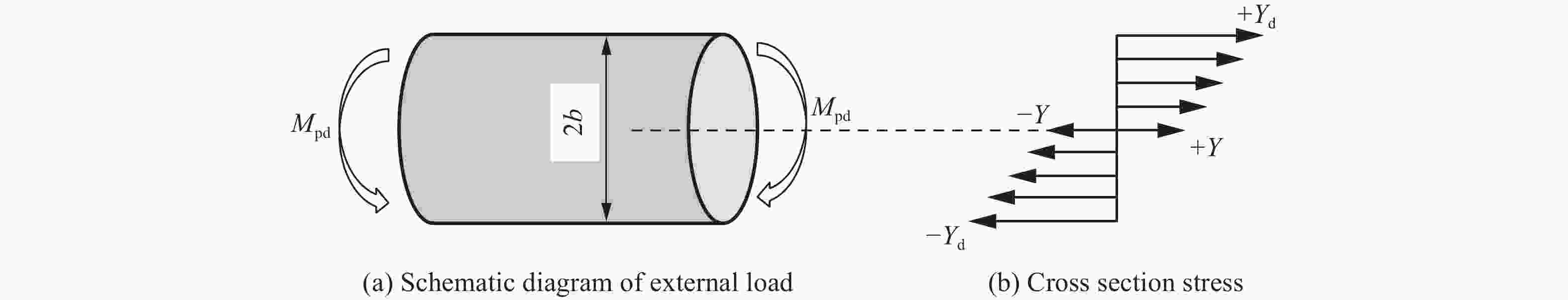
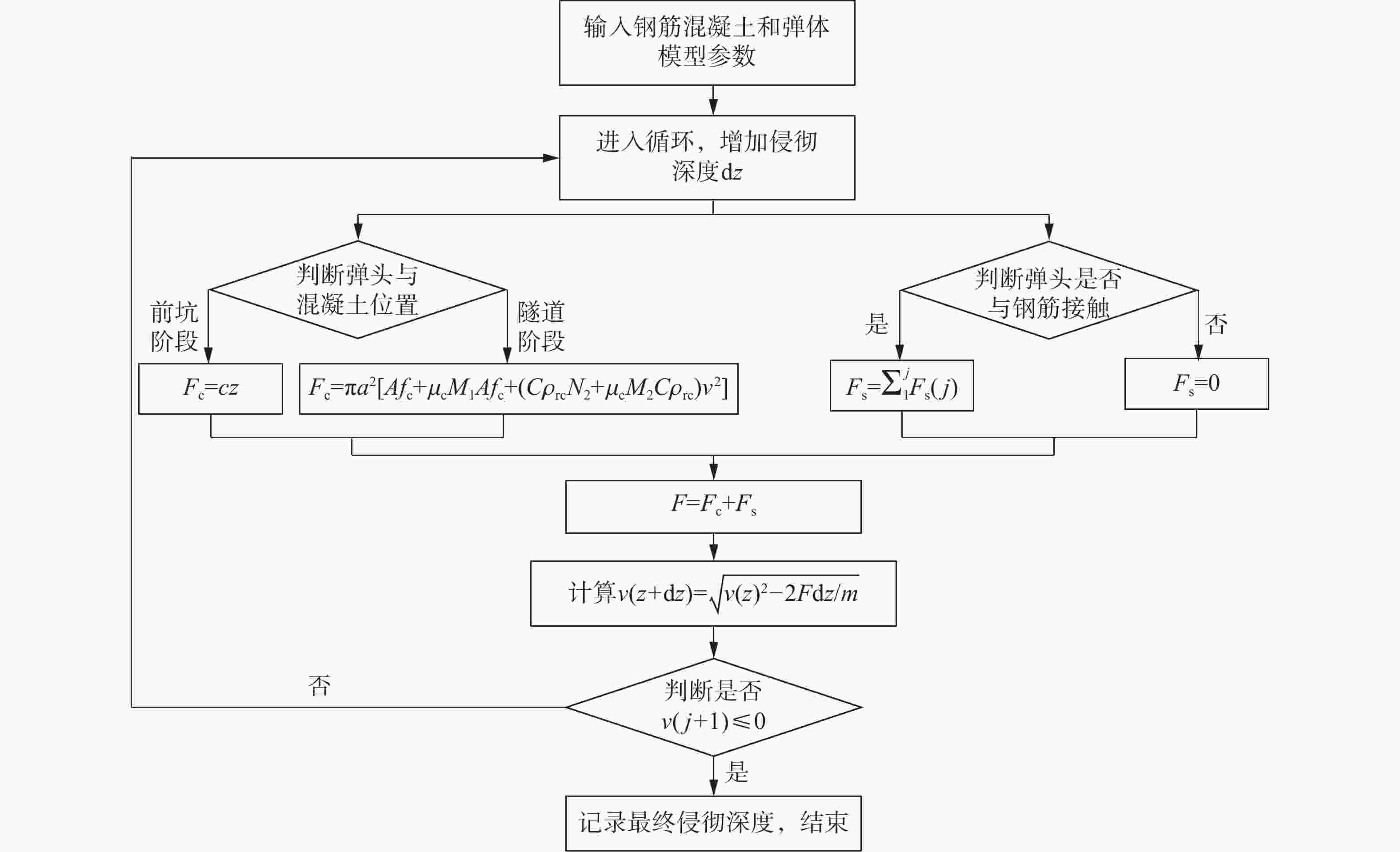
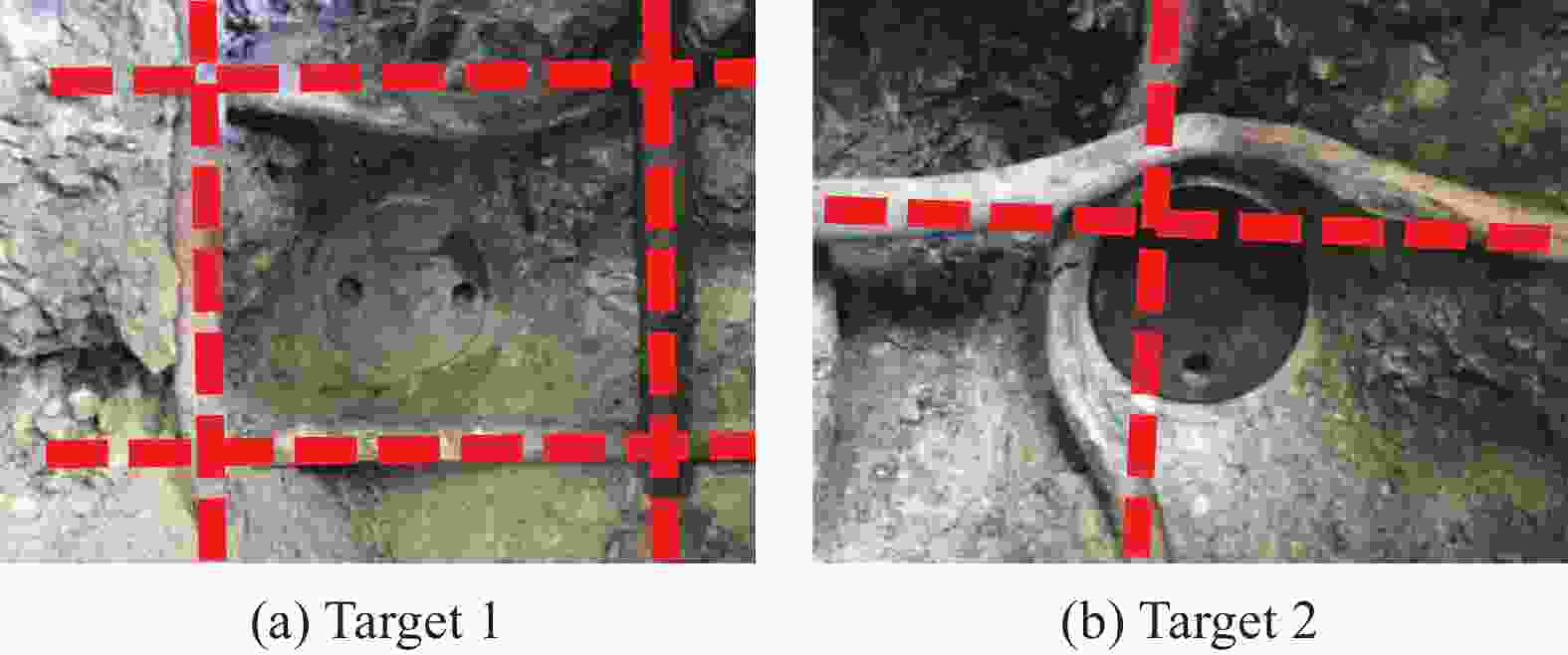
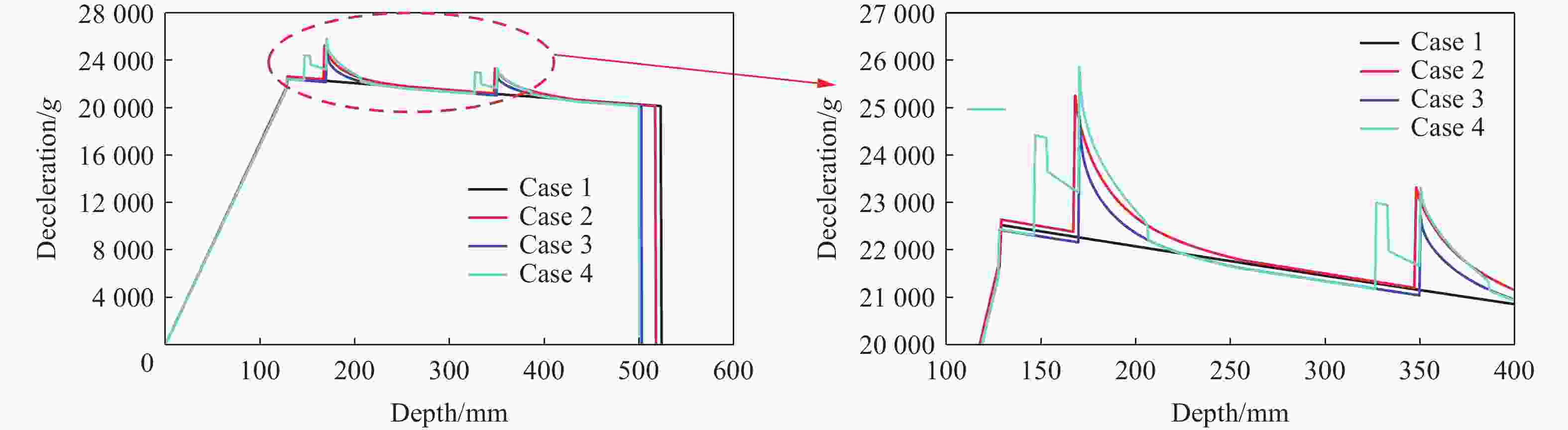
Resistance equation of projectile penetrating into reinforced concrete shield
-
摘要: 为研究弹体在侵彻钢筋混凝土受到阻力的问题,分析了现有钢筋有限长度固支梁理论模型的局限,根据钢筋屈服准则研究和耗能分析,提出了弹体直接命中钢筋剪切-塑性铰链模型,以及弹体与钢筋侧面接触时的塑性弦模型,通过耗能分析得到了弹体直接阻力函数;以空腔膨胀理论模型为基础,根据弹体侵彻深度经验公式计算结果,得到了钢筋间接影响下混凝土的阻力方程。通过与已有试验数据对比,验证了理论模型的合理性。通过分析钢筋屈服强度、直径、网眼尺寸等配筋方式,以及弹体命中部位对遮弹层抗侵彻性能的影响,给出了遮弹层配筋设计建议:相邻两层钢筋网错孔设置;钢筋网眼与弹体直径之比宜设为0.5~0.8;应结合钢筋极限塑性应变进行高强钢筋选择。Abstract: To study the penetration resistance to the projectile by the reinforced concrete, the mechanical response of reinforcing bars under the dynamic constraint of both the projectile and concrete was analysed and the limitation of existing finite-length rigid beam models have been obtained. Based on this foundation, a shear-plastic hinge model was used to analyze the case of a projectile directly hitting the reinforcing bars, and a plastic string model was used to analyze the case of a projectile colliding with the side of the reinforcing bars, resulting in a more accurate equation for penetration resistance. In the shear-plastic hinge model, stress analysis was performed based on the shear sliding of the reinforcing bar before fracture, and energy dissipation was calculated based on the deformation of the plastic hinge after the reinforcing bar fractures. In the plastic string model, the yield criterion of reinforcing bars under the combined action of bending moment and axial force was analyzed, and the plastic energy dissipation equations for reinforcing bar tension and bending were established. At the same time, the influence of changes in reinforcing bar kinetic energy was considered. Based on the theoretical model of cavity expansion and the empirical formula for the depth of projectile penetration, the concrete resistance equation under the indirect influence of steel reinforcement was obtained. By comparing with existing test data, the rationality of the theoretical models was verified. By analyzing the yield strength, diameter, mesh size of reinforcing bars, as well as the impact location of projectile, suggestions for the reinforcement design of the bulletproof layer were given. The adjacent two layers of reinforcing bars mesh should be staggered. The ratio of steel mesh to projectile diameter should be set between 0.5 and 0.8. It is not advisable to simply pursue high-strength reinforcing bars, and the ultimate plastic strain of reinforcing bars should also be considered as an important factor.
-
Key words:
- reinforced concrete /
- penetration resistance /
- theoretical model /
- reinforcement design
-
表 1 钢筋混凝土靶侵彻试验工况及结果
Table 1. Test conditions and results of reinforced concrete target penetration test
靶板编号 计划撞击点位置 配筋方式/mm 弹体质量/g 弹体初速度/(m·s−1) 侵彻深度/mm 相对误差/% 试验结果[29] 理论计算结果 1 网眼中心 $ \varnothing $10@75 4914 439 568 523 7.92 2 钢筋交叉点 $ \varnothing $10@75 4920 439 546 503 7.88 3 网眼中心 $ \varnothing $6.5@30 4968 430 552 517 6.34 4 钢筋交叉点 $ \varnothing $6.5@30 4962 431 501 表 2 弹体侵彻钢筋混凝土靶部分影响参数
Table 2. Impact parameters of projectile penetration into reinforced concrete targets
γvol/% 2b/mm sh/mm sh/2a γvol/% 2b/mm sh/mm sh/2a γvol/% 2b/mm sh/mm sh/2a 4 10 26.18 0.17 5 12 30.16 0.2 6 14 34.21 0.23 12 37.70 0.25 14 41.05 0.27 16 44.68 0.3 14 51.31 0.34 16 53.62 0.36 18 56.55 0.38 16 67.02 0.45 18 67.86 0.45 20 69.81 0.47 18 84.82 0.57 20 83.78 0.56 22 84.47 0.56 20 104.72 0.7 22 101.37 0.68 24 100.53 0.67 22 126.71 0.84 24 120.64 0.8 26 117.98 0.79 24 150.8 1.01 26 141.58 0.94 28 136.83 0.91 注:$ {\gamma }_{\text{vol}} $为体积配筋率,2b为钢筋直径,sh为钢筋网眼大小。 -
[1] KENNEDY R P. A review of procedures for the analysis and design of concrete structures to resist missile impact effects [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1976, 37(2): 183–203. DOI: 10.1016/0029-5493(76)90015-7. [2] LI Q M, REID S R, WEN H M, et al. Local impact effects of hard missiles on concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 32(1/2/3/4): 224–284. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2005.04.005. [3] RIERA J D. Penetration, scabbing and perforation of concrete structures hit by solid missiles [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1989, 115(1): 121–131. DOI: 10.1016/0029-5493(89)90265-3. [4] 邓勇军, 陈小伟, 钟卫洲, 等. 弹体正侵彻钢筋混凝土靶的试验及数值模拟研究 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2020, 40(2): 023101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0001.DENG Y J, CHEN X W, ZHONG W Z, et al. Experimental and numerical study on normal penetration of a projectile into a reinforced concrete target [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2020, 40(2): 023101. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2019-0001. [5] LUK V K, FORRESTAL M J. Penetration into semi-infinite reinforced-concrete targets with spherical and ogival nose projectiles [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1987, 6(4): 291–301. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(87)90096-0. [6] BARR P. Guidelines for the design and assessment of concrete structures subjected to impact: SRD-R-439-Issue-2 [R]. London: HMSO, 1988. [7] NDRC. Effects of impact and explosion: summary technical report of division 2, Vol. 1 [R]. Washington DC: National Defense Research Committee, 1946. [8] BERRIAUD C, SOKOLOVSKY A, GUERAUD R, et al. Local behaviour of reinforced concrete walls under missile impact [J]. Nuclear Engineering & Design, 1978, 45(2): 457–469. DOI: 10.1016/0029-5493(78)90235-2. [9] DANCYGIER A N. Effect of reinforcement ratio on the resistance of reinforced concrete to hard projectile impact [J]. Nuclear Engineering & Design, 1997, 172(1/2): 233–245. DOI: 10.1016/S0029-5493(97)00055-1. [10] CHEN X W, LI X L, HUANG F L, et al. Normal perforation of reinforced concrete target by rigid projectile [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(10): 1119–1129. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.01.002. [11] GRISARO H, DANCYGIER A N. A modified energy method to assess the residual velocity of non-deforming projectiles that perforate concrete barriers [J]. International Journal of Protective Structures, 2014, 5(3): 307–321. DOI: 10.1260/2041-4196.5.3.307. [12] XU X Z, MA T B, NING J G. Failure mechanism of reinforced concrete subjected to projectile impact loading [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, 96: 468–483. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2018.11.006. [13] DENG Y J, CHEN X W, SONG W J. Dynamic cavity-expansion penetration model of elastic-cracked-crushed response for reinforced-concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 157: 103981. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103981. [14] LEE S, KIM C, YU Y, et al. Effect of reinforcing steel on the impact resistance of reinforced concrete panel subjected to hard-projectile impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 148: 103762. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103762. [15] 朱擎, 李述涛, 陈叶青. 配筋对超高性能混凝土抗侵彻性能的影响 [J]. 工程力学, 2023, 40(S1): 62–73, 91. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2022.05.S046.ZHU Q, LI S T, CHEN Y Q. Influence of reinforcement on anti-penetration resistance of ultra-high-performance concrete [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2023, 40(S1): 62–73, 91. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2022.05.S046. [16] 张爽, 武海军, 黄风雷. 刚性弹正侵彻钢筋混凝土靶阻力模型 [J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(11): 2081–2092. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.001.ZHANG S, WU H J, HUANG F L. Resistance model of rigid projectile penetrating into reinforced concrete target [J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2017, 38(11): 2081–2092. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.11.001. [17] 黄民荣, 顾晓辉, 高永宏. 刚性弹丸侵彻钢筋混凝土的实验和简化分析模型 [J]. 实验力学, 2009, 24(4): 283–290.HUANG M R, GU X H, GAO Y H. Experiment and simplified analytical model for penetration of rigid projectile in a reinforced concrete target [J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2009, 24(4): 283–290. [18] 黄民荣. 刚性弹体对混凝土靶的侵彻与贯穿机理研究 [D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2011.HUANG M R. Penetration and perforation mechanism of rigid projectile into the concrete target [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2011. [19] HUANG C L, WANG Z Q, LI S T, et al. Analytical model of penetration depth and energy dissipation considering impact position [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2024, 191: 104997. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2024.104997. [20] 刘志林, 孙巍巍, 王晓鸣, 等. 卵形弹丸垂直侵彻钢筋混凝土靶的工程解析模型 [J]. 弹道学报, 2015, 27(3): 84–90. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2015.03.016.LIU Z L, SUN W W, WANG X M, et al. Engineering analytical model of ogive-nose steel projectiles vertically penetrating reinforced concrete target [J]. Journal of Ballistics, 2015, 27(3): 84–90. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-499X.2015.03.016. [21] CHEN X W, LI Q M. Deep penetration of a non-deformable projectile with different geometrical characteristics [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2002, 27(6): 619–637. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00005-2. [22] PENG Y, WU H, FANG Q, et al. A note on the deep penetration and perforation of hard projectiles into thick targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2015, 85: 37–44. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.06.013. [23] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB/T 50081—2019 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019: 145–146.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB/T 50081—2019 Standard for test methods of concrete physical and mechanical properties [S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2019: 145–146. [24] 黄晓莹, 陶俊林. 三种建筑钢筋材料高应变率下拉伸力学性能研究 [J]. 工程力学, 2016, 33(7): 184–189. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.12.1064.HUANG X Y, TAO J L. Tensile mechanical properties research of three construction steel bars in high strain rate [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(7): 184–189. DOI: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.12.1064. [25] NONAKA T. Some interaction effects in a problem of plastic beam dynamics-Part 2: analysis of a structure as a system of one degree of freedom [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1967, 34(3): 631–637. DOI: 10.1115/1.3607754. [26] FREW D J, HANCHAK S J, GREEN M L, et al. Penetration of concrete targets with ogive-nose steel rods [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1998, 21(6): 489–497. DOI: 10.1016/S0734-743X(98)00008-6. [27] FORRESTAL M J, ALTMAN B S, CARGILE J D, et al. An empirical equation for penetration depth of ogive-nose projectiles into concrete targets [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1994, 15(4): 395–405. DOI: 10.1016/0734-743X(94)80024-4. [28] 王安宝, 邓国强, 杨秀敏, 等. 一个新的通用型侵彻深度计算公式 [J]. 土木工程学报, 2021, 54(10): 36–46. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.10.004.WANG A B, DENG G Q, YANG X M, et al. A new general formula for calculating penetration depth [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2021, 54(10): 36–46. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2021.10.004. [29] ZHANG X Y, WU H J, ZHANG S, et al. Projectile penetration of reinforced concrete considering the effect of steel reinforcement: Experimental study and theoretical analysis [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 144: 103653. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103653. -







 下载:
下载: