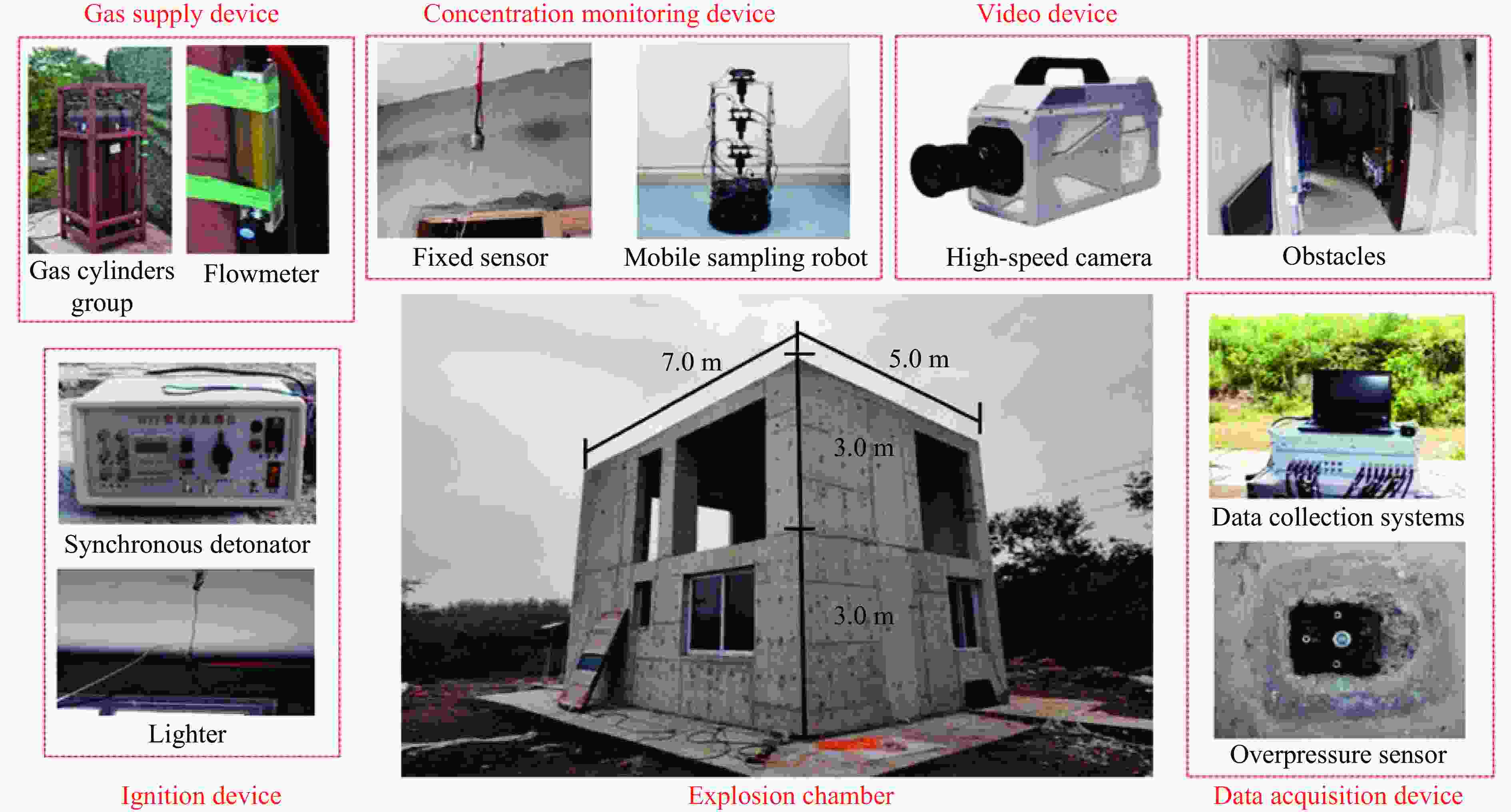
Combustible gas leakage and diffusion prediction based on graph neural network
-
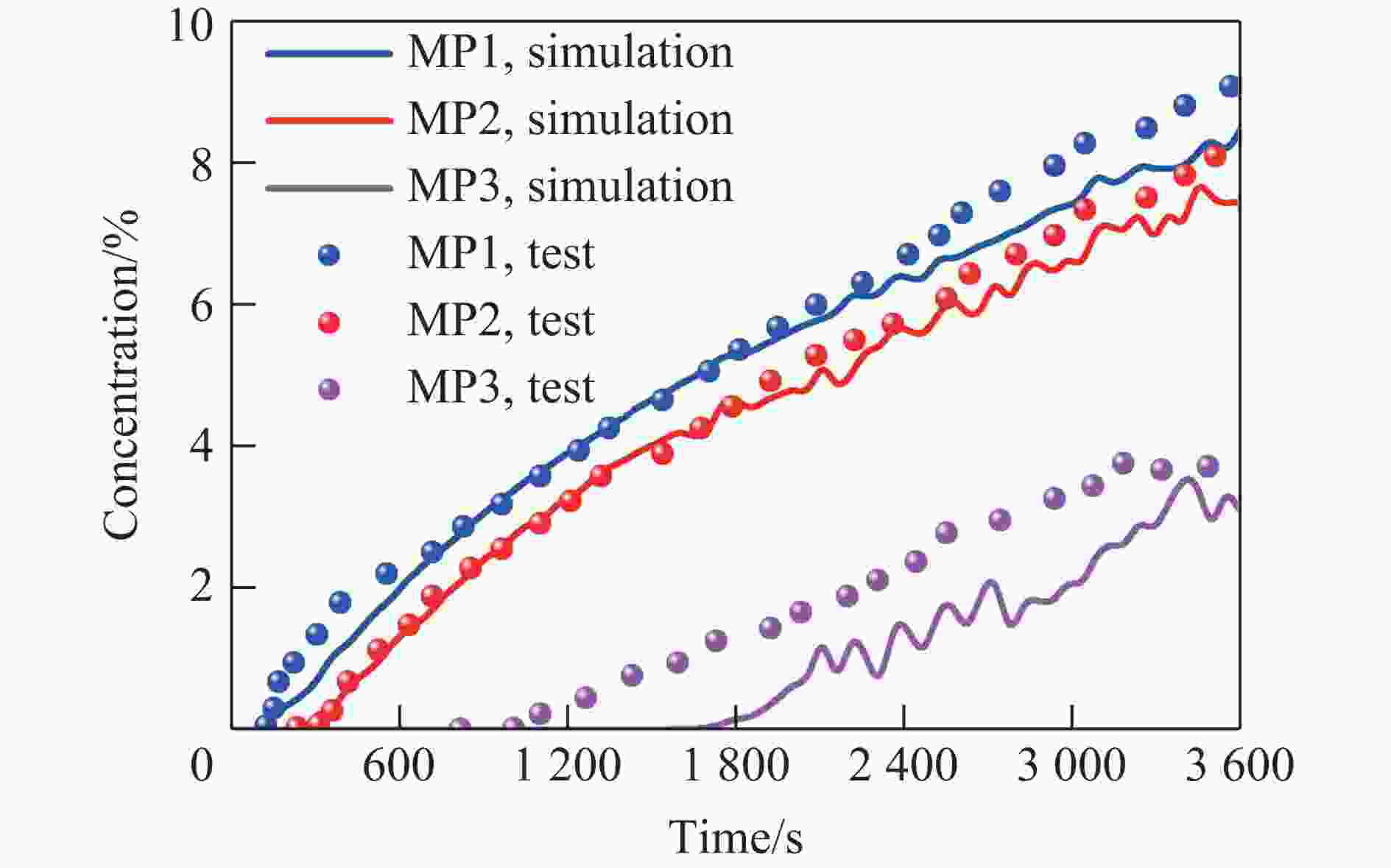
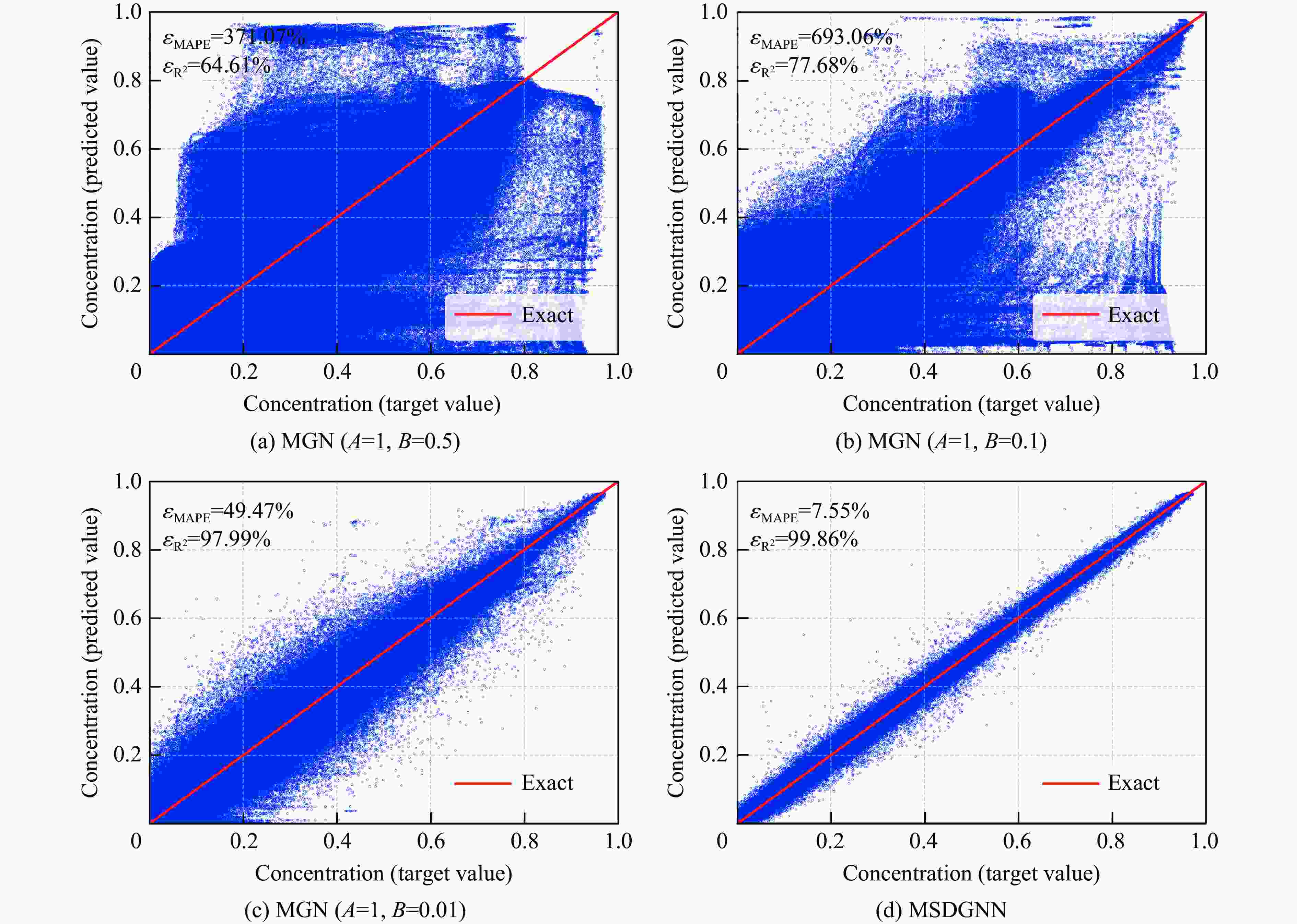
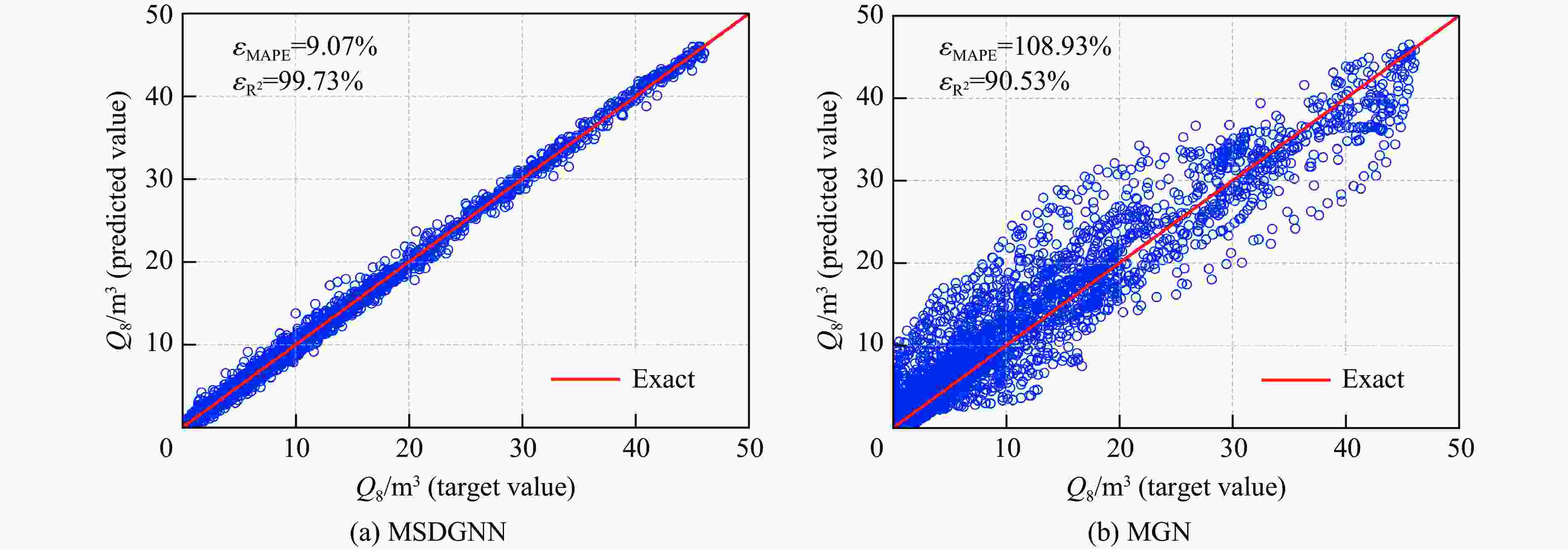
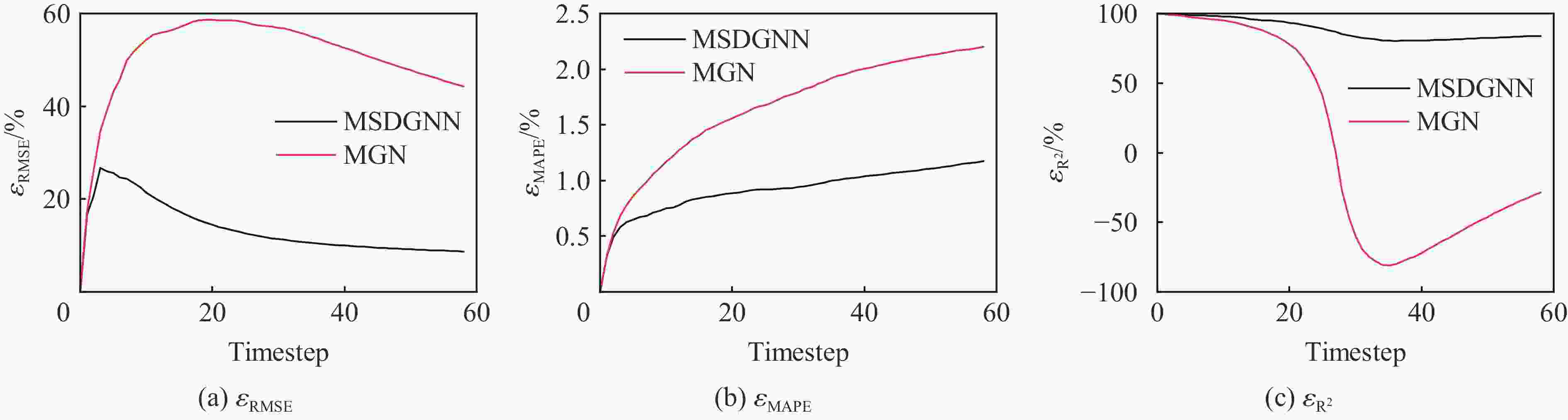
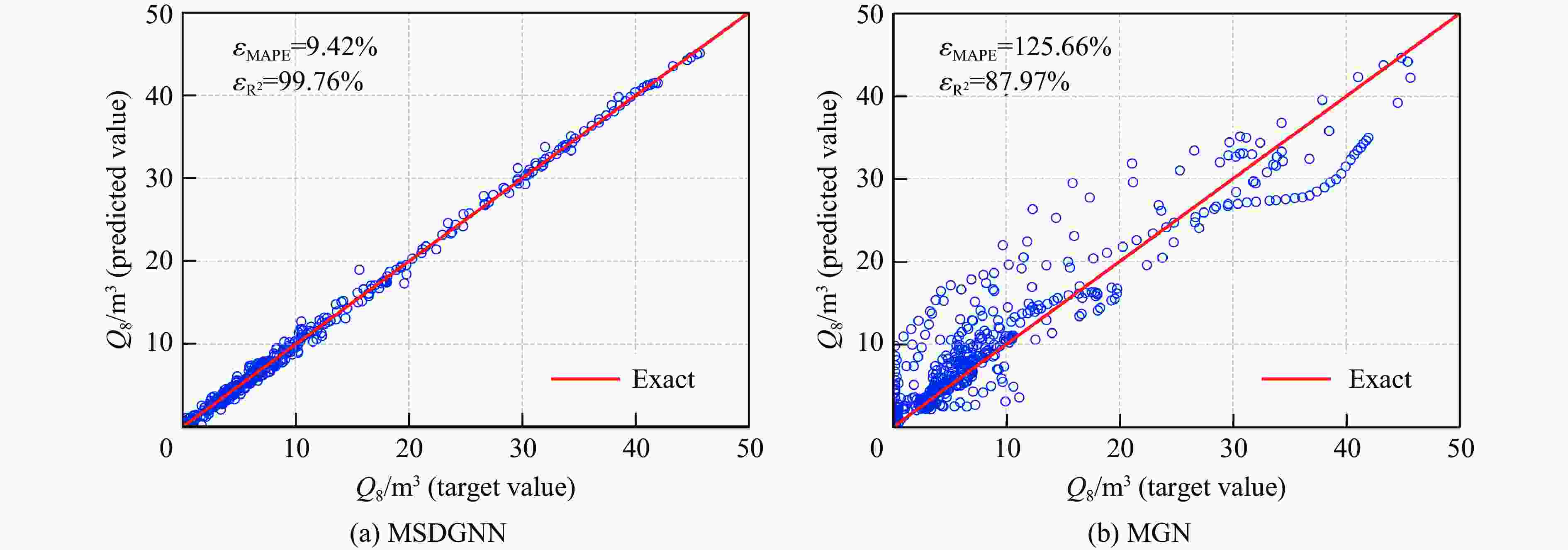
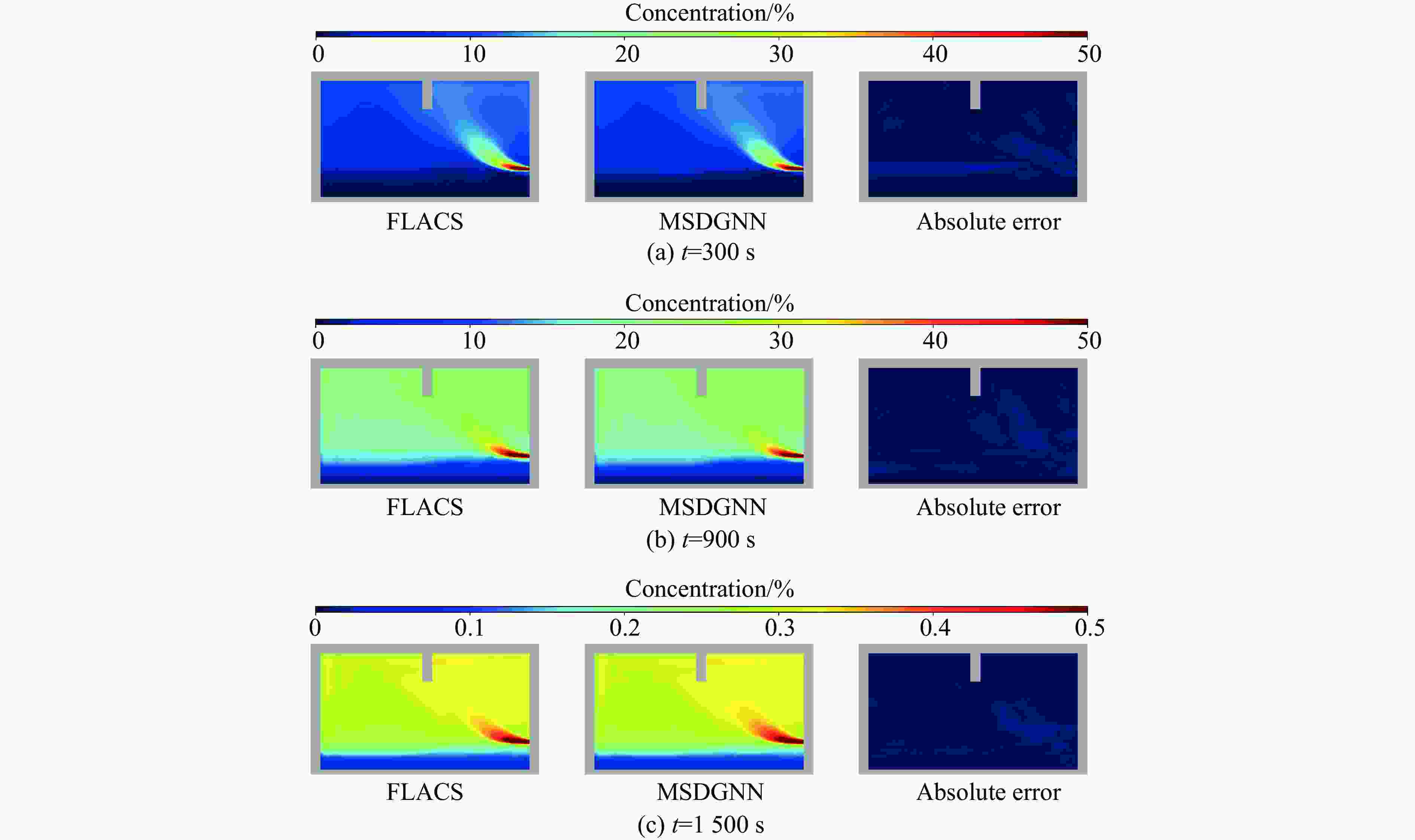
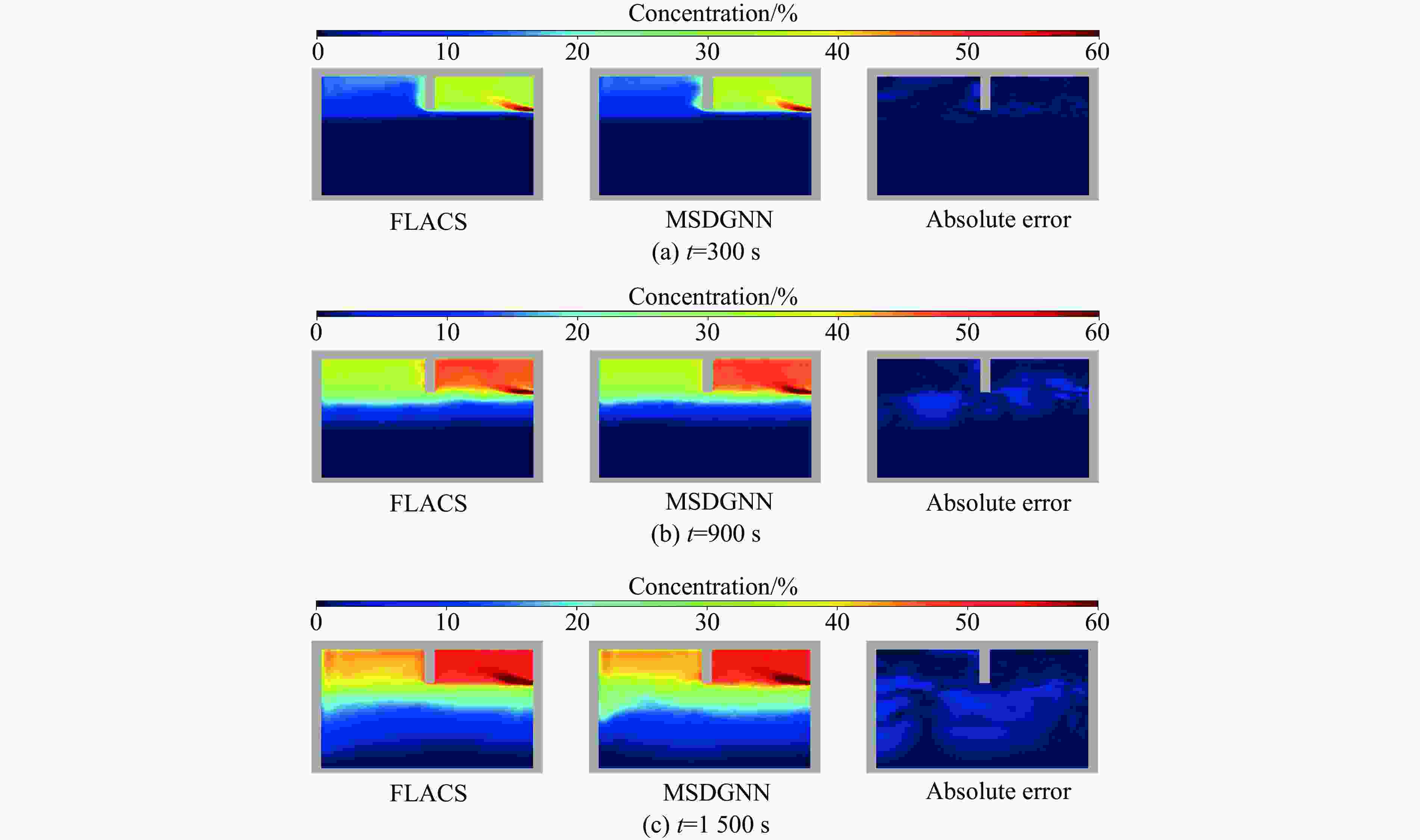
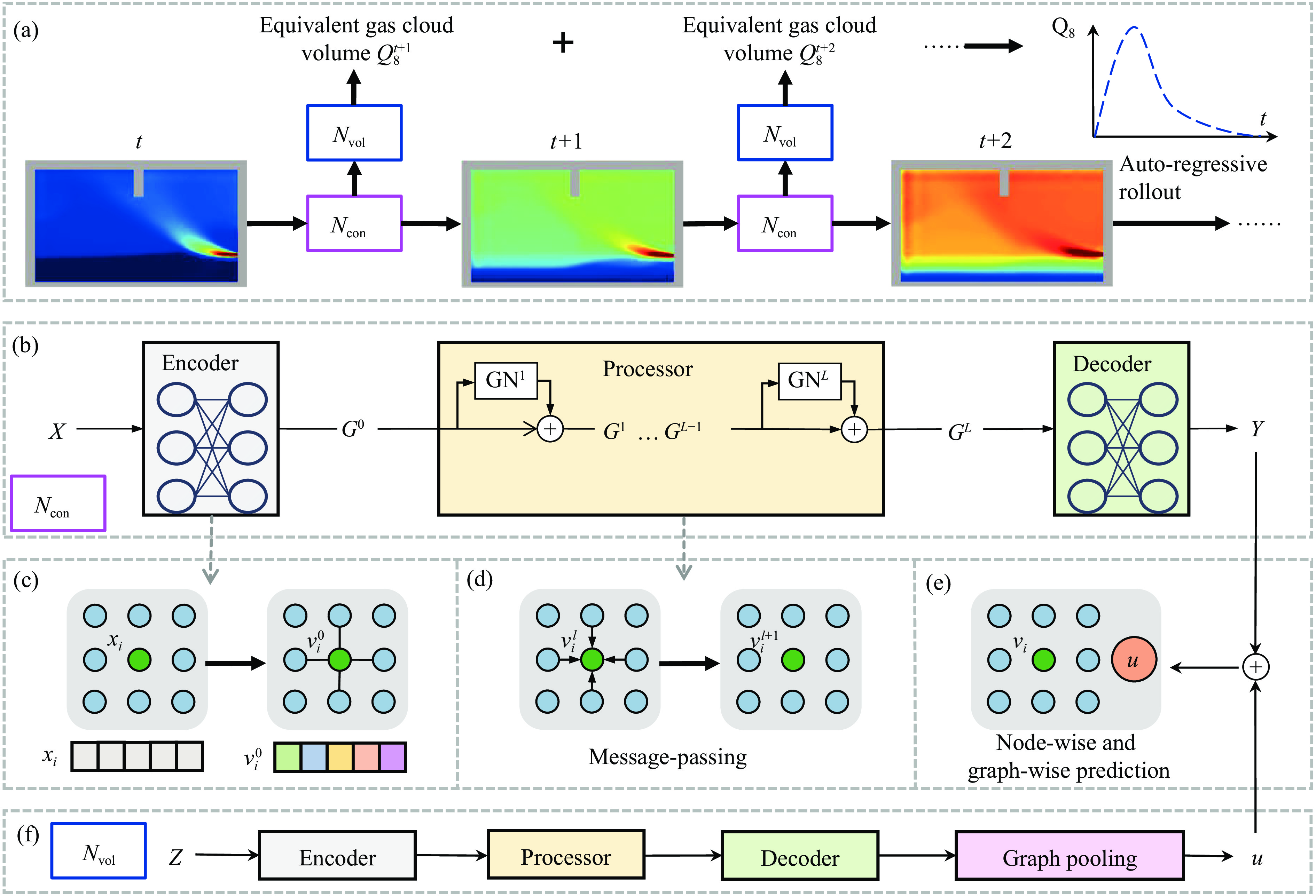
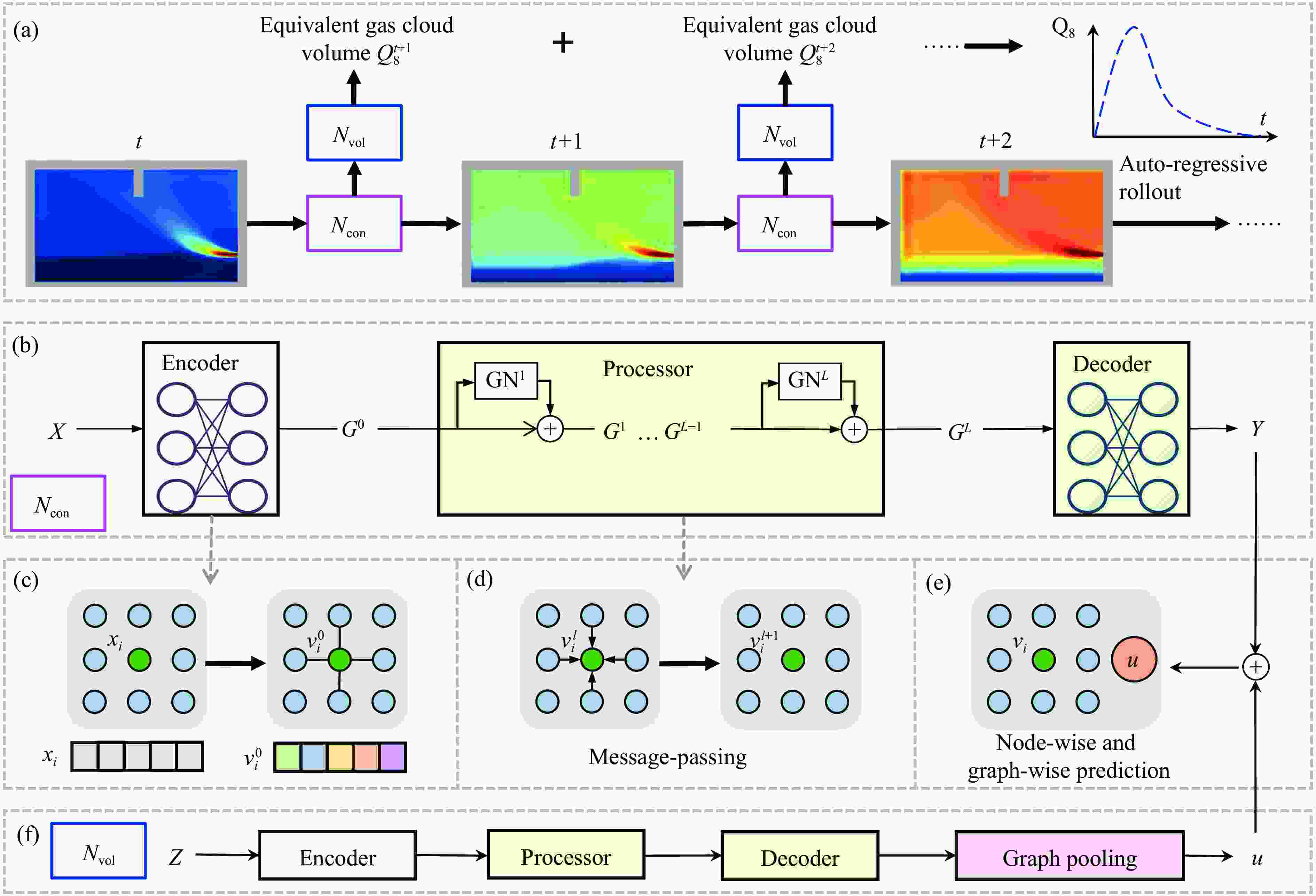
摘要: 燃气泄漏爆炸事故严重威胁公共安全,而准确预测可燃气体泄漏爆炸效应的先决条件是确定气体泄漏后的浓度分布。为构建可燃气体泄漏扩散的实时全场时空预测模型,实现等效气云体积的高效预测,提出一种基于双神经网络架构与多阶段训练策略的图神经网络模型(multi-stage dual graph neural network, MSDGNN)。该模型包含2个协同工作的子网络:(1)浓度网络(Ncon),用于建立连续时间步浓度场之间的映射关系;(2)体积网络(Nvol),用于生成每个时间步的等效气体云体积,为爆炸风险评估提供量化指标。为进一步提升模型性能,开发了分阶段渐进式训练策略对双网络进行联合优化。验证结果表明:相较于传统单一网络架构(如mesh-based graph network,MGN),双网络架构通过解耦浓度场预测与等效气云体积预测任务,有效规避了单目标损失函数中权重因子对训练过程的干扰。多阶段训练策略通过分步参数优化,可解决传统方法对训练数据拟合不足的问题,使浓度场与等效气云体积的平均绝对百分误差
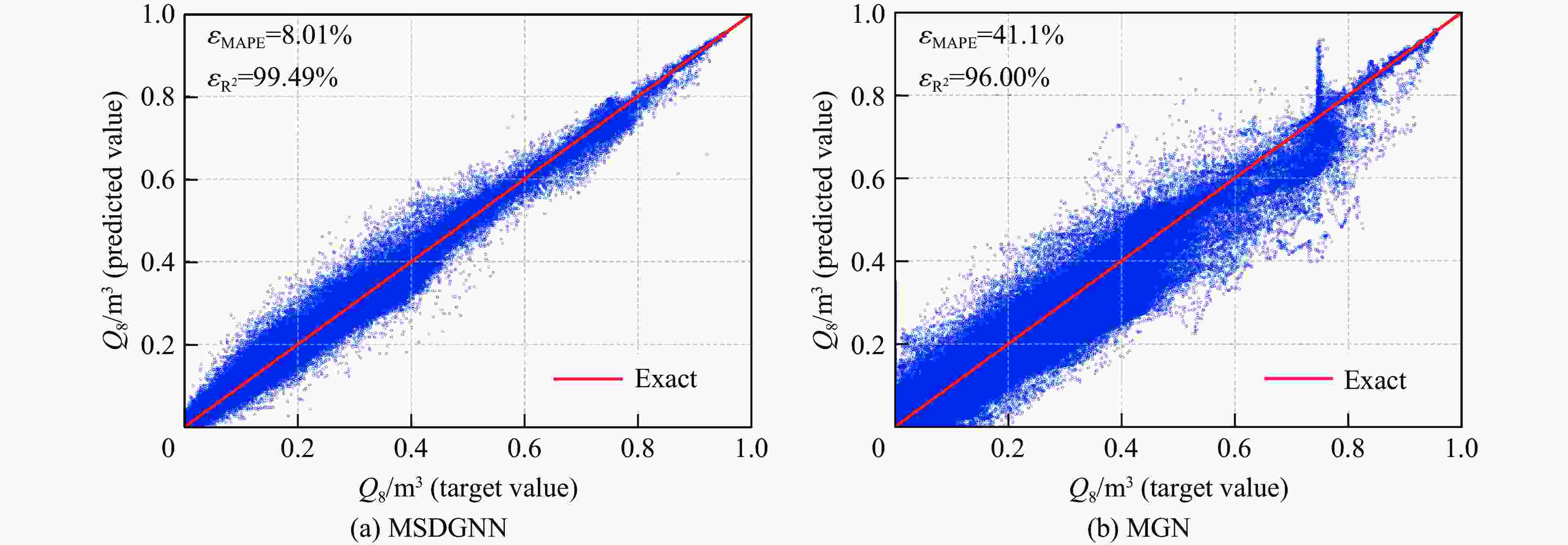
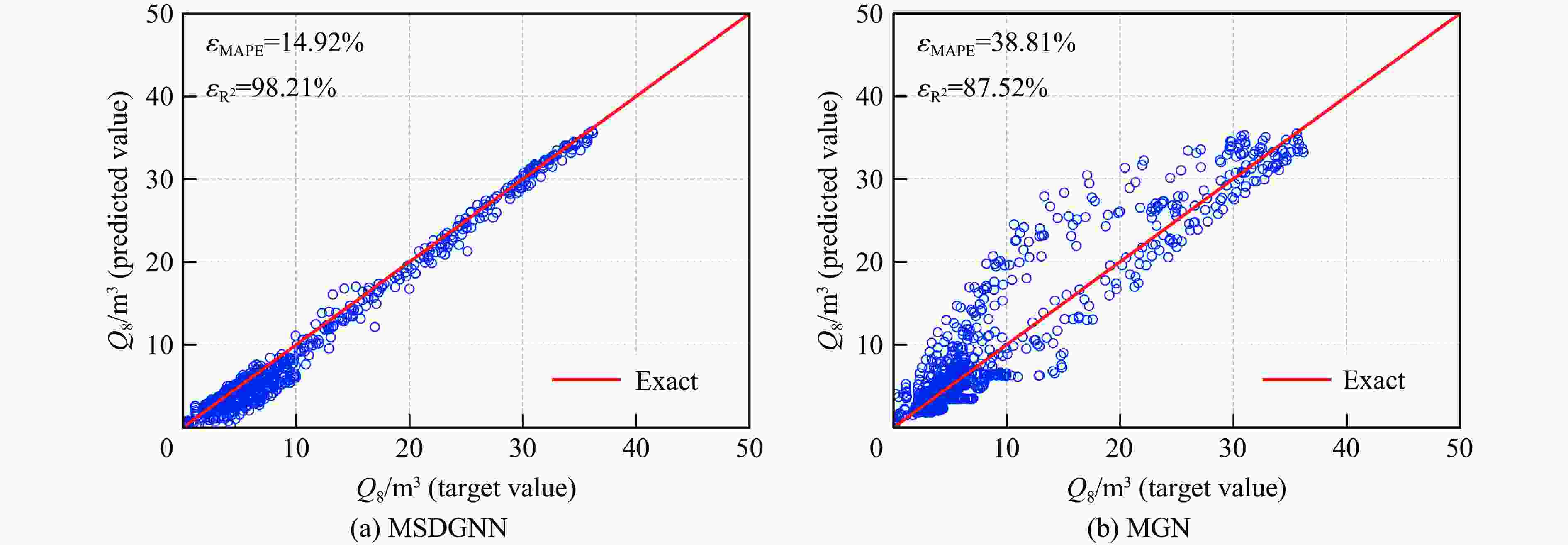
$ {{ \varepsilon }}_{\rm{MAPE}} $ 分别从49.47%和108.93%大幅降低至7.55%和9.07%;同时,模型泛化误差从41.18%(浓度场)和38.81%(等效气云体积)分别降至8.01%和14.92%。此外,在泄漏速率、泄漏高度及持续时间等关键参数超出训练数据范围时,MSDGNN仍表现出良好的预测鲁棒性。与数值模拟方法相比,本模型在保持预测精度的同时,计算效率提升了3个数量级,可为可燃气体安全监测提供有效的实时分析工具。Abstract: Gas leakage and explosion accidents pose a serious threat to public safety. A critical prerequisite for accurately predicting the explosive effects of combustible gas leakage lies in determining the concentration distribution following the leakage. To develop a real-time, full-field spatiotemporal prediction model for combustible gas leakage and diffusion, and to achieve efficient prediction of the equivalent gas cloud volume, a novel graph neural network model based on a dual-neural-network architecture and a multi-stage training strategy, named multi-stage dual graph neural network (MSDGNN), was proposed. The MSDGNN model consists of two synergistic sub-networks: (1) a concentration network (Ncon), which establishes the mapping relationship between the concentration fields of two consecutive timesteps, and (2) a volume network (Nvol), which generates the equivalent gas cloud volume at each timestep to provide a quantitative metric for explosion risk assessment. To further enhance model performance, a multi-stage progressive training strategy was developed to jointly optimize the dual networks. Experimental results demonstrate that compared with mesh-based graph network (MGN), the dual-network architecture effectively decouples the tasks of concentration field prediction and equivalent gas cloud volume prediction. This approach significantly mitigates the interference of weight factors in single-objective loss functions during the training process. The multi-stage training strategy, through stepwise parameter optimization, addresses the issue of insufficient data fitting encountered in traditional methods, significantly reducing the mean absolute percentage error$ {{ \varepsilon }}_{\rm{MAPE}} $ for concentration fields and equivalent gas cloud volumes from 49.47% and 108.93% to 7.55% and 9.07%, respectively. Furthermore, the generalization error of MSDGNN for concentration fields and equivalent gas cloud volumes is reduced from 41.18% and 38.81% to 8.01% and 14.92%, respectively. In addition, MSDGNN exhibits robust prediction performance even when key parameters such as leakage rate, leakage height, and leakage duration exceed the range of training data. Compared with numerical simulation methods, the proposed model achieves a three-order-of-magnitude improvement in computational efficiency while maintaining prediction accuracy, providing an effective real-time analytical tool for combustible gas safety monitoring. -
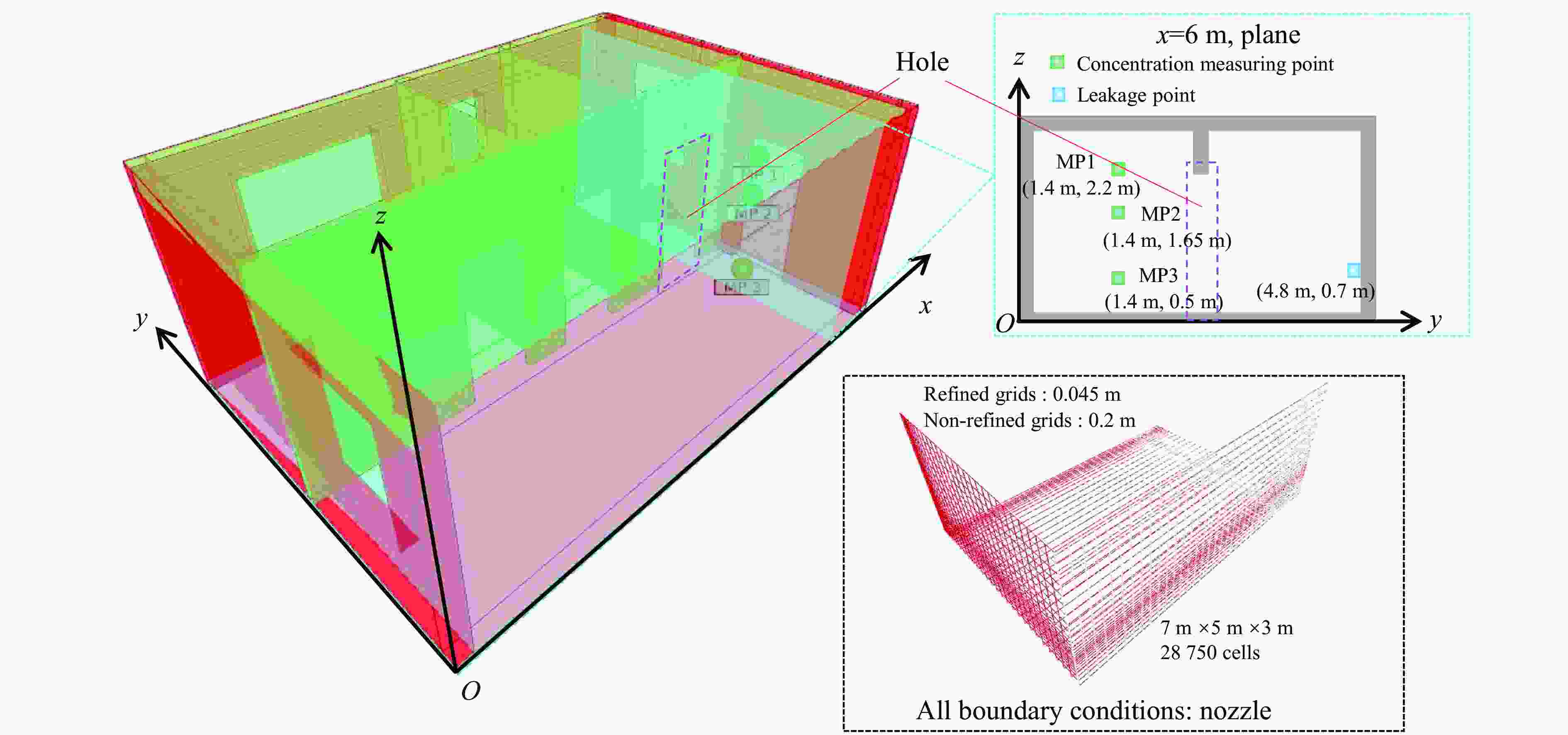
表 1 可燃气体泄漏扩散数据集
Table 1. Combustible gas leakage diffusion dataset
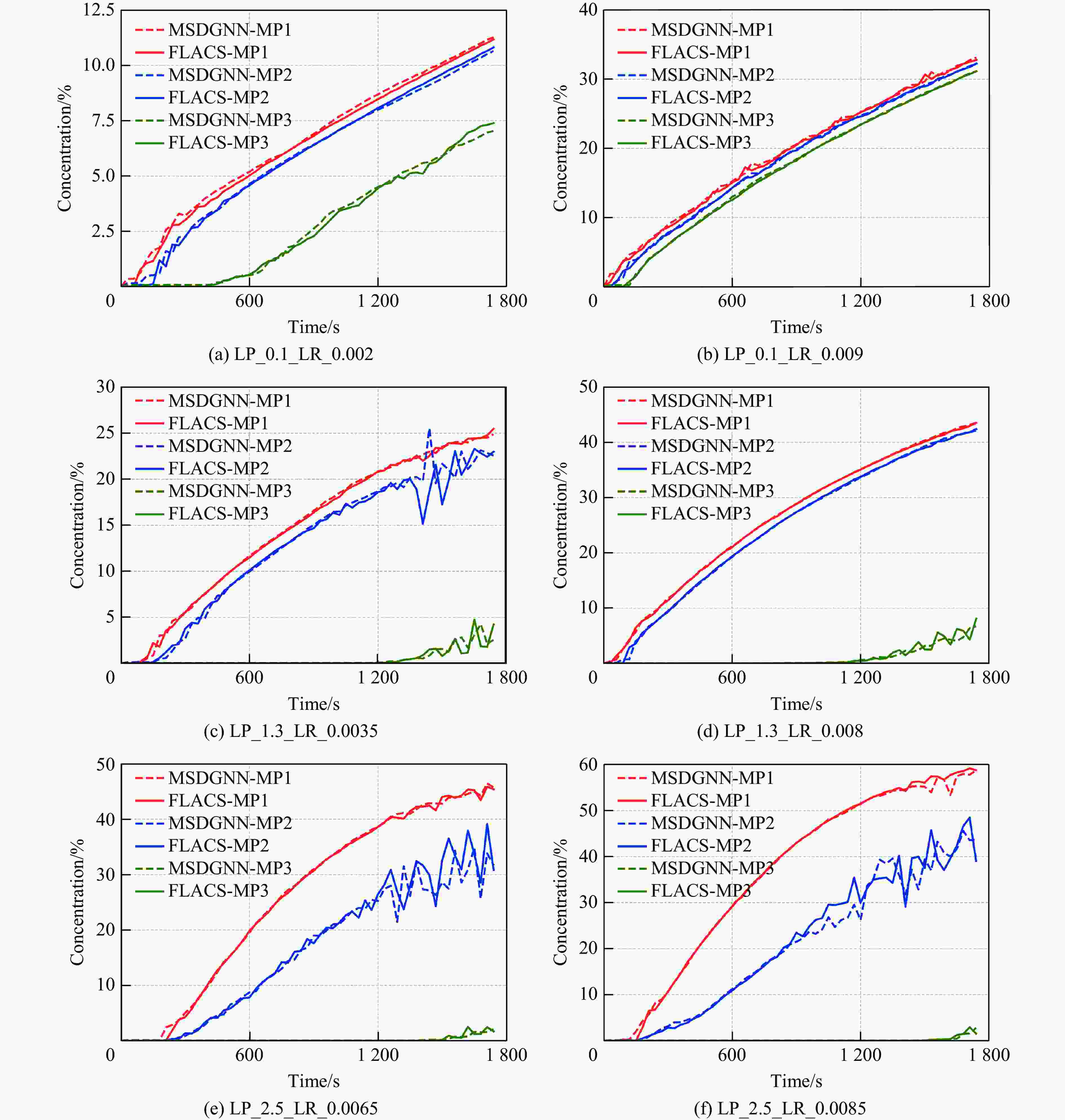
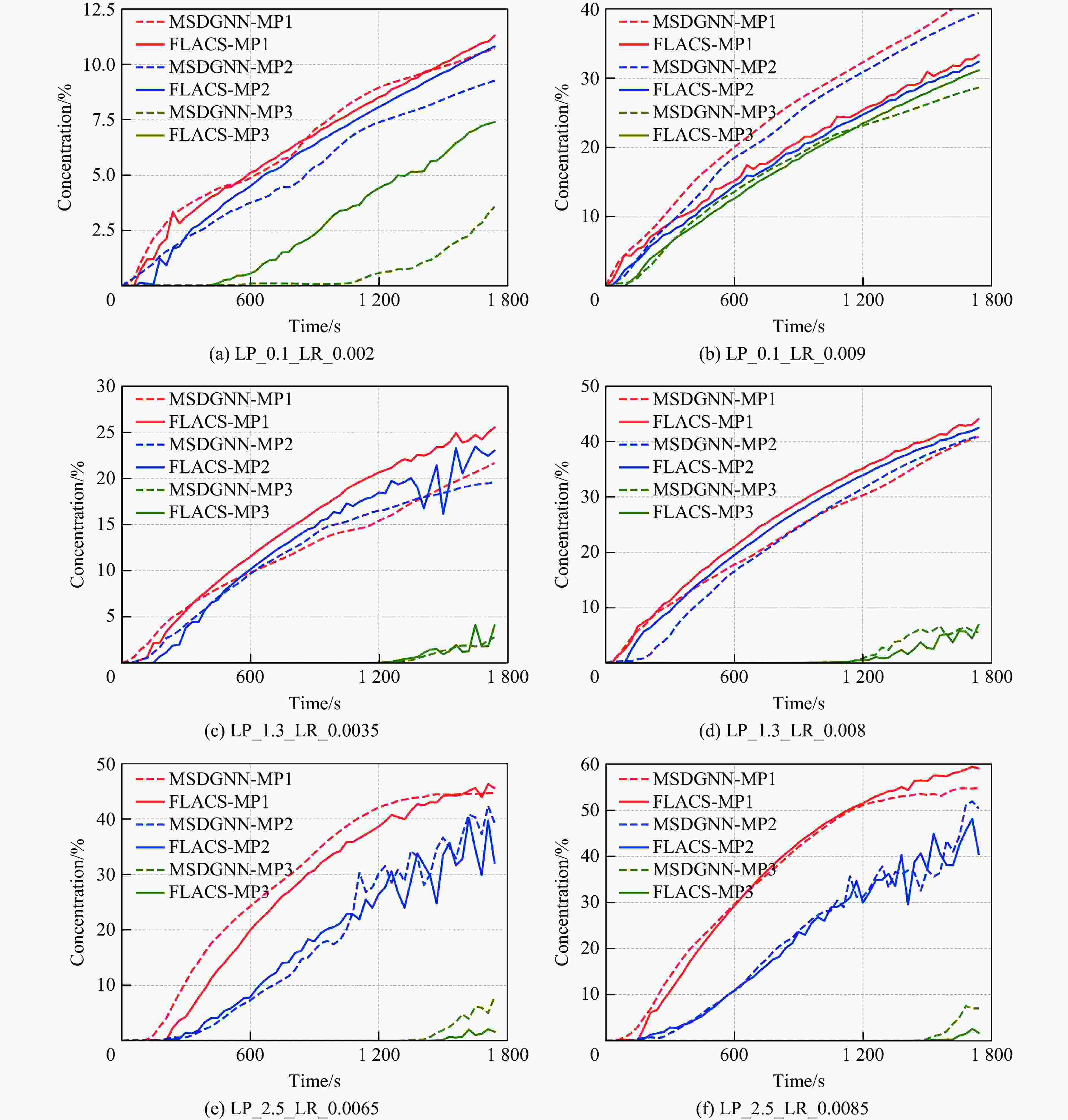
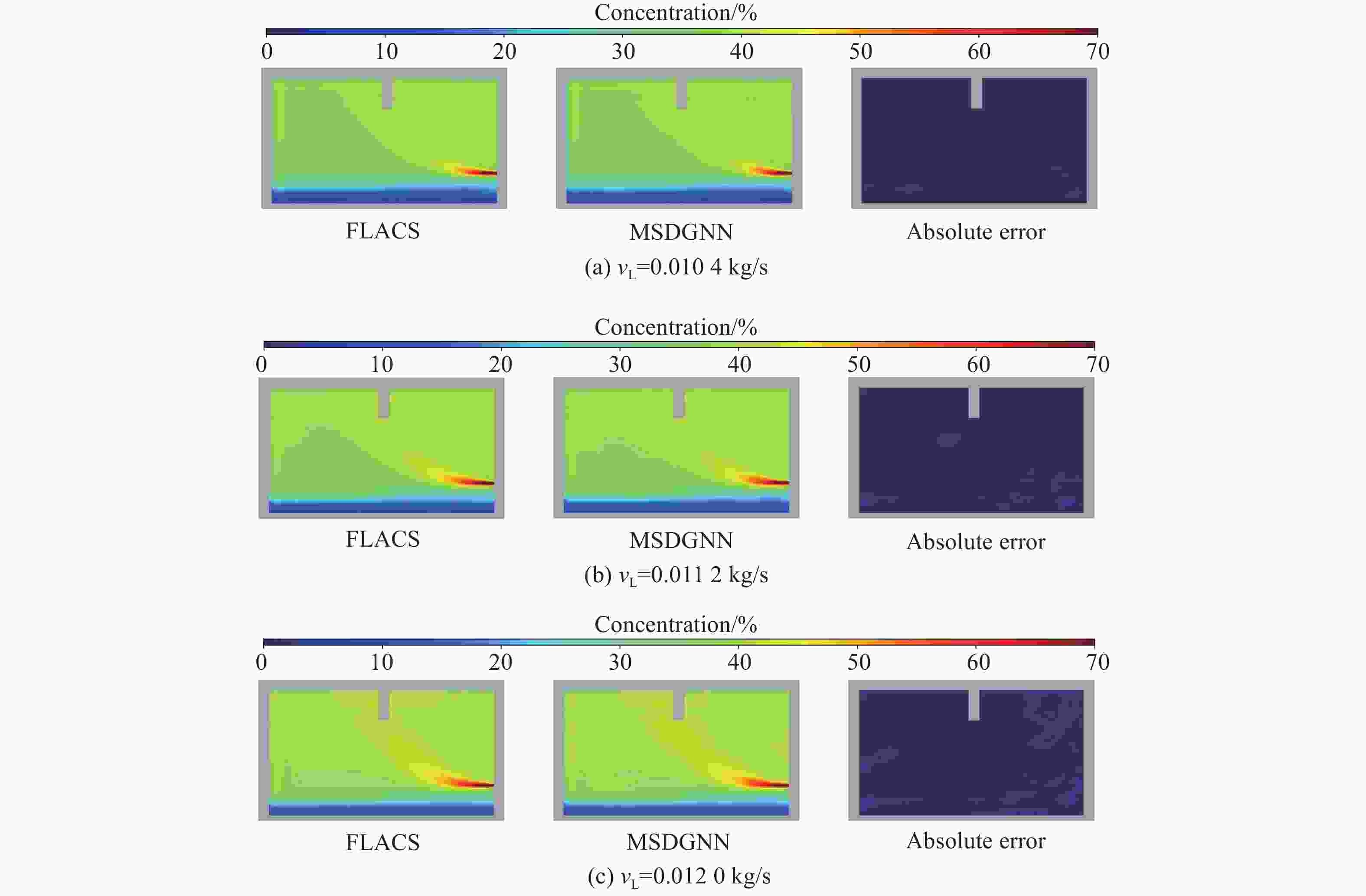
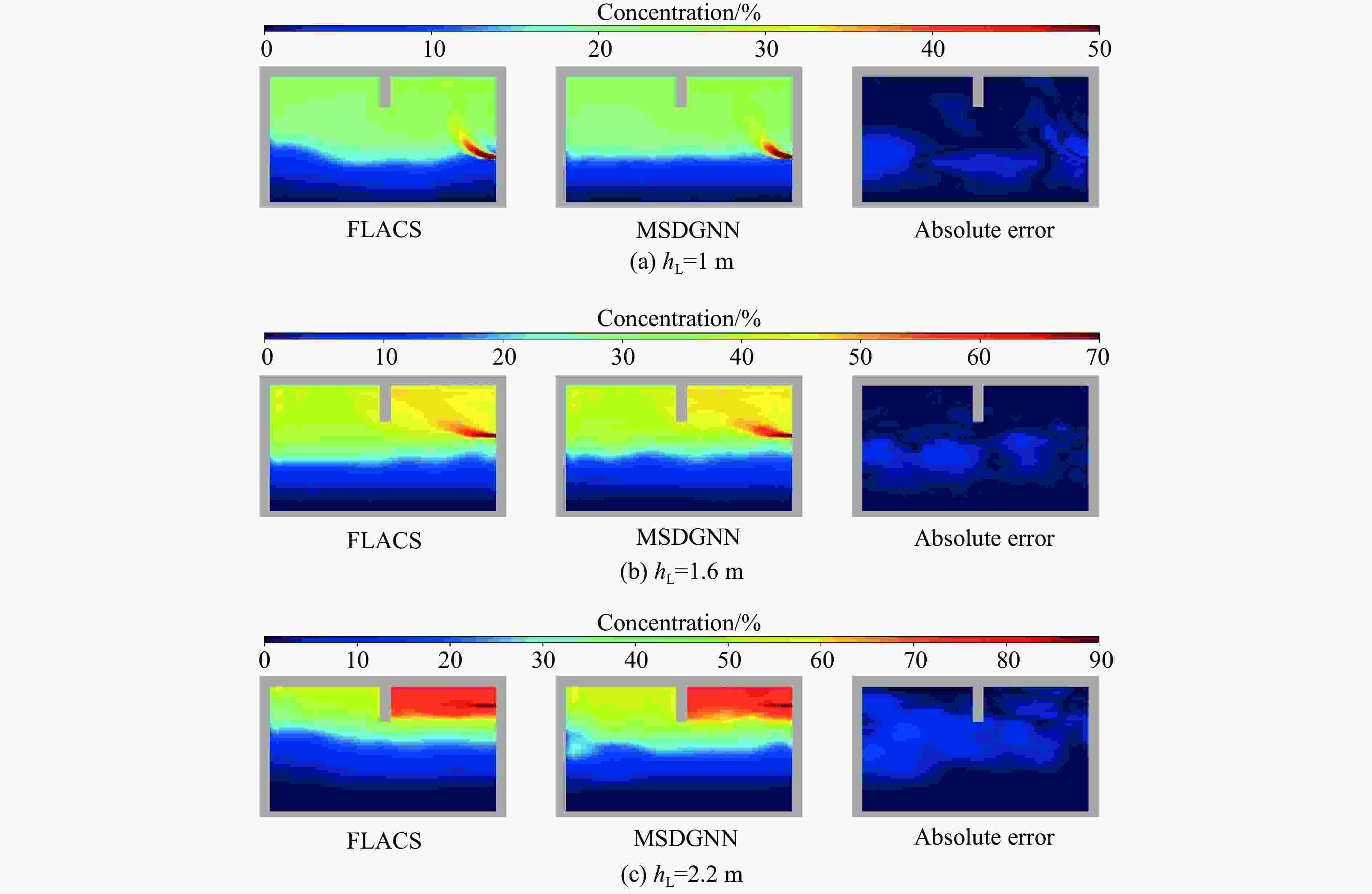
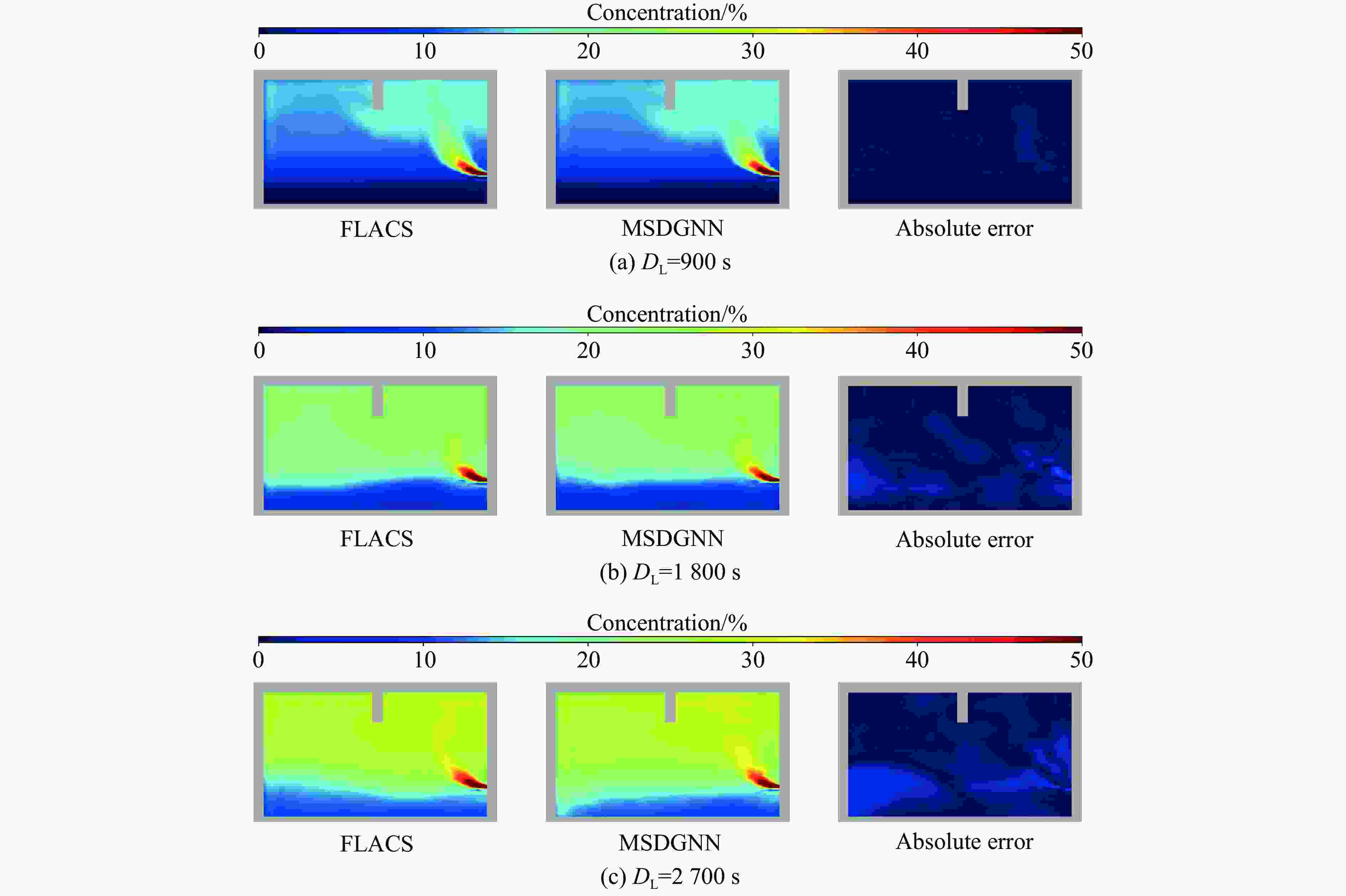
参数 vL/(kg·s−1) hL/m DL/s 工况数量 训练集 0.000 5~0.010 0 0.1, 0.7, 1.3, 1.9, 2.5 1800 (Δt = 30 s)100 泛化集 0.010 0~0.012 0 1.0, 1.6, 2.2 1800 、2700 (Δt = 30 s)15 表 2 MSDGNN模型预测时间
Table 2. MSDGNN model prediction efficiency evaluation
工况 计算时间/s MSDGNN MGN FLACS 1 2 0.5 19975 2 2 0.5 12007 3 2 0.5 9381 4 2 0.5 7846 5 2 0.5 15126 -
[1] NECCI A, COZZANI V, SPADONI G, et al. Assessment of domino effect: state of the art and research needs [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2015, 143: 3–18. DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2015.05.017. [2] LI X F, CHEN G H, AMYOTTE P, et al. Vulnerability assessment of storage tanks exposed to simultaneous fire and explosion hazards [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2023, 230: 108960. DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2022.108960. [3] 李欣, 乐有邦, 张刚, 等. 基于事故调查技术的天然气泄漏爆炸分析——以十堰“6·13”重大燃气爆炸事故为例 [J]. 爆破, 2023, 40(3): 39–45. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.006.LI X, LE Y B, ZHANG G, et al. Analysis of natural gas explosion based on accident investigation technique——taking Shiyan "6·13" major gas explosion accident as example [J]. Blasting, 2023, 40(3): 39–45. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1001-487X.2023.03.006. [4] 作业后未有效紧闭 燃气泄漏遇火花爆炸——辽宁省沈阳市和平区太原南街222号“10·21”较大管道燃气泄漏爆炸事故分析 [J]. 吉林劳动保护, 2022(1): 42-48. [5] 徐涛. 燃气爆炸建筑坍塌事故救援对策分析——以江苏常州“5·24”瓶装液化气泄漏爆炸救援为例 [J]. 中国应急救援, 2023(4): 70–74. DOI: 10.19384/j.cnki.cn11-5524/p.2023.04.013.XU T. Analysis of rescue strategy for building collapse accidents caused by gas explosion——a case study of “5·24” bottled liquefied gas leakage and explosion in Changzhou, Jiangsu [J]. China Emergency Rescue, 2023(4): 70–74. DOI: 10.19384/j.cnki.cn11-5524/p.2023.04.013. [6] 刘可心, 刘炜, 孙亚松. 多因素耦合作用对甲烷爆炸特性的影响 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(3): 032101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0352.LIU K X, LIU W, SUN Y S. Influence of multi-factor coupling on methane explosion characteristics [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(3): 032101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2022-0352. [7] 许晓元, 孙金华, 刘晅亚. 具有体积分数梯度的连通装置甲烷-空气爆炸特性数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2021, 41(4): 045401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0086.XU X Y, SUN J H, LIU X Y. Numerical simulation of methane-air explosion in a connected device with volume fraction gradient [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2021, 41(4): 045401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0086. [8] 任少云. 开敞空间液化天然气泄漏低温扩散及爆炸传播规律 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(4): 891–897. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0323.REN S Y. The leakage, low temperature diffusion and explosion of liquefied natural gas in open space [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(4): 891–897. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2016-0323. [9] 刘洋, 李展, 张亚栋, 等. 基于FLACS的某城市燃气储配站气云爆炸安全评估 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2021, 35(1): 015201. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200595.LIU Y, LI Z, ZHANG Y D, et al. Safety evaluation of gas cloud explosions in an urban distribution stations based on FLACS [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2021, 35(1): 015201. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.20200595. [10] 王秋红, 孙艺林, 李鑫, 等. 乙烯储罐气体泄漏诱发蒸气云爆炸的数值模拟 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(12): 125401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0202.WANG Q H, SUN Y L, LI X, et al. Numerical simulation on gas dispersions and vapor cloud explosions induced by gas released from an ethylene storage tank [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(12): 125401. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2020-0202. [11] ABG SHAMSUDDIN D S N, MOHD FEKERI A F, MUCHTAR A, et al. Computational fluid dynamics modelling approaches of gas explosion in the chemical process industry: a review [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 170: 112–138. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.11.090. [12] PRASAD K, PITTS W M, YANG J C. A numerical study of the release and dispersion of a buoyant gas in partially confined spaces [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(8): 5200–5210. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.01.118. [13] MEI Y, SHUAI J. Research on natural gas leakage and diffusion characteristics in enclosed building layout [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 161: 247–262. DOI: 10.1016/j.psep.2022.03.040. [14] SU Y, LI J F, YU B, et al. Numerical investigation on the leakage and diffusion characteristics of hydrogen-blended natural gas in a domestic kitchen [J]. Renewable Energy, 2022, 189: 899–916. DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.038. [15] KANG Y, MA S Y, SONG B X, et al. Simulation of hydrogen leakage diffusion behavior in confined space [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 53: 75–85. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.12.026. [16] WANG B, CHEN B Z, ZHAO J S. The real-time estimation of hazardous gas dispersion by the integration of gas detectors, neural network and gas dispersion models [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 300: 433–442. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.07.028. [17] QIU S H, CHEN B, WANG R X, et al. Atmospheric dispersion prediction and source estimation of hazardous gas using artificial neural network, particle swarm optimization and expectation maximization [J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2018, 178: 158–163. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.01.056. [18] TANG X, WU D L, WANG S M, et al. Research on real-time prediction of hydrogen sulfide leakage diffusion concentration of new energy based on machine learning [J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(9): 7237. DOI: 10.3390/su15097237. [19] ZHANG X Q, SHI J H, LI J J, et al. Hydrogen jet and diffusion modeling by physics-informed graph neural network [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2025, 207: 114898. DOI: 10.1016/j.rser.2024.114898. [20] HANSEN O R, GAVELLI F, DAVIS S G, et al. Equivalent cloud methods used for explosion risk and consequence studies [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2013, 26(3): 511–527. DOI: 10.1016/j.jlp.2012.07.006. [21] TAM V H Y, TAN F, SAVVIDES C. A critical review of the equivalent stoichiometric cloud model Q9 in gas explosion modelling [J]. Eng, 2021, 2(2): 156–180. DOI: 10.3390/eng2020011. [22] 齐心歌, 王海清, 田英帅, 等. 基于等价气云爆炸风险评估的气体防护区域定量划分 [J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(3): 1587–1594. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2018-0153.QI X G, WANG H Q, TIAN Y S, et al. Quantitative division of gas protection area based on risk assessment of equivalent gas cloud explosion [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(3): 1587–1594. DOI: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2018-0153. [23] 师吉浩. 海洋平台燃爆风险分析及抗爆减灾设计研究 [D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2018. DOI: 10.27644/d.cnki.gsydu.2018.001848.SHI J H. Research on explosion risk analysis and mitigation design of offshore platforms [D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2018. DOI: 10.27644/d.cnki.gsydu.2018.001848. [24] 师燕超, 么志远, 袁明德, 等. 综合管廊天然气泄漏爆炸的定量风险评估 [J]. 建筑结构学报, 2023, 44(11): 129–136. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2021.0677.SHI Y C, YAO Z Y, YUAN M D, et al. Quantitative risk assessment of natural gas leakage and explosion in utility tunnel [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2023, 44(11): 129–136. DOI: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2021.0677. [25] BATTAGLIA P W, HAMRICK J B, BAPST V, et al. Relational inductive biases, deep learning, and graph networks [EB/OL]. arXiv: 1806.01261. (2018-10-17)[2024-01-17]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1806.01261. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1806.01261. [26] SCARSELLI F, GORI M, TSOI A C, et al. The graph neural network model [J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(1): 61–80. DOI: 10.1109/TNN.2008.2005605. [27] GILMER J, SCHOENHOLZ S S, RILEY P F, et al. Neural message passing for quantum chemistry [C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney: PMLR, 2017: 1263-1272. [28] PFAFF T, FORTUNATO M, SANCHEZ-GONZALEZ A, et al. Learning mesh-based simulation with graph networks [C]//9th International Conference on Learning Representations. ICLR, 2021. [29] LI Q L, WANG Y, CHEN W S, et al. Machine learning prediction of BLEVE loading with graph neural networks [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2024, 241: 109639. DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2023.109639. [30] SHI J H, LI J J, TAM W C, et al. Physics_GNN: towards physics-informed graph neural network for the real-time simulation of obstructed gas explosion [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2025, 256: 110777. DOI: 10.1016/j.ress.2024.110777. [31] SANCHEZ-GONZALEZ A, GODWIN J, PFAFF T, et al. Learning to simulate complex physics with graph networks [C]//Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2020: 8459–8468. [32] LI B B, FENG B, CHEN L. A graph network-based learnable simulator for spatial-temporal prediction of rigid projectile penetration [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2025, 195: 105123. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2024.105123. [33] GEXCON. FLACS-CFD v25.2 User’s Manual [EB/OL]. 2025. https://www.gexcon.com/support/flacs-documents/. [34] MA J Q, ZHAO Z, YI X Y, et al. Modeling task relationships in multi-task learning with multi-gate mixture-of-experts [C]//Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. London: ACM, 2018: 1930–1939. DOI: 10.1145/3219819.3220007. [35] LI Q L, LI L, SHAO Y D, et al. A multi-task machine learning approach for data efficient prediction of blast loading [J]. Engineering Structures, 2025, 326: 119577. DOI: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.119577. [36] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition [C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas: IEEE, 2016: 770–778. DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. [37] MICHAUD E J, LIU Z M, TEGMARK M. Precision machine learning [J]. Entropy, 2023, 25(1): 175. DOI: 10.3390/e25010175. [38] WANG Y J, LAI C Y. Multi-stage neural networks: function approximator of machine precision [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2024, 504: 112865. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcp.2024.112865. [39] YUE C J, CHEN L, LI Z, et al. Experimental study on gas explosions of methane-air mixtures in a full-scale residence building [J]. Fuel, 2023, 353: 129166. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.129166. [40] KANG Y, MA S Y, SONG B X, et al. Study on the hydrogen leakage diffusion behavior by obstacles in confined spaces [J]. Fuel, 2024, 358: 130110. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130110. [41] 国家安全生产监督管理总局. 化工企业定量风险评价导则: AQ/T 3046-2013 [S]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 2013. [42] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 家用燃气灶具: GB 16410-2020 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. [43] 贾烁宇. 室内燃气泄漏扩散规律及预警机制研究 [D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2022.JIA S Y. Study on the law and early warning mechanism of indoor gas leakage and diffusion [D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2022. [44] 中华人民共和国建设部和国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 城镇燃气设计规范: GB 50028-2006 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2020. [45] 中华人民共和国化学工业部. 家用煤气软管: HG 2486-1993 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1993. [46] YUE C J, CHEN L, LI Z, et al. Research on the hazards of gas leakage and explosion in a full-scale residential building [J]. Defence Technology, 2025, 43: 168–181. DOI: 10.1016/j.dt.2024.06.014. [47] HUANG L, QIN J, ZHOU Y, et al. Normalization techniques in training DNNs: methodology, analysis and application [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(8): 10173–10196. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2023.3250241. [48] BA J L, KIROS J R, HINTON G E. Layer normalization [EB/OL]. arXiv: 1607.06450. (2016-07-21)[2024-10-11]. http://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1607.06450. [49] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization [C]//3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego: ICLR, 2015. [50] LINO M, CANTWELL C, BHARATH A A, et al. Simulating continuum mechanics with multi-scale graph neural networks [EB/OL]. [2021-06-09]. http://arxiv.org/abs/2106.04900. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2106.04900. [51] HAN X, GAO H, PFAFF T, et al. Predicting physics in mesh-reduced space with temporal attention [C]//The Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations. ICLR, 2022. -








 下载:
下载: