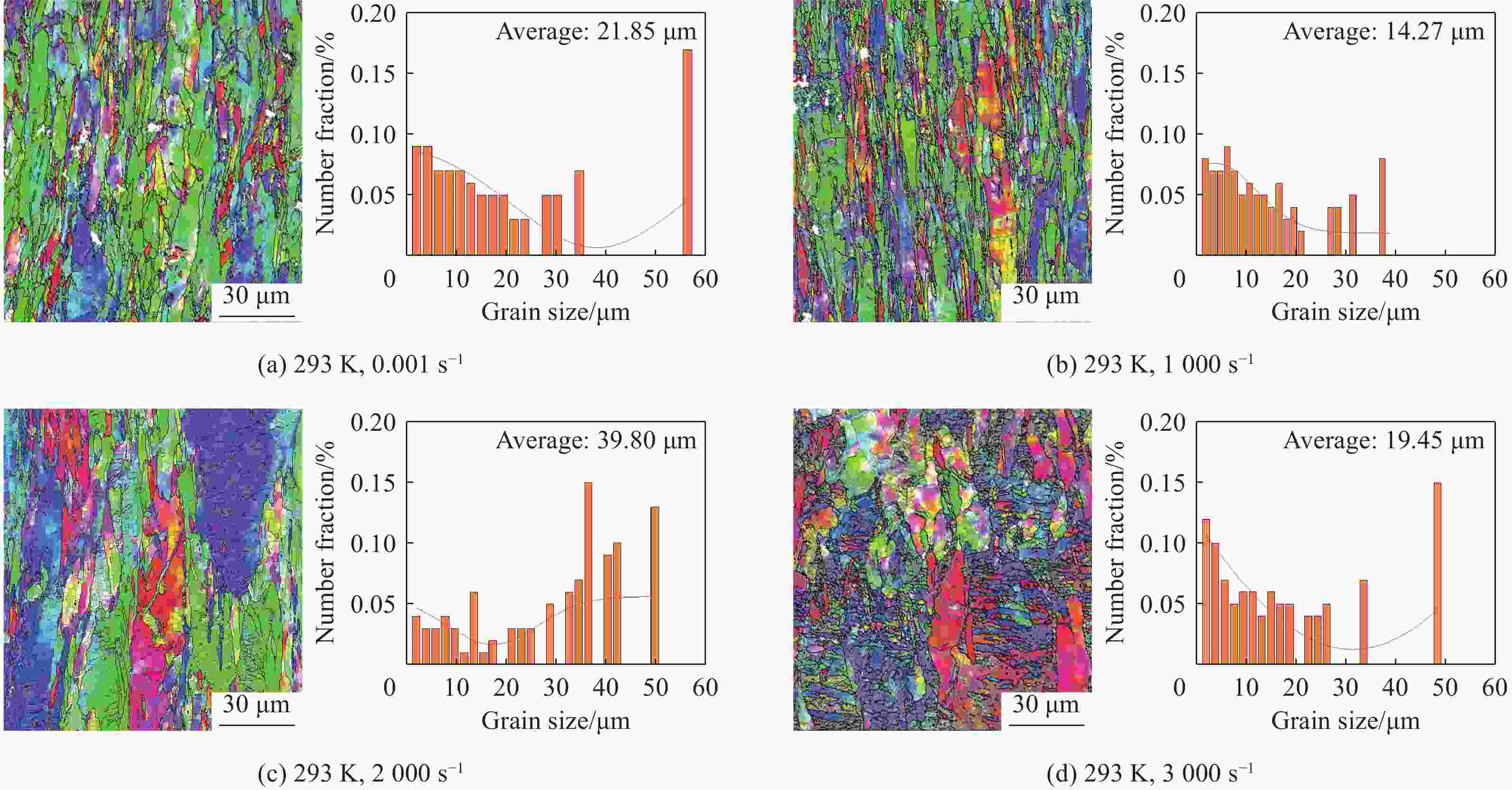
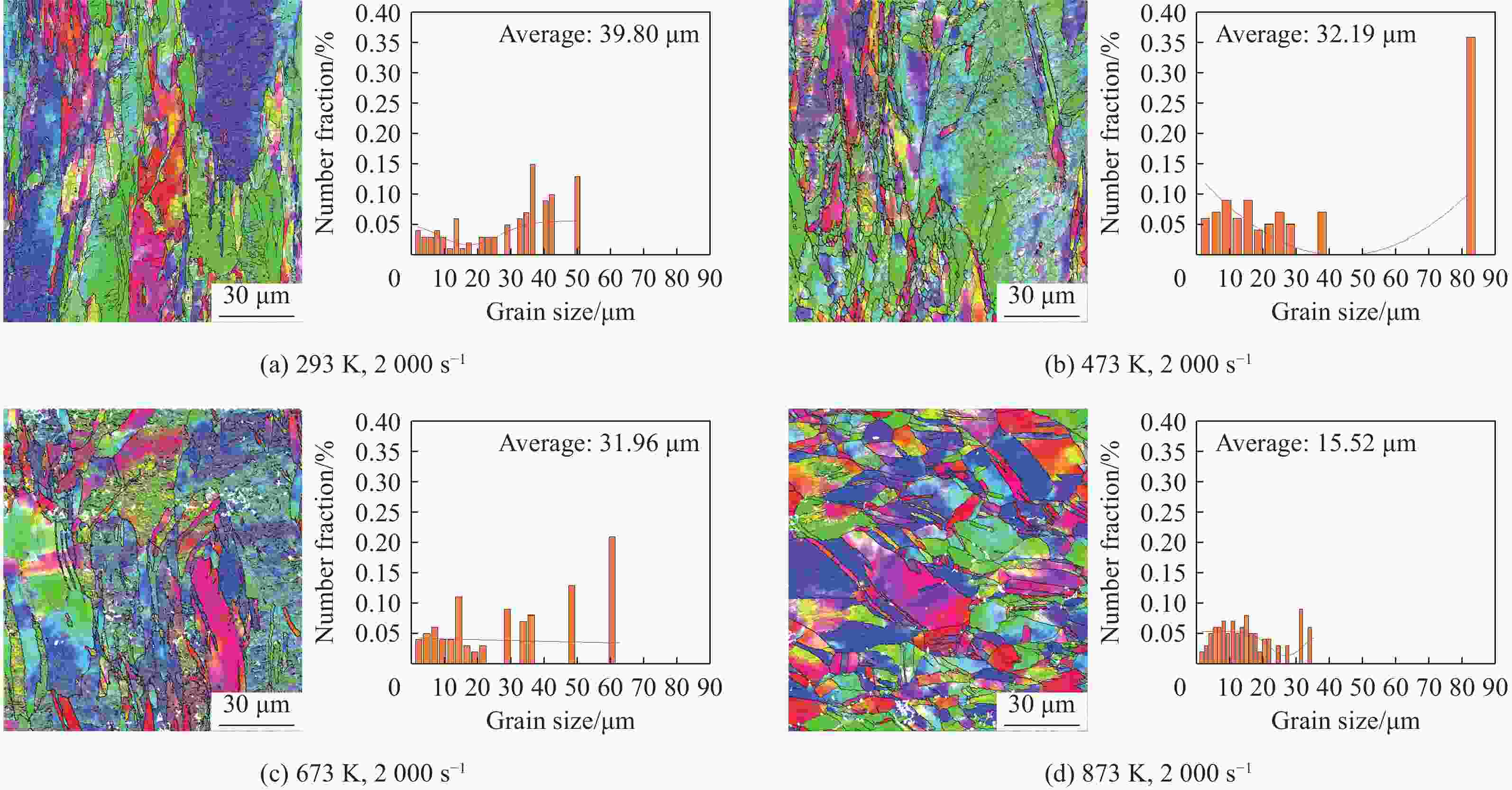
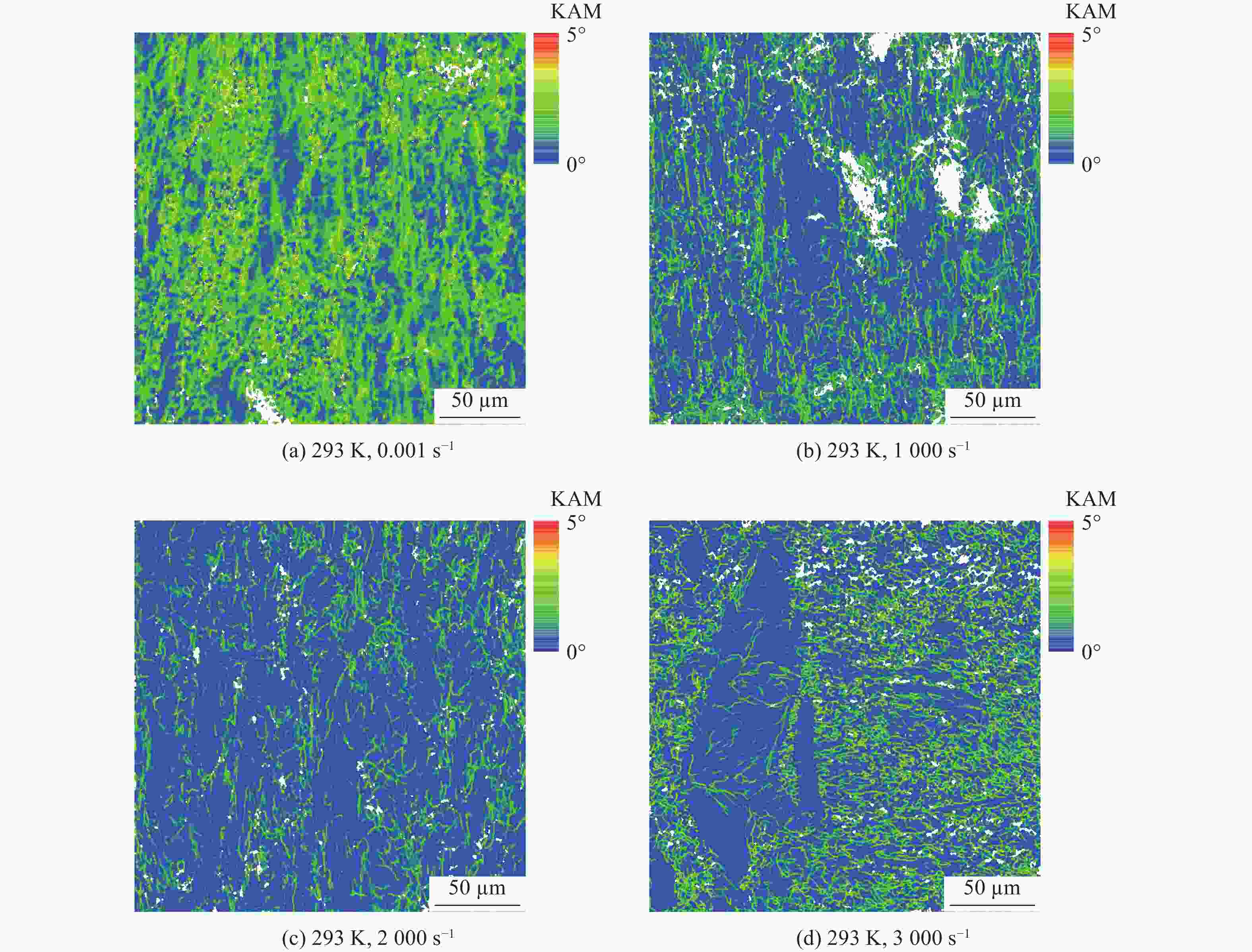
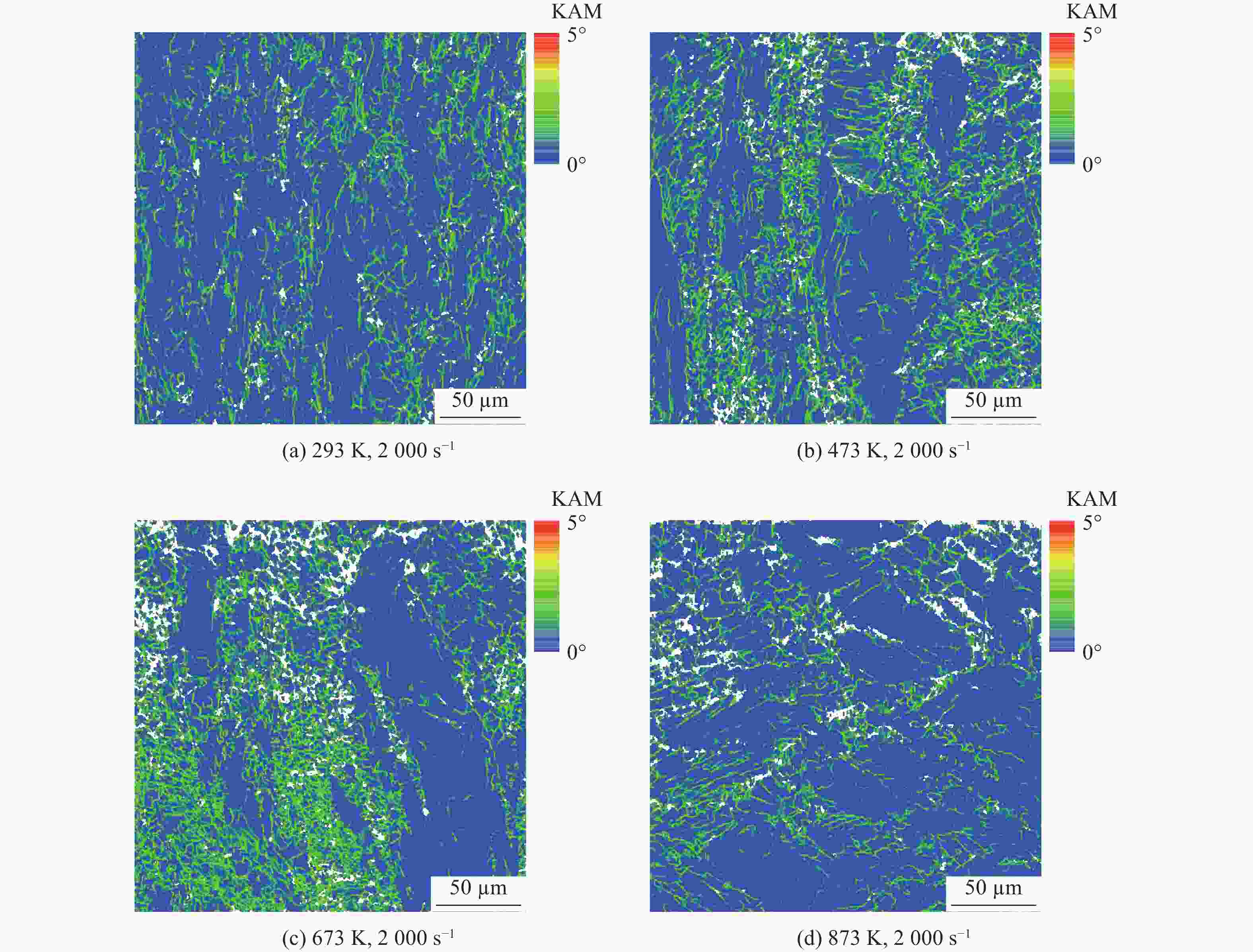
| [1] |
WU G N, DONG K L, XU Z L, et al. Pantograph-catenary electrical contact system of high-speed railways: recent progress, challenges, and outlooks [J]. Railway Engineering Science, 2022, 30(4): 437–467. DOI: 10.1007/s40534-022-00281-2.
|
| [2] |
MEI G M. Tribological performance of rigid overhead lines against pantograph sliders under DC passage [J]. Tribology International, 2020, 151: 106538. DOI: 10.1016/j.triboint.2020.106538.
|
| [3] |
SONG Y, LIU Z G, DUAN F C, et al. Wave propagation analysis in high-speed railway catenary system subjected to a moving pantograph [J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2018, 59: 20–38. DOI: 10.1016/j.apm.2018.01.001.
|
| [4] |
SONG Y, LIU Z G, RØNNQUIST A, et al. Contact wire irregularity stochastics and effect on high-speed railway pantograph-catenary interactions [J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(10): 8196–8206. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2020.2987457.
|
| [5] |
SONG Y, ANTUNES P, POMBO J, et al. A methodology to study high-speed pantograph-catenary interaction with realistic contact wire irregularities [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2020, 152: 103940. DOI: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2020.103940.
|
| [6] |
雷静果, 刘平, 井晓天, 等. 高速铁路接触线用时效强化铜合金的发展 [J]. 金属热处理, 2005, 30(3): 1–5. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2005.03.001.LEI J G, LIU P, JING X T, et al. Development of aging-strengthening copper alloy used in contact wire of high-speed railway [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2005, 30(3): 1–5. DOI: 10.13251/j.issn.0254-6051.2005.03.001.
|
| [7] |
WEI X K, MENG H F, HE J H, et al. Wear analysis and prediction of rigid catenary contact wire and pantograph strip for railway system [J]. Wear, 2020, 442/443: 203118. DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2019.203118.
|
| [8] |
DING T, CHEN G X, BU J, et al. Effect of temperature and arc discharge on friction and wear behaviours of carbon strip/copper contact wire in pantograph–catenary systems [J]. Wear, 2011, 271(9/10): 1629–1636. DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2010.12.031.
|
| [9] |
YANG H J, CHEN G X, GAO G Q, et al. Experimental research on the friction and wear properties of a contact strip of a pantograph-catenary system at the sliding speed of 350 km/h with electric current [J]. Wear, 2015, 332/333: 949–955. DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2014.11.004.
|
| [10] |
XU Z, SONG Y, LIU Z G. Stress analysis and fatigue life prediction of contact wire located at steady arms in high-speed railway catenary system [J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2022, 71: 9001212. DOI: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3144747.
|
| [11] |
吴朋越, 谢水生, 黄国杰. 高速列车用铜合金接触线用材料及其加工工艺 [J]. 稀有金属, 2006, 30(2): 203–208. DOI: 10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.2006.02.018.WU P Y, XIE S S, HUANG G J. Materials and process technics of copper contact wires for high-speed train [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2006, 30(2): 203–208. DOI: 10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.2006.02.018.
|
| [12] |
敬霖, 冯超, 苏兴亚, 等. 高速动车组D2车轮钢的率温耦合变形机理与本构关系 [J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(34): 4068–4079. DOI: 10.1360/TB-2022-0437.JING L, FENG C, SU X Y, et al. Strain rate-temperature coupling deformation mechanism and constitutive relationship of D2 wheel steel for high-speed EMUs [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(34): 4068–4079. DOI: 10.1360/TB-2022-0437.
|
| [13] |
ZHANG T, LU S H, WU Y X, et al. Optimization of deformation parameters of dynamic recrystallization for 7055 aluminum alloy by cellular automaton [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(6): 1327–1337. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60154-7.
|
| [14] |
PECZAK P, LUTON M J. A Monte Carlo study of the influence of dynamic recovery on dynamic recrystallization [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 1993, 41(1): 59–71. DOI: 10.1016/0956-7151(93)90339-T.
|
| [15] |
DING R, GUO Z X. Coupled quantitative simulation of microstructural evolution and plastic flow during dynamic recrystallization [J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia, 2001, 49(16): 3163–3175. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00233-6.
|
| [16] |
WEN D X, LIN Y C, LI H B, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of a typical Ni-based superalloy [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 591: 183–192. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.09.049.
|
| [17] |
LIN Y C, CHEN X M. A critical review of experimental results and constitutive descriptions for metals and alloys in hot working [J]. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(4): 1733–1759. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.11.048.
|
| [18] |
LIU Y H, NING Y Q, YANG X M, et al. Effect of temperature and strain rate on the workability of FGH4096 superalloy in hot deformation [J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 95: 669–676. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.01.032.
|
| [19] |
LI J, WENG G J. A micromechanical approach to the stress-strain relations, strain-rate sensitivity and activation volume of nanocrystalline materials [J]. International Journal of Mechanics and Materials in Design, 2013, 9(2): 141–152. DOI: 10.1007/s10999-013-9214-1.
|
| [20] |
袁康博, 姚小虎, 王瑞丰, 等. 金属材料的率-温耦合响应与动态本构关系综述 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(9): 091401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0416.YUAN K B, YAO X H, WANG R F, et al. A review on rate-temperature coupling response and dynamic constitutive relation of metallic materials [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(9): 091401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2021-0416.
|
| [21] |
LIU Y, ZHANG S, FENG C, et al. Dynamic mechanical behaviors of pearlitic U71MnG rail steel: deformation mechanisms and constitutive model [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2024, 897: 146353. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2024.146353.
|
| [22] |
申坤, 汪明朴, 郭明星, 等. Cu-0.23%Al2O3弥散强化铜合金的高温变形特性研究 [J]. 金属学报, 2009, 45(5): 597–604. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2009.05.014.SHEN K, WANG M P, GUO M X, et al. Study on high temperature deformation characteristics of Cu-0.23%Al2O3 dispersion-strengthened copper alloy [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2009, 45(5): 597–604. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2009.05.014.
|
| [23] |
SABIROV I, BARNETT M R, ESTRIN Y, et al. The effect of strain rate on the deformation mechanisms and the strain rate sensitivity of an ultra-fine-grained Al alloy [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2009, 61(2): 181–184. DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.03.032.
|
| [24] |
JING L, SU X Y, ZHAO L M. The dynamic compressive behavior and constitutive modeling of D1 railway wheel steel over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures [J]. Results in Physics, 2017, 7: 1452–1461. DOI: 10.1016/j.rinp.2017.04.015.
|
| [25] |
LONG M J, JIANG F, SU Y M, et al. Dynamic recrystallization mechanisms and microstructure evolution of a novel Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy by isothermal compression [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 33: 1740–1755. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.09.200.
|
| [26] |
LIU Y, LIU X B, FENG C, et al. Mechanical properties and microstructure of the heterogeneous DZ2 axle steel under high-strain-rate compression at ambient temperature [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 26: 8456–8471. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.09.192.
|
| [27] |
KUBIN L P, MORTENSEN A. Geometrically necessary dislocations and strain-gradient plasticity: a few critical issues [J]. Scripta Materialia, 2003, 48(2): 119–125. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-6462(02)00335-4.
|
| [28] |
李定远, 朱志武, 卢也森. 冲击加载下42CrMo钢的动态力学性能及其本构关系 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2017, 31(6): 761–768. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.06.011.LI D Y, ZHU Z W, LU Y S. Mechanical properties and constitutive relation for 42CrMo steel under impact load [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2017, 31(6): 761–768. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2017.06.011.
|
| [29] |
JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures [C]// Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics. The Hague, The Netherlands, 1983: 541–548.
|
| [30] |
周伦, 苏兴亚, 敬霖, 等. 6061-T6铝合金动态拉伸本构关系及失效行为 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(9): 111–122. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0154.ZHOU L, SU X Y, JING L, et al. Dynamic tensile constitutive relationship and failure behavior of 6061-T6 aluminum alloy [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(9): 111–122. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0154.
|
| [31] |
刘晓燕, 李帅康, 杨西荣. 基于修正J-C和BP神经网络模型的超细晶纯钛动态本构行为 [J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2024, 53(2): 409–416. DOI: 10.12442/j.issn.1002-185X.20230015.LIU X Y, LI S K, YANG X R. Dynamic constitutive behavior of ultrafine-grained pure titanium based on modified J-C and BP artificial neural network model [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2024, 53(2): 409–416. DOI: 10.12442/j.issn.1002-185X.20230015.
|






 下载:
下载: