Study on the damage constitutive model of rock considering the influence of dynamic ratio of tension to compression
-
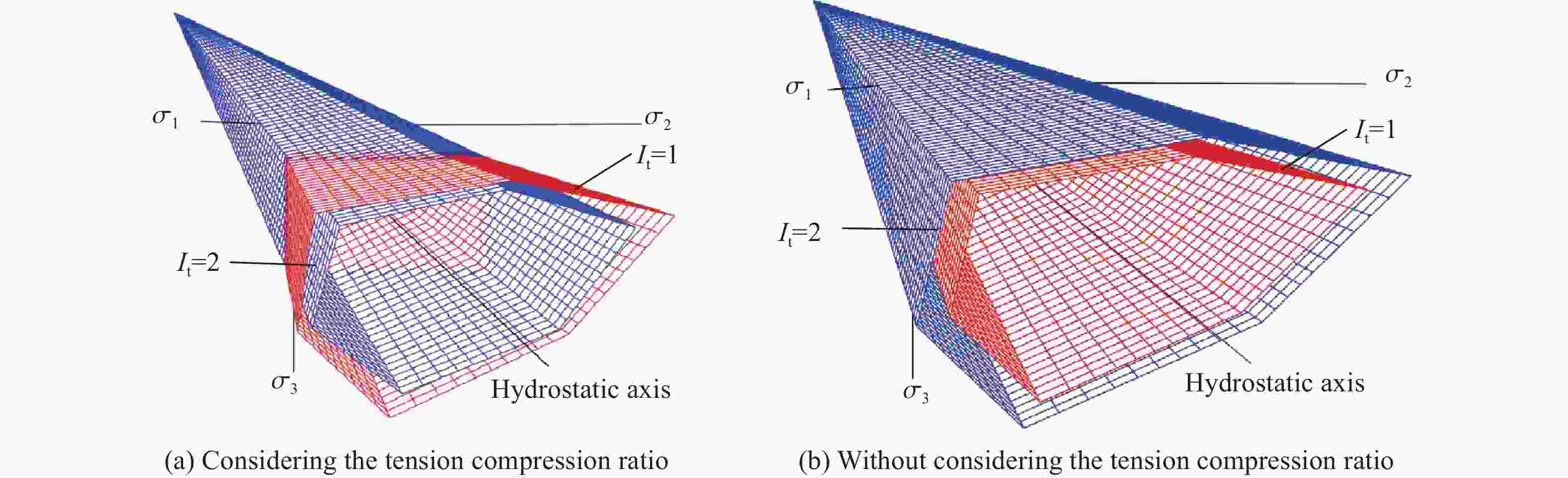
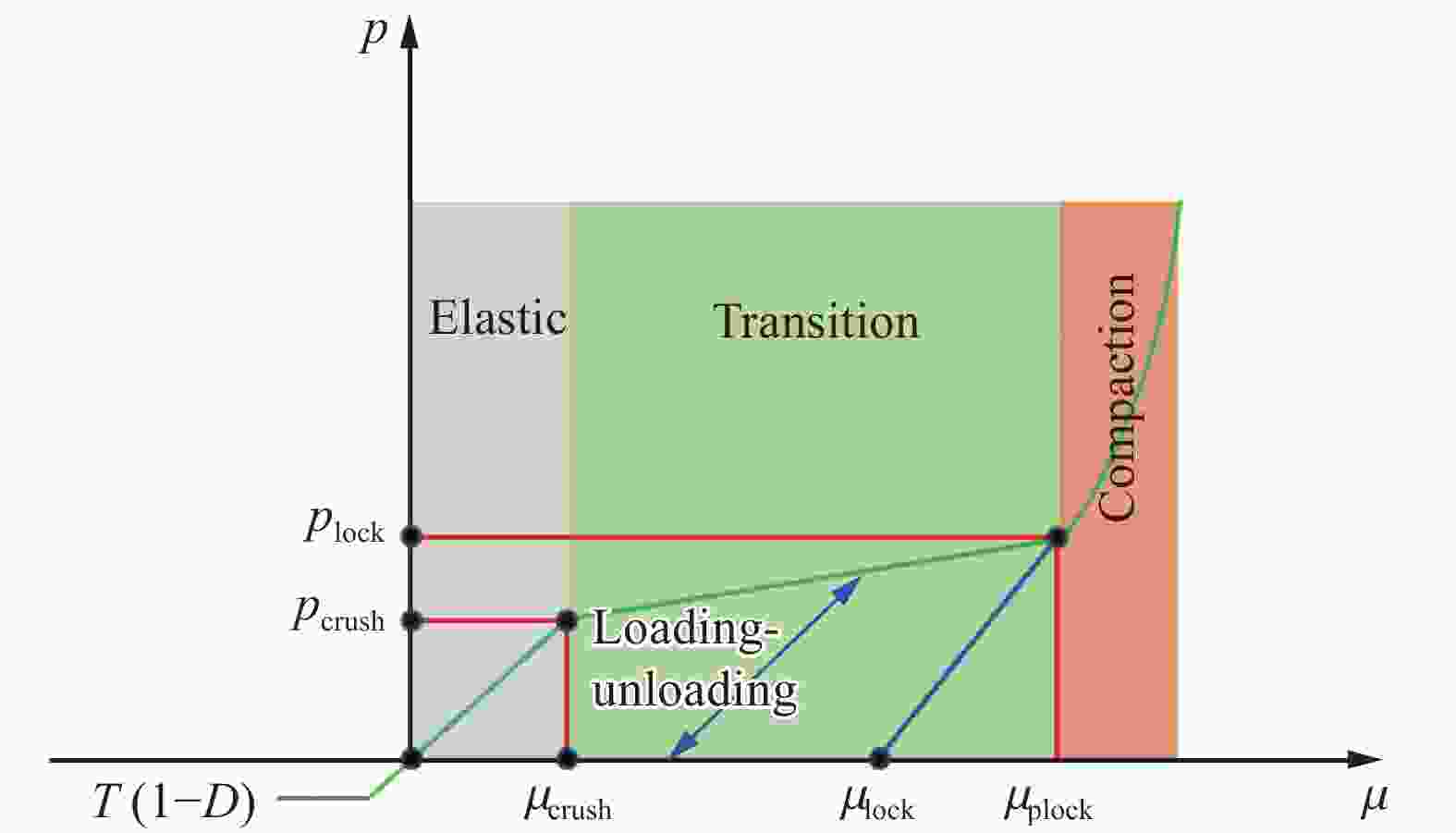
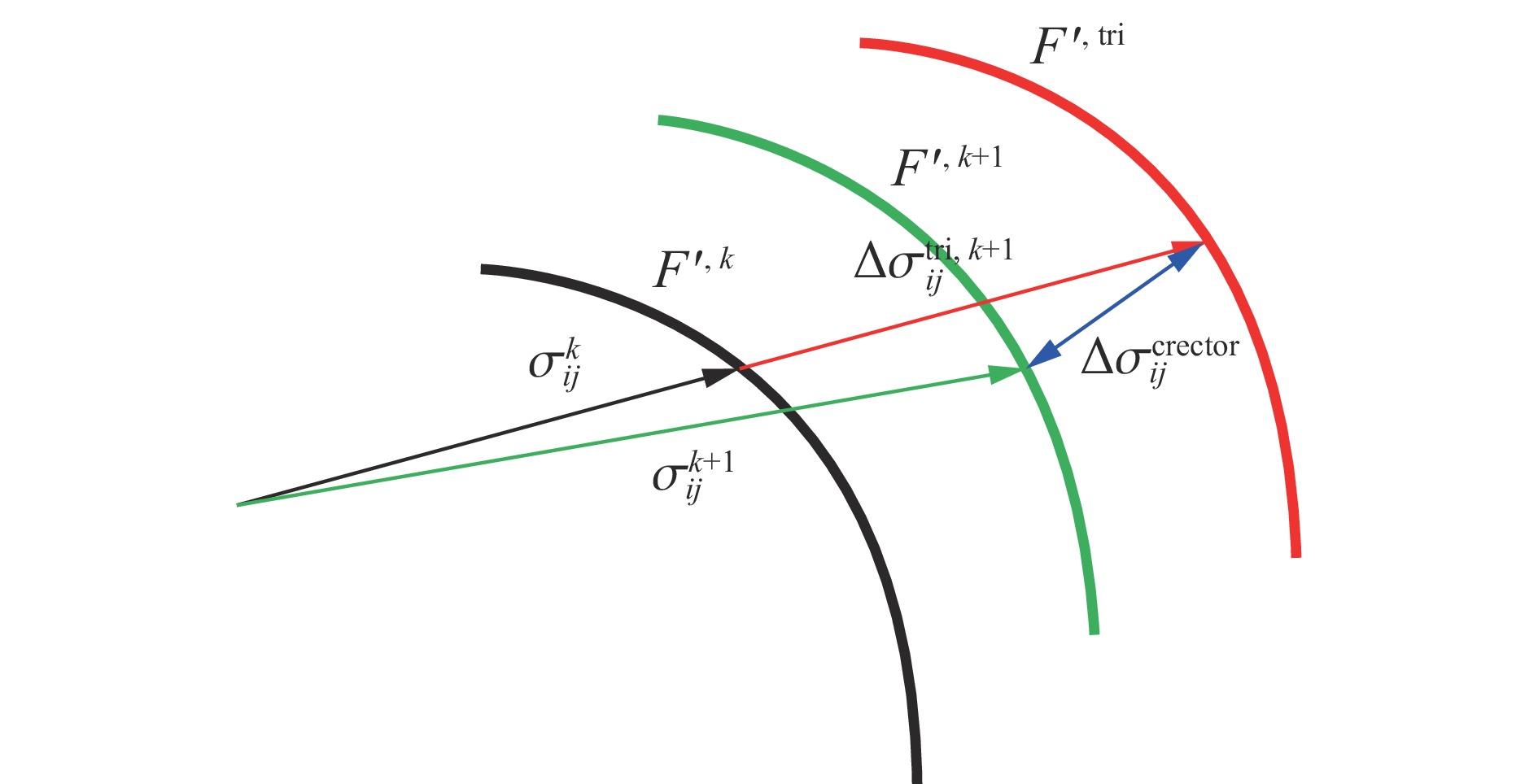
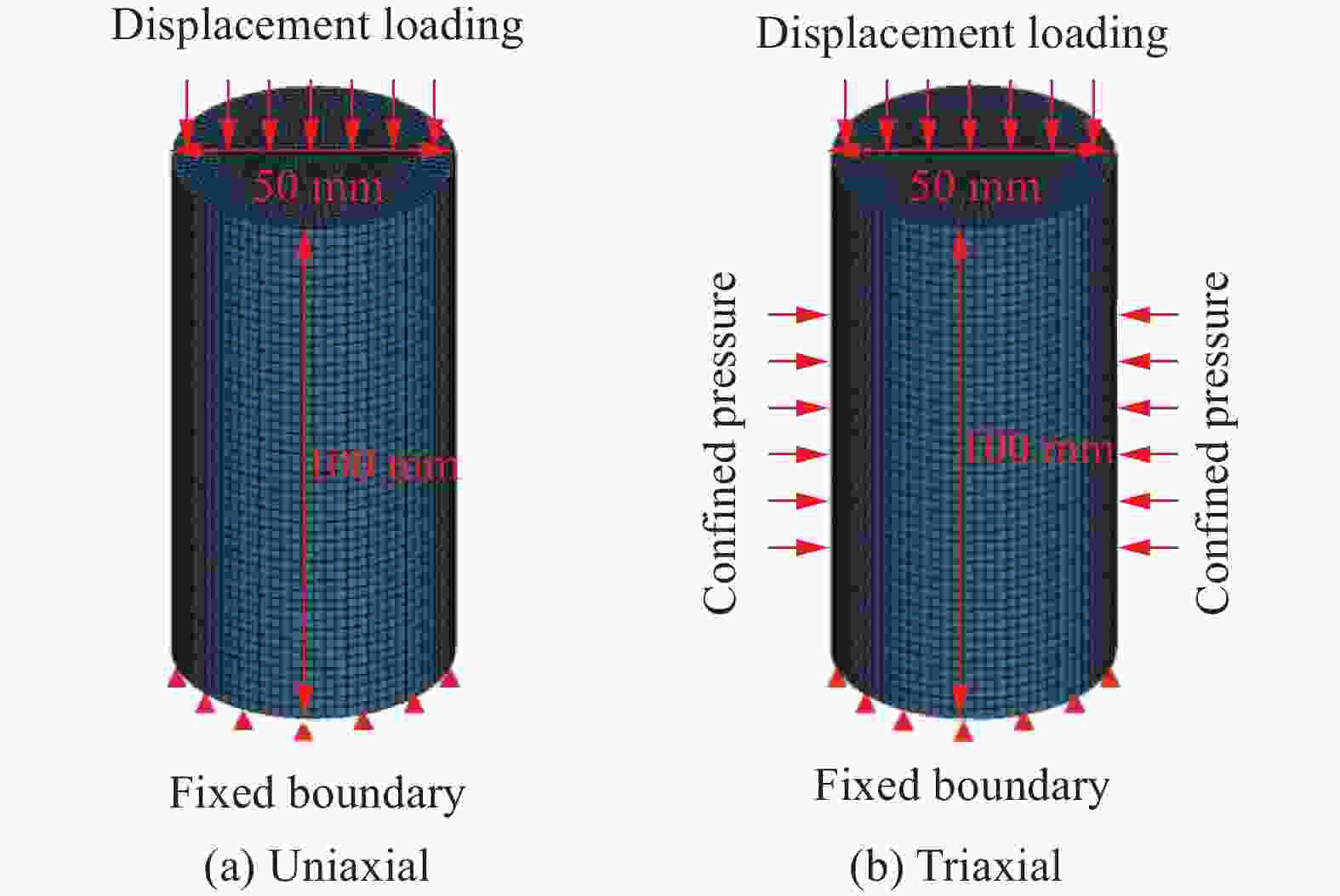
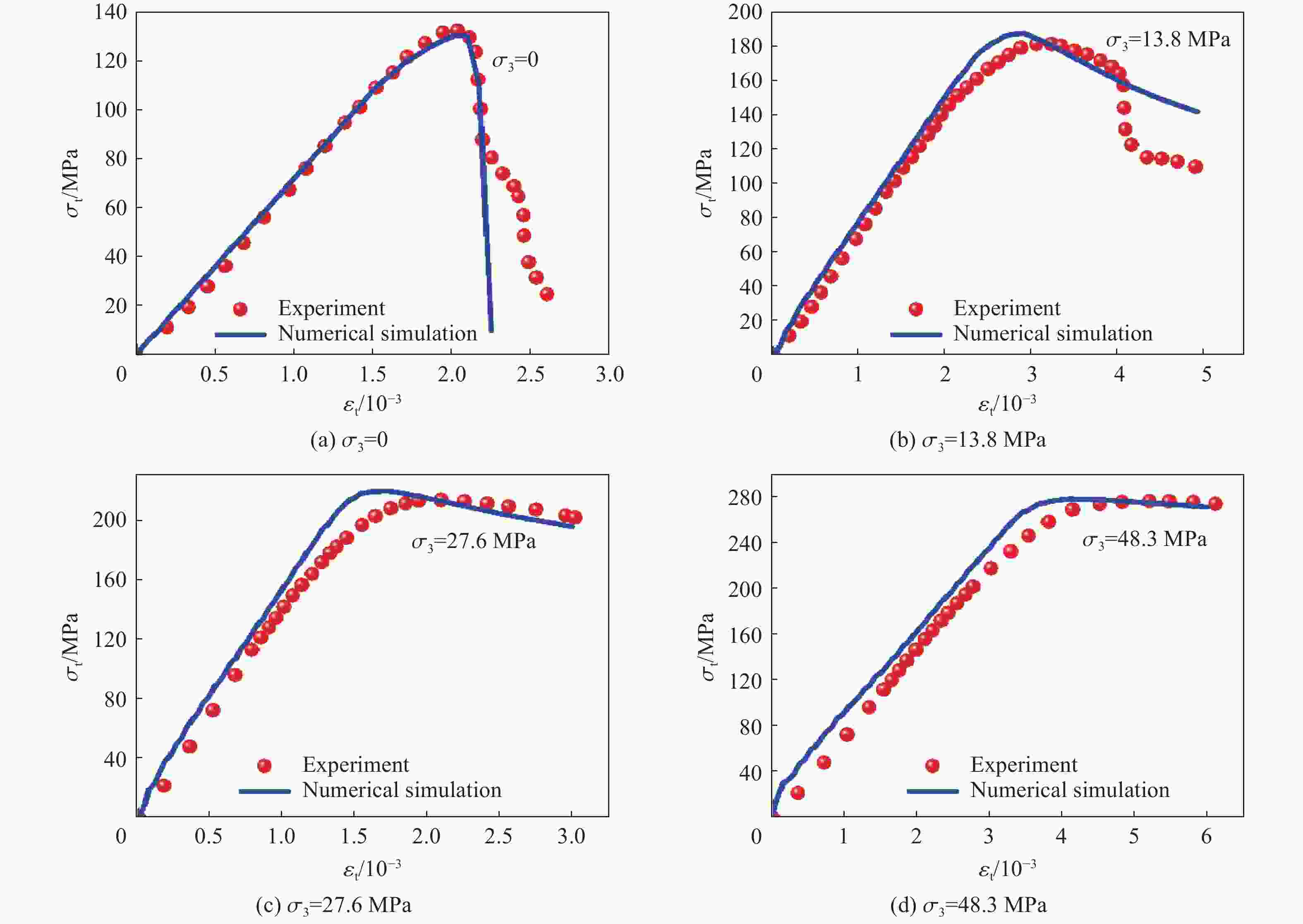
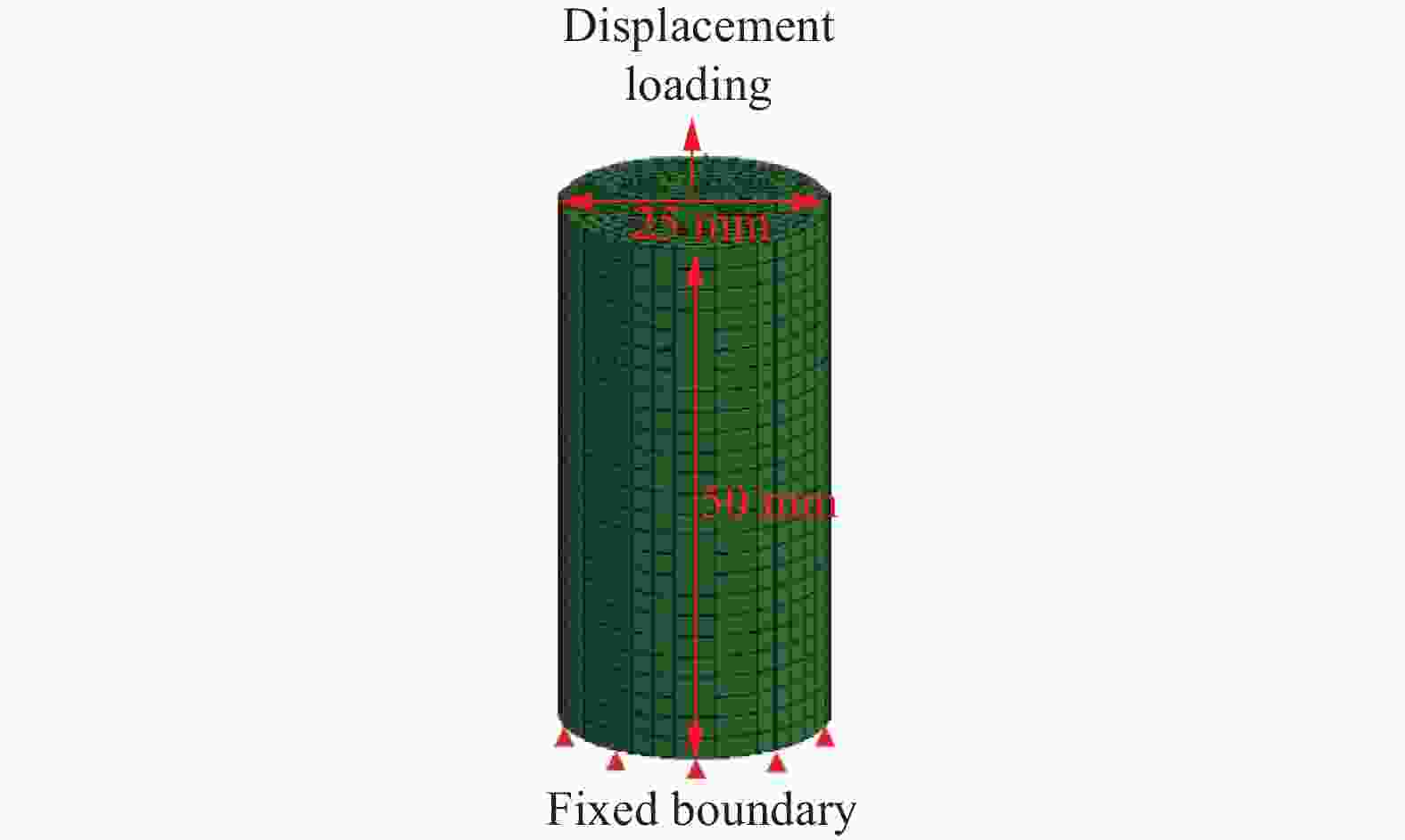
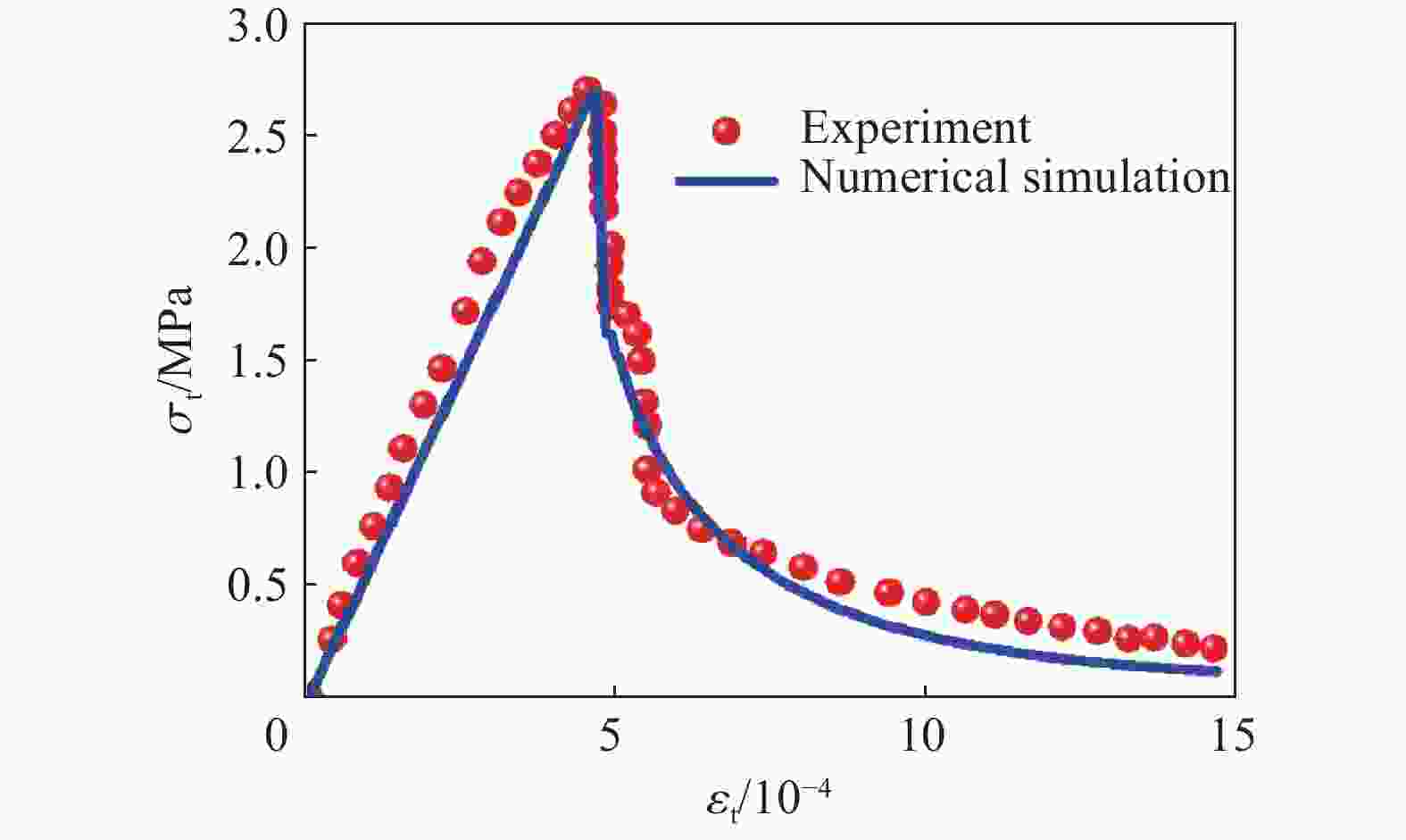
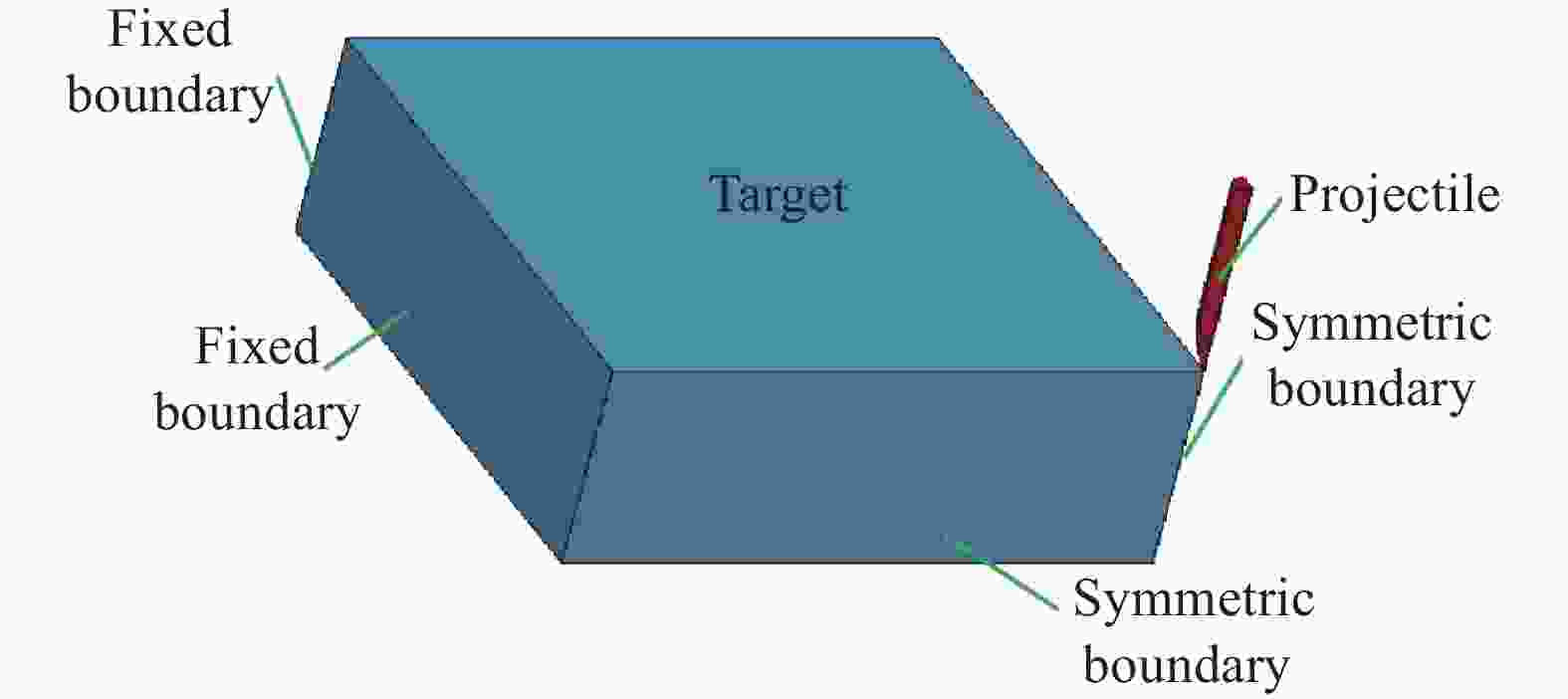
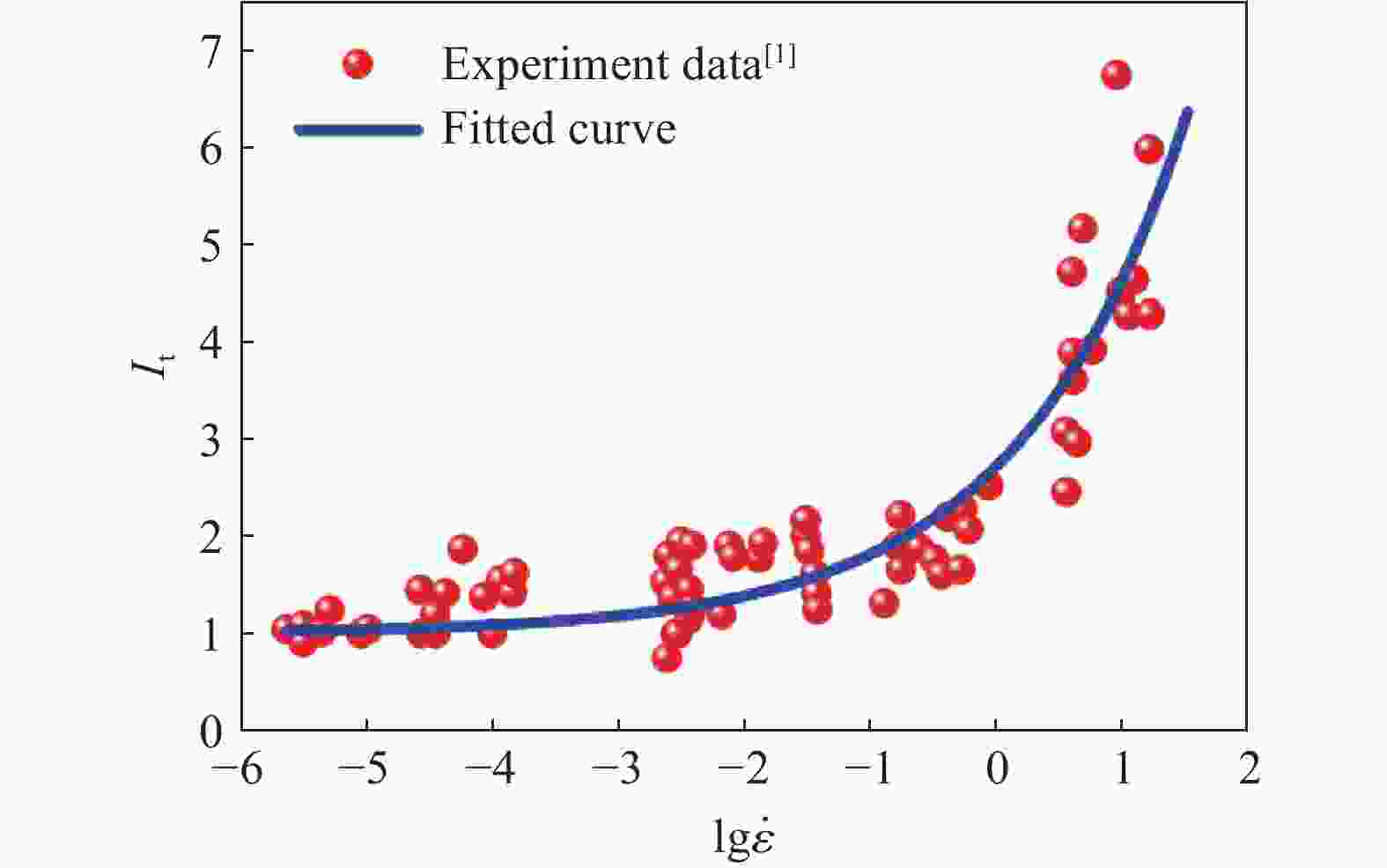
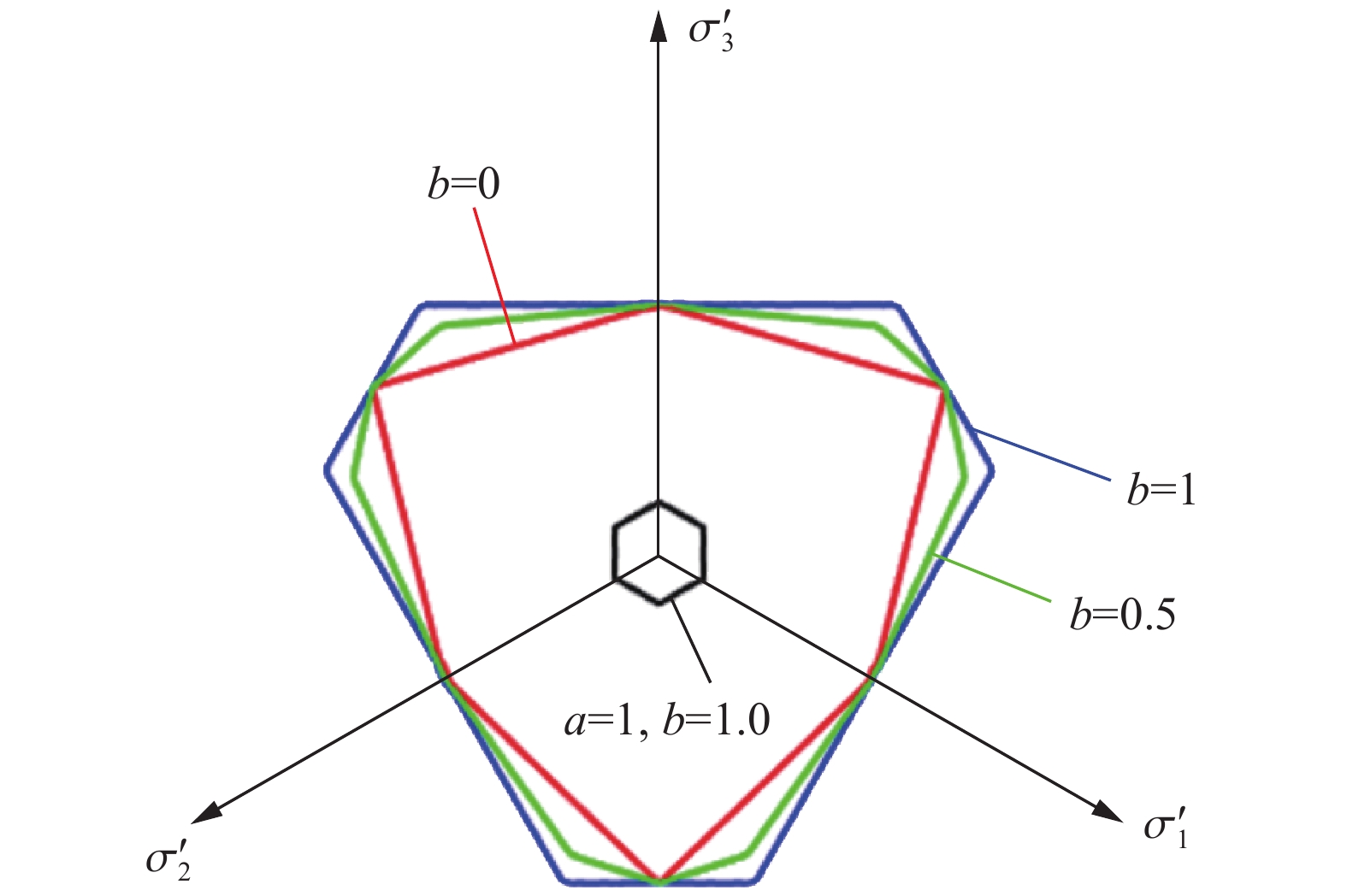
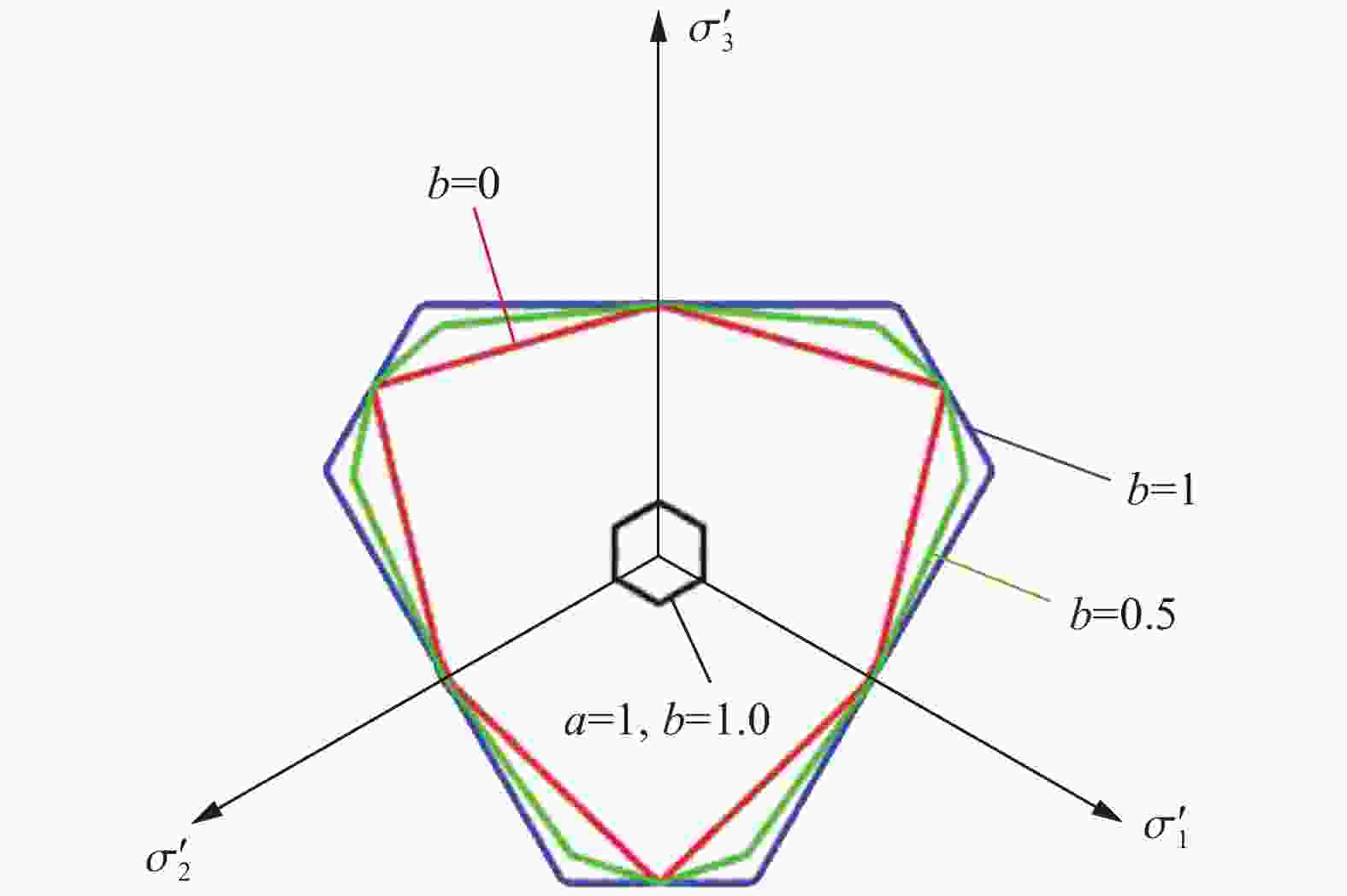
摘要: 基于连续介质损伤力学,建立了一个弹塑性损伤耦合的岩石动态本构模型。该模型以统一强度理论作为屈服准则,并引入动态拉压比充分反映应变率效应;采用有效塑性应变和体积塑性应变表示压损伤变量和用有效塑性应变表示拉损伤变量从而反映拉压条件下岩石不同的损伤演化规律;采用分段函数来刻画岩石拉压条件下的不同塑性硬化行为;基于Fortran语言和LS-DYNA用户材料自定义接口(Umat)对所建立的本构模型进行数值实现;通过岩石单轴和三轴压缩试验、岩石单轴拉伸试验和岩石弹道试验等三个经典算例对所建立的本构模型展开验证。结果表明,该本构模型能全面刻画岩石的动静态力学行为。Abstract: Based on continuum damage mechanics, a rock dynamic constitutive model with coupled elastic-plastic damage was established. This model took the unified strength theory as the yield criterion and introduces the dynamic tensile-compressive ratio to fully reflect the strain rate effect. The effective plastic strain and volumetric plastic strain were used to represent the compressive damage variable, and the effective plastic strain was used to represent the tensile damage variable, thereby reflecting the different damage evolution laws of rocks under tensile and compressive conditions. A piecewise function was adopted to describe the different plastic hardening behaviors of rocks under tensile and compressive conditions. The established constitutive model was numerically implemented based on Fortran language and the LS-DYNA user material customization interface (Umat). The established constitutive model is verified by three classical calculation examples, namely, the uniaxial and triaxial compression tests of rocks, the uniaxial tensile test of rocks, and the ballistic test of rocks. The results showed that this constitutive model can comprehensively describe the static and dynamic mechanical behaviors of rocks.
-
Key words:
- constitutive model /
- damage /
- ratio of tension to compression /
- strain rate
-
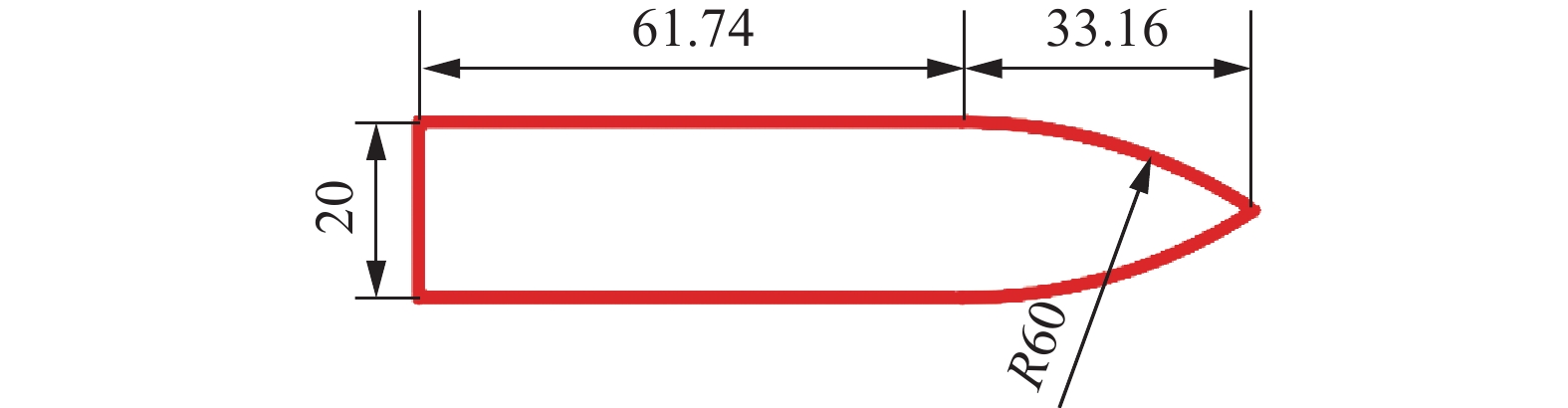
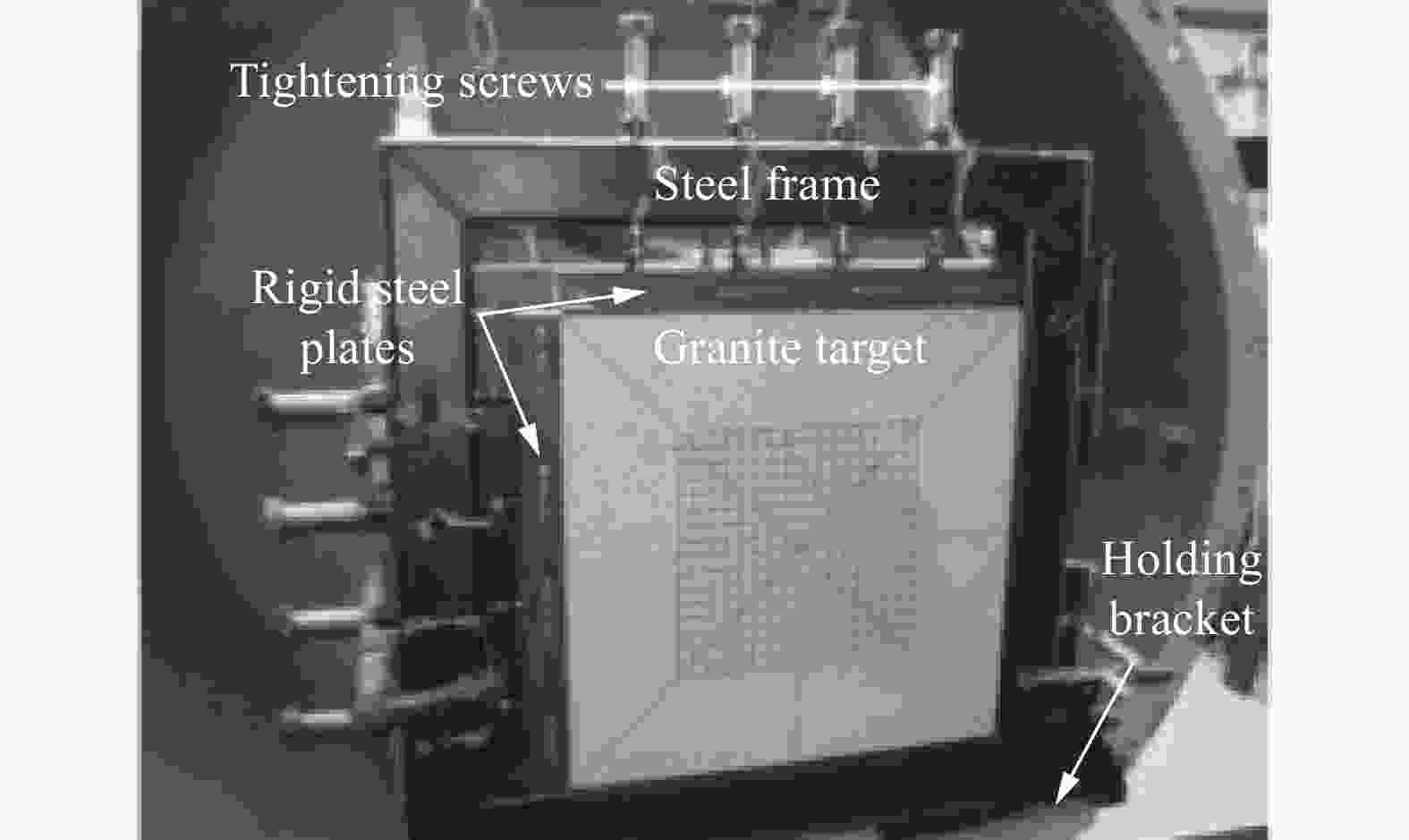
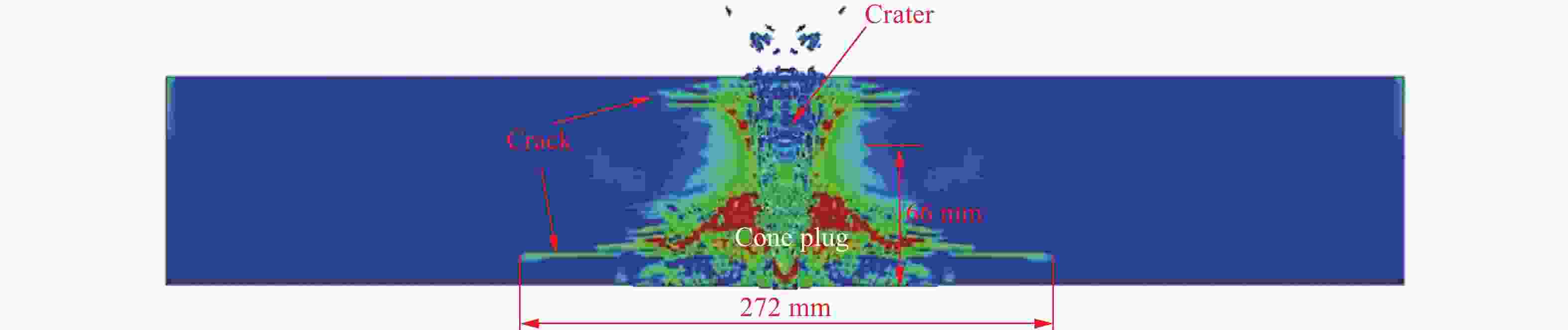
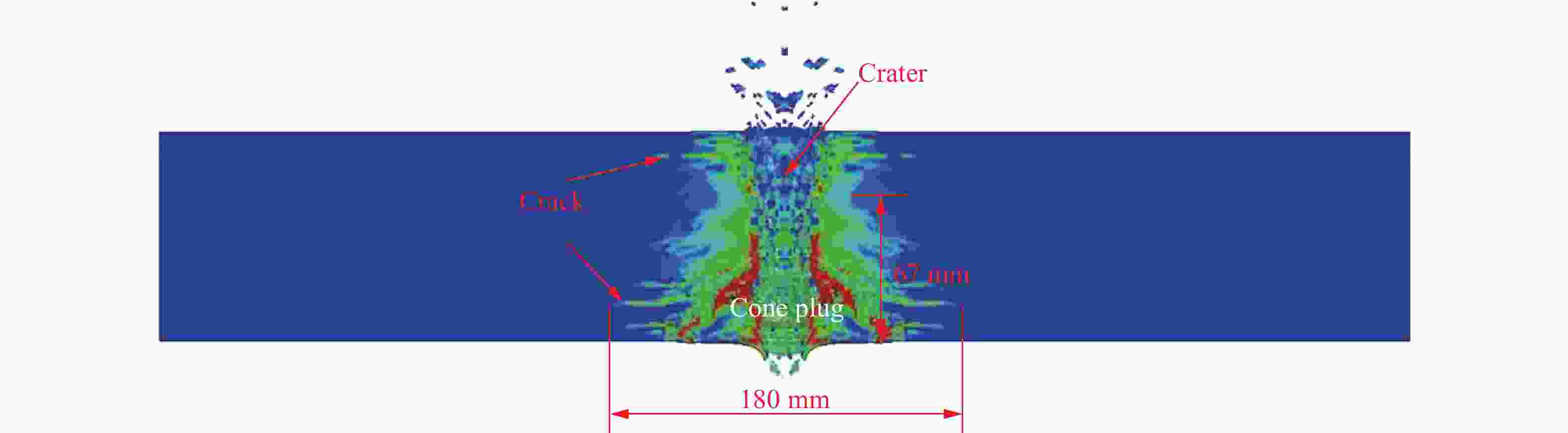
表 1 花岗岩靶板受子弹冲击后锥形塞高度和靶板背面弹坑的直径
Table 1. The cone plug height of granite target plate impacted by bullets and the diameter of crater on the back of target plate
-
[1] HUANG X P, KONG X Z, CHEN Z Y, et al. A computational constitutive model for rock in hydrocode [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2020, 145: 103687. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2020.103687. [2] 胡学龙. 基于统一强度理论的岩石动态损伤模型研究 [D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2020. DOI: 10.26945/d.cnki.gbjku.2020.000096.HU X L. Study of rock dynamic damage model based on unified strength theory [D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2020. DOI: 10.26945/d.cnki.gbjku.2020.000096. [3] AI H A, AHRENS T J. Simulation of dynamic response of granite: a numerical approach of shock-induced damage beneath impact craters [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2006, 33(1): 1−10. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2006.09.046. [4] BANADAKI M M D, MOHANTY B. Numerical simulation of stress wave induced fractures in rock [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 40/41: 16–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.08.010. [5] HOLMQUIST T J, JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A computational constitutive model for concrete subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high pressures [C]// Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Ballistics. Quebec: ADPA, 1993: 591−600. DOI: 10.1115/1.4004326. [6] MALVAR L J, CRAWFORD J E, WESEVICH J W, et al. A plasticity concrete material model for DYNA3D [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 1997, 19(9/10): 847–873. DOI: 10.1016/s0734-743x(97)00023-7. [7] RIEDEL W, THOMA K, HIERMAIER S, et al. Penetration of reinforced concrete by BETA-B-500 numerical analysis using a new macroscopic concrete model for hydrocodes [C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Interaction of the Effects of Munitions with Structures. Berlin Strausberg: ISIEMS, 1999: 315-322. [8] MURRAY Y D. Users manual for LS-DYNA concrete material model 159: FHWA-HRT-05-062 [R]. McLean: U. S. Department Transportation Federal Highway Administration, 2007. [9] POLANCO-LORIA M, HOPPERSTAD O S, BØRVIK T, et al. Numerical predictions of ballistic limits for concrete slabs using a modified version of the HJC concrete model [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2008, 35(5): 290–303. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.03.001. [10] KONG X Z, FANG Q, LI Q M, et al. Modified K&C model for cratering and scabbing of concrete slabs under projectile impact [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2017, 108: 217–228. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.02.016. [11] JIANG H, ZHAO J D. Calibration of the continuous surface cap model for concrete [J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design, 2015, 97: 1–19. DOI: 10.1016/j.finel.2014.12.002. [12] 凌天龙, 王宇涛, 刘殿书, 等. 修正RHT模型在岩体爆破响应数值模拟中的应用 [J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(S2): 434–442. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.1698.LING T L, WANG Y T, LIU D S, et al. Modified RHT model for numerical simulation of dynamic response of rock mass under blasting load [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(S2): 434–442. DOI: 10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.1698. [13] YANG L, WANG G S, ZHAO G F, et al. A rate-and pressure-dependent damage-plasticity constitutive model for rock [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 133: 104394. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104394. [14] LI H Y, SHI G Y. A dynamic material model for rock materials under conditions of high confining pressures and high strain rates [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 89: 38–48. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2015.11.004. [15] KONG X Z, FANG Q, CHEN L, et al. A new material model for concrete subjected to intense dynamic loadings [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 120: 60–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.05.006. [16] 胡学龙, 璩世杰, 李克庆. 基于统一强度理论的岩石弹塑性损伤模型研究 [J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(2): 305–312. DOI: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000985.HU X L, QU S J, LI K Q. Study of rock elastoplastic constitutive damage model based on the unified strength theory [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(2): 305–312. DOI: 10.13247/j.cnki.jcumt.000985. [17] 谢福君, 张家生, 陈俊桦. 冲击荷载作用下岩石压动态和拉动态损伤模型 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 50(2): 420–427. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.02.022.XIE F J, ZHANG J S, CHEN J H. Dynamic damage model of rock under impact loads of compression and tension [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2019, 50(2): 420–427. DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2019.02.022. [18] 江雅勤, 吴帅峰, 刘殿书, 等. 基于元件组合理论的砂岩动态损伤本构模型 [J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2018, 38(4): 827–833. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0173.JIANG Y Q, WU S F, LIU D S, et al. Dynamic damage constitutive model of sandstone based on component combination theory [J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(4): 827–833. DOI: 10.11883/bzycj-2017-0173. [19] SHU Y, ZHU Z M, WANG M, et al. A plastic damage constitutive model for rock-like material focusing on the hydrostatic pressure induced damage and the interaction of tensile and shear damages under impact and blast loads [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2022, 150: 104921. DOI: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2022.104921. [20] HUANG L C, LIANG J G, MA J J, et al. A dynamic bounding surface plasticity damage model for rocks subjected to high strain rates and confinements [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2022, 168: 104306. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104306. [21] XU X, CHI L Y, YU Q, et al. An elastoplastic damage constitutive model for capturing dynamic enhancement effect of rock and concrete through equivalent stress history [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 181: 104736. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104736. [22] YU M H, HE L N. A new model and theory on yield and failure of materials under the complex stress state [J]. Mechanical Behaviour of Materials VI, 1992: 841-846. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-08-037890-9.50389-6. [23] YU M H, ZAN Y W, ZHAO J, et al. A unified strength criterion for rock material [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2002, 39(8): 975–989. DOI: 10.1016/S1365-1609(02)00097-7. [24] SI X F, GONG F Q, LI X B, et al. Dynamic Mohr-Coulomb and Hoek-Brown strength criteria of sandstone at high strain rates [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2019, 115: 48–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.12.013. [25] ALVES M. Material constitutive law for large strains and strain rates [J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2000, 126(2): 215–218. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(2000)126:2(215). [26] XU H, WEN H M. Semi-empirical equations for the dynamic strength enhancement of concrete-like materials [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2013, 60: 76–81. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2013.04.005. [27] KAMRAN, IQBAL M A. A new material model for concrete subjected to high rate of loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 180: 104673. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104673. [28] OKUBO S, FUKUI K. Complete stress-strain curves for various rock types in uniaxial tension [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1996, 33(6): 549–556. DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(96)00024-1. [29] OKUBO S, FUKUI K, QI Q X. Uniaxial compression and tension tests of anthracite and loading rate dependence of peak strength [J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2006, 68(3/4): 196–204. DOI: 10.1016/j.coal.2006.02.004. [30] HU X L, ZHANG M, ZHANG X Y, et al. A coupled elastoplastic damage dynamic model for rock [J]. Shock and Vibration, 2021, 2021: 5567019. DOI: 10.1155/2021/5567019. [31] YU M H, YANG S Y, FAN S C, et al. Unified elasto-plastic associated and non-associated constitutive model and its engineering applications [J]. Computers & Structures, 1999, 71(6): 627–636. DOI: 10.1016/s0045-7949(98)00306-x. [32] DE BORST R, CRISFIELD M A, REMMERS J J C, et al. Non-linear finite element analysis of solids and structures [M]. 2nd ed. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2012. [33] WAWERSIK W R, FAIRHURST C. A study of brittle rock fracture in laboratory compression experiments [J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1970, 7(5): 561–575. DOI: 10.1016/0148-9062(70)90007-0. [34] SEAH C C, BØRVIK T, REMSET S, et al. Penetration and perforation of rock targets by hard projectiles [M]//ZHOU Y X, ZHAO J. Advances in Rock Dynamics and Applications. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2011. -






 下载:
下载: