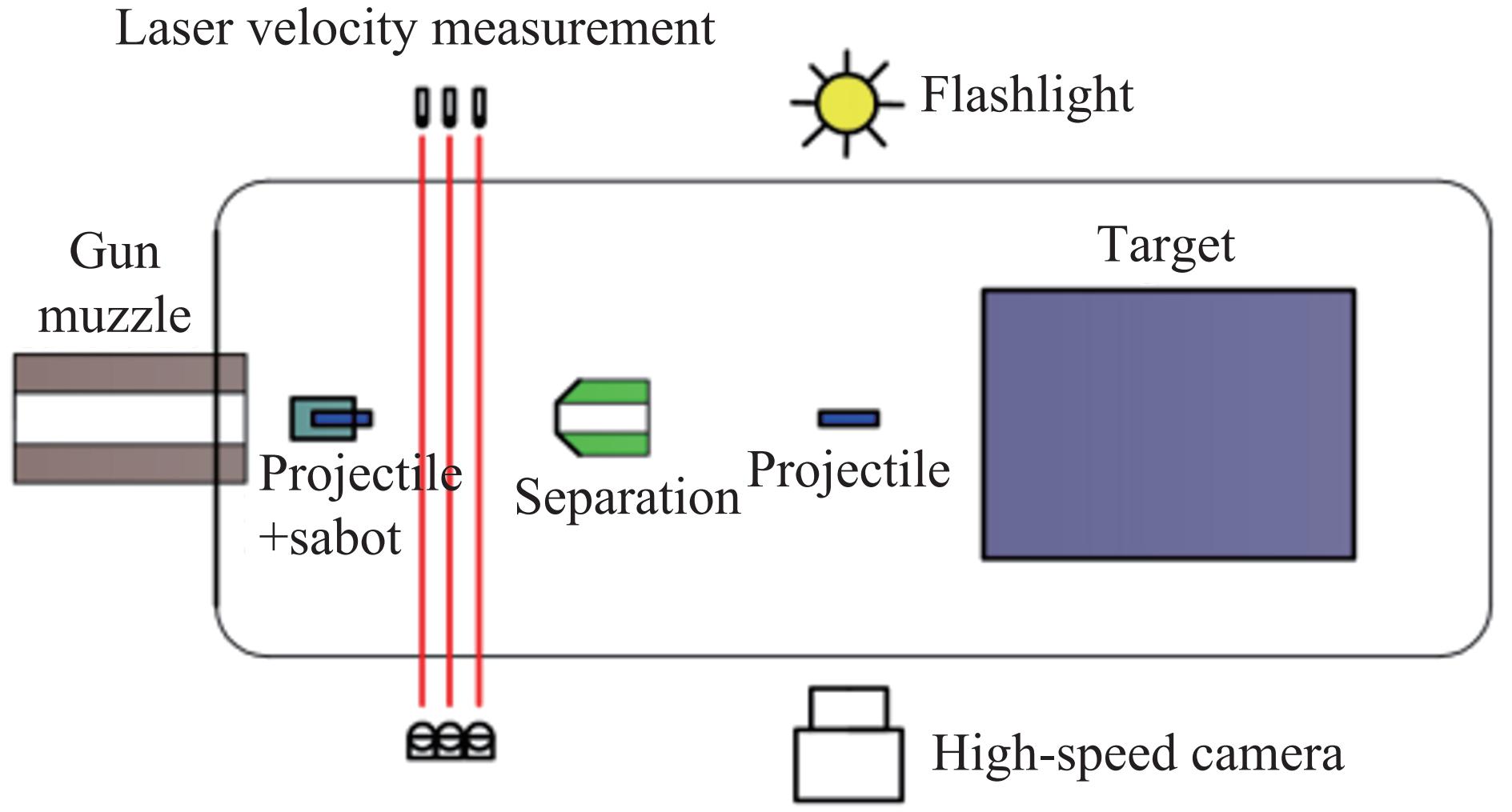
Measurement and analysis of stress waves in concrete target under hypervelocity impact
-
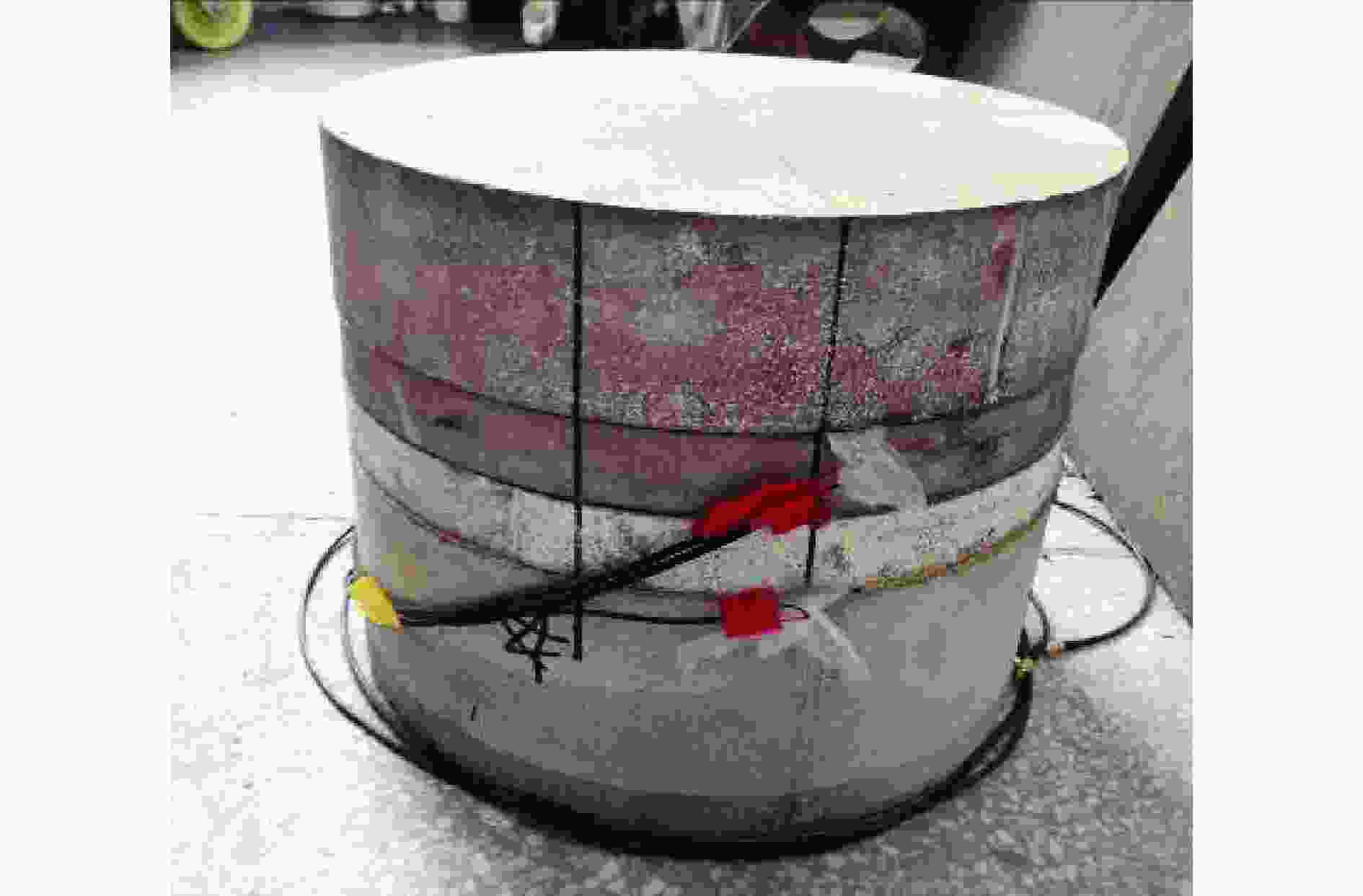
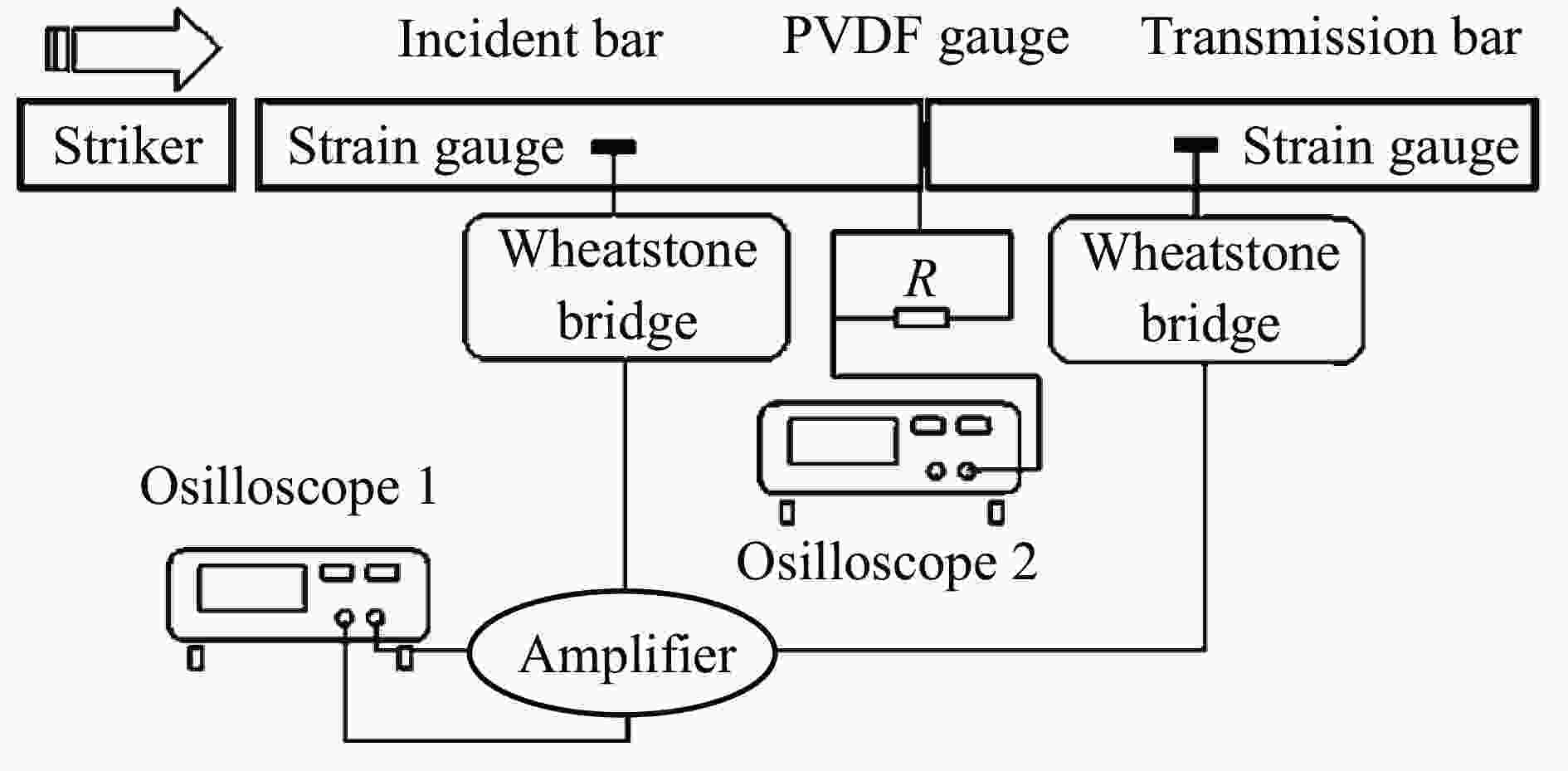
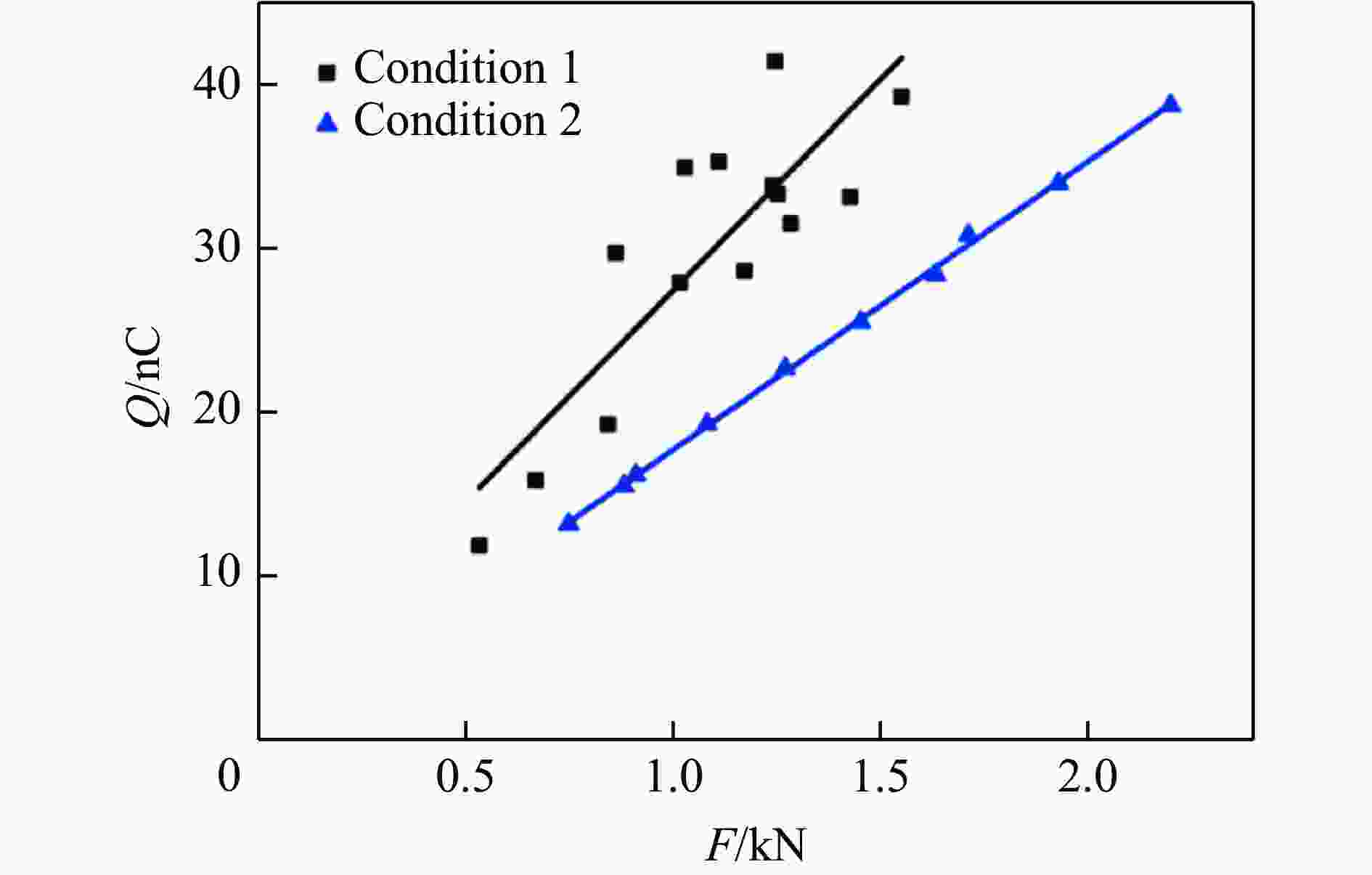
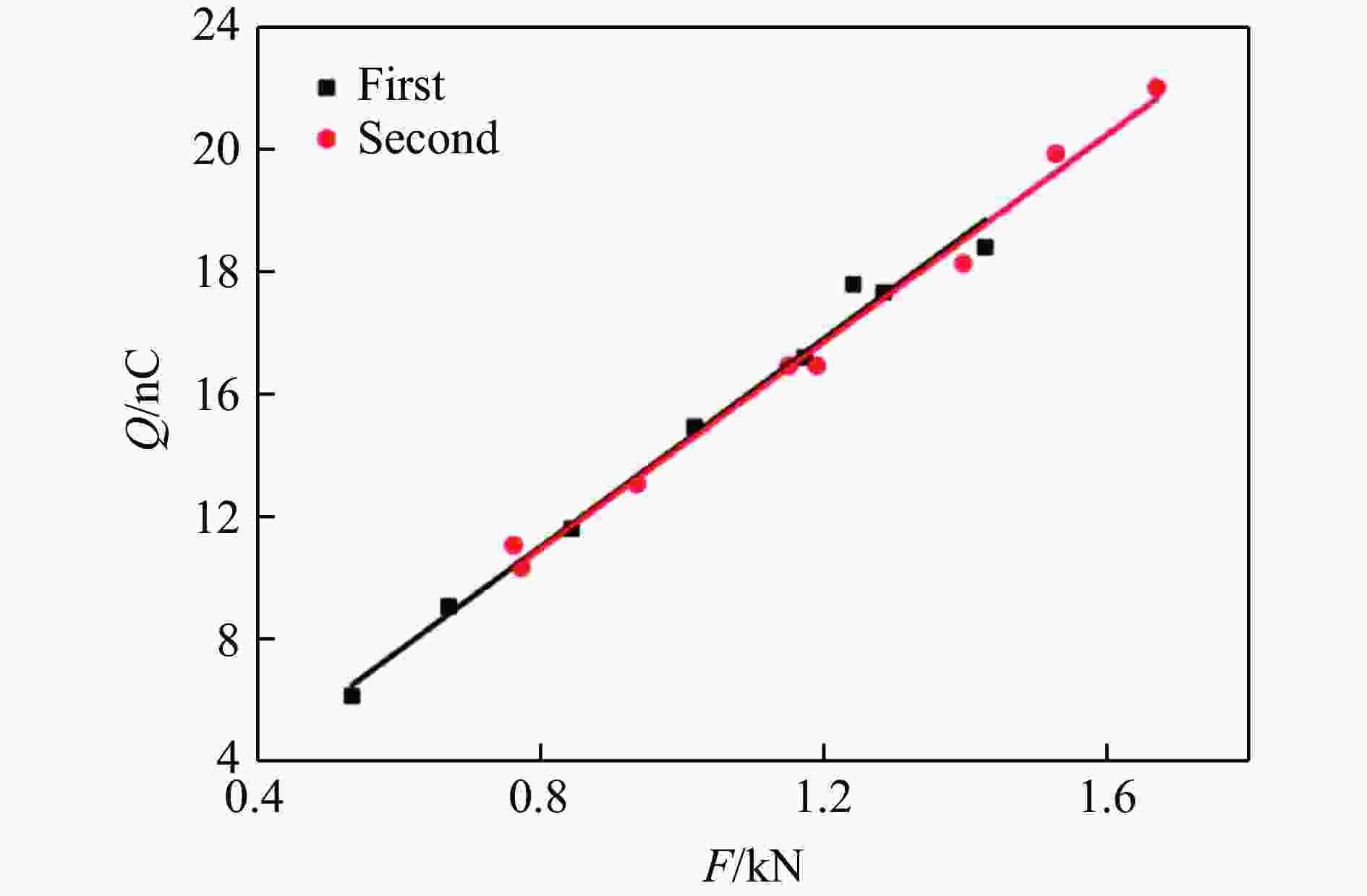
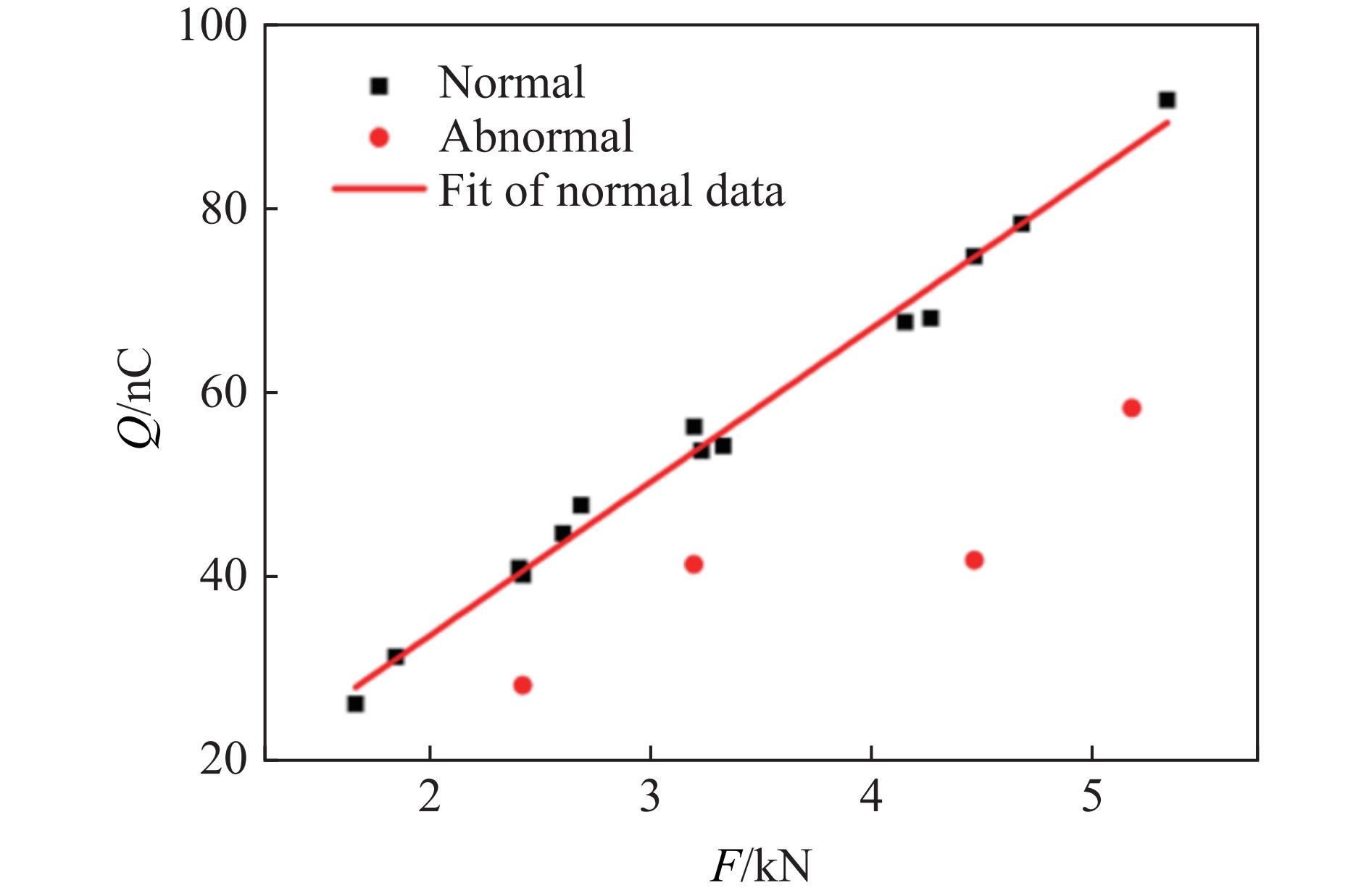
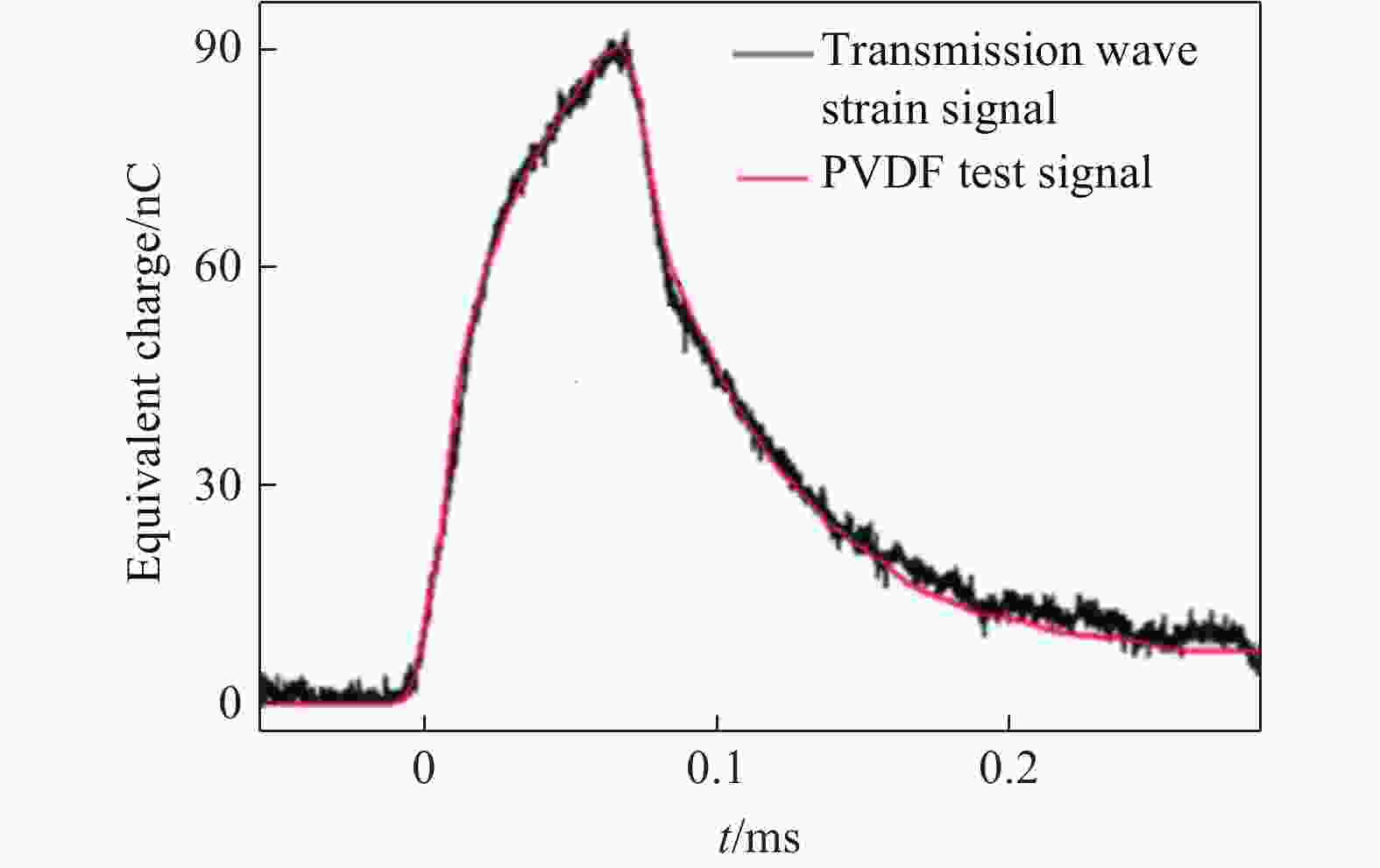
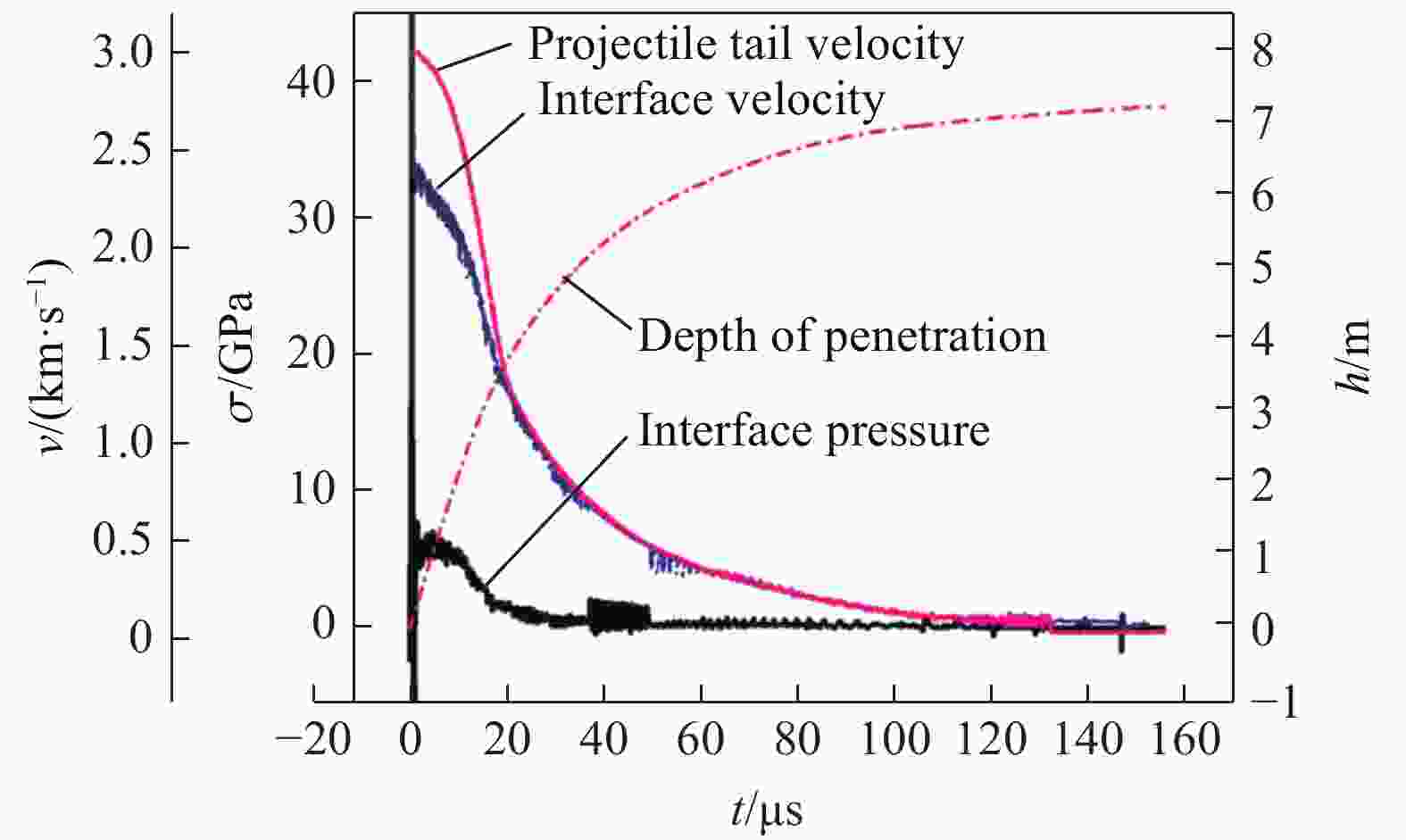
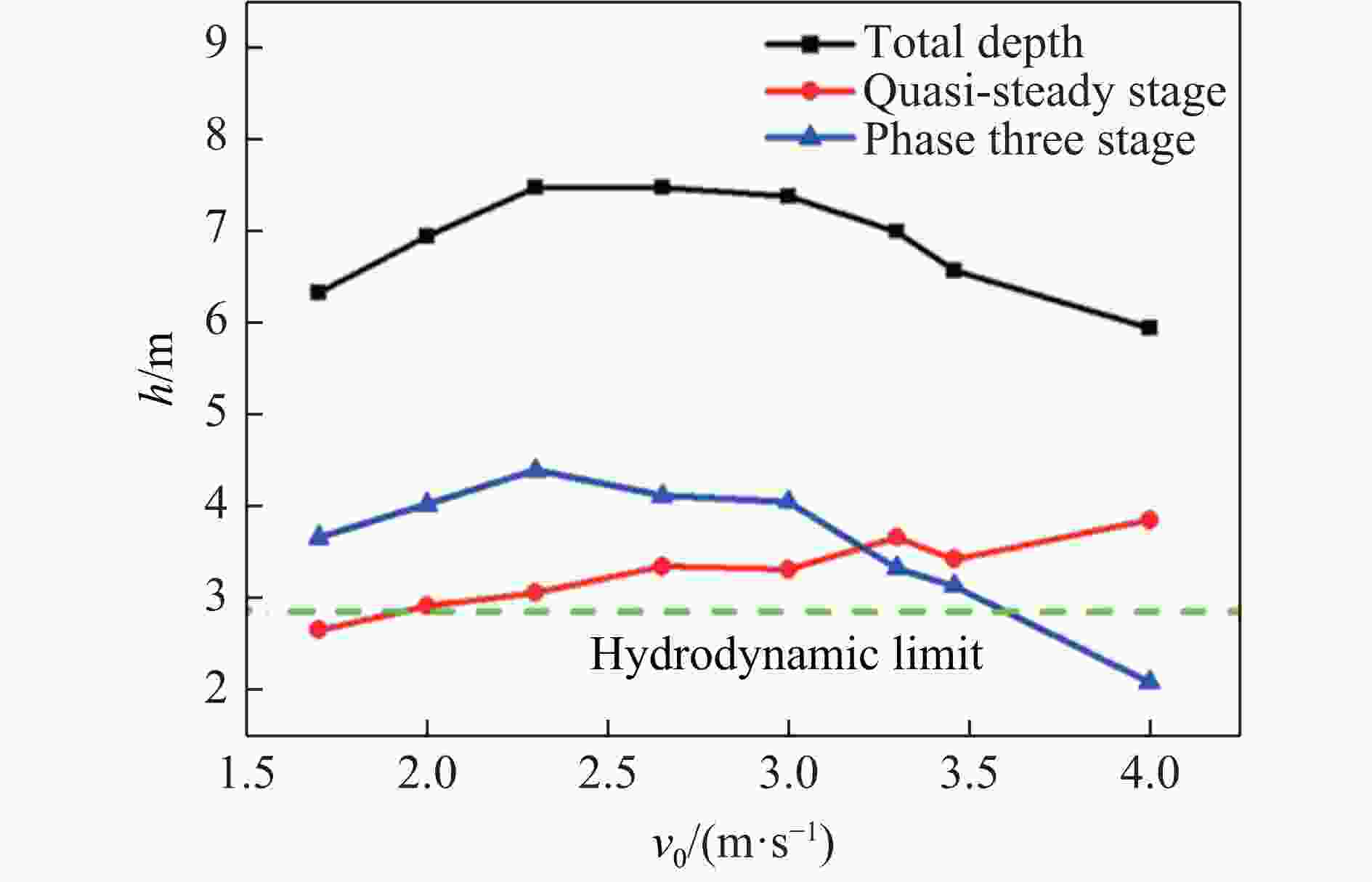
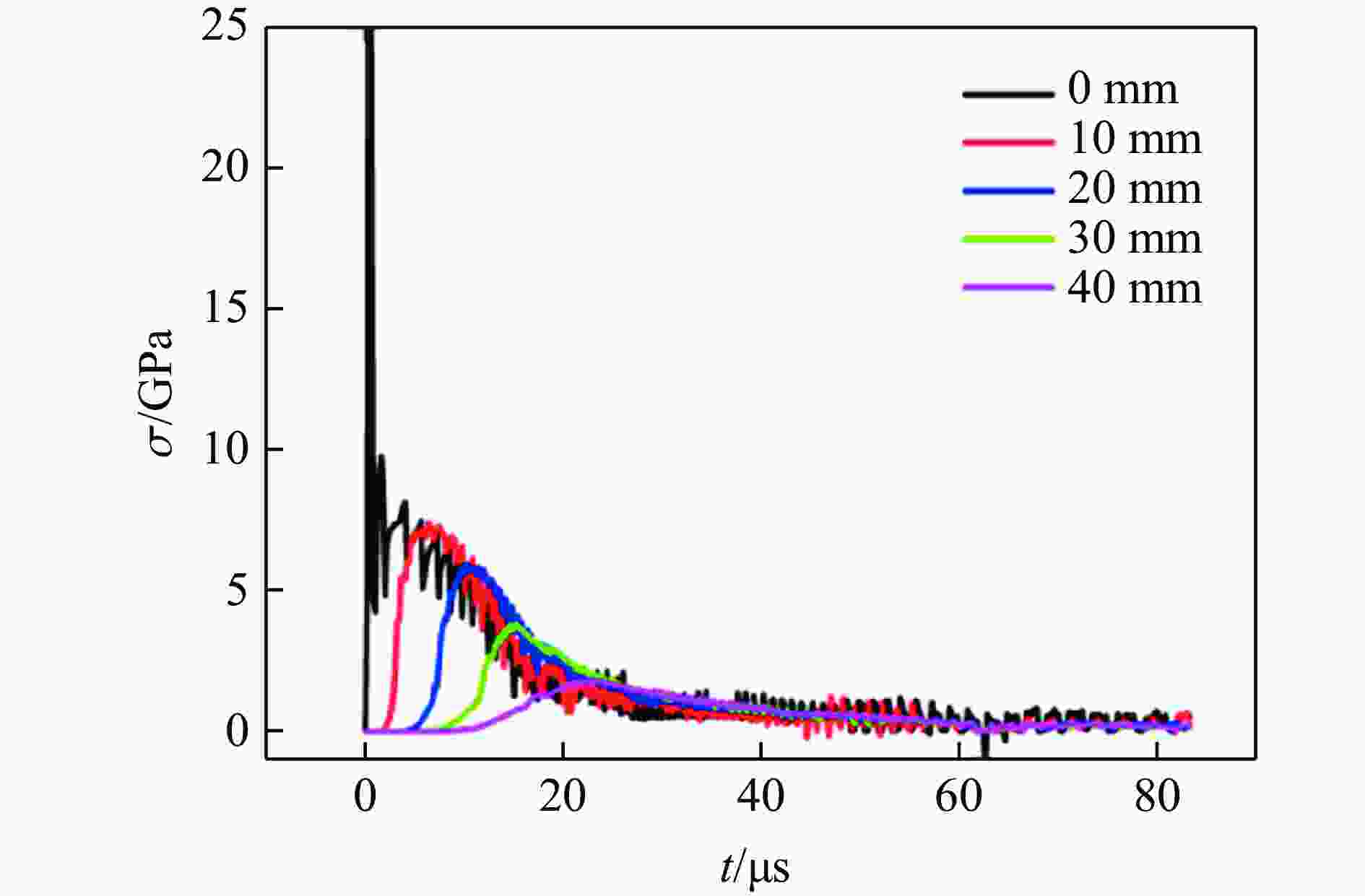
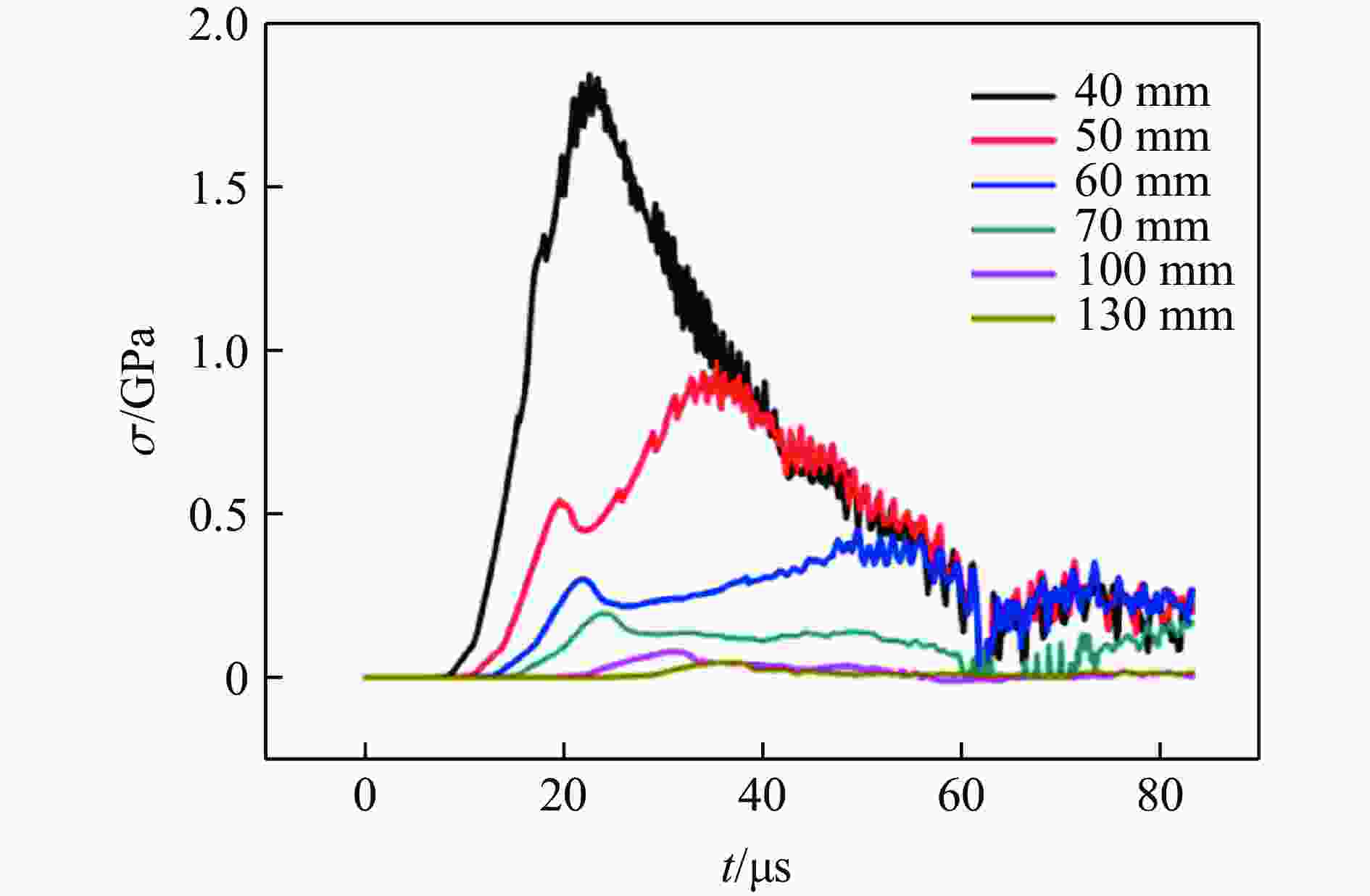
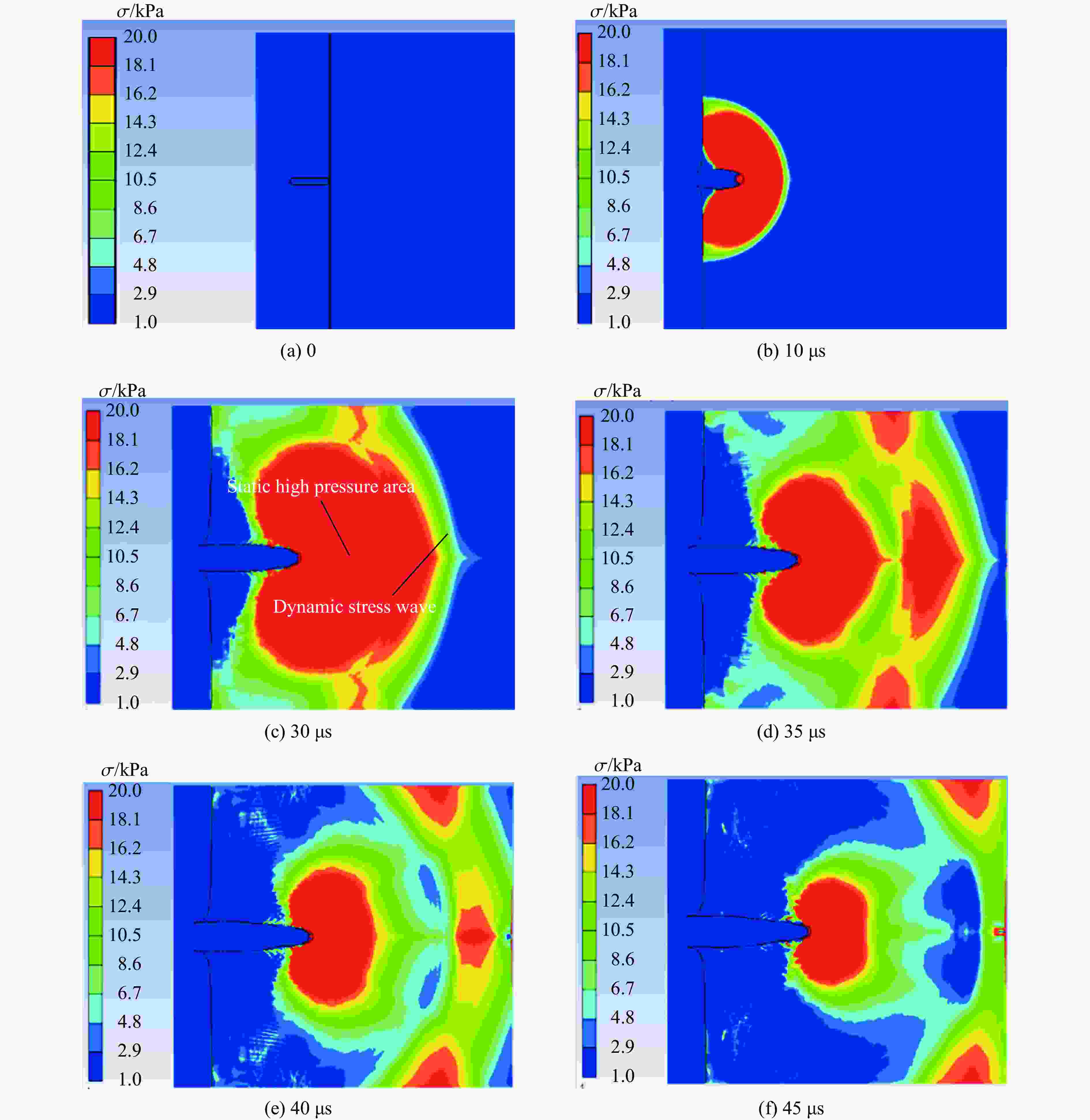
摘要: 为探究超高速撞击条件下混凝土靶内的应力波特性,建立了基于PVDF(polyvinylidene difluoride)压电应力计的应力波测试系统,研究了PVDF压电应力计的标定方法,测量了克级柱形93W钨合金弹体超高速撞击条件下混凝土靶体内的应力波形,并利用数值模拟方法分析了应力波的产生和传播机制。结果表明:PVDF压电应力计的动态灵敏度系数为(17.5±0.5) pC/N;信噪比高的超高速撞击条件下实验测量的混凝土靶内的应力波形与数值模拟结果吻合较好,模拟和实验获得的应力波峰值的最大偏差不超过20%。Abstract: To investigate the stress wave characteristics within concrete targets under hypervelocity impact, a stress wave testing system based on polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) piezoelectric stress gauges was established. A calibration method for PVDF piezoelectric stress gauges was proposed and conducted. The stress waveforms within concrete targets impacted by kilogram-scale cylindrical 93W tungsten alloy projectiles at hypervelocity were measured, and the generation and propagation mechanisms of stress waves were analyzed using numerical simulation methods. The following conclusions were drawn: (1) the dynamic characteristic parameters of the PVDF piezoelectric stress gauge were calibrated to yield a dynamic sensitivity coefficient of (17.5±0.5) pC/N for the PVDF piezoelectric stress gauge; (2) high signal-to-noise ratio stress waveforms within the concrete target under hypervelocity impact conditions were obtained using the PVDF piezoelectric stress gauge; (3) the stress waveforms obtained from numerical simulation were in good agreement with the experimentally measured waveforms where the maximum deviation of the stress wave peak values between simulation and experimental results is less than 20%, providing a useful tool for mechanism exploration; (4) the characteristics of stress waves within the concrete target and the mechanisms of generation and attenuation were further explored using numerical simulation methods.
-
Key words:
- hypervelocity impact /
- stress wave /
- PVDF /
- tungsten alloy projectile /
- concrete target /
- two-stage light gas gun
-
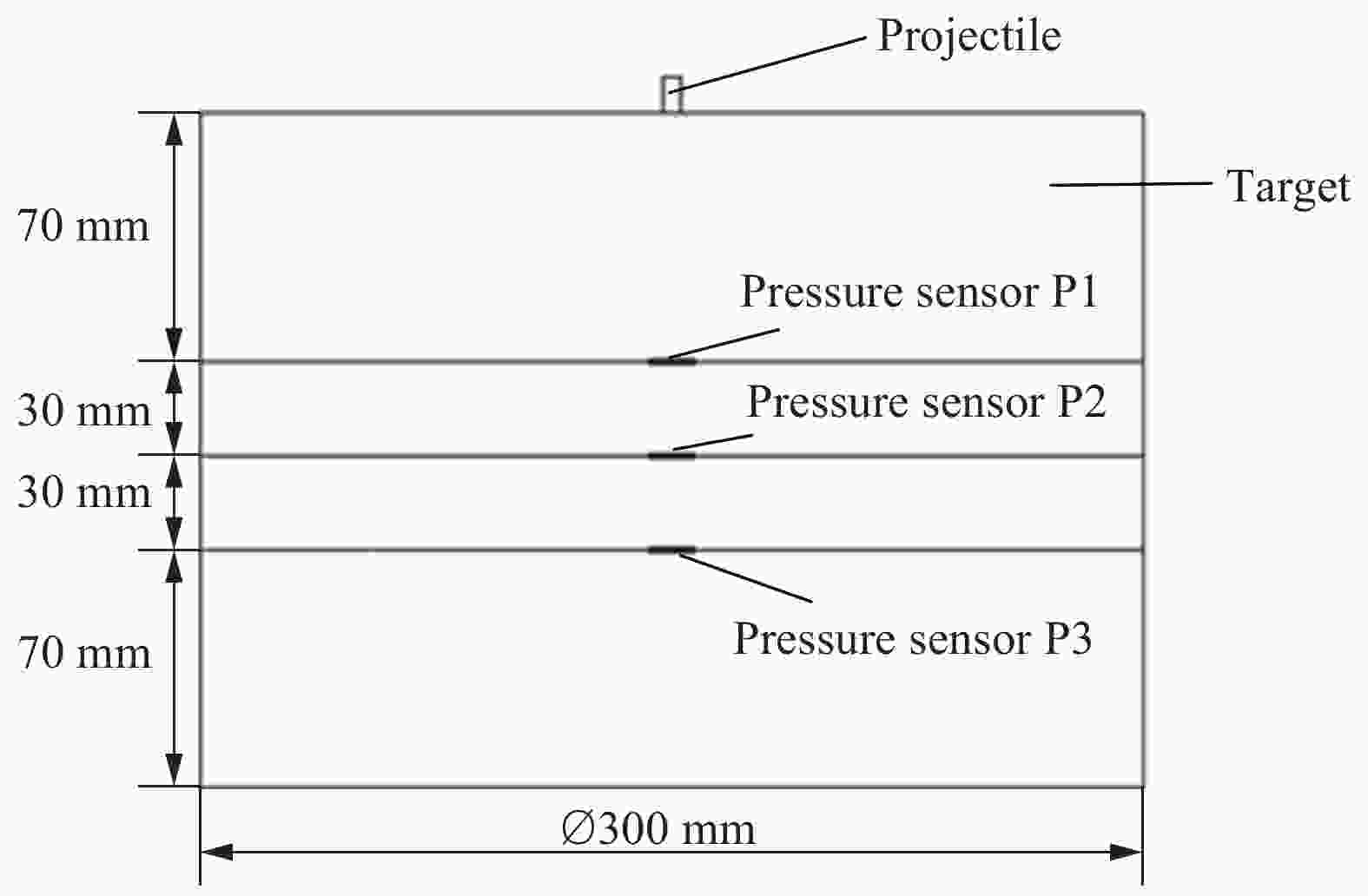
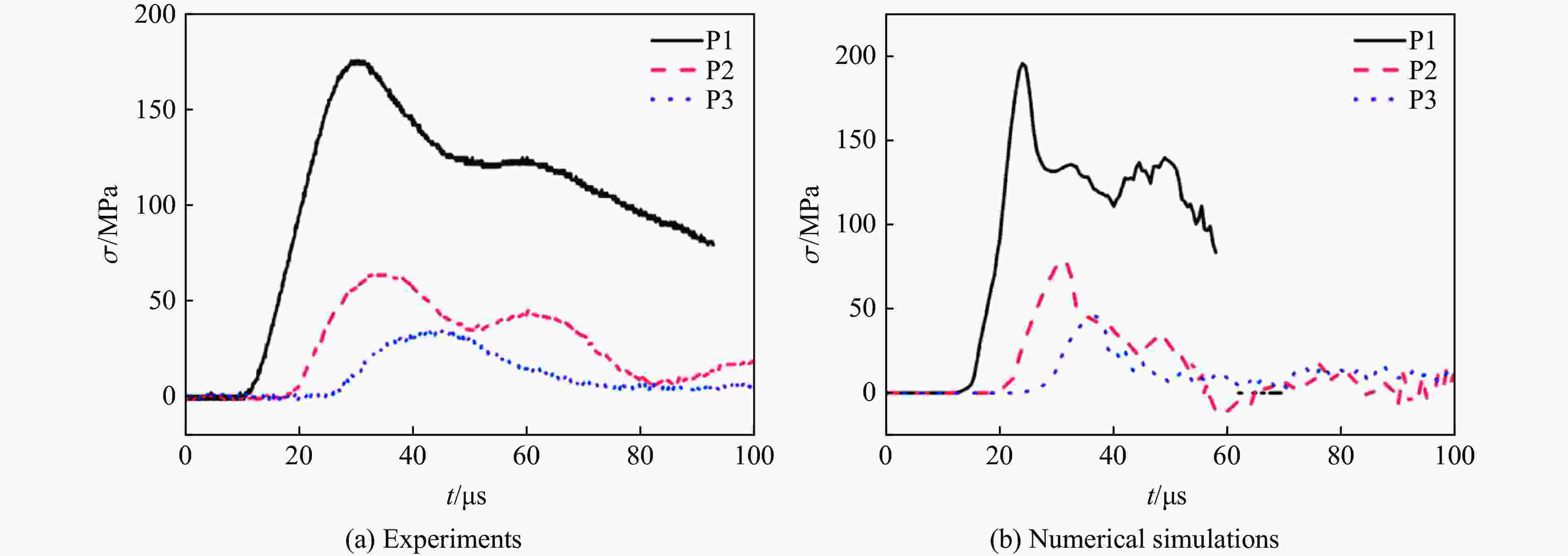
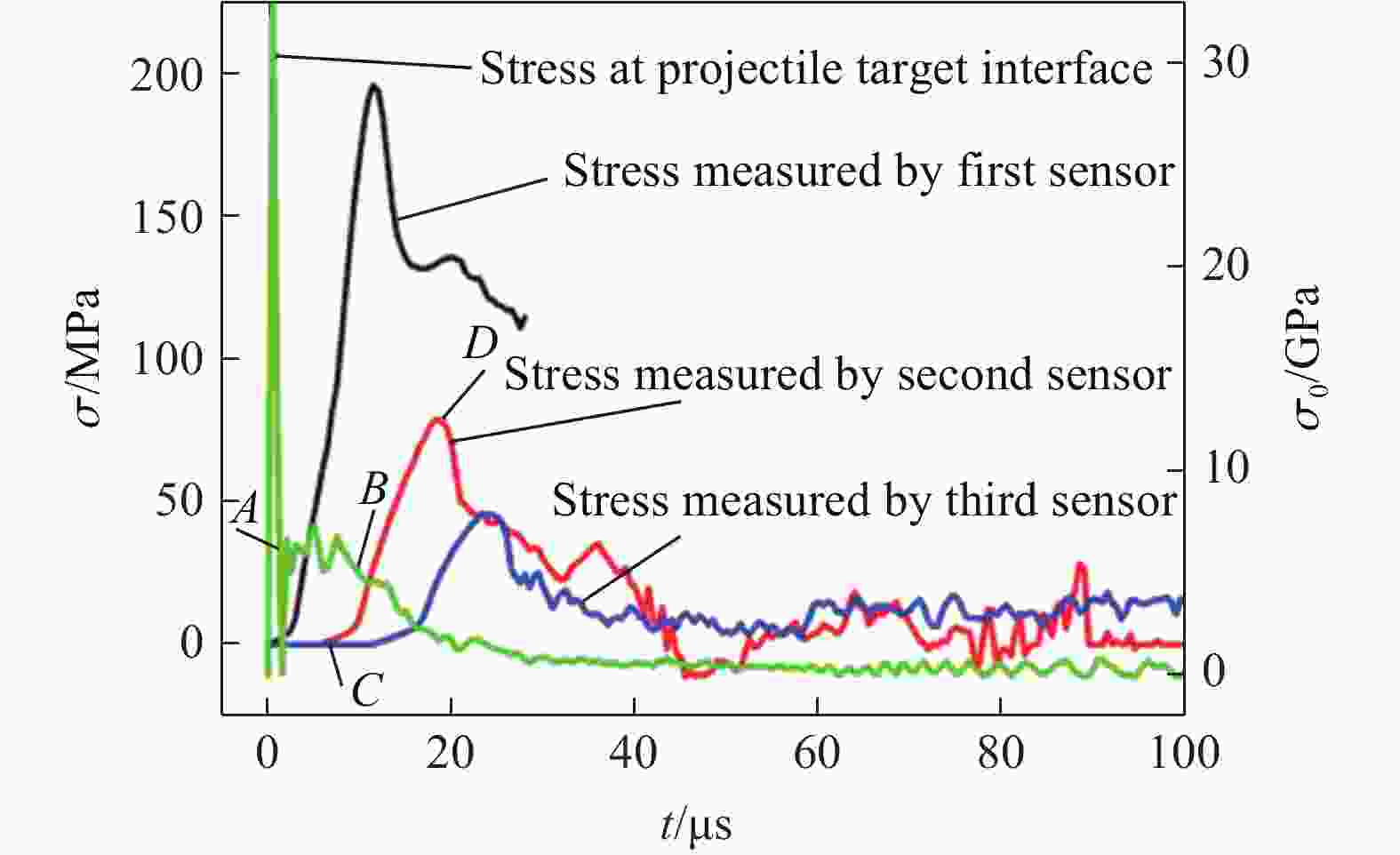
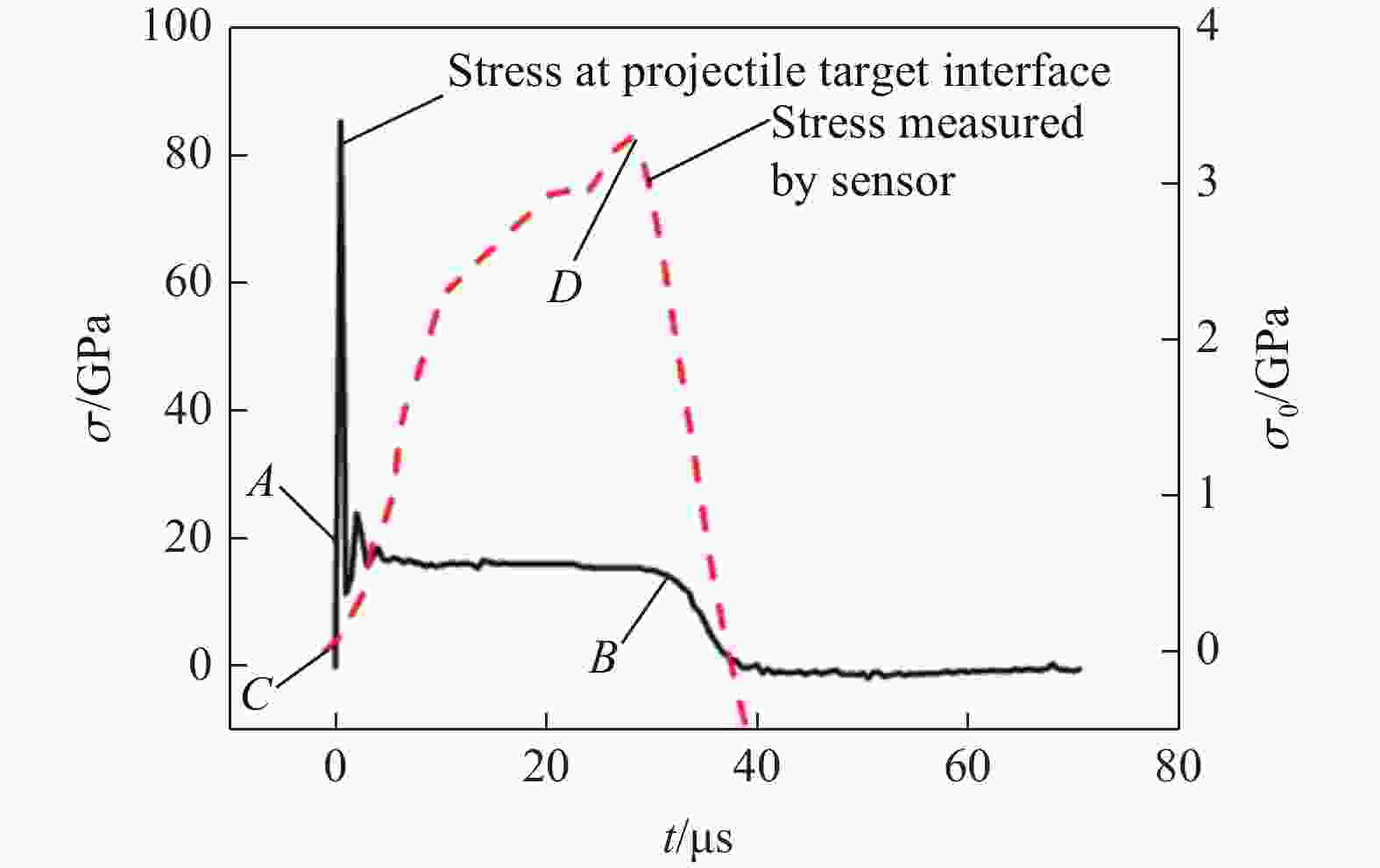
表 1 弹速为3.08 km/s时数值模拟得到的 应力峰值与实验结果的对比
Table 1. Comparison of stress wave peaks obtained by numerical simulation and experiment at the impact velocity of 3.08 km/s
传感器 应力峰值/MPa 误差/% 实验 模拟 P1 175.1 196 11.94 P2 64.1 75.6 17.94 P3 34.5 39.5 14.49 -
[1] SHIRAI K, KATO M, MITANI N K, et al. Laboratory impact experiments and numerical simulations on shock pressure attenuation in water ice [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 2008, 113(E11): E11002. DOI: 10.1029/2008JE003121. [2] NAKAZAWA S, WATANABE S, IIJIMA Y, et al. Experimental investigation of shock wave attenuation in basalt [J]. Icarus, 2002, 156(2): 539–550. DOI: 10.1006/icar.2001.6729. [3] 王明洋, 岳松林, 李海波, 等. 超高速弹撞击岩石的地冲击效应等效计算 [J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(12): 2655–2663. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0473.WANG M Y, YUE S L, LI H B, et al. An equivalent calculation method of ground shock effects of hypervelocity projectile striking on rock [J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(12): 2655–2663. DOI: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0473. [4] 牛雯霞, 黄洁, 罗锦阳, 等. 超高速撞击混凝土冲击压力测量与分析 [J]. 兵工学报, 2009, 30(S2): 242–246.NIU W X, HUANG J, LUO J Y, et al. Measurement and analysis for shock pressure in hypervelocity impact on concrete target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(S2): 242–246. [5] KAWAI H. The piezoelectricity of poly (vinylidene fluoride) [J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 1969, 8(7): 975. DOI: 10.1143/JJAP.8.975. [6] BAUER F. Method and device for polarizing ferroelectric materials: US4611260 [P]. 1986. [7] GRAHAM R A, LEE L M, BAUER F. Response of Bauer piezoelectric polymer stress gauges (PVDF) (polyvinylidene fluoride) to shock loading [R]. Albuquerque: Sandia National Labs. , 1987. [8] 席道瑛, 郑永来. PVDF压电计在动态应力测量中的应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1995, 15(2): 174–179.XI D Y, ZHENG Y L. Application of PVDF gauges to dynamical stress measurements [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1995, 15(2): 174–179. [9] 李焰, 钟方平, 刘乾, 等. PVDF在动态应变测量中的应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2003, 23(3): 230–234.LI Y, ZHONG F P, LIU Q, et al. Application of PVDF to dynamic strain measurement [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2003, 23(3): 230–234. [10] 巫绪涛, 胡时胜, 田杰. PVDF应力测量技术及在混凝土冲击实验中的应用 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2007, 27(5): 411–415. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)05-0411-05.WU X T, HU S S, TIAN J. Stress-measurement method by PVDF gauge and its application to impact test for concrete [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2007, 27(5): 411–415. DOI: 10.11883/1001-1455(2007)05-0411-05. [11] 黄家蓉, 王晓峰, 吴飚, 等. 超高速撞击过程产生的电磁脉冲对测试信号的干扰 [J]. 防护工程, 2018, 40(2): 24–29.HUANG J R, WANG X F, WU B, et al. Electromagnetic pulse interference to measure signal in hypervelocity impact [J]. Protective Engineering, 2018, 40(2): 24–29. [12] 李孝兰. 硬岩中大当量地下爆炸应力波的测试和分析 [J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 20(4): 393–395. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2001.04.003.LI X L. Stress wave measurement and analyses of the underground explosions in hard rock with large yield [J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 2001, 20(4): 393–395. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2001.04.003. [13] 张景森, 裴明敬, 胡华权, 等. 基于PVDF薄膜的水中冲击波压力测量技术 [J]. 现代应用物理, 2013, 4(3): 289–292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6223.2013.03.013.ZHANG J S, PEI M J, HU H Q, et al. Measurement of underwater shock waves pressure with PVDF film [J]. Modern Applied Physics, 2013, 4(3): 289–292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6223.2013.03.013. [14] 才源, 庞宝君, 曲鑫, 等. 球形压力容器超高速撞击应力波传播特性研究 [J]. 热加工工艺, 2021, 50(4): 25–28. DOI: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20193055.CAI Y, PANG B J, QU X, et al. Research on stress wave propagation characteristics of gas-filled spherical pressure vessel under hypervelocity impact [J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021, 50(4): 25–28. DOI: 10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.20193055. [15] 谢呈瑞. 基于PVDF的空间碎片撞击航天器定位算法及系统集成 [D]. 沈阳: 沈阳理工大学, 2023. DOI: 10.27323/d.cnki.gsgyc.2023.000184.XIE C R. Space debris impact spacecraft location algorithm and system integration based on PVDF [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Ligong University, 2023. DOI: 10.27323/d.cnki.gsgyc.2023.000184. [16] 刘震. 柔性防护结构嵌入式超高速撞击感知技术研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2022. DOI: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2022.004542.LIU Z. Research on embedded hypervelocity impact sensing technology of flexible protective structure [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022. DOI: 10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2022.004542. [17] 张德志, 唐润棣, 林俊德, 等. 新型气体驱动二级轻气炮研制 [J]. 兵工学报, 2004, 25(1): 14–18. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.01.004.ZHANG D Z, TANG R D, LIN J D, et al. Development of a new type gas-driven two-stage light gas gun [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2004, 25(1): 14–18. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1093.2004.01.004. [18] 钱秉文, 周刚, 李进, 等. 钨合金弹体超高速撞击混凝土靶成坑特性研究 [J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2018, 38(10): 1012–1017. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.10.004.QIAN B W, ZHOU G, LI J, et al. Study of the crater produced by hypervelocity tungsten alloy projectile into concrete target [J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2018, 38(10): 1012–1017. DOI: 10.15918/j.tbit1001-0645.2018.10.004. [19] 钱秉文, 周刚, 李进, 等. 钨合金柱形弹超高速撞击水泥砂浆靶的侵彻深度研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(8): 139–147. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0141.QIAN B W, ZHOU G, LI J, et al. Penetration depth of hypervelocity tungsten alloy projectile penetrating concrete target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2019, 39(8): 139–147. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0141. [20] 庞宝君, 杨震琦, 王立闻, 等. PVDF压电计的动态响应特性及其在橡胶材料SHPB实验中的应用 [J]. 高压物理学报, 2010, 24(5): 359–367. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2010.05.007.PANG B J, YANG Z Q, WANG L W, et al. PVDF stress gauges dynamic stress measurement and its application to SHPB experiment for rubber materials [J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2010, 24(5): 359–367. DOI: 10.11858/gywlxb.2010.05.007. [21] 邓国强, 杨秀敏. 超高速武器对地打击效应数值仿真 [J]. 科技导报, 2015, 33(16): 65–71. DOI: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.16.010.DENG G Q, YANG X M. Numerical simulation of damage effect of hyper velocity weapon on ground target [J]. Science & Technology Review, 2015, 33(16): 65–71. DOI: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.16.010. [22] 唐奎. 两种非均质长杆弹芯侵彻半无限厚金属靶研究 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2020. DOI: 10.27241/d.cnki.gnjgu.2020.000068.TANG K. Investigations on the penetration of semi-infinite metal target by two types of heterogeneous long rod penetrators [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2020. DOI: 10.27241/d.cnki.gnjgu.2020.000068. -






 下载:
下载: