Determination of critical damage PPV near the blast hole of rock-mass
-
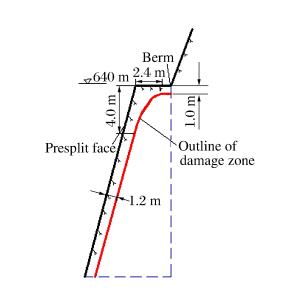
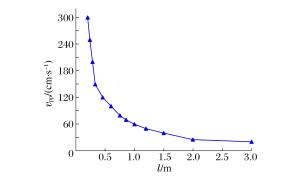
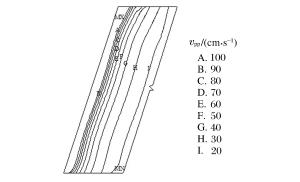
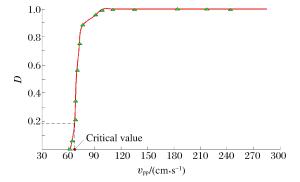
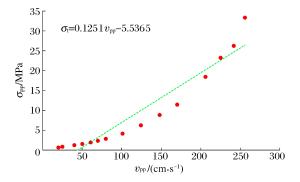
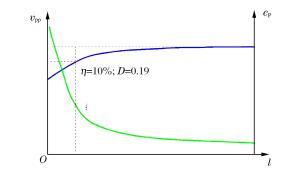
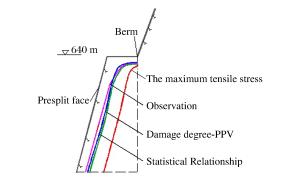
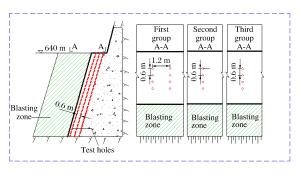
摘要: 质点峰值振动速度(PPV)是爆破开挖扰动的重要指标,研究确定岩体临界损伤PPV对爆破损伤控制具有重要意义。以溪洛渡水电站640 m高程马道下边坡岩体的爆破开挖为工程背景,依据岩体跨孔声波测试结果,采用基于LS-DYNA的二次开发技术对保留岩体的损伤演化过程进行了数值模拟,结合数值模拟结果研究了爆破近区PPV的分布特征及其与损伤程度的对应关系,结果表明PPV存在门槛值,当PPV大于该值时,岩体的损伤变量从零开始迅速增加至0.8左右,之后随着PPV的增大,损伤增长速度明显减慢,直至岩体完全损伤;分别基于岩体的损伤度、最大拉应力的PPV判据以及近区拉应力峰值与PPV的统计关系等3种方法确定岩体临界损伤PPV,从定量衡量损伤区范围看,常用的基于最大拉应力的PPV判据确定的临界损伤PPV偏小,而其余2种方法确定的临界损伤PPV相对精确。Abstract: Based on the blasting excavation for the berm at the elevation of 640 m on the high slope of Xiluodu hydropower station, the blasting induced damage zone were obtained through sonic wave test and numerical simulation. The relationship between PPV and damage scalarD was studied. If PPV is bigger than one certain value, the damage scalar D increased quickly to about 0.8, then the increased speed became slow. A method of determining critical damage PPV was put forward based on the damage degree and it was compared with the methods of statistics relationship between the maximum tensile stress and PPV and the PPV criterion based on the maximum tensile stress. Results demonstrate that the accuracy of methods based on the damage degree and statistic relationship between the maximum tensile stress and PPV is better than the result according to the maximum tensile stress.
-
Key words:
- mechanics of explosion /
- blasting damage /
- critical damage PPV /
- rock-mass /
- damage scalar
-
vpp/(cm·s-1) 岩体损伤效果 (0, 25) 完整岩石不会致裂 (25, 63.5) 发生轻微的拉伸层裂 (63.5, 254) 严重的拉伸裂缝及一些径向裂缝 (254, ∞) 岩体完全破碎 岩体损伤表现 损伤程度 vpp/(cm·s-1) 斑岩 页岩 石英质中长岩 台阶面松动岩块的偶尔掉落 没有损伤 12.7 5.1 63.5 台阶面松动岩块的部分掉落 可能有损伤但可接受 38.1 25.4 127.0 部分台阶面松动、崩落 轻微的爆破损伤 63.5 38.1 190.5 台阶面严重破碎 爆破损伤 >63.5 >38.1 >190.5 表 3 岩体的材料参数及损伤模型相关参数
Table 3. Rock mass parameters and some special parameters about damage models
ρ/(kg·m-3) Ek/GPa ν σk/MPa k m KIC/(MN·m-3/2) λ/(kg·J-1) 2 530 25 0.228 2 2.33×1024 6 0.92 0.000 1 -
[1] 朱传云, 卢文波.三峡工程临时船闸与升船机中隔墩爆破安全判据的研究[J].爆炸与冲击, 1998, 18(4): 375-380. http://www.bzycj.cn/article/id/10431Zhu Chuan-yun, Lu Wen-bo. Blasting safety criterion for the rock wall between temporary ship lock and ship lift in the Three Gorges Project[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1998, 18(4): 375-380. http://www.bzycj.cn/article/id/10431 [2] 李俊如, 夏祥, 李海波, 等.核电站基岩爆破开挖损伤区研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(S1): 4674-4678. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_5917364.aspxLi Jun-ru, Xia Xiang, Li Hai-bo, et al. Study on blast-induced bedrock damage extension for a nuclear power station project[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(S1): 4674-4678. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference_5917364.aspx [3] Taylor L M, Chen E P, Kuszmaul J S. Micro-crack induced damage accumulation in brittle rock under dynamic loading[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1986; 55(3): 301-320. [4] Kuszmaul J S. A new constitutive model for fragmentation of rock under dynamic loading[C]//Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Rock Fragmentation by Blasting. Keystone, Canada, 1987: 412-423. [5] Thorne B J, Hommert P J, Brown B. Experimental and computational investigation of the fundamental mechanisms of cratering[C]//Proceedings of 3nd International Symposium on Rock Fragmentation by Blasting. Brisbane, Australia, 1990. [6] Yang R, Bawden W F, Katsabanis P D. A new constitutive model for blast damage[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1996, 33(3): 245-254. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/014890629500064X [7] Li Haibo, Xia Xiang, Li Jianchun. Rock damage control in bedrock blasting excavation for a nuclear power plant[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science, 2010, 48(2): 210-218. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1365160910002182 [8] 卢文波.三峡工程临时船闸与升船机开挖中的爆破方案优化和爆破振动控制[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 1999, 18(5): 497-502 Lu Wen-bo. Optimization of blasting procedure and vibration control during excavation of temporary ship lock and ship lift in three gorges project[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1999, 18(5): 497-502. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSLX199905004.htm [9] 陈明, 卢文波, 吴亮, 等.小湾水电站岩石高边坡爆破振动速度安全阈值研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(1): 51-55. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200701007Chen Ming, Lu Wen-bo, Wu Liang, et al. Safety threshold of blasting vibration velocity to high rock slope of xiaowan hydropower station[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(1): 51-55. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yslxygcxb200701007 [10] 中华人民共和国行业标准编写组. SL47-94水工建筑物岩石基础开挖工程施工技术规范[S].北京: 水利电力出版社, 1995. [11] Bauer A, Calder P N. Open pit and blast seminar, 63221[R]. Kingston, Ontario, Canada: Mining Engineering Department, Queens University, 1978. [12] Savely J P. Designing a final blast to improve stability[C]//Proceedings of the SME Annual Meeting. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 1986. [13] 胡英国, 卢文波, 金旭浩, 等.岩石高边坡开挖爆破动力损伤的数值模拟[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(11): 2204-2213. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96026X/201211/43896933.htmlHu Ying-guo, Lu Wen-bo, Jin Xu-hao, et al. Numerical simulation for excavation blasting dynamic damage of rock high slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(11): 2204-2213. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96026X/201211/43896933.html [14] Furlong J R, Davis J F, Alme M L. Modeling the dynamic load/unload behavior of ceramics under impact loading: RDA-TR-00.0-0001[R]. Arlington, Virginia, USA: R & D Associates Meeting, 1990. [15] LSTC. LS-DYNA theoretical manual[M]. Livermore, CA, USA: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2010. [16] Livermore, CA, USA: Livermore Software Technology Corporation, 2010. [17] Barton N. The influence of joint properties in modeling jointed rock masses[C]//Proceedings of the 8th ISRM Congress. Tokyo, Japan, 1995. -






 下载:
下载: