Characterization method of material constitutive relationship at high strain rates based on GNN/KAN
-
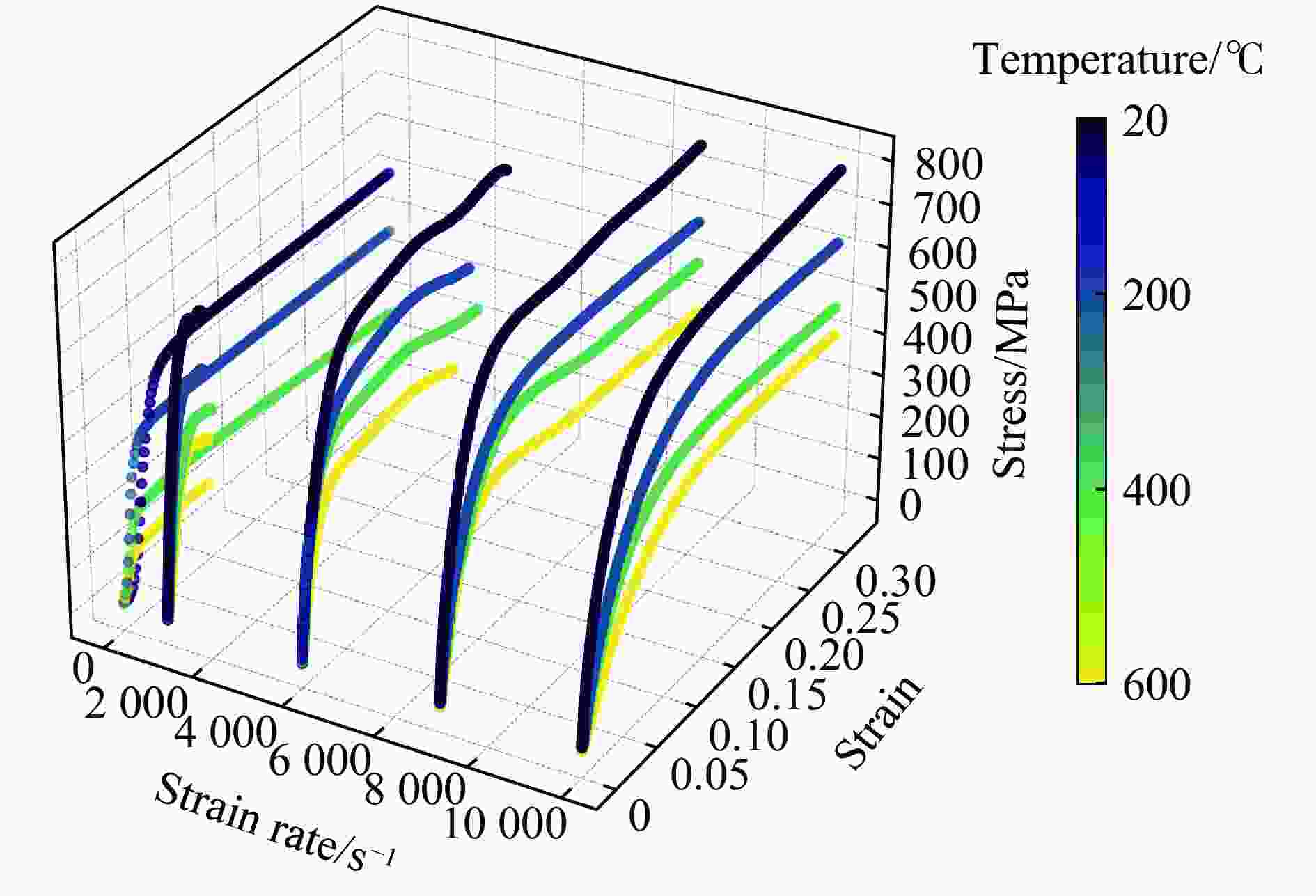
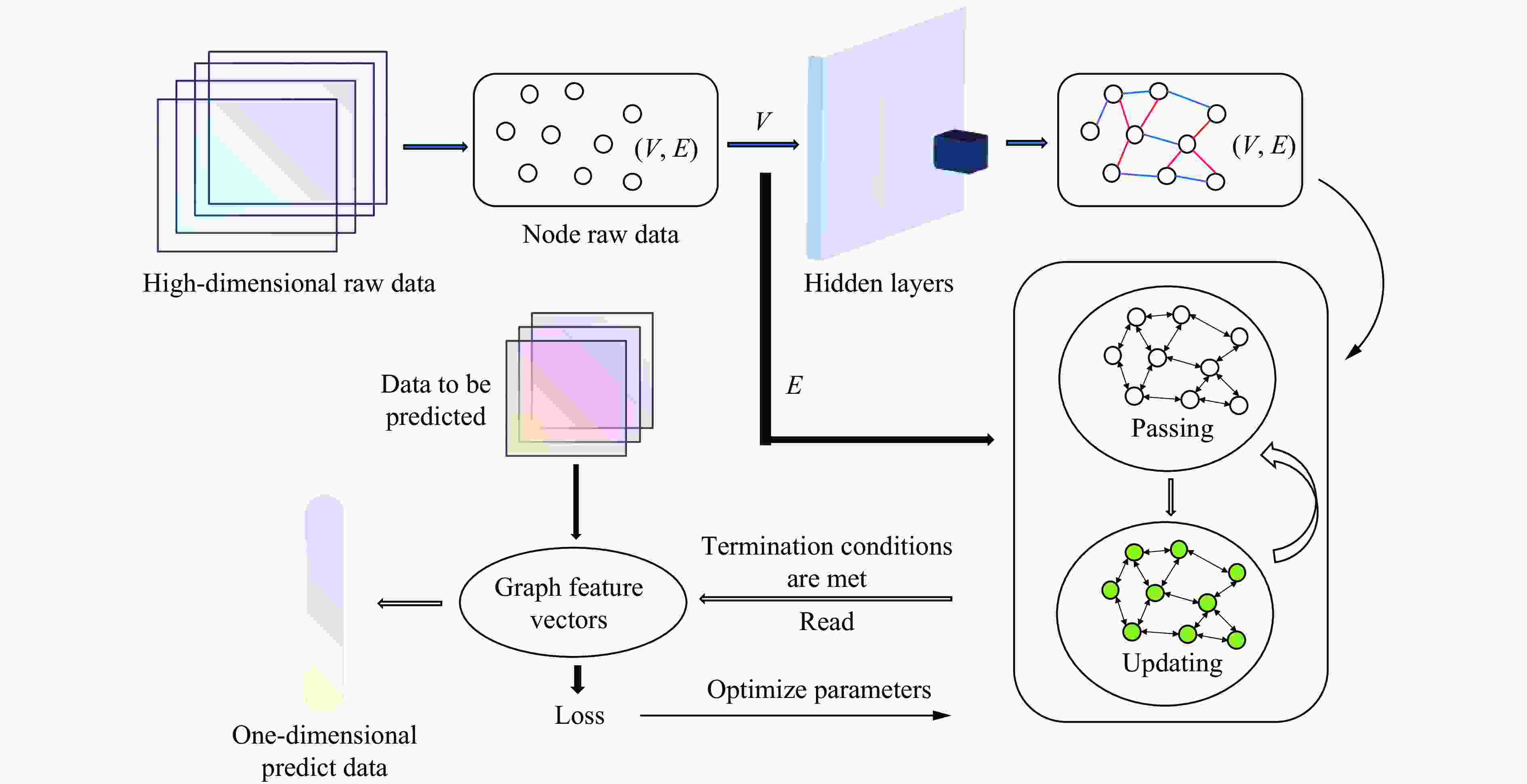
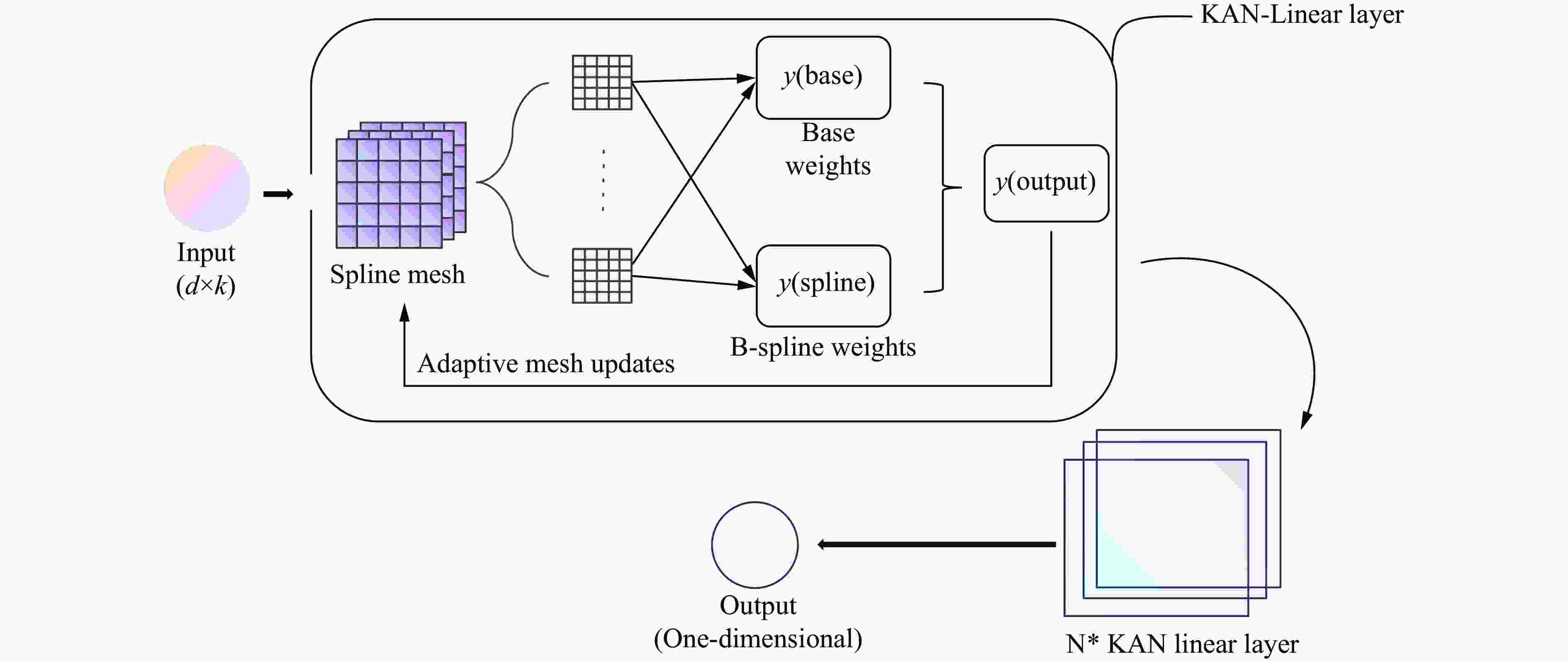
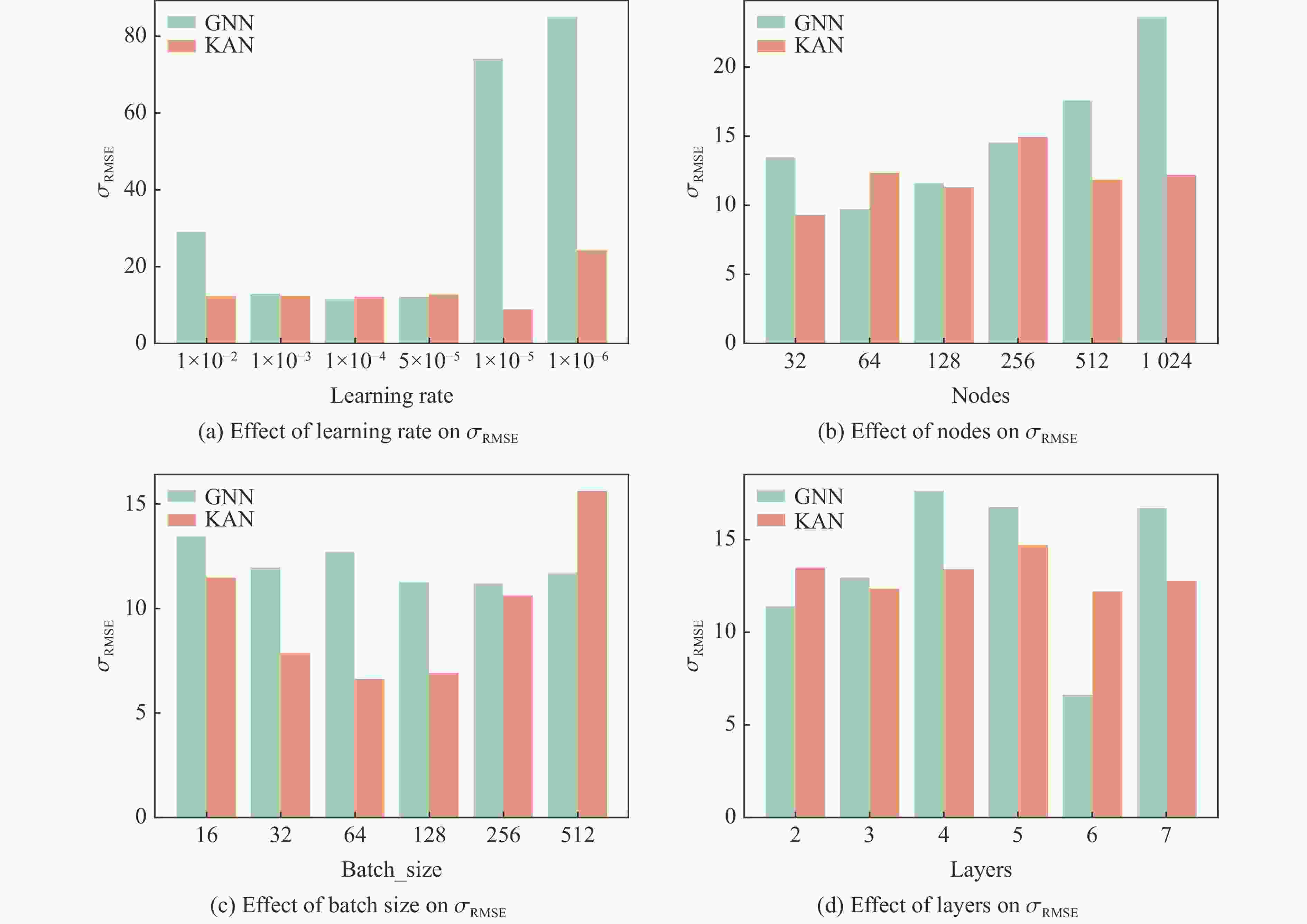
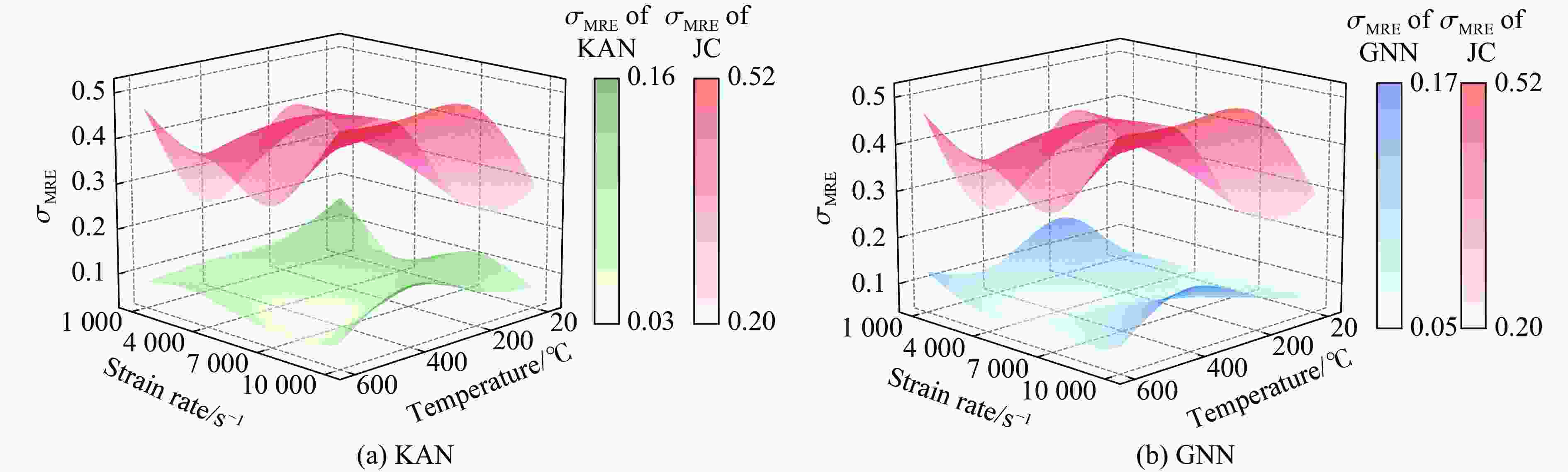
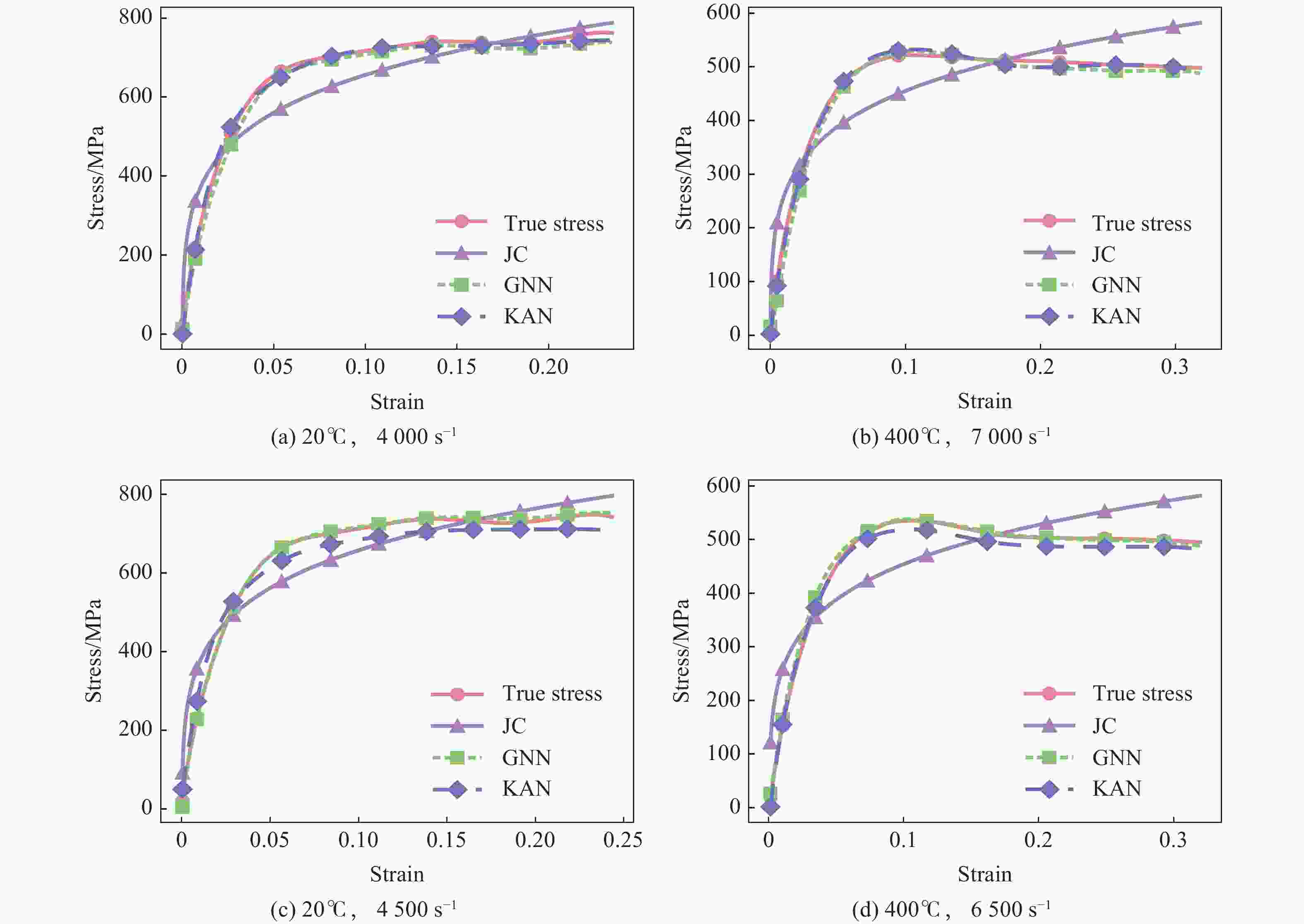
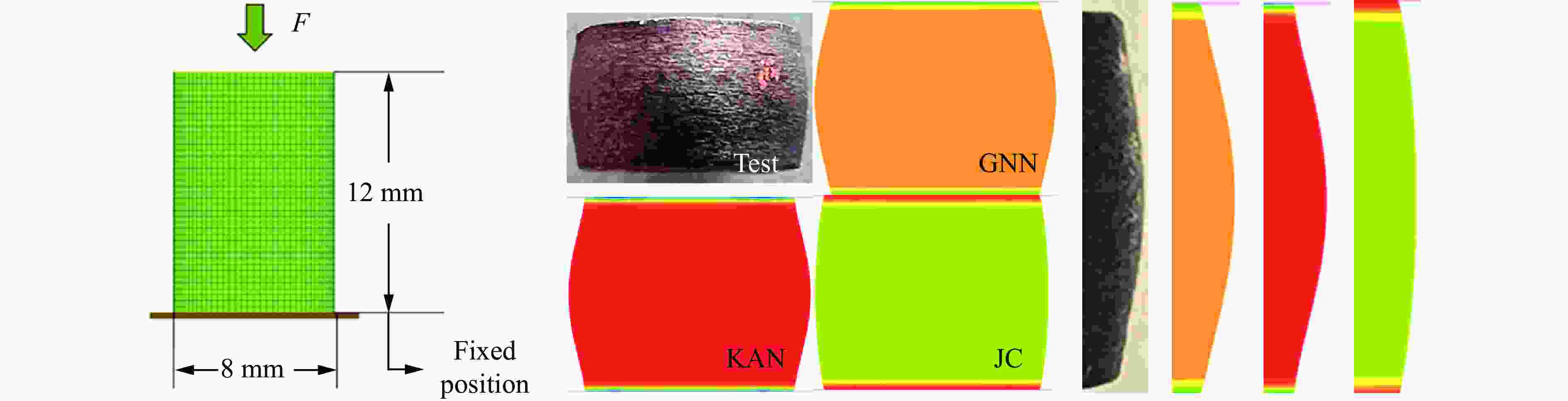
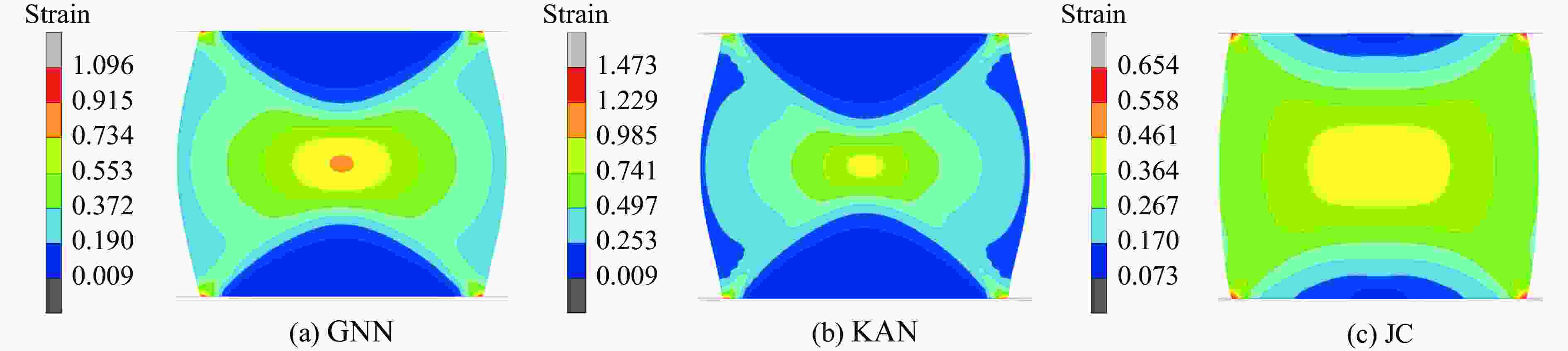
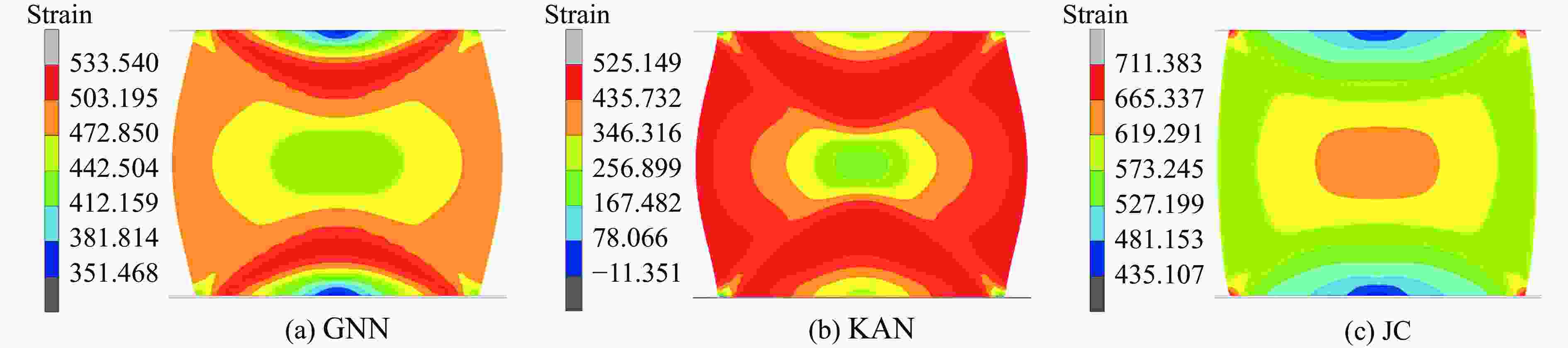
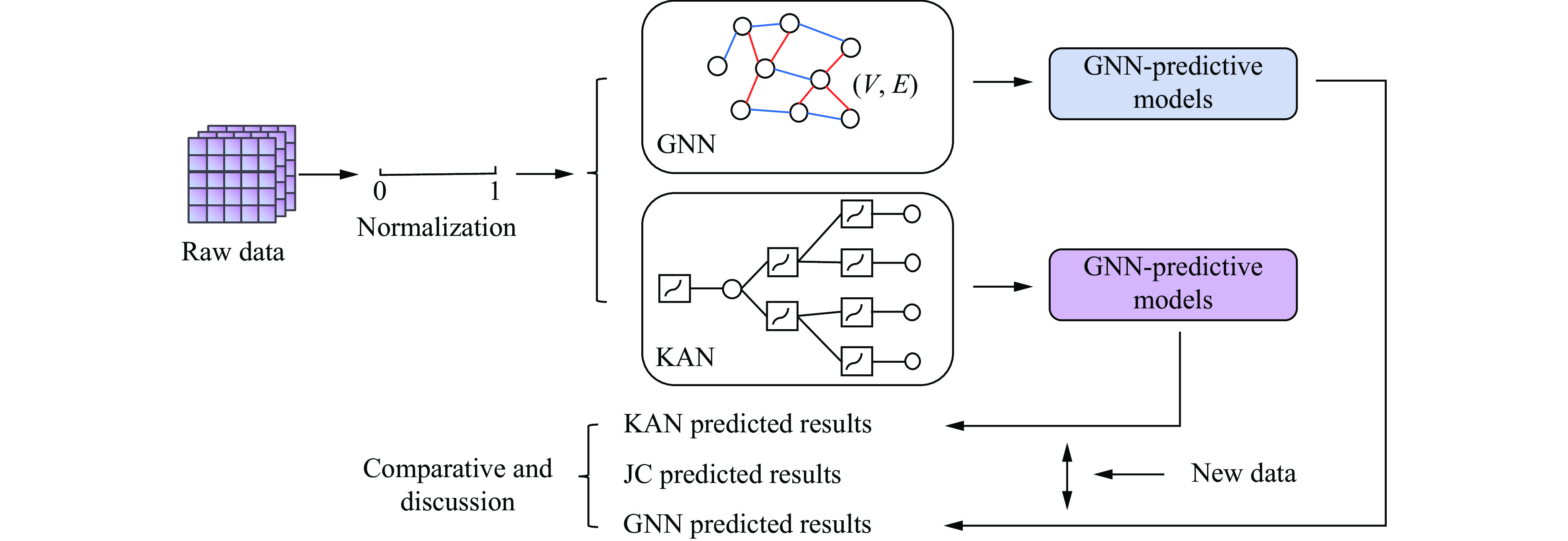
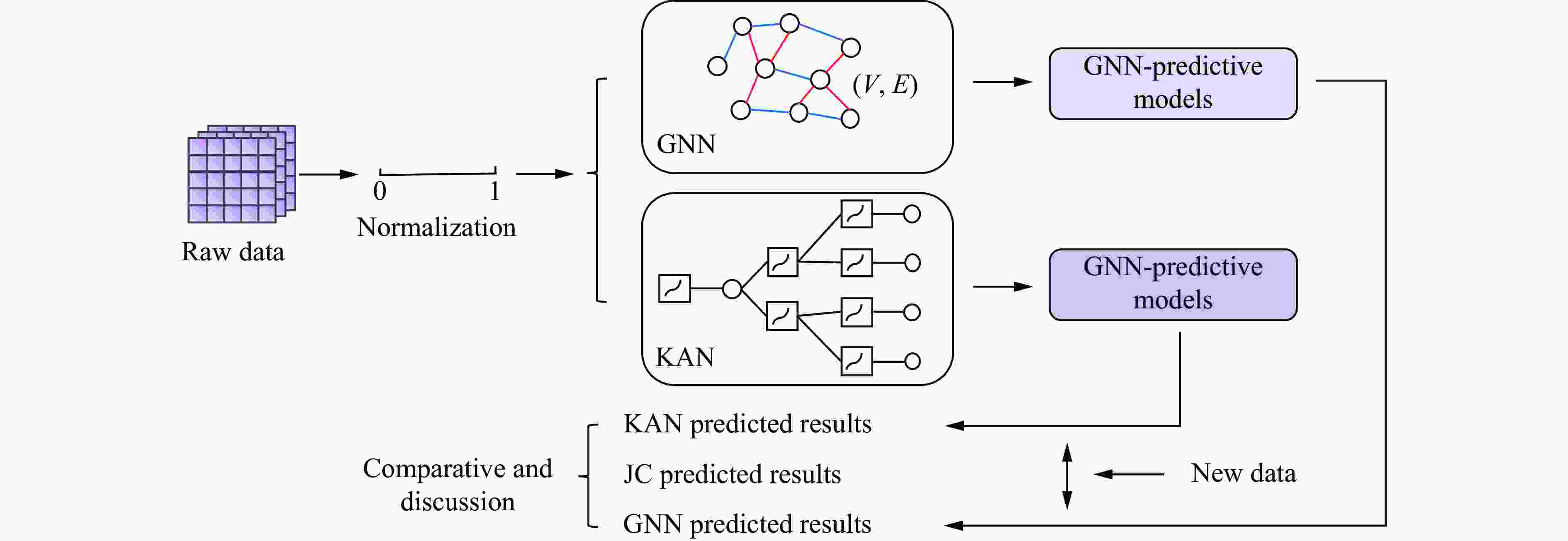
摘要: 为准确表征金属材料在高应变速率下的应力-应变本构关系,提出了基于图神经网络(graph neural networks,GNN)和KAN(Kolmogorov-Arnold networks)的本构关系的高精度预测模型。为解决传统Johnson-Cook(JC)模型不考虑温度、应变速率与应变之间的耦合效应问题,在GNN模型中构建图结构数据以描述多维参数的非线性关联,在KAN模型中基于Kolmogorov-Arnold定理实现高维输入空间的非线性映射。基于ODS(oxide dispersion strengthened)铜合金的高应变率压缩实验,评估了GNN、KAN和JC的本构关系描述和预测精度。结果表明:GNN与KAN模型在测试集中的平均相对误差分别为8.0%与9.0%,决定系数均高于0.95,显著优于JC模型(平均相对误差为38.0%,决定系数为0.75);将所构建的本构关系模型应用在有限元仿真中,GNN和KAN模型预测的等效塑性应变与应力分布更符合理论特征,而JC模型无法准确描述材料的软化阶段,仿真结果偏差较大。所构建的模型能有效捕捉高应变速率下材料的多场耦合特性,为极端载荷条件下的应力-应变本构关系提供了新的预测方法。Abstract: To accurately characterize the stress-strain constitutive relationship of metal materials under high strain-rate conditions, a novel, high-precision constitutive-relationship-prediction model based on Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) was developed. Traditional Johnson-Cook (JC) models often fail to account for the coupling effects among temperature, strain rate, and strain, all of which are crucial for describing the dynamic behavior of materials under extreme conditions. This limitation was addressed by constructing graph-structured data in the GNN model to capture the nonlinear correlations of multidimensional parameters and by leveraging the Kolmogorov-Arnold theorem in the KAN model to achieve precise mapping of high-dimensional input spaces. The research methodology involved several key steps. Experimental data from ODS copper subjected to high-strain-rate compression were collected using a split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) system and subsequently preprocessed. The dataset included temperature, strain rate, strain, and stress. In the GNN model, when temperature and strain rate were held constant, nodes were connected sequentially based on strain values to form edges. When temperature was held constant, a reasonable threshold was established between nodes with adjacent strain rates, and nodes within this threshold were connected to form edges. The GNN employed a Message Passing Neural Network (MPNN) architecture to learn and predict material properties. Model parameters were optimized using the Adam optimizer, with the Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) serving as the loss function. The KAN model was constructed based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem and consisted of multiple KAN-Linear layers. Each KAN-Linear unit included base weights and spline weights. Base weights handled linear relationships through traditional linear transformations, while spline weights managed nonlinear mappings via B-spline interpolation. Both models were trained on the preprocessed dataset, and their performance was evaluated using metrics such as the Mean Relative Error (MRE), Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and the coefficient of determination (R2). The GNN model achieved an average MRE of 9.2% with an R2 value exceeding 0.95, while the KAN model recorded an MRE of 9.1% with a similar R2 value. Both models significantly outperformed the JC model, which had an MRE of 38% and an R2 value of 0.75. Furthermore, the predictive capabilities of the GNN and KAN models were validated through finite element simulations. The simulation results demonstrated that the stress-strain distributions predicted by the GNN and KAN models were more consistent with theoretical expectations compared to those predicted by the JC model, particularly in capturing the material's softening phase. The findings highlight the potential of integrating advanced machine - learning techniques, such as GNNs and KANs, into the field of materials science to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of constitutive modeling. These models offer a promising alternative to traditional empirical models and hold significant implications for engineering applications in aerospace, automotive, and other industries where materials are subjected to high strain rates.
-
表 1 模型预测结果的精度对比
Table 1. Comparison of the prediction accuracy of different models
工况 σMRE R2 GNN/% KAN/% JC/% GNN KAN JC 20 ℃/4 000 s−1 6.5 4.0 36.0 0.9927 0.9972 0.9073 20 ℃/4 500 s−1 1.5 8.3 24.2 0.9993 0.9785 0.8978 400 ℃/6 500 s−1 3.0 4.8 38.1 0.9970 0.9929 0.7975 400 ℃/7 000 s−1 9.0 9.2 42.7 0.9896 0.9980 0.8590 -
[1] ZERILLI F J, ARMSTRONG R W. Dislocation-mechanics-based constitutive relations for material dynamics calculations [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1987, 61(5): 1816–1825. DOI: 10.1063/1.338024. [2] PERZYNA P. Fundamental problems in viscoplasticity [J]. Advances in Applied Mechanics, 1966, 9: 243–377. DOI: 10.1016/S0065-2156(08)70009-7. [3] Johnson G R. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics, The Hague, Netherlands, 1983. [4] LIU F X, WANG S J, XIE G L, et al. Microstructural evolution and modified constitutive model of nanoscale Al2O3 dispersion-strengthened copper under high strain rate deformation [J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2024, 913: 146997. DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2024.146997. [5] BREIMAN L. Random forests [J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1): 5–32. DOI: 10.1023/A:1010933404324. [6] MITCHELL M. An introduction to genetic algorithms [M]. Cambridge: The MIT Press, 1998. DOI: 10.7551/mitpress/3927.001.0001. [7] CORTES C, VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks [J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273–297. DOI: 10.1007/bf00994018. [8] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors [J]. Nature, 1986, 323(6088): 533–536. DOI: 10.1038/323533a0. [9] LECUN Y, BOSER B, DENKER J S, et al. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition [J]. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(4): 541–551. DOI: 10.1162/neco.1989.1.4.541. [10] 初红艳, 赵凯林, 程强. 盘形锻件等效应力分析及神经网络预测 [J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(2): 103–111. DOI: 10.11936/bjutxb2019080014.CHU H Y, ZHAO K L, CHENG Q. Equivalent stress analysis and neural network prediction of disk forgings [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2021, 47(2): 103–111. DOI: 10.11936/bjutxb2019080014. [11] 林启权, 卜根, 王镇柱, 等. 基于BP神经网络的DP980钢板本构关系 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2022, 29(8): 139–144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2022.08.017.LIN Q Q, BU G, WANG Z, et al. Constitutive relationship of DP980 steel sheet based on BP neural network [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2022, 29(8): 139–144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2022.08.017. [12] 魏令港, 黄靓, 曾令宏. 基于改进特征筛选的随机森林算法对锂渣混凝土强度的预测研究 [J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(9): 22050319. DOI: 10.11896/cldb.22050319.WEI L G, HUANG L, ZENG L H. Using random forest with improved variable selection to predict the compressive strength of concrete with lithium slag [J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(9): 22050319. DOI: 10.11896/cldb.22050319. [13] 王彦磊, 王仁超, 龙益彬, 等. 基于改进随机森林算法的渡槽位移及应力预测模型 [J]. 水电能源科学, 2020, 38(5): 122–124,10. DOI: 10.20040/j.cnki.1000-7709.2020.05.030.WANG Y L, WANG R C, LONG Y B, et al. Aqueduct displacement and stress prediction model based on improved random forest algorithm [J]. Water Resources and Power, 2020, 38(5): 122–124,10. DOI: 10.20040/j.cnki.1000-7709.2020.05.030. [14] 丁军, 古愉川, 黄霞, 等. 基于改进遗传算法优化人工神经网络的304不锈钢流变应力预测准确性研究 [J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(10): 78–86. DOI: 10.3901/JME.2022.10.078.DING J, GU Y C, HUANG X, et al. Research on prediction accuracy of flow stress of 304 stainless steel based on artificial neural network optimized by improved genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(10): 78–86. DOI: 10.3901/JME.2022.10.078. [15] 黄俊杰, 朱剑琴, 程泽源. 基于卷积神经网络双层壁三维热应力预测方法 [J]. 航空动力学报, 2023, 38(7): 1658–1667. DOI: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20220754.HUANG J J, ZHU J Q, CHENG Z Y. Three-dimensional thermal stress prediction method in double-wall structure using convolutional neural networks [J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2023, 38(7): 1658–1667. DOI: 10.13224/j.cnki.jasp.20220754. [16] SCARSELLI F, GORI M, TSOI A C, et al. The graph neural network model [J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(1): 61–80. DOI: 10.1109/TNN.2008.2005605. [17] 董志浩. 基于图神经网络的材料性质预测及其应用研究 [D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2023. DOI: 10.27351/d.cnki.gszhu.2023.000186.DONG Z H. Research and applications of material property prediction based on graph neural networks [D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2023. DOI: 10.27351/d.cnki.gszhu.2023.000186. [18] MAURIZI M, GAO C, BERTO F. Predicting stress, strain and deformation fields in materials and structures with graph neural networks [J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 21834. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-26424-3. [19] 郑哲, 江文强, 王璋奇, 等. 基于图神经网络的结构力学响应预测模型研究 [J/OL]. 工程力学, 1–11. [2024-12-09]. https://engineeringmechanics.cn/cn/article/doi/ 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2023.10.0801. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2023.10.0801.ZHENG Z, JIANG W Q, WANG Z Q, et al. Research on the prediction model of mechanical response for structures based on graph neural network [J/OL]. Engineering Mechanics, 1–11[2024-12-09]. https://engineeringmechanics.cn/cn/article/doi/ 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2023.10.0801. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2023.10.0801. [20] LIU Z M, WANG Y X, VAIDYA S, et al. KAN: Kolmogorov-Arnold networks [C]//Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations. Singapore: ICLR, 2025: 1–47. [21] 夏天, 高志玉, 赵斐, 等. 金属材料塑性本构模型建立研究进展 [J]. 塑性工程学报, 2024, 31(9): 23–35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2024.09.002.XIA T, GAO Z Y, ZHAO F, et al. Research progress on establishing of plastic constitutive models for metal materials [J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2024, 31(9): 23–35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2024.09.002. [22] GILMER J, SCHOENHOLZ S S, RILEY P F, et al. Neural message passing for quantum chemistry [C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney: PMLR, 2017: 1263–1272. [23] 王平. 金属塑性成型力学 [M]. 第2版. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013. -






 下载:
下载: