Effects of discharge state on mechanical responses and failure behaviors of lithium-ion batteries under mechanical abuse conditions
-
摘要: 为厘清放电状态对锂离子电池动态力学响应和失效模式的影响规律,系统地开展了锂离子电池在不同放电状态下的准静态压缩特性及其安全性的实验分析。通过预设电池至特定的放电电量,并在放电过程中、放电后静置1和24 h的时间节点上实施压缩测试,深入探究了电池的力-位移响应特性、最大承载力及安全性表现。实验结果显示,相较于其他状态,放电状态下的电池展现出较低的力-位移曲线,表明其刚度在静置之后相比于放电过程中有所提升。此外,放电状态下的电池展现出显著高于静置后状态的最大承载力,且在放电过程中进行压缩测试更容易使电池发生爆炸,而静置后的电池则表现出显著提升的安全性。借助扫描电子显微镜分析,进一步确认了放电状态下电池内部电极颗粒的破损程度更剧烈,观测到的现象被归因于放电过程中产生的扩散诱导应力,该应力在电池内部累积,加剧了电池在机械压缩下的损伤风险。Abstract: To clarify the influence of the discharge state on the dynamic mechanical response and failure mode of lithium-ion batteries, an experimental analysis of the quasi-static compression characteristics and safety performance of lithium-ion batteries under different discharge states was systematically conducted. By presetting the battery to a specific discharge capacity and conducting compression tests at the time nodes of 1 and 24 h after standing during and after the discharge process, the force-displacement response characteristics, maximum load-bearing capacity and safety performance of the battery were thoroughly explored under varying electrochemical states. The experimental results show that, compared with other states, the battery in the discharge state exhibits a lower force-displacement curve, indicating that its stiffness increases after standing compared with that during the discharge process and this decrease is attributed to the electro-chemical reaction inside the battery during the discharge process. In addition, the battery in the discharge state shows a significantly higher maximum load-bearing capacity than that in the standing state after discharge, and the compression test during the discharge process is more likely to cause the battery to explode, while the battery after standing shows a significantly improved safety. The analysis using scanning electron microscope (SEM) further indicates that the damage degree of the internal electrode particles of the battery in the discharge state is more severe. The observed damage and increased risk of mechanical failure are primarily attributed to the diffusion-induced stress generated during the discharge process, which accumulate and intensify the vulnerability of the battery structure under mechanical compression. This study contributes valuable experimental evidence and theoretical insights that are crucial for advancing the understanding of the mechanical integrity and safety of lithium-ion batteries under operational stresses. The findings underscore the importance of considering discharge states in the safety design and evaluation of lithium-ion batteries, potentially leading to enhanced durability and safer application in practical scenarios.
-
在新能源汽车领域,锂离子电池在面临外部冲击载荷时所产生的潜在安全风险,已成为该领域亟待解决的关键问题。具体而言,当电池遭受如碰撞、压缩或挤压等极端机械载荷时,可能会引发电池内部短路、热失控,甚至起火和爆炸等严重安全事故,这些问题已成为当前电池安全性研究的热点与难点。因此,深入探究锂离子电池在上述极端条件下的性能表现与安全性,开展模拟实际工况的测试与分析,具有重要的理论和应用价值[1-2]。
学者们通过多样化的力学测试方法来深入探究电池在受到冲击载荷时的性能表现与失效机理。初期研究聚焦于基础力学测试,用以评估电池在准静态及动态加载下的机械结构完整性。Sahraei等[3]和Zhu等[4]通过压缩、压痕和三点弯曲等基本力学测试,系统地分析了锂离子电池在准静态和动态加载条件下的力学性能。Xu等[5]和Liu等[6]进一步对电池在动态加载下的失效模式进行了细致的分类研究,深化了对电池动态失效过程和失效机制的理解。之后,贴近实际工况的动态加载条件,以及电池在这些条件下出现的内部损伤与安全问题得到更多关注。Wang等[7]利用分离式霍普金森压杆(split Hopkinson pressure bar,SHPB)技术提升了电池冲击测试的速度,分析了锂离子电池在轴向冲击波载荷作用下的动态响应和安全性能。Zheng等[8]聚焦于锂离子电池在受限压缩条件下的失效行为,直观地揭示了方形锂离子电池受冲击后卷绕层的断裂和分层现象。Yu等[9] 采用爆炸载荷测试评估了电池的耐损伤性能,为电池在极端加速度影响下的安全使用提供了重要依据。同时,电池冲击失效的研究也逐渐从单一电池拓展至更为复杂的电池包系统。Hu等[10]系统探讨了动态碰撞条件下电池包的冲击响应,为电池包的安全性分析提供了重要参考。Santosa等[11]则通过SHPB模拟了子弹高速穿透电池包的过程,分析了电池包在极端情况下的失效破坏模式。
随着研究的不断深入,电池在冲击载荷下的力-电耦合行为以及潜在的内部损伤也逐渐得到关注。Zhou等[12]研究了锂离子电池在碰撞后的损伤评估方法,特别关注了电池在适度变形但未发生热失控情况下的性能表现。Liu等[13]通过压痕测试监测了软包锂离子电池受损后的力-电-热响应,为电池的安全性评估提供了更全面的数据支持。在这一背景下,Wang等[14]和Chen等[15]对方形锂离子电池进行了不同位置、不同速度和不同次数的冲击实验研究,精确量化了电池受到机械冲击后的损伤程度和热失控发生的临界条件。
尽管上述研究取得了显著进展,丰富了对锂离子电池在受到外部冲击载荷时安全性表现的认识,但大多数研究仍为基于电池处于静态或特定电化学状态的实验测试。然而,在汽车服役过程中的真实工作状态下,电池通常处于动态放电状态,其在此状态下的冲击响应特性与静置状态存在显著差异,这一点在现有测试研究中尚未得到充分考虑。因此,亟需研究电池在放电状态下遭受机械冲击的行为,以更准确地模拟和评估汽车在实际碰撞情况下的电池安全性。
鉴于锂离子电池在实际应用中的广泛性和其安全性问题的日益凸显,本文中致力于系统地探究锂离子电池在不同放电状态下的准静态压缩特性及其安全性表现。具体而言,通过精确控制电池的放电电量,并在多个关键时间点(即放电过程中、放电后静置1和24 h)进行压缩测试,以全面捕捉电池的力学响应特性和安全性变化。借助扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)技术,进一步深入分析放电状态下电池内部电极颗粒的微观破损机制。通过这些综合性的实验分析和理论探讨,以期为锂离子电池在实际应用中的安全性评估和提升提供科学依据和技术支撑。
1. 实验方法
1.1 试样选择
选用SAMSUNG公司生产的INR21700电池为研究对象。该电池正极材料为三元锂材料NMC,负极材料为石墨,电池尺寸为
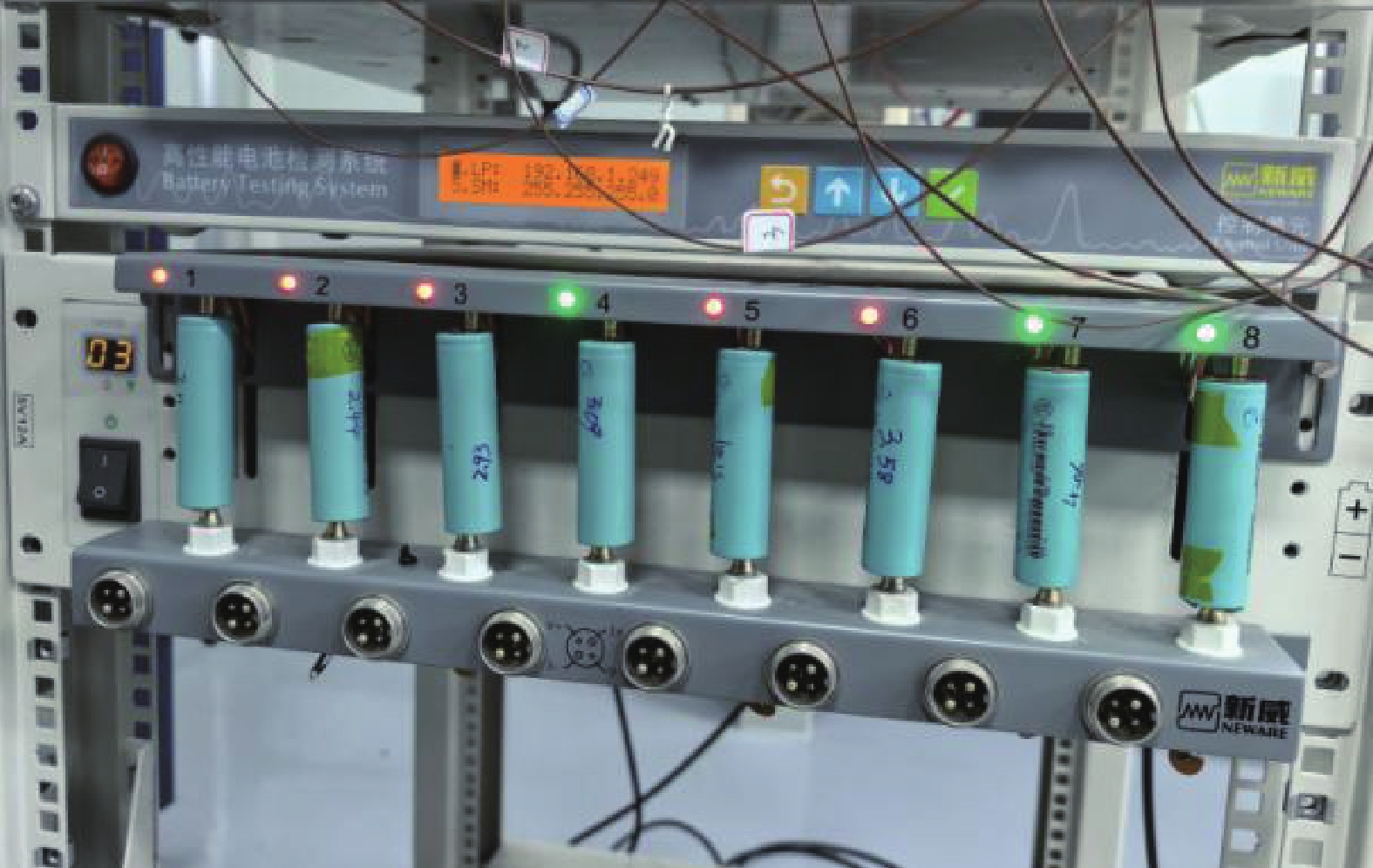
∅ 21 mm × 70 mm,容量为5000 mA∙h,额定电压为3.6 V。为了确保锂离子电池电化学性质的一致性,在新威CT-4000高性能电池测试系统中进行充放电测试,如图1所示。首先,以5.0 A的电流对电池进行恒流放电至电压降至2.80 V,随后进行恒压放电直至截止电流0.1 A;接着,以5.0 A的电流进行恒流充电至电压升至4.20 V,再进行恒压充电直至截止电流0.1 A。从经过测试的电池中挑选出容量一致的样品。
1.2 实验设置
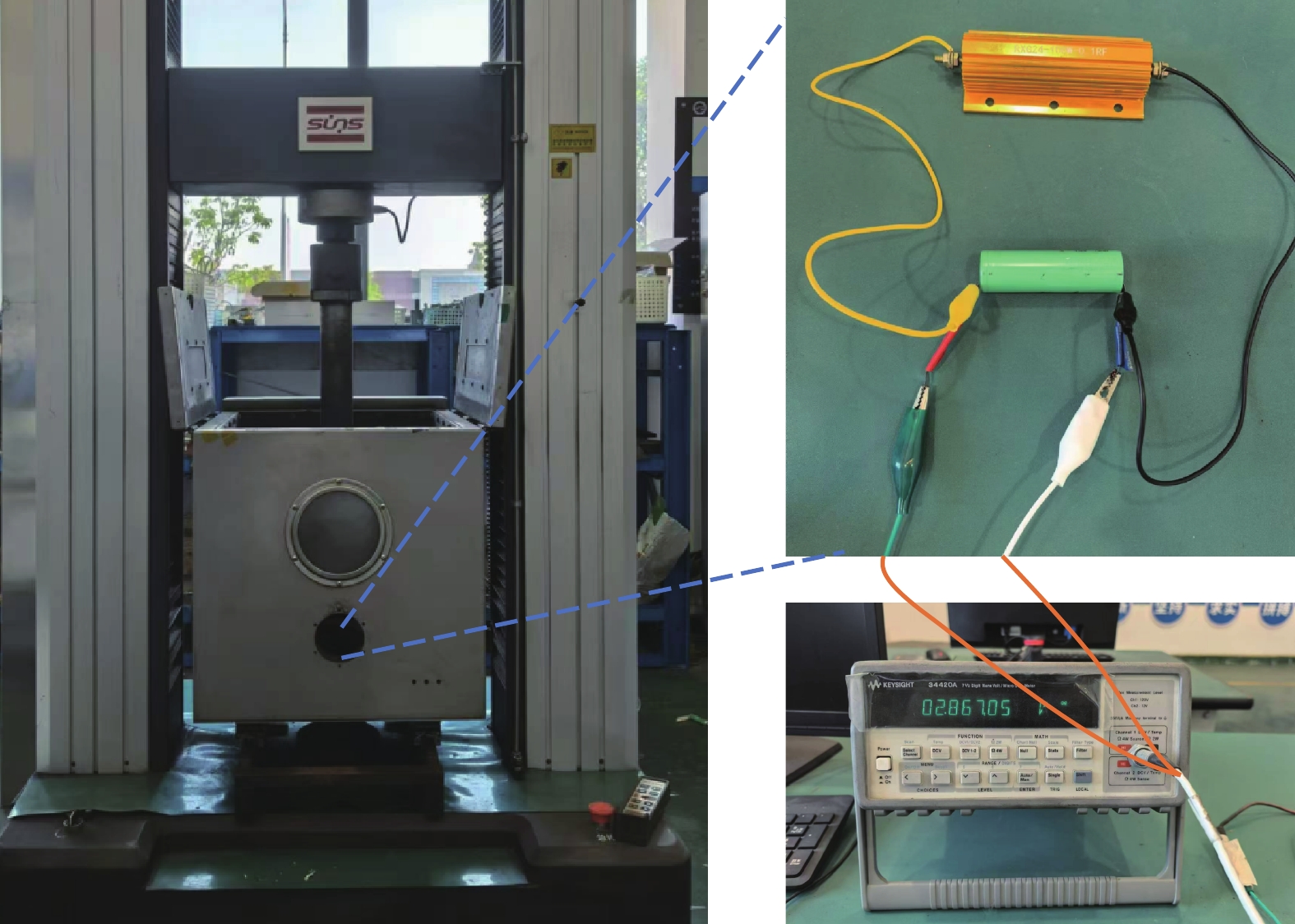
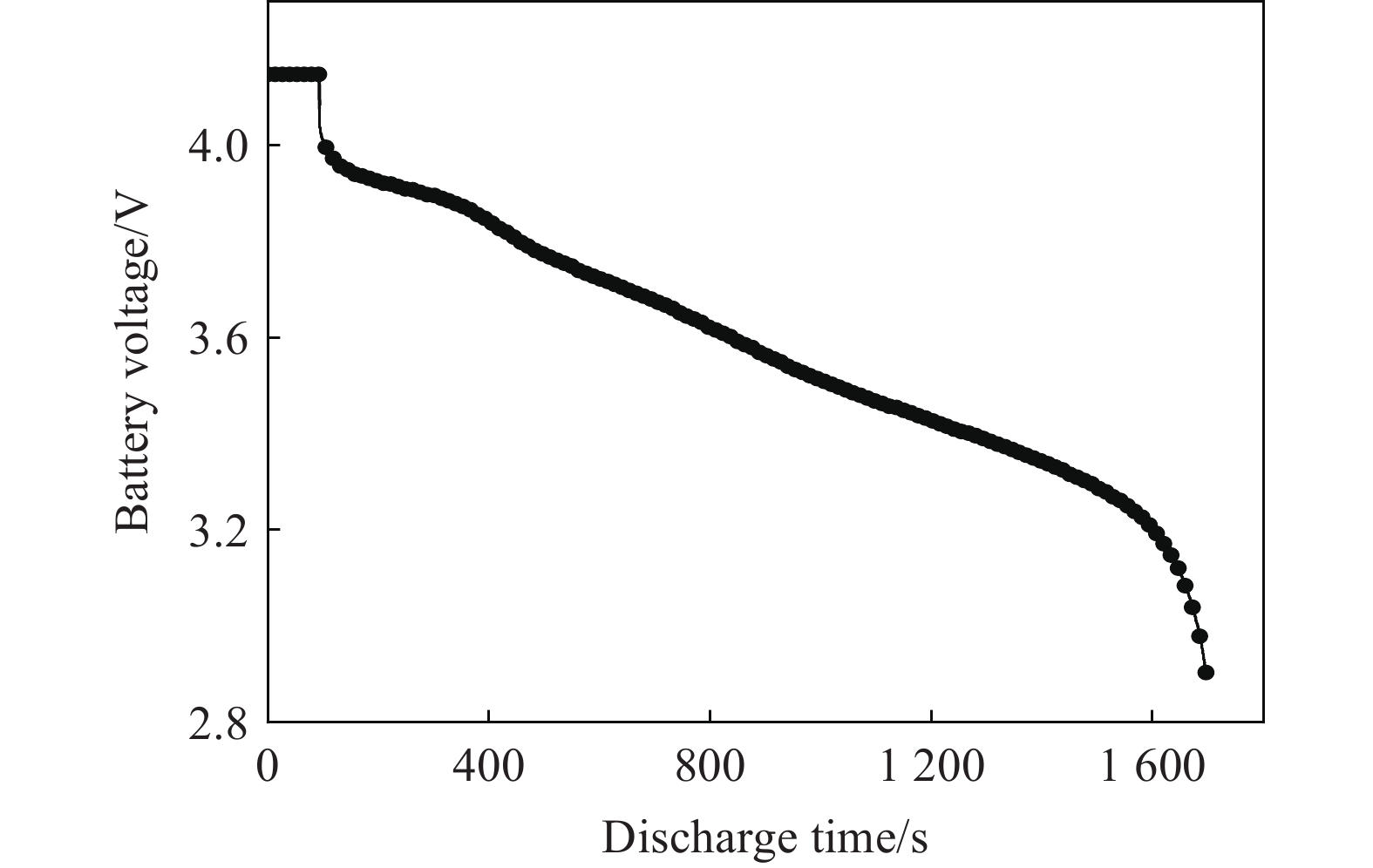
为了探究锂离子电池在放电过程中受到机械载荷作用下的动态力学性能,本研究设计并实施了一系列实验。实验中,通过在电池上外接0.5 Ω的电阻,模拟了电池在实际使用中的放电过程,并利用Keysight 34420A万用表精确记录了电池放电过程中的电压变化,电池的典型放电过程如图2所示。
在实验准备阶段,将充满电的电池静置3 h,以确保电池的电化学状态达到平衡,并将此满电状态作为电池力学测试的初始状态。共设置3组实验,首先将3组电池均进行不同时间的放电,放电时长分别为0、5、11、16、21和26 min。参考现有国家标准GB 38031—2021《电动汽车用动力蓄电池安全要求》和GB/T 21498—2021《电动汽车碰撞后安全要求》中实验电池静置时长,取出2组实验电池在放电后分别静置1和24 h,并记录电压的恢复值,并使用三思材料试验机对电池进行机械载荷滥用的准静态平面压缩测试,实验平台及实验方法如图3所示。压缩测试速度设定为60 mm/min,记录电池在受压缩过程中的反作用力-位移曲线变化。电池的放电过程和机械滥用测试过程均在室温状态下进行。
2. 实验结果
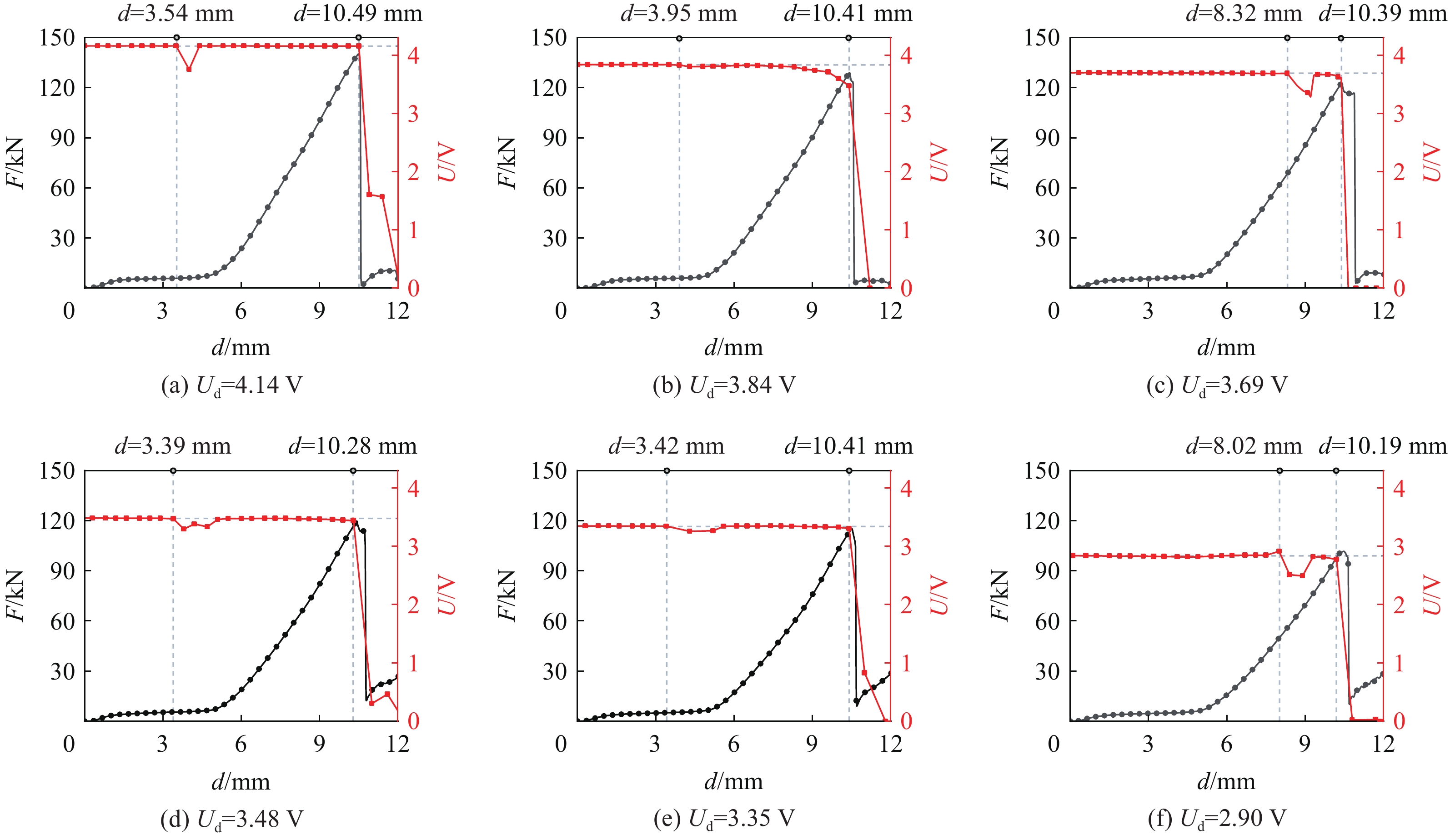
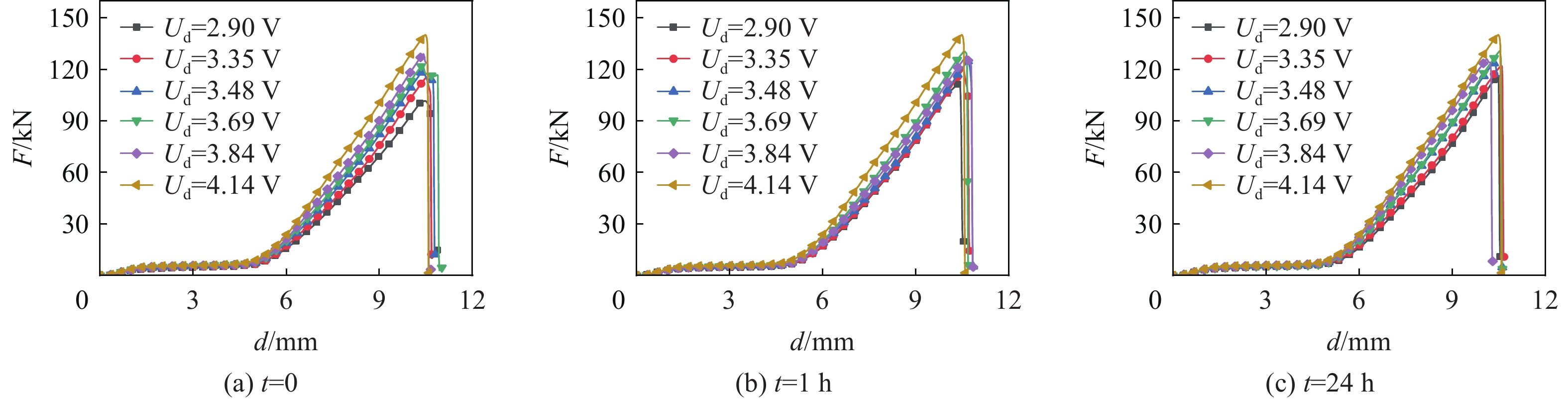
为了确保结果的可靠性和准确性,对各种工况都进行了3次重复性实验。由于3次实验结果重复性较好,数据间的差异在可接受范围内,因此,在后续的分析和讨论中,只选择了其中一组最具代表性的数据进行了展示。当电池放电到不同电压Ud后直接(即静置时间t=0)受到机械滥用载荷作用,产生的反作用力-位移(F-d)曲线和电池电压-位移(U-d)曲线如图4所示。当电池受到机械滥用载荷时的电压分别为4.14、3.84、3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V时,电压-位移曲线分别在位移为3.54、3.95、8.32、3.39、3.42和8.02 mm时发生不同程度的下降,之后再恢复到初始状态,即电池发生软短路,而后在位移分别达到10.49、10.41、10.39、10.28、10.41和10.19 mm时,电池发生硬短路,电压快速下降至2 V以下。
在电池放电到不同程度直接进行压缩测试的所有反作用力-位移曲线中,电池的反作用力均表现出先上升,随后经过一段缓慢的上升阶段后急速上升,到达最大值后急剧下降,电池发生破裂。当电池受到挤压作用时的电压分别为4.14、3.84、3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V时,对应的最大反作用力分别为140.22、129.02、122.96、119.69、114.80和100.93 kN。随着电池放电深度的增加,电池的最大反作用力逐渐降低。
当电池放电到4.14、3.84和3.69 V进行机械滥用测试时,电池在硬短路后发生起火爆炸,而电池放电到3.48、3.35和2.90 V进行机械滥用测试时,电池并未发生起火爆炸。
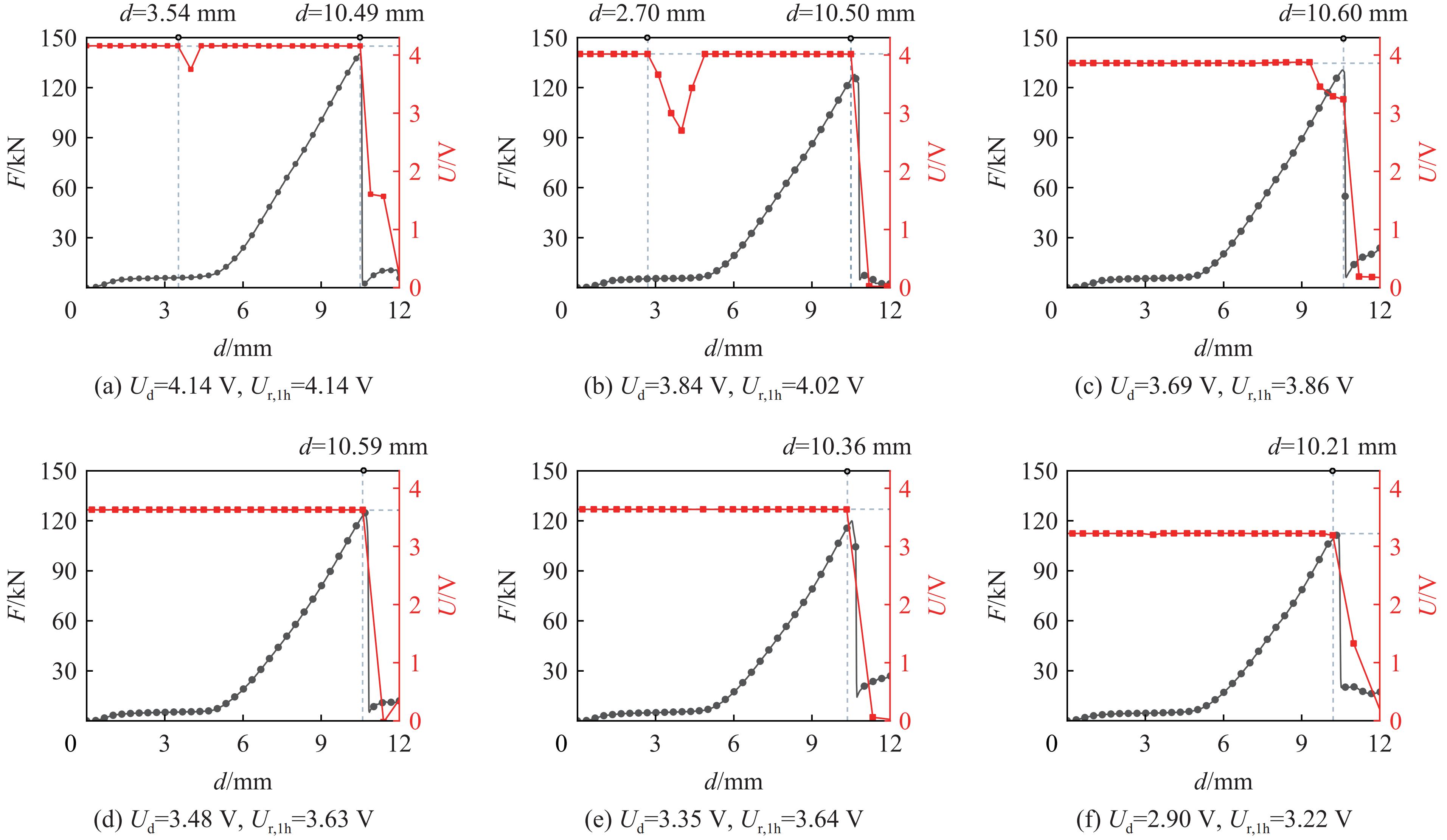
当电池放电到4.14、3.84、3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V并静置1 h后,电池电压Ur,1h分别为4.14、4.02、3.86、3.63、3.64和3.22V,对电池进行机械滥用测试的电池电压-位移曲线和反作用力-位移曲线如图5所示。可以看出,只有放电到3.84和4.14 V的电池发生软短路而放电到3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V的电池均不发生软短路。当电池放电到4.14、3.84、3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V并静置1 h后进行机械滥用测试,发生硬短路的电池位移分别为10.49、10.50、10.60、10.59、10.36和10.21 mm,而反作用力-位移曲线的最大反作用力则分别为104.22、127.82、130.32、124.78、120.03和106.80 kN。与放电过程中直接进行机械滥用测试的峰值力变化趋势相同,随着电池放电深度的增加,电池的最大反作用力逐渐降低。当电池放电到4.14和3.84 V并静置1 h后进行机械滥用测试时,电池在硬短路后发生起火爆炸,而电池放电到3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V并静置1 h后进行机械滥用测试时,电池并未发生起火爆炸。
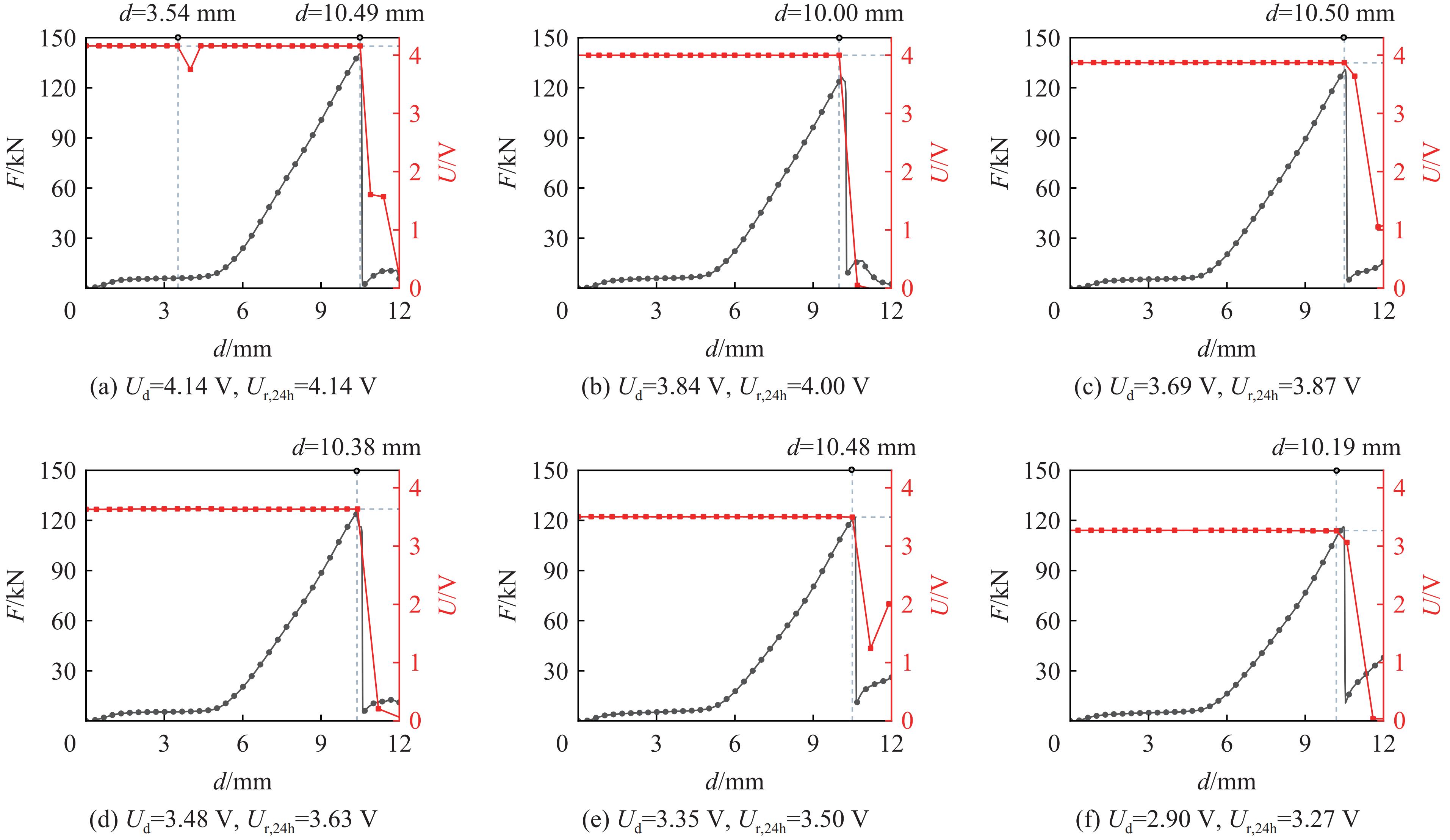
当电池放电到4.14、3.84、3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V并静置24 h后,电池电压Ur,24h分别为4.14、4.00、3.87、3.63、3.50和3.27 V,对电池进行机械滥用测试的电池电压-位移曲线和反作用力-位移曲线如图6所示。结果表明,只有放电到4.14 V的电池发生软短路,而放电到3.84、3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V的电池均不发生软短路。当电池放电到4.14、3.84、3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V并静置24 h后进行机械滥用测试时,发生硬短路的电池位移变为10.49、10.00、10.50、10.38、10.48和10.19 mm,而反作用力-位移曲线的最大反作用力则变为104.22、126.62、121.06、123.57、122.32和115.98 kN。与放电过程中直接进行机械滥用测试的峰值力变化趋势相同,随着电池放电深度的增加,电池的最大反作用力逐渐降低。静置24和1 h电池受机械滥用受的热失控结果相同,当电池放电到4.14和3.84 V并静置24 h后进行机械滥用测试时,电池在硬短路后发生起火爆炸,而电池放电到3.69、3.48、3.35和2.90 V后进行机械滥用测试时,电池并未发生起火爆炸。
图7对比了放电到不同程度的电池在放电中、静置1 h和静置24 h后受机械滥用载荷测试的反作用力-位移曲线。图8对比了静置时间对不同放电程度的锂离子电池的受机械滥用测试时的反作用力-位移曲线。从图7~8发现,电池在经过不同的放电深度和不同的静置时间后,受机械滥用测试时的反作用力随位移的变化基本相同。随着放电深度的提高,放电中、静置1 h和静置24 h后测试得到的反作用力-位移曲线差异更明显,静置后电池的刚度提升更明显。从整体上看,在不同的放电程度下,随着电池静置时间的延长,电池受机械滥用测试时的反作用力-位移曲线呈上升趋势,说明电池的刚度会随着静置时间的延长而逐渐提高。
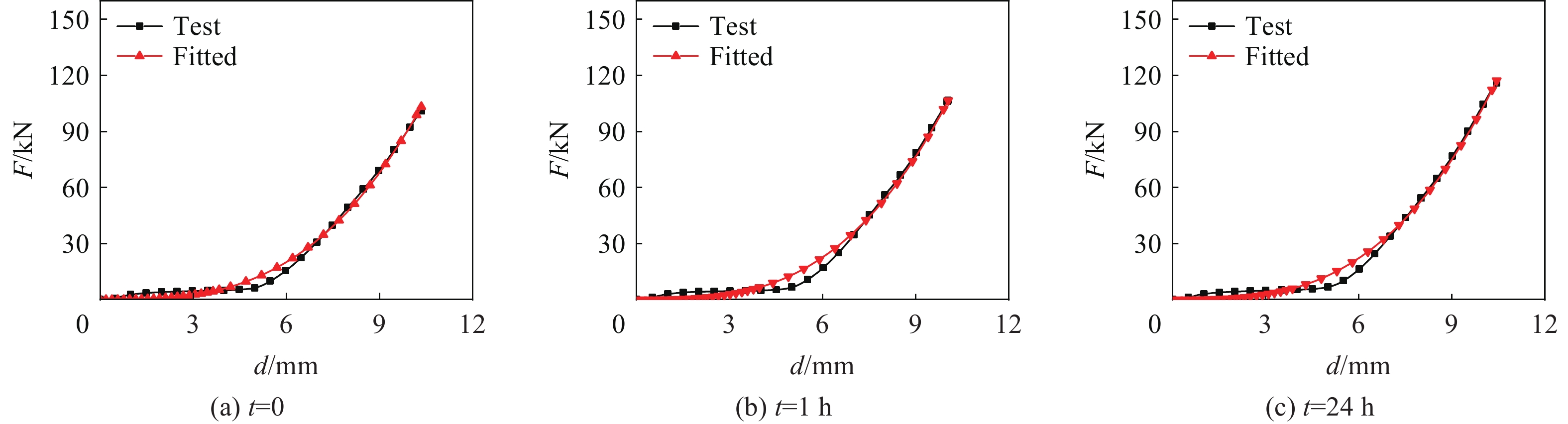
为了进一步量化电池的刚度并分析电池放电深度和静置时间对电池刚度的影响,采用F=Bd3模型对电池机械滥用测试实验所得曲线进行了拟合,如图9所示,其中F为电池受机械滥用载荷时的反作用力,B为电池刚度参数,d为电池的在压缩方向上的位移量。
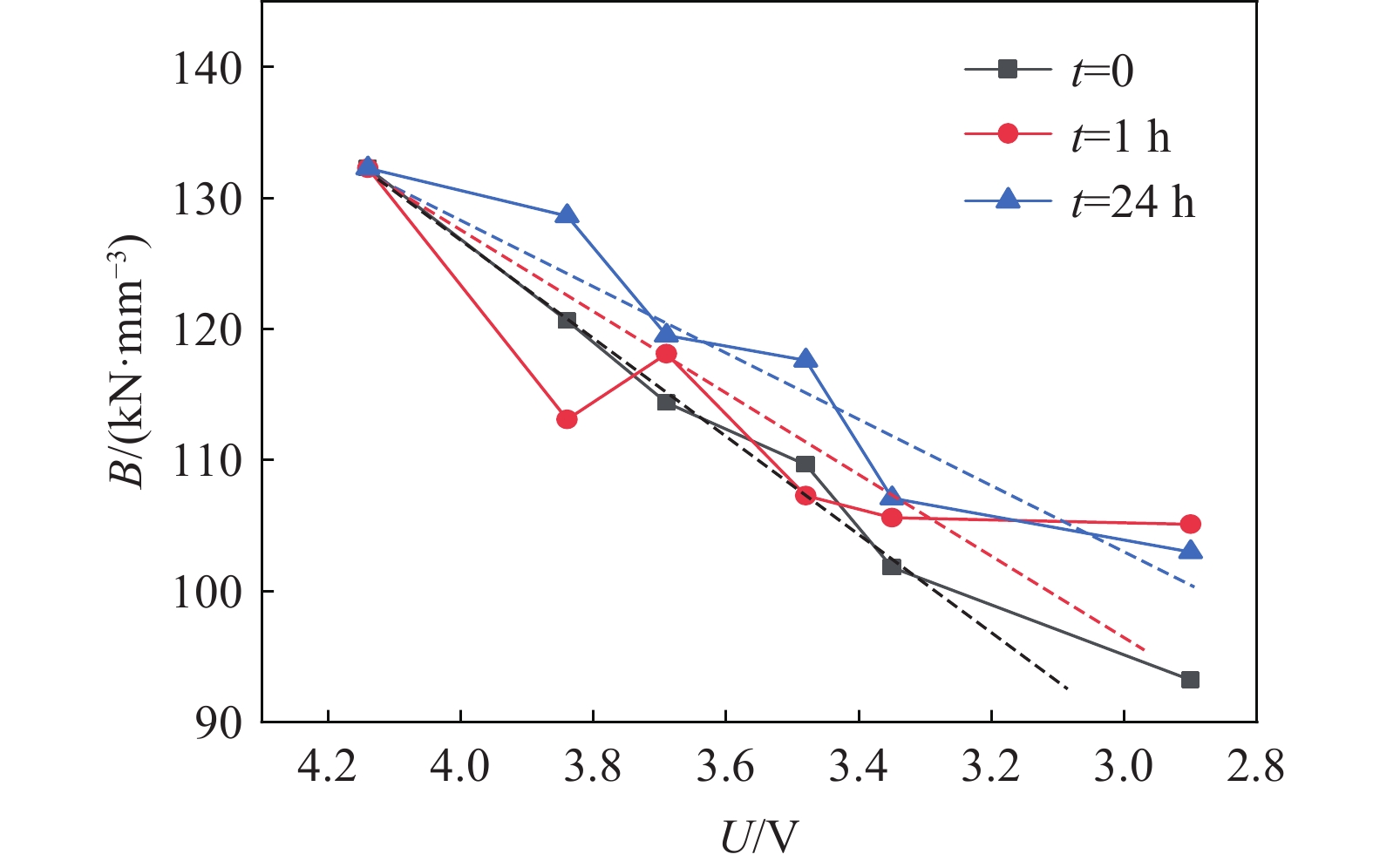
采用F=Bd3模型进行拟合后,各实验结果的曲线拟合可决系数(R²)均达到了0.988以上,这有力地验证了利用电池刚度参数B来表征电池刚度的有效性和准确性。电池刚度参数B随着放电深度和静置时间的变化如图10所示。从图10可看出,在整体上,随着电池放电深度的增加,B值呈现明显的下降趋势。特别地,对放电过程中进行压缩和放电后静置24 h再进行压缩的2种情况,其B-U曲线的下降趋势均接近线性,通过直线拟合获得了极高的拟合度(R2>0.98)。然而,对于放电后静置1 h再进行压缩的情况,B-U曲线的变化规律不明显,这是因为在锂脱嵌过程中电池的宏观刚度变化并非完全线性。尽管如此,若尝试以直线拟合该情况下的B-U曲线(R2=0.76),所得直线恰好位于放电过程中进行压缩与放电后静置24 h再进行压缩2种情况所得直线之间。这一结果支持了电池刚度随静置时间延长整体逐渐提高的结论。
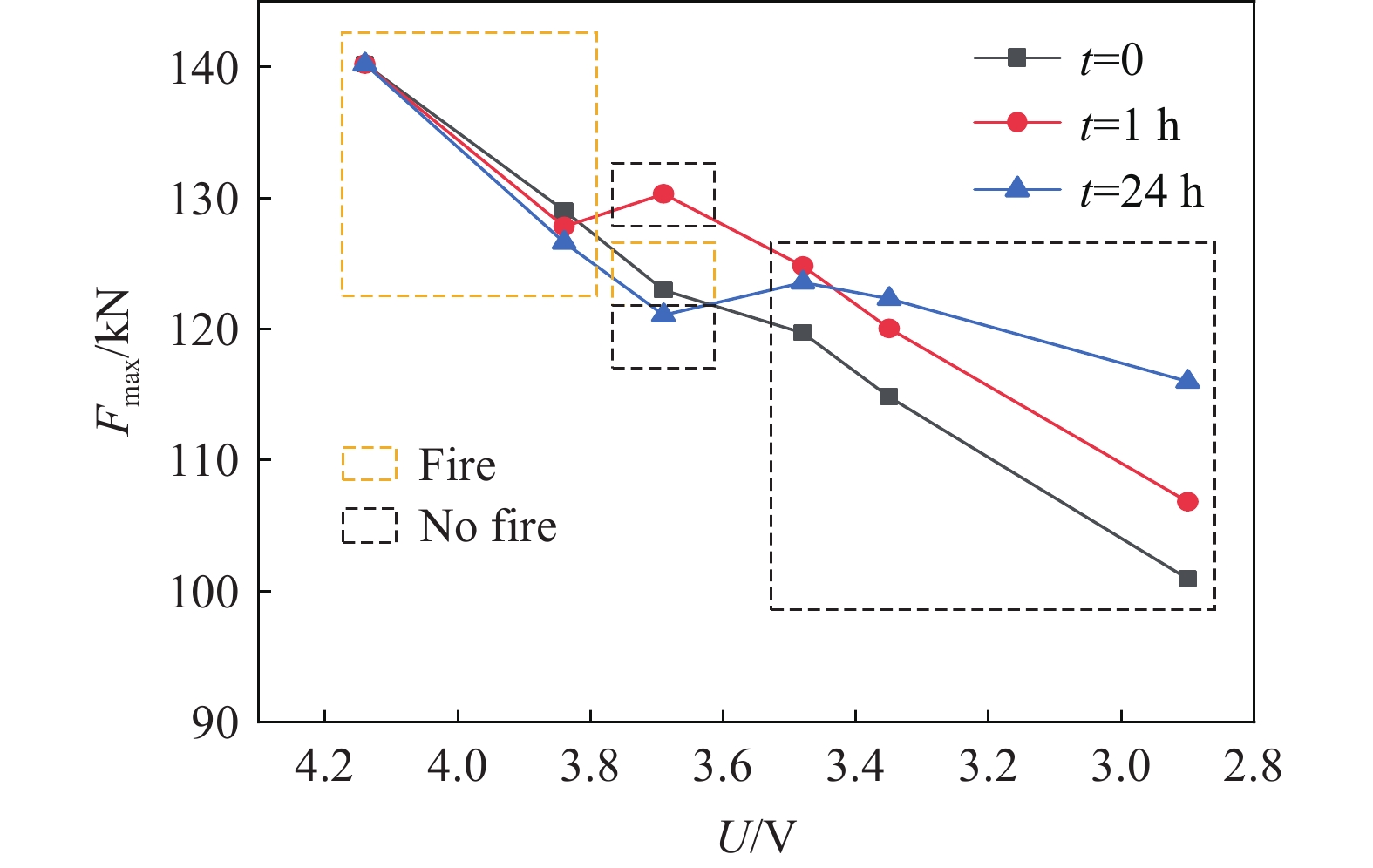
图11对比了放电至不同状态的电池在静置不同时间后受压缩过程中的最大反作用力Fmax。结果表明,随着放电深度的增加,电池的最大反作用力呈现明显的下降趋势;总体上看,静置24 h后的承载力优于静置1 h,而放电中进行机械滥用测试的电池承载力最低;在放电程度较低的情况下(≥3.84 V),放电中进行机械滥用测试的电池最大承载力高于静置1和24 h的情况,随着放电深度的进一步提高,这一趋势发生逆转,静置24 h后的压缩测试承载力高于静置1 h和放电过程中机械滥用测试的最大承载力。
3. 结果分析
为进一步探究静置时间对锂离子电池在机械滥用测试条件下微观机理的影响,本研究深入分析了不同静置时长后电池在机械滥用测试中所展现的力学响应差异,并将此现象归因于扩散应力的动态变化及其作用机制。
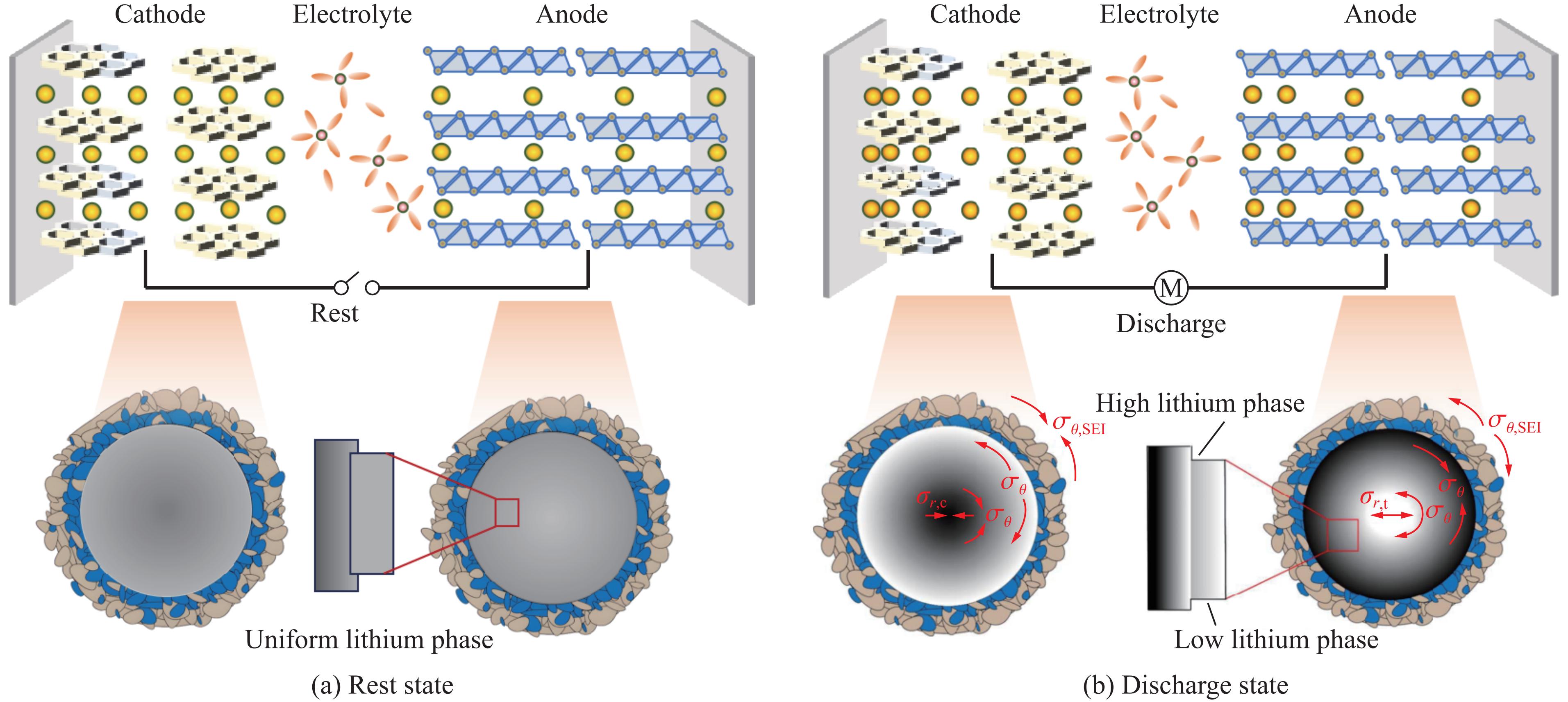
在锂离子电池的放电进程中,内部化学反应诱发的电极材料极化效应,导致电极层与电极颗粒间锂离子分布不均匀,进而产生扩散应力,如图12所示。当处于放电状态的电池遭受外部机械载荷时,尽管电池的临界失效应力在理论上保持恒定,但内部存在的扩散应力与外部载荷的相互作用,却可能引发电池内部应力状态的复杂演变[16]。具体而言,在放电初期,锂离子嵌入负极材料时,可能会产生局部的径向拉应力σr,t,这种拉应力在一定程度上有助于材料内部微观结构的致密化,从而可能增强材料的刚度与强度。随着放电过程的持续,正极材料中的锂离子脱出,则可能产生径向压应力σr,c,此压应力在材料能承受一定压力而不破坏的前提下,同样可能对材料的力学性能产生积极影响。然而,当放电深入进行,扩散应力逐渐累积并达到临界值时,环向剪应力σθ和固体电解质界面环向剪应力σθ,SEI开始成为主导。这些应力的存在,可能导致材料内部微观结构的错动与滑移,进而削弱材料的刚度与强度。特别是在材料的薄弱环节,如晶界、相界等处,剪应力和综合应力的集中更易触发裂纹的萌生与扩展,加速电池结构的失效。此类过早的结构失效,极易诱发电池内部短路与热失控,从而严重损害电池的整体安全。
因此,静置时间的延长,为扩散应力的释放提供了有利条件。在静置期间,电池内部的锂离子得以更充分地再分布,从而缓解由放电过程产生的应力集中现象。这一变化有助于提升电池在后续机械载荷下的稳定性,降低因内部应力过大而引发的结构失效风险。
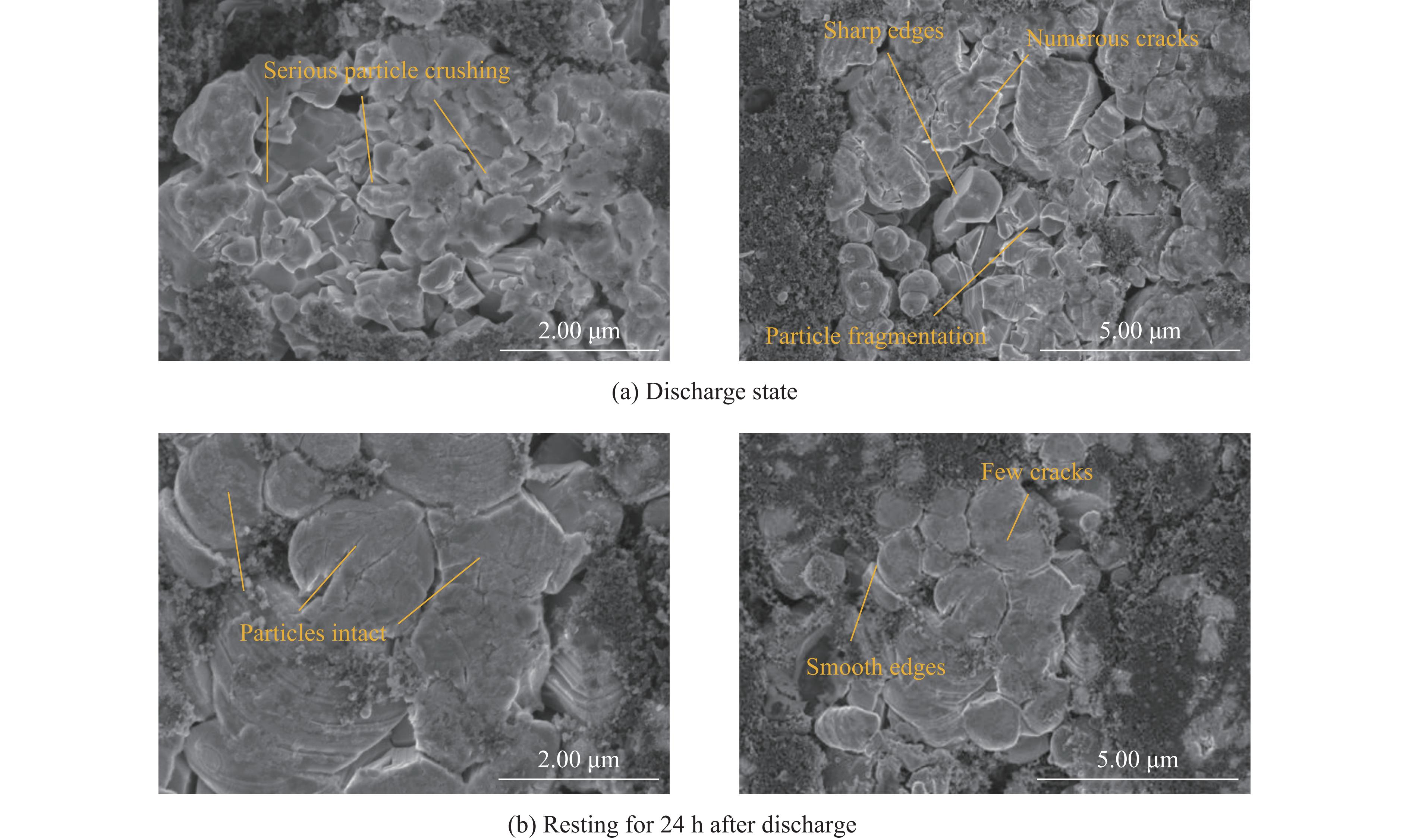
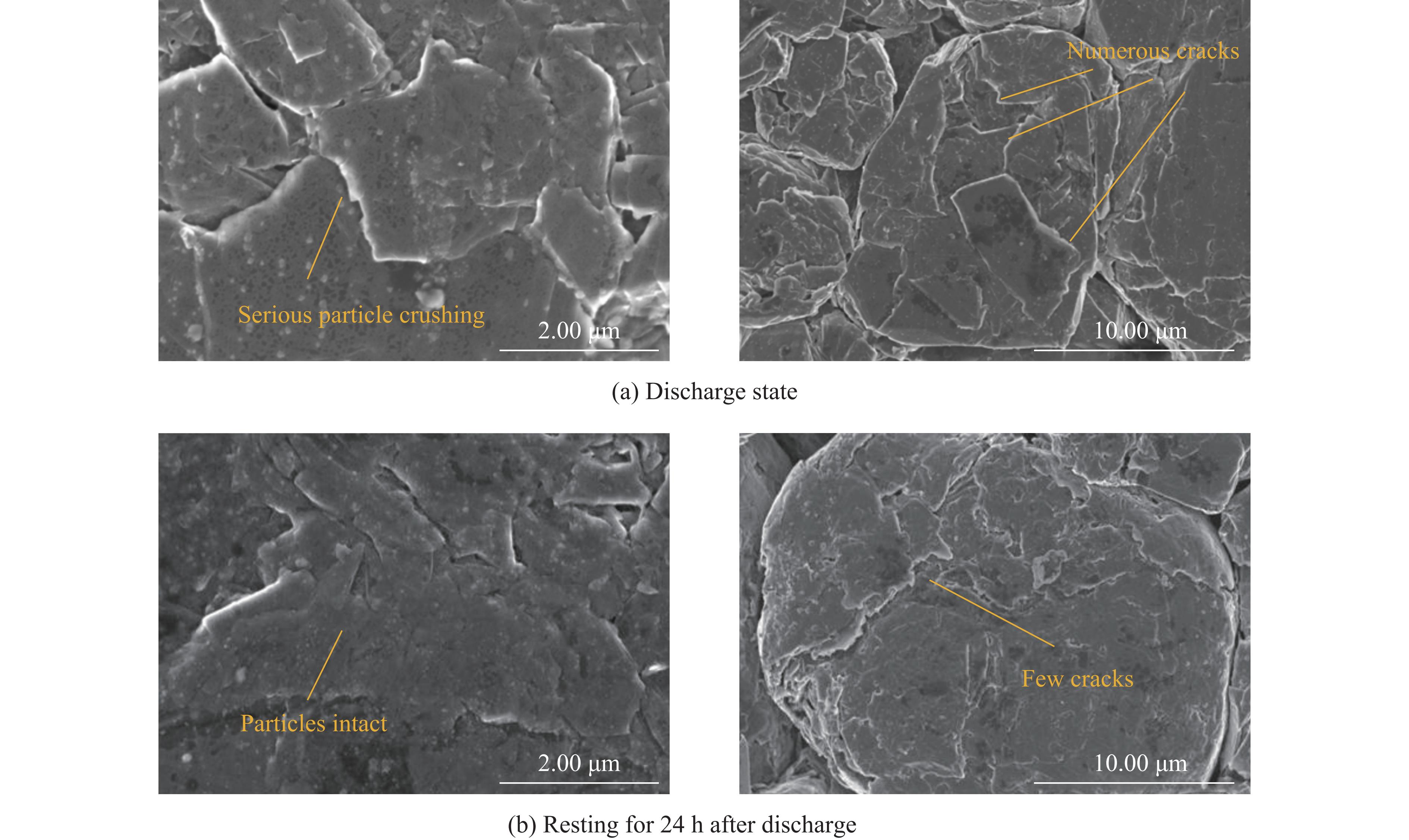
为了验证扩散应力的影响,对放电至2.90 V后立即压缩和静置24 h后压缩的实验电池进行了拆解,从距离试验机挤压头接触面较近的电池外层中心位置,筛选出拆解后较完整的正负极片,截取出10 mm×10 mm的正方形样本,并通过扫描电子显微镜对电池内部电极颗粒的破损程度进行了观察和分析,结果如图13~14所示。
从图13(a)可以看出,放电状态下压缩的正极颗粒显示出高度的破碎性,许多颗粒边缘出现碎片或小片剥离的现象。颗粒内部存在大量裂纹,这些裂纹数量众多且深度较大,表明在放电过程中颗粒承受了显著的机械应力。这些裂纹通常沿着颗粒的最弱方向扩展,反映电池内部活跃的电化学反应和材料机械性能的变化。相比之下,图13(b)显示,静置后的颗粒破碎程度较低,表面相对平滑,裂纹数量明显减少,且裂纹深度较浅。这表明,随着电池内部电化学反应的停止,化学物质趋于稳定,静置后的颗粒内部应力得到一定程度的释放,从而减少了应力集中,降低了进一步的物理损伤。
负极颗粒的表现与正极颗粒相似。如图14(a)所示,放电状态下压缩的负极颗粒破碎程度显著,颗粒边缘出现大量不规则的碎片和锋利的断面,裂纹数量多且分布广泛。相比之下,图14(b)显示,静置后的负极颗粒结构较为完整,尽管表面存在一定的破损,但整体破碎程度较低,颗粒形态更为完整,裂纹数量减少,且裂纹尺寸较小。
以上SEM结果表明,在放电过程中,由于电化学反应产生的强烈扩散应力,颗粒在承受机械应力时更容易产生广泛的裂纹和破碎。相反,静置后的颗粒在没有持续电化学反应的条件下,扩散应力得到释放,使得颗粒结构更稳定。从安全性的角度来看,静置后的颗粒表现出更好的结构完整性,而放电中的颗粒则更容易发生结构失效,从而增大了电池失效的风险。
4. 结 论
通过对锂离子电池在不同放电状态下经历不同静置时间后的力学行为进行系统测试和分析,揭示了静置时间对电池刚度和强度的显著影响。实验结果表明,随着静置时间的延长,电池的刚度和强度均呈现出明显的提高趋势,且这一影响随着放电深度的提高而更显著。放电过程中的电池表现出更高的活跃性,在相同电压条件下,电池更容易在压缩测试中发生热失控。此现象归因于放电过程中剧烈的电化学反应所引发的扩散应力,该应力导致电极颗粒的破损加剧,从而增大了电池的结构失效风险,并显著降低了电池的安全性能。
通过深入探讨锂离子电池在放电状态下的力学特性,明确了静置时间在缓解扩散应力、提升电池结构稳定性方面的重要作用。这一发现不仅丰富了电池在实际应用场景中的安全性评估理论,也为电池设计与安全性优化提供了新的思路和依据,对推动电动汽车及储能系统的安全发展具有重要的实践意义。
-
-
[1] 许骏, 王璐冰, 刘冰河. 锂离子电池机械完整性研究现状和展望 [J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2017, 8(1): 15–29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2017.01.002.XU J, WANG L B, LIU B H. Review for mechanical integrity of lithium-ion battery [J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2017, 8(1): 15–29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8484.2017.01.002. [2] LIU B H, JIA Y K, YUAN C H, et al. Safety issues and mechanisms of lithium-ion battery cell upon mechanical abusive loading: a review [J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 24: 85–112. DOI: 10.1016/j.ensm.2019.06.036. [3] SAHRAEI E, HILL R, WIERZBICKI T. Calibration and finite element simulation of pouch lithium-ion batteries for mechanical integrity [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 201: 307–321. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.10.094. [4] ZHU J E, LUO H L, LI W, et al. Mechanism of strengthening of battery resistance under dynamic loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 131: 78–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.05.003. [5] XU J, LIU B H, WANG L B, et al. Dynamic mechanical integrity of cylindrical lithium-ion battery cell upon crushing [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2015, 53: 97–110. DOI: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.03.025. [6] LIU B H, YIN S, XU J. Integrated computation model of lithium-ion battery subject to nail penetration [J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 183: 278–289. DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.101. [7] WANG G W, ZHANG S, LI M, et al. Deformation and failure properties of high-Ni lithium-ion battery under axial loads [J]. Materials, 2021, 14(24): 7844. DOI: 10.3390/ma14247844. [8] ZHENG G, TAN L L, TIAN G L, et al. Dynamic crashing behaviors of prismatic lithium-ion battery cells [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 192: 110902. DOI: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.110902. [9] YU D, REN D S, DAI K R, et al. Failure mechanism and predictive model of lithium-ion batteries under extremely high transient impact [J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 43: 103191. DOI: 10.1016/j.est.2021.103191. [10] HU L L, ZHANG Z W, ZHOU M Z, et al. Crushing behaviors and failure of packed batteries [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 143: 103618. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103618. [11] SANTOSA S P, NIRMALA T. Numerical and experimental validation of fiber metal laminate structure for lithium-ion battery protection subjected to high-velocity impact loading [J]. Composite Structures, 2024, 332: 117924. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2024.117924. [12] ZHOU D, LI H G, LI Z H, et al. Toward the performance evolution of lithium-ion battery upon impact loading [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 432: 141192. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2022.141192. [13] LIU Y J, XIA Y, XING B B, et al. Mechanical-electrical-thermal responses of lithium-ion pouch cells under dynamic loading: a comparative study between fresh cells and aged ones [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 166: 104237. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104237. [14] WANG T, CHEN X P, CHEN G, et al. Investigation of mechanical integrity of prismatic lithium-ion batteries with various state of charge [J]. Journal of Electrochemical Energy Conversion and Storage, 2021, 18(3): 031002. DOI: 10.1115/1.4048330. [15] CHEN X P, WANG T, ZHANG Y, et al. Dynamic behavior and modeling of prismatic lithium-ion battery [J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(4): 2984–2997. DOI: 10.1002/er.5126. [16] EDGE J S, O’KANE S, PROSSER R, et al. Lithium ion battery degradation: what you need to know [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23(14): 8200–8221. DOI: 10.1039/D1CP00359C. -







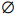

 下载:
下载:














 下载:
下载: