Dynamic deformation model of thin-walled ellipsoidal shells under impact loading
-
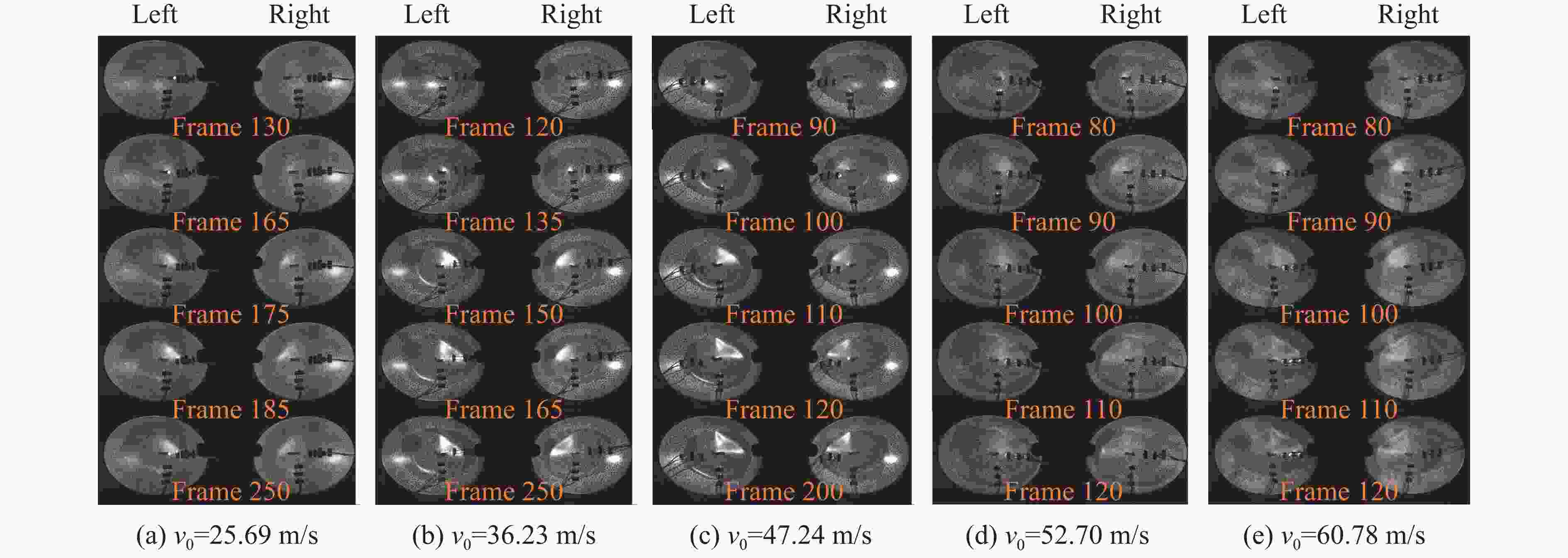
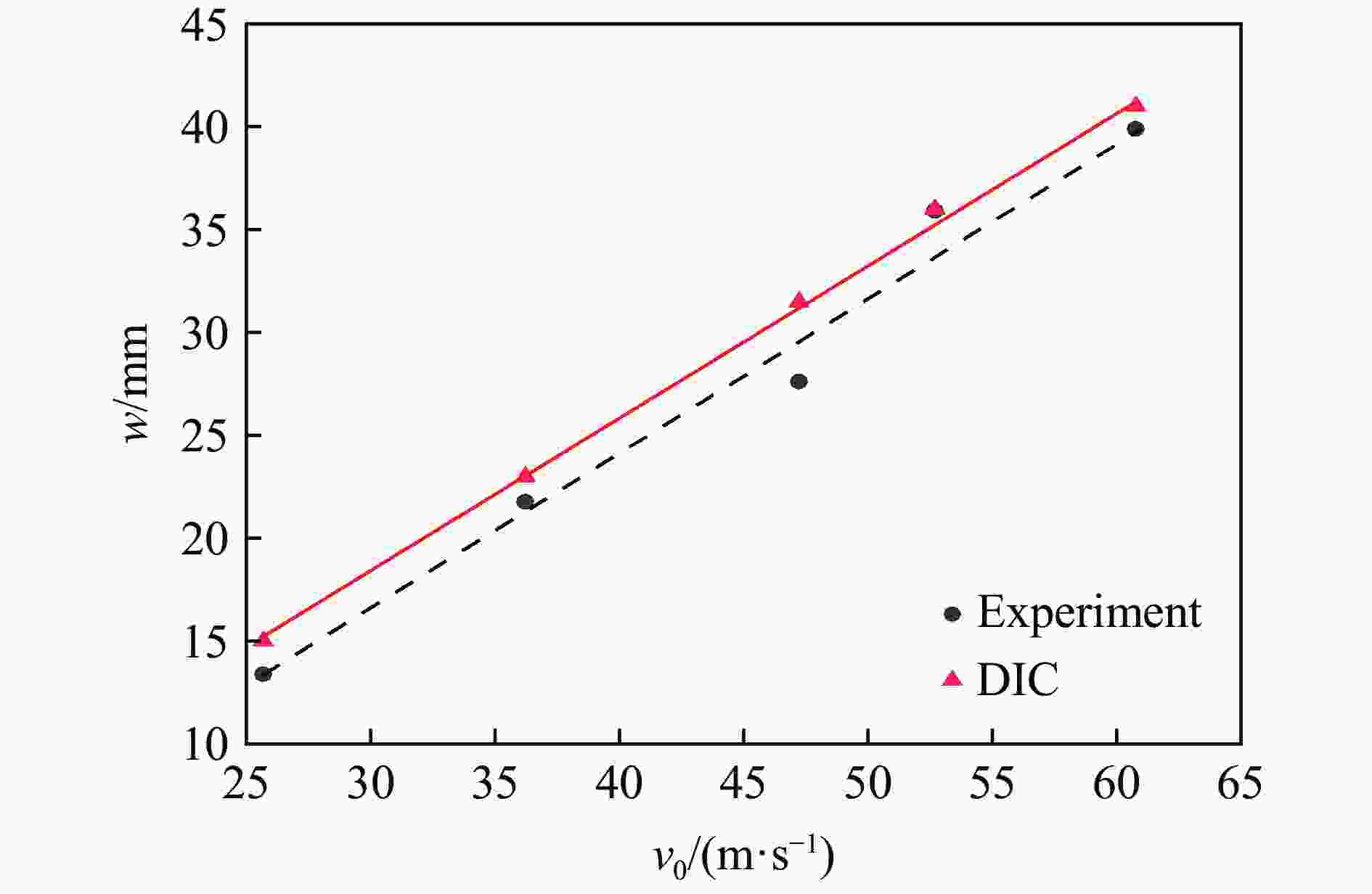
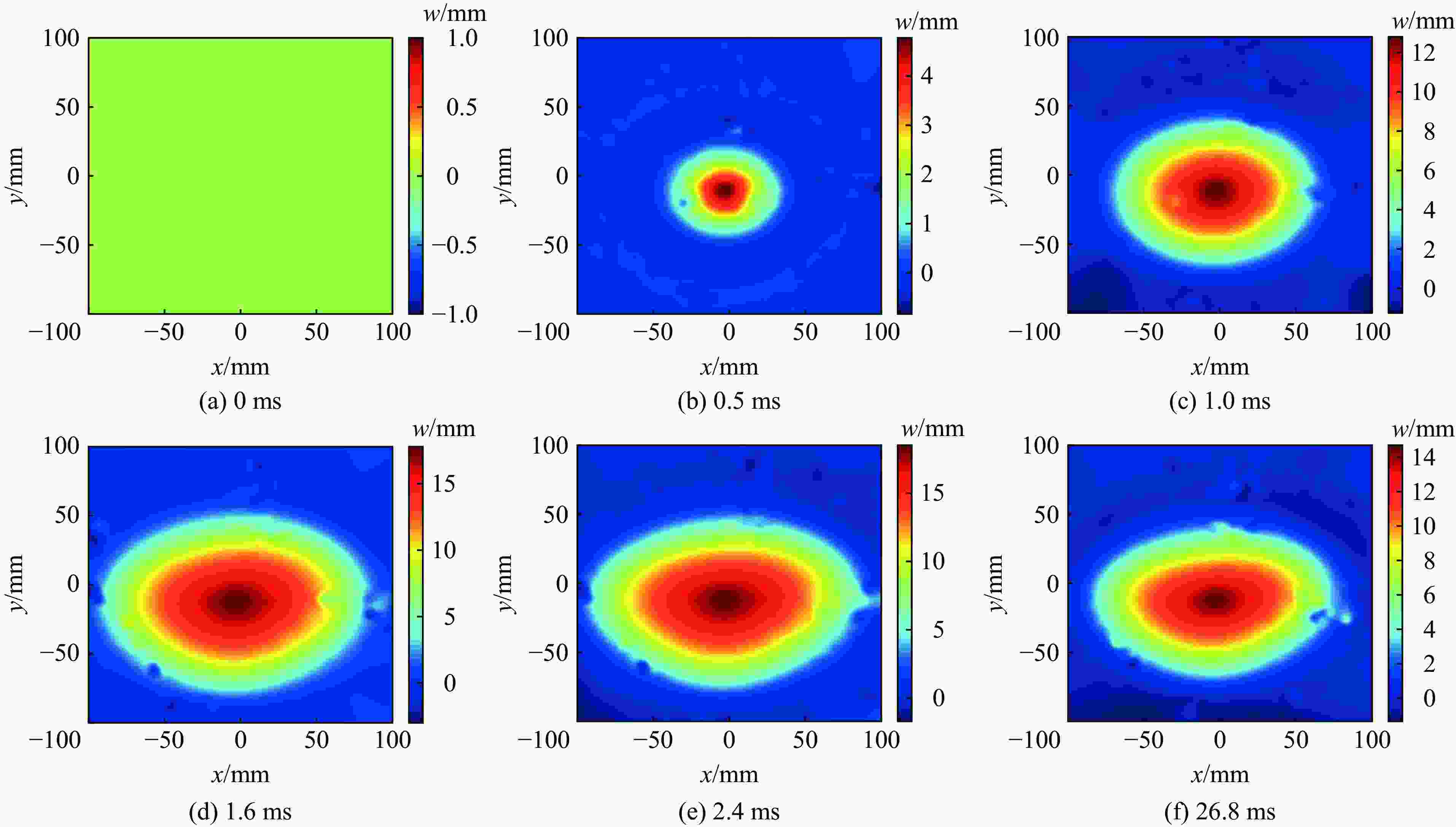
摘要: 为探究薄壁椭球壳在局部冲击载荷作用下的变形特征,开展了实验和数值模拟研究。利用轻气枪开展弹丸冲击实验,采用三维数字图像相关技术记录变形过程,得到了圆柱弹丸以不同速度冲击作用下椭球壳的全局变形形貌以及中心凹陷深度和凹陷边界。在弹丸冲击椭球壳的数值模拟中,重点研究了3种曲率半径变化对椭球壳凹陷深度、凹陷长短轴的影响,采用量纲分析方法得到了无量纲变形特征所依赖的主要无量纲自变量,通过参数敏感性分析消减影响较小的参数,在保持相同材料、弹体尺寸与壳体厚度同一缩比时,得到了无量纲变形特征与3种曲率半径和速度之间的响应面函数表达式,并提出了根据凹陷深度和凹陷边界预测全局变形的公式,所得表达式尺寸效应良好,预测精度较高,可为工程中大尺寸曲面薄壳冲击载荷防护设计提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 薄壁椭球壳 /
- 冲击载荷 /
- 三维数字图像相关技术 /
- 量纲分析 /
- 响应面模型
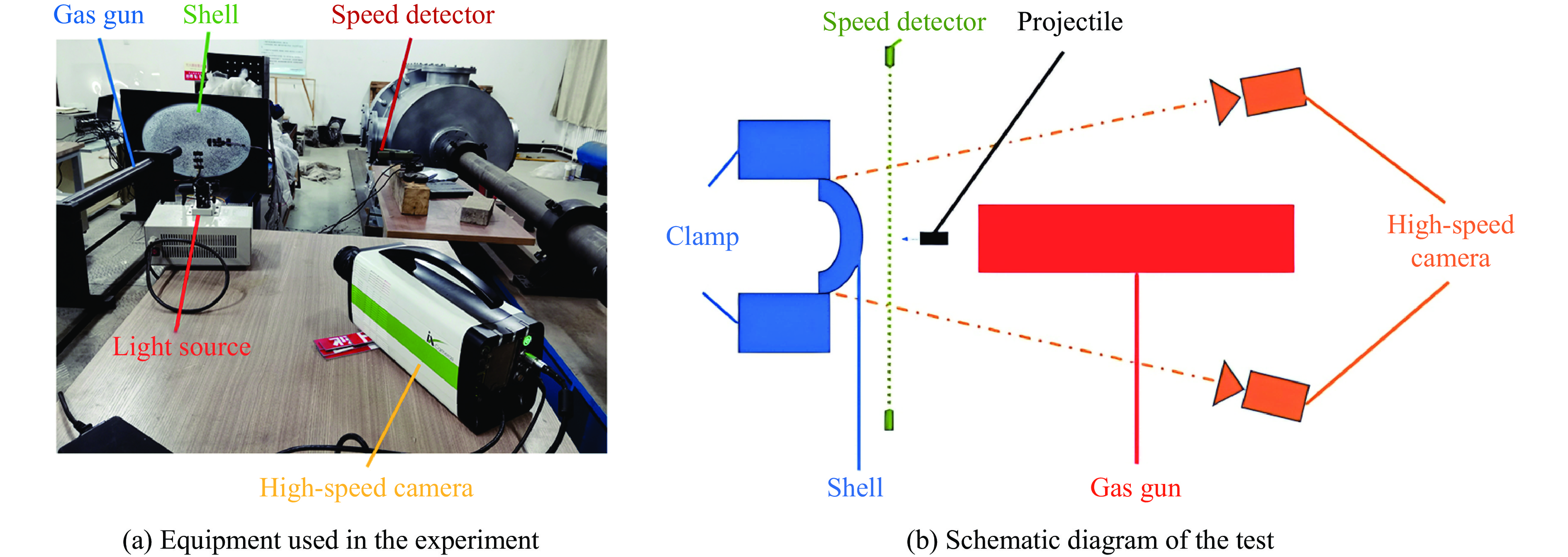
Abstract: In order to study the deformation characteristics of thin-walled ellipsoidal shells under localized impact loading, experimental investigations and numerical simulations were conducted. The global deformation characteristics, central dent depth and dent boundary of the recovery ellipsoidal shell impacted by cylindrical projectiles at different velocities were obtained by projectile impact tests on a light gas gun apparatus and three-dimensional digital image correlation (DIC) technology for deformation process record. The simulation analysis focused on the effects of three different curvature radii on the depression depth and the lengths of the major and minor axes of the ellipsoidal shell. The primary dimensionless independent variables on which the dimensionless deformation characteristics depend were determined by means of dimensional analysis. The influence of less significant parameters was reduced through parameter sensitivity analysis. Under the condition of maintaining consistent scaling ratios for material properties, projectile dimensions, and shell thickness, specific response surface function expressions between dimensionless deformation characteristics vs. three curvature radii and velocity parameters were derived. A formula for predicting global deformation based on the depth of the depression and the depression boundary was proposed. The established expression can well describe the size effect and has a high prediction accuracy, and can provide reference for the design of impact load protection of large-sized curved thin shells in engineering. -
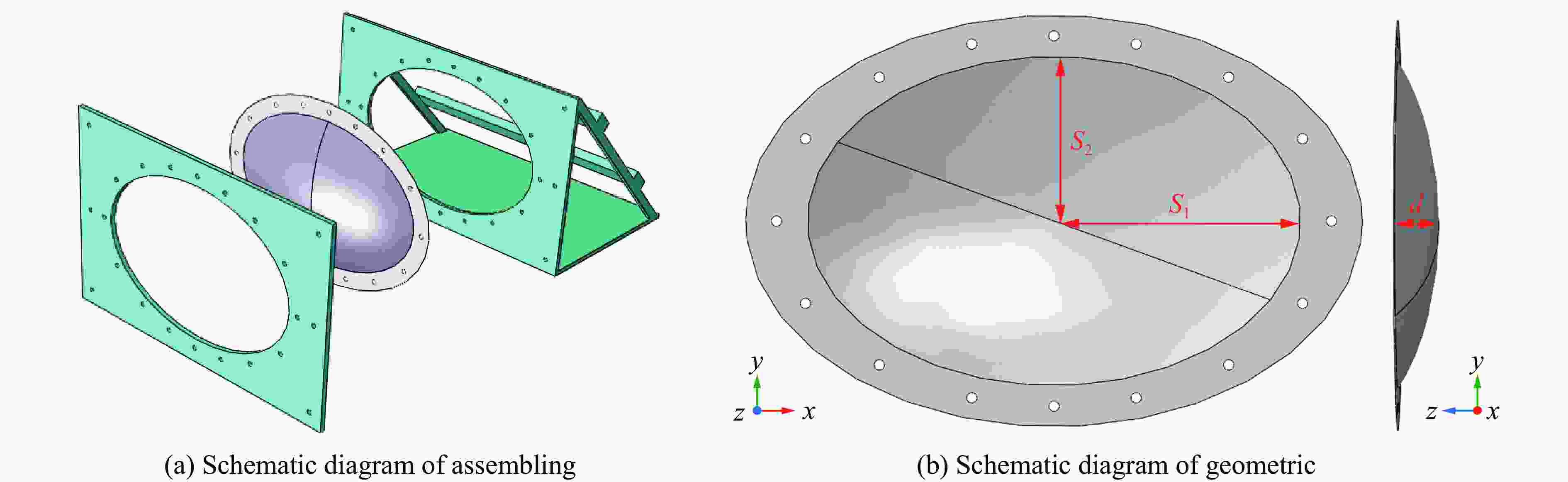
表 1 薄壁金属椭球壳几何与材料参数[20]
Table 1. Geometric and material parameters of thin-walled metal ellipsoidal shells[20]
S1/mm S2/mm d/mm E/GPa ρ/(kg∙m−3) μ 240 160 40 70 2 700 0.3 A/MPa B/MPa C n m 121 327 0.009 0.544 1.12 表 3 物理量参数
Table 3. Physical quantity parameters
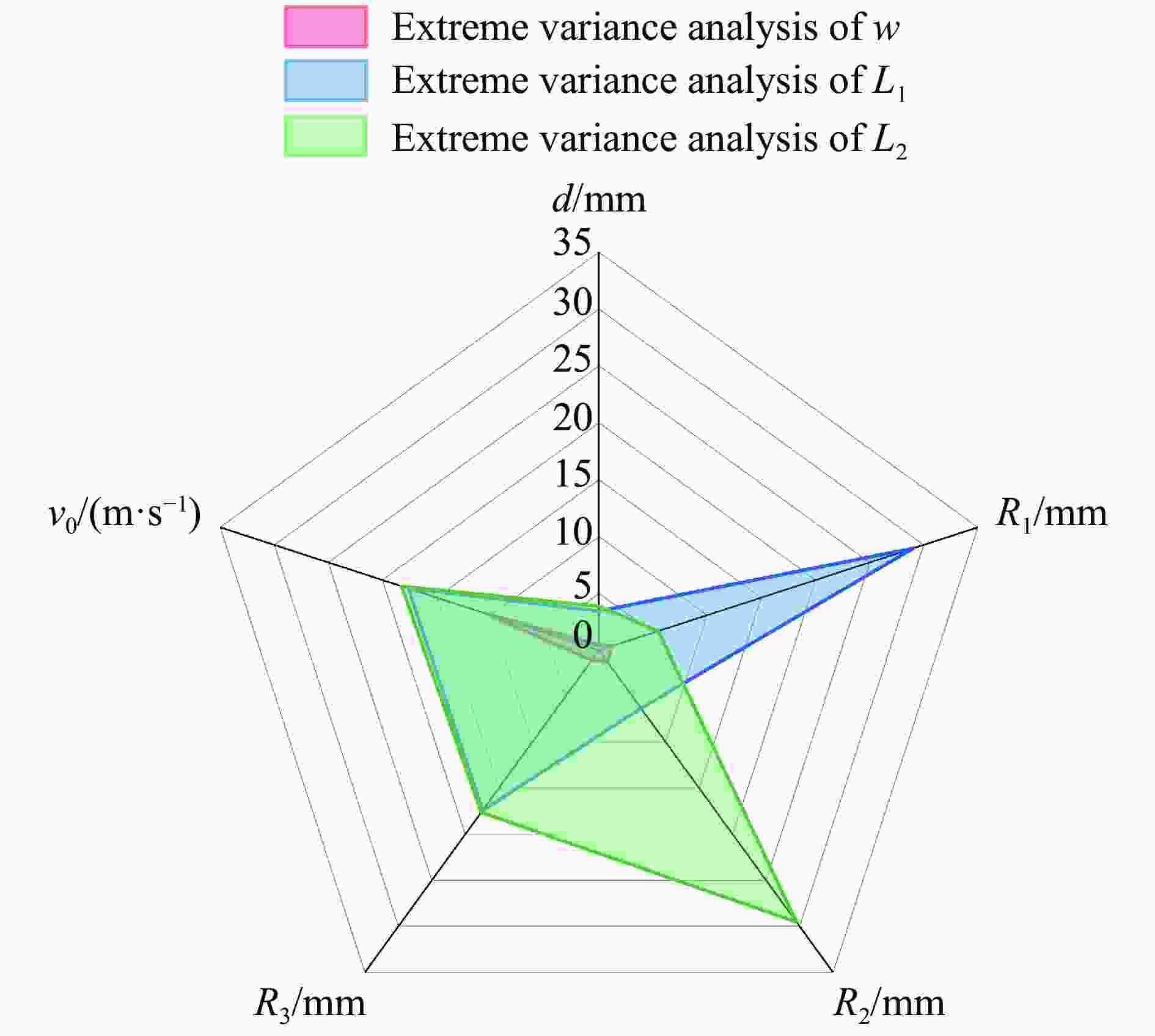
分析对象 参数 量纲 分析对象 参数 量纲 薄壁椭球壳 R1 L 圆柱弹丸 Ls L R2 L ms M R3 L Rs L ρ ML−3 Es ML−1T−2 E ML−1T−2 μs 1 Y ML−1T−2 v0 LT−1 μ 1 h L d L 表 4 正交实验工况设计及数值模拟结果
Table 4. Orthogonal experimental design and simulation results
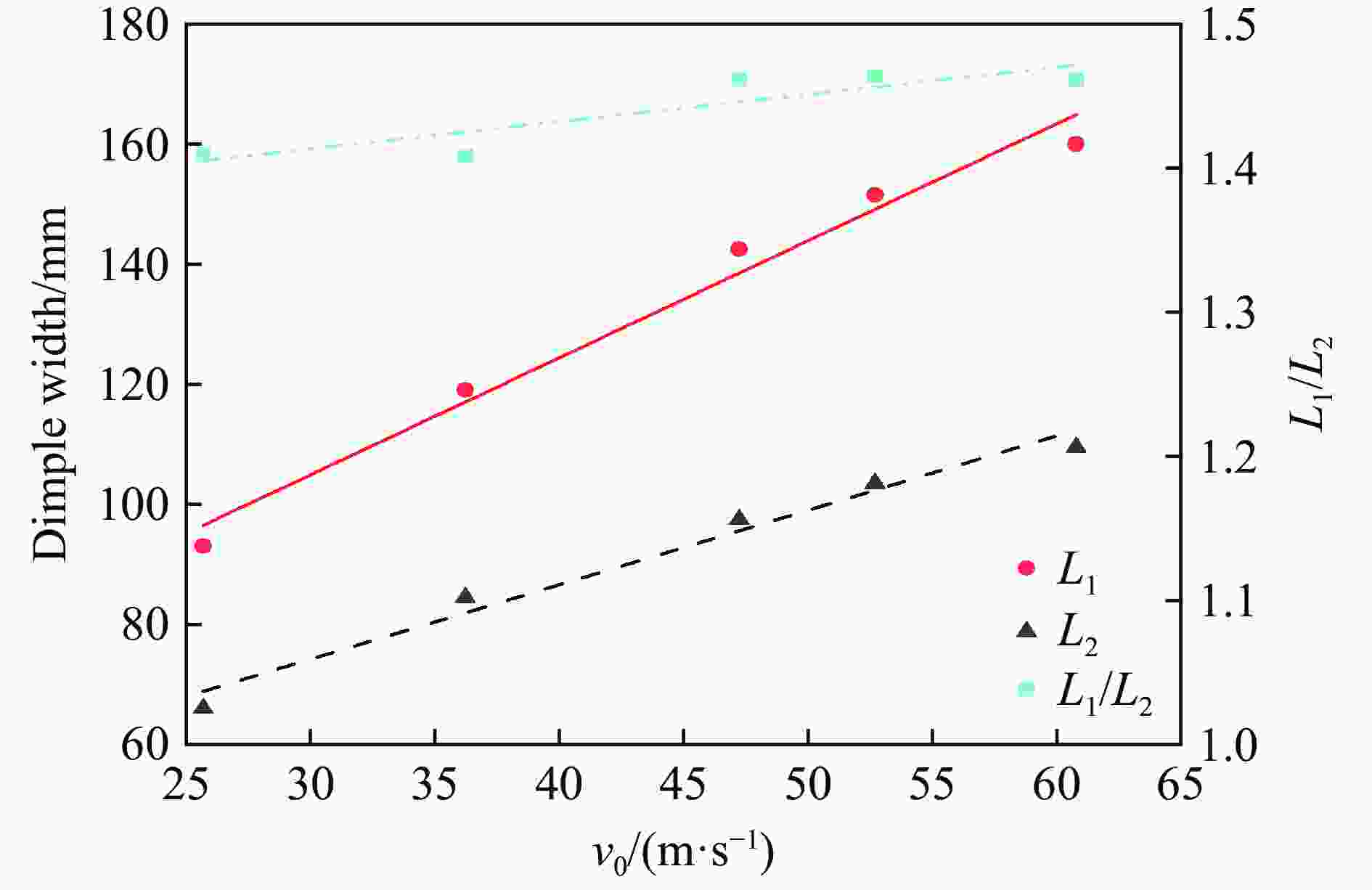
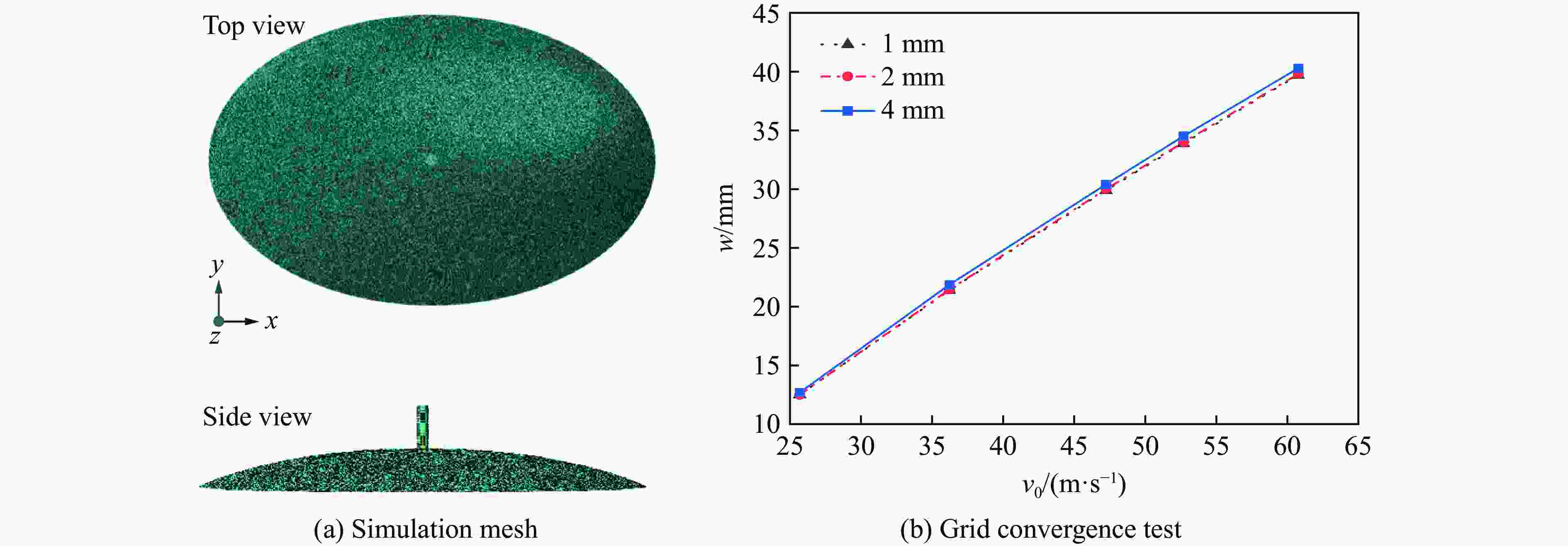
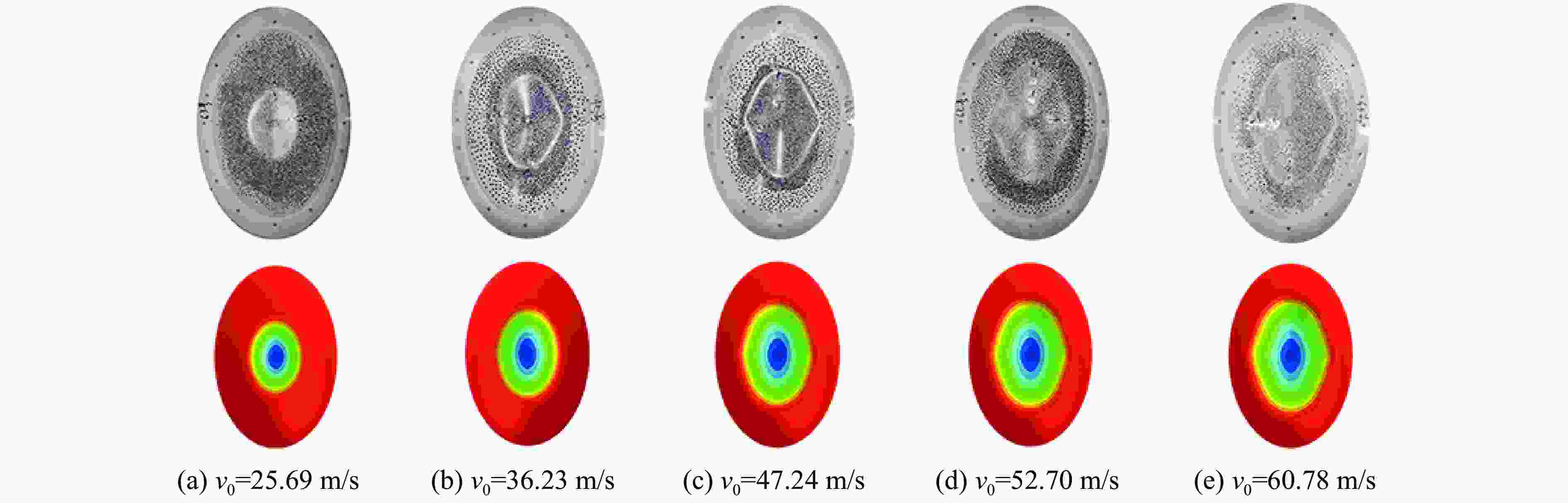
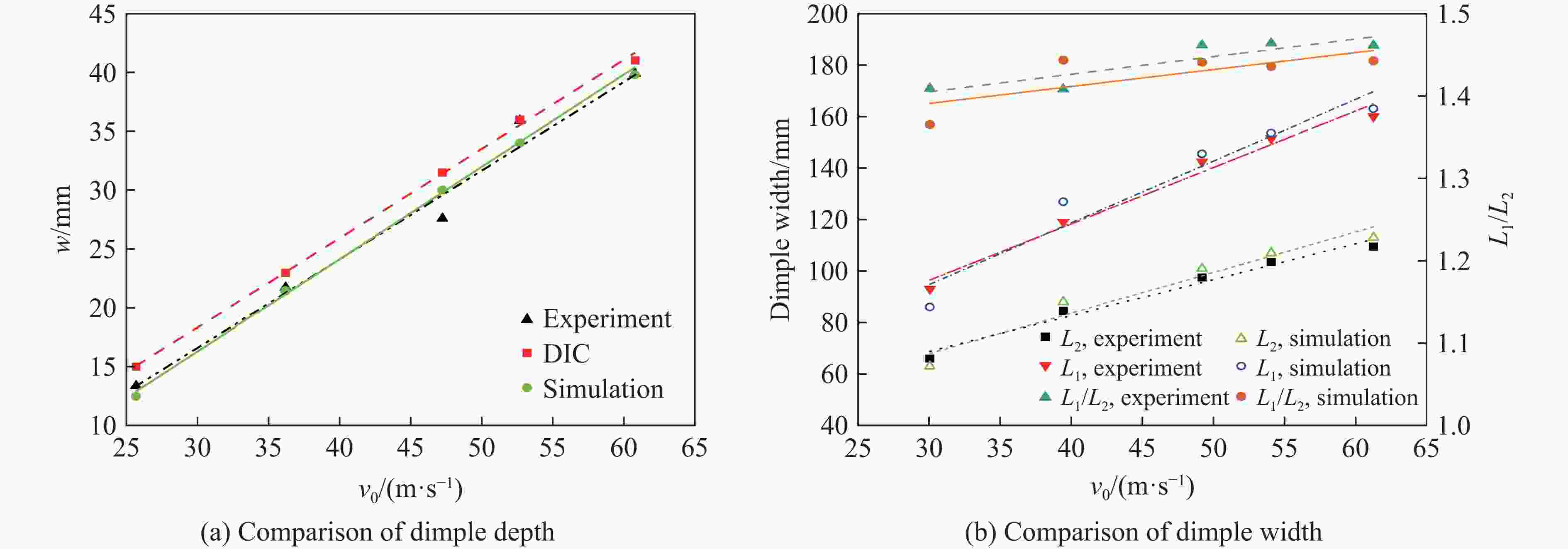
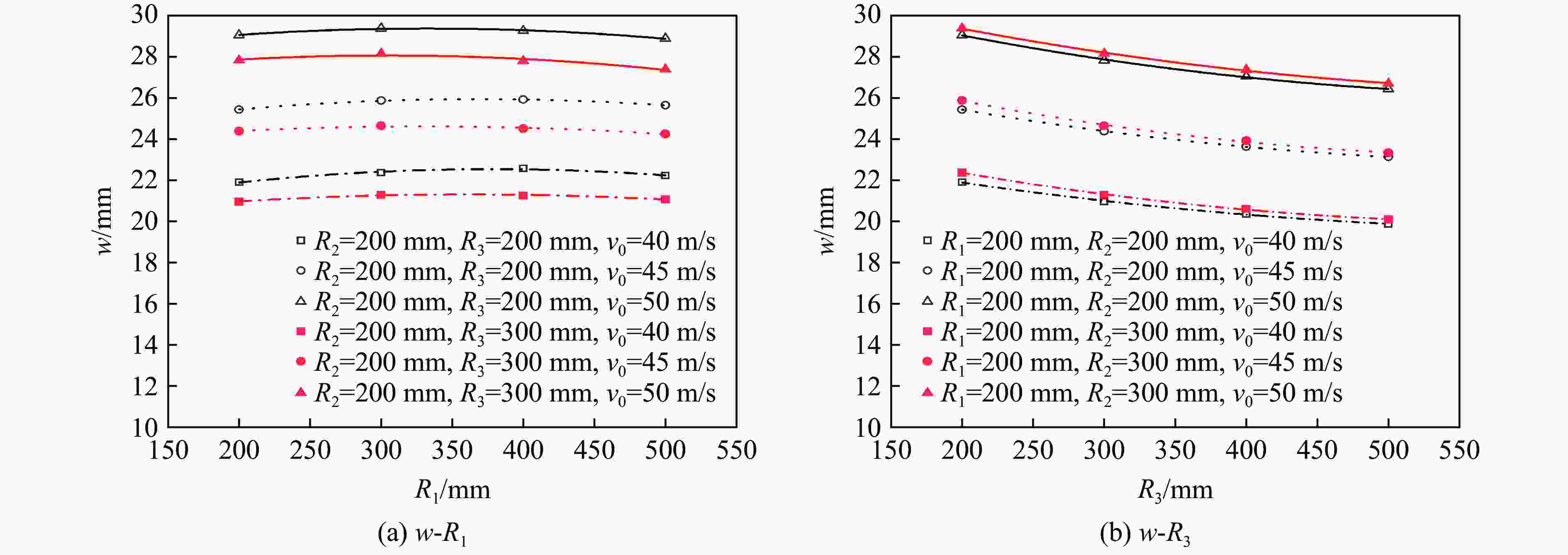
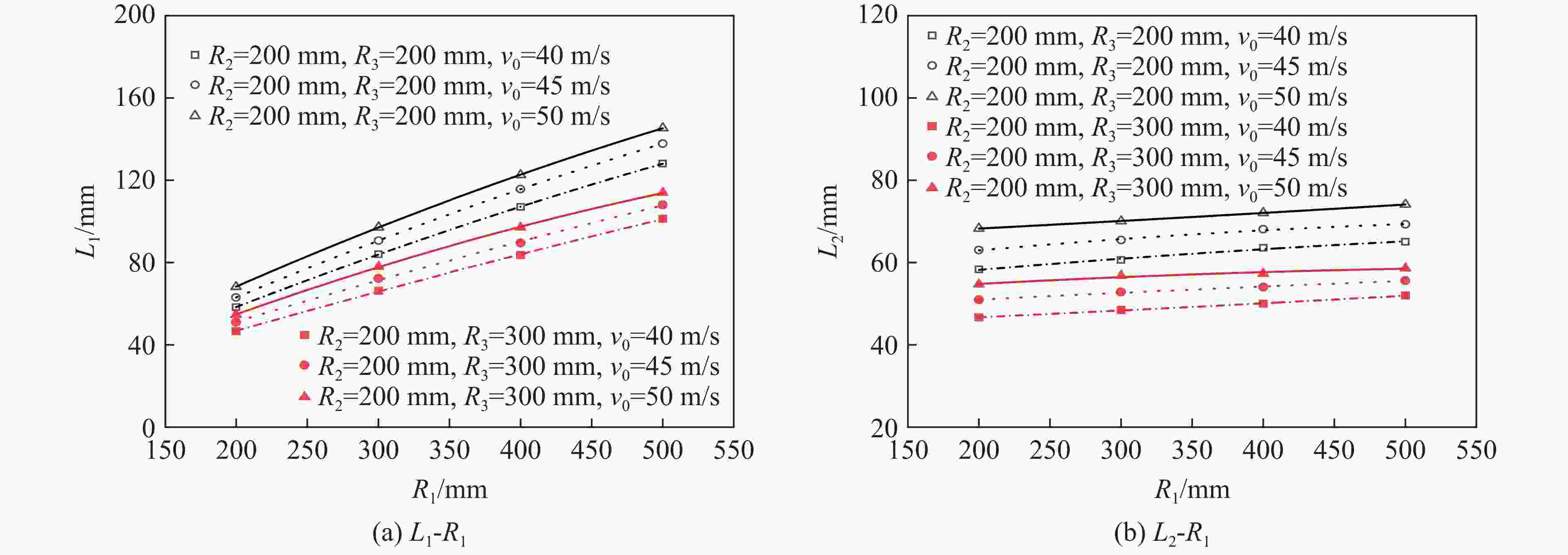
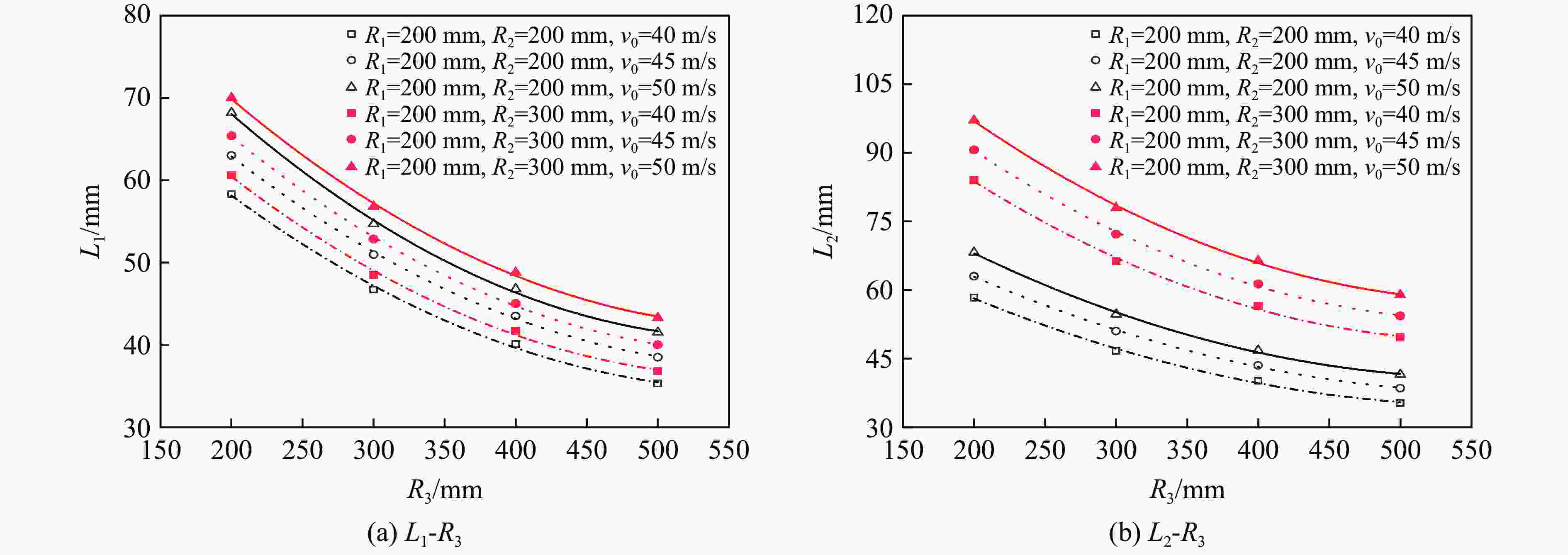
工况 d/mm R1/mm R2/mm R3/mm v0/(m·s−1) w/mm L1/mm L2/mm 1 50 200 200 200 30 15.14 47.1 47.1 2 50 240 240 240 35 19.31 64.8 64.8 3 50 280 280 280 40 22.72 70.7 70.7 4 50 320 320 320 45 26.87 82.7 82.7 5 60 200 240 280 45 24.85 54.0 62.3 6 60 240 200 320 40 21.12 53.1 46.3 7 60 280 320 200 35 20.29 79.5 89.6 8 60 320 280 240 30 16.28 71.9 63.9 9 70 200 280 320 35 17.92 42.6 55.0 10 70 240 320 280 30 15.56 50.3 63.2 11 70 280 200 240 45 25.39 76.0 58.0 12 70 320 240 200 40 23.30 94.2 73.6 13 80 200 320 240 40 22.09 55.1 80.4 14 80 240 280 200 45 26.84 78.7 90.0 15 80 280 240 320 30 15.19 51.5 45.8 16 80 320 200 280 35 18.28 66.2 46.5 表 5 响应面模型的计算工况
Table 5. Calculation conditions of response surface model
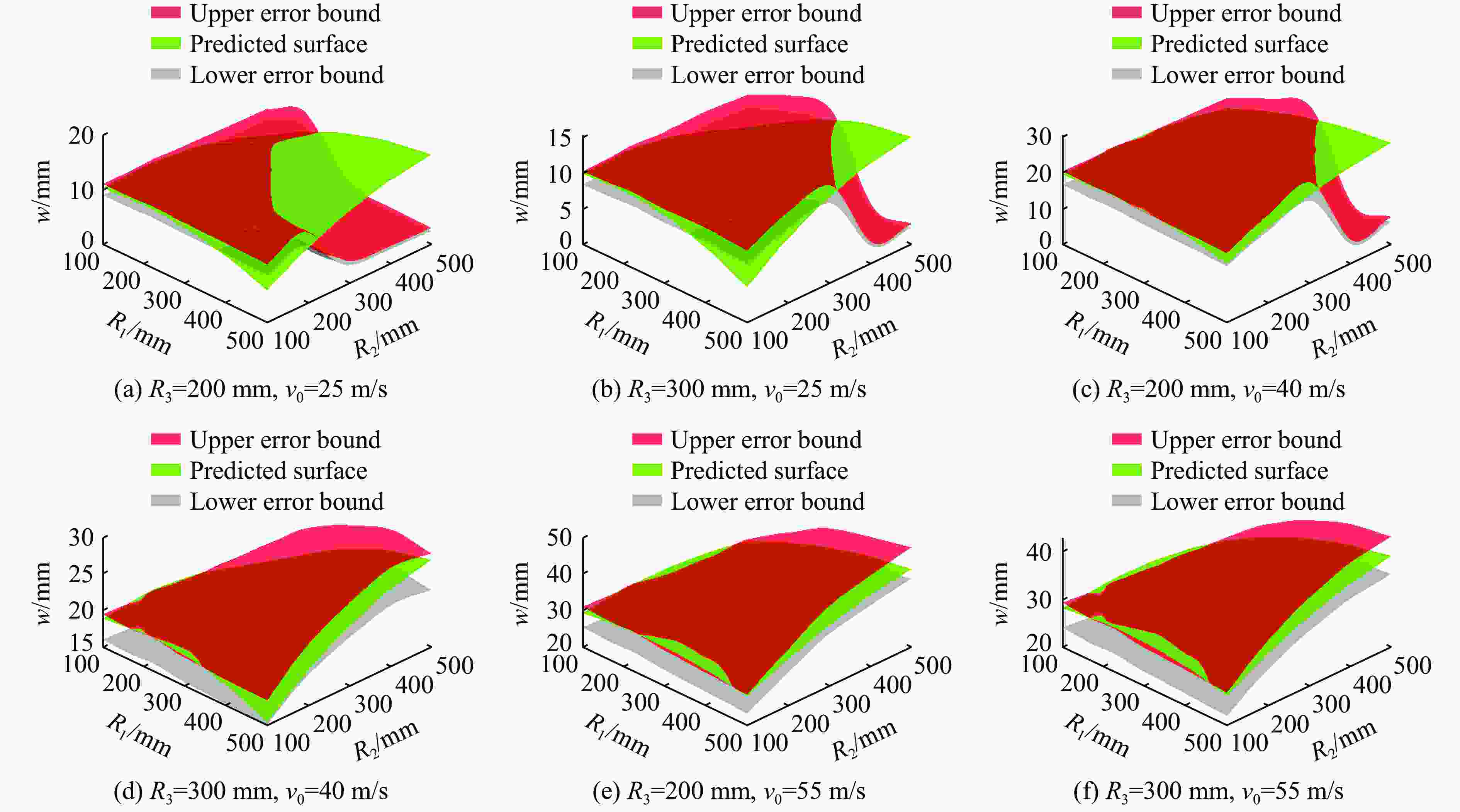
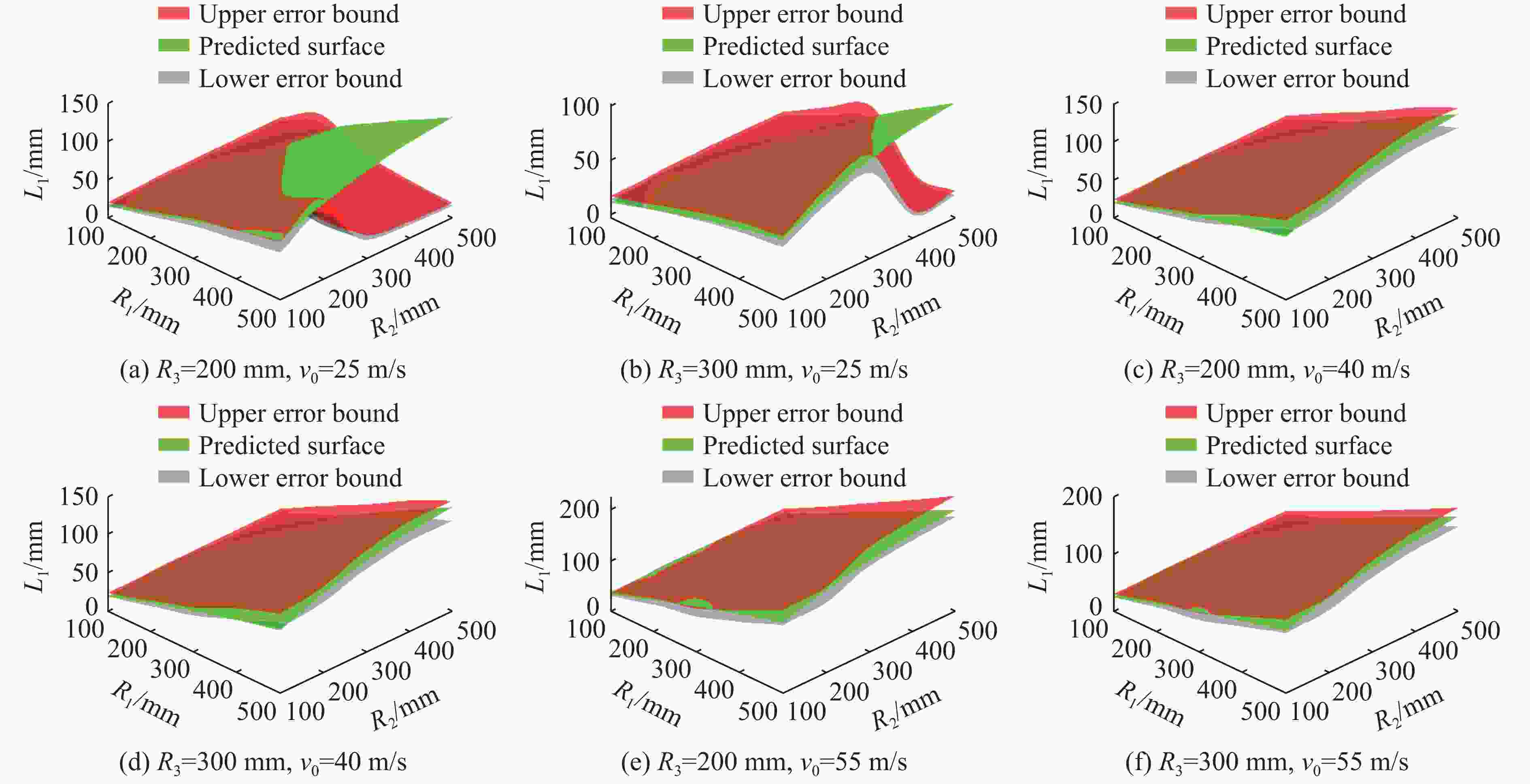
R1/mm R2/mm R3/mm v0/(m·s−1) w/mm L1/mm L2/mm 200 200 200 35 18.45 52.9 52.9 200 300 200 35 18.95 55.5 77.0 200 400 200 35 19.15 57.4 99.4 300 300 200 35 20.37 85.0 85.0 300 400 200 35 20.64 87.0 113.0 200 200 200 40 21.90 58.3 58.3 200 300 200 40 22.37 60.6 84.0 200 400 200 40 22.57 63.5 107.0 300 300 200 40 24.09 92.7 92.7 300 400 200 40 24.82 95.7 123.5 200 200 200 45 25.43 63.0 63.0 200 300 200 45 25.87 65.4 90.6 200 400 200 45 25.91 68.0 115.6 300 300 200 45 27.90 99.6 99.6 300 400 200 45 28.82 102.5 132.9 200 200 200 50 29.05 68.2 68.2 200 300 200 50 29.38 70.0 97.1 200 400 200 50 29.26 72.0 122.5 300 300 200 50 31.63 106.0 106.0 300 400 200 50 32.98 109.6 141.8 200 200 300 35 17.67 42.5 42.5 200 300 300 35 18.00 44.4 60.0 200 400 300 35 18.08 45.6 76.4 300 300 300 35 19.43 66.9 66.9 300 400 300 35 19.89 67.5 86.4 400 400 300 35 20.98 94.4 94.4 200 200 300 40 20.96 46.7 46.7 200 300 300 40 21.29 48.5 66.3 200 400 300 40 21.26 50.0 83.6 300 300 300 40 23.10 73.6 73.6 300 400 300 40 23.53 76.0 97.7 400 400 300 40 24.77 102.8 102.8 200 200 300 45 24.38 51.0 51.0 200 300 300 45 24.64 52.83 72.2 200 400 300 45 24.51 54.0 89.4 300 300 300 45 26.70 79.5 79.5 300 400 300 45 27.19 81.8 104.6 400 400 300 45 28.56 110.8 110.8 200 200 300 50 27.83 54.7 54.7 200 300 300 50 28.15 56.8 78.0 200 400 300 50 27.80 57.3 97.1 300 300 300 50 30.42 85.3 85.3 300 400 300 50 30.86 87.6 111.2 400 400 300 50 32.63 118.6 118.6 200 200 400 35 17.11 36.3 36.3 200 300 400 35 17.36 37.5 50.7 200 400 400 35 17.14 38.5 62.8 200 200 400 40 20.37 40.1 40.1 200 300 400 40 20.60 41.7 56.5 200 400 400 40 20.31 42.3 70.0 200 200 400 45 23.63 43.5 43.5 200 300 400 45 23.92 45.0 61.3 200 400 400 45 23.51 45.7 76.2 200 200 400 50 27.04 46.8 46.8 200 300 400 50 27.37 48.8 66.4 200 400 400 50 26.81 48.8 81.9 300 300 400 35 18.70 56.7 56.7 300 400 400 35 19.14 58.8 74.6 300 300 400 40 22.22 62.5 62.5 300 400 400 40 22.72 64.8 81.9 300 300 400 45 25.87 68.2 68.2 300 400 400 45 26.30 70.2 88.8 300 300 400 50 29.52 73.7 73.7 300 400 400 50 29.84 75.3 94.6 表 6 响应面模型误差
Table 6. Response surface model error
变形特征 R2 δRAAE δRMAE δRMS w/h 0.995 0.015 0.032 0.019 L1/h 0.996 0.012 0.036 0.017 L2/h 0.996 0.018 0.050 0.025 表 7 数值模拟变形特征与响应面预测变形特征的对比
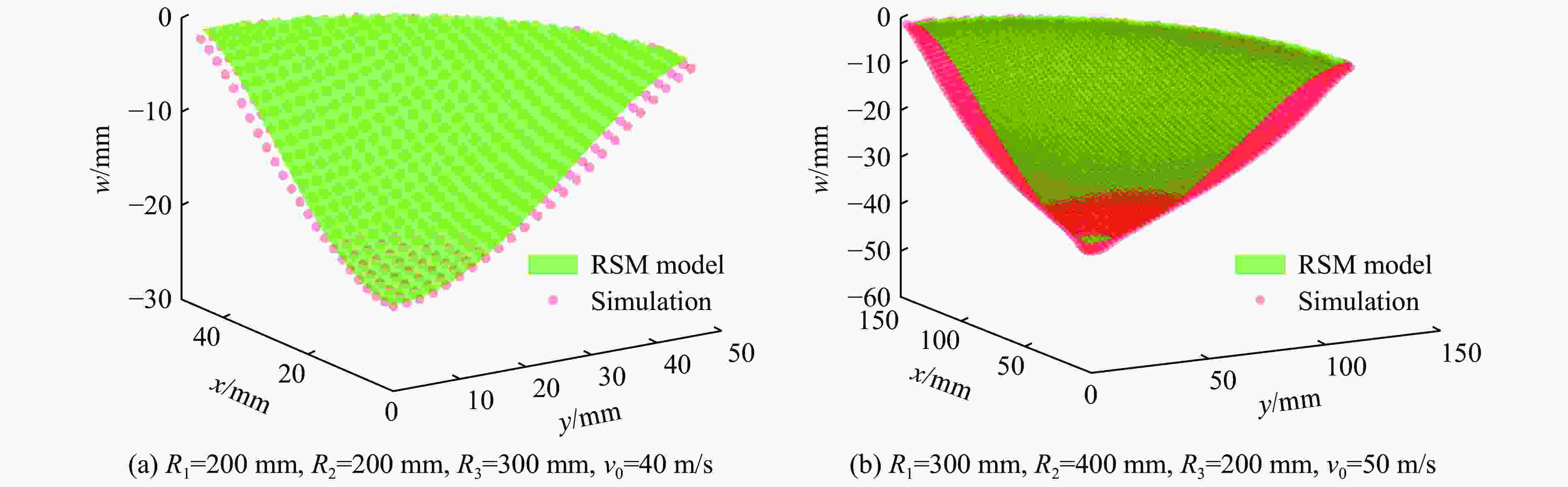
Table 7. Comparison of simulated deformation characteristics with response surface predicted deformation features
材料 h/mm R1/mm R2/mm R3/mm v0/(m·s−1) ws/mm wa/mm L1s/mm L1a/mm L2s/mm L2a/mm 5052Al 0.5 200 160 180 15 12.5 12.5 46.5 45.5 37.7 38.1 5052Al 2.0 450 500 480 80 27.1 29.2 90.8 96.8 97.2 104.9 45 steel 0.5 150 100 200 30 7.5 10.8 24.0 28.7 17.8 21.9 -
[1] LIM H K, LEE J S. On the structural behavior of ship’s shell structures due to impact loading [J]. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 2018, 10(1): 103–118. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnaoe.2017.03.002. [2] MOHAMMAD Z, GUPTA P K, BAQI A, et al. Ballistic performance of monolithic and double layered thin-metallic hemispherical shells at normal and oblique impact [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 159: 107257. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107257. [3] UPDIKE D P, KALNINS A. Axisymmetric behavior of an elastic spherical shell compressed between rigid plates [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1970, 37(3): 635–640. DOI: 10.1115/1.3408592. [4] UPDIKE D P. On the large deformation of a rigid-plastic spherical shell compressed by a rigid plate [J]. Journal of Engineering for Industry, 1972, 94(3): 949–955. DOI: 10.1115/1.3428276. [5] KITCHING R, HOULSTON R, JOHNSON W. A theoretical and experimental study of hemispherical shells subjected to axial loads between flat plates [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1975, 17(11/12): 693–703. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7403(75)90072-7. [6] GUPTA N K, MOHAMED S N, VELMURUGAN R. Experimental and numerical investigations into collapse behaviour of thin spherical shells under drop hammer impact [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2007, 44(10): 3136–3155. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2006.09.014. [7] WEN H M. Large plastic deformation of spherical shells under impact by blunt-ended missiles [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 1997, 73(2): 147–152. DOI: 10.1016/S0308-0161(97)00043-4. [8] 宁建国, 杨桂通. 球形扁壳在冲击载荷作用下的超临界变形 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1992, 12(3): 206–212. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1992)03-0206-7.NING J G, YANG G T. Supercritical deformations of shallow spherical shells under impact [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1992, 12(3): 206–212. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(1992)03-0206-7. [9] LI J Q, REN H L, NING J G. Deformation and failure of thin spherical shells under dynamic impact loading: experiment and analytical model [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 161: 107403. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107403. [10] ZHENG J, LI K, LIU S, et al. Effect of shape imperfection on the buckling of large-scale thin-walled ellipsoidal head in steel nuclear containment [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 124: 514–522. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2018.01.001. [11] PALIWAL D N, GUPTA R, JAIN A. Stress analysis of ellipsoidal shell on an elastic foundation [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 1993, 56(2): 229–242. DOI: 10.1016/0308-0161(93)90095-B. [12] PATEL P R, GILL S S. Experiments on the buckling under internal pressure of thin torispherical ends of cylindrical pressure vessels [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1978, 20(3): 159–175. DOI: 10.1016/0020-7403(78)90003-6. [13] BUSHNELL D. Nonsymmetric buckling of internally pressurized ellipsoidal and torispherical elastic-plastic pressure vessel heads [J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 1977, 99(1): 54–63. DOI: 10.1115/1.3454520. [14] CHAO Y J, SUTTON M A. Stress analysis of ellipsoidal shell with radial nozzle [J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 1985, 21(2): 89–108. DOI: 10.1016/0308-0161(85)90042-0. [15] ROSS C T F, HUAT B H, CHEI T B, et al. The buckling of GRP hemi-ellipsoidal dome shells under external hydrostatic pressure [J]. Ocean Engineering, 2003, 30(5): 691–705. DOI: 10.1016/s0029-8018(02)00039-2. [16] BLACHUT J, JAISWAL O R. On the choice of initial geometric imperfections in externally pressurized shells [J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 1999, 121(1): 71–76. DOI: 10.1115/1.2883670. [17] SMITH P, BŁACHUT J. Buckling of externally pressurized prolate ellipsoidal domes [J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 2008, 130(1): 011210. DOI: 10.1115/1.2834457. [18] LIU L, LI J Q. Dynamic deformation and perforation of ellipsoidal thin shell impacted by flat-nose projectile [J]. Materials, 2022, 15(12): 4124. DOI: 10.3390/ma15124124. [19] 陈旭东, 叶康生. 中厚椭球壳自由振动动力刚度法分析 [J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(6): 85–90. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2016.06.015.CHEN X D, YE K S. Free vibration analysis of moderately thick elliptical shells using the dynamic stiffness method [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(6): 85–90. DOI: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2016.06.015. [20] MA T B, SHEN Y, NING J G, et al. Analysis on dynamic shear fracture based on a novel damage evolution model [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 183: 104810. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104810. [21] 陈刚, 陈忠富, 徐伟芳, 等. 45钢的J-C损伤失效参量研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2007, 27(2): 131–135. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)02-0131-05.CHEN G, CHEN Z F, XU W F, et al. Investigation on the J-C ductile fracture parameters of 45 steel [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2007, 27(2): 131–135. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)02-0131-05. -






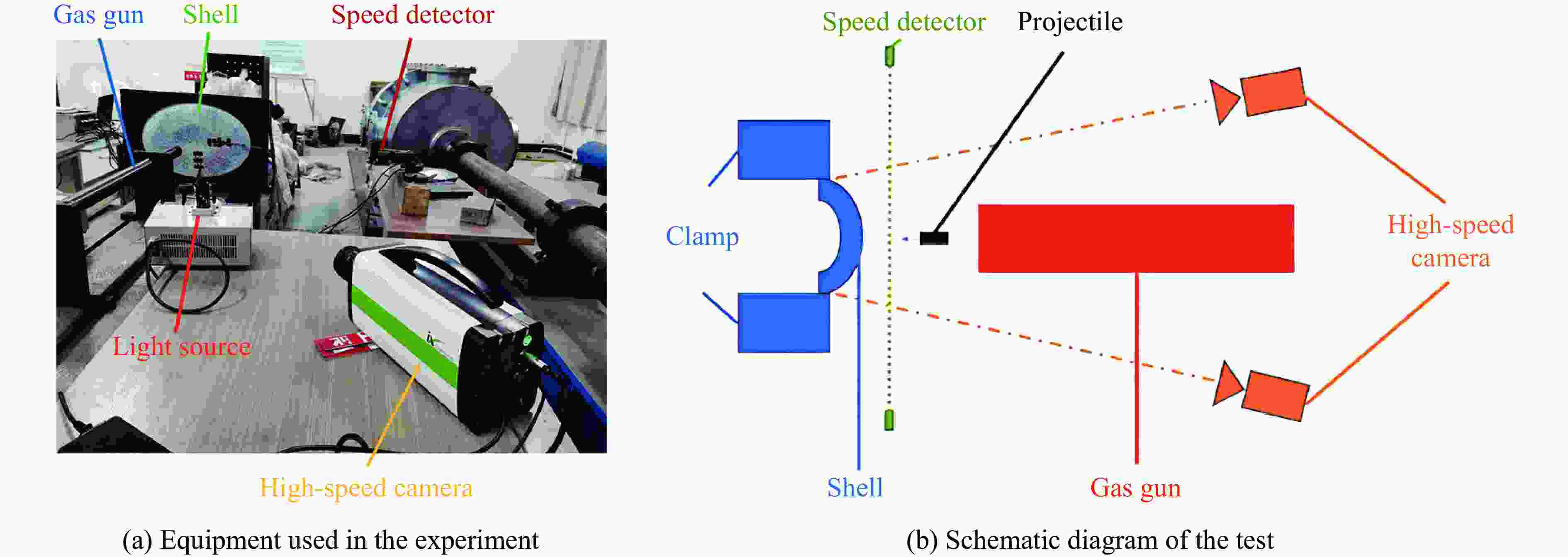
 下载:
下载: