在应变硬化、热软化和应变率强化现象。随着应变率从准静态增加到5000 s−1,温度敏感指数s逐渐减小,而在800 ℃时,K447A合金在高应变率范围出现反常应力峰。随着温度的升高,应变率敏感因子p逐渐增大;材料内部的微观组织结构受应变率和温度耦合影响,应变率增加会导致晶粒细化,而温度升高会导致材料内部低角晶界占比减少,从而出现动态再结晶现象。基于流动应力受温度和应变率耦合影响的考虑,建立了修正的Johnson-Cook本构模型,与修正前相比,预测误差从26.36%降低到9.05%。Abstract: K447A, a nickel-based superalloy, is widely used in critical hot-end components of aerospace engines due to its excellent high-temperature performance. Through quasi-static and high strain rate compression experiments within the temperature range of 25 ℃ to1000 ℃, the dynamic mechanical properties of K447A superalloy were systematically investigated. The effects of temperature and strain rate on its plastic flow behavior and material microstructure were analyzed. By examining the stress-strain curves under quasi-static conditions and utilizing electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD), the microstructural characteristics of specimens deformed at various strain rates and temperatures were analyzed. The results reveal that during the plastic deformation of K447A, strain hardening, temperature softening, and strain rate strengthening phenomena coexist. As the strain rate increases from quasi-static levels to5000 s−1, the temperature sensitivity index (s) gradually decreases, indicating a diminishing temperature softening effect at higher strain rates. Notably, at an elevated strain rate of 800 ℃, an anomalous stress peak appears in the flow stress-strain curve of the K447A alloy, suggesting complex interactions between temperature and strain rate during deformation. Furthermore, the strain rate sensitivity coefficient (p) increases with temperature, highlighting a more pronounced strain rate strengthening effect at elevated temperatures. Microstructural changes within the material, which are influenced by the coupling of strain rate and temperature, are also examined. An increase in strain rate leads to grain refinement, while higher temperatures result in a decrease in the proportion of low-angle grain boundaries, facilitating dynamic recrystallization within the material. To accurately describe the flow stress influenced by the interplay of temperature and strain rate, a modified Johnson-Cook constitutive model was developed. This revised model demonstrates improved predictive capability compared to the original formulation, effectively capturing the plastic flow behavior of K447A across a broad range of temperatures and strain rates. The predictive error is significantly reduced from 26.36% to 9.05%, underscoring the model’s enhanced accuracy and reliability in simulating the mechanical performance of K447A alloy under varying operational conditions. -
C Cr Co W Mo Ta Al Ti Hf B Zr Ni 0.13~0.17 8.0~8.8 9.0~11.0 9.5~10.5 0.5~0.8 2.8~3.3 5.3~5.7 0.9~1.2 1.2~1.6 0.01~0.02 0.03~0.08 余量 表 2 K447A高温合金压缩试验矩阵
Table 2. Experimental matrix for high-temperature compression of K447A alloy
应变率/s−1 温度/℃ 准静态(0.005) 室温、400、600、800、 1000 1000 室温、600、800、 1000 5000 室温、600、800、 1000 表 3 K447A合金的J-C修正本构模型参数
Table 3. J-C modified constitutive model parameters for K447A alloy
A/MPa B/MPa n C1 C2 C3 C4 m1 m2 m3 784.25 2026.43 0.599 1.635×10−4 0.5093 − 0.0295 −0.03 2.04605 0.31807 − 0.01434 表 4 本构模型与试验结果对比的相对均方根误差结果
Table 4. Comparison of relative root mean square errors of pre-experimental results and constitutive models
应变率/s−1 温度/℃ $ {\lambda _{{\text{RRMSEK}}}} $/% J-C模型 修正J-C模型 准静态 室温 11.55 2.57 400 3.94 5.47 600 9.28 7.65 800 22.98 15.37 1000 20.12 18.89 1000 室温 6.79 1.61 600 27.84 2.04 800 44.15 8.72 1000 55.29 10.88 5000 室温 5.31 1.98 600 24.70 16.66 800 52.35 15.45 1000 58.36 10.33 -
[1] 刘阳, 叶洪涛, 张军, 等. 航空用镍基高温合金切削现状研究 [J]. 航空制造技术, 2011, 54(14): 48–51. DOI: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2011.14.014.LIU Y, YE H T, ZHANG J, et al. Research on cutting status of Ni-based superalloy in aviation industry [J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2011, 54(14): 48–51. DOI: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2011.14.014. [2] YANG G X, XU Y F, JIANG L, et al. High temperature tensile properties and fracture behavior of cast nickel-base K445 superalloy [J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2011, 21(5): 418–425. DOI: 10.1016/S1002-0071(12)60078-1. [3] CHEN J, ZHOU X Y, WANG W L, et al. A review on fundamental of high entropy alloys with promising high-temperature properties [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 760: 15–30. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.067. [4] EYLON D, FUJISHIRO S, POSTANS P J, et al. High-temperature titanium alloys—a review [J]. JOM, 1984, 36(11): 55–62. DOI: 10.1007/BF03338617. [5] 李鹏, 叶雷, 程耀永, 等. K447A镍基高温合金钎焊接头组织及性能 [J]. 焊接, 2016(3): 11–13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2016.03.003.LI P, YE L, CHENG Y Y, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of K447A nickel-base superalloy brazed joint [J]. Welding & Joining, 2016(3): 11–13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2016.03.003. [6] PAN C L, YAO Z H, MA Y W, et al. Solidification microstructure characteristics and their formation mechanism of K447A nickel-based superalloy for dual-performance blisk [J]. Materials Characterization, 2023, 203: 113155. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2023.113155. [7] ZHANG Z L, ZHAO Y, SHAN J G, et al. Influence of heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of K447A cladding layers obtained by laser solid forming [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 790: 703–715. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.136. [8] ZHANG Z L, ZHAO Y, SHAN J G, et al. The role of shot peening on liquation cracking in laser cladding of K447A nickel superalloy powders over its non-weldable cast structure [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021, 823: 141678. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141678. [9] 谷怀鹏, 李相辉, 盖其东, 等. K447A合金的热处理组织和拉伸性能研究 [J]. 铸造, 2014, 63(8): 824–827. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2014.08.013.GU H P, LI X H, GAI Q D, et al. Study on the heat-treated microstructure and tensile property of K447A alloy [J]. Foundry, 2014, 63(8): 824–827. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2014.08.013. [10] WANG J J, WANG Z C, HAN Z W, et al. Effect of rejuvenation heat treatment on the microstructure and stress relaxation behavior of nickel-based superalloy with excess hardness [J]. Materials Characterization, 2023, 204: 113189. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2023.113189. [11] 焦明木, 宋健民. 一种铸造镍基高温合金显微组织与力学性能研究 [J]. 铸造, 2024, 73(5): 621–625. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2024.05.005.JIAO M M, SONG J M. Research on microstructure and mechanical properties of casting nickel base superalloy [J]. Foundry, 2024, 73(5): 621–625. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4977.2024.05.005. [12] KORKMAZ M E, GÜNAY M, VERLEYSEN P. Investigation of tensile Johnson-Cook model parameters for Nimonic 80A superalloy [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 801: 542–549. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.06.153. [13] LIU J, ZHENG B L, ZHANG K, et al. Ballistic performance and energy absorption characteristics of thin nickel-based alloy plates at elevated temperatures [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 126: 160–171. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.12.012. [14] WANG J J, HU X Y, YUAN K B, et al. Impact resistance prediction of superalloy honeycomb using modified Johnson-Cook constitutive model and fracture criterion [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 131: 66–77. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.001. [15] UGODILINWA N E, KHOSHDARREGI M, OJO O A. Analysis and constitutive modeling of high strain rate deformation behavior of Haynes 282 aerospace superalloy [J]. Materials Today Communications, 2019, 20: 100545. DOI: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100545. [16] 陈杰, 杨庆祥, 翟若岱. GH4720Li镍基高温合金高应变率动态力学性能研究 [J]. 信息记录材料, 2020, 21(10): 14–16. DOI: 10.16009/j.cnki.cn13-1295/tq.2020.10.007.CHEN J, YANG Q X, ZHAI R D. Study of high strain rate dynamic mechanical properties of GH4720Li nickel-based high temperature alloy [J]. Information Recording Materials, 2020, 21(10): 14–16. DOI: 10.16009/j.cnki.cn13-1295/tq.2020.10.007. [17] KUHN H, MEDLIN D. ASM handbook volume 8: mechanical testing and evaluation [M]. Materials Park, OH: ASM International, 2000: 462–476. DOI: 10.31399/asm.hb.v08.9781627081764. [18] WANG J J, GUO W G, GAO X S, et al. The third-type of strain aging and the constitutive modeling of a Q235B steel over a wide range of temperatures and strain rates [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2015, 65: 85–107. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2014.08.017. [19] SONG Y, GARCIA-GONZALEZ D, RUSINEK A. Constitutive models for dynamic strain aging in metals: strain rate and temperature dependences on the flow stress [J]. Materials, 2020, 13(7): 1794. DOI: 10.3390/ma13071794. [20] KUMAR N, YING Q, NIE X, et al. High strain-rate compressive deformation behavior of the Al0.1CrFeCoNi high entropy alloy [J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 86: 598–602. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.07.161. [21] LEYENS C, PETERS M. Titanium and titanium alloys: fundamentals and applications [M]. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2003. DOI: 10.1002/3527602119. [22] MA H J, HUANG L, TIAN Y, et al. Effects of strain rate on dynamic mechanical behavior and microstructure evolution of 5A02-O aluminum alloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 606: 233–239. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.03.081. [23] KHAN A S, MEREDITH C S. Thermo-mechanical response of Al6061 with and without equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) [J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2010, 26(2): 189–203. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2009.07.002. [24] 王忠堂, 张士宏, 冯斌. TC11钛合金应变速率和温度敏感系数 [J]. 沈阳理工大学学报, 2009, 28(3): 5–8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1251.2009.03.002.WANG Z T, ZHANG S H, FENG B. Strain-rate and temperature sensitivity coefficient for TC11 titanium alloy [J]. Journal of Shenyang Ligong University, 2009, 28(3): 5–8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1251.2009.03.002. -






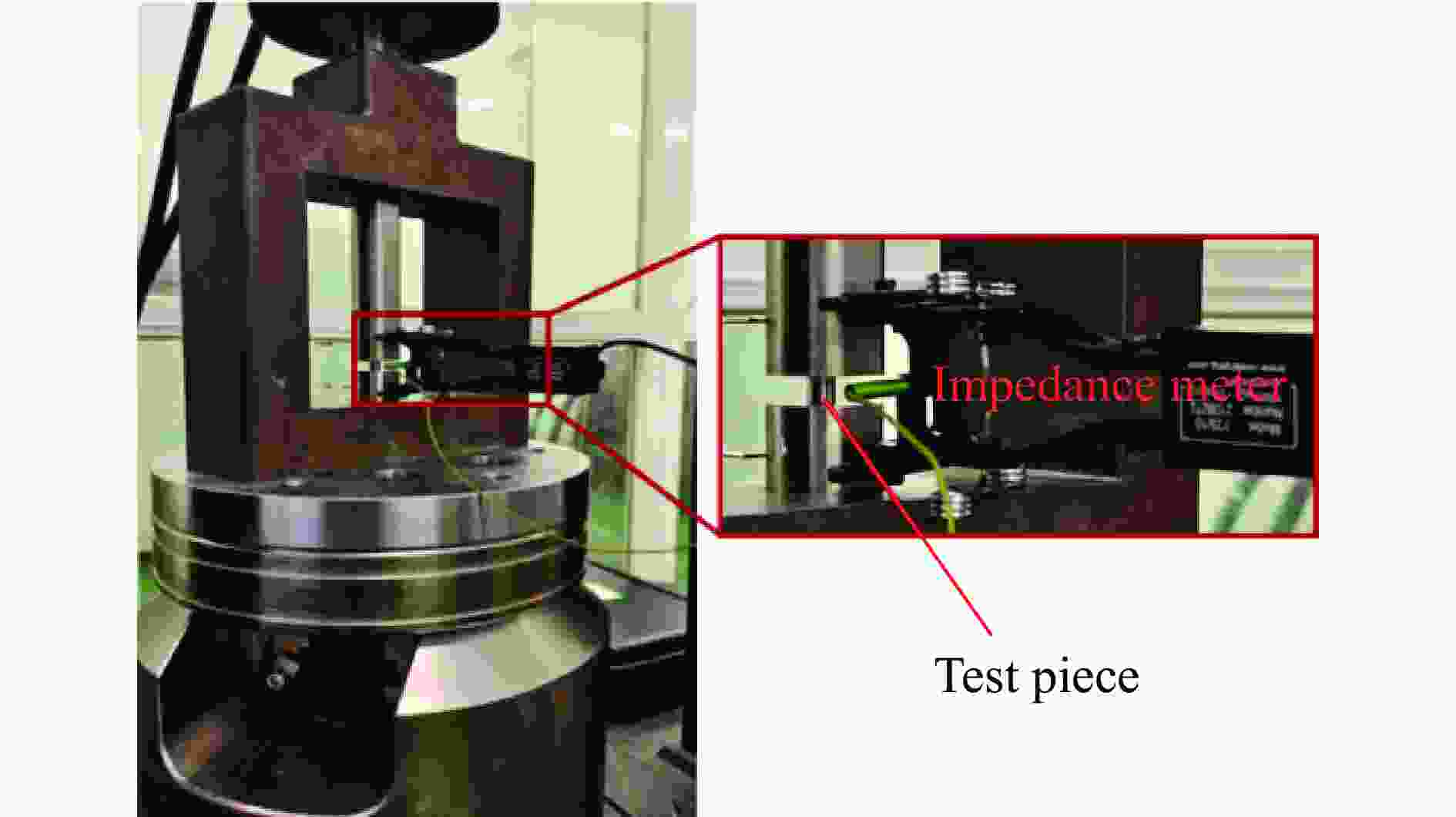
 下载:
下载: